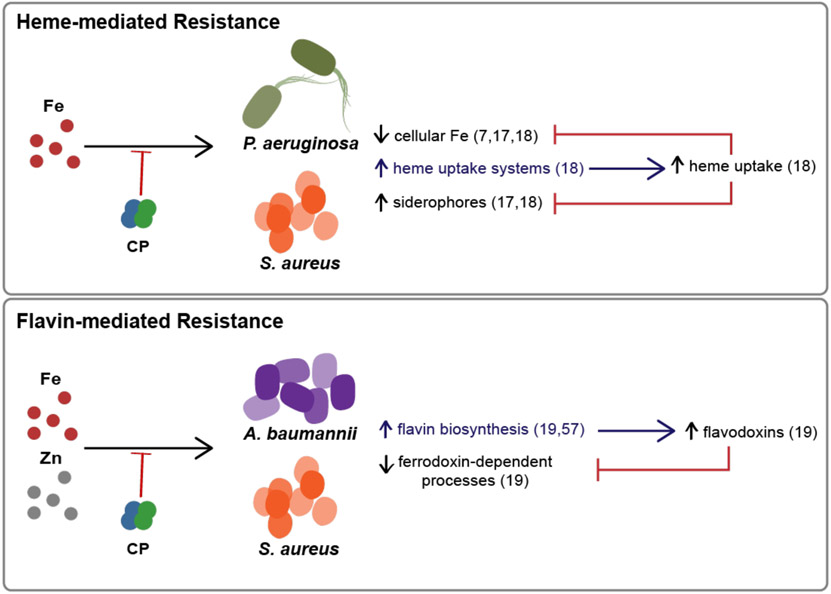
Figure 3. Models for how Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Acinetobacter baumannii resist Fe withholding by CP.
(Top) When experiencing Fe starvation by CP, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus upregulate heme uptake machinery and can use heme as an Fe source to resist CP-mediated depletion of cellular Fe and CP-mediated Fe starvation responses.18 (Bottom) When A. baumannii and S. aureus face metal starvation by CP, the pathogen upregulates enzymes involved in flavin biosynthesis, which could increase the use of flavodoxins. Flavodoxins can then be used as substitutes for ferredoxins, which reduces the cellular metabolic Fe requirement.19, 57.