Figure 4. IFN-γ-induced suppression of glycolytic gene expression is mediated by the interactions between the IDO1-AHR-HIF1 transcriptional regulatory pathways.
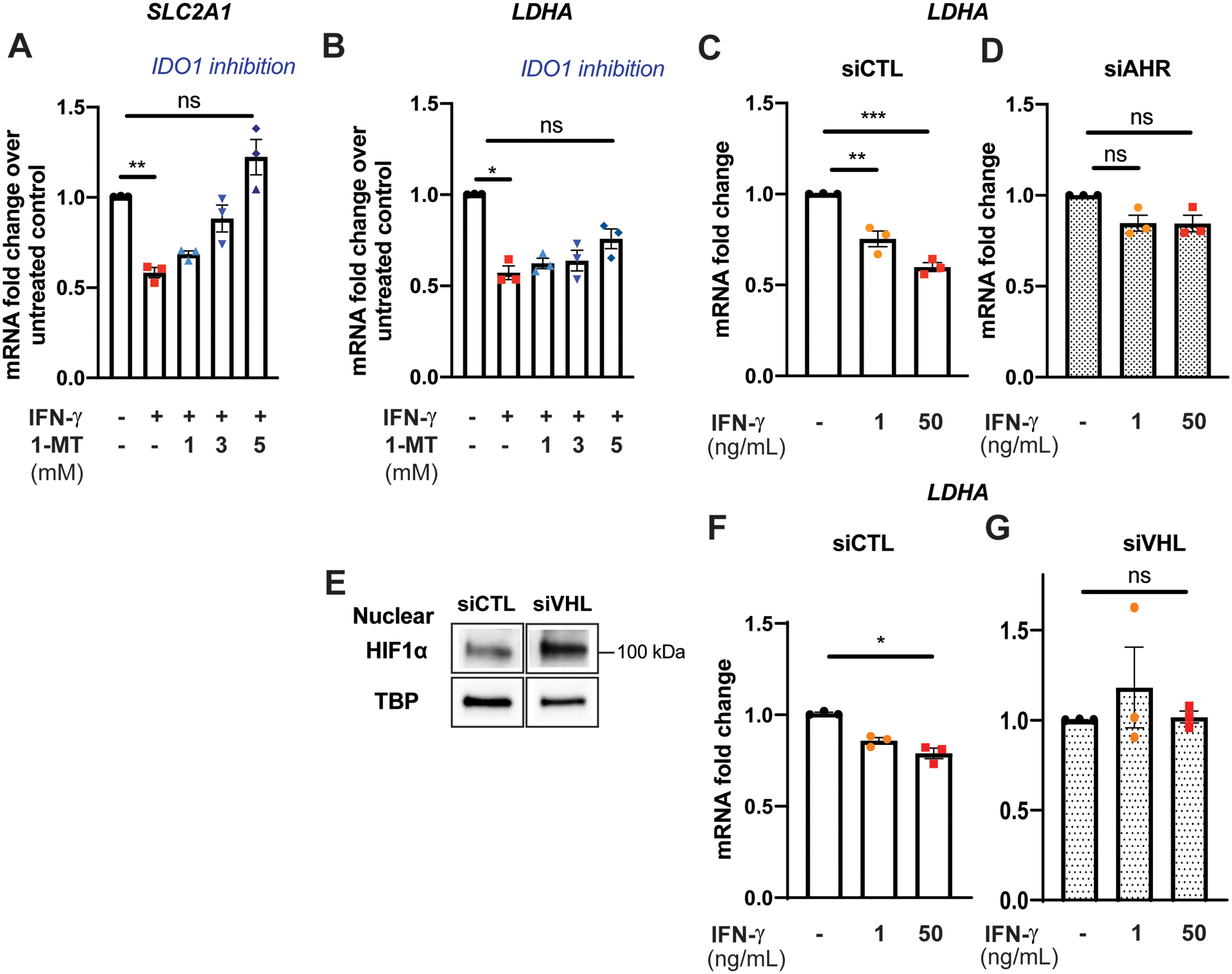
A-B, Pharmacological inhibition of IDO1 by 1-methyltryptophan (1-MT) abrogates IFN-γ induced suppression of SLC2A1 gene expression (A) and partially attenuates suppression of LDHA (B) in HCEAC. Data represent mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments.
C-D, Gene silencing of AHR attenuates IFN-γ induced suppression of LDHA gene expression in HCEAC. Data represent mean mRNA fold changes with IFN-γ treatment compared to those not exposed to IFN-γ within each siRNA treatment group ± SEM from 3 independent experiments.
E, Gene silencing of von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL) stabilizes nuclear HIF1α protein expression in normoxia. TATA binding protein (TBP) was used as a loading control. Representative Western blot.
F-G, HIF1α stabilization in normoxia by gene silencing of VHL abrogates IFN-γ induced suppression of LDHA gene expression in HCAEC. Data represent mean mRNA fold changes with IFN-γ treatment compared to those not exposed to IFN-γ within each siRNA treatment group ± SEM from 3 independent experiments.
Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (A-D) or Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (F-G).
*p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** < 0.001
