Abstract
Background:
Premutation sized (55–200) CGG repeat expansions in the FMR1 gene cause Fragile X-associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS). Most studies of premutation carriers utilized reverse ascertainment to identify cases, leading to a selection bias for larger repeats. As shorter CGG premutation repeats are common in the population, understanding their impact on health outcomes has a potentially large public health footprint.
Objectives:
The study’s objective was to compare an unselected group of premutation carriers (n=35, 55–101 CGG repeats) with matched controls (n=61, 29–39 CGG repeats) with respect to FXTAS-type signs using structured neurological assessments.
Methods:
Three neurologists independently rated signs, using an adapted version of the FXTAS Rating Scale (1). This was a double-blind study, as genetic status (premutation versus control) was known neither by the participants nor any of the neurologists. Analyses controlled potentially confounding comborbid conditions in the electronic health record (e.g., osteoarthritis, stroke) and probed the association of age with signs.
Results:
Although there was no overall difference between carriers and controls, among individuals without any potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses, there was a statistically significant age-associated elevation in FXTAS-type signs in premutation carriers compared to controls.
Conclusions:
Among those who do not have other comorbid diagnoses, women who have CGG repeats at the lower end of the premutation range may be at greater risk for ataxia and parkinsonism than their age peers, although their overall risk of developing such clinical features is low. This study should provide reassurance to those who share characteristics with the present cohort.
The fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene plays a critical role in normal neurological development and functioning, regulating the translation of approximately 30% of all transcripts in the synaptic proteome (2). Changes in the CGG repeat copy number within the 5’ untranslated region of FMR1 result in three distinct disorders – fragile X syndrome (FXS), fragile X-associated primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI), and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). FXS is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is the most prevalent inherited cause of intellectual disability and autism, resulting from expansions of >200 CGG repeats and transcriptional silencing of FMR1 (3). FXS is inherited from a mother who carries an FMR1 premutation (4). The premutation is defined by 55 to 200 CGG repeats and occurs in approximately 1 in 150–200 females and 1 in 450 males (5, 6). Premutation carriers are at risk for FXTAS and FXPOI, both of which are clinically and mechanistically distinct from FXS (7, 8). FXPOI is the most prevalent genetic cause of impaired ovarian functioning and infertility (7). FXTAS, which is the focus of the present research, is a late-onset and progressive neurodegenerative disorder, manifested in a subset of premutation carriers after age 50 (7, 9, 10).
FXTAS is defined clinically by intention tremor, gait ataxia, and cognitive decline due to memory issues and executive dysfunction. Pathologically, FXTAS presents with ubiquitinated inclusions in neuronal and non-neuronal cells, white matter disease, and global brain atrophy (11). Considerably more research on FXTAS has been conducted on men than women, due to the more severe manifestation and higher penetrance of the syndrome in men (affecting approximately 40% of carrier men vs.16% of carrier women over age 50). The lower prevalence and milder severity of FXTAS in women is due to the effect of the non-mutated FMR1 gene on the second X chromosome (12). Most past studies identified participants from specialized FXS clinics or via family cascade testing (13, 14), possibly resulting in ascertainment bias. For this reason, the prevalence and severity of FXTAS-type symptoms in premutation carriers in the general population have not been adequately studied and may differ from what is reported in the research literature.
Two major factors affect the diagnosis and manifestation of FXTAS in premutation carriers – age and CGG repeat number. After age 50, the diagnosis of FXTAS becomes increasingly likely (1), and is more frequent in those with more than 100 CGG repeats (1, 15). Although younger carriers, as well as carriers who have lower numbers of repeats, may manifest mild clinical features similar to FXTAS, this has been studied in only a few investigations (13, 16 – 18).
Present Research
These gaps in past research shaped the present investigation, which was designed to advance understanding of FXTAS-type signs among premutation carriers in the general population. To accomplish this, we accessed a unique biobank that included DNA samples from 20,000 members of a single health care system (19). These DNA samples were screened to identify premutation carriers (20). Unlike past research, none of these individuals were identified based on family history of FXS or via a FXS specialty clinic, nor were they aware of their status as premutation carriers. Thus, study of this cohort offers a window into how FXTAS-type signs may be manifested in unselected premutation carriers in the general population. Given the more limited research on premutation women, the focus of the present study is on how premutation women differ in FXTAS-type signs from matched controls, based on a structured neurological assessment.
Importantly, this was a double-blind study where neither the participants nor the three rating neurologists were aware of who was a premutation carrier versus a control. When enrolling in the biobank, members consented to give access to their electronic health records (EHRs) for research, and thus, in addition to the neurological assessment, we reviewed the EHRs to identify any potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses (e.g., hip replacement, stroke) that might affect both patients and controls and that would need to be controlled in the present analysis.
We examined two research questions: Do premutation carrier women and controls differ in the severity of the neuromotor signs associated with FXTAS? Is there evidence of more severe FXTAS-related neuromotor signs associated with advancing age? We hypothesized that premutation carriers would have more FXTAS-related neuromotor signs than controls, and these would become greater with advancing age.
Methods
Participants were drawn from the Marshfield Clinic’s Personalized Medicine Research Project (PMRP), a population-based cohort (n=20,353, 40% of the eligible population of the Marshfield Epidemiologic Study Area, a 19-zip code region around Marshfield, Wisconsin, and a 9-zip code area in northern Wisconsin) who consented to share their EHRs and DNA for research. PMRP recruitment began in 2002. Health records were digitized back to 1979, and thus an average of 40 years of EHRs are available for these members. IRB approval was obtained from the Marshfield Clinic and University of Wisconsin-Madison. According to the initial protocol, participants consented at the time of enrollment in PMRP to contribute their de-identified EHRs and DNA to be used in research without expectation of return of research results. Additional written consent was obtained prior to the neurological assessment, which per IRB was not described as a study related to FMR1 or FXTAS.
Identification of Premutation Carriers and Controls
We screened all PMRP participants for whom DNA samples were available (n=19,989, including 11,526 females) using procedures described previously (20). The goal of screening was to identify premutation carriers (i.e., those with 55–200 CGG repeats), resulting in the identification of 72 premutation carrier women. Next, the specific number of CGG repeats within the premutation range was quantified for each carrier. Subsequently carrier status and repeat number were confirmed in an additional assay using the Asuragen AmplideX® Kit (21, 22), conducted in the Rush University Medical Center Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory (supervised by author EB-K). Buccal swab kits were provided to participants who obtained their own samples, returned via courier packages. DNA was isolated using standard methods. The same CGG repeat assays were followed to identify a pool of control women (24–40 CGG repeats) who were matched with premutation carriers at approximately a 2:1 ratio (n = 137 controls) based on age and duration of receiving care in the Marshfield health care system.
Of these potential sample members, 10 carriers and 21 controls were unable to provide informed consent at the time of data collection for the present study due dementia, residence in long-term care settings, or death. An additional 10 carriers and 17 controls declined to participate in the larger study. The neurological assessment required an in-clinic visit and agreement to being video-recorded. Those who no longer lived in the area or who refused video recording were not included in the current report. The single exclusion criterion was having a child with a neurodevelopmental disorder (three premutation carriers, four controls).
Rates of participation of eligible carriers and controls were comparable (72.2% and 72.3%, respectively), and the two groups did not differ in rates of refusal, inability to participate due to dementia or residence in a long-term care setting, or death prior to this study. There was no association between participation and diagnoses of depression and anxiety, as noted in the electronic health record (F = 0.21, p = 0.644). Notably, the recruiter for the study was blind to premutation versus control group status.
Neurological Assessment
A video-recorded structured neurological assessment (FXTAS Rating Scale) (1) was administered to 35 premutation carriers and 61 controls by a clinical neurologist at the Marshfield Clinic (JB). In addition, the video recordings were independently rated by two movement disorder neurologists with expertise in performing FXTAS-related evaluations (DH and PT).
The FXTAS Rating Scale was the dependent variable in the present analysis. It was developed to assess the three major motor features of FXTAS -- tremor, ataxia, and parkinsonism (1, 23). We used an adapted version of the measure (adapted by DH), which is composed of 56 items from the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor, the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale, the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale, and the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale. Most items were rated from 0 (normal) to 4 (severe impairments), with 0 signifying normal in all items. For each item, the ratings from the three neurologists were averaged, and items were summed to create scores for the three subdomains as well as the total score. The percentage of agreement across raters for the total score averaged 93.2%. Since the current data set had many 0s (thus high rates of agreement among raters), an alternative to the Kappa statistic was employed (24). Gwet’s AC (25), which is a more appropriate metric of agreement in such instances, averaged 0.91. See Table S1 for the inter-rater reliability of the three sub-scale scores.
Comorbidities in EHRs
The EHRs of participants were screened to identify potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses that might result in motor dysfunction not due to FXTAS. A list of such diagnoses was developed by one of the authors (PT). The EHRs of study participants were independently mined by another author (AM), and the specific codes that were found in the EHRs of study participants are listed in Table 1. Premutation carriers and controls were classified into two groups – those having any of the diagnoses, and those with no such diagnoses.
Table 1.
Potentially Confounding Comorbidity Diagnoses Recorded in Participants’ Electronic Health Recordsa.
| Category | Description | ICD10 |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular disease | Brain stem stroke syndrome | G46.3 |
| Cerebrovascular disease, unspecified | I67.9 | |
| Gait problems | Abnormalities of gait and mobility | R26 |
| Ataxic gait | R26.0 | |
| Difficulty in walking, not elsewhere classified | R26.2 | |
| Other abnormalities of gait and mobility | R26.89 | |
| Unspecified abnormalities of gait and mobility | R26.9 | |
| Ataxia, unspecified | R27.0 | |
| Hip osteoarthritis | Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, right hip | M16.11 |
| Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, left hip | M16.12 | |
| Unilateral osteoarthritis resulting from hip dysplasia, unspecified hip | M16.3 | |
| Osteoarthritis of hip, unspecified | M16.9 | |
| Hip replacement | Presence of right artificial hip joint | Z96.641 |
| Presence of left artificial hip joint | Z96.642 | |
| Presence of unspecified artificial hip joint | Z96.649 | |
| Knee osteoarthritis | Bilateral primary osteoarthritis of knee | M17.0 |
| Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, unspecified knee | M17.10 | |
| Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, right knee | M17.11 | |
| Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, left knee | M17.12 | |
| Osteoarthritis of knee, unspecified | M17.9 | |
| Knee replacement | Presence of right artificial knee joint | Z96.651 |
| Presence of left artificial knee joint | Z96.652 | |
| Presence of artificial knee joint, bilateral | Z96.653 | |
| Presence of unspecified artificial knee joint | Z96.659 | |
| Other movement disorders | Parkinson’s disease | G20 |
| Myoclonus | G25.3 | |
| Abnormal involuntary movements | R25 | |
| Essential tremor | G25 | |
| Tremor, unspecified | R25.1 | |
| Neuropathy | Idiopathic progressive neuropathy | G60.3 |
| Hereditary and idiopathic neuropathy, unspecified | G60.9 | |
| Inflammatory polyneuropathy, unspecified | G61.9 | |
| Polyneuropathy, unspecified | G62.9 | |
| Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy | G90.0 | |
| Radiculopathy | Radiculopathy, lumbar region | M54.16 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor of unspecified hip without organ or systems involvement | M0/5.79 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor, unspecified | M05.9 | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, unspecified | M06.9 | |
| Spondylolisthesis | Spondylolisthesis, site unspecified | M43.10 |
| Spondylolisthesis, lumbar region | M43.16 | |
| Fusion of spine, site unspecified | M43.2 | |
| Spinal stenosis | Spinal stenosis, site unspecified | M48.00 |
| Spinal stenosis, occipito-atlanto-axial region | M48.01 | |
| Spinal stenosis, thoracic region | M48.04 | |
| Spinal stenosis, lumbar region | M48.06 | |
| Spinal stenosis, lumbar region without neurogenic claudication | M48.061 | |
| Spinal stenosis, lumbar region with neurogenic claudication | M48.062 |
Codes are organized in 12 categories using the ICD10 hierarchies or similarity of diagnoses.
Statistical Analysis
The distribution of scores on the FXTAS Rating Scale and its sub-scales were first checked to determine if any would be considered statistical outliers (using Cook’s D). No outliers were detected. Subsequently, the statistical analysis included four steps. First, independent sample t-tests were used to compare premutation carriers and controls on the FXTAS Rating Scale. Second, to evaluate the effect of potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses in the EHR, two-way ANCOVAs were used to examine mean differences in FXTAS Rating Scale scores by premutation status and by having any of the comorbid diagnoses. Third, for the primary question addressed by this study, multiple regression was used to examine three-way interactions to determine if the association between premutation status and FXTAS Rating Scale scores varies based on age and having any of the potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses. Fourth, we conducted two sensitivity analyses. We removed the eight participants (two premutation, six controls) who had comorbidities in their EHRs involving movement disorders that were not signs of FXTAS (e.g., abnormal involuntary movements, drug-induced akathisia; see Table 1, “Other Movement Disorders” category) and then repeated the analysis. Subsequently, following the approach of Leehey et al. (1), we restricted the analysis to participants age 50 or older to specifically focus on those at highest risk of FXTAS-type signs. Due to the small size of the sample, an alpha level of p = 0.05 was used throughout.
Results
Descriptive Data
Participants averaged 57.2 years of age (s.d. = 13.7), with a range from 26 to 86. Most (n = 69, 71.9%) were age 50 or older. There was no significant age difference between premutation carriers and controls, due to matching. However, those with potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses were significantly older than those without such diagnoses (age 64.2 [s.d. = 12.9] vs. 52.2 [s.d. = 12.0], p < 0.001). The CGG repeat length of the controls ranged from 29 to 39 repeats (mean = 31.6). The CGGs of premutation carriers ranged from 55 to 101 (mean = 68.5), spanning the lower range of the premutation (Figure 1). Among the premutation carriers, there was no association between CGG repeat number and FXTAS Rating Scale scores (total or any sub-scale scores, all ps > .24).
FIG 1.
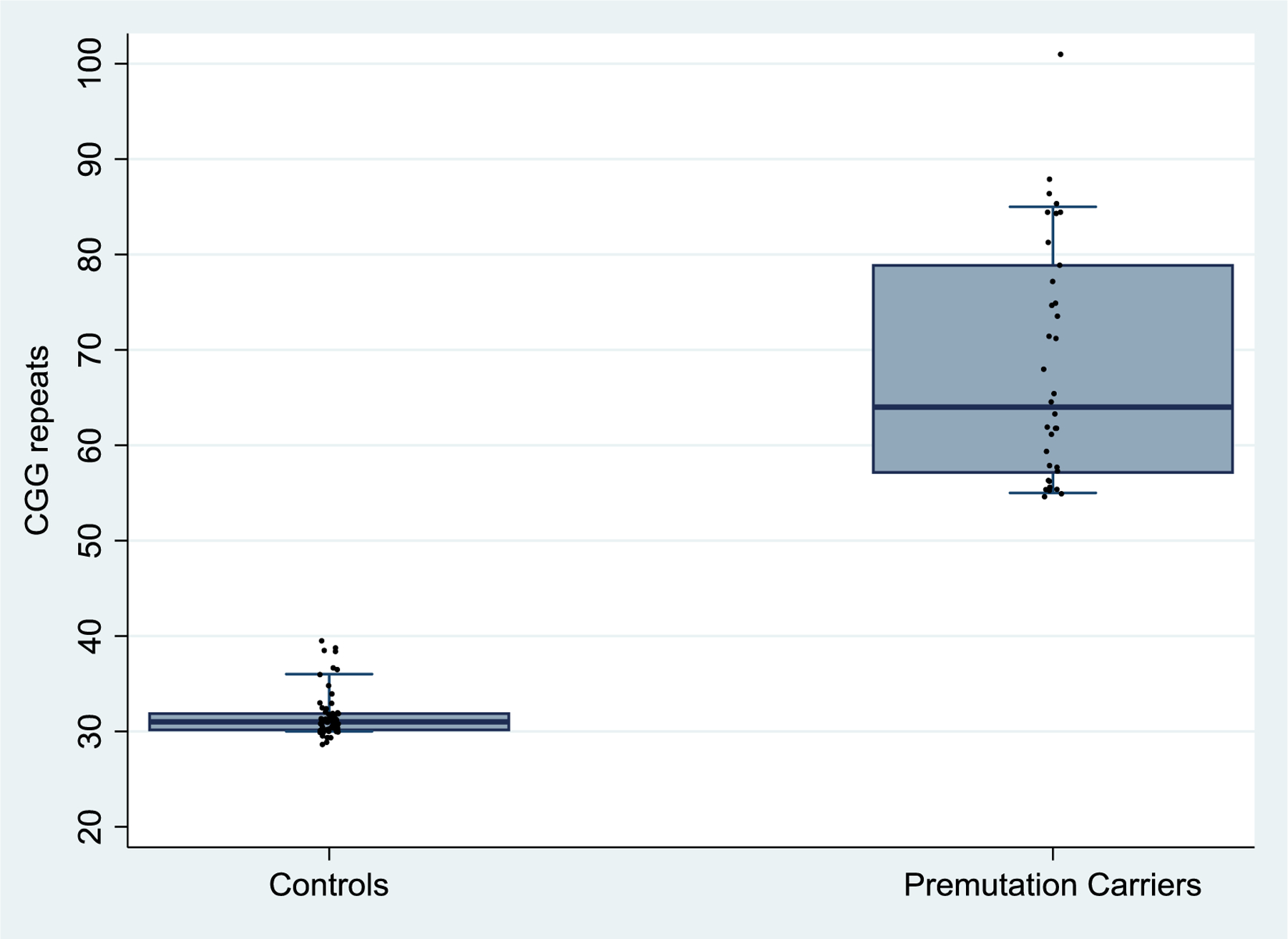
Distributions of CGG Repeats by Premutation Carriers vs. Controls.
Table 2 presents comparisons between premutation and control participants regarding potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses in the EHR. Many participants had at least one such diagnosis, but there was no significant difference between premutation and controls in the percentage with diagnoses (45.7% vs. 39.3%, respectively), nor were there group differences in individual diagnostic categories. The most common comorbid diagnosis was osteoarthritis of the knee.
Table 2.
Comparison of Premutation Carriers and Controls Based on Potentially Confounding Comorbidity Code Categories in the Electronic Health Records.
| Controls (n=61) | Premutation Carriers (n=35) | F-values | p-values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % having at least one potentially confounding comorbidity code category | 39.3% (24) | 45.7% (16) | 0.30 | .582 |
| Total number of unique categories of confounding comorbidity codes among individuals with at least one comorbidity codes | 2.12 (1.5) [1, 7] | 1.69 (1.2) [1, 5] | 0.64 | .430 |
| % (n) with each category of potentially confounding comorbidity codes | ||||
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.6% (1) | 0% (0) | 0.61 | .437 |
| Gait problems | 11.5% (7) | 5.7% (2) | 0.94 | .334 |
| Hip osteoarthritis | 8.2% (5) | 2.9% (1) | 1.34 | .250 |
| Hip replacement | 4.9% (3) | 0% (0) | 2.06 | .155 |
| Knee osteoarthritis | 26.2% (16) | 25.7% (9) | 0.05 | .831 |
| Knee replacement | 1.6% (1) | 8.6% (3) | 2.61 | .110 |
| Other movement disorders | 9.8% (6) | 5.7% (2) | 0.47 | .657 |
| Neuropathy | 3.3% (2) | 8.6% (3) | 1.18 | .280 |
| Radiculopathy | 3.3% (2) | 5.7% (2) | 0.29 | .589 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 1.6% (1) | 2.9% (1) | 0.14 | .713 |
| Spondylolisthesis | 1.6% (1) | 2.9% (1) | 0.15 | .696 |
| Spinal stenosis | 6.6% (4) | 5.7% (2) | 0.05 | .822 |
Research Question 1: Comparison of Motor Sinds in Premutation Carriers and Controls
Next, we compared premutation carriers and controls with respect to the FXTAS Rating Scale and the sub-scales. The two groups did not differ significantly on either the total scale score (p = 0.458) or any of the subscales (ps > 0.412; see Supplemental Materials, Table S2). Next, to separate the effects of premutation status and potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses in the EHR, two-way ANCOVAs were conducted. There were significant interaction effects between premutation status and having comorbid diagnoses with respect to the total score of the FXTAS Rating Scale and the subdomains of parkinsonism and ataxia (ps < 0.05). The control participants with comorbid diagnoses had substantially more severe impairments than the other three groups (see Table S3).
Research Question 2: Age-Related Differences in Motor Severity
To examine whether the FXTAS Rating Scale scores of carriers and controls differed with advancing age, multiple regression analyses were carried out including a three-way interaction effect term (age X premutation status X presence vs. absence of comorbid diagnoses), predicting symptom severity. The three-way interaction term was the primary test of the study’s hypothesis. There were significant three-way interaction effects on the FXTAS Rating Scale total score (p < 0.001) and the two subdomains of ataxia (p < 0.001) and parkinsonism (p = 0.005), with a trend-level interaction for the tremor subdomain (p = 0.052). See Table 3, Figure 2, and Supplementary Material Figures S1– S3. Among those women who had no potentially confounding comorbid diagnoses in their EHR, it was only among the premutation group where FXTAS signs were more severe with advancing age, a pattern not evident among the controls. In contrast, among those who had at least one such diagnosis, it was the control group that showed more severe signs associated with advancing age, likely due to the comorbidity, a pattern not evident among the carriers.
Table 3.
Multiple Regression Models Predicting FXTAS Rating Scale Total Score and Sub-scale Scores (n = 96).
| Total score | Tremor | Ataxia | Parkinsonism | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | s.e. | p-value | b | s.e. | p-value | b | s.e. | p-value | b | s.e. | p-value | |
| Agea | .15 | .12 | .200 | .08 | .05 | .072 | .03 | .04 | .481 | .02 | .05 | .653 |
| PM status (premutation=1) | 3.89 | 2.46 | .118 | .14 | .96 | .887 | 1.91 | .84 | .025 | 1.61 | .99 | .106 |
| Any comorbidity codes (any code = 1) | 5.73 | 2.47 | .023 | 1.23 | .96 | .203 | 2.06 | .84 | .016 | 2.08 | .99 | .039 |
| Age × PM status | .29 | .19 | .123 | .04 | .07 | .596 | .13 | .06 | .049 | .11 | .08 | .156 |
| Any comorbidity codes × Age | .69 | .18 | < .001 | .10 | .07 | .158 | .28 | .06 | < .001 | .27 | .07 | < .001 |
| Any comorbidity codes × PM status | −7.01 | 3.86 | .073 | −.71 | 1.50 | .640 | −2.85 | 1.31 | .033 | −2.79 | 1.55 | .075 |
| Age × PM status × Any comorbidity codes | −1.05 | .28 | < .001 | −.21 | .11 | .052 | −.44 | .10 | < .001 | −.32 | .11 | .005 |
| Constant | 9.19 | 1.49 | < .001 | 4.06 | .58 | < .001 | 3.23 | .51 | < .001 | 1.46 | .60 | .017 |
| R-sq | .511 | .294 | .538 | .424 | ||||||||
Abbreviation: PM, Premutation; b regression coefficient, s.e., standard error
Age is mean-centered.
FIG. 2.
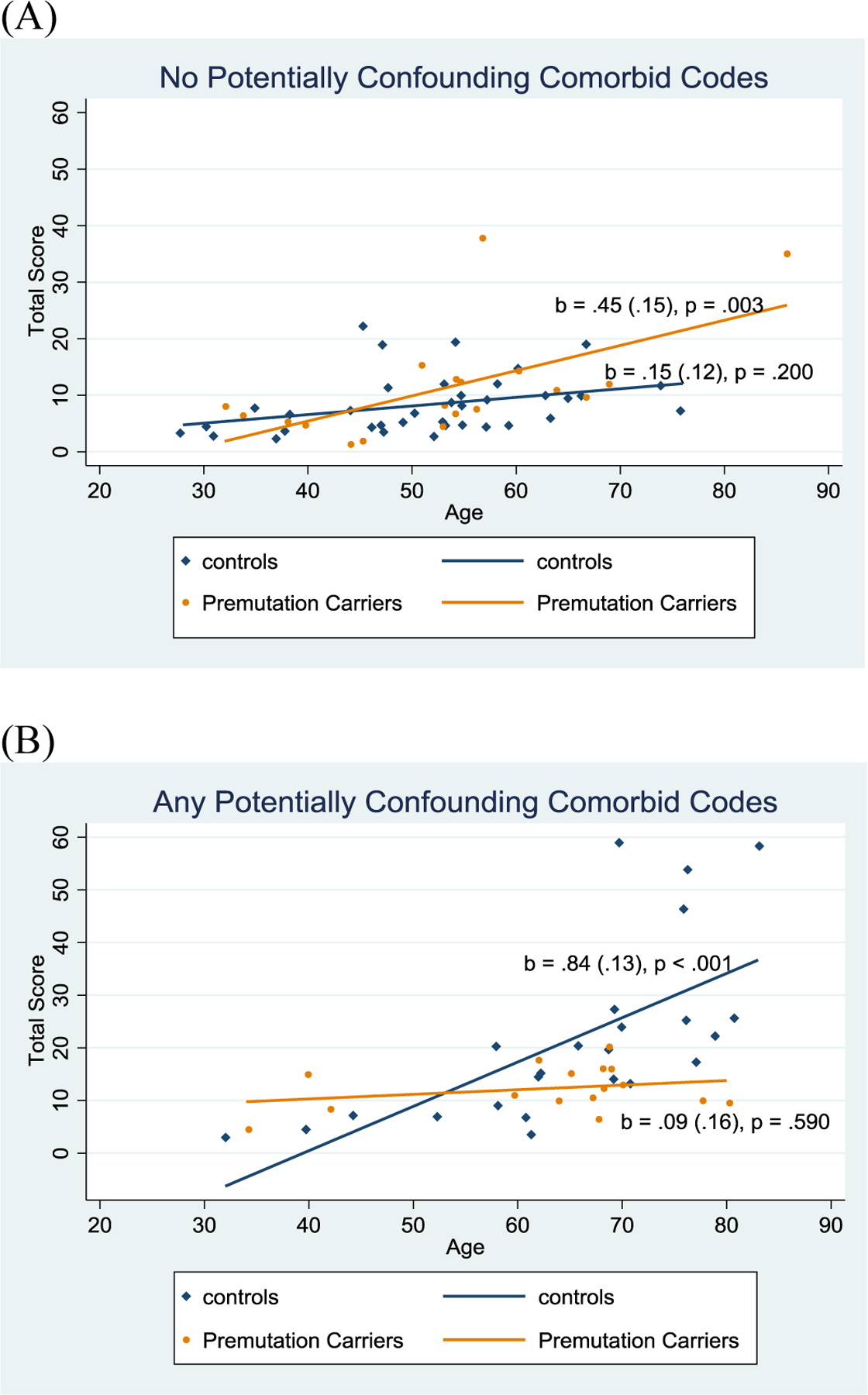
Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on FXTAS Rating Scale Total score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the total FXTAS Rating Scale. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard error of the coefficient (in parenthesis) and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
Sensitivity Analyses
We removed eight participants with potentially confounding other movement disorder diagnoses from the analysis (see Tables 1 and 2). The significant three-way interactions reported above (for the total score, parkinsonism, ataxia) remained significant when these eight participants were removed from the analysis. In addition, the interaction term predicting the tremor sub-scale became statistically significant in the regression models that did not include these participants (See Supplemental Materials, Table S4).
Subsequently, we restricted the analysis to participants who were age 50 or older (n = 69) to focus on those at or above the age at which clinical signs of FXTAS tend to be observed among premutation carriers. The same pattern of results was found as reported in Table 3, namely that among those without potentially confounding comorbidities, the premutation carriers had significantly greater impairments with advancing age, a pattern not evident among controls. (See Supplemental Materials, Table S5.)
Discussion
Based on a population-based cohort, the present study yielded information about FXTAS-type neurological signs in a group of premutation carriers not often evaluated in previous research – premutation women with lower numbers of CGG repeats, some of whom were younger than age 50, who were ascertained in an unbiased fashion. Overall, these women had FXTAS Rating Scale scores that were no different than their peers who had CGG repeats in the normal range. As premutation carriers with shorter repeat lengths are much more common in the population than those with repeats in the upper premutation range, the present results are significant from a public health perspective.
Although none of the participants was diagnosed with FXTAS, and although initial comparisons did not reveal greater evidence of mild clinical FXTAS-type neurological signs in premutation carriers than controls, after comorbid diagnoses were controlled, an age-associated vulnerability of premutation carriers was observed with respect to the total FXTAS Rating Scale and the ataxia and parkinsonism sub-scales. In other words, it was only among otherwise healthy carriers that we begin to see any impact of the CGG repeat. The same pattern was observed when we restricted the data to only those age 50 and older, and to those who had no other movement disorder-type comorbid codes.
What is the clinical significance of these findings? It is valuable to note that the CGG repeat is not the dominant driver of related signs and symptoms in this cohort of women. The participants in the present study differ from many participants in past studies who generally had larger numbers of CGG repeats than those evaluated here (1, 15, 26). Nevertheless, there was evidence of a statistically significant pattern of ataxia and parkinsonism signs in premutation carriers who did not have potentially confounding diagnoses. This may suggest that these women were manifesting early signs of FXTAS, or they have neurological signs that are not related to underlying FXTAS pathology, or they have other yet-to-be diagnosed movement disorders. Additional studies are warranted to determine which of these explanations accounts for the results. Future research should also probe the possible effect of reproductive aging on such symptoms, as premutation carriers experience menopause earlier than controls.
The study design addressed the risk of ascertainment bias by recruiting participants from a general health care system rather than from families of individuals with FXS or from FXS specialty clinics. Thus, study of this cohort can offer insights into how mild clinical FXTAS-type signs may be manifested in unselected premutation carrier women in the general population. A notable feature of the study is that it brought together sources of data – DNA, neurological assessments, and EHRs – that are not often integrated into a single research endeavor. Were it not for each of these diverse data sources and the integrative analytic approach, the underlying pattern of symptoms would not have been detected. Another strength of the present study was the double-blind approach and the inclusion of independent ratings from three neurologists with high inter-rater reliability.
The study was limited by a number of factors, particularly the small sample size, which limited statistical power. Due to this limitation, the present study warrants replication in larger cohorts. Additionally, we did not have neuroimaging data needed for a formal FXTAS diagnosis. We also did not have access to activation ratios on participants, which have been found to be important in past studies using the FXTAS Rating Scale (1). Why the control group participants with confounding diagnoses were substantially more impaired than the other three groups is not clear. This pattern may be a chance finding of the present study or it might point to an area for investigation in future research. Further, the scale may be picking up neurological signs related to other co-morbidities rather than FXTAS itself. Finally, among women who did not have confounding diagnoses, an association between FXTAS Rating Scale scores and age was observed among premutation carriers but was not observed among controls; however this observation was based on cross-sectional data, and warrants confirmation in longitudinal research.
Conclusion
Women who have CGG repeats at the lower end of the premutation range may be at greater risk for ataxia and parkinsonism signs than their age peers, although their overall risk of developing such conditions is low. Importantly, the findings of the present study cannot be attributed to ascertainment bias. Rather, these signs were detected among an unselected group of premutation carrier women in the general population. The severity of such signs was more subtle than that which was observed in past studies of family members of children with FXS, and only evident among otherwise healthy carriers. This should provide reassurance to premutation carriers who share characteristics with the present cohort.
Supplementary Material
FIG. S1. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Ataxia Sub-scale score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Ataxia Sub-scale score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
FIG. S2. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Parkinsonism Sub-scale Score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Parkinsonism Sub-scale Score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
FIG. S3. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Tremor Sub-scale Score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Tremor Sub-scale Score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
Acknowledgements:
Grant support for this research was provided by R01 HD082110. Support was also provided by the Waisman Center Core Grant (U54 HD090256) and the Marshfield Clinic Research Institute. Special thanks to the participants in the Personalized Medicine Research Project and to Renee Makuch and Terrie Kitchener for their coordination of data collection across sites.
Financial disclosure related to research covered in this article:
Marsha Mailick: Chair, Scientific Advisory Board, John Merck Fund Developmental Disabilities Program. PI: R01 R01 HD082110. Co-I, Signature Research Project: U54 HD090256
Jinkuk Hong: none
Arezoo Movaghar: none
Leann DaWalt: MPI: R01 HD084563
Elizabeth M. Berry-Kravis: Funding from Asuragen Inc., which is directed to RUMC in support of rare disease programs. E B-K receives no personal funds and has no relevant financial interest in this commercial entity.
Murray Brilliant: none
Jaime Boero: none
Peter Todd: none
Deborah Hall: none
Full financial disclosure for the previous 12 months:
Marsha Mailick: Chair, Scientific Advisory Board, John Merck Fund Developmental Disabilities Program. PI: R01 R01 HD082110. Co-I: Signature Research Project: U54 HD090256. MPI: K12HD101368
Jinkuk Hong: none
Arezoo Movaghar: none
Leann DaWalt: Research Support: MPI: R01 HD084563. Site PI: R324C1006. MPI: R01MH121438. PI: 90DDUC0072
Elizabeth M. Berry-Kravis: Funding from the following, all of which is directed to RUMC in support of rare disease programs. E B-K receives no personal funds and has no relevant financial interest in any of the commercial entities listed: Acadia, Alcobra, Anavex, Biogen, BioMarin, Cydan, Fulcrum, GeneTx, GW, Ionis, Lumos, Marinus, Neuren, Neurotrope, Novartis, Orphazyme, Ovid, Roche, Seaside Therapeutics, Tetra, Ultragenyx, Yamo, and Zynerba to consult on trial design, development strategies, and/or conducting clinical studies in FXS or other NNDs or neurodegenerative disorders; Vtesse/Sucampo/Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals to conduct clinical trials in NPC; Asuragen Inc to develop testing standards for FMR1 testing
Murray Brilliant: none
Jaime Boero: none
Peter Todd: Travel and Speaker Honoraria: Denali Therapeutics. American Academy of Neurology. National Fragile X Foundation. Japanese Society of Neurology.
Patents: BIOL0326US.L - this patent covers ASOs aimed at blocking RAN translation in Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome. Publishing Royalties: Overview of cerebellar ataxia in adults, UpToDate, 2013- present (updated every 6 months). Research Support: 1) NIH/NINDS 1R01NS086810 Role: PI. 04/01/14-01/01/25 2) VAMC/BLRD Merit Award Role: PI. 1/1/20-12/31/24. Research Support, Foundations and Societies: 1) National Fragile X Foundation. 2) National Ataxia Foundation. 3) Muscular Dystrophy Association. 4) Alzheimer’s Association. 5) Ann Arbor Active Against ALS. License fee payments, Technology or Inventions: Antibodies developed by our group to Millipore for distribution to scientists and commercial groups.
Vectors and Antibodies developed by our group to Denali Therapeutics. Stock/Stock Options, Research Sponsor: Denali Therapeutics, 2016-Present.
Deborah Hall: Research support: NIH, Parkinson’s Foundation, Michael J. Fox Foundation, Anti-Aging Foundation, CHDI, Biohaven, Uniqure, Neurocrine, Fujifilm. Editorial Support: American Academy of Neurology
References
- 1.Leehey MA, Berry-Kravis E, Goetz CG, et al. FMR1 CGG repeat length predicts motor dysfunction in premutation carriers. Neurology. 2008;70(16 Part 2):1397. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000281692.98200.f5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Darnell JC, Van Driesche SJ, Zhang C, et al. FMRP stalls ribosomal translocation on mRNAs linked to synaptic function and autism. Cell. 2011;146(2):247–261. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brown W Fragile X Syndrome Diagnosis, Treatment and Research. (Hagerman R, Hagerman P, eds.). The Johns Hopkins University Press; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nolin SL, Lewis FA 3rd, Ye LL, et al. Familial transmission of the FMR1 CGG repeat. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59(6):1252–1261. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8940270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Seltzer MM, Baker MW, Hong J, Maenner M, Greenberg J, Mandel D. Prevalence of CGG expansions of the FMR1 gene in a US population-based sample. Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2012;159B(5):589–597. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tassone F, Iong KP, Tong T-H, et al. FMR1 CGG allele size and prevalence ascertained through newborn screening in the United States. Genome Med. 2012;4(12):100. doi: 10.1186/gm401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hagerman R, Hagerman P. Advances in clinical and molecular understanding of the FMR1 premutation and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(8):786–798. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70125-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Roberts JE, Tonnsen BL, McCary LM, Ford AL, Golden RN, Bailey DB. Trajectory and Predictors of Depression and Anxiety Disorders in Mothers With the FMR1 Premutation. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(10):850–857. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hagerman RJ, Hagerman P. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome — features, mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(7):403–412. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hall DA, Robertson E, Shelton AL, et al. Update on the Clinical, Radiographic, and Neurobehavioral Manifestations in FXTAS and FMR1 Premutation Carriers. Cerebellum. 2016;15(5):578–586. doi: 10.1007/s12311-016-0799-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berry-Kravis E, Abrams L, Coffey SM, et al. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome: Clinical features, genetics, and testing guidelines. Mov Disord. 2007;22(14):2018–2030. doi: 10.1002/mds.21493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jacquemont S, Hagerman RJ, Leehey MA, et al. Penetrance of the Fragile X–Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in a Premutation Carrier Population. JAMA. 2004;291(4):460–469. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.4.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Allen EG, Charen K, Hipp HS, et al. Clustering of comorbid conditions among women who carry an FMR1 premutation. Genet Med. 2020;22(4):758–766. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0733-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hagerman RJ, Leavitt BR, Farzin F, et al. Fragile-X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in Females with the FMR1 Premutation. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74(5):1051–1056. doi: 10.1086/420700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tassone F, Adams J, Berry-Kravis EM, et al. CGG repeat length correlates with age of onset of motor signs of the fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007;144(4):566–569. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hall D, Tassone F, Klepitskaya O, Leehey M. Fragile X–associated tremor ataxia syndrome in FMR1 gray zone allele carriers. Mov Disord. 2012;27(2):297–301. doi: 10.1002/mds.24021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu Y, Winarni TI, Zhang L, Tassone F, Hagerman RJ. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) in grey zone carriers. Clin Genet. 2013;84(1):74–77. doi: 10.1111/cge.12026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shelton AL, Cornish KM, Kraan CM, Lozano R, Bui M, Fielding J. Executive Dysfunction in Female FMR1 Premutation Carriers. The Cerebellum. 2016;15(5):565–569. doi: 10.1007/s12311-016-0782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McCarty CA, Wilke RA, Giampietro PF, Wesbrook SD, Caldwell MD. Marshfield Clinic Personalized Medicine Research Project (PMRP): design, methods and recruitment for a large population-based biobank. Per Med. 2005;2(1):49–79. doi: 10.1517/17410541.2.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maenner MJ, Baker MW, Broman KW, et al. FMR1 CGG expansions: Prevalence and sex ratios. Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2013;162(5):466–473. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen L, Hadd A, Sah S, et al. An information-rich CGG repeat primed PCR that detects the full range of fragile X expanded alleles and minimizes the need for southern blot analysis. J Mol Diagnostics. 2010;12(5):589–600. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Grasso M, Boon EMJ, Filipovic-Sadic S, et al. A novel methylation PCR that offers standardized determination of FMR1 methylation and CGG repeat length without southern blot analysis. J Mol Diagnostics. 2014;16(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hall DA, Stebbins GT, Jacquemont S, et al. Clinimetric Properties of the Fragile X-associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome Rating Scale. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2019;6(2):120–124. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.12708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Viera AJ, Garrett JM. Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam Med. 2005;37(5):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gwet KL. Computing inter-rater reliability and its variance in the presence of high agreement. Br J Math Stat Psychol. 2008;61(1):29–48. doi: 10.1348/000711006X126600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jacquemont S, Leehey MA, Hagerman RJ, Beckett LA, Hagerman PJ. Size bias of fragile X premutation alleles in late-onset movement disorders. J Med Genet. 2006;43:804–809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
FIG. S1. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Ataxia Sub-scale score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Ataxia Sub-scale score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
FIG. S2. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Parkinsonism Sub-scale Score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Parkinsonism Sub-scale Score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.
FIG. S3. Scatter plots and fitted lines showing three-way interactions: Age, Premutation status, and Potentially Confounding Comorbid Diagnoses Codes on the FXS Rating Scale Tremor Sub-scale Score. The fitted lines are drawn from data points, illustrating the bivariate associations between age and the FXS Rating Scale Tremor Sub-scale Score. For each fitted line, the unstandardized regression coefficient (simple slope), the standard effort of the coefficient (in parenthesis), and the p-value are presented. (A) Participants who did not have potentially confounding comorbid codes. (B) Participants who had any potentially confounding comorbid codes.


