Fig. 1.
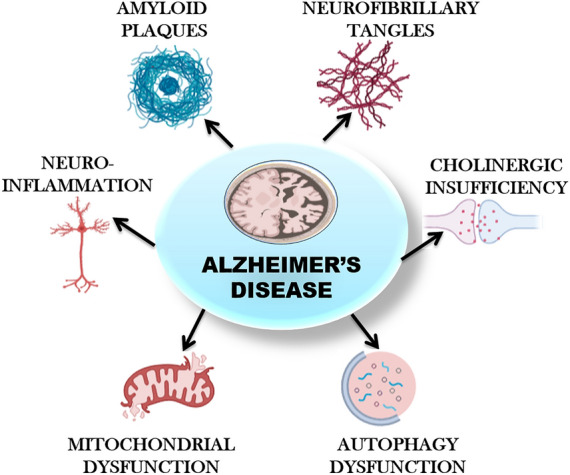
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Figure 1 depicts the multiple factors responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Amyloid plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau are the major ones. Extracellular amyloid β deposition leads to the generation of senile plaques. Hyperphosphorylated tau leads to the disassembly of microtubules and damages the cytoskeleton and signal transduction processes in neuronal cells. Other factors like neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, cholinergic insufficiency, mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy dysfunction also play major role in the disease progression
