Significance
Type IV pili (T4P) are among the most widespread adhesive factors in prokaryotes. In pathogenic Neisseria, the major pilin, which provides the structural framework for the filamentous T4P, undergoes antigenic variation allowing the bacteria to evade the humoral immune response without impacting host-cell adhesion. Here, we show that a minor pilin, PilV, is distributed throughout the pilus and contributes to Neisseria meningitidis adhesion and that antibodies to PilV block meningococcal adhesion in vivo. Our results provide a mechanism whereby N. meningitidis varies its immunodominant major pilin to escape antibody recognition while maintaining conserved sites throughout the pilus for host receptor binding. They further suggest a strategy to prevent or block deadly N. meningitidis infections by targeting this minor pilin.
Keywords: type IV pili, Neisseria meningitidis, host–pathogen interaction, PilV, adhesion
Abstract
Neisseria meningitidis utilizes type IV pili (T4P) to adhere to and colonize host endothelial cells, a process at the heart of meningococcal invasive diseases leading to meningitis and sepsis. T4P are polymers of an antigenically variable major pilin building block, PilE, plus several core minor pilins that initiate pilus assembly and are thought to be located at the pilus tip. Adhesion of N. meningitidis to human endothelial cells requires both PilE and a conserved noncore minor pilin PilV, but the localization of PilV and its precise role in this process remains to be clarified. Here, we show that both PilE and PilV promote adhesion to endothelial vessels in vivo. The substantial adhesion defect observed for pilV mutants suggests it is the main adhesin. Consistent with this observation, superresolution microscopy showed the abundant distribution of PilV throughout the pilus. We determined the crystal structure of PilV and modeled it within the pilus filament. The small size of PilV causes it to be recessed relative to adjacent PilE subunits, which are dominated by a prominent hypervariable loop. Nonetheless, we identified a conserved surface-exposed adhesive loop on PilV by alanine scanning mutagenesis. Critically, antibodies directed against PilV inhibit N. meningitidis colonization of human skin grafts. These findings explain how N. meningitidis T4P undergo antigenic variation to evade the humoral immune response while maintaining their adhesive function and establish the potential of this highly conserved minor pilin as a vaccine and therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of N. meningitidis infections.
The human-restricted bacterial pathogen Neisseria meningitidis is a leading cause of meningitis and sepsis worldwide and represents a significant global public health threat (1, 2). N. meningitidis is carried asymptomatically in the protective mucus layer of the throat for 5 to 25% of the population (3–5). In some cases, N. meningitidis disseminates into the bloodstream, an environment to which this bacterium is remarkably well adapted. Meningococci possess a polysaccharide capsule that protects them against complement deposition plus several membrane associated factors that are important for survival, including factor H binding protein and iron uptake systems (6). Critical to N. meningitidis survival in the bloodstream are the type IV pili (T4P), which mediate vascular colonization; nonpiliated meningococci are rapidly cleared from the blood (7–9). T4P are long filamentous appendages displayed peritrichously on the bacterium. The major pilin protein, PilE, is the primary building block of the pilus. This and other surface-displayed N. meningitidis proteins undergo antigenic variation, allowing this pathogen to evade a protective immune response (10–12).
T4P are responsible for acute colonization of human blood vessels and are thus essential in establishing invasive meningococcal diseases (7, 9, 13, 14). T4P are helical polymers of the major pilin assembled by the T4P machinery (15, 16). The conserved N terminus of the major pilin is a hydrophobic α-helix that tethers the C-terminal globular domain in the inner membrane prior to pilus assembly and forms a helical array in the core of the intact pilus, displaying the globular domain on the filament surface. Pilus assembly is initiated by a cluster of pilin-like proteins called minor pilins (17–20). These “core” minor pilins are thought to localize to the pilus tip. The major pilin, PilE, is highly conserved in amino acid sequence and structure between N. meningitidis and the urogenital pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae with the exception of a hypervariable β-hairpin near the C terminus that is prominent on the pilus surface (21–24). In N. meningitis, PilE has been shown to bind to sialylated N-glycans on the human endothelial cell receptor CD147 (also called EMMPRIN or Basigin) (25) and the β2-adrenergic receptor (26), two membrane proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex with cytoplasmic α-actinin 4 (27).
The pathogenic Neisseria possess a set of core minor pilins, PilH (FimT), PilI (PilV), PilJ (PilW), PilK, and PilX, that are encoded within a single gene cluster and prime pilus assembly (28), plus “noncore” minor pilins PilV and ComP, which are encoded elsewhere on the genome. ComP shares the canonical T4P–pilin structure of the major pilin, PilE, with the N-terminal α-helix and C-terminal globular domain (29). ComP is involved in natural transformation of exogenous DNA (30). PilV, which is highly conserved in N. meningitidis isolates (31), participates in adhesion and signaling in host cells (13, 26, 32–34). In N. meningitidis, PilV, like PilE, directly interacts with CD147 and the β2-adrenergic receptor, suggesting that PilV colocalizes with PilE within the T4P filament (13, 26). However, another report concluded that PilV functions exclusively from within the periplasm, fine-tuning pilus surface display to regulate its interactions with host cells (35).
The T4P–receptor interaction represents a key step in N. meningitidis adhesion and colonization of endothelial cells in peripheral and brain vasculature and is thus an attractive target for preventive and therapeutic approaches to tackle meningococcal infection. Interfering with piliation prevents N. meningitidis colonization of human endothelial cells and vasculature (36) and improves sepsis outcome in a mouse model grafted with human skin (9). Although both PilE and PilV are involved in adhesion, PilE exhibits considerable amino acid sequence variability in its exposed hypervariable region. This variability contributes to Neisseria immune escape. In contrast, PilV is highly conserved and has been shown to be immunogenic in humans (37). Thus, PilV may prove to be a more promising target than PilE for blocking endothelial cell adhesion. A molecular understanding of this minor pilin with respect to its structure, localization within the pilus, and interactions with host receptors will be valuable in assessing its potential as a therapeutic target. Here, we report the atomic structure of PilV and superresolution microscopy images showing that it is incorporated throughout the N. meningitidis T4P. We identify residues involved in adhesion to host cells and map these onto the PilV structure, modeled within the cryoelectron microscopy (cryoEM)-derived pilus filament structure. Finally, we show that anti-PilV antibodies inhibit meningococcal adhesion in vivo. These data provide insights into PilV-mediated adhesion and suggest that blocking its adherence functions may inhibit N. meningitidis vascular colonization and pathogenesis.
Results
PilE and PilV Make Distinct Contributions to T4P-Dependent Meningococcal Adhesion.
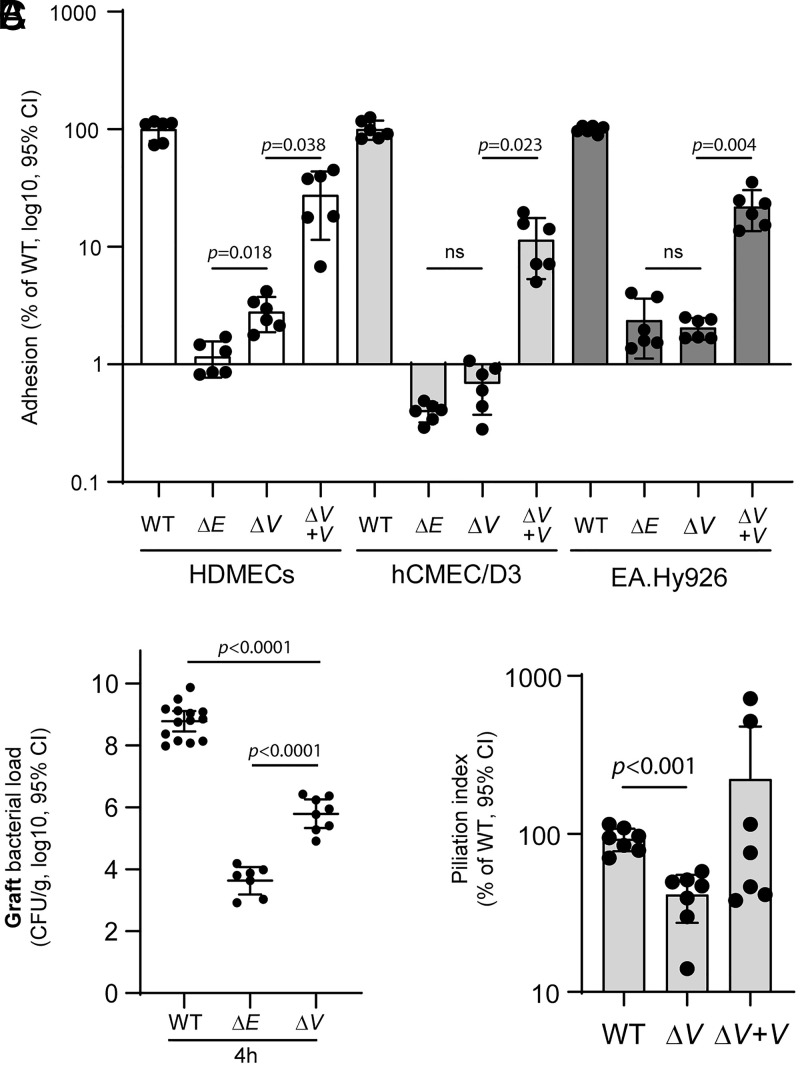
Both PilE and PilV have been shown to directly interact with host-cell receptors (13, 26). To investigate their specific roles in meningococcal adhesion to human cells, we compared adhesion for wild-type (WT) N. meningitidis strain 2C4.3 with that of derivative strains lacking either PilE or PilV on three endothelial cell types (Fig. 1A): primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) that are thought to have conserved their in vivo phenotype (38); the human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line D3 (hCMEC/D3) that possesses characteristics of brain endothelial cells; and EA.Hy926 cells obtained by fusion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with the human epithelial carcinoma cell line A549. While both ΔpilE (ΔE) and ΔpilV (ΔV) mutants showed substantial adhesion defects compared to WT bacteria, the defect of the ΔE mutant is more pronounced on primary HDMECs compared to the ΔV mutant (2.4-fold decrease between means of ΔV versus ΔE). PilV complementation of the ΔpilV strain (ΔV + V) partially restored adhesion to endothelial cells.
Fig. 1.
Differential adhesion of PilE- and PilV-defective strains of N. meningitidis. (A) HDMECs, hCMEC/D3, and EA.Hy926 human endothelial cells were incubated 30 min with meningococci. Following infection, unbound bacteria were removed, and adherent bacteria were quantified by plating serial dilution on GCB agar plates and counting CFUs after overnight growth. Adhesion is expressed as the mean ± 95% CI of CFUs normalized to the control infection (WT). Data were analyzed using the Brown–Forsythe test and Welch’s ANOVA. (B) Human skin–grafted SCID mice were infected intravenously with 5 × 106 N. meningitidis (WT; ΔE; ΔV). Graft bacterial loads were quantified at 4 h after infection by serial dilutions on GCB agar plates. Two independent experiments performed with a skin batch from a different donor. Each dot represents a single mouse; data are expressed as log10 of the mean ± 95% CI of CFU/g (B). Data were analyzed using Bonferroni's multiple comparisons. (C) Piliation index. Pili of WT, ΔV, and ΔpilV-complemented strain (ΔV + V) were sheared from the bacterial cells by vortexing and then precipitated with ammonium sulfate. To determine the piliation index, the sheared pilus fraction and the bacterial fraction were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-PilE antibodies. Piliation indices were normalized to that of the WT. Data are expressed as the mean ± 95% CI and were analyzed using the Brown–Forsythe test and Welch’s ANOVA.
To assess the adhesive role of PilE in vivo, we used a severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mouse model grafted with human skin (14) to quantify bacterial adhesion on human vessels in vivo. Grafted mice were infected intravenously with the WT ΔE or ΔV mutant strains, and bacterial loads in the graft and in the blood were quantified by counting colony forming units (CFUs) at different time points (Fig. 1B and SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). Blood bacterial loads were identical between the three strains at 1 h postinfection, indicating that equivalent inocula were administered for each bacterial strain (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). Whereas more than 108 CFUs were recovered 4 h after infection from the graft infected with WT N. meningitidis, only 6 × 103 CFUs were recovered from the grafts infected with PilE-defective meningococci, representing ∼0.0005% of the WT strain. The small number of ΔE bacteria are likely nonadherent cells present in the bloodstream of the graft microvasculature, as shown previously (14). The colonization efficiency of the PilV-defective strain was also impaired substantially at ∼0.08% of the WT strain, yet it was 170-fold greater than that of the PilE-defective strain, suggesting an important role for PilV in human endothelial cell adhesion.
We next assessed pilus levels in the ΔV strain to determine whether loss of piliation might explain its adhesion defect. T4P were mechanically sheared from WT, ΔV, and ΔV + V strains by vortexing, separated from the cells by centrifugation, and concentrated using ammonium sulfate (AS) precipitation, producing a crudely purified pilus fraction that contains both major and minor pilins (32, 39, 40). Pilus levels were reported as a piliation index determined by quantifying the PilE content in the sheared pilus fraction normalized to the PilE in the bacteria fraction. As shown in Fig. 1C and SI Appendix, Fig. S1B, all three strains express equivalent amounts of PilE in the whole cell lysates, but PilE is reduced in the sheared fraction of the ΔV strain relative to WT, corresponding to a piliation index of 50%. Thus, while deletion of PilV reduces pilus levels in the ΔV, this reduction does not account for the pronounced adhesion defects observed for the PilV-defective strain in cell culture and in the mouse graft model. These results suggest that PilV is, in fact, the major adhesin on the N. meningitidis T4P.
PilV-Mediated Adhesion Is a Conserved Feature of N. meningitidis.
In contrast to PilE, which contains a surface-exposed hypervariable loop providing extensive antigenic variation, PilV is conserved among clinical isolates (31). We examined 17,732 N. meningitidis genomes available in the PubMLST database, and we identified 699 distinct PilV sequences having a mean sequence identity greater than 80% (86.6 ±5.9% SD) between every possible sequence pair, indicating high conservation (Dataset S1).
N. meningitidis PilV Is Distributed Throughout the T4P Filament.
Both PilV and PilE were shown previously to bind to CD147 and the β2-adrenergic (13, 26), suggesting that PilV colocalizes with PilE in the pilus filament. To investigate PilV localization and understand how it might serve as the main adhesin in vivo, we tested for the presence of PilV in N. meningitidis T4P. Immunoblotting of AS-precipitated pili with anti-PilV antibody showed that PilV is present along with PilE (SI Appendix, Fig. S2A). This finding does not appear to be due to contamination of cell-associated proteins as the sheared fractions lacked both the cytosolic marker nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate glutamate deshydrogenase (NADPGH) and the membrane marker, Rmp4 (SI Appendix, Fig. S2A). To further demonstrate that PilV is incorporated into the meningococcal T4P filament, we immunoprecipitated pili from a crude preparation using anti-PilE and anti-PilV antibodies. PilV is present in the pilus fraction immunoprecipitated with anti-PilE antibody, and, conversely, PilE is present in the pilus fraction immunoprecipitated with anti-PilV antibody, consistent with these proteins colocalizing within the pilus (SI Appendix, Fig. S2 B and C).
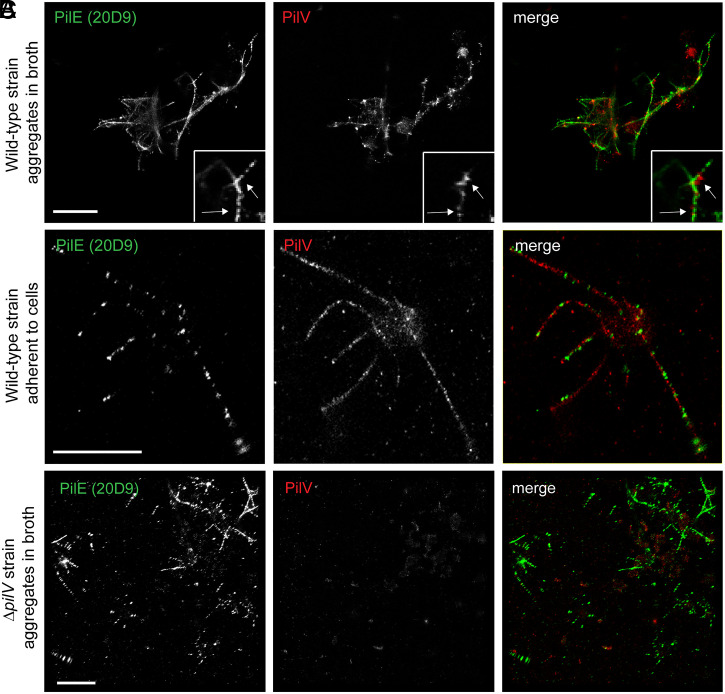
To directly visualize PilV in the T4P filaments, we analyzed the spatial organization of both PilV and PilE at the molecular level (∼20 nm) using a superresolution microscopy technique based on single-molecule localization (direct STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy, dSTORM) (9, 27). Anti-PilE antibody 20D9 binds in a continuous pattern to pili on WT bacteria grown in broth, whereas the pattern is punctate for adherent diplococci grown on endothelial cells, in which the pili are under stress (41, 42) (Fig. 2 A and B). Surprisingly, PilV also shows a punctate and abundant distribution along the same filaments. As control, PilE, but not PilV, was detected on type IV filaments in the ΔpilV mutant, confirming the specificity of the antibodies. Together, these data demonstrate that the minor pilin PilV is incorporated throughout the pilus filament, consistent with its role as an adhesin.
Fig. 2.
PilV is distributed throughout the N. meningitidis T4P. (A–C) dSTORM images of N. meningitidis grown in liquid broth (WT or ΔpilV) or attached to endothelial cells (WT). Images were acquired on a Leica SR GSD 3D system. A total of 50,000 frames were recorded and reconstructed using LAS X Software. (Scale bar, 2 μm.)
Structure of N. meningitidis PilV.
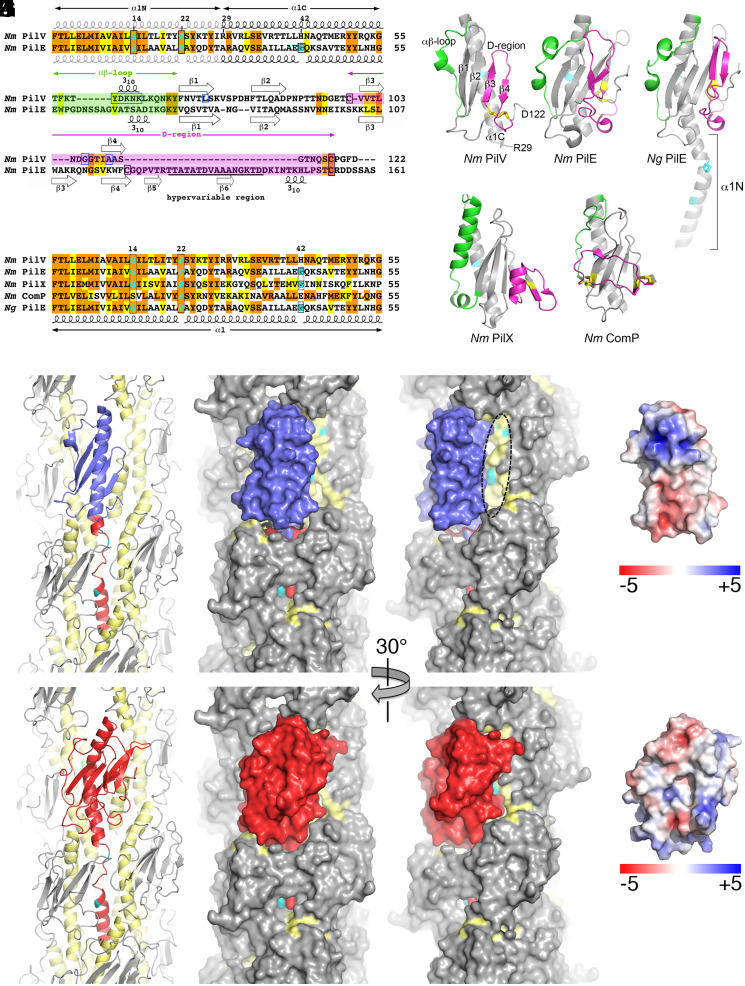
To better understand the role of PilV in host-cell adhesion, we solved the X-ray crystal structure of recombinant PilV (rPilV, residues 29 through 122, Fig. 3 A and B) in two space groups, C2 (monoclinic) and P212121 (orthorhombic) at 1.41 Å and 1.96 Å, respectively (Table 1). The structures are very similar, superimposing with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 0.5 Å for main chain atoms. The higher-resolution monoclinic structure is described here. The rPilV structure represents the pilin globular domain; the missing residues 1 through 28 correspond to the N-terminal half of an extended α-helix, α1. rPilV possesses the canonical T4P fold, with the C-terminal half of α1, α1C, packed against a four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet (Fig. 3B). The αβ-loop that connects the end of α1C to the beginning of strand β1 is extended and has a central 310 helix. On the opposite side of the β-sheet, a C-terminal loop curves under β4 and links back to the outer face of the β-sheet via a disulfide bond to the β2-β3 loop just before β3 (Cys99 and Cys118). The disulfide bond delineates the D-region of the pilin. Short loops of six and five residues at the top of the globular domain connect strands β1-β2 and β3-β4, respectively, whereas the β2-β3 loop at the bottom of this domain is longer, with 12 amino acids.
Fig. 3.
X-ray crystal structure of N. meningitidis PilV and model of PilV within N. meningitidis T4P. (A) Sequence alignment of the N. meningitidis (Nm) minor pilin PilV (National Center for Biotechnology Information WP_002244869) and the major pilin PilE (WP_014573675). Identical residues are highlighted orange and conserved residues in yellow. Helix-breaking Gly and Pro in α1 are highlighted in cyan and are boxed in black, as are Cys. Residues implicated in host-cell adhesion are boxed in blue. Secondary structures are indicated. The hypervariable region of PilE is underlined. (B) Crystal structure of N. meningitidis recombinant PilV, residues 29 through 122. The αβ-loop between α1 and the β-sheet is colored green, and the D-region, delineated by the disulfide-bonded cysteines, is magenta. Cysteines are shown as yellow sticks. The histidine at position 42 is colored cyan. (C) N. meningitidis major pilin PilE (residues 29 through 161, Protein Data Bank [PDB] 5JW8). (D) N. gonorrhoeae (Ng) major pilin PilE (full-length, residues 1 through 158, 2HI2). (E) Sequence alignment of α1 for N. meningitidis pilins and N. gonorrhoeae PilE, colored as in A (Nm PilX, CWT82783; Nm ComP, WP_002218144; Ng PilE, P02974). (F) N. meningitidis minor pilin PilX (residues 28 through 147, 2OPE). (G) N. meningitidis minor pilin ComP (residues 29 through 118, 5HZ7). Residues at positions 14 and 22 (N. gonorrhoeae PilE) and 42 (all pilins) are colored cyan. (H) The globular domain of a PilE subunit in the N. meningitidis T4P reconstruction (5KUA) was replaced with the rPilV structure (blue) by superimposing the N- and C-terminal ends of α1C, leaving only α1N of PilE (red). All other PilE subunits are colored gray, with α1 (residues 1 through 55) shown in yellow and α1N residues Gly14 and Pro22 in cyan. The model is shown in cartoon (Left) and space-filling representations (Middle and Right). The filament has been rotated about its long axis in the right panel to show how the narrower PilV globular domain exposes α1N of a higher PilE subunit (dashed oval). (I) For comparison, the N. meningitidis T4P reconstruction is shown with a single PilE subunit colored red. (J, K) Electrostatic surface representation of PilV (J) and PilE (K), shown in approximately the same orientation as in H and I.
Table 1.
X-ray data collection and refinement statistics
| Data collection | PilV (orthorhombic) | PilV (monoclinic) | |
| SSRL beamline | SSRL 7-1 | SSRL 7-1 | SSRL 12-2 |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.976 | 0.979 | 0.969 |
| Space group | P212121 | P212121 | C2 |
| Unit-cell parameters | |||
| a, b, c (Å) | 21.8, 39.3, 109.6 | 21.8, 39.3, 109.6 | 46.3, 21.8, 83.8 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 104, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) | 1.96 | 1.96 (2.07 to 1.96) | 1.41 (1.43 to 1.41) |
| Solvent content (%) | 42.4 | 42.4 | 33.8 |
| Molecules/AU* | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total no. of reflections† | 53,268 (2,538) | 52,638 (6,230) | 91,105 (4,625) |
| Unique reflections | 7,263 (442) | 7,182 (947) | 15,424 (772) |
| Multiplicity | 7.3 (5.7) | 7.3 (6.6) | 5.9 (6.0) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.7 (89.2) | 98.8 (94.6) | 95.9 (97.0) |
| ≤I/σ(I)≥ | 23.9 (5.5) | 24.3 (6.9) | 12.2 (4.0) |
| Rmerge‡ (%) | 6.6 (28.8) | 5.4 (23.7) | 10.8 (90.0) |
| Rpim§ (%) | 2.6 (12.9) | 2.5 (10.8) | 4.3 (0.359) |
| CC1/2¶ | 0.999 (0.981) | 0.999 (0.986) | 0.997 (0.843) |
| Wilson B factor (Å2) | 17.1 | 8.8 | |
| Refinement and model statistics | |||
| No. of reflections used | 7,217 | 1,5402 | |
| Rwork# | 0.185 | 0.172 | |
| Rfreeǁ | 0.255 | 0.206 | |
| RMSD | |||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.007 | 0.009 | |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.932 | 1.024 | |
| No. of non-H atoms | |||
| Protein | 792 | 835 | |
| Ligand | 18 | 14 | |
| Water oxygens | 73 | 106 | |
| Average B factor (Å2) | |||
| Protein atoms | 27.1 | 13.3 | |
| Ligands | 46.8 | 33.5 | |
| Water oxygens | 35 | 22.6 | |
| Ramachandran plot | |||
| Favored (%) | 100 | 99 | |
| Allowed (%) | 100 | 0 | |
| Outlier (%) | 0 | 1 | |
| PDB code | 5V23 | 5V0M | |
*Values in parentheses indicate the highest resolution shell.
†AU, asymmetric unit.
‡Rmerge = ΣhΣi | Ii(h) - <I(h)> | / ΣhΣiIi(h).
§Rpim = Σhkl {1/(Nhkl – 1)} 1/2 Σi | Ii(hkl) - <I(hkl) > | / Σhkl Σi Ii(hkl).
¶CC1/2.
#Rwork = Σhkl | |Fobs| - |Fcalc| | / Σhkl |Fobs|.
ǁRfree is the cross-validation R factor for 5% of the reflections against which the model was not refined.
Though PilV has only limited sequence homology beyond α1N to the N. meningitidis major pilin PilE and is substantially smaller, with 122 amino acids compared to PilE’s 161 amino acids (Fig. 3A), PilV is similar in structure to PilE from both N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae (Fig. 3D). The most significant differences are 1) the β-strands, which decrease in length from β1 to β4 for PilV but become increasingly longer for PilE; 2) the absence on PilV of the hypervariable β-hairpin loop insertion comprising much of the D-region of PilE; and 3) the α1C structure, which is curved in PilE due to the presence of the helix-breaking Gly42 but straight in PilV, which has a histidine at this position (Fig. 3E). This straight α1C is seen in other N. meningitidis minor pilins of known structure, the core minor pilin PilX, and the competence-associated minor pilin ComP, despite PilX having a glycine at position 42 (Fig. 3 E–G). However, all these pilins possess the conserved curvature-inducing Gly14 and Pro22. These conserved residues delineate a segment of α1N that is helical in the full-length pilin subunit but melted in the pilus filament, presumably to allow packing of α1N into the hydrophobic core of the filament (23, 24). PilV is the smallest and simplest of the Neisseria pilins; each of the others have unique αβ-loop and/or D-region structural features that contribute to pilus functions and are predicted to be surface exposed: the hypervariable β-hairpin contributes to immune escape for the Neisseria major pilins; the PilX D-region has a short “pigtail” α-helix that is involved in pilus-mediated bacterial aggregation and adhesion (43); and ComP has an extended loop that lies across the β-sheet and is implicated in DNA recognition (29).
Model of Minor Pilin within Pilus Filament.
To understand how PilV might integrate into the pilus filament to influence its functions, the PilV structure was fit into the N. meningitidis pilus filament model, derived by cryoEM reconstruction (23), in place of one of the major pilins, PilE (Fig. 3H and SI Appendix, Fig. S3). The two α1Cs were aligned at their N- and C-terminal ends, resulting in good superposition of the αβ-loop and β-sheet, including its loops, with no steric clashes. However, the PilV globular domain is smaller than that of PilE, with a shorter β3-β4 strand–loop–strand and a more compact C terminus, which leaves a gap between PilV and the adjacent PilE that exposes the melted region of α1 of a higher subunit (Fig. 3 H and I). The structure of the exposed face of PilV, which lacks the hypervariable loop, and its chemistry (Fig. 3J) differ substantially from that of PilE (Fig. 3K). Thus, inserting PilV in place of PilE would change both the packing of the pilin subunits and the surface stereochemistry, which may impact the flexibility of the pilus and its interactions with host receptors. Importantly, the N. meningitidis T4P structure used in this model was built using only PilE as the building block (23). Our findings here show that PilV is distributed randomly throughout the pilus, which will have averaged out the electron density and likely limited the resolution of the reconstruction.
Mutational Scanning of pilV.
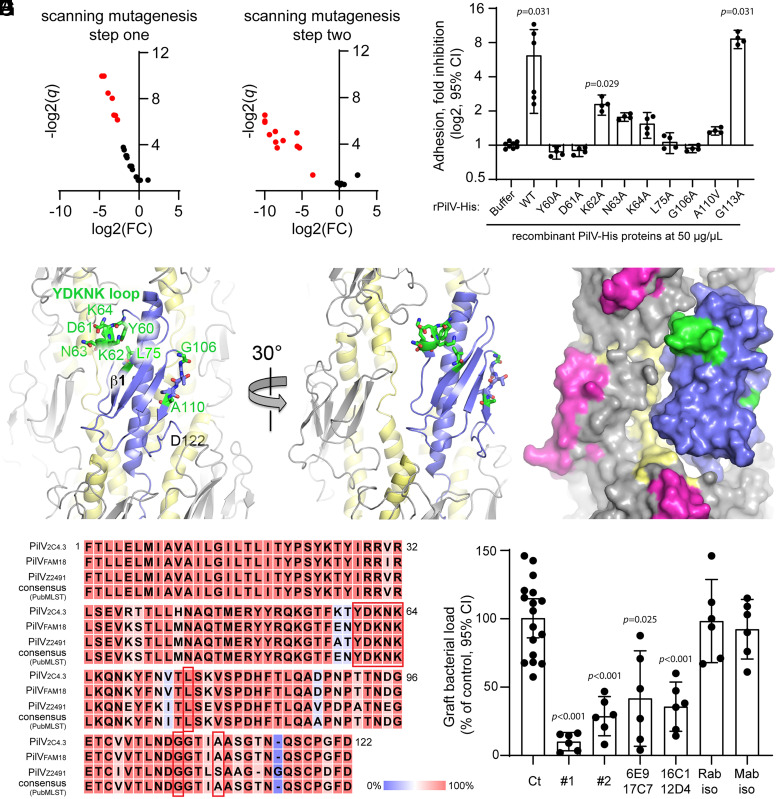
To identify the residues/regions of PilV responsible for interactions with host cell receptors, we used a two-step scanning mutagenesis protocol. Mutations were introduced into the pilV gene inserted in the pKH37 plasmid (44), which was used to transform the PilV-deficient N. meningitidis 2C4.3 strain. Step 1: consecutive amino acid triplets throughout the globular domain were substituted with alanine triplets (or valine when the WT amino acid was alanine). Mutants expressing PilV variants within the pilus were screened for adhesion to hCMEC/D3 cells (Fig. 4A). Mutants that express PilV and incorporate this minor pilin into surface pili but showed poor adhesion indicate PilV defects related to adhesion rather than to protein stability, pilus biogenesis, or integration into the pilus. Such mutants were selected for Step 2 (Fig. 4A and SI Appendix, Supplemental Methods). Step 2: A panel of single amino acid alanine substitutions were generated at sites associated with adhesion defects. These pilV mutants were expressed in the ΔV strain, as for the triplet mutants. The single amino acid mutants were tested for PilV localization within pili and then for adhesion to hCMEC/D3 cells (Fig. 4B). Of particular interest were the ΔV mutants that have WT levels of PilV in their sheared pilus fractions yet showed little or no adhesion (Fig. 4B and SI Appendix, Supplemental Methods): residues corresponding to these substitutions, 60 through 64 as well as L75, P91, G106, G107, A110, and G113, may be directly involved in host cell adhesion (SI Appendix, Supplemental Methods). To further confirm the roles of these amino acids in adhesion to endothelial cells, we introduced the corresponding alanine/valine changes into the pilV plasmid used to produce recombinant His-tagged PilV (rPilV-His, residues 29 through 122) and generated rPilV-His variants. As demonstrated previously (13), addition of WT rPilV-His reduces adhesion of meningococci to endothelial cells (hCMEC/D3) by ∼70%, whereas a similar dose of recombinant minor pilin ComP (rComP-His) has no effect on binding (SI Appendix, Fig. S4 A and B). The ability of these rPilV-His variants to inhibit N. meningitidis adhesion to hCMEC/D3 endothelial cells is shown in Fig. 4C and summarized in SI Appendix, Table S1. Among the rPilV-His variants that were produced at levels comparable to that of WT PilV-His, the rPilV-His-G113A variant inhibited adhesion at a level comparable to that of WT rPilV-His, ruling this residue out as a receptor binding candidate. rPilV-His-K62A showed a twofold inhibition of adhesion, which was not statistically significant compared to buffer. rPilV-His-N63A, -K64A and -A110V showed only partial inhibition of adhesion and rPilV-His-Y60A, -D61A, -L75A, and -G106A showed little to no inhibition. These results are consistent with the adhesion defects observed for the N. meningitidis PilV point mutants and implicate residues Y60-D61, N63-K64, L75, G106, and A110 in adhesion to endothelial cells.
Fig. 4.
PilV residues involved in host cell adhesion. (A and B) Identification of PilV mutant defective for adhesion. Volcano plots, adhesion of N. meningitidis ΔpilV strain expressing PilV variants. Data are shown for mutants in which pili are produced at approximately WT levels and PilV is detected in the pilus preparation. Adhesion is expressed as log2 of fold change [log2(FC)] between mutated and WT PilV, and statistical significance is expressed as −log2(q value) (−log2(q)). Red dots represent mutants defective for adhesion. (A) Mutants selected during the first step of mutagenesis with triplet Ala/Val substitutions; (B) mutants selected during the second step of mutagenesis looking at single Ala/Val substitutions at sites of adhesion defects (SI Appendix, Supplemental Methods). (C) The ability of WT rPilV and rPilV variants to competitively inhibit N. meningitidis adhesion to hCMEC/D3 cells was assessed. Endothelial cells were treated with 50 μg/mL recombinant proteins for 30 min prior to infection with N. meningitidis WT strain for 30 min. The number of adherent cell-associated bacteria was determined by counting CFUs. Data shown are averaged values for two independent experiments. Adhesion is expressed as log2(mean) ± 95% CI of fold inhibition, normalized on bacterial adhesion of cells treated with buffer only. Statistical analyses were performed against buffer using the Kruskal–Wallis test. (D–F) N. meningitidis T4P structure with one PilE subunit replaces with PilV as for Fig. 3. (D) Cartoon representation of the pilus with PilV shown in blue, PilE in gray with α1 colored yellow. Residues implicated in host cell binding are shown in stick representation with carbon atoms in green, nitrogens in blue, and oxygens in red. The YDKNK loop is the Y60-K64 loop. (E and F) Cartoon and space-filling representations of the pilus model rotated about its axis to show how the Y60-K64 loop contacts the neighboring PilE and may form part of a larger receptor binding site. The hypervariable loop, which is part of the protruding β-hairpin of PilE, is colored magenta in F. (G) Alignment of PilV protein sequences from N. meningitidis 2C4.3, FAM18, and Z2491 strains and that of the PubMLST consensus sequence (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). Conserved residues are highlighted in red, and nonconserved residues are highlighted in blue. Residues implicated in host-cell adhesion are boxed in red. (H) Graft bacterial loads of human skin–grafted SCID mice injected intravenously with buffer (control), 100 μg anti-PilV rabbit polyclonal Immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti bodies (#1 and #2), 100 μg anti-PilV peptide mouse monoclonal IgG antibodies (raised against the P80DHFTLQADPNPTTNDGE97 peptide: 6E9 + 17C7 and 16C1 + 12D4) or their respective isotype control antibodies, followed by infection with 5 × 105 CFUs of WT meningococci. Graft bacterial loads were determined 4 h after infection and normalized to that of the control (buffer only). Values shown are the averages of two independent experiments performed with a skin patch from different donors. Each dot represents a single mouse; data are expressed as the mean ± 95% CI of CFU/g. Statistical analyses were performed against the control with the Brown–Forsythe test and Welch’s ANOVA.
These amino acids are highlighted on PilV in Fig. 4 D–F. Residues Y60-K64 are centered on the 310 helix within the αβ-loop of PilV. The aromatic side chain of Tyr60 is buried within the globular domain and may be required to orient this loop and properly present the polar/charged side chains of Asp61, Asn63, and K64 on the PilV surface for binding to host cell receptors. Leu75 lies on strand β1 and appears to stabilize the Y60-K64 loop, contacting the side chains of Tyr60, Leu65, and the aliphatic portion of the Lys62 side chain. The Y60-K64 loop protrudes from the globular domain and lies on the pilus surface and is adjacent to the PilE subunit in our filament model (Fig. 4 E and F). Thus, this loop may influence the conformation of PilE and comprise part of a larger binding site that involves one or more PilE subunits. A graphical representation of the amino acid multiple sequence alignment shows Y60, D61, and K64 as conserved among 699 distinct PilV sequences identified (see Methods), and K62 and N63 are present in about 50% of these sequences (Dataset S1 and SI Appendix, Fig. S4D), consistent with the importance of these residues in adhesion (Fig. 4C). The three N. meningitidis genomes, 2C4.3, FAM18, and Z2491, which are commonly used in the laboratory, have several amino acid differences but share the residues implicated in adhesion, Y60-K64, L75, and G106, while A110 is replaced by a serine in the Z2491 PilV sequence (Fig. 4G). In further support of these residues being involved in T4P-mediated adhesion, complementation of the 2C4.3 ΔV with pilV of FAM18 or Z2491 had no significant impact on adhesion to endothelial cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S4C).
Interestingly, no pilV mutants were identified that produced WT levels of PilV that were not incorporated into the pilus. Such mutants might have indicated residues involved in PilV:PilE interactions within the pilus. However, these results are consistent with our knowledge of T4P structure, in which subunits are held together primarily by interactions among α1N residues: hydrophobic interactions as well as a salt bridge between Glu5 and the N-terminal amino group (23, 24, 45). To test the role of key residues in α1N, we substituted the conserved Phe1 and Glu5 with alanine. As predicted, these changes do not impact PilV expression, but PilV is poorly incorporated into the pilus (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). Pilus levels, as assessed by PilE in the crude pilus preparations, are not affected in these mutants.
Anti-PilV Antibodies Inhibit N. meningitidis Adhesion.
We next investigated the potential for PilV-targeted antibodies to inhibit bacterial adhesion in vivo using the human skin–grafted mouse model (14). Anti-PilV polyclonal antibodies were produced from rabbits immunized with rPilV, and monoclonal antibodies were produced from mice immunized with PilV peptides spanning the residues implicated in adhesion (peptide 58-66 and 98-119) and the β-strand 2 (peptide 80-97). No antibodies were obtained in mice with the peptide spanning either the Y60-K64 adhesive loop nor the 98-119 D-region. Only immunizations with peptide 80-97 (residues PDHFTLQADPNPTTNDGE of mature PilV) were successful, resulting in four monoclonal antibodies. Antibodies were injected in the tail vein of grafted animals 2 h prior to intravenous infection with WT N. meningitidis. Bacterial colonization of human skin grafts was determined 4 h after infection by counting CFUs (Fig. 4H). Two different batches of rabbit polyclonal antibodies raised against rPilV reduced vascular colonization 9.8-fold and 3.4-fold, respectively, relative to the unimmunized controls. Two different mixtures of monoclonal antibodies raised against peptide 80-97 also significantly inhibited vascular colonization (6E9 + 17C7 2.4-fold; 16C1 + 12D4 2.8-fold), while rabbit and mouse isotype control antibodies had no effect. The reduced colonization in the presence of these antibodies is not due to a bactericidal effect of the antibodies, since counts of CFU in the blood of the grafted mice were not statistically different between the control and antibody groups 4 h after infection (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). These results demonstrate that anti-PilV antibodies can efficiently block N. meningitidis T4P-dependant adhesion to human host-cell receptors.
Discussion
Here, we show that the conserved noncore minor pilin PilV is involved in adhesion to host endothelial cells by virtue of its incorporation throughout the pilus filament. PilV has a canonical T4P fold but lacks the surface adornments seen in PilE (the hypervariable β-hairpin), PilX (the α-helix “pigtail”), and ComP (the DNA-binding strand). When modeled into the pilus filament in place of PilE, a gap is created that may expose additional binding sites and influence filament flexibility.
This demonstration of a minor pilin being abundantly distributed throughout the pilus indeed calls into question its designation as a minor pilin. Core minor pilins are encoded within a single gene cluster and have been shown to interact with each other and with the major pilin (17). These low-abundance pilins share the canonical T4P fold and are thought to form a cluster that initiates pilus assembly and caps the filament. In contrast to the core minor pilins, both PilV and ComP are encoded in separate sites on the N. meningitidis genome. They share the pilin fold but have specific roles in the bacterial life cycle in adhesion and DNA uptake, respectively. The reduction in pili in the ΔpilV mutant suggests that PilV may have an additional nonessential role in pilus assembly or stability. The localization of PilV, and presumably ComP, further distinguishes them from the putative tip-associated core minor pilins. These noncore minor pilins are unique to the pathogenic Neisseria, perhaps because their major pilin undergoes antigenic variability.
PilV maintains a low profile on the pilus surface due to the small size of its globular domain relative to that of the major pilin PilE. The critical Y60-K64 adhesion loop identified by iterative alanine scanning mutagenesis appears to be located in close apposition to PilE, in a shallow well beneath the protruding, hypervariable β-hairpin of PilE. The Y60-K64 loop is conserved among N. meningitidis strains and thus provides a recessed receptor binding site, distributed abundantly along the length of the pilus. We show here that PilV mediates adhesion to host cells in vitro and in vivo. Yet rather than simply providing a filamentous scaffold for the primary adhesin PilV, PilE is itself adhesive, as the piliated ΔV mutant retains some adhesion capability, whereas a nonpiliated ΔE mutant is nonadherent. Our data are consistent with previous observations that both PilE and PilV interact with host cell receptors and are required for efficient adhesion (13, 25, 26). Our findings help to explain how N. meningitidis can alter the amino acid sequence of its major pilin from one generation to the next to evade the host immune response while maintaining its ability to adhere to host endothelial cells. The hypervariable PilE β-hairpin is prominently displayed on the pilus surface and may elicit neutralizing antibodies, but these would be rendered ineffective due to antigenic variation, whereas the recessed and conserved PilV maintains adhesion capability for the pilus.
The recessed nature of the Y60-64 loop in the context of the intact pilus makes it less likely to be recognized by human antibodies. Nonetheless, monoclonal antibodies targeting peptide 80-97 and rabbit sera raised against rPilV inhibit vascular colonization in vivo, demonstrating the viability of PilV to elicit a protective immune response. Consistent with these findings, convalescent sera from patients with meningococcal disease recognized PilV in an ELISA assay (37), although their impact on bacterial adhesion was not tested. The ability of anti-PilV antibodies to inhibit vascular colonization by N. meningitidis in a human skin graft is a key finding of this study. PilV may be the Achilles heel of the N. meningitidis T4P, providing a conserved and critical target to block adhesion and treat meningococcal infections and a protective antigen for meningococcal subunit vaccines, a finding that may also be relevant for N. gonorrhoeae, which also possesses PilV.
Methods
Bacterial Strains and Endothelial Cells.
N. meningitidis 2C4.3 strain (formerly clone 12) that is a piliated encapsulated Opa− Opc− variant of the serogroup C meningococcal clinical isolate NEM8013 and its isogenic nonpiliated PilE-defective mutant (ΔE), the PilV-defective mutant (ΔV), and the PilV-complemented strain (ΔV + V2C4.3) were described previously (13). The pilV gene of strains FAM18 (46) and Z2491 (47) was cloned from genomic DNA by PCR, and pilV genes were inserted by Gibson assembly into plasmid pKH37 between the N. meningitidis genes lctP and aspC and downstream of the lacP promoter (44). Bacterial strains were stored frozen at −80 °C and routinely grown at 37 °C in a moist atmosphere with 5% CO2 on gonococcal base (GCB) agar plates (Difco) containing Kellogg’s supplements. Antibiotics were added as indicated. Strains, plasmids, and primers are listed in SI Appendix, Table S2.
hCMEC/D3 are a fully differentiated brain endothelial cell line derived from human brain capillaries that recapitulate the major phenotypic features of the blood–brain barrier (48). hCMEC/D3 were grown onto Cultrex rat collagen type I–coated dishes (R&D) in Endothelial Cell Basal Medium-2 (Lonza) supplemented with 5% of fetal calf serum (FCS), 1.4 μM hydrocortisone (Lonza), 5 μg/mL ascorbic acid (Lonza), and 1 ng/mL b-FGF (Lonza), at 37 °C in 5% CO2. HDMECs were purchased from Promocell and grown onto Cultrex rat collagen type I–coated dishes (R&D) in Endothelial Cell Growth Medium MV (Promocell) supplemented with Endothelial Cell Growth Medium Supplement Mix (Promocell) at 37 °C under 5% CO2. EA.Hy926 (ATCC CRL-2922) are endothelial cells established by fusing primary human umbilical vein cells with a thioguanine-resistant clone of A549. Cells were grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium supplemented with 10% FCS at 37 °C under 5% CO2.
Endothelial Cell Infection and Adhesion Assays.
On the day of infection, a suspension of bacteria from an overnight culture on GCB agar plate was adjusted to optical density 600nm (OD600) 0.05 and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C in prewarmed cell culture medium (according to cell type). Cells were infected with bacteria at a multiplicity of infection of 100 bacteria per cell for 30 min, washed six times to remove unbound bacteria, and CFUs were counted by plating serial dilutions on GCB agar plates. When required, cells were treated with recombinant His–PilV at indicated concentrations for 30 min before infection.
Infection of Human Skin–Grafted Mice.
The 6- to 8-wk-old CB17/Icr-Prkdcscid SCID female mice were obtained from Janvier Labs. Mice were grafted with normal human skin as previously described (14). Briefly, full-thickness human skin was grafted onto the back of SCID mice by surgical stitching. Grafted mice were randomized into control and treated groups. When required, anti-PilV antibodies or buffer (physiological saline) were administered intravenously 2 h prior to infection at a total dose of 100 μg for polyclonal anti-PilV or 50 μg each of two monoclonal anti-PilV preparations. N. meningitidis strains were grown overnight on GCB agar plates without iron (Kellogg supplement II) and supplemented with deferoxamine (Desferal, Novartis) at 37 °C. On the day of infection, bacteria were harvested and grown under agitation in RPMI medium with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 0.06 μM deferoxamine to exponential phase. Bacteria were then resuspended in physiological saline, and mice were infected intravenously with N. meningitidis 2C4.3 WT strain or the mutant strains defective for PilE or PilV (ΔE and ΔV) (5 × 105 or 5 × 106 bacteria). Bacteremia was assessed at 1 h and 4 h by collecting a blood sample by tail vein puncture. Mice were killed 4 h after infection, and human skin grafts were removed sterilely. The grafts were crushed and homogenized with Lysing Matrix M tubes using FastPrep (MP Biomedicals) with two cycles of 15 s at speed 6 m/s. Bacterial counts were determined by plating serial dilution of the samples onto GCB agar plates.
Crude Pilus Purification.
AS precipitation.
N. meningitidis strains were grown overnight on GCB agar plates, scraped off of the plates, and resuspended in 2 mL 20 mM ethanolamine, pH 10.5 supplemented with 1 mM dithiothreitol at 4 °C. To shear pili off, the bacteria were vortexed vigorously three times for 1-min bursts and returned to ice for 1 min between each burst. Bacterial cells were removed from the pilus suspension by two successive centrifugations at 10,000 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. Cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 25 mM Hepes, 2 mM EDTA, 1% [wt/vol] SDS—bacterial fraction). The supernatant containing the pili was collected and supplemented with saturated ammonium sulfate (AS) in 20 mM ethanolamine, pH 10.5 at a final concentration of 0.15 M before overnight agitation at 4 °C. Aggregated pili were pelleted by centrifugation at 17,000 × g for 20 min at 4 °C and resuspended overnight at 4 °C in 400 μL 20 mM ethanolamine, pH 10.5. The pili solution was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 20 min at 4 °C to remove residual cell debris, and the supernatant was concentrated 10-fold using an Amicon 10-kDa MWCO membrane (Merck Millipore).
Colocalization of PilV and PilE by Immunoprecipitation.
Bacteria grown on GCB agar plates were adjusted to OD600 = 0.2 in prewarmed liquid GCB medium and then incubated at 37 °C under 5% CO2 for 1 h. The bacterial suspension was vortexed, passed through a 26 G needle, and centrifuged at 1,500 × g for 15 min. The cleared supernatants were used for immunoprecipitation with specific antibodies against PilE (5C5 mAb) or PilV (rabbit serum Acfp) coated on protein G magnetic beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Precipitated proteins were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose (GE Healthcare). After blocking for 1 h in PBS, 1% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20, filters were probed overnight with specific antibodies against PilE (rabbit polyclonal antibody No. 9410), PilV (Acfp), anti-NADPGH (cytosolic marker), and anti-Rmp4 (membrane marker) and revealed using enhanced chemiluminescent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) after probing with peroxidase-coupled secondary antibodies (GE Healthcare).
Immunoblotting and Piliation Index Calculations.
Bacteria grown overnight were scraped from GCB plates and resuspended in PBS and Laemmli buffer for whole bacterial lysate samples. Laemmli buffer was added to pilus preparations and bacterial fractions (Crude Pilus Purification). Samples were analyzed for the presence of PilV, PilE, NADPGH, or Rmp4 by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The piliation index was determined by quantifying PilE in the sheared pilus fraction based on densitometry of immunoblot bands and normalizing this value to the PilE content in the corresponding bacterial fraction (ImageJ Software).
PilV Sequence Comparison.
All sequences correspond to the query pilV (NEIS0487) in the Meningitis Research Foundation Meningococcus Genome Library (PubMLST) database (864 nonredundant nucleotide sequences on January 14, 2019). DNA sequences were translated into protein sequences using EMBOSS Transeq (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/st/emboss_transeq/). The redundancy of the corresponding protein sequence dataset was reduced using CD-HIT version 4.7 (49) with a 100% identity threshold yielding 699 clusters. The longest representative sequence of each cluster was aligned with Clustal Omega version 1.2.4 (50) using the default parameters. We then used the SIAS (Sequence Identity and Similarity) server (http://imed.med.ucm.es/Tools/sias.html) to calculate pairwise sequence identity and similarity from the multiple sequence alignment with default parameters for similarity, amino acid grouping, and length of multiple sequence alignment for the denominator (Dataset S1). A graphical representation of the amino acid multiple sequence alignment is shown as a sequence logo (51) generated by using Weblogo 3.7.4.
Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM).
Bacteria were grown in Endothelial Cell Growth medium MV (Promocell), spread in 22-mm high-precision cover glasses with thickness of 170 μm, (No. 1.5H, Marienfield) with cytospin, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min before immunolabeling. HDMECs were seeded on the high-precision cover glasses (No. 1.5H, Marienfield), infected with meningococci for 90 min, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min. Bacteria or endothelial cells were blocked with 3% BSA–PBS for 10 min, labeled with the monoclonal anti-PilE antibody 20D9 and the polyclonal anti-PilV antibody 6488 (1:100 in 2% BSA–PBS) 4 °C overnight, and then incubated with goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 647F(ab’)2 secondary antibody fragments and goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 555 F(ab’)2 secondary antibody fragments (Life Technologies; A-21237) (1:500). Marienfield cavity slides were poured with blinking reagent (Smart Kit buffer optimized for dSTORM, Abbelight), and the cover glasses were sealed with a Twinsil 22 silicon-glue (Rotec) as described previously (27). Images were acquired on a Leica SR GSD system, with a ×160 oil (NA 1.43) objective. Fluorescence images were collected using an EMCCD camera (Andor Technology), providing an effective pixel size of 100 nm, and processed with the LAS X Software (Leica). Approximately 50,000 frames were recorded for each acquisition with a 10-ms exposure time, electron-multiplying gain of 300, and the number of photons per pixels set to 75. Two-dimensional reconstructions were obtained from stacks (16 planes) with 50 nm axial step size using the LAS X Software (Leica) or ImageJ.
PilV Expression, Crystallization, and Structure Determination.
Methods for PilV expression for crystallization and that of His-tagged PilV and His-tagged ComP for competition assay are described in SI Appendix, Supplemental Methods.
Crystallization and structure determination.
Initial crystallization conditions for PilV were identified using the High-Throughput Crystallization Screening Center at the Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute. Conditions were optimized in-house using the hanging drop vapor diffusion method. Crystals were grown in 100 mM sodium acetate pH 5, 100 mM ammonium chloride, and 28% (wt/vol) polyethylene glycol 8000. The crystals were cryocooled in mother liquor containing 30% vol/vol glycerol as cryoprotectant. Crystals were screened at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) Beamline 7-1, and X-ray diffraction data were collected at Beamlines 7-1 and 12-1 using Blu-Ice (53) (Table 1). PilV datasets were processed, integrated, and scaled using XDS and the CCP4 programs iMosflm, POINTLESS, AIMLESS, and TRUNCATE (54, 55). PilV crystals belonging to two different space groups, monoclinic C2 and orthorhombic P212121, were obtained in similar crystallization conditions. Data were collected for the orthorhombic crystal form at wavelengths corresponding to inflection point and high-energy remote, and the PilV structure was solved by the two-wavelength anomalous diffraction method (Table 1). The automated structure solution program SOLVE located two selenium sites, and initial phases were calculated (56). Density modification was performed using RESOLVE (57), resulting in an interpretable electron density map. A Matthews coefficient of 2.1 was calculated for the orthorhombic crystal, indicating a single molecule in the asymmetric unit with 42.4% solvent content. An initial model for PilV was built in COOT (58). The model was refined, and water oxygens were located using the PHENIX suite (59). R-values for the refined model are Rwork = 0.185 and Rfree = 0.255, with a resolution of 1.96 Å. Data were collected to 1.4 Å for one of the monoclinic PilV crystals. The Matthews coefficient is 1.9 for this crystal, giving one molecule per asymmetric unit and a solvent content of 33.8%. The monoclinic PilV structure was solved by the molecular replacement method using the lower-resolution orthorhombic PilV structure as a model. PHASER (60) gave a solution with high Z-scores (RFZ = 7.6 and TFZ = 24.3). This model was further improved using the crystallographic macromolecular model building program ARP/wARP. Several cycles of fitting and refinement were performed in COOT and PHENIX, respectively. Water oxygens were located, and the final PilV model was anisotropically refined with hydrogen atoms. Both monoclinic and orthorhombic crystal structures were validated using MOLPROBITY (61). The resolution of the monoclinic PilV structure is 1.41 Å, with an Rwork of 0.172 and an Rfree of 0.206. Data collection and model statistics are given in Table 1.
Scanning Mutagenesis.
The mutations were introduced by PCR mutagenesis (primers are listed in SI Appendix, Table S2) into the pilV gene inserted into the pKH37 plasmid. Plasmids were used to transform the PilV-deficient N. meningitidis 2C4.3 strain (ΔV). To examine the impact of the alanine substitutions, complemented ΔV mutants were first tested for their ability to assemble T4P and to incorporate PilV into the pili by shearing the pili of the bacterial surface, concentrating them using AS, and assessing PilE and PilV levels by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Next, the piliated alanine-substituted mutants were tested for their ability to adhere to hCMEC/D3 endothelial cells. Mutations in the PilV sequence affecting PilV incorporation into pilus filament or T4P stability were excluded from our study.
Generation of Anti-PilV Antibodies.
Anti-PilV polyclonal antibodies were produced in two rabbits immunized with rPilV (Proteogenix). Anti-PilV monoclonal antibodies were produced in mice against three different PilV peptides (peptide 58-66, 80-97, and 98-119). Hybridomas were selected for their production of antibodies that inhibited bacterial adhesion to human endothelial cells. Selected hybridomas were amplified, and antibodies were purified. No antibodies for peptides 58-66 and 98-119 were obtained, either because they are not immunogenic or hybridomas were unstable. Two different antibody-producing companies were involved (Proteogenix and Biotem). Peptide 80-97 allowed for hybridoma selection and purification of antibodies (Biotem). Isotype control antibodies were produced and purified by Biotem.
Statistical Analysis.
Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism. Multiple comparison analyses were assessed with a one-way ANOVA or a one-way Brown–Forsythe and Welch’s ANOVA test depending on the variance analysis, and data were expressed as mean ± 95% CI (relevant P values were reported in the figures). In case of a failed normality test or positive Bartlett’s test and important differences in mean and SD, a Kruskal–Wallis test was used, and data were expressed as median ± interquartile range (corrected P values were reported in the figures). The H0 hypothesis was rejected for a significance level of P ≤ 0.05. Multiple comparison reports and descriptive statistics are available in SI Appendix, Supplemental Statistics.
Ethics Statements.
The animal experimental procedures described in this work conform to European Union ethical regulations (Directive 2010/63/EU). The project was approved by Comité d'Ethique en matière d’Expérimentation Animale Paris Descartes and the Ministère de l’Eduction Nationale de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche (Project No. APAFIS#16345-2018012515596498 v5). Human skin tissues were obtained from surgical wastes from patients undergoing plastic surgery, and samples were disidentified prior to use (Groupe Hospitalier Paris Saint-Joseph). In accordance with French legislation, the study was declared to the Comité d’Ethique de la Recherche Paris Descartes and approved. Patients were informed of the research purpose, and oral consent was recorded.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research grants ANR-15-CE15-0002-01 (to M.C.), Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (X.N. and E.C.), ANR-14-IFEC-0006-01 (to S.B. and X.N.), INSERM and Université de Paris (to M.C., S.B., and X.N.), and by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council Grant (to L.C.). We thank the staff at SSRL for assistance in X-ray diffraction data collection. Use of SSRL, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is supported by the US Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515. The SSRL Structural Molecular Biology Program is supported by the DOE Office of Biological and Environmental Research, and by the NIH, National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) (P30GM133894). The contents of this publication are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIGMS or NIH.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2109364118/-/DCSupplemental.
Data Availability
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.
References
- 1.Chang Q., Tzeng Y. L., Stephens D. S., Meningococcal disease: Changes in epidemiology and prevention. Clin. Epidemiol. 4, 237–245 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Muttalif A. R., et al., Incidence and prevention of invasive meningococcal disease in global mass gathering events. Infect. Dis. Ther. 8, 569–579 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Christensen H., May M., Bowen L., Hickman M., Trotter C. L., Meningococcal carriage by age: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 10, 853–861 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coureuil M., et al., Molecular interactions between Neisseria meningitidis and its human host. Cell. Microbiol. 21, e13063 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Audry M., et al., Airway mucus restricts Neisseria meningitidis away from nasopharyngeal epithelial cells and protects the mucosa from inflammation. mSphere 4, e00494-19 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Siena E., Bodini M., Medini D., Interplay between virulence and variability factors as a potential driver of invasive meningococcal disease. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 16, 61–69 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Barnier J.-P., et al., Type IV pilus retraction enables sustained bacteremia and plays a key role in the outcome of meningococcal sepsis in a humanized mouse model. PLoS Pathog. 17, e1009299 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Capel E., et al., Peripheral blood vessels are a niche for blood-borne meningococci. Virulence 8, 1808–1819 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Denis K., et al., Targeting Type IV pili as an antivirulence strategy against invasive meningococcal disease. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 972–984 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cahoon L. A., Seifert H. S., An alternative DNA structure is necessary for pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Science 325, 764–767 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vink C., Rudenko G., Seifert H. S., Microbial antigenic variation mediated by homologous DNA recombination. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 36, 917–948 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wörmann M. E., et al., Sequence, distribution and chromosomal context of class I and class II pilin genes of Neisseria meningitidis identified in whole genome sequences. BMC Genomics 15, 253 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bernard S. C., et al., Pathogenic Neisseria meningitidis utilizes CD147 for vascular colonization. Nat. Med. 20, 725–731 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Join-Lambert O., et al., Meningococcal interaction to microvasculature triggers the tissular lesions of purpura fulminans. J. Infect. Dis. 208, 1590–1597 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Craig L., Forest K. T., Maier B., Type IV pili: Dynamics, biophysics and functional consequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17, 429–440 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McCallum M., Burrows L. L., Howell P. L., The dynamic structures of the Type IV pilus. Microbiol. Spectr. 7, 2 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nguyen Y., et al., Pseudomonas aeruginosa minor pilins prime type IVa pilus assembly and promote surface display of the PilY1 adhesin. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 601–611 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kolappan S., Ng D., Yang G., Harn T., Craig L., Crystal structure of the minor Pilin CofB, the initiator of CFA/III Pilus assembly in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 25805–25818 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ng D., et al., The Vibrio cholerae minor pilin TcpB initiates assembly and retraction of the toxin-coregulated pilus. PLoS Pathog. 12, e1006109 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Treuner-Lange A., et al., PilY1 and minor pilins form a complex priming the type IVa pilus in Myxococcus xanthus. Nat. Commun. 11, 5054 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parge H. E., et al., Structure of the fibre-forming protein pilin at 2.6 A resolution. Nature 378, 32–38 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Craig L., et al., Type IV pilus structure by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography: Implications for pilus assembly and functions. Mol. Cell 23, 651–662 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kolappan S., et al., Structure of the Neisseria meningitidis Type IV pilus. Nat. Commun. 7, 13015 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang F., et al., Cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Neisseria gonorrhoeae Type IV Pili at sub-nanometer resolution. Structure 25, 1423–1435.e4 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Le Guennec L., et al., Receptor recognition by meningococcal type IV pili relies on a specific complex N-glycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 2606–2612 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Virion Z., et al., Sialic acid mediated mechanical activation of β2 adrenergic receptors by bacterial pili. Nat. Commun. 10, 4752 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maïssa N., et al., Strength of Neisseria meningitidis binding to endothelial cells requires highly-ordered CD147/β2-adrenoceptor clusters assembled by alpha-actinin-4. Nat. Commun. 8, 15764 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Winther-Larsen H. C., et al., A conserved set of pilin-like molecules controls type IV pilus dynamics and organelle-associated functions in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 903–917 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berry J.-L., et al., A comparative structure/function analysis of two Type IV Pilin DNA receptors defines a novel mode of DNA binding. Structure 24, 926–934 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cehovin A., et al., Specific DNA recognition mediated by a type IV pilin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 3065–3070 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cehovin A., et al., Sequence conservation of pilus subunits in Neisseria meningitidis. Vaccine 28, 4817–4826 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Winther-Larsen H. C., et al., Neisseria gonorrhoeae PilV, a type IV pilus-associated protein essential to human epithelial cell adherence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 15276–15281 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mikaty G., et al., Extracellular bacterial pathogen induces host cell surface reorganization to resist shear stress. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000314 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takahashi H., Yanagisawa T., Kim K. S., Yokoyama S., Ohnishi M., Meningococcal PilV potentiates Neisseria meningitidis type IV pilus-mediated internalization into human endothelial and epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 80, 4154–4166 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Imhaus A. F., Duménil G., The number of Neisseria meningitidis type IV pili determines host cell interaction. EMBO J. 33, 1767–1783 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Aubey F., et al., Inhibitors of the Neisseria meningitidis PilF ATPase provoke type IV pilus disassembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 8481–8486 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cehovin A., Kroll J. S., Pelicic V., Testing the vaccine potential of PilV, PilX and ComP, minor subunits of Neisseria meningitidis type IV pili. Vaccine 29, 6858–6865 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aird W. C., Endothelial cell heterogeneity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2, a006429 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hélaine S., et al., PilX, a pilus-associated protein essential for bacterial aggregation, is a key to pilus-facilitated attachment of Neisseria meningitidis to human cells. Mol. Microbiol. 55, 65–77 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wolfgang M., et al., PilT mutations lead to simultaneous defects in competence for natural transformation and twitching motility in piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 29, 321–330 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Biais N., Higashi D. L., Brujic J., So M., Sheetz M. P., Force-dependent polymorphism in type IV pili reveals hidden epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 11358–11363 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brissac T., Mikaty G., Duménil G., Coureuil M., Nassif X., The meningococcal minor pilin PilX is responsible for type IV pilus conformational changes associated with signaling to endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 80, 3297–3306 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Helaine S., Dyer D. H., Nassif X., Pelicic V., Forest K. T., 3D structure/function analysis of PilX reveals how minor pilins can modulate the virulence properties of type IV pili. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 15888–15893 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ramsey M. E., Hackett K. T., Kotha C., Dillard J. P., New complementation constructs for inducible and constitutive gene expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 3068–3078 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li J., Egelman E., Craig L., Electron microscopy reconstruction of the Vibrio cholerae toxin coregulated pilus and comparative analysis with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae GC pilus. J. Mol. Biol. 418, 47–64 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dyer D. W., McKenna W., Woods J. P., Sparling P. F., Isolation by streptonigrin enrichment and characterization of a transferrin-specific iron uptake mutant of Neisseria meningitidis. Microb. Pathog. 3, 351–363 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Achtman M., et al., Purification and characterization of eight class 5 outer membrane protein variants from a clone of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A. J. Exp. Med. 168, 507–525 (1988). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Weksler B. B., et al., Blood-brain barrier-specific properties of a human adult brain endothelial cell line. FASEB J. 19, 1872–1874 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fu L., Niu B., Zhu Z., Wu S., Li W., CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28, 3150–3152 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sievers F., Higgins D. G., Clustal omega. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 48, 3.13.1-16 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Crooks G. E., Hon G., Chandonia J.-M., Brenner S. E., WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 14, 1188–1190 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Luft J. R., A deliberate approach to screening for initial crystallization conditions of biological macromolecules. J. Struct. Biol. 142, 170–179 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.A. Gonzalez, et al., Web-Ice: integrated data collection and analysis for macromolecular crystallography. J. App. Cryst. 41, 176–184 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 54.T. G. G. Battye, L. Kontogiannis, O. Johnson, H. R. Powell, A. G. W. Leslie, iMOSFLM: a new graphical interface for diffraction-image processing with MOSFLM. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 271–281 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. The CCP4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.T. C. Terwilliger, Maximum-likelihood density modification. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 56, 965–972 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.T. C. Terwilliger, J. Berendzen, Automated MAD and MIR structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 55, 849–861 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.P. Emsley, K. Cowtan, Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.P. D. Adamset al., . PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.A. J. McCoy, R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, P. D. Adams, M. D. Winn, L. C. Storoni, R. J. Read, Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.I. W. Daviset al., . MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W375–W383 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.