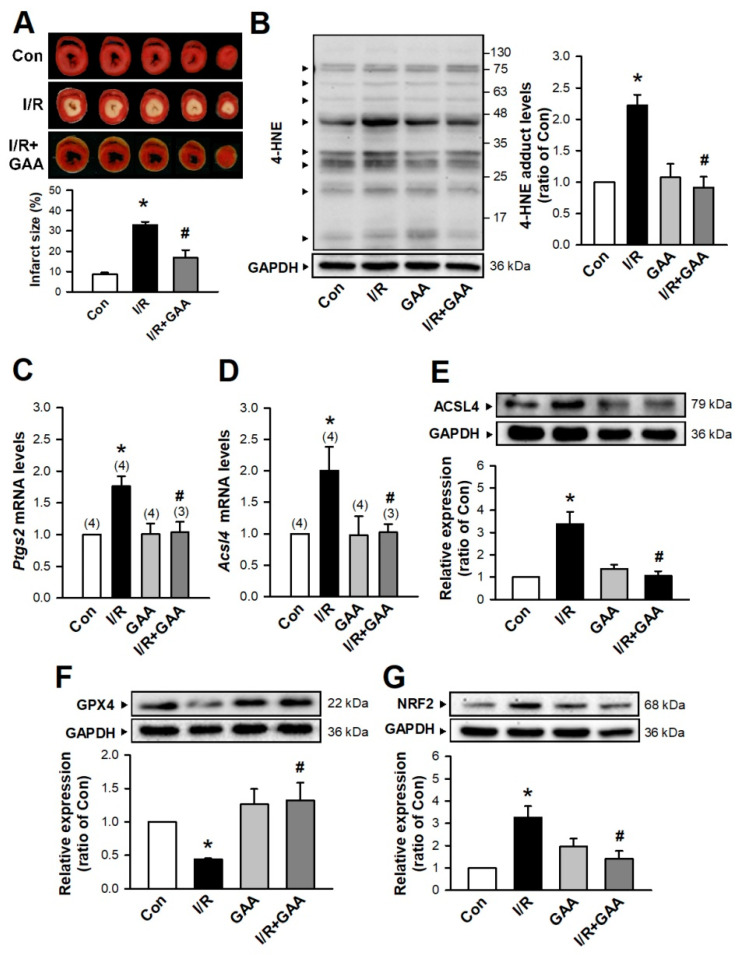
Figure 7.
The mechanism by which GAA attenuates myocardial I/R-induced ferroptotic cell death in ex vivo rat hearts. (A) Representative images (Top) and quantitative data (Bottom) showed that GAA (5 μM) significantly reduced the I/R-induced increase in myocardial infarct size (n = 3). (B) Cotreatment with I/R and GAA (10 μM) significantly decreased the 4-HNE adduct levels (n = 4). GAA significantly decreased levels of Ptgs2 (C) and Acsl4 (D) mRNA in myocardial ischemia-treated hearts according to quantitative PCR analysis. Values shown in parenthesis represent the number in each group. (E) Treatment with GAA significantly inhibited the I/R-increased levels of ACSL4 protein enhancement (n = 9). (F) Treatment with GAA increased GPX4 protein levels compared with those observed in the I/R-treated group (n = 9). (G) Treatment with GAA significantly inhibited I/R-increased levels of NRF2 protein (n = 6). All data represent means ± SEM. * p < 0.05 versus the control group; # p < 0.05 versus I/R. Con, control; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; GAA, gossypol acetic acid.