Abstract
Serratia marcescens is an opportunistic pathogen that causes diverse nosocomial infections. S. marcescens has developed considerable resistance to different antibiotics and is equipped with an armory of virulence factors. These virulence factors are regulated in S. marcescens by an intercellular communication system termed quorum sensing (QS). Targeting bacterial virulence and QS is an interesting approach to mitigating bacterial pathogenesis and overcoming the development of resistance to antimicrobials. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the anti-virulence activities of secnidazole on a clinical isolate of S. marcescens. The effects of secnidazole at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) on virulence factors, swarming motility, biofilm formation, proteases, hemolysin activity, and prodigiosin production were evaluated in vitro. Secnidazole’s protective activity against S. marcescens pathogenesis was assessed in vivo in mice. Furthermore, a molecular docking study was conducted to evaluate the binding ability of secnidazole to the S. marcescens SmaR QS receptor. Our findings showed that secnidazole at sub-MICs significantly reduced S. marcescens virulence factor production in vitro and diminished its pathogenesis in mice. The insilico docking study revealed a great ability of secnidazole to competitively hinder the binding of the autoinducer to the SmaR QS receptor. In conclusion, secnidazole is a promising anti-virulence agent that may be used to control infections caused by S. marcescens.
Keywords: Serratia marcescens, quorum sensing, secnidazole, anti-virulence agents, anti-quorum sensing agents, virulence factors, pathogenesis
1. Introduction
Serratia marcescens (family Enterobacteriaceae) is a motile facultative anaerobic Gram-negative rod that spreads abundantly in soil, plants, water, animals, and on surfaces [1]. S. marcescens was considered a non-pathogenic microbe until 1951 when it caused a nosocomial infection outbreak [2]. S. marcescens is a frequent opportunistic human pathogen that can cause several hospital-acquired infections, for instance, pneumonia, intravenous catheter-associated infections, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and urinary tract infections [2,3]. It was reported in the USA as the tenth most frequent etiological agent of healthcare-associated blood infections and the seventh most common causative agent of nosocomial pneumonia [4]. Furthermore, S. marcescens developed significant resistance to various antibiotic groups, such as aminoglycosides, β-lactam, and fluoroquinolones; this characteristic greatly enhanced its pathogenesis [5,6].
S. marcescens pathogenesis is credited to a diverse panel of virulence factors, including biofilm formation; bacterial motility; and the production of several exo-enzymes, such as nuclease, protease, hemolysins, and lipase [1,7]. These virulence factors are operated under the control of a signaling system known as quorum sensing (QS). QS is considered a chemically encoded language that is utilized to orchestrate the expression of virulence genes, as it regulates the expression of several virulence factor-encoding genes [1,8,9]. QS controls numerous physiological functions in S. marcescens, such as swarming motility; biofilm formation; hemolytic activity; butanediol fermentation; and the production of extracellular enzymes, prodigiosin, biosurfactant, and antibiotics [1,10,11,12]. Controlling QS and virulence factors is an interesting option to mitigate bacterial pathogenesis, and as a consequence, it provides a great chance to conquer and eradicate bacterial infections [1,7,13]. In this context, several research groups have designed several approaches to target bacterial virulence and QS [7,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Drug repurposing is one of these approaches and aims to discover the uses of already approved drugs other than their known clinical uses. This strategy confers several advantages and decreases costs and time [21].
Imidazole nucleus has been employed extensively to develop a diverse array of antimicrobial agents, including antibacterial, antifungal, and antiprotozoal agents, as reviewed in [22]. Recently, we investigated the anti-virulence and anti-QS activities of metronidazole, which harbors the imidazole moiety, against Proteus mirabilis isolated from macerated diabetic foot ulcers. Metronidazole showed superior efficiency in diminishing the virulence factors of multi-resistant Proteus mirabilis. [18]. These findings encouraged us to investigate the anti-virulence activities of another member of imidazoles, namely secnidazole. Secnidazole, which shares the 5-nitroimidazole nucleus with metronidazole, is clinically used to treat protozoal infections, such as amoebiasis and giardiasis, and bacterial vaginitis [23]. Moreover, secnidazole was shown to act as an analog of acylhomoserine lactones and effectively inhibited QS resulting in the attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis [24]. Bearing in mind these observations, this study aimed to explore the anti-virulence activities of secnidazole against S. marcescens pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
Secnidazole was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). All the used solvents and chemicals were of pharmaceutical grade. All used media—Mueller–Hinton (MH) broth and agar, Luria–Bertani (LB) broth and agar, and Tryptone soy broth (TSB)—were purchased from Oxoid (Hampshire, UK).
2.2. Bacterial Strain
The used S. marcescens strain in this study was isolated from the endotracheal aspiration of an admitted patient in the intensive care unit at Zagazig University Hospital, Zagazig, Egypt. Alongside the biochemical identification of the isolated S. marcescens, its ribosomal proteins were identified using a Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization–Time of Flight (MALDI–TOF) mass spectrometry instrument, and the percentage of identity was 100% [7,14,19]. The bacterial strain was not isolated specifically for this study; the patient’s consent was obtained according to the applied routine protocols for pathological and microbiological examination at Zagazig University Hospital, Zagazig, Egypt, which are in complete compliance with the Helsinki declarations and without any risk, danger, or burden for the patient.
2.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
To determine the MIC of secnidazole, the broth microdilution method was employed according to the Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute Guidelines (CLSI, 2015) [13,18]. The secnidazole solution was two-fold serially diluted using Mueller–Hinton broth to obtain dilutions ranging from 80 to 0.3125 mg/mL. The wells of a 96-well microtiter plate were filled with 100 µL aliquots of the different secnidazole dilutions. The Serratia marcescens strain was inoculated in Mueller–Hinton broth and incubated overnight at 37 °C. The resulting suspension was diluted with sterile saline to a turbidity equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standard and then diluted 1:100 with Mueller–Hinton broth to yield an approximate cell density of 1 × 106 CFU/mL. Aliquots of 100 µL of the prepared suspension were added to all secnidazole dilutions, and the plate was incubated for 20 h at 37 °C. The minimum inhibitory concentration was calculated by observing the lowest concentration of the drug that inhibited the visible turbidity.
2.4. Effect of Secnidazole at Sub-MIC on the Growth of S. marcescens
To avoid any expected effect of secnidazole on bacterial growth, S. marcescens was cultured in the presence or absence of secnidazole at sub-MIC (2 mg/mL) according to Nalca et al. [25]. The turbidities of fresh S. marcescens overnight cultures were adjusted to 0.5 McFarland standard. A standard inoculum size (1 × 108 CFU/mL) was used to inoculate LB broth containing 2 mg/mL of secnidazole and control LB broth free from secnidazole. The optical densities were then measured at 600 nm after overnight incubation at 37 °C using a Biotek Spectrofluorimeter (Biotek, Shoreline, WA, USA).
Secnidazole was used at a sub-inhibitory concentration (sub-MIC equal to 2 mg/mL) in all subsequent experiments to investigate its effect on S. marcescens virulence without an influence on its growth. It is worth emphasizing that the bacterial cultures were adjusted to an optical density OD600 of 0.4 (1 × 108 CFU/ mL) in all subsequent experiments to normalize the obtained results.
2.5. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
The biofilm formation capability of the tested S. marcescens strain was evaluated according to Stepanovic et al. [26]. Briefly, 200 μL aliquots from S. marcescens (1 × 106 CFU/mL at OD600 0.4) fresh overnight cultures were inoculated overnight in sterile 96-microtiter plates at 37 °C. The non-adherent cells were aspirated, and the adherent cells were fixed with methanol (95%) for 20 min at room temperature. The adhered cells were simply stained with crystal violet (1%) for 30 min. After washing out the excess stain, the bound dye was dissolved with 95% ethanol, and the optical density was measured at 590 nm. The ratio of the obtained OD of the dissolved dye bound to adhered cells and the cutoff OD (ODc) were calculated. The bacterial strain biofilm-forming capability was categorized as strong (OD > 4 × ODc), moderate (4 × ODc ≥ OD > 2 × ODc), weak (2 × ODc ≥ OD > ODc), or not biofilm-forming (OD ≤ ODc).
For the evaluation of the inhibitory effect of secnidazole on biofilm formation, the same steps that were used to assess biofilm formation were repeated but in the presence of secnidazole. S. marcescens aliquots (100 μL) were added to the wells of 96-microtitre plates containing 100 μL of secnidazole at sub-MIC. The absorbances of the dissolved bound crystal violet to the adhered cells in the presence or absence of secnidazole at sub-MIC were measured at 590 nm. Secnidazole’s inhibitory effect on biofilm formation was calculated as a percentage change from the control [7,20,27,28].
2.6. Assay of S. marcescens Motility Inhibition
The inhibitory ability of secnidazole against S. marcescens swarming motility was assessed as described earlier [13,17,18]. Briefly, a fresh overnight culture of S. marcescens was suspended in LB broth, and the optical density of bacterial growth was adjusted to OD 0.4. Five microliters from the prepared suspension was inoculated into the center of LB agar plates containing secnidazole (2 mg/mL) and control plates. After overnight incubation at 28 °C, the swarming zones were measured.
2.7. Protease Inhibition Assay
The semi-quantitative skim milk agar method was employed to quantify the production of protease in the presence and absence of secnidazole at sub-MIC as described previously [7,29]. Briefly, fresh S. marcescens cultures were grown overnight in LB broth in the presence or absence secnidazole at sub-MIC at 37 °C. The supernatants were collected by centrifugation, and 100 μL aliquots were added to the wells of skim milk agar plates. After overnight incubation at 37 °C, the diameters of the clear zones surrounding the wells were measured in mm. The inhibition of protease production by secnidazole at sub-MIC was calculated as a percentage change from untreated bacteria as shown previously [7].
2.8. Prodigiosin Inhibition Assay
The prodigiosin production by S. marcescens in the presence or absence of secnidazole was quantified as described earlier [7,13,14,19]. The optical densities of suspensions prepared from fresh S. marcescens cultures were adjusted to 1 × 106 CFU/mL at an OD of 0.4 and inoculated into LB broth with or without secnidazole at sub-MIC. After 20 h of incubation at 37 °C, the cells were collected by centrifugation, and the prodigiosin was extracted by 4% 1 M HCl in ethanol. The absorbance was measured at 534 nm, and the inhibitory effect of secnidazole on prodigiosin production was calculated as a percentage change from the untreated control.
2.9. Hemolysis Inhibition Assay
For the assay of hemolysin, S. marcescens isolate was cultured in LB broth containing or not containing secnidazole at sub-MIC at 37 °C overnight, and the supernatants were collected by centrifugation [17,19]. Briefly, 2% erythrocyte suspensions (obtained from experimental animals) in sterile saline (0.8 mL) were mixed with 0.5 mL of bacterial supernatants and incubated at 37 °C. After 2 h, the mixtures were centrifuged, and the absorbances were measured at 540 nm. The obtained measures were compared with the absorbances of the negative control (un-hemolyzed erythrocytes) and the positive control of hemolyzed erythrocytes, which was prepared by adding 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. The inhibitory effect of secnidazole at sub-MIC on hemolysis activity was assessed as a percentage change from the untreated bacterial control.
2.10. In Silico Docking of Secnidazole into the S. marcescens SmaR QS Receptor
In this work, secnidazole and the co-crystallized natural ligand C4HSL were docked into the active site of our prior model for the SmaR protein [13] using AutoDock Vina [30]. Ligand structures were drawn into Marvin Sketch v.18.23.0 (Marvin Sketch, v.19.12, ChemAxon), and the most energetically favored conformer was exported as a (*.pdb) file. The AutoDockTools package [31] was used to assign Gasteiger atomic partial charges, and all the rotatable bonds in the ligands were set to be flexible. For receptor preparation, hydrogen atoms were added, Gasteiger atomic partial charges were assigned, and all receptors and ligands were converted to the PDBQT format using the AutoDockTools package for the docking process. In the AutoDock Vina configuration files, the parameter num modes was set to 10, and exhaustiveness was set to 10. The grid box center (x = 20.67, y = 20.59, and z = 20.06) with a size (x = 13, y = 13, and z = 13) was used to define the active site for docking. AutoDock Vina was executed. Pymol (PyMOL Molecular Visualization System, v.2.0, Schrödinger, New York, NY, USA) was used for 3D visualization, and the 2D schematic presentation was generated using LigPlot+ v.1.4.5 (European Bioinformatics Institute, Cambridgeshire, UK) [32].
2.11. In-Vivo Mice Protection Assay
The mouse in vivo survival model was applied to evaluate the secnidazole protective activity against S. marcescens pathogenesis as previously described [7,13,33]. Briefly, the optical densities of a fresh S. marcescens overnight culture in LB broth containing or not containing secnidazole at sub-MIC, along with LB broth with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at the same concentration that was used as a solvent, were adjusted to OD 0.4 (≈1 × 108 CFU/mL) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Female healthy albino mice (Mus musculus, 3 weeks old) were divided into five groups (n = 10) as follows: one group intraperitoneally injected with 100 μL of secnidazole-treated S. marcescens in sterile PBS; two positive groups, one that was injected with 100 μL of untreated S. marcescens and another that was injected with 100 μL of DMSO-treated S. marcescens; and two negative groups, one that was left uninoculated and another that was injected with 100 μL of sterile PBS. The survival of the mice in each group was documented daily over the experimental period (5 days) and plotted using the Kaplan–Meier method.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
All the performed experiments were done in triplicate, and the results are presented as the means ± standard error. The Student’s t-test was employed to evaluate significance, where a p value < 0.05 was considered significant (GraphPad Prism Software, v.8, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Secnidazole MIC and Its Effect on S. marcescens Growth
Secnidazole inhibited S. marcescens growth at 10 mg/mL. The secnidazole anti-virulence activity was evaluated at 2 mg/mL (equivalent to 1/5 MIC). To exclude any effect of secnidazole on S. marcescens growth, the optical densities of the bacterial suspensions were measured in the absence or presence of secnidazole (2 mg/mL) at 600 nm. There was no significant difference between the bacterial suspension turbidities in the absence or presence of secnidazole at sub-MIC (p = 0.5946), which emphasizes that secnidazole has no inhibitory effect on S. marcescens growth.
3.2. Secnidazole Inhibits Biofilm Formation
To evaluate biofilm production, the absorbance of crystal violet of biofilm-forming S. marcescens was measured, and it was found to be 4 times greater than the cutoff value, indicating that the S. marcescens isolate is strongly biofilm-forming [7,14]. Furthermore, biofilm formation was quantified in the absence and presence of secnidazole at sub-MIC. Secnidazole produced a statistically significant reduction in biofilm formation of about 60% (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Biofilm inhibition of S. marcescens by secnidazole. The experiment was performed in triplicate, and the results are shown as the means ± standard error. Significance of mean difference between secnidazole-untreated and -treated S. marcescens was tested using the Student’s t-test on obtained optical densities values and the result was assumed statistically significant when p < 0.05. The results were shown as means ± standard error of biofilm production percent change by secnidazole in sub-MIC-treated S. marcescens from untreated S. marcescens. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced biofilm production (p < 0.0001, *** = p < 0.001.
3.3. Secnidazole Interferes with Swarming Motility
The diameters of S. marcescens swarming on LB agar plates without or with 2 mg/mL of secnidazole were measured. Secnidazole significantly reduced the swarming motility by about 65% (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Inhibition of S. marcescens swarming motility by secnidazole. LB agar plates without or with 2 mg/mL secnidazole were prepared. Student’s t-test was used to compare S. marcescens not treated and treated with secnidazole at sub-MIC, and statistical significance was considered when p values were <0.05. The experiments were repeated in triplicate, and the results are presented as the means ± standard error. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced S. marcescens swarming (p < 0.0001), *** = p < 0.001.
3.4. Secnidazole Diminishes S. marcescens Virulence Factors
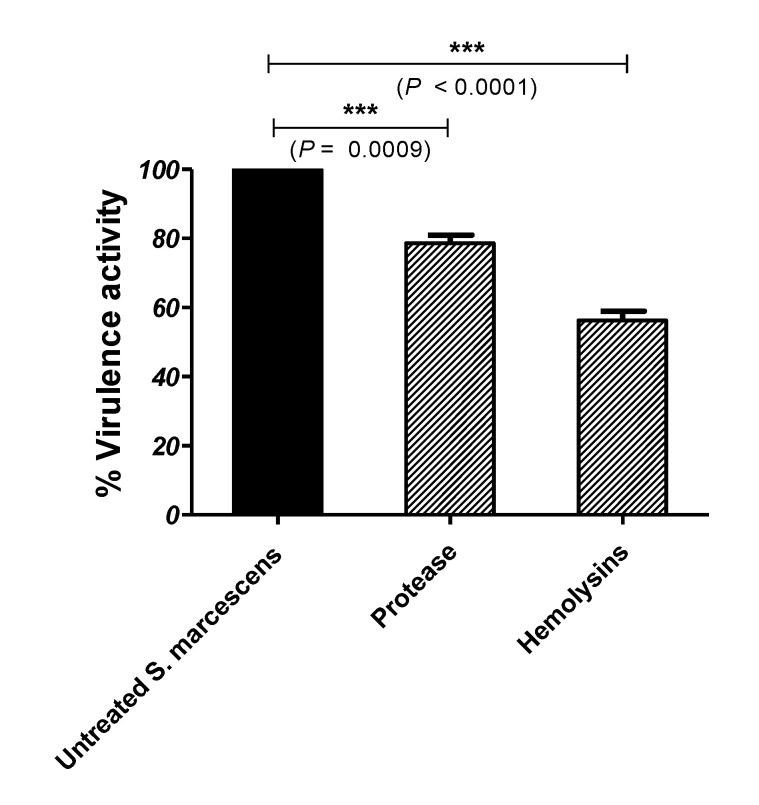
The secnidazole inhibitory effect on S. marcescens’ production of protease was assessed using the skim milk agar method. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly decreased the protease production by about 22% (Figure 3). Furthermore, the hemolysin activity of S. marcescens in the absence or presence of secnidazole at sub-MIC was evaluated in comparison with the negative control (non-hemolyzed erythrocytes) and the positive control (completely hemolyzed erythrocytes). Secnidazole at sub-MIC could significantly decrease the hemolytic activity of S. marcescens to about 44% compared with the untreated control (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Inhibition of S. marcescens’ protease and hemolysins activities by secnidazole. Student’s t-test was used to compare between S. marcescens not treated and treated with secnidazole at sub-MIC, and statistical significance was considered when p values were <0.05. The experiment was conducted in triplicate, and the results are shown as the means ± standard error. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced the production of protease and hemolysins by S. marcescens, *** = p < 0.001.
3.5. Secnidazole Reduces Prodigiosin Production
The prodigiosin produced by S. marcescens was quantified in the absence and presence of secnidazole at sub-MIC. Secnidazole showed a significant ability to reduce the production of the QS-controlled prodigiosin pigment by S. marcescens to about 71% (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Inhibition of prodigiosin pigment of S. marcescens by secnidazole. The significance of the mean difference between secnidazole untreated and treated S. marcescens was tested using Student’s t-test on absolute values of optical densities, and the result was considered statistically significant when p < 0.05. Data are shown as means ± standard error of the percent change of biofilm production by secnidazole at sub-MIC-treated S. marcescens from the untreated control. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced the prodigiosin pigment production (p < 0.0001), *** = p < 0.001.
3.6. Secnidazole Hinders the Binding of Autoinducer to S. marcescens QS Receptor
The binding mode of secnidazole to the SmaR protein inhibitor was revealed by the molecular docking study. The binding interactions of secnidazole and C4-HSL with the target receptor are shown in Figure 5. Secnidazole could bind by a wide range of interactions, including hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic, and electrostatic interaction. The autodock scores for each ligand, in addition to the interacting residues, are shown in Table 1. Furthermore, secnidazole lacks the hydrophobic tail that is present in the natural ligand, and this might impart the inhibitory mode of binding to secnidazole.
Figure 5.
The molecular docking of (A) secnidazole and (B) C4-HSL into the active site of the SmaR protein: 3D representation (left) and 2D schematic interaction (right); hydrogen bonds (blue lines) and electrostatic interaction (red dashed).
Table 1.
The binding mode of each ligand with the different residues inside the active site of SmaR protein.
| Ligand | H-Bonding | Hydrophobic Interaction | AutoDock Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secnidazole | Arg 50, Tyr 57, Asp 66 69 | Ala32, Ala34, Ile 46, Val 68, Leu 69, Trp 81, Thr110, Val 122, Ser 124, Met 126 | −5.3 |
| C4-HSL | Arg 50, Trp 53, Asp 66, Thr 110 | Val 68, Leu 69, Trp 81, Phe 97, Ala 100, Ile 105, Val 122, Ser 124, Met 126 | −6.4 |
3.7. Secnidazole Protects Mice against S. marcescens In Vivo
The secnidazole protective activity against S. marcescens virulence was assessed in vivo. Five mouse groups, each comprised of 10 mice, were intraperitoneally injected with treated or untreated S. marcescens, and the dead animals in each group were recorded during the 5 days of the experiment. All mice survived in the negative control groups (PBS or uninfected), while only 6 out of 10 mice survived in the positive control groups (untreated or DMSO-treated S. marcescens). On the other hand, 9 out of 10 mice survived of those that were injected with secnidazole-treated S. marcescens, indicating that secnidazole conferred about 30% protection in comparison with mice injected with untreated bacteria (Figure 6). The treatment of S. marcescens with secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly diminished the bacteria’s capacity to kill mice (p = 0.0023) according to the log-rank test for the trend.
Figure 6.
Protection of mice from S. marcescens by secnidazole. Five mouse groups comprising 10 mice each were used. The survival of mice in each group was reported every day for 5 days and plotted using the Kaplan–Meier method. The significance (p < 0.05) was tested using the log-rank test. All mice in the negative control groups survived, while only 60% of mice survived in the positive control groups. Meanwhile, 90% of mice injected with secnidazole-treated S. marcescens survived, showing that secnidazole conferred 30% protection in comparison with mice injected with untreated S. marcescens. Log-rank test for trend p = 0.0023, ** = p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
S. marcescens is an opportunistic pathogen that is armed with an arsenal of diverse virulence factors. In addition to these virulence factors, the increasing capability of S. marcescens to develop resistance to several antibiotics constitutes an additional burden [6,34]. QS modulates the physiological functions in S. marcescens and regulates the expression of its virulence factors, as reviewed in [1]. Bacterial resistance development is one of the top risks, and hence overcoming such resistance is a priority [35]. This can be accomplished by identifying new strategies to conquer bacterial infections. Targeting virulence factors controlled by QS and/or QS itself may offer an interesting approach that possesses several merits [33,36,37]. This approach does not lead to complete eradication of bacteria, which leads to (i) the stimulation of the immune system for their complete eradication and (ii) a decrease in the pressure on bacterial growth, leading to the avoidance of resistance development [7,33]. In this direction, several chemical and natural compounds have been screened for their anti-virulence and anti-QS activities [13,15,17,18,19,20,33,37,38,39,40]. Furthermore, the anti-virulence activities of several approved drugs have been screened in order to repurpose them as anti-virulence and anti-QS agents [7,14,16,18,27,39,41].
Imidazole moiety has been employed extensively to develop antifungal, antiprotozoal, and antibacterial drugs. The imidazoles’ capability to interact with microbial DNA, which results in the inhibition of microbial protein synthesis, is believed to be the main mechanism of their action [22,42]. In previous work, we showed that one member of nitroimidazoles, metronidazole, diminished the pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis isolated from diabetic foot wounds [18]. Intriguingly, we aimed in the current study to explore the anti-virulence activities of another member of imidazoles, secnidazole, by challenging the pathogenesis of a nosocomial S. marcescens isolate.
Before the evaluation of the anti-virulence activities of secnidazole, and to exclude any effect on bacterial growth, S. marcescens was grown in the absence and presence of secnidazole at sub-MIC (1/5 MIC). It was found that secnidazole at sub-MIC had no influence on bacterial growth, and all the anti-virulence activities of secnidazole were assessed at the same sub-MIC. Bacterial motility is an important factor in their adhesion and biofilm formation. Bacterial motility greatly enhances the invasion of epithelial cells and facilitates bacterial spread and biofilm formation [43,44]. Furthermore, biofilm formation is decreased in non-motile bacteria [45]. This means that bacterial motility and bacterial biofilm formation ability both facilitate infection spread and enhance the development of antibiotic resistance [46]. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced biofilm formation and swarming motility by 60% and 65%, respectively. Extracellular enzyme production plays a crucial role in S. marcescens virulence; S. marcescens produces several extracellular enzymes [1]. Protease cleaves several important proteins, such as albumin, casein, secretory components, and gelatin, and breaks immunoglobulins A and G, resulting in the facilitation of the spread of infection and suppression of the host defense [29,47]. Hemolysins’ cytotoxicity causes damage to host cells and inflammation and hinders neutrophils’ defense effect. S. marcescens’ hemolytic activity is attributed to the pore-forming toxin ShlA, which is secreted by a two-component secretion system on cell-to-cell junctions [48,49]. Secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced the production of protease and hemolysin activity of S. marcescens by 22% and 44%, respectively.
Although pigments that are produced by pathogenic bacteria are usually assumed to be essential virulence factors, the red pigment prodigiosin’s role in the S. marcescens pathogenesis is a matter of debate [50]. The QS-controlled S. marcescens red pigments prodigiosin and prodiginine are widely used as antimalarial, antiprotozoal, anticancer, insecticidal, bactericidal algicidal, immunosuppressives, and coloring agents [51]. However, the lack of evidence of the virulent activity of S. marcescens’ red pigment, prodigiosin; its QS-controlled release, and the inhibition of its production indicate the diminishing of QS functions. Our findings showed that secnidazole at sub-MIC significantly reduced S. marcescens’ production of prodigiosin by 71%.
The most predominant QS systems in Gram-negative bacteria are the LuxI/LuxR systems; S. marcescens employs one of the LuxR family members, SmaR. Several virulence factors of S. marcescens, including motility; biofilm formation; and the production of prodigiosin, antibiotics, and extracellular enzymes are controlled by the SmaI/SmaR QS system, as reviewed in [1]. S. marcescens’ SmaR senses the N-acylhomoserine lactone analogs C4-HSL and C6-HSL [13,19]. For a more adequate understanding of how secnidazole diminishes the S. marcescens virulence factors, a molecular in silico docking study was performed to evaluate secnidazole’s ability to hinder the binding of the natural ligand to the SmaR QS receptor. Clearly, secnidazole could bind the SmaR receptor through several interaction modes, including hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, and electrostatic interactions. These findings are in compliance with the previous results, which showed the inhibitory effects of secnidazole at sub-MIC on bacterial virulence. This leads us to propose that the anti-virulence activities of secnidazole are principally attributable to its ability to hinder QS receptors and compete with QS natural inducers.
To test the in vitro anti-virulence findings, a mouse survival in vivo model was used to assess secnidazole’s protection against S. marcescens. In compliance with the in vitro phenotypic findings, secnidazole at sub-MIC offered about 30% protection to mice, showing a trend for more survival compared with mice injected with untreated bacteria. In agreement with our data, secnidazole was shown to mitigate the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and protect mice from its pathogenesis [24]. On the basis of these findings, treating S. marcescens with secnidazole at sub-MIC noticeably decreased the bacterial capacity to produce virulence factors both in vitro and, hence, bacterial host pathogenesis in vivo.
5. Conclusions
Targeting bacterial virulence and QS is a promising strategy to conquer bacterial pathogenesis, particularly when already approved safe drugs are repurposed. This strategy possesses several advantages; mainly, it is less likely to result in the emergence of bacterial resistance, and it enhances host immunity. This work offers a new use of secnidazole comprising the efficient diminishing of S. marcescens virulence factors, which might be conferred by suppressing the QS bacterial system. Secnidazole reduced S. marcescens biofilm formation; motility; and production of prodigiosin, protease, and hemolysins. Furthermore, secnidazole protected mice from S. marcescens in vivo. Our results suggest that secnidazole has potent anti-virulence and anti-QS activities, and herein, we present the application of secnidazole and other related imidazoles as an adjuvant therapy to traditional antibacterial agents to treat resistant bacterial infections after further pharmacological studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.A.H.H., H.A.A., and A.N.K.; methodology, A.N.K., H.A.A. and M.A.; software, M.A.S.; validation, W.A.H.H. and A.N.K.; formal analysis, A.N.K. and H.A.A.; investigation, M.T.K. and W.A.H.H.; resources, H.Z.A.; data curation, A.S.A.L. and E.-S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; writing—review and editing, H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; visualization, A.N.A.; supervision, H.A.A.; project administration, W.A.H.H.; funding acquisition, M.T.K.; A.N.K. and H.Z.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia funded this project under grant no. (RG-16-166-42).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Faculty of Pharmacy, Zagazig University Ethical Committee allowed in vivo mouse tests in this study. The experiments were conducted in agreement with the ARRIVE guidelines and the UK Animals Act of 1986 (ECAHZU, 18 July 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
This study does not include any studies with human participants.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Van Houdt R., Givskov M., Michiels C.W. Quorum sensing in Serratia. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007;31:407–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Su L.H., Ou J.T., Leu H.S., Chiang P.C., Chiu Y.P., Chia J.H., Kuo A.J., Chiu C.H., Chu C., Wu T.L., et al. Extended epidemic of nosocomial urinary tract infections caused by Serratia marcescens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003;41:4726–4732. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4726-4732.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cristina M.L., Sartini M., Spagnolo A.M. Serratia marcescens Infections in Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019;16:610. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16040610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones R.N. Microbial etiologies of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010;51((Suppl. S1)):S81–S87. doi: 10.1086/653053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stock I., Burak S., Sherwood K.J., Gruger T., Wiedemann B. Natural antimicrobial susceptibilities of strains of ‘unusual’ Serratia species: S. ficaria, S. fonticola, S. odorifera, S. plymuthica and S. rubidaea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003;51:865–885. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Traub W.H. Antibiotic susceptibility of Serratia marcescens and Serratia liquefaciens. Chemotherapy. 2000;46:315–321. doi: 10.1159/000007304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Abbas H.A., Hegazy W.A.H. Repurposing anti-diabetic drug “Sitagliptin” as a novel virulence attenuating agent in Serratia marcescens. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mion S., Remy B., Plener L., Bregeon F., Chabriere E., Daude D. Quorum Quenching Lactonase Strengthens Bacteriophage and Antibiotic Arsenal Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2049. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hegazy W.A.H., Abbas H.A. Evaluation of the role of SsaV ‘Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 dependent type III secretion system components on the virulence behavior of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017;16:718–726. doi: 10.5897/AJB2016.15852. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Coulthurst S.J., Williamson N.R., Harris A.K., Spring D.R., Salmond G.P. Metabolic and regulatory engineering of Serratia marcescens: Mimicking phage-mediated horizontal acquisition of antibiotic biosynthesis and quorum-sensing capacities. Microbiology. 2006;152:1899–1911. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28803-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moons P., Van Houdt R., Aertsen A., Vanoirbeek K., Engelborghs Y., Michiels C.W. Role of quorum sensing and antimicrobial component production by Serratia plymuthica in formation of biofilms, including mixed biofilms with Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006;72:7294–7300. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01708-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Van Houdt R., Moons P., Aertsen A., Jansen A., Vanoirbeek K., Daykin M., Williams P., Michiels C.W. Characterization of a luxI/luxR-type quorum sensing system and N-acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent regulation of exo-enzyme and antibacterial component production in Serratia plymuthica RVH1. Res. Microbiol. 2007;158:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2006.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khayyat A.N., Hegazy W.A.H., Shaldam M.A., Mosbah R., Almalki A.J., Ibrahim T.S., Khayat M.T., Khafagy E.S., Soliman W.E., Abbas H.A. Xylitol Inhibits Growth and Blocks Virulence in Serratia marcescens. Microorganisms. 2021;9:1083. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9051083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Abbas H.A., Hegazy W.A.H. Targeting the virulence factors of Serratia marcescens by ambroxol. Roumanian Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017;76:27–32. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bendary M.M., Ibrahim D., Mosbah R.A., Mosallam F., Hegazy W.A.H., Awad N.F.S., Alshareef W.A., Alomar S.Y., Zaitone S.A., Abd El-Hamid M.I. Thymol Nanoemulsion: A New Therapeutic Option for Extensively Drug Resistant Foodborne Pathogens. Antibiotics. 2020;10:25. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10010025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hegazy W.A.H. Diclofenac inhibits virulence of Proteus mirabilis isolated from diabetic foot ulcer. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016;10:733–743. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2016.8043. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hegazy W.A.H., Khayat M.T., Ibrahim T.S., Nassar M.S., Bakhrebah M.A., Abdulaal W.H., Alhakamy N.A., Bendary M.M. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms. 2020;8:1285. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Khayyat A.N., Abbas H.A., Mohamed M.F.A., Asfour H.Z., Khayat M.T., Ibrahim T.S., Youns M., Khafagy E.-S., Abu Lila A.S., Safo M.K., et al. Not Only Antimicrobial: Metronidazole Mitigates the Virulence of Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Macerated Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:6847. doi: 10.3390/app11156847. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hegazy W.A.H., Khayat M.T., Ibrahim T.S., Youns M., Mosbah R., Soliman W.E. Repurposing of antidiabetics as Serratia marcescens virulence inhibitors. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021;52:627–638. doi: 10.1007/s42770-021-00465-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aldawsari M.F., Khafagy E.S., Saqr A.A., Alalaiwe A., Abbas H.A., Shaldam M.A., Hegazy W.A.H., Goda R.M. Tackling Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the Natural Furanone Sotolon. Antibiotics. 2021;10:871. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pushpakom S., Iorio F., Eyers P.A., Escott K.J., Hopper S., Wells A., Doig A., Guilliams T., Latimer J., McNamee C., et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019;18:41–58. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chopra P.N., Sahu J.K. Biological Significance of Imidazole-based Analogues in New Drug Development. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2020;17:574–584. doi: 10.2174/1570163816666190320123340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gillis J.C., Wiseman L.R. Secnidazole. A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in the management of protozoal infections and bacterial vaginosis. Drugs. 1996;51:621–638. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199651040-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saleh M.M., Abbas H.A., Askoura M.M. Repositioning secnidazole as a novel virulence factors attenuating agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2019;127:31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nalca Y., Jansch L., Bredenbruch F., Geffers R., Buer J., Haussler S. Quorum-sensing antagonistic activities of azithromycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: A global approach. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1680–1688. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.5.1680-1688.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stepanovic S., Vukovic D., Dakic I., Savic B., Svabic-Vlahovic M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2000;40:175–179. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abd El-Hamid M.I., El-Naenaeey E.Y., M kandeel T., Hegazy W.A.H., Mosbah R.A., Nassar M.S., Bakhrebah M.A., Abdulaal W.H., Alhakamy N.A., Bendary M.M. Promising Antibiofilm Agents: Recent Breakthrough against Biofilm Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2020;9:667. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9100667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Askoura M., Hegazy W.A.H. Ciprofloxacin interferes with Salmonella Typhimurium intracellular survival and host virulence through repression of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 (SPI-2) genes expression. Pathog. Dis. 2020;78:ftaa011. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftaa011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang X., Shuai Y., Tao H., Li C., He L. Novel Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Protease Activity: The Casein Plate Method and Its Applications. ACS Omega. 2021;6:3675–3680. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Trott O., Olson A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sanner M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999;17:57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Laskowski R.A., Swindells M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011;51:2778–2786. doi: 10.1021/ci200227u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim H.S., Lee S.H., Byun Y., Park H.D. 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:8656. doi: 10.1038/srep08656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stock I., Grueger T., Wiedemann B. Natural antibiotic susceptibility of strains of Serratia marcescens and the S. liquefaciens complex: S. liquefaciens sensu stricto, S. proteamaculans and S. grimesii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2003;22:35–47. doi: 10.1016/S0924-8579(02)00163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gebreyohannes G., Nyerere A., Bii C., Sbhatu D.B. Challenges of intervention, treatment, and antibiotic resistance of biofilm-forming microorganisms. Heliyon. 2019;5:e02192. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Abbas H.A., Shaldam M.A., Eldamasi D. Curtailing Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Sitagliptin. Curr. Microbiol. 2020;77:1051–1060. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-01909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mohabi S., Kalantar-Neyestanaki D., Mansouri S. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Quercus infectoria gall extracts. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2017;9:26–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aldawsari M.F., Alalaiwe A., Khafagy E.S., Al Saqr A., Alshahrani S.M., Alsulays B.B., Alshehri S., Abu Lila A.S., Danish Rizvi S.M., Hegazy W.A.H. Efficacy of SPG-ODN 1826 Nanovehicles in Inducing M1 Phenotype through TLR-9 Activation in Murine Alveolar J774A.1 Cells: Plausible Nano-Immunotherapy for Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:6833. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vishwa B., Moin A., Gowda D.V., Rizvi S.M.D., Hegazy W.A.H., Abu Lila A.S., Khafagy E.S., Allam A.N. Pulmonary Targeting of Inhalable Moxifloxacin Microspheres for Effective Management of Tuberculosis. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:79. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hegazy W.A.H., Henaway M. Hepatitis C virus pathogenesis: Serum IL-33 level indicates liver damage. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015;9:1386–1393. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2015.7496. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Al Saqr A., Khafagy E.S., Alalaiwe A., Aldawsari M.F., Alshahrani S.M., Anwer M.K., Khan S., Lila A.S.A., Arab H.H., Hegazy W.A.H. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Using Green Machinery: Characterization and In Vitro Toxicity. Nanomaterials. 2021;11:808. doi: 10.3390/nano11030808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Youns M., Askoura M., Abbas H.A., Attia G.H., Khayyat A.N., Goda R.M., Almalki A.J., Khafagy E.S., Hegazy W.A.H. Celastrol Modulates Multiple Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer via DDIT3 and ATF3 Up-Regulation and RRM2 and MCM4 Down-Regulation. OncoTargets Ther. 2021;14:3849–3860. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S313933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jacobsen S.M., Stickler D.J., Mobley H.L., Shirtliff M.E. Complicated catheter-associated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008;21:26–59. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00019-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rather P.N. Swarmer cell differentiation in Proteus mirabilis. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;7:1065–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sekhar S., Vyas N., Unnikrishnan M., Rodrigues G., Mukhopadhyay C. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern in diabetic foot ulcer: A pilot study. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2014;4:742–745. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.141541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Perim M.C., Borges Jda C., Celeste S.R., Orsolin Ede F., Mendes R.R., Mendes G.O., Ferreira R.L., Carreiro S.C., Pranchevicius M.C. Aerobic bacterial profile and antibiotic resistance in patients with diabetic foot infections. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015;48:546–554. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0146-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Askoura M., Youns M., Halim Hegazy W.A. Investigating the influence of iron on Campylobacter jejuni transcriptome in response to acid stress. Microb. Pathog. 2020;138:103777. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Reboud E., Bouillot S., Patot S., Beganton B., Attree I., Huber P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExlA and Serratia marcescens ShlA trigger cadherin cleavage by promoting calcium influx and ADAM10 activation. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006579. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lazzaro M., Krapf D., Garcia Vescovi E. Selective blockage of Serratia marcescens ShlA by nickel inhibits the pore-forming toxin-mediated phenotypes in eukaryotic cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2019;21:e13045. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhou W., Li J., Chen J., Liu X., Xiang T., Zhang L., Wan Y. The red pigment prodigiosin is not an essential virulence factor in entomopathogenic Serratia marcescens. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016;136:92–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2016.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tsai Y.H., Wei J.R., Lin C.S., Chen P.H., Huang S., Lin Y.C., Wei C.F., Lu C.C., Lai H.C. RssAB signaling coordinates early development of surface multicellularity in Serratia marcescens. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e24154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.