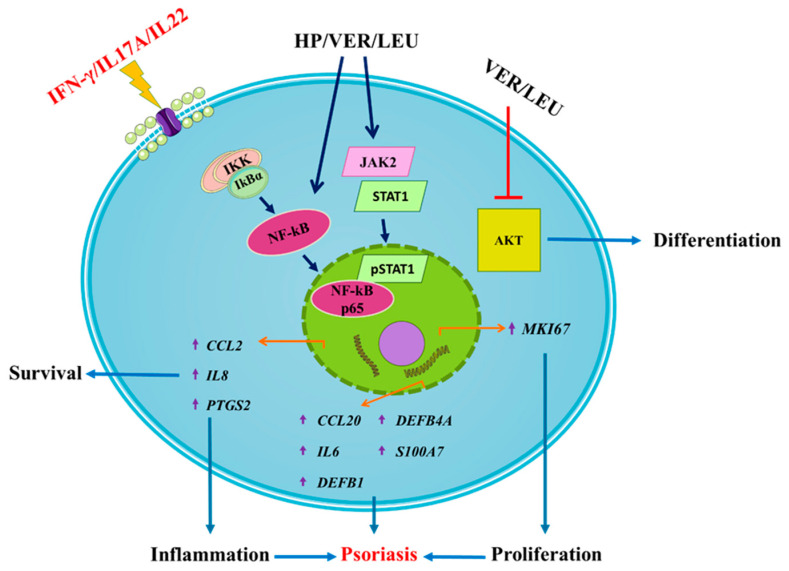
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism of action of H. procumbens extract (HP), pure verbascoside (VER) and leucosceptoside A (LEU) on the transcriptional regulation of genes related to inflammation and psoriasis in IFN-γ/IL-17A/IL-22-stimulated keratinocytes. The HaCaT cells exposed to the combination of pro-inflammatory cytokines respond with activation of NF-κB, JAK2/STAT1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Activation of JAK2 upon cytokine stimulation leads to STAT1 activation and its subsequent phosphorylation. Following NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation the phosphorylated STAT1 transcriptional activation of psoriasis-related inflammatory genes in the activated keratinocytes is induced (e.g., IL6, IL8, CCL20, CCL2, PTGS2, DEFB1, DEFB4A and S100A7). Simultaneously, the activation of the PI3K/AKT axis in psoriatic keratinocytes correlates with induction of hyperproliferation, disrupted differentiation and aggravation of the inflammatory milieu. The phenylethanoid glycosides VER and LEU both interfere with the psoriasis-related inflammation through suppression of the AKT signaling.