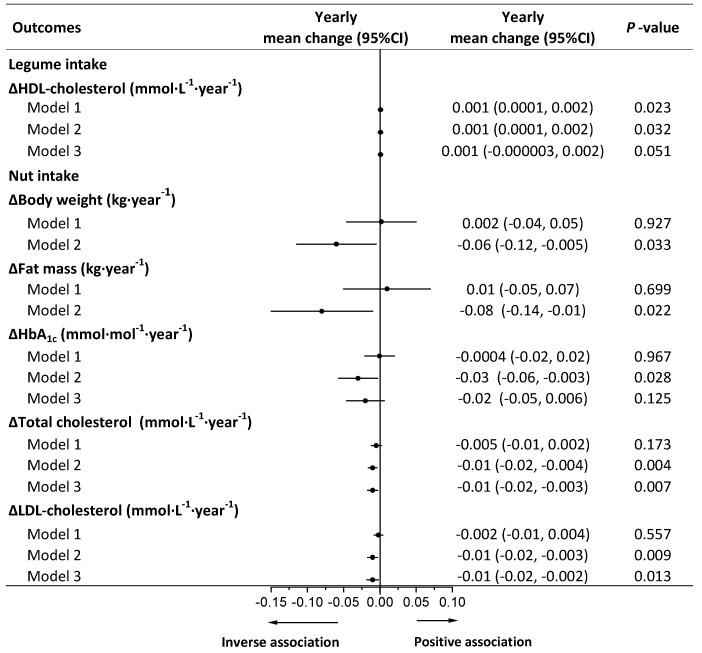
Figure 3.
Longitudinal associations of legume (10 g·day−1) or nut (5 g·day−1) intake with yearly weight regain and changes in cardiometabolic risk factors during weight-loss maintenance. Yearly mean change and 95% CI of main effects indicating changes in body weight or cardiometabolic risk factors per year associated with 10 g increment in legume intake or 5 g increment in vegetable intake. Analyses were conducted using a linear mixed model with repeated measures. Model 1 was adjusted for fixed factors including age, sex, ethnicity, BMI at 8 weeks, body weight, or cardiometabolic risk factors at 8 weeks and time and random factors including study center and participant ID. Model 2 was adjusted for covariates in model 1 plus fixed factors including time-varying physical activity, energy intake (kJ·day−1), alcohol intake (g·day−1), animal-based food intake (g·day−1), and other plant food intake (g·day−1). Model 3 was adjusted for covariates in model 2 plus time-varying yearly changes in body weight as a fixed factor. HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; HDL cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.