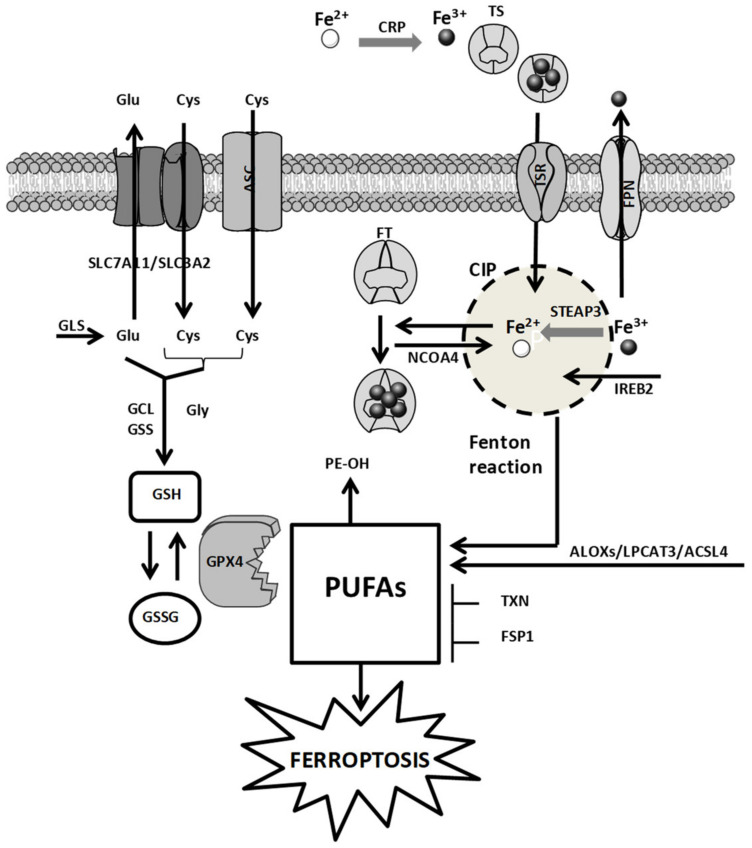
Figure 1.
Cellular mechanisms of ferroptosis. The metabolic pathways involving iron, ROS, and amino acids are reported. CIP: cellular iron lipid; FT: ferritin; CRP: ceruloplasmin; TS: transferrin; TSR: transferrin receptor; FPN: ferroprotein; ACSL4: acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3: lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; ALOXs: arachidonate lipoxygenase; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; ASC: alanine–serine–cysteine system; SLC7A11: solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC3A2: solute carrier family 3 member 2; GLS: glutaminases; GSS: glutathione synthetase; GCL: glutamate-cysteine ligase; NCOA4: nuclear receptor coactivator 4; PUFAs: polyunsaturated fatty acids; FSP1: ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; TXN: thioredoxin; IREB2: iron response element binding protein 2. The figure was prepared using tools from Servier Medical Art (http://www.servier.fr/servier-medical-art, accessed on 15 September 2021).