SUMMARY
CD4 T cell effector function, including IFNγ production, is required for optimal containment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. Despite this, lung-infiltrating CD4 T cells have a relatively limited ability to produce IFNγ, which plays a lesser protective role within the lung than at sites of Mtb dissemination. Using a physiologic murine model of Mtb infection and quantitative microscopy, we observed that IFNγ production by Mtb-specific CD4 T cells is rapidly extinguished within the granuloma, but not unaffected lung regions, suggesting localized immunosuppression. We identified a signature of TGFβ signaling within granuloma-infiltrating T cells in both mice and Rhesus macaques. Selective blockade of T cell TGFβ signaling resulted in an accumulation of terminally differentiated effector CD4 T cells, improved IFNγ production within granulomas, and reduced bacterial burdens. Together, these findings uncover a spatially-localized immunosuppressive mechanism associated with Mtb infection and provide potential targets for host-directed therapy.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, tuberculosis, adaptive immunity, IFNγ, KLRG1, granuloma, quantitative imaging, TGFβ
INTRODUCTION
The tuberculous granuloma, an organized aggregate of macrophages and other immune cells, is the epicenter of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection in the lung (Pagán and Ramakrishnan, 2015). For years, the granuloma was thought to be host-beneficial, walling off Mtb infection and providing protection against disseminated disease. More recently, however, there has been growing awareness of the role of the granuloma in tuberculosis (TB) pathogenesis. Pathogenic mycobacteria have been shown to promote macrophage aggregation and early granuloma formation to facilitate bacterial expansion and dissemination (Davis and Ramakrishnan, 2009; Volkman et al., 2004, 2010). Later during infection, mature granulomas provide a niche for Mtb persistence. It is commonly believed that granulomas provide an immunosuppressive milieu that restricts anti-Mtb immune effector function (Ernst, 2018), but the mechanistic basis of this purported inhibition is poorly understood.
CD4 T cells are critically important for immunity against Mtb (Cooper, 2009; Sileshi et al., 2013) and their protective capacity depends dually on their function and their location. IFNγ produced by CD4 T cells is a key contributor to protection (Flynn et al., 1993; Green et al., 2013). Although IFNγ accounts for almost all the protective capacity of CD4 T cells in the spleen, for unknown reasons, it is responsible for less than half of CD4-mediated immunity in the lung (Sakai et al., 2016). In addition to proper function, CD4 T cells must traffic to sites of infection and directly recognize antigen presented by infected cells to confer optimal protection (Srivastava and Ernst, 2013). In mice, we and others have shown that terminally-differentiated KLRG1+ Mtb-specific CD4 T cells that are robust producers of IFNγ traffic poorly into the lung parenchyma and are not protective upon adoptive transfer, whereas less differentiated KLRG1− Mtb-specific T cells that enter and persist within the parenchyma are protective (Moguche et al., 2015; Sakai et al., 2014). In non-human primates (NHP), T cells accumulate in the lymphocyte cuff surrounding the granuloma, but are present in lesser numbers in the central granuloma core where Mtb-infected cells reside (Kauffman et al., 2017). Inhibition of tryptophan metabolism has been shown to promote T cell re-localization to the center of the granuloma and decrease bacterial burdens (Gautam et al., 2017). These observations underscore the importance of T cell effector responses occurring in the proper location, and strongly suggest that inhibitory mechanisms within the granuloma modulate T cell differentiation, function, and possibly survival.
Here, we leverage the ultra-low dose Mtb infection model, which better reflects hallmark features of human Mtb granulomas (Plumlee et al., 2020), to investigate T cell responses within pulmonary granulomas. Using multiplex confocal imaging, as well as quantitative spatial analysis with histocytometry and CytoMAP (Gerner et al., 2012; Plumlee et al., 2020; Stoltzfus et al., 2020), we characterize the spatial organization of the CD4 T cell response during pulmonary ULD Mtb infection. Our findings reveal that CD4 T cell infiltration into granulomas is associated with partial TCR-mediated activation but poor production of IFNγ, suggesting localized immunosuppression. We reveal a signature of TGFβ signaling in pulmonary T cells, and find TGFβ to be a non-redundant mediator of this localized T cell suppression within the granuloma. Conditional ablation of T cell TGFβ signaling results in increased T cell proliferation, reduced cell death, and an accumulation of Mtb-specific T cells at the site of pulmonary Mtb infection. In addition, T cells lacking TGFβ signaling exhibit an increased capacity to secrete IFNγ. These studies identify an important pathway restricting T cell-mediated immunity in the Mtb granuloma.
RESULTS
IFNγ production by CD4 T cells is diminished in the pulmonary Mtb granuloma
To investigate the spatial organization of CD4 T cell localization, IFNγ production and antigen sensing within the pulmonary tuberculous granuloma in an experimentally tractable system, we used the murine ULD aerosol infection model, in which mice develop a solitary pulmonary granuloma. This granuloma is typically well-organized and shares several key features with human Mtb granulomas, including spatial segregation of infected myeloid cells from CD4 T cells (analogous to the central core of infection with surrounding lymphocytic cuff), as well as presence of B cell aggregates within the granuloma cuff, consistent with early tertiary lymphoid structure formation (Figures 1A, 1B) (Plumlee et al., 2020).
Figure 1: Despite antigen sensing, CD4 T cells produce minimal IFNγ within Mtb granulomas.
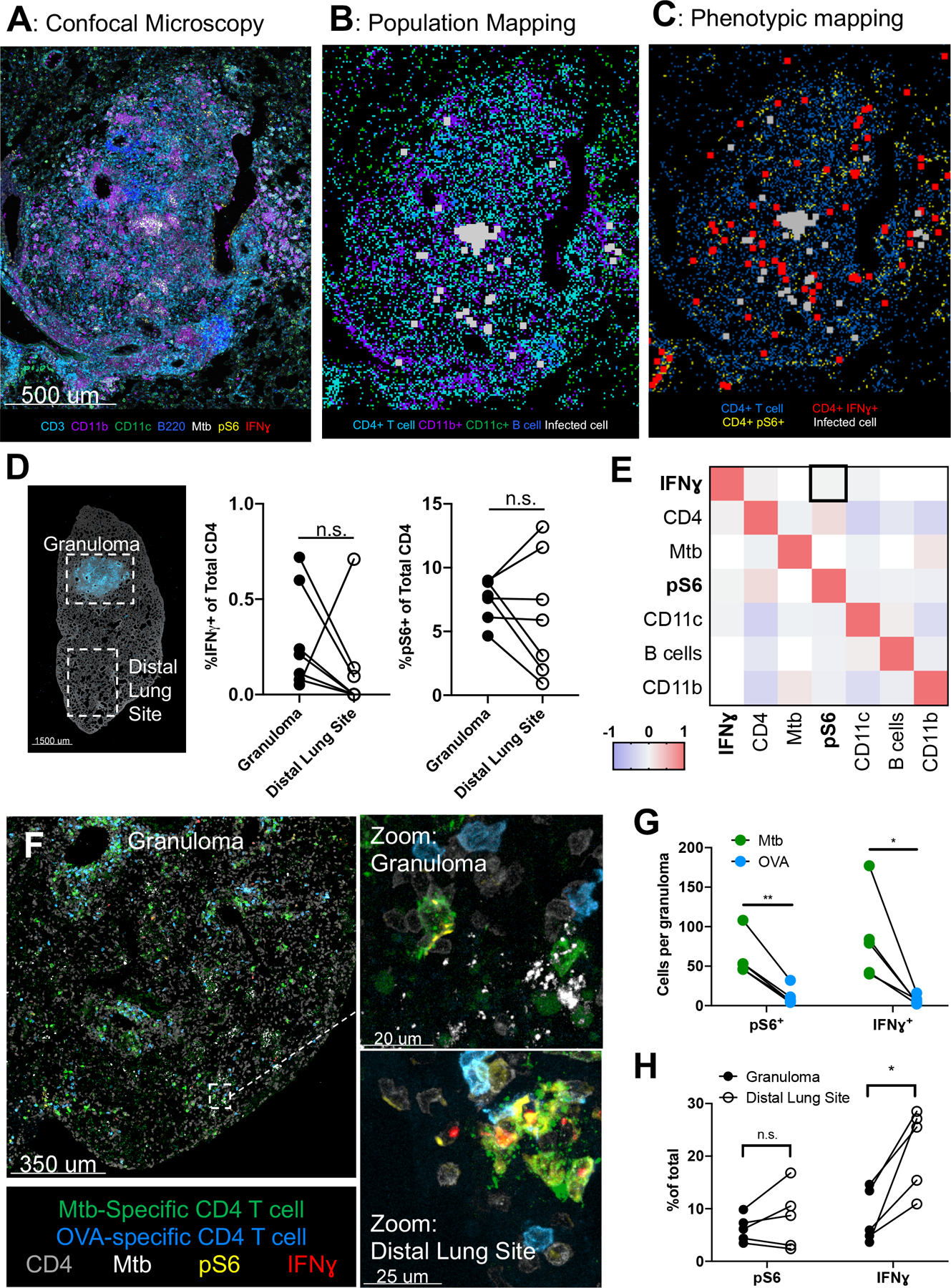
A-E: Wild-type mice infected with ULD Mtb, lungs taken at d34 p.i. (n=7) A) Representative confocal microscopy image of a pulmonary granuloma. B) Histocytometry positional mapping of different cell types within the granuloma. C) Location of IFNγ+ and pS6+ CD4 T cells in relation to Mtb. D) Image of an infected lung lobe (left), demonstrating strategy for analysis for investigating granuloma and distal lung sites. Histocytometry quantification (right) of IFNγ+ and pS6+ CD4 T cells, by location. E) Spatial correlation analysis of cell types within 25 μm radius neighborhoods. F-G: Mice infected with ULD Mtb, received 5×106 Th1-polarized Mtb-specific and OVA specific cells intravenously at d34 p.i. Lungs taken 20 hours later. (n=5) F) Representative confocal microscopy image, showing Mtb (green) and OVA (blue) specific Th1-polarized CD4 T cells. G) Histocytometry quantification of IFNγ and pS6 staining in Mtb vs OVA-specific transferred cells. H) Staining for pS6 and IFNγ in Mtb-specific CD4 T cells in granuloma vs distal lung site. Single-group comparisons by paired t test. Correlations and corresponding P values (E) by Pearson’s correlation test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Points represent individual mice and lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal. Data are representative of two independent experiments. See also Figures S1 and S2.
To visualize the location of polyclonal T cell activation relative to Mtb-infected cells within these granulomas, we performed multiplex confocal microscopy on lung sections from mice infected with ULD Mtb 34 days prior. Sections were stained with a panel of antibodies recognizing various immune cell lineage-defining markers, as well as functional proteins, such as IFNγ and ribosomal protein phospho-S6 (pS6), which is downstream of mTORC1, and thus TCR signaling. Phospho-S6 been shown to be upregulated within one hour following TCR signaling in vitro in T cells (Hawse et al., 2017; Salmond et al., 2009; Sauer et al., 2008), is downstream of antigen exposure in Mtb infected lungs (Delahaye et al., 2019), and was highly upregulated in Mtb-specific T cells in vitro following incubation with cognate peptide, but not IL-2 or IL-12, in a similar fashion as Nur77 and IRF4 (Figure S1A). We also stained sections with an antibody to Mtb purified protein derivative (PPD) to identify Mtb-infected cells (Kayanuma et al., 2018; Mehra et al., 2012; Plumlee et al., 2020; Rahman et al., 2014), as many fluorescent Mtb strains undergo plasmid loss over time and do not reliably delineate infected cells at later time points. Using histocytometry (Gerner et al., 2012), we found that Mtb was harbored almost exclusively by CD11b+ myeloid cells located within the central core of the granuloma (Figures 1A, 1B, S1B, S1C). T cell infiltration was observed throughout the lung, but with greater overall density in and around the granuloma, with the infiltrating T cells spatially segregated from the core of infected cells. We next compared antigen sensing and IFNγ production of T cells within the granulomas versus those in the same lobe of the lung, but distal to the granulomatous site of infection (Figures 1C, 1D, S1D). Despite Mtb infection being contained solely within the granuloma, we observed no difference in the proportion of CD4 T cells that recently recognized antigen (5–10% pS6+) within the granuloma compared to those in distal regions of the lung. Very few CD4 T cells produced IFNγ (<1% on average) at either site (Figures 1D, S1D). The presence of pS6+ CD4 T cells in these distal regions could reflect local TCR sensing of Mtb antigen, or recent TCR activation in the lymph node followed by migration to the infected lung. To test the latter, we treated ULD-Mtb infected mice with fingolimod, which blocks lymphocyte egress from lymphatic tissues, at d35 p.i. for 48 hours, which exceeds the duration of residual pS6 expression after TCR engagement (24 hours) (Katzman et al., 2010; Sauer et al., 2008). We found no significant difference in the proportion of pS6+ cells in fingolimod-treated vs. control mice (Figure S1E), suggesting that ongoing TCR signaling is occurring throughout the lung (potentially due to distal presentation of exported antigen (Srivastava et al., 2016)), including areas quite distant from the site of infection. To discriminate between cells in the lung vasculature and the lung parenchyma, we performed paired flow and histocytometry on lungs from mice infected with Mtb and given an intravascular antibody label. We found that histocytometry resulted in preferential detection of IV antibody negative cells (Figure S1F), with nearly 100% of CD4 T cells within the granuloma and >80% of cells within the distal lung being IV negative (Figure S1F). Importantly, the vast majority of activated cells (IFNγ+ and pS6+) detected by histocytometry, were IV antibody negative (Figure S1F), indicating that our technique is not biased toward detecting non-parenchymal T cells.
To obtain additional granularity on the spatial relationships between localized TCR signaling and effector function, we next used CytoMAP to calculate the spatial correlations between the different cell types and phenotypes with one another within 25μm-radius spatial neighborhoods across the granuloma histocytometry datasets (Stoltzfus et al., 2020). This revealed that neighborhoods with higher numbers of T cells that recently sensed TCR signals (pS6+) were only weakly correlated (R=0.05, p<0.0001) with those having more IFNγ+ CD4 T cells (Figures 1E). These data indicate the paucity of IFNγ-producing effector CD4 T cells within the tuberculous granuloma is only partially explained by limited antigen recognition and suggest that additional inhibitory mechanisms may be at play.
Inhibition of IFNγ production by Mtb-specific CD4 T cells
Given that these findings were obtained from polyclonal CD4 T cells, which are comprised of both Mtb-specific and T cells with irrelevant specificities, as well as those with varying differentiation states, we next tested whether fully functional Mtb-specific Th1 effector CD4 T cells would demonstrate similar properties. We adoptively transferred 5×106 Th1-polarized TCR-transgenic CD4 T cells (C7) that were specific for the Mtb antigen ESAT-6 (Gallegos et al., 2008), as well as control TCR-transgenic CD4 T cells (OT-II) with an irrelevant specificity (OVA) (Barnden et al., 1998), into wild-type mice infected with ULD Mtb 34 days prior. Twenty hours after transfer, lungs were taken for microscopy and flow cytometry. Although both Mtb-specific and control OVA-specific T cells showed evidence of trafficking into pulmonary granulomas within 20 hours after transfer (Figure 1F), Mtb-specific cells comprised the vast majority of transferred T cells that expressed pS6, IRF4, and ex-vivo IFNγ by histo- and flow cytometry and also produced more IFNγ on a per cell basis (Figures 1G, S2A, S2B, S2C), suggesting in vivo Mtb-antigen recognition. Notably, the relative ratio of Mtb-specific vs. OVA-specific cell isolation was greater with histocytometry compared to flow cytometry (Figure S2D), which may reflect preferential loss of activated Mtb-specific cells with dissociation-based methods (Borges da Silva et al., 2019; Steinert et al., 2015). Despite their prior capacity to robustly produce IFNγ upon restimulation immediately prior to transfer (~20h before tissue harvest) (Figure S2E), we found diminished IFNγ production by Mtb-specific T cells located within the granuloma compared to those in the distal lung (Figure 1H). This difference did not seem to reflect reduced antigen recognition within the granuloma, as both pS6 and IRF4 expression was similar in both locations (Figures 1H, S2F), mirroring the pattern found in the polyclonal population (Figure 1D). Taken together, these results suggest that IFNγ production by Mtb-specific CD4 T cells is restricted locally by the granuloma microenvironment despite ongoing antigen recognition.
TGFβ signaling in CD4 T cells in the Mtb-infected lung parenchyma
To identify potential suppressive mediators influencing T cell function within the Mtb-infected lung parenchyma, we sorted Mtb ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells using MHCII tetramers and compared mRNA expression of vascular vs. parenchymal Mtb-specific T cells. To increase the statistical power of this analysis we utilized conventional dose (CD) infection (~50 CFU), as the heterogeneity of the ULD model leads to considerable mouse-to-mouse variation. We found upregulation of a number of genes associated with T cell immunosuppression within the lung relative to the vasculature, including TIGIT, CTLA4, Lag3, CCR8, and HAVCR2 (Figure 2A). To better understand which inhibitory pathways had the greatest downstream effects on T cells, we used gene set enrichment analysis to identify transcriptional signatures associated with immunosuppression (Figures S3A, S3B). Within the lung, we found upregulation of IL-2, hypoxia and glycolysis pathways. Importantly, we also observed strong enrichment in target genes downstream of TGFβ signaling (Figures 2B, S3C). TGFβ has been previously observed to restrict T cell proliferation and differentiation and can directly inhibit IFNγ production (Oh and Li, 2013). Furthermore, an Mtb cell wall component (ManLam) has been shown to induce TGFβ production in macrophages (Dahl et al., 1996), and TGFβ production has been shown to increase in the lungs of Mtb-infected mice (Rook et al., 2007). TGFβ has also been previously detected in bronchoalveolar lavage specimens from patients with active pulmonary TB (Bonecini-Almeida et al., 2004), and lung TGFβ levels decrease with antibiotic treatment in NHPs (DiFazio et al., 2016). Thus, TGFβ signaling emerged as a strong candidate for local CD4 T cell suppression in the granuloma.
Figure 2: TGFβ signaling by immune cells within the granuloma.
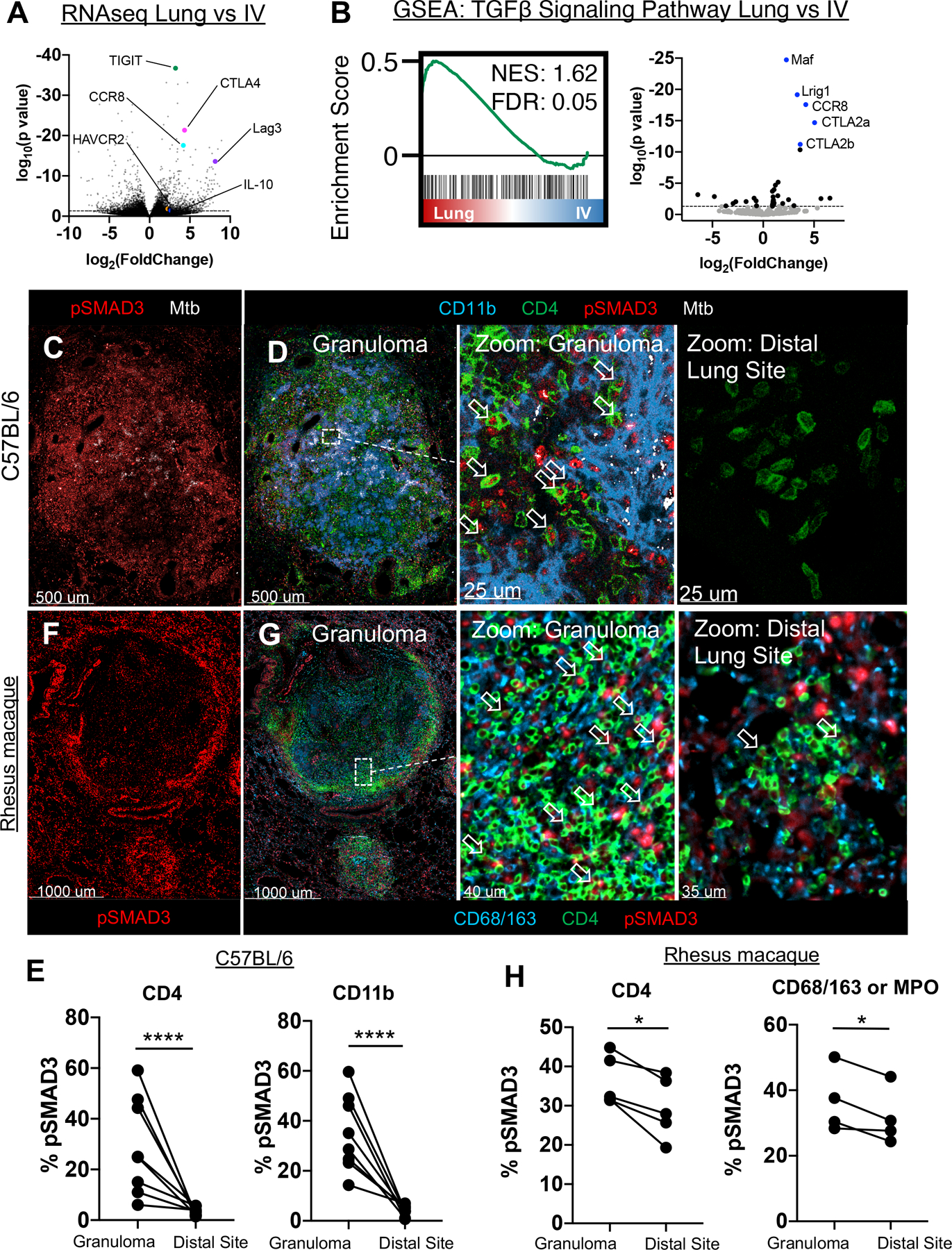
A-B: WT mice infected with 50 CFU Mtb, lungs taken at 28 days p.i. for transcriptome analysis of ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells in the vasculature vs lung parenchyma. (n=5) A) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes by Mtb-specific T cells within the parenchyma vs intravascular space. Highlighted genes associated with immunosuppressive signals on T cells. B) GSEA analysis of genes downstream of TGFβ signaling in the parenchyma (Lung), versus vasculature (IV). C-E: Mice infected with ULD Mtb, lungs harvested at d35 p.i. (n=7) C) Representative confocal image of pSMAD3 staining within the granuloma. D) Zoom-in images show pSMAD3 staining within T cells (arrows) and myeloid cells near Mtb-infected cells (left), or at a distal lung site (right). E) Histocytometry quantification of pSMAD3 staining in CD4 T cells and CD11b+ myeloid cells by site. F-H: Rhesus macaques infected with 4–8 CFU, lungs harvested at d62–89 p.i. (n=5) F) Representative confocal image of granuloma, showing pSMAD3 staining. G) Zoom-in images showing pSMAD3 signal in relation to CD4 (arrows) and CD68/163 cells (macrophages). H) Histocytometry quantification of pSMAD3 staining in CD4+ and CD68/163+ cells. Single-group comparisons by paired t test. Points represent individual animals and lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal. FDRs (B) were calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg method and p values were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Data are representative of one (A, B, F-H) or two (C, D) independent experiments. See also Figure S3.
To examine if there was active TGFβ signaling occurring within Mtb-infected lungs, we examined SMAD3 phosphorylation (pSMAD3), downstream of TGFβ signaling (Derynck and Zhang, 2003), in d34-infected lungs by microscopy. We observed robust pSMAD3 staining within the granulomas in both CD4 T cells (6–59%) and CD11b+ myeloid cells (14–59%), but not in unaffected areas of the same lobe (Figures 2C–E), indicating spatially localized TGFβ signaling by both cell types within the pulmonary Mtb granulomas. We next assessed pSMAD3 expression in pulmonary Mtb granulomas in rhesus macaques that had been infected with 4–8 CFU via bronchoscope instillation 62–89 days prior. Overall, these granulomas were larger in size and contained a more defined lymphocytic cuff than murine ULD granulomas. We also observed a highly heterogeneous spectrum of granulomas, including necrotic (which are not present in Mtb-infected C57BL/6 mice) and non-necrotic granulomas that were adjacent to each other within the same lobe, as described previously (Lin et al., 2009). Similar to our data in mice, while T cells did not preferentially-localize to the infected core of non-necrotic granulomas, a substantial percentage of these cells were distributed near infected myeloid cells. Importantly, there was evidence of strong pSMAD3 signaling within T cells (30–45%), as well as in macrophages and neutrophils (28–50%) within the granuloma, particularly in the lymphocytic cuff, in both non-necrotic (Figures 2F,2G) and necrotic granulomas (Figures S3D, S3E). Compared to pSMAD3 localization in mice, there was less signal within the granuloma core, likely due to the reduced density of immune cells in this region. Although rhesus macaques exhibited higher baseline pSMAD3 expression in distal areas of the lung compared to mice, which could be reflective of species, animal age, infectious dose, time point, or microbiome differences, pSMAD3 expression was significantly increased for CD4 T cells and macrophages/neutrophils within the granuloma compared to those located distally (Figure 2H). Together these data indicate that immune cells residing within pulmonary Mtb granulomas experience localized TGFβ signaling in both mice and caseating and non-caseating lesions in NHP.
TGFβR-signaling in CD4 T cells restricts terminal differentiation, promotes cell death, and inhibits Mtb control.
To test whether TGFβ actively suppresses T cells and restricts immunity within the granuloma we used dLck-cre TGFβR2f/f mice (TGFβR.KO), which lack TGFβR on T cells but express the receptor normally on other immune cell types (Zhang and Bevan, 2012). We first infected these animals with a conventional dose of aerosolized Mtb (~50 CFU) to assess the role of TGFβ in modulating immunity in a model with well-established bacterial load kinetics. We found that TGFβR.KO mice exhibited a significantly reduced (0.33 logs, p<0.01) lung and spleen bacterial burdens at d28–78 p.i. (Figures 3A, S4A), indicating a non-redundant role for T cell-intrinsic TGFβ signaling in restricting immunity against Mtb. Despite this decreased bacterial burden, which suggests reduced antigen abundance, many TGFβR.KO mice had an increase in IFNγ-producing ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells (though this did not reach statistical significance), and had similar total numbers of ESAT-6-specific T cells (Figure 3B, S4C, S4D). Intriguingly, ESAT6-specific TGFβR.KO T cells within the parenchyma were also much more likely to express KLRG1 (Figure 3C), a marker of terminally differentiated CD4 T cells, which are typically found in the vasculature in WT infected mice (Moguche et al., 2015; Sakai et al., 2014). Furthermore, we found that IV− ESAT6 specific TGFβR.KO cells within the lung were also less likely to undergo apoptosis (Figure 3D), and this difference was more pronounced in parenchyma-localized cells than those in the vasculature (Figure S4E). In contrast, there were no significant differences in FoxP3+ or RORγt+ ESAT-specific CD4 T cells, and these encompassed a very small percentage of the overall cell population (Figure S4F), consistent with prior reports (Cruz et al., 2006; Shafiani et al., 2013).
Figure 3: TGFβR-signaling in CD4 T cells restricts terminal differentiation, promotes cell death, and inhibits Mtb control.
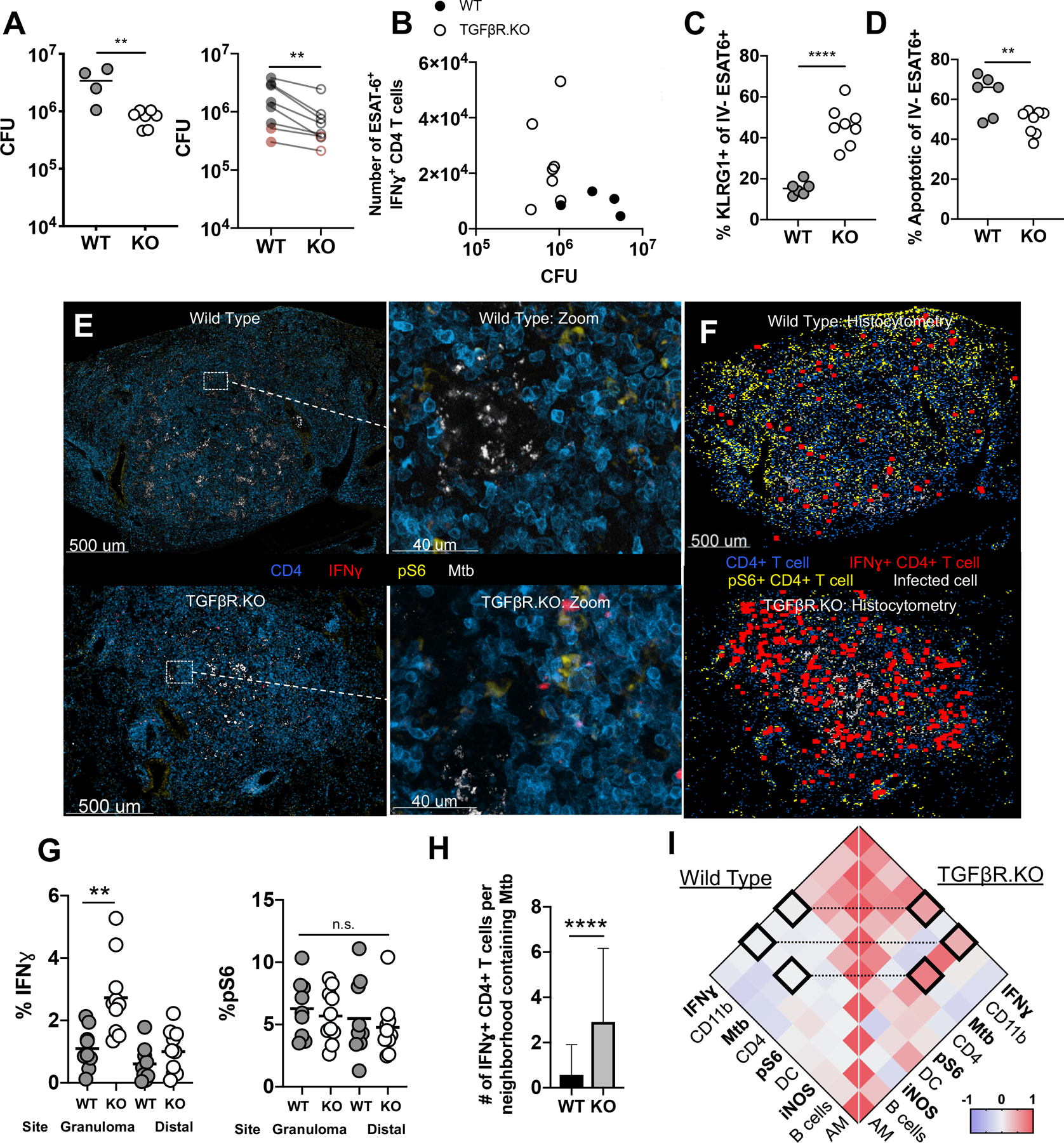
A-D: TGFβR.KO (KO) and WT mice infected with 50–100 CFU of Mtb, lungs taken at d30 p.i. A) Mtb lung burden in WT and KO animals. Left: Representative experiment. Right: Group means from 6 independent experiments across early (d21–39, gray) and late (d75–78, red) timepoints. total n=40 WT and n=45 KO mice. B) Number of IFNγ+ ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells compared against bacterial burden. C) Proportion of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD4+ T cells that are KLRG1+. D) Proportion of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD4+ T cells that are Annexin V+, SYTOX−. E-I: WT mouse and in TGFβR.KO mice infected with ULD Mtb, lungs taken at d35 p.i. (n=10 per group) E) Representative confocal images of granulomas from WT (top) and TGFβR.KO (bottom) mice, with zoom-ins. F) Histocytometry positional analysis demonstrating the location of pS6+ or IFNγ+ cells in WT and TGFβR.KO lung granulomas. G) Histocytometry quantitation of CD4 cells positive for pS6 and IFNγ by site. H) Number of IFNγ+ CD4 T cells per local tissue neighborhood containing Mtb-infected cells. I) Comparison of cell-cell correlations across local neighborhoods in WT (left) and TGFβR.KO (right) lungs. Single-group comparisons (A, B,F,G) by unpaired or paired (A) t test. Correlations and corresponding P values (H) by Pearson’s correlation test. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Points are representative of individual mice, except where otherwise noted. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. See also Figure S4.
To directly assess how TGFβ signaling alters effector T cell function within pulmonary granulomas, we infected TGFβR.KO and WT mice with ULD Mtb and 34 days later isolated lungs for quantitative microscopy. In contrast to WT granulomas, TGFβR.KO granulomas exhibited a pronounced increase in IFNγ+ CD4 T cells that were directly adjacent to the areas of Mtb infection, while there was no significant difference within distal lung sites (Figures 3E, 3F, 3G). No differences in pS6 staining of CD4 T cells were observed between TGFβR.KO and WT mice (Figure 3G), suggesting that antigen presentation and TCR-signaling were not affected by TGFβ. Additional statistical analysis of cellular spatial neighborhoods revealed a significant increase in the total IFNγ+ CD4 T cells located within regions containing Mtb-infected cells in TGFβR.KO compared to WT mice (Figure 3H). Neighborhoods containing IFNγ+ CD4+ T cells were also positively correlated with those containing pS6+ T cells, suggesting that enhanced antigen-dependent IFNγ production was occurring in a spatially localized fashion in TGFβR.KO (R = 0.53, p<0.0001) but not WT (R = 0.03, p=0.06) settings (Figures 3I). Given that the production of IFNγ by T cells may be short-lived, and would be challenging to detect after cell-mediated secretion, we also examined myeloid cell iNOS production, a biomarker reflecting cellular memory of IFNγ sensing, as well as a molecule directly involved in mycobactericidal activity (Braverman and Stanley, 2017). We found markedly increased iNOS staining in TGFβR.KO granulomas (Figure S4G), with the number of iNOS+ CD11b+ cells positively correlated with both IFNγ+ CD4+ T cells (R = 0.44, p<0.001) and Mtb-infected cells in TGFβR.KO (R = 0.76, p<0.0001) but not WT mice (R = −0.01, p=0.54 and R2 = −0.03, p=0.05, respectively) (Figure 3I), suggesting enhanced coupling of localized T cell function with myeloid cell activation in the absence of TGFβ sensing. Together, these data indicate that ablation of TGFβ signaling in T cells results in marked enhancement in effector T cell cellularity and function directly within the granuloma, which in turn is associated with increased downstream myeloid cell activation and decreased bacterial burden.
TGFβ acts intrinsically on CD4 T cells to regulate Th1 cell differentiation and cellularity.
To further investigate the intrinsic effects of TGFβ signaling on CD4 T cell expansion, differentiation, and survival during Mtb infection, we generated mixed bone marrow chimera mice containing both WT and TGFβR.KO T cells. In a pilot experiment using chimeric mice with a 1:1 WT:KO donor marrow ratio, we observed that WT T cells were outcompeted by TGFβR.KO T cells, reflective of differences in proliferative capacity (Li and Flavell, 2008), and subsequent analysis was confounded by a paucity of WT cells. Therefore, we utilized a 3:1 WT:KO ratio and infected these animals with ULD Mtb following immune reconstitution. Thirty days later, we compared the phenotype and function of WT and TGFβR.KO CD4 T cells subjected to the same bacterial burden and inflammatory milieu. As expected, WT and TGFβR.KO cells were present in a ~ 3:1 ratio amongst naïve (CD44 low) CD4 T cells suggesting normal reconstitution. Importantly, ESAT-6 tetramer-binding CD44+ CD4 T cells were markedly enriched for the TGFβR.KO cells as compared to WT, with cellular ratios on average reaching 16:1, indicating ~50-fold enrichment in responding lymphocytes when accounting for the skewed naïve cell starting ratios (Figure 4A). Furthermore, as seen in the full KO animals, a higher proportion of the ESAT-6-specific TGFβR.KO T cells in the lung parenchyma expressed KLRG1 (Figure 4B), suggesting enhanced recovery of terminally differentiated effector cells. Consistent with this notion, TGFβR.KO T cells displayed markedly higher levels of T-bet staining and importantly had a significantly higher frequency of IFNγ production within the lung parenchyma as comparted to WT CD4 T cells (Figures 4C, 4D), suggesting enhanced effector T cell differentiation in the absence of TGFβ signaling. Together, these findings indicate that during Mtb infection, TGFβ acts intrinsically on T cells to regulate effector T cell differentiation and cellularity.
Figure 4: TGFβ acts intrinsically on CD4 T cells to regulate Th1 cell differentiation and cellularity.
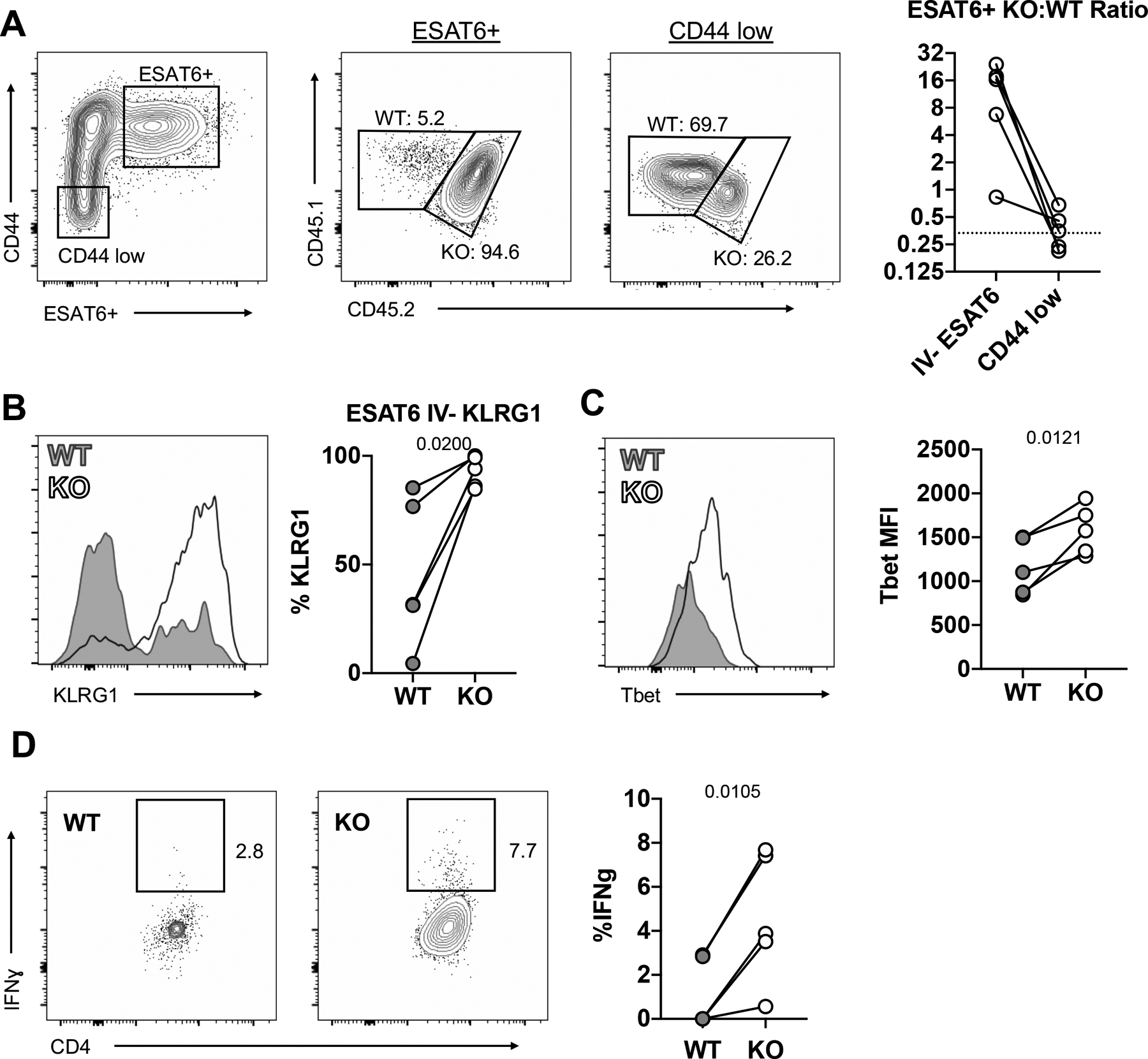
Mixed WT:TGFβR.KO bone marrow chimeric mice infected with 50–100 CFU of Mtb. (n=5) A) TGFβR.KO:WT ratio of ESAT-6-specific cells and CD44 low naïve cells. B) Percentage of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells that are KLRG1+ in WT vs TGFβR.KO mice C) T-bet MFI of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells. D) Ex-vivo IFNγ production by parenchymal ESAT-6-specific cells. Lines connect WT and KO cells within the same chimeric animals. Single-group comparisons by paired t test. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Points are individual mice, lines connect WT and KO cells within the same chimeric animals., Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. See also Figure S4 and S5.
T cell-intrinsic suppression of Mtb-specific TCR transgenic T cells
Given the pleiotropic effects of TGFβ on T cells, and that our previous data were observed in the polyclonal CD4 population with varied TCR specificities and response kinetics, we next tested the contribution of TGFβ on Mtb-specific T cells using an adoptive transfer model. We generated mice with Mtb-specific (C7) TCR-transgenic T cells lacking TGFβR (Tg.KO), and then co-transferred equal numbers of both naïve Tg.KO and WT C7 T cells (Tg.WT) into mice infected with Mtb 11 days prior (the approximate timepoint when T cell priming is initiated in the LN). CD Mtb infection was used for these studies to reduce the variation in infection and to ensure reliable T cell priming kinetics (Reiley et al., 2008). As expected, Tg.WT cells generated a robust early response, with large numbers of effector cells found within the lung parenchyma as early as 9 days after transfer (Figure 5A). However, over time, the Tg.WT population underwent a marked contraction (>100-fold decline), suggesting overall attrition of cellular responses and limited persistence of effector T cells throughout the infection. Tg.KO also underwent robust clonal expansion, but in contrast to Tg.WT cells, did not undergo contraction and vastly outnumbered Tg.WT cells (>50-fold) at later time points (Figure 5A). Consistent with their improved survival, significantly fewer Tg.KO cells underwent apoptosis (Figure 5B). Moreover, higher frequencies of Tg.KO cells were Ki67 positive (Figure 5B), together suggesting a pivotal role of TGFβ in inhibiting both survival and proliferation of Mtb-specific T cells during Mtb infection. Consistent with the mixed bone marrow chimera findings, many more IV− Tg.KO cells expressed KLRG1, a marker of terminal differentiation, and more of these differentiated cells were also Ki67 positive by 14 days after transfer (Figures 5C, 5D). Moreover, parenchymal Tg.KO cells also exhibited significantly higher levels of T-bet expression (Figure 5E), and importantly produced higher levels IFNγ and TNF, but not IL-2 (Figures 5F, S5A), suggesting enhanced effector function, which did wane at later timepoints (Figure S5B). Very low percentages of FoxP3+ and RORγt+ cells were observed in either the Tg.KO and Tg.WT cells, although as expected, minor reductions in expression of these transcription factors were observed in the absence of TGFβ signaling (Figure S5C). Together, these findings indicate that TGFβ plays critical roles in limiting the proliferation, survival, terminal differentiation, and function of effector T cells within the Mtb-infected lung.
Figure 5: T cell-intrinsic suppression of Mtb-specific TCR transgenic T cells.

A-F: Mice infected with 50–100 CFU Mtb, received 104 naïve Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells at d11 p.i. Lungs taken at specified timepoints. (n=4) A) Number of IV− Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells detected. B) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are Annexin V+, SYTOX− (left), or Ki67+ (right). C) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are KLRG1+ D) Proportion of parenchymal KLRG1+ Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are Ki67+ E) T-bet MFI of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells F) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are IFNγ+ (G-I) Mice infected with ULD Mtb, received 106 each Tg.WT and Tg.KO Th1-polarized CD4 T cells at d34 p.i. Lungs harvested 20 hours after transfer. n=6 G) Number of cells detected per granuloma section H) Representative section (left) demonstrating presence of Tg.WT (green) and Tg.KO (blue) cells within the granuloma. Zoom-in panel (right) showing localization of both cell types proximal to Mtb-infected cells, as well as demonstrating IFNγ staining. I) Histocytometry quantification of pS6, IFNγ and Ki67 staining in Tg.WT vs Tg.KO transferred cells within the granuloma. J-L: Mice infected with ULD Mtb and starting d14 p.i., received two adoptive transfers of either Tg.WT or Tg.KO Th1-polarized cells (and no-transfer controls), spaced one week apart. Lungs harvested 3–4 days after last transfer. (n=17–20 per group) J) Number of Tg.WT or Tg.KO cells per million lymphocytes. K) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are KLRG1+ L) Number of IFNγ+ Tg.WT or Tg.KO cells per million lymphocytes. Single-group comparisons by paired t test (A-G, I) and unpaired T test (J-L). Data are representative of two (H-L) or one (A-G) independent experiments. Points are individual mice, lines (when present) connect Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells within the same host animals. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. See also Figure S5.
In addition to effects on the survival and proliferation of infiltrating effector CD4 T cells, we hypothesized that TGFβ may also directly suppress localized cytokine production by fully differentiated effector T cells (Oh and Li, 2013). To test this, we generated in vitro Th1-polarized Tg.KO or Tg.WT effector T cells and co-transferred equal numbers of these cells into mice infected with ULD Mtb 34 days prior. Lack of TGFβR did not impact Th1 polarization, as Tg.KO and Tg.WT T cells both made similar amounts of IFNγ cells prior to transfer (Figure S5D). Lungs were isolated for microscopy 20 hours after transfer, a time point sufficient for T cell infiltration into infected tissues but prior to T cell proliferation. Indeed, both Tg.WT and Tg.KO Th1 T cells were found at equal numbers within the granulomas (Figures 5G, 5H) and displayed similar levels of TCR signaling, as identified by pS6 staining, suggesting equivalent early recruitment and activation (Figure 5I). Importantly, we observed a ~2.5 fold increase in the frequency of IFNγ+ Tg.KO T cells as compared to Tg.WT cells within granulomas (Figure 5I), suggesting rapid and highly localized suppressive effects of TGFβ on effector T cell function. Moreover, even though similar numbers of effector T cells were recovered, Tg.KO cells displayed significantly increased Ki67 staining (Figure 5I), suggesting that TGFβ rapidly inhibits both function and proliferative ability of effector T cells within the granuloma.
To further dissect the more prolonged effects of TGFβ signaling on fully differentiated effector T cells and to test their therapeutic efficacy, we again transferred Th1-polarized Tg.WT or Tg.KO cells into mice infected with ULD Mtb 14 days prior. In agreement with our previous findings, we found ~10-fold more Tg.KO cells as compared to Tg.WT (Figure 5J), and a higher frequency of these cells were Ki67+ (Figure S5E). Similarly, a large frequency of parenchymal Tg.KO cells were KLRG1 positive (Figure 5K), again indicating enhanced survival of terminally differentiated effector cells. As before, no differences in antigen sensing were noted between Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells, suggesting similar ability to recognize antigen. Strikingly, despite these large increases in the number of total and IFNγ+ Tg.KO effector T cells (Figures 5J, 5L), we found no significant differences in the frequency of direct ex vivo IFNγ production by Tg.WT vs. Tg.KO cells (Figure S5F), or in the bacterial burdens (Figure S5G), albeit slight decreases in total lung and spleen CFU were seen with both transfers as compared to no transfer controls. This minimal impact of effector Tg.WT and Tg.KO T cells may reflect caveats associated with transfer of large numbers of monoclonal T cells, such as in restricting the priming of endogenous Mtb-specific T cells (Tg.KO cells actually outnumbered the endogenous CD4 population (Figure S5H)), and/or gradual loss of IFNγ production over time, suggesting additional mechanisms of immune suppression involved in Mtb disease (Ernst, 2018). Nevertheless, our findings identify a prominent role of the TGFβ suppressive axis in restricting the proliferation, survival, and function of terminally differentiated effector T cells within the Mtb-infected lung.
DISCUSSION
Optimal Mtb containment requires cognate interactions between Mtb antigen-specific CD4 T cells and Mtb-infected macrophages presenting antigen/MHCII complexes on their surface (Srivastava and Ernst, 2013). This necessitates co-localization of Mtb-specific T cells and infected macrophages throughout chronic infection and persistence of a long-lived Mtb-specific T cell response. Maintenance of effector T cell function is also required, but the precise functional properties that mediate immunity within the Mtb-infected lung is incompletely understood. IFNγ production by CD4 T cells has long been considered the cornerstone of Mtb protective immunity (Bustamante, 2020; Green et al., 2013). However, T cells within the lung parenchyma have limited ability to produce effector cytokines (Moguche et al., 2015, 2017; Sakai et al., 2014), and IFNγ has been estimated to account for only 30% of CD4-mediated immunity in the lung (Sakai et al., 2016). Here we use quantitative imaging to show that little IFNγ is produced by CD4 T cells within Mtb-infected granulomas, and that fully differentiated Mtb-specific Th1 effector T cells rapidly lose the ability to produce IFNγ within the pulmonary granuloma compared to distal areas of unaffected lung, despite ongoing antigen recognition. We further find that in both mice and NHPs, T cells as well as myeloid cells experience high levels of TGFβ signaling within the pulmonary Mtb granuloma, and less within the rest of the lung. Finally, we demonstrate that effector T cell survival, expansion and differentiation is actively modulated by this granuloma-localized TGFβ, and that genetic manipulation of TGFβ signaling on T cells restores T cell function and limits pulmonary and splenic bacterial burdens.
We, and others, have shown that terminally differentiated Th1 cells, defined by expression of KLRG1 and high levels of T-bet, do not localize within the parenchyma of Mtb-infected lungs, but instead reside within the lung vasculature (Moguche et al., 2015; Sakai et al., 2014). This is in part due to the poor trafficking of KLRG1+ CD4 T cells into the lung parenchyma, and because CD4 T cells within the lung undergo limited terminal differentiation. Although a small number of KLRG1+ CD4 T cells can be found in the lung parenchyma of Mtb-infected WT mice, unlike their T-bethi counterparts in the vasculature, these cells express intermediate levels of T-bet, akin to PD-1+ parenchymal T cells (Moguche et al., 2015). We now show that Mtb-infected conditional TGFβRII KO mice exhibit an abundance of T-bethi, KLRG1+ T cells in the lung parenchyma, and these cells are highly proliferative (Ki67+) and undergo less apoptosis as compared to their WT counterparts. This is consistent with prior studies showing that TGFβ shapes the homeostasis of effector CD4 T cells (Śledzińska et al., 2013) and limits the survival of effector CD8 T cells (Ma and Zhang, 2015; Sanjabi et al., 2009; Tinoco et al., 2009; Zhang and Bevan, 2012), and establishes that analogous processes shape CD4 T cell responses during Mtb infection. Our data are also consistent with findings during chronic LCMV infection (Lewis et al., 2016), although in contrast to LMCV, TGFβ signaling during Mtb infection appears to directly influence T-bet expression and function of Th1 effector CD4 T cells. The finding that the parenchyma-localized TGFβR.KO KLRG1+ T cells express high levels of T-bet and robustly produce IFNγ suggests that they are similar to the intravascular terminally differentiated KLRG1+ CD4 T cells of WT mice. Thus, intrinsic TGFβ-signaling on T cells prevents terminal Th1 differentiation during pulmonary Mtb infection, perhaps in large part by limiting their survival within this inflammatory milieu. TGFβ may also alter the positioning of terminally differentially Th1 cells and restrict them from the infected lungs, and these effects require further examination. In addition, we find that TGFβ rapidly and potently suppresses effector T cell function even in fully differentiated Mtb-specific Th1 CD4 T cells, collectively pointing to profound effects of TGFβ on T cell expansion, survival, differentiation and effector function.
In addition to TGFβ, one previously identified suppressive mechanism utilized by Mtb is its ability to limit MHCII antigen presentation within infected cells. Our observation that some pS6+ T cells reside adjacent to Mtb-infected macrophages in the granuloma core indicates that this inhibition is not complete. However, the fact that the proportion of pS6+ T cells in the granuloma core is similar to that in uninfected regions of the lung suggests that antigen-presentation by infected cells is impaired to some degree. We were also surprised to find evidence of recent antigen recognition by T cells located throughout the lung, and that this was not abrogated by blockade of lymphocyte egress from the lymph node. This TCR stimulation is potentially due to recognition of exported Mtb antigen to distal regions of the lung by antigen-bearing, non-infected cells, a possible decoy strategy that has been suggested to direct T cell responses to where they are not needed (Baena and Porcelli, 2009; Srivastava and Ernst, 2014; Srivastava et al., 2016).
What implications do our findings have about the role of CD4 T cells and IFNγ in Mtb infection? In our studies, mice with T cells lacking the TGFβ receptor have increased number of IFNγ-producing T cells and a decreased bacterial burden. On the surface this seems at odds with published findings that in patients who received PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade (Barber et al., 2019; Suliman et al., 2020), increased IFNγ responses were associated with more severe disease outcomes, though other studies in mice have shown varying results (Kamboj et al., 2020; Lazar-Molnar et al., 2010). We speculate that the location of IFNγ production may help to reconcile these differences. In our system, the increase in T cells producing IFNγ is greatest near Mtb-infected cells within the granuloma, while the above studies measured an increase in systemic IFNγ levels, which may not be reflective of granuloma-restricted processes and could also trigger immune pathology. It is also likely that checkpoint blockade alone is not sufficient to overcome TGFβ-mediated suppression within the granuloma, leading to enhanced effector responses everywhere but the most critical sites.
Given the elevated levels of TGFβ during Mtb infection, the potential therapeutic use of TGFβ inhibitors has been postulated by in silico analysis (Warsinske et al., 2017). Indeed, pharmacologic inhibition of TGFβ signaling has been shown to improve pulmonary immunopathology and bacterial burdens when given shortly after infection (Jayaswal et al., 2010), and in chronic settings (Rosas-Taraco et al., 2011). While these studies did not resolve individual effects of TGFβ on specific cell types and had limited effects, together with our findings, they support the notion that TGFβ signaling blockade during chronic disease can enhance localized T cell-mediated immunity with minimal off-target effects. Besides T cells, TGFβ blockade could promote anti-microbial function in macrophages and other cell types, as well as reduce pulmonary fibrosis (Walton et al., 2017).
It is also important to highlight that we find evidence of additional non-redundant suppressive mechanisms at play during Mtb infection, as the benefits of the absence of TGFβ signaling on T cells clearly wanes over time. This suggests that combination therapy of TGFβ blockade with antibiotics or additional immunotherapeutics may provide synergy. Regardless, our studies suggest that TGFβ is a major and highly localized regulator of T cell responses during Mtb infection and suggest that future studies to test the therapeutic role for TGFβ blockade may be warranted.
STAR Methods
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Kevin Urdahl (kevin.urdahl@seattlechildrens.org).
Materials Availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Data and Code Availability
The mouse lung RNAseq data generated during this study are available at GEO under accession number GSE134186.
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
Mice
C57BL/6 and TCRβ−/−δ−/− mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME). ESAT-6 TCR Tg (C7) mice were provided by Dr. Eric Pamer (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY) and have been described previously (Gallegos et al., 2008). OTII mice were obtained from Taconic Laboratories (Rensselaer, NY). DLck-cre TGFβR2f/f mice were a generous gift from Dr. Michael Bevan (University of Washington). All mice were housed in specific pathogen-free conditions at Seattle Children’s Research Institute (SCRI). Experiments were performed in compliance with the SCRI Animal Care and Use Committee. Both male and female mice between the ages of 8–12 weeks were used.
Rhesus macaques
The research-naïve Indian-origin male and female rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) utilized in this study were bred and raised at the Oregon National Primate Research Center (ONPRC). All animals were single-housed in cages for Mtb infection in environmentally controlled rooms in the ONPRC’s Animal Biosafety Level-3 facility. At assignment, these rhesus macaques were specific-pathogen free (SPF) as defined by being free of macacine herpesvirus 1, D-type simian retrovirus, simian T lymphotrophic virus type 1, simian immunodeficiency virus and Mtb. The age of the animals at Mtb infection ranged from 2.18 to 3.04 years (average 2.74 years). All animals had pulmonary lesions consistent with Mtb in computerized tomography (CT) scans and were electively euthanized on post-infection days 62–89 days (average 75 days).The monkeys received commercial monkey chow twice daily supplemented with fresh fruit and water ad libitum. Environmental enrichment included food treats, manipulatable items in cages, human interactions with care takers and perches. All animals were observed twice daily by trained husbandry staff for activity, appetite and normal species-specific behavior. Ketamine HCl was used to induce anesthesia for all routine non-invasive clinical procedures associated with the study protocol such as blood sampling, intra bronchial agent administration via bronchoscope and biweekly diagnostic computerized tomography scans. For euthanasia macaques were sedated with ketamine HCl (15 mg/kg IM) and painlessly killed with greater than 50 mg/kg body weight of sodium pentobarbital. Euthanasia was assured by exsanguination and bilateral pneumothorax. This method is consistent with the recommendations of the American Veterinary Medical Association’s Guidelines on Euthanasia.
Studies were performed at the Oregon National Primate research Center (ONPRC), Beaverton, Oregon. All animal work was conducted in accordance with the recommendations of the Weatherall report, “The use of non-human primates in research.” Specifically, the research was regulated by the United States Department of Agriculture for compliance with the “Animal Welfare Act” and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare for compliance with the “Guide for the Care and use of Laboratory Animals”. The ONPRC Laboratory Animal Care and Use Program is fully accredited by the American Association for Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AALAC), and it has an approved Assurance (#A3304–01) for the care and use of animals on file with the Office for Protection from Research Risks at NIH. The study’s experimental protocols were approved 05/18/18 by the Oregon National Primate Center, Oregon Health & Science University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, IACUC Protocol 0941 [IP00001720].
METHOD DETAILS
Generation of mixed bone marrow chimera mice
WT CD45.2 mice were irradiated with 1000 rads and reconstituted with a 1:3 mixture (to account for differences in reconstitution of CD45.1/2 TGFβR.KO:CD45.1 WT bone marrow).
Aerosol infections
All infections were done with a stock of Mtb H37Rv, as previously described (Urdahl et al., 2003). To perform conventional dose aerosol infections, mice were enclosed in a Glas-Col aerosol infection chamber, and 50–100 CFU were deposited directly into their lungs. In order to confirm the infectious dose, two mice in each infection were immediately sacrificed and their lung homogenates plated onto 7H10 plates for CFU enumeration. To perform ULD aerosol infections, mice were enclosed in a Glas-Col aerosol infection chamber, and 1–3 CFU were deposited directly into their lungs (Plumlee et al., 2020).
CFU determination
Mouse organs (right lung, left lung or spleen) were homogenized separately using a Miltenyi GentleMACS machine with PBS+0.05% Tween-80 in an M tube (Miltenyi). Homogenates were subsequently diluted and plated onto 7H10 plates. Following dilution for ultra-low dose infections, the remainder of the undiluted homogenate plated onto two 7H10 plates. Plates were incubated for at least 21 days at 37° before enumeration.
Fingolimod treatment
To block lymphocyte egress from lymphoid tissues, mice infected with ULD Mtb at d35 pi were given fingolimod (Sigma-Aldrich) 1mg/kg, intraperitoneally, every 24 hours for 2 doses. Lungs were taken for analysis 24 hours following last dose.
Th1 polarization and adoptive transfers
CD4 T cells from the indicated TCR transgenic mice (Tg.WT (CD90.1+), Tg.KO (CD90.1+, CD45.1+) and OTII (CD45.1+)) were negatively enriched from spleens using EasySep magnetic microbeads (STEMCELL). T cells were Th1 polarized by culturing 1.6 × 106 transgenic T cells with 8.3 × 106 irradiated splenocytes from TCRβ−/−δ−/− mice per 2ml well. 5 μg/ml of ESAT-6 or OVA peptide, 10 ng/ml IL-12, and 10 μg/ml of anti–IL-4 antibody (R&D Systems) were added to RP10 media at day 0. On day 3, cells were split 2:1, and 10 ng/ml IL-12 added (R&D Systems). On day 5, Th1 cells were intravenously injected into C57BL/6 CD45.2+ recipient mice at the indicated timepoints.
Naïve cell isolation and adoptive transfers
Spleens from Tg.WT (CD90.1+) and Tg.KO (CD90.1+, CD45.1+) were enriched for CD4 T cells using the EasySep Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (StemCell Technologies). Cells were counted, then intravenously injected into C57BL/6 CD45.2+ recipient mice at the indicated timepoints.
Lung Single Cell Suspensions
At the indicated times post-infection, mouse lungs were removed and gently homogenized in HEPES buffer containing Liberase Blendzyme 3 (70 mg/ml; Roche) and DNaseI (30 mg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich) using a gentleMACS dissociator (Miltenyi Biotec). The lungs were then incubated for 30 min at 37°C and again thoroughly homogenized with the gentleMACS. Homogenates were then filtered through a 70μm cell strainer and RBC lysed with RBC lysing buffer (Thermo), then resuspended in FACS buffer (PBS containing 2.5% FBS and 0.1% NaN3).
Antibody and MHCII Tetramer Staining
MHCII tetramers containing amino acids 4–17 of Mtb ESAT-6 (made in our lab using a construct generated by Dr. Marc Jenkins) were used to detect Mtb-specific CD4 T cells. Single-cell suspensions were stained at saturating concentrations with the tetramers and incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. For intracellular cytokine staining (ICS), tissues were processed in the presence of Brefeldin A (10 mg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich). All surface staining was done at room temperature for 60 minutes. After tetramer and/or surface staining, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with antibodies against intracellular targets at 4°C for 30 minutes (or room temperature for 60 minutes for panels with anti-pS6 antibody) using eBioscience fixation/permeabilization and permeabilization buffers. For experiments utilizing intravascular antibody to identify intravascular T cells, mice were given an intravenous injection in the retroorbital sinus of 0.25μg of CD4-PE, CD4-APC, CD45.1-APC, or CD45.2 -APC antibody 10 min prior to sacrificing, as previously described (Sakai et al., 2014). For experiments using anti-Annexin antibodies, surface staining was completed as above. Cells were then washed twice in PBS, then resuspended in 100uL supplied annexin V binding buffer, with 5uL of anti-annexin V and 1ul SYTOX Green (ThermoFisher) and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. 400uL of binding buffer was then added and cells were stored on ice until analyzed by flow cytometry as soon as possible.
Stimulations
After single-cell preparations were made, murine lung cells were stimulated with either: ESAT-6 (4–17) (5 mg/ml), IL-2 (5ng/ml) or IL-12 (10ng/ml) for 4 hours in complete growth media (RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10 mM HEPES, 0.5 mM 2-ME) in the presence of brefeldin-A at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cells were then washed and stained with antibodies as described above.
Sorting, RNAseq, and GSEA
CD4 T cells were negatively enriched to >95% purity from freshly isolated lungs (taken from mice receiving an intravascular label, as above) using Miltenyi Biotec magnetic microbeads and subsequent column purification according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The negatively enriched cells were stained with anti-mouse PD-1 and anti-mouse KLRG1 antibodies (BioLegend), as well as ESAT-6 tetramer (as above) presence of 1μg/ml Cyclosporin A (R&D Systems) to prevent tetramer-mediated activation of T cells. The cells were then sorted on a cell sorter (FACSAria; BD Bioscience) directly into a buffer containing TRIzol (Invitrogen). Samples were shipped to Expression Analysis (Durham, NC), RNA was isolated and amplified linearly followed by RNA sequencing. RNASeq data were analyzed at the Institute for Systems Biology (Seattle, WA). The Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) tool was used to map the RNASeq reads to University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) mouse genome. Aligned reads were sorted and mapped to transcripts and counts were output into a matrix using HTseq-count. Quality control of samples was conducted by ensuring biological replicates clustered together more closely than samples from other test conditions using Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Differentially expressed genes were discovered by inputting the counts matrix into the DESeq2 package in R with Benjamini-Hochberg corrected p-values less than or equal to 0.05 and fold-change greater than or equal to 2. We used Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA, Broad Institute) to analyze the enrichment dataset using the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB). GSEA identified sets of genes differentially expressed between comparison groups that were over-represented at the top or bottom of the ranked set of genes. Data will be deposited in GEO upon publication.
Staining and imaging of rhesus macaques
Rhesus macaques in a dose titration study were inoculated with 4–8 CFUs of Mtb Erdman (BEI Resources) diluted in saline and lightly sonicated, and delivered to a segmental bronchus in the right caudal lung lobe using a bronchoscope as previously described (Hansen et al., 2018). The humane TB end-stage criteria were previously described (Hansen et al., 2018), at which time animals were immediately euthanized and taken to necropsy. Lung tissues were collected from animals according to BSL-3 necropsy procedures. Tissues were dissected into ~ 20mm2 × 5mm thick sections, placed in pre-labeled cassettes and immersed in freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours at room temperature in the ABSL-3 necropsy laboratory. This fixation protocol resulted in complete inactivation of Mtb, as no bacterial growth was noted after 8 weeks of culture with homogenized fixed tissue. After 24 hours post paraformaldehyde fixation the cassettes were transferred to 70% EtOH for an additional 24–72 hours at ~4–8°C in the ABSL-3 necropsy laboratory prior to processing and paraffin embedding. Immunofluorescent staining was performed as previously published (Mudd, Nature Communications, 2018) on formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded right caudal lung tissue collected at necropsy from Mtb infected RM. In brief, HIER was performed on deparaffinized slides with 0.1% citraconic anhydride (125318; Sigma-Aldrich) buffer in the absence of enzymatic retrieval, followed by rounds of sequential antibody staining, detection, and stripping. Antibody detection was performed using species specific polymer HRP-conjugated systems (GBI Labs) coupled with tyramide signal amplification (TSA) reactions using Alexa Fluor tyramide reagents (Invitrogen). Antibody stripping was performed by heating slides in 0.1% citraconic anhydride or citrate pH6 (B05C-100B; GBI Labs) buffers for 15 minutes at 95–99°C on a hot plate. Whole slide imaging was performed on a Zeiss Axio Scan.Z1 using a 20x objective. Serial sections were taken and Ziehl-Neelsen staining performed by the University of Washington Histology core, for identification of acid-fast bacilli.
Confocal Microscopy
Lungs were excised and submerged in BD Cytofix diluted 1:3 with PBS for 24hr at 4°C. Lungs were washed twice in PBS and dehydrated in 30% sucrose for 24 hours prior to embedding in OCT and rapid freezing in a 2-methylbutane and dry ice slurry. A cryostat was used to generate 20μm sections, which were stained overnight with fluorescently conjugated antibodies at room temperature and cover-slipped with Fluoromount G mounting media (SouthernBiotech). Images were acquired on a Leica SP8X confocal microscope.
Histocytometry
Histocytometry analysis was performed as previously described, with minor modifications (Gerner et al., 2012). Briefly, multiparameter confocal images were first corrected for fluorophore spillover using the built-in Leica Channel Dye Separation module. For acquisition of single stained controls, UltraComp beads (Affymetrix) were incubated with fluorescently conjugated antibodies, mounted on slides, and imaged. Cell surfaces were created using Jojo1 nuclear staining using the Imaris surface creation module, and the object statistics were exported to Excel (Microsoft). Object statistics were combined into unified CSV files and finally imported into FlowJo software for cellular gating and analysis. For correlation analyses, histocytometry data are spatially subdivided into cylindrical neighborhoods via virtual raster scanning (CytoMAP, (Stoltzfus et al., 2020)). Pearson correlation coefficients are then calculated for the numbers of cells in these neighborhoods. For visual clarity, presented images were manipulated in Imaris and PowerPoint (Microsoft), with identical manipulation applied across experimental groups.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical tests were selected based on appropriate assumptions with respect to data distribution and variance characteristics. Statistical details of experiments can be found in the figure legends. No statistical methods were used to predetermine sample size. The statistical significance of differences in mean values was analyzed by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. Paired t test was performed only when comparing responses within the same experimental animal or tissue, or group means within the same experiment (indicated in the legend). Correlations and corresponding P values by Pearson’s correlation test. ****,p ≤ 0.0001; ***, p ≤ 0.001; **,p ≤ 0.01; and *, p ≤ 0.05; NS, p > 0.05.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Related to Figure 1. Despite antigen sensing, CD4 T cells produce minimal IFNγ within Mtb granulomas: A) Expression of pS6, IRF4, and Nur77 of ESAT6-specific CD4 T cells (C7) after 4 hour in vitro stimulation with media alone, IL-2, IL-12 or cognate peptide. B) Example histocytometry gating scheme of indicated cell populations within infected lungs C) Example histocytometry gating overlayed onto confocal imaging (refer to Figure S1B): For 5/6 panels, antibody marker used for gating shown in red, with nuclei or CD4 in gray to show cells. Negative cells are denoted by cyan dot, while positive cells are denoted with yellow dot. For top left panel, CD11b+ CD11c- negative cells are denoted with yellow dot, while CD11c+ cells are denoted with magenta dot. Cyan cells = negative for both markers. D) Individual experiments showing endogenous CD4 T cell IFNγ and pS6 frequency by site (See Figure 1D). N=16 across 3 independent experiments. Different colors reflect different independent experiments. E) Histocytometry data showing percent pS6+ cells of total CD4 T cell by site, comparing fingolimod-treated and control ULD Mtb-infected mice, d37 p.i. F) Mice were given an IV antibody label, and lungs were taken for flow cytometry (right lung) and histocytometry (left lung) at day 29 post Mtb infection. Shown are representative confocal images (left); proportion of IV negative cells detected by flow and histocytometry (top right); and proportion of IV negative cells within noted cell populations, as determined by histocytometry.Single group comparisons by paired t test (A, B, D, E, F) or unpaired t test (E). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Points represent individual mice, connecting lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal.
Figure S2. Related to Figure 1. Despite antigen sensing, CD4 T cells produce minimal IFNγ within Mtb granulomas: A) Flow cytometry gating strategy for identification of Mtb-specific and OVA-specific T cells using congenic marker staining, as well as demonstration of IFNγ staining after ex-vivo restimulation. B) Paired flow cytometry data from figure 2, demonstrating ex-vivo IFNγ staining by proportion and MFI, in Mtb-specific and control OVA-specific T cells. C) Quantification of IRF4 staining in Mtb vs OVA-specific transferred cells, as determined by histocytometry (See figure 1G). D) Analysis of relative Mtb-specific vs. OVA-specific T cell abundance as determined by flow cytometry vs. histocytometry. E) Analysis of IFNγ production by the media alone or peptide-stimulated, Th1 polarized CD4 T cells prior to adoptive transfer. F) Proportion of Mtb-specific cells that are IRF4+, by tissue site (See figure 1H). Single-group comparisons by paired (B, C, F) or unpaired (D) t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Points represent individual mice, connecting lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal (C, F) or C7 and OTII cells within the same transfer recipient (B).
Figure S3. Related to Figure 2. Genes associated with TGFβ signaling are increased within the granuloma: A) GSEA analysis of parenchymal Mtb-specific cells vs. naïve T cells, showing increased pathways consistent with activation. B) GSEA analysis highlighting the indicated pathways which were differentially associated with the parenchymal vs. intravascular Mtb-specific cells. C) Relative expression of genes in the TGFβ signaling pathway in parenchymal vs. intravascular Mtb-specific cells is shown. D) Representative confocal image of a necrotic NHP granuloma, showing pSMAD3 staining. CD68/163 denotes macrophages. MPO denotes neutrophils. E) Zoom-in images showing pSMAD3 signal in relation to CD4 and CD68/163. F) Ziehl-Neelsen staining of granulomas from rhesus macaques shown in Figures 2F and S3D. Zoom-ins showing areas with acid-fast bacilli. FDRs were calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg method.
Figure S4. Related to Figures 3 and 4. Lack of TGFβRII on T cells results in decreased CFUs and increased IFNγ production: A) Left plot showing lung bacterial burdens from 6 independent experiments of TGFβR.KO mice (open circles) and littermate controls (grey circles). Each color denotes separete infection. Right plot showing spleen bacterial burdens at d28 p.i. B) Example flow cytometry gating strategy for the identification of parenchymal Mtb-specific T cells and quantification of IFNγ production by these cells is shown. C) Proportion of IFNγ+ ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells compared against bacterial burden. D) Number of ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells. E) Proportion of intravascular ESAT-6 specific CD3+CD4+ T cells that are Annexin V+, SYTOX−(see figure 3D). F) Proportion of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD3+CD4+ T cells that are FoxP3+ or RORγt+. G) Representative confocal images demonstrating staining of iNOS within CD11b+ cells. H) Flow cytometry gating strategy for identifying and phenotyping ESAT6 tetramer-positive TGFβR.KO vs WT cells in the lung parenchyma on mixed bone marrow chimeras (Figure 4). Single-group comparisons by unpaired t test. Line denotes mean. Points represent individual mice. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Figure S5. Related to Figure 5. T cell-intrinsic suppression of Mtb-specific TCR transgenic T cells: A-C: See figures 5A–F A) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are IFNγ+, TNF+, or IL-2+ following 4 hours in vitro peptide stimulation. B) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are ex-vivo IFNγ+, at specified timepoints. Significance reflective of differences between timepoints within each cell population. C) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are FoxP3+ or RORγt+. D) Analysis of IFNγ production by the media-only or peptide-stimulated, Th1 polarized Tg.WT vs Tg.KO CD4 T cells prior to adoptive transfer (See figures 5G–I). E-H: See figures 5J–L E) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are Ki67+. F) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are ex-vivo IFNγ+. G) Pulmonary and splenic bacterial burdens of mice that received either transfer of Tg.WT or Tg.KO Th1 cells. H) Ratio of either Tg.WT or Tg.KO to endogenous CD4 T cells. Single-group comparisons by paired (A, C) or unpaired (B, E, F, G, H) t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Anti-mouse CD11c BV480 | BD; clone HL3 | Cat# 565627, RRID: AB_2739309 |
| Anti-mouse CD11b BV510 | BioLegend; clone M1/70 | Cat# 101263, RRID: AB_2629529 |
| Anti-mouse CD11b BV650 | BioLegend; clone M1/70 | Cat# 101239, RRID: AB_11125575 |
| Anti-mouse CD11b PerCP-Cy5.5 | BioLegend; clone M1/70 | Cat# 101228; RRID: AB_893232 |
| Anti-mouse CD45.1 BV421 | BioLegend; clone A20 | Cat# 110732, RRID:AB_2562563 |
| Anti-mouse CD45.1 APC | BioLegend; clone A20 | Cat# 110713, RRID:AB_313502 |
| Anti-mouse CD45.1 APCeF780 | Thermo Fisher; clone A20 | Cat# 47-0453-82, RRID:AB_1582228 |
| Anti-mouse Ly6G BV650 | BioLegend; clone IA8 | Cat# 127641, RRID:AB_2565881 |
| Anti-mouse Ly6G PerCP-Cy5.5 | BioLegend; clone IA8 | Cat# 127616, RRID:AB_1877271 |
| Anti-mouse CD45.2 AF700 | BioLegend; clone 104 | Cat# 109822, RRID:AB_493731 |
| Anti-mouse CD45.2 APC | BioLegend; clone 104 | Cat# 109813, RRID:AB_389210 |
| Anti-mouse MHCII AF700 | Thermo Fisher; clone M5/114.15.2 | Cat# 56-5321-82, RRID:AB_49400 |
| Anti-mouse CD3 CF633 [conjugated in house] | BioLegend; clone 17A2 | 100202, RRID:AB_312659 |
| Anti-mouse CD3 BV480 | BD; clone 17A2 | Cat# 565642, RRID:AB_2739318 |
| Anti-mouse CD3 BV786 | BD; clone 17A2 | Cat# 564010, RRID:AB_2738540 |
| Anti-mouse CD8a, BV650 | BD; clone 53-6.7 | Cat# 563234, RRID:AB_2738084 |
| Anti-mouse CD8a, PerCP-Cy5.5 | BioLegend; clone 53-6.7 | Cat# 100734, RRID:AB_2075238 |
| Anti-mouse IFNγ PE | BioLegend; clone XMG1.2 | Cat# 505807, RRID:AB_315401 |
| Anti-mouse IFNγ PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher; clone XMG1.2 | Cat# 505826, RRID:AB_2295770 |
| Anti-mouse IFNγ AF488 | Thermo Fisher; clone XMG1.2 | Cat# 505813, RRID:AB_493312 |
| Anti-mouse pS6 AF488 | Cell Signaling; clone 2F9 | Cat# 4854, RRID:AB_390782 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 APC | BioLegend; clone RM4-4 | Cat# 116013, RRID:AB_2563024 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 PE | BioLegend; clone RM4-4 | Cat# 116005, RRID:AB_313690 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 CF660 [conjugated in house] | BioLegend; clone RM4-5 | Cat# 100506, RRID:AB_312709 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 e506 | Thermo Fisher; clone RM4-5 | Cat# 69-0042-82, RRID:AB_2637459 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 CF594 [conjugated in house] | BioLegend; clone RM4-5 | Cat# 100506, RRID:AB_312709 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 BV510 | BioLegend; clone RM4-5 | Cat# ; RRID: AB_2562608 |
| Anti-mouse CD4 AF700 | BioLegend; clone RM4-5 | Cat# 56-0042-82, RRID:AB_494000 |
| Anti-mouse CD44 BV650 | BioLegend; clone IM7 | Cat# 103049, RRID:AB_2562600 |
| Anti-mouse CD44 APC-eF780 | Thermo Fisher; clone IM7 | Cat# 47-0441-80, RRID:AB_1272248 |
| Anti-mouse KLRG1 BV421 | BD; clone 2F1 | Cat# 566284, RRID:AB_273965 |
| Anti-mouse KLRG1 PerCP Cy 5.5 | BioLegend; clone 2F1 | Cat# 138418, RRID:AB_2563015 |
| Anti-mouse KLRG1 PE-Cy7 | BioLegend; clone 2F1 | 138416, RRID:AB_2561736 |
| Anti-mouse KLRG1 APCe780 | Thermo Fisher; clone 2F1 | Cat# 47-5893-82, RRID:AB_2573988 |
| Anti-mouse PD-1, PE-Cy7 | BioLegend; clone RMP1-30 | Cat# 109110, RRID:AB_572017 |
| Anti-mouse PD-1, BV786 | BD; clone RMP1-30 | Cat# 748264, RRID:AB_2872692 |
| Anti-mouse B220 Dy395XL [conjugated in house] | BioLegend; clone RA3-6B2 | Cat# 103202, RRID:AB_312987 |
| Anti-mouse B220 BV650 | BioLegend; clone RA3-6B2 | Cat# 103241, RRID:AB_11204069 |
| Anti-mouse B220 PerCP-Cy5.5 | BioLegend; clone RA3-6B2 | Cat# 103236, RRID:AB_89335 |
| Anti-mouse NOS2 AF405 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology; clone C-11 | Cat# sc-7271, RRID:AB_627810 |
| Anti-purified protein derivative | Abcam; polyclonal | ab905, RRID:AB_306965 |
| Anti-mouse CD90.1 eF450 | Thermo Fisher; clone HIS51 | Cat# 48-0900-82, RRID:AB_1272254 |
| Anti-mouse CD90.1 AF647 | BioLegend; clone OX-7 | Cat# 202507, RRID:AB_492885 |
| Anti-mouse pSMAD3 CF594 [conjugated in house] | Abcam; clone EP823Y | Cat# ab52903, RRID:AB_882596 |
| Anti-mouse Ki67 e506 | Thermo Fisher; clone SolA15 | Cat# 69-5698-82, RRID:AB_2637482 |
| Anti-mouse Ki67 PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher; clone SolA15 | Cat# 25-5698-82, RRID:AB_11220070 |
| Anti-mouse TNF AF700 | BioLegend; clone MP6-XT22 | Cat# 506338, RRID:AB_2562918 |
| Anti-mouse T-bet, AF488 | BioLegend; clone 4B10 | Cat# 644829, RRID:AB_2566018 |
| Anti-mouse T-bet, PE-Cy7 | BioLegend; clone 4B10 | Cat# 644823, RRID:AB_2561760 |
| Anti-mouse IL-2, PE | Thermo Fisher; clone JES6-5H4 | Cat# 12-7021-41, RRID:AB_11042257 |
| Anti-mouse IL-2, PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher; clone JES6-5H4 | Cat# 25-7021-82, RRID:AB_1235004 |
| Anti-mouse IRF4 CF594 [conjugated in house] | BioLegend; clone IRF4.3E4 | Cat# 646402, RRID:AB_2280462 |
| Anti-mouse RORγt AF488 | Thermo Fisher; clone B2D | Cat# 53-6981-82, RRID:AB_2811877 |
| Anti-mouse RORγt PE | Thermo Fisher; clone AFKJS-9 | Cat# 12-6988-80, RRID:AB_1257212 |
| Anti-mouse Jojo-1 iodide | Invitrogen | Discontinued |
| Anti-mouse Foxp3 e450 | Thermo Fisher; clone FJK-16s | Cat# 48-5773-82, RRID:AB_1518812 |
| Anti-mouse Foxp3 AF700 | Thermo Fisher; clone FJK-16s | Cat# 56-5773-80, RRID:AB_469950 |
| Anti-human Myeloperoxidase | Dako; clone A0398 | Cat# A0398, RRID:AB_2335676 |
| Anti-human CD68 | Biocare; clone KP1 | Cat# 033, RRID: RRID:AB_2885063. |
| Anti-human CD163 | Thermo Fisher; clone 10D6 | Cat# MA5-11458, RRID:AB_10982556 |
| Anti-human CD4 | Abcam; clone EPR6855 | Cat# ab195842, RRID:AB_2819211 |
| Bacterial and Virus Strains | ||
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv | Obtained from Joel Ernst (NYU) | ATCC 27294 |
| M. tuberculosis Erdman | BEI Resources | Cat# NR-15404 |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ESAT-6 (4-17) peptide (QQWNFAGIEAAASA) | GeneMed Synthesis | N/A |
| OVA (323-339) peptide (ISQAVHAAHAEINEAGR) | GeneMed Synthesis | N/A |
| Fingolimod | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# SML0700 |
| Mix-n-Stain CF Dye Antibody Labeling Kits | Biotium | Cat# 92433-92339 |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| EasySep Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | StemCell Technologies | Cat# 19852 |
| Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with Annexin V Pacific Blue and Sytox Green | Thermo Fisher | Cat# A35122 |
| Deposited Data | ||
| RNAseq of pulmonary ESAT-6-specific T cells | This paper | GEO GSE134186 |
| Experimental Models: Organisms/Strains | ||
| Mouse: C57BL/6J | The Jackson Laboratory | JAX: 000664 |
| Mouse: ESAT-6 TCR transgenic (C7) | Obtained from Eric Pamer (MSK) | |
| Mouse: OVA TCR transgenic (OTII) | Obtained from Pamela Fink (UW) | |
| Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) | Oregon National Primate Research Center | |
| Software and Algorithms | ||
| FlowJo | BD | https://www.flowjo.com/ |
| Prism | Graphpad | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
| CytoMAP | Stoltzfus et al., 2020 | https://gitlab.com/gernerlab/cytomap |
| LASX | Leica Microsystems | https://www.leica-microsystems.com/products/microscope-software/p/leica-las-x-ls/ |
| Imaris | Bitplane | https://imaris.oxinst.com/ |
| Other | ||
| ESAT-64-17:I-Ab tetramer (mouse) PE [generated and tetramerized in house] | Construct from Marc Jenkins (University of Minnesota) | |
| ESAT-64-17:I-Ab tetramer (mouse) APC [generated and tetramerized in house] | Construct from Marc Jenkins (University of Minnesota) | |
Acknowledgements
We thank Sara Cohen for comments on the manuscript and Sarah Stanley for helpful discussions. This study was supported by the NIH grants 1R01AI134246 (K.B.U.), 1R01AI076327 (K.B.U.), U19AI135976 (K.B.U.), contract 75N93019C00070 (K.B.U.), R01AI134713 (M.Y.G.), R21AI142667 (M.Y.G.), and T32HD007233 (B.H.G. and K.N.A), Washington Research Foundation postdoctoral fellowship (C.R.S.), and a grant from the Firland Foundation (B.H.G).
Footnotes
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Baena A, and Porcelli SA (2009). Evasion and subversion of antigen presentation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tissue Antigens 74, 189–204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber DL, Sakai S, Kudchadkar RR, Fling SP, Day TA, Vergara JA, Ashkin D, Cheng JH, Lundgren LM, Raabe VN, et al. (2019). Tuberculosis following PD-1 blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnden MJ, Allison J, Heath WR, and Carbone FR (1998). Defective TCR expression in transgenic mice constructed using cDNA-based alpha- and beta-chain genes under the control of heterologous regulatory elements. Immunol. Cell Biol 76, 34–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonecini-Almeida MG, Ho JL, Boechat N, Huard RC, Chitale S, Doo H, Geng J, Rego L, Lazzarini LCO, Kritski AL, et al. (2004). Down-Modulation of Lung Immune Responses by Interleukin-10 and Transforming Growth Factor (TGF- ) and Analysis of TGF- Receptors I and II in Active Tuberculosis. Infection and Immunity 72, 2628–2634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges da Silva H, Wang H, Qian LJ, Hogquist KA, and Jameson SC (2019). ARTC2.2/P2RX7 Signaling during Cell Isolation Distorts Function and Quantification of Tissue-Resident CD8 + T Cell and Invariant NKT Subsets. J.I. 202, 2153–2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman J, and Stanley SA (2017). Nitric Oxide Modulates Macrophage Responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection through Activation of HIF-1α and Repression of NF-κB. The Journal of Immunology 199, 1805–1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J (2020). Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease: recent discoveries. Hum Genet 139, 993–1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper AM (2009). Cell-Mediated Immune Responses in Tuberculosis. Annual Review of Immunology 27, 393–422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A, Khader SA, Torrado E, Fraga A, Pearl JE, Pedrosa J, Cooper AM, and Castro AG (2006). Cutting edge: IFN-gamma regulates the induction and expansion of IL-17-producing CD4 T cells during mycobacterial infection. J Immunol 177, 1416–1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl KE, Shiratsuchi H, Hamilton BD, Ellner JJ, and Toossi Z (1996). Selective Induction of Transforming Growth Factor  in Human Monocytes by Lipoarabinomannan of. INFECT. IMMUN 64, 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis JM, and Ramakrishnan L (2009). The Role of the Granuloma in Expansion and Dissemination of Early Tuberculous Infection. Cell 136, 37–49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahaye JL, Gern BH, Cohen SB, Plumlee CR, Shafiani S, Gerner MY, and Urdahl KB (2019). Cutting Edge: Bacillus Calmette–Guérin–Induced T Cells Shape Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection before Reducing the Bacterial Burden. The Journal of Immunology ji1900108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R, and Zhang YE (2003). Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 425, 577–584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFazio RM, Mattila JT, Klein EC, Cirrincione LR, Howard M, Wong EA, and Flynn JL (2016). Active transforming growth factor-β is associated with phenotypic changes in granulomas after drug treatment in pulmonary tuberculosis. Fibrogenesis & Tissue Repair 9, 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst JD (2018). Mechanisms of M. tuberculosis Immune Evasion as Challenges to TB Vaccine Design. Cell Host & Microbe 24, 34–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn JL, Chan J, Triebold KJ, Dalton DK, Stewart TA, and Bloom BR (1993). An essential role for interferon gamma in resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Exp. Med 178, 2249–2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallegos AM, Pamer EG, and Glickman MS (2008). Delayed protection by ESAT-6–specific effector CD4+ T cells after airborne M. tuberculosis infection. J Exp Med 205, 2359–2368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam US, Foreman TW, Bucsan AN, Veatch AV, Alvarez X, Adekambi T, Golden NA, Gentry KM, Doyle-Meyers LA, Russell-Lodrigue KE, et al. (2017). In vivo inhibition of tryptophan catabolism reorganizes the tuberculoma and augments immune-mediated control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PNAS 201711373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner MY, Kastenmuller W, Ifrim I, Kabat J, and Germain RN (2012). Histo-Cytometry: A Method for Highly Multiplex Quantitative Tissue Imaging Analysis Applied to Dendritic Cell Subset Microanatomy in Lymph Nodes. Immunity 37, 364–376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green AM, DiFazio R, and Flynn JL (2013). IFN- from CD4 T Cells Is Essential for Host Survival and Enhances CD8 T Cell Function during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. The Journal of Immunology 190, 270–277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen SG, Zak DE, Xu G, Ford JC, Marshall EE, Malouli D, Gilbride RM, Hughes CM, Ventura AB, Ainslie E, et al. (2018). Prevention of tuberculosis in rhesus macaques by a cytomegalovirus-based vaccine. Nat Med 24, 130–143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawse WF, Boggess WC, and Morel PA (2017). TCR Signal Strength Regulates Akt Substrate Specificity To Induce Alternate Murine Th and T Regulatory Cell Differentiation Programs. J.I. 199, 589–597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswal S, Kamal MA, Dua R, Gupta S, Majumdar T, Das G, Kumar D, and Rao KVS (2010). Identification of Host-Dependent Survival Factors for Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis through an siRNA Screen. PLOS Pathogens 6, e1000839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamboj D, Gupta P, Basil MV, Mohan A, Guleria R, Bhatnagar A, Mehta G, Kumar P, Saurabh A, Deepak R, et al. (2020). Improved Mycobacterium tuberculosis clearance after the restoration of IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ CD4+ T cells: Impact of PD-1 inhibition in active tuberculosis patients. Eur J Immunol 50, 736–747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman SD, O’Gorman WE, Villarino AV, Gallo E, Friedman RS, Krummel MF, Nolan GP, and Abbas AK (2010). Duration of antigen receptor signaling determines T-cell tolerance or activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107, 18085–18090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman KD, Sallin MA, Sakai S, Kamenyeva O, Kabat J, Weiner D, Sutphin M, Schimel D, Via L, Barry CE, et al. (2017). Defective positioning in granulomas but not lung-homing limits CD4 T-cell interactions with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages in rhesus macaques. Mucosal Immunol. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayanuma H, Ogihara K, Yoshida S, Yamamoto K, Wada T, Yamamoto T, Tsuyuki Y, and Madarame H (2018). Disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial disease in a cat caused by Mycobacterium sp. strain MFM001. Veterinary Microbiology 220, 90–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar-Molnar E, Chen B, Sweeney KA, Wang EJ, Liu W, Lin J, Porcelli SA, Almo SC, Nathenson SG, and Jacobs WR (2010). Programmed death-1 (PD-1)-deficient mice are extraordinarily sensitive to tuberculosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107, 13402–13407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis GM, Wehrens EJ, Labarta-Bajo L, Streeck H, and Zuniga EI (2016). TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections. Journal of Clinical Investigation 126, 3799–3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li MO, and Flavell RA (2008). TGF-β: A Master of All T Cell Trades. Cell 134, 392–404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin PL, Rodgers M, Smith L, Bigbee M, Myers A, Bigbee C, Chiosea I, Capuano SV, Fuhrman C, Klein E, et al. (2009). Quantitative Comparison of Active and Latent Tuberculosis in the Cynomolgus Macaque Model. Infection and Immunity 77, 4631–4642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C, and Zhang N (2015). Transforming growth factor-β signaling is constantly shaping memory T-cell population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 11013–11017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra S, Golden NA, Stuckey K, Didier PJ, Doyle LA, Russell-Lodrigue KE, Sugimoto C, Hasegawa A, Sivasubramani SK, Roy CJ, et al. (2012). The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Stress Response Factor SigH Is Required for Bacterial Burden as Well as Immunopathology in Primate Lungs. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 205, 1203–1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moguche AO, Shafiani S, Clemons C, Larson RP, Dinh C, Higdon LE, Cambier CJ, Sissons JR, Gallegos AM, Fink PJ, et al. (2015). ICOS and Bcl6-dependent pathways maintain a CD4 T cell population with memory-like properties during tuberculosis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 212, 715–728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moguche AO, Musvosvi M, Penn-Nicholson A, Plumlee CR, Mearns H, Geldenhuys H, Smit E, Abrahams D, Rozot V, Dintwe O, et al. (2017). Antigen Availability Shapes T Cell Differentiation and Function during Tuberculosis. Cell Host &Microbe 21, 695–706.e5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SA, and Li MO (2013). TGF-β: Guardian of T Cell Function. The Journal of Immunology 191, 3973–3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagán AJ, and Ramakrishnan L (2015). Immunity and Immunopathology in the Tuberculous Granuloma. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5, a018499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumlee CR, Duffy FJ, Gern BH, Delahaye JL, Cohen SB, Stoltzfus CR, Rustad TR, Hansen SG, Axthelm MK, Picker LJ, et al. (2020). Ultra-low Dose Aerosol Infection of Mice with Mycobacterium tuberculosis More Closely Models Human Tuberculosis. Cell Host & Microbe. Online publication date: 11/2/2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.10.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Md.A., Sobia P, Gupta N, Kaer LV, and Das G (2014). Mycobacterium tuberculosis Subverts the TLR-2 - MyD88 Pathway to Facilitate Its Translocation into the Cytosol. PLoS ONE 9, e86886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiley WW, Calayag MD, Wittmer ST, Huntington JL, Pearl JE, Fountain JJ, Martino CA, Roberts AD, Cooper AM, Winslow GM, et al. (2008). ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cell responses to aerosol Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are initiated in the mediastinal lymph nodes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105, 10961–10966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook GAW, Lowrie DB, and Hernàndez‐Pando R (2007). Immunotherapeutics for Tuberculosis in Experimental Animals: Is There a Common Pathway Activated by Effective Protocols? J INFECT DIS 196, 191–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosas-Taraco AG, Higgins DM, Sánchez-Campillo J, Lee EJ, Orme IM, and González-Juarrero M (2011). Local pulmonary immunotherapy with siRNA targeting TGFβ1 enhances antimicrobial capacity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected mice. Tuberculosis 91, 98–106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai S, Kauffman KD, Schenkel JM, McBerry CC, Mayer-Barber KD, Masopust D, and Barber DL (2014). Cutting Edge: Control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection by a Subset of Lung Parenchyma–Homing CD4 T Cells. J Immunol 192, 2965–2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai S, Kauffman KD, Sallin MA, Sharpe AH, Young HA, Ganusov VV, and Barber DL (2016). CD4 T Cell-Derived IFN-γ Plays a Minimal Role in Control of Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection and Must Be Actively Repressed by PD-1 to Prevent Lethal Disease. PLOS Pathogens 12, e1005667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond RJ, Emery J, Okkenhaug K, and Zamoyska R (2009). MAPK, Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathways Converge at the Level of Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation to Control Metabolic Signaling in CD8 T Cells. The Journal of Immunology 183, 7388–7397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjabi S, Mosaheb MM, and Flavell RA (2009). Opposing Effects of TGF-β and IL-15 Cytokines Control the Number of Short-Lived Effector CD8+ T Cells. Immunity 31, 131–144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer S, Bruno L, Hertweck A, Finlay D, Leleu M, Spivakov M, Knight ZA, Cobb BS, Cantrell D, O’Connor E, et al. (2008). T cell receptor signaling controls Foxp3 expression via PI3K, Akt, and mTOR. PNAS 105, 7797–7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiani S, Dinh C, Ertelt JM, Moguche AO, Siddiqui I, Smigiel KS, Sharma P, Campbell DJ, Way SS, and Urdahl KB (2013). Pathogen-specific Treg cells expand early during mycobacterium tuberculosis infection but are later eliminated in response to Interleukin-12. Immunity 38, 1261–1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sileshi B, Deyessa N, Girma B, Melese M, and Suarez P (2013). Predictors of mortality among TB-HIV Co-infected patients being treated for tuberculosis in Northwest Ethiopia: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Infectious Diseases 13, 297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Śledzińska A, Hemmers S, Mair F, Gorka O, Ruland J, Fairbairn L, Nissler A, Müller W, Waisman A, Becher B, et al. (2013). TGF-β Signalling Is Required for CD4+ T Cell Homeostasis But Dispensable for Regulatory T Cell Function. PLoS Biol 11, e1001674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S, and Ernst JD (2013). Cutting Edge: Direct Recognition of Infected Cells by CD4 T Cells Is Required for Control of Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis In Vivo. The Journal of Immunology 191, 1016–1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S, and Ernst JD (2014). Cell-to-Cell Transfer of M. tuberculosis Antigens Optimizes CD4 T Cell Priming. Cell Host & Microbe 15, 741–752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S, Grace PS, and Ernst JD (2016). Antigen Export Reduces Antigen Presentation and Limits T Cell Control of M. tuberculosis. Cell Host & Microbe 19, 44–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert EM, Schenkel JM, Fraser KA, Beura LK, Manlove LS, Igyártó BZ, Southern PJ, and Masopust D (2015). Quantifying Memory CD8 T Cells Reveals Regionalization of Immunosurveillance. Cell 161, 737–749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus CR, Filipek J, Gern BH, Olin BE, Leal JM, Wu Y, Lyons-Cohen MR, Huang JY, Paz-Stoltzfus CL, Plumlee CR, et al. (2020). CytoMAP: A Spatial Analysis Toolbox Reveals Features of Myeloid Cell Organization in Lymphoid Tissues. Cell Reports 31, 107523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suliman AM, Bek SA, Elkhatim MS, Husain AA, Mismar AY, Eldean MZS, Lengyel Z, Elazzazy S, Rasul KI, and Omar NE (2020). Tuberculosis following programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) inhibitor in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer. Case report and literature review. Cancer Immunol Immunother. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco R, Alcalde V, Yang Y, Sauer K, and Zuniga EI (2009). Cell-intrinsic transforming growth factor-beta signaling mediates virus-specific CD8+ T cell deletion and viral persistence in vivo. Immunity 31, 145–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdahl KB, Liggitt D, and Bevan MJ (2003). CD8+ T Cells Accumulate in the Lungs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Kb−/−Db−/− Mice, But Provide Minimal Protection. The Journal of Immunology 170, 1987–1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman HE, Clay H, Beery D, Chang JCW, Sherman DR, and Ramakrishnan L (2004). Tuberculous granuloma formation is enhanced by a mycobacterium virulence determinant. PLoS Biol. 2, e367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman HE, Pozos TC, Zheng J, Davis JM, Rawls JF, and Ramakrishnan L (2010). Tuberculous granuloma induction via interaction of a bacterial secreted protein with host epithelium. Science 327, 466–469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton KL, Johnson KE, and Harrison CA (2017). Targeting TGF-β Mediated SMAD Signaling for the Prevention of Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warsinske HC, Pienaar E, Linderman JJ, Mattila JT, and Kirschner DE (2017). Deletion of TGF-β1 Increases Bacterial Clearance by Cytotoxic T Cells in a Tuberculosis Granuloma Model. Front. Immunol 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang N, and Bevan MJ (2012). Transforming growth factor-β signaling to T cells inhibits autoimmunity during lymphopenia-driven proliferation. Nat Immunol 13, 667–673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Related to Figure 1. Despite antigen sensing, CD4 T cells produce minimal IFNγ within Mtb granulomas: A) Expression of pS6, IRF4, and Nur77 of ESAT6-specific CD4 T cells (C7) after 4 hour in vitro stimulation with media alone, IL-2, IL-12 or cognate peptide. B) Example histocytometry gating scheme of indicated cell populations within infected lungs C) Example histocytometry gating overlayed onto confocal imaging (refer to Figure S1B): For 5/6 panels, antibody marker used for gating shown in red, with nuclei or CD4 in gray to show cells. Negative cells are denoted by cyan dot, while positive cells are denoted with yellow dot. For top left panel, CD11b+ CD11c- negative cells are denoted with yellow dot, while CD11c+ cells are denoted with magenta dot. Cyan cells = negative for both markers. D) Individual experiments showing endogenous CD4 T cell IFNγ and pS6 frequency by site (See Figure 1D). N=16 across 3 independent experiments. Different colors reflect different independent experiments. E) Histocytometry data showing percent pS6+ cells of total CD4 T cell by site, comparing fingolimod-treated and control ULD Mtb-infected mice, d37 p.i. F) Mice were given an IV antibody label, and lungs were taken for flow cytometry (right lung) and histocytometry (left lung) at day 29 post Mtb infection. Shown are representative confocal images (left); proportion of IV negative cells detected by flow and histocytometry (top right); and proportion of IV negative cells within noted cell populations, as determined by histocytometry.Single group comparisons by paired t test (A, B, D, E, F) or unpaired t test (E). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Points represent individual mice, connecting lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal.
Figure S2. Related to Figure 1. Despite antigen sensing, CD4 T cells produce minimal IFNγ within Mtb granulomas: A) Flow cytometry gating strategy for identification of Mtb-specific and OVA-specific T cells using congenic marker staining, as well as demonstration of IFNγ staining after ex-vivo restimulation. B) Paired flow cytometry data from figure 2, demonstrating ex-vivo IFNγ staining by proportion and MFI, in Mtb-specific and control OVA-specific T cells. C) Quantification of IRF4 staining in Mtb vs OVA-specific transferred cells, as determined by histocytometry (See figure 1G). D) Analysis of relative Mtb-specific vs. OVA-specific T cell abundance as determined by flow cytometry vs. histocytometry. E) Analysis of IFNγ production by the media alone or peptide-stimulated, Th1 polarized CD4 T cells prior to adoptive transfer. F) Proportion of Mtb-specific cells that are IRF4+, by tissue site (See figure 1H). Single-group comparisons by paired (B, C, F) or unpaired (D) t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Points represent individual mice, connecting lines connect different sites (granuloma, distal lung) within the same animal (C, F) or C7 and OTII cells within the same transfer recipient (B).
Figure S3. Related to Figure 2. Genes associated with TGFβ signaling are increased within the granuloma: A) GSEA analysis of parenchymal Mtb-specific cells vs. naïve T cells, showing increased pathways consistent with activation. B) GSEA analysis highlighting the indicated pathways which were differentially associated with the parenchymal vs. intravascular Mtb-specific cells. C) Relative expression of genes in the TGFβ signaling pathway in parenchymal vs. intravascular Mtb-specific cells is shown. D) Representative confocal image of a necrotic NHP granuloma, showing pSMAD3 staining. CD68/163 denotes macrophages. MPO denotes neutrophils. E) Zoom-in images showing pSMAD3 signal in relation to CD4 and CD68/163. F) Ziehl-Neelsen staining of granulomas from rhesus macaques shown in Figures 2F and S3D. Zoom-ins showing areas with acid-fast bacilli. FDRs were calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg method.
Figure S4. Related to Figures 3 and 4. Lack of TGFβRII on T cells results in decreased CFUs and increased IFNγ production: A) Left plot showing lung bacterial burdens from 6 independent experiments of TGFβR.KO mice (open circles) and littermate controls (grey circles). Each color denotes separete infection. Right plot showing spleen bacterial burdens at d28 p.i. B) Example flow cytometry gating strategy for the identification of parenchymal Mtb-specific T cells and quantification of IFNγ production by these cells is shown. C) Proportion of IFNγ+ ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells compared against bacterial burden. D) Number of ESAT-6 specific CD4 T cells. E) Proportion of intravascular ESAT-6 specific CD3+CD4+ T cells that are Annexin V+, SYTOX−(see figure 3D). F) Proportion of parenchymal ESAT-6 specific CD3+CD4+ T cells that are FoxP3+ or RORγt+. G) Representative confocal images demonstrating staining of iNOS within CD11b+ cells. H) Flow cytometry gating strategy for identifying and phenotyping ESAT6 tetramer-positive TGFβR.KO vs WT cells in the lung parenchyma on mixed bone marrow chimeras (Figure 4). Single-group comparisons by unpaired t test. Line denotes mean. Points represent individual mice. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Figure S5. Related to Figure 5. T cell-intrinsic suppression of Mtb-specific TCR transgenic T cells: A-C: See figures 5A–F A) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are IFNγ+, TNF+, or IL-2+ following 4 hours in vitro peptide stimulation. B) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are ex-vivo IFNγ+, at specified timepoints. Significance reflective of differences between timepoints within each cell population. C) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are FoxP3+ or RORγt+. D) Analysis of IFNγ production by the media-only or peptide-stimulated, Th1 polarized Tg.WT vs Tg.KO CD4 T cells prior to adoptive transfer (See figures 5G–I). E-H: See figures 5J–L E) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are Ki67+. F) Proportion of parenchymal Tg.WT and Tg.KO cells that are ex-vivo IFNγ+. G) Pulmonary and splenic bacterial burdens of mice that received either transfer of Tg.WT or Tg.KO Th1 cells. H) Ratio of either Tg.WT or Tg.KO to endogenous CD4 T cells. Single-group comparisons by paired (A, C) or unpaired (B, E, F, G, H) t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Data Availability Statement
The mouse lung RNAseq data generated during this study are available at GEO under accession number GSE134186.


