Table 1.
Classification of phytocannabinoids. Adapted from [9], MDPI, 2021.
| Class of Compounds | The Number of Compounds in Each Class |
The First Representative Compound of the Class | Chemical Structure of the Representative Compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δ9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol | 25 | Δ9-THC—isolated in 1964 by Goani and Mecholum using chromatography techniques [10] |
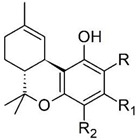
|
| Δ8-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol | 5 | Δ8-THC—isolated in Maryland in 1966 [11] |
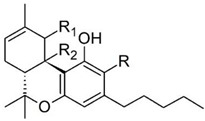
|
| cannabidiol | 10 | CBD-C5—isolated in 1940 from native Minnesota hemp [12] |
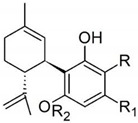
|
| cannabigerol | 16 | CBG—isolated in 1964 using florisil chromatography [13] |
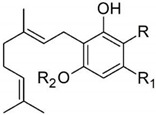
|
| cannabichromene | 9 | CBC—isolated in 1966 by Gaoni Y. [14] |
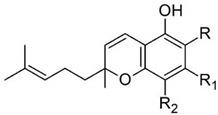
|
| cannabinol | 11 | CBN synthesized by Adams et al. in the US and by Todd’s group in the UK in 1940 [15,16] |
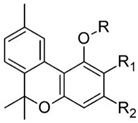
|
| cannabinodiol | 2 | CBND-C3—isolated in 1973 [17] CBND-C5—isolated in 1977 [18] |
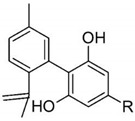
|
| cannabicyclol | 3 | CBL—compound was isolated by Korte and Sieper in 1964, and the structure was elucidated by Crombie et al. in 1968 [19,20] |
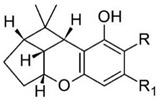
|
| cannabielsoin | 5 | CBE-C5—isolated in 1973 from Lebanese hashish [21] |
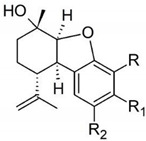
|
| cannabitriol | 9 | CBT-C5—isolated in 1966 from Japanese hemp, but the complete chemical structure was established 10 years later [21,22] |
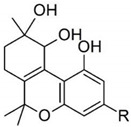
|
| other unclassified types of cannabinoids | 30 | The first ones isolated in 1975 (examples: dehydrocannabifuran DCBF-C5, cannabifuran CBF-C5) [23] |
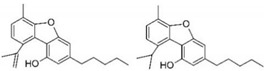
|
