Abstract
Objective
Pheochromocytomas are a hallmark feature of von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL). To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review with meta-analysis evaluating the frequency of pheochromocytomas and/or paragangliomas (PPGLs) in patients with vHL, as well as among patients with different vHL subtypes.
Design
Systematic review with meta-analysis.
Methods
We searched on MEDLINE, Scopus, and Web of Science. We included primary studies assessing participants with vHL and reporting on the frequency of PPGL. We performed random-effects meta-analysis to quantitatively assess the frequency of PPGL, followed by meta-regression and subgroup analysis. Risk of bias analysis was performed to assess primary studies’ methodological quality.
Results
We included 80 primary studies. In 4263 patients with vHL, the pooled frequency of PPGL was 19.4% (95% CI = 15.9–23.6%, I2 = 86.1%). The frequency increased to 60.0% in patients with vHL type 2 (95% CI = 53.4–66.3%, I2 = 54.6%) and was determined to be of 58.2% in patients with vHL type 2A (95% CI = 49.7–66.3%, I2 = 36.2%), compared to 49.8% in vHL type 2B (95% CI = 39.9–59.7%, I2 = 42.7%), and 84.1% in vHL type 2C (95% CI = 75.1–93.1%, I2 = 0%). In meta-regression analysis, more recent studies were associated with a higher frequency of PPGL. All studies had at least one internal validity item classified as 'high risk of bias,' with 13% studies having low risk of bias in all external validity items.
Conclusions
PPGLs are a common manifestation of vHL. Despite methodological limitations and differences across primary studies, our results point to the importance of PPGL screening in patients with vHL.
Keywords: pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, von Hippel–Lindau, frequency, systematic
Introduction
Von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL) is a rare hereditary autosomal dominant disorder resulting from the presence of pathogenic variants on the VHL gene (1), with a point prevalence estimated (as per the first nationwide study on the subject) at 1:46,900 individuals, a birth incidence at 1:27,300 live births, and an overall penetrance of 87% at 60 years of age (2). Carriers of disease-causing VHL germline variants are at an increased risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms, such as hemangioblastomas and pheochromocytomas. Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGLs), arising either through germline VHL mutations in a syndromic setting or via somatic VHL mutations sporadically, associate with the pseudo-hypoxic mRNA expressional cluster 1 in which an increased risk of metastatic events is seen compared to tumors arising within the kinase-associated cluster 2, containing more biologically indolent tumors (3, 4). Pheochromocytomas are more frequently diagnosed during the third decade of life although they may also be the presenting feature in the pediatric setting (2, 5). Pheochromocytoma is such a hallmark feature of vHL that its absence or presence, respectively, underlies the phenotypic classification in type 1, which is typically associated with protein-truncating mutations, or vHL type 2, which mainly associates with missense mutations (6). vHL type 2 is further subdivided into types 2A (low risk of renal cell carcinoma), 2B (high risk of renal cell carcinoma), and 2C (only pheochromocytoma without other vHL manifestations) (6, 7). In the clinical setting, even though surveillance protocols are generally similar for all vHL patients, this classification is particularly useful for appropriate intrafamilial risk management and prognosis assessment since the risk of developing pheochromocytomas in vHL-affected family members increases once the history of pheochromocytoma in the family is reported and the family is considered of type 2 vHL.
An Italian nationwide prospective study assessing individuals with vHL found that 30% of participants developed pheochromocytoma, resulting in a cumulative incidence of adrenal disability of 11% after surgery, requiring adrenal substitutive therapy. Those patients underwent surgery for pheochromocytoma at a mean age of 27 years, similar to those who underwent surgery for hemangioblastoma (28 years) and earlier than those who underwent surgery for renal and pancreatic neoplasms (37 and 35 years old, respectively) (8). Therefore, international clinical practice guidelines support early detection of pheochromocytomas in vHL patients, as it may allow for more advanced surgical techniques – such as cortical-sparing and laparoscopic procedures – to be performed, resulting in lower risk of recurrence and maintenance of corticosteroid independence (9, 10).
However, notwithstanding the burden of pheochromocytoma in vHL and despite the benefits of early and lifetime screening for this neoplasm in patients with vHL (11), the prevalence of pheochromocytoma in patients with vHL has not been systematically ascertained. Several studies have reported the frequency of pheochromocytoma in cohorts of patients with vHL, but with relevant disparities, mirroring their differences in study design, methodological quality, and sample size. Thus, this systematic review aims to determine the frequency of pheochromocytoma and/or PPGL in patients with vHL (and in patients with each vHL subtype), as well as to identify variables potentially explaining across-study differences on the frequency of PPGL.
Materials and methods
This study corresponds to a systematic review with meta-analysis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (12).
Eligibility criteria
To determine the frequency of PPGL in vHL, we included cohorts of patients with vHL – either fulfilling clinical diagnostic criteria of vHL or carrying VHL germline pathogenic mutations – which have reported data on the number of patients/mutation carriers with PPGL. In order to determine the frequency of PPGL in each vHL subtype, we also included family reports that have reported data on the number of patients/mutation carriers with vHL of each subtype with PPGL. To assess the frequency of PPGL in vHL type 2C, we included only studies that have performed molecular screening of asymptomatic family members (once PPGL is the only phenotypic feature in vHL type 2C, all patients clinically diagnosed with vHL type 2C have a history of PPGL; therefore, we included only primary studies that performed genetic screening of asymptomatic family members so that we were able to assess the frequency of PPGL in all family members with the vHL type 2C mutation). We excluded case–control studies, case series of pheochromocytoma/PPGL patients, and studies in which patient selection was based on specific phenotypic manifestations (e.g. case series of vHL patients with hemangioblastomas).
Search strategy and study selection
Studies were identified in February 2020 through a search conducted on three electronic bibliographic databases (MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus) using the queries displayed in Supplementary Table 1 (see section on supplementary materials given at the end of this article). No language or date restrictions were applied.
Following duplicate removal, screening of the titles and abstracts was independently conducted by two researchers. The full texts of selected studies were then independently read by two researchers, who decided on their final inclusion. For publications in which complete or partial overlap of participants with other studies occurred, we presented only information from the publication with more participants, eventually complementing with relevant information from other publications on covariates of interest.
Data extraction
Two researchers independently extracted relevant data from included studies regarding their year of publication, country, sampling method, method of vHL diagnosis (clinical and/or molecular), number of vHL patients/mutation carriers, participants’ gender and age distributions, number of asymptomatic carriers of VHL pathogenic mutations, number of patients with positive family history of vHL disease, and number of patients with PPGL (including the number of patients with bilateral adrenal presentation). Our outcome variable consisted of the number of patients with PPGL (instead of the number of patients with pheochromocytoma), as many studies did not differentiate between adrenal pheochromocytoma and PPGL/extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma (13). Nevertheless, we also collected separate data regarding the frequency of pheochromocytoma and PPGL whenever these entities were adequately distinguished. We also retrieved information concerning the number of vHL patients/mutation carriers with each vHL phenotypic subtype (vHL type 2A, vHL type 2B, vHL type 2C) and the number of patients with each vHL subtype who had PPGL.
For data collection, we used a purpose-built form developed after a pilot version. Authors were contacted to provide relevant missing information. In cases of disagreement regarding study selection or data extraction, a consensus was achieved.
Quality assessment
Study quality was independently assessed by two researchers according to an adapted version of the Hoy et al. judgments on the risk of bias of prevalence studies (14). Three risk of bias items were excluded as they did not adequately apply to our study, namely that regarding data provenance (directly from subjects vs from a proxy) on account of the type of data we were retrieving, that concerning reliability and validity of the study instrument used to measure the parameter of interest, and that regarding the suitability of the length of the shortest prevalence period (as we were not assessing a specific prevalence period).
Quantitative synthesis
We performed random-effects meta-analyses to estimate the pooled frequency of PPGL among patients with vHL, as well as among patients with each vHL subtype. In addition, we computed the meta-analytical frequency of patients with PPGL who presented with bilateral neoplasms or who were of the male sex. To account for possible bias resulting from studies assessing small samples (with the possibility of most patients being from a small number of families), we performed sensitivity analyses restricted to studies with more than 25 participants.
Meta-analysis was performed based on the restricted maximum likelihood method, using logit-transformed proportions. Pooled results were back-transformed to their original scale to facilitate their interpretation. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic and Cochran Q test P value – an I2 > 50% and a P value < 0.10 were considered to represent substantial heterogeneity. In the presence of substantial heterogeneity, we performed meta-regression and subgroup analyses in order to identify variables possibly explaining across-study differences. Covariates tested include the publication year, sample size, percentage of male participants, mean participants’ age, region (Europe, America, and Asia and Pacific), sampling method (consecutive, convenience, or not specified), and vHL diagnosis method (clinical criteria only or including genetic testing/not specified). All statistical analyses were performed using metafor package of software R (version 4.0.0.).
Results
Search results
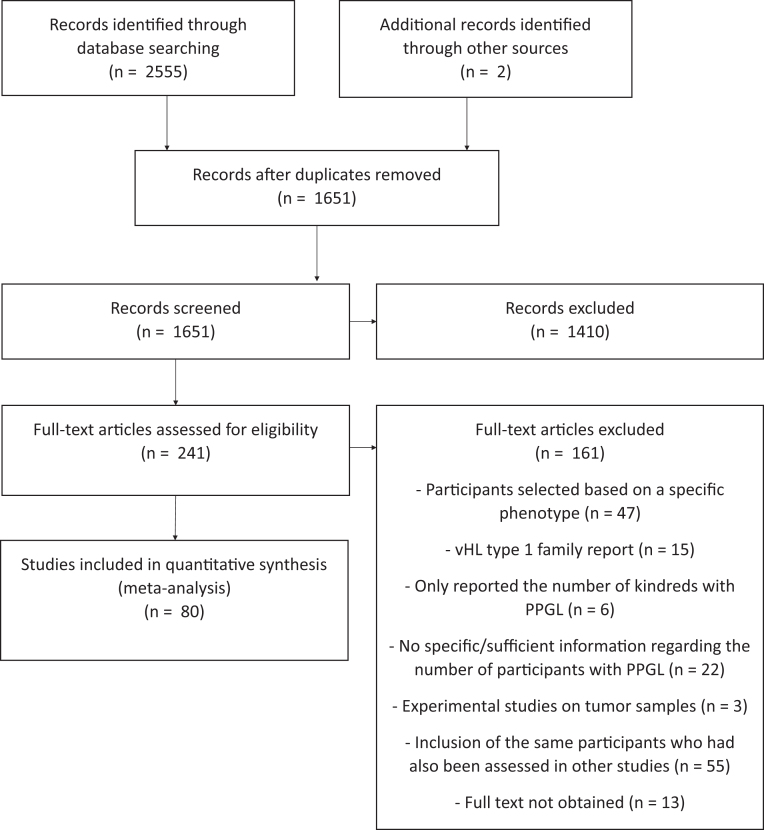
Our search yielded 2557 publications, of which 906 were duplicates. One thousand four hundred ten studies were excluded on the basis of application of eligibility criteria (Fig. 1). Fifty-five records were excluded due to partial or complete overlap of participants with included publications. We could not obtain the full text of 13 publications despite contacting corresponding authors (Supplementary Table 2). Seven of these articles were published in a language other than English, and six were published before 2000.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram illustrating study selection process.
A total of 80 studies were included in this systematic review. Of these, 45 cohort studies were used in the meta-analytical quantitative synthesis of the frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL (8, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58). On the other hand, 52 studies were used in the frequency analysis of PPGL in vHL type 2 (16, 17, 21, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 40, 44, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 56, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93), of which 24 corresponded to cohort studies (16, 17, 21, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 40, 44, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 56, 62, 63, 64, 66, 77, 78, 79) and 28 to family reports (59, 60, 61, 65, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93). In total, 17 studies were used in both analyses (16, 17, 21, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 40, 44, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 56).
Frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL
The meta-analysis assessing the frequency of PPGL comprised 45 studies with a total of 4263 participants with vHL (8, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58). Most of these studies were conducted in Europe (n = 21) (8, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34), followed by Eastern Asia (n = 14) (35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48) and North America (n = 6) (49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54). All studies assessed patients of all age groups, with the mean age of onset of vHL being 30.6 years (as reported in 13 publications (17, 24, 30, 31, 39, 41, 43, 46, 49, 50, 52, 55, 58)) and the mean onset age of PPGL being 28.7 years (8, 21, 24, 26, 31, 35, 40, 44, 47, 49, 50, 52, 55, 58). Nineteen studies sampled their participants consecutively (8, 16, 17, 18, 19, 24, 27, 29, 31, 32, 37, 38, 39, 43, 46, 49, 50, 51, 52), whereas in 11 studies a convenience sample was assessed (20, 21, 22, 25, 34, 35, 45, 47, 53, 56, 57). A total of 1340 participants – from 25 studies – had information regarding their vHL family history status, of whom 1059 reported having family history of vHL disease (15, 17, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28, 29, 30, 34, 37, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 52, 53, 56, 57, 58). Description of studies can be consulted in Supplementary Table 3, and information regarding other phenotypic manifestations is displayed in Supplementary Table 4.
The meta-analytical frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL was 19.4% (95% CI = 15.9–23.6%), with severe heterogeneity being detected (I2 = 86.1%, Q Cochran P value ≤ 0.001) (Table 1). In meta-regression analysis (Table 2), studies published in more recent years were associated with a significantly increased frequency of PPGL (OR = 1.04, 95% CI = 1.01–1.08, P = 0.013). No statistically significant differences were observed regarding the mean age of assessed patients (OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 0.96–1.16, P = 0.300). When assessing the frequency of PPGL in the general cohort of vHL participants, we found significant heterogeneity in all subgroup analyses. Similar results were observed in sensitivity analyses restricted to studies with more than 25 participants (Supplementary Table 5). Similar results were also observed when pooling the meta-analytical frequency of pheochromocytoma (excluding PPGLs) among vHL participants assessed in studies with adequate definition of this outcome (Supplementary Table 6).
Table 1.
Meta-analytical results on the frequency of pheochromocytoma and/or paraganglioma (PPGL) among patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL).
| N studies | N vHL | Frequency (%, 95% CI) | Q Cochran P value | I² | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants with vHL (all vHL types) | |||||
| Frequency of participants with PPGL | 45 | 4263 | 19.4 (15.9–23.6) | <0.001 | 86.1% |
| Participants with bilateral pheochromocytoma | 14 | 59.5 (47.0–70.9) | 0.611 | 0% | |
| Males with PPGL | 15 | 58.3 (47.6–68.4) | 0.837 | 0% | |
| Participants with vHL type 2 | 840 | ||||
| Frequency of participants with PPGL | 52 | 60.0 (53.4–66.3) | <0.001 | 54.6% | |
| Participants with PPGL in vHL type 2A | 28 | 411 | 58.2 (49.7–66.3) | 0.010 | 36.2% |
| Participants with PPGL in vHL type 2B | 24 | 256 | 49.8 (39.9–59.7) | 0.013 | 42.7% |
| Participants with PPGL in vHL type 2C | 11 | 52 | 84.1 (75.1–93.1) | 0.932 | 0% |
Table 2.
Results of meta-regression and subgroup analysis concerning the frequency of pheochromocytoma and/or paraganglioma (PPGL) among patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL) of all types.
| Meta-regression | Subgroup analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N studies | N vHL | OR (95% CI) | P value | Frequency (%, 95% CI) | Q Cochran P value | I² | |
| Publication year | 45 | 4263 | 1.04 (1.01–1.08) | 0.013* | –a | –a | –a |
| Sample size | 45 | 4263 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.818 | –a | –a | –a |
| % of males | 24 | 648 | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.554 | –a | –a | –a |
| Mean cohort age | 9 | 444 | 1.05 (0.96–1.16) | 0.300 | –a | –a | –a |
| Mean onset age of vHL | 13 | 1863 | 0.98 (0.91–1.07) | 0.697 | –a | –a | –a |
| Region | 45 | 4263 | – | 0.802b | |||
| Europe | 21 | 2148 | –c | –c | 19.1 (14.5–24.9) | <0.001 | 84.4% |
| Asia and Pacific | 16 | 1116 | 0.97 (0.55–1.71) | 0.923 | 18.5 (12.9–25.9) | <0.001 | 76.7% |
| America | 8 | 999 | 1.23 (0.62–2.44) | 0.558 | 21.0 (11.4–35.3) | <0.001 | 92.6% |
| Sampling method | 45 | 4263 | – | 0.352b | |||
| Consecutive | 19 | 3684 | –c | –c | 20.5 (16.3–25.5) | <0.001 | 90.1% |
| Convenience | 11 | 178 | 1.22 (0.61–2.41) | 0.576 | 22.4 (11.7–38.7) | <0.001 | 69.4% |
| Not specified | 15 | 401 | 0.72 (0.40–1.28) | 0.261 | 15.3 (9.9–23.0) | <0.001 | 61.2% |
| Diagnosis method | 45 | 4263 | – | 0.888b | |||
| Included genetic testing/not specified | 42 | 4086 | –c | –c | 19.7 (16.1– 23.8) | <0.001 | 85.0% |
| Clinical criteria only | 3 | 177 | 0.93 (0.32–2.70) | 0.888 | 27.7 (3.2–81.6) | <0.001 | 91.8% |
aNot performed, as this is a continuous variable; bOmnibus P value for this variable; cReference category; *Statistically significant P value.
The pooled frequency of asymptomatic carriers of VHL pathogenic mutations was 6.2% (95% CI = 3.7–10.3%, I2 = 84.7%, P ≤ 0.001) (15, 16, 17, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 30, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58). Among participants with pheochromocytoma, 59.5% had bilateral synchronous or metachronous disease (95% CI = 47.0–70.9%, I2 = 0%, P = 0.611) (20, 22, 25, 26, 28, 30, 35, 40, 41, 45, 47, 55, 57, 58). In addition, 58.3% participants with PPGL were males (95% CI = 47.6–68.4%, I2 = 0%, P = 0.837) (20, 25, 26, 32, 35, 37, 41, 43, 44, 45, 47, 52, 53, 56, 58).
Frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL type 2
A total of 52 studies, assessing 840 participants with vHL type 2, provided information on the frequency of PPGL. Most of these studies were conducted in Europe (n =18) (16, 17, 21, 25, 26, 28, 29, 62, 66, 68, 70, 71, 72, 73, 76, 83, 91, 92), followed by Eastern Asia (n =17) (35, 36, 40, 44, 45, 47, 48, 74, 75, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 86, 87) and North America (n =9) (53, 59, 60, 61, 63, 64, 65, 69, 84). All studies assessed patients of all age groups, with the mean onset age of PPGL being 28.8 years (as reported in 21 studies (21, 26, 35, 40, 44, 47, 55, 59, 60, 61, 65, 67, 71, 72, 74, 77, 79, 85, 86, 87, 88)). Six studies reported a consecutive sample (16, 17, 29, 66, 77, 78), whereas in 39 studies a convenience sample was assessed (21, 25, 35, 45, 47, 53, 56, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93).
The frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL type 2 was 60.0% (95% CI = 53.4–66.3%), with moderate heterogeneity being observed (I2 = 54.6%) (16, 17, 21, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 40, 44, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 56, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93) (Table 1). We observed lower heterogeneity in subgroup analyses restricted to convenience sampling (I2 = 25.6%) and to patients whose diagnosis was performed only clinically (I2 = 23.1%) (Supplementary Table 7). Similar results were obtained with sensitivity analyses restricted to studies with more than 25 participants (Supplementary Table 5), as well as when assessing the meta-analytical frequency of pheochromocytoma without considering PPGLs (Supplementary Table 6).
Twenty-eight studies, with a total of 411 participants with vHL type 2A, reported the frequency of PPGL among these patients (16, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 47, 55, 60, 61, 62, 63, 65, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 85, 92). The pooled frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL type 2A was 58.2% (95% CI = 49.7–66.3%, I2 = 36.2%) (Table 1) (16, 25, 26, 28, 29, 35, 36, 47, 55, 60, 61, 62, 63, 65, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 85, 92). In most subgroup analysis, moderate heterogeneity was observed (Table 3).
Table 3.
Results of meta-regression and subgroup analysis concerning the frequency of pheochromocytoma and/or paraganglioma (PPGL) among patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL) type 2A.
| Meta-regression | Subgroup analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N studies | N vHL | OR (95% CI) | P value | Frequency (%, 95% CI) | Q Cochran p value | I² | |
| Publication year | 28 | 411 | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 0.384 | –a | –a | –a |
| Sample size | 28 | 411 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.573 | –a | –a | –a |
| Region | 28 | 411 | – | 0.306b | –a | –a | –a |
| Europe | 11 | 255 | –c | –c | 59.6 (48.9–69.5) | <0.165 | 35.4% |
| Asia and Pacific | 11 | 69 | 0.60 (0.25–1.41) | 0.239 | 48.8 (32.3–65.5) | 0.135 | 32.2% |
| America | 6 | 87 | 1.29 (0.48–3.44) | 0.617 | 73.4 (37.2–92.8) | 0.009 | 80.1% |
| Sampling method | 28 | 411 | – | 0.118b | |||
| Consecutive | 3 | 24 | –c | –c | 55.8 (24.3–83.2) | 0.142 | 50.3% |
| Convenience | 21 | 370 | 0.99 (0.32–3.01) | 0.981 | 56.1 (47.4–64.5) | 0.012 | 33.9% |
| Not specified | 4 | 17 | 5.39 (0.81–35.76) | 0.081 | 87.6 (61.0– 97.0) | 0.767 | 0% |
| Diagnosis | 28 | 411 | – | 0.427b | |||
| Included genetic testing/not specified | 27 | 409 | –c | –c | 57.9 (49.3–66.0) | 0.008 | 36.9% |
| Clinical criteria only | 1 | 2 | 2.69 (0.38–19.08) | 0.427 | 83.3 (19.4–99.0) | <0.001 | 0% |
aNot performed, as this is a continuous variable; bOmnibus P value for this variable; cReference category.
Twenty-four studies, with a total of 256 participants with vHL type 2B, reported the frequency of PPGL among these patients (21, 29, 36, 40, 44, 45, 48, 53, 55, 56, 64, 66, 67, 68, 72, 77, 78, 83, 84, 86, 88, 89, 91, 93). The meta-analytical frequency of PPGL among participants with vHL type 2B was 49.8% (95% CI = 39.9–59.7%, I2 = 42.7%) (21, 29, 36, 40, 44, 45, 48, 53, 55, 56, 64, 66, 67, 68, 72, 77, 78, 83, 84, 86, 88, 89, 91, 93) (Table 1). Low or undetectable heterogeneity was observed when performing subgroup analyses restricted to European studies (pooled frequency = 37.8%, 95% CI = 27.8–48.9%, P = 0.778, I2 = 0%) or to studies using convenience sampling (pooled frequency = 55.9%, 95% CI = 46.1–65.2%, P = 0.135, I2 = 12.7%) (Table 4). All other tested covariates were associated with moderate heterogeneity.
Table 4.
Results of meta-regression and subgroup analysis concerning the frequency of pheochromocytoma and/or paraganglioma (PPGL) among patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease (vHL) type 2B.
| Meta-regression | Subgroup analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N studies | N vHL | OR (95% CI) | P value | Frequency (%, 95% CI) | Cochran P value | I² | |
| Publication year | 24 | 256 | 1.00 (0.95–1.05) | 0.965 | –a | –a | –a |
| Sample size | 24 | 256 | 1.00 (0.96–1.04) | 0.975 | –a | –a | –a |
| Region | 24 | 256 | – | 0.138b | –a | –a | –a |
| Europe | 7 | 83 | –c | –c | 37.8 (27.8–48.9) | 0.778 | 0% |
| Asia and Pacific | 11 | 105 | 1.97 (0.85–4.57) | 0.112 | 55.0 (39.3–70.0) | 0.066 | 45.2% |
| America | 6 | 68 | 2.55 (0.91–7.12) | 0.074 | 58.8 (30.4–82.4) | 0.052 | 58.0% |
| Sampling method | 24 | 256 | – | 0.361b | |||
| Consecutive | 4 | 62 | –c | –c | 45.6 (24.0–69.0) | 0.094 | 59.1% |
| Convenience | 15 | 155 | 1.48 (0.58–3.80) | 0.412 | 55.9 (46.1–65.2) | 0.135 | 12.7% |
| Not specified | 5 | 39 | 0.72 (0.21–2.51) | 0.606 | 40.8 (17.2–69.4) | 0.118 | 47.7% |
| Diagnosis | 24 | 256 | – | 0.301b | |||
| Included genetic testing/not specified | 20 | 222 | –c | –c | 46.2 (35.8–56.9) | 0.021 | 44.4% |
| Clinical criteria only | 4 | 34 | 2.04 (0.70–5.92) | 0.301 | 73.5 (45.7–90.0) | 0.272 | 29.6% |
aNot performed, as this is a continuous variable; bOmnibus P value for this variable; cReference category.
Lastly, in 11 studies, with a total of 52 participants with vHL type 2C, information was provided on the frequency of PPGL among these patients (25, 26, 29, 40, 44, 45, 59, 74, 76, 87, 90). The meta-analytical frequency was 84.1% (95%CI = 75.1–93.1%), with no heterogeneity observed (I2 = 0%) (25, 26, 29, 40, 44, 45, 59, 74, 76, 87, 90) (Table 1).
Risk of bias assessment
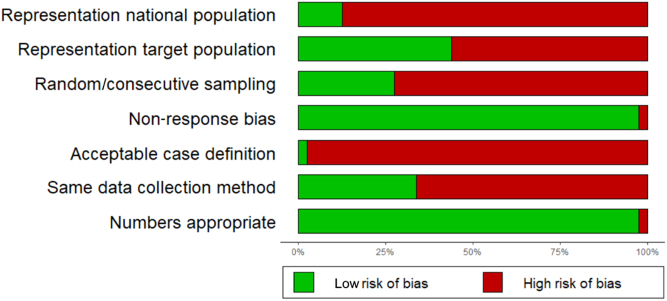
All studies had at least one high risk of bias item concerning internal validity (Fig. 2). Ten studies (12.5%) had low risk of bias in all items concerning external validity (16, 17, 18, 24, 27, 29, 31, 38, 49, 51). The two items for which studies were most commonly classified as having 'low risk of bias' concerned the possibility of nonresponse bias (97.5%) and the presentation of an appropriate numerator and denominator for the parameter of interest (97.5%). Conversely, the case definition was the item for which studies were most frequently classified as having 'high risk of bias', with only two studies (2.5%) using an acceptable case definition (55, 71). 44% of all included studies were considered representative of the target population. However, this percentage rises to 73% when analyzing only those 45 cohort studies used in the meta-analysis pooling the frequency of PPGL in patients with vHL of any subtype. On the other hand, only 23% studies are considered representative of the target population when considering solely those studies assessing the frequency of PPGL in patients with vHL type 2.
Figure 2.
Risk of bias graph depicting the assessment of the methodological quality of included primary studies. Risk of study bias items assessed: aStudy’s target population as a close representation of the vHL national population. bSampling frame as a true or close representation of the target population. cSample selection based on a random/consecutive process. dLikelihood of nonresponse bias. eAcceptable case definition used in the study. fSame mode of evaluation for all subjects. gNumerator and denominator appropriate.
Discussion
In this systematic review, we assessed the frequency of PPGL in patients with vHL, as well as in patients with each subtype of vHL. The meta-analytical frequency of PPGL in patients with vHL was 19%, which is in agreement with previous estimates (11, 31). This frequency increased to 60% in vHL type 2 participants and was determined to be 58, 50, and 84% among participants with vHL type 2A, type 2B, and type 2C, respectively. Most participants who developed pheochromocytoma had bilateral adrenal involvement (60%), including both synchronous and metachronous processes. Overall, these results point to the high frequency of PPGL among patients with vHL (particularly in patients belonging to type 2 families, in whom this frequency is exceptionally high), as well as to a high propensity for bilateral adrenal involvement, supporting the benefit of lifetime screening for PPGL in patients with vHL. Meta-regression analysis revealed that more recent studies were associated with a higher frequency of PPGL, which is likely related to an improvement in diagnostic procedures for PPGL and to the expanding application of annual screening protocols in vHL patients. We found no statistically significant differences regarding the mean age of assessed patients – in this setting, it would be expected for studies assessing cohorts of older patients to be associated with a higher frequency of PPGL, as the disease penetrance increases with age, being estimated to be as high as 95% by 60 years of age (49). However, the interpretation of this analysis may be limited by the fact that we used the mean cohort age rather than individual patient-level information regarding participants’ age. Additionally, it should be noted that the mean age of onset of PPGL of 28.7 years, in the upper end of the third decade of life, probably reflects a substantial number of clinically diagnosed cases, compared to the genetic screening and surveillance that increasingly allow for earlier diagnosis.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, most primary studies did not present clear outcome definitions, with some using the term 'pheochromocytoma' to broadly refer to tumors arising from adrenal and extra-adrenal chromaffin cells, others using the term to strictly refer to tumors of adrenomedullary origin, and others not appropriately defining the term. To tackle this limitation, our outcome variable corresponded to PPGL rather than pheochromocytoma. Secondly, some primary studies reported single-institution experiences with small sample series, possibly consisting of a reduced number of families, which conveys a risk of overrepresentation of certain vHL subtypes – to account for this limitation, we performed sensitivity analyses restricted to studies with more than 25 participants, with similar results being observed. Additionally, we came across some studies that disclosed only the number of families with vHL type 2 phenotype rather than the number of participants with PPGL – these reports could not be included in the quantitative synthesis. Another limitation concerns the possibility of selection bias, particularly in the calculation of the frequency of PPGL in vHL type 2C participants – as discussed earlier, to account for the fact that PPGL is the only phenotypic manifestation in the rare vHL type 2C and, therefore, the diagnostic feature in the clinical diagnosis of this subtype, we included only primary studies that have tested asymptomatic members of vHL type 2C families for germline pathogenic VHL mutations; however, in most cases, the testing coverage of the pedigree was not disclosed and therefore it is likely that some members were not tested. This fact combined with the limited number of studies assessing vHL type 2C participants may have contributed to an overestimation of the frequency of PPGL in this subtype. Another limitation concerns the recently described germline mutations in the E1’ cryptic exon of the VHL gene in patients previously considered mutation negative, consisting of a small subset of patients possibly not assessed in the studies included in this meta-analysis (94). Another limitation concerns the lack of important information provided by primary studies, namely regarding sociodemographic data of the vHL participants and adequate characterization of PPGL when these occurred (i.e. mean age of onset, data regarding recurrences or second primary tumors, and data regarding biochemical and imaging procedures). As a result, we were not able to assess several variables that could potentially contribute to explain heterogeneity. Another limitation concerns the fact that information regarding the rate of metastatic PPGL arising in vHL patients was not included in the scope of the query used in this study. In result, the majority of included studies did not provide specific information regarding this subject, preventing from drawing reliable conclusions on this topic. Finally, another important limitation concerns the methodological quality of included primary studies, with all of them having at least one high risk of bias item concerning internal validity.
This study also has several strengths. We conducted a search using three electronic bibliographic databases and did not apply date- or language-based exclusion criteria, so as to minimize the risk of publication bias. We also performed meta-regression and subgroup analysis to identify variables responsible for explaining across-studies heterogeneity. In addition, we assessed the methodological quality of included primary studies, pointing that future primary studies should particularly minimize the risk of bias related to the use of equivocal outcome definitions and disclose more detailed patient-level information, namely regarding the development and coexpression of manifestations, for further establishment of phenotypic associations in frame with the genetic findings. Finally, the results of this systematic review have clinical relevance, as they provide additional information for the endocrinological management of vHL patients and their respective families, supporting the benefit of early and lifetime screening for PPGL, as the review points that PPGL is more frequent than that acknowledged in some of the previous reports, particularly among type 2 vHL families.
Conclusions
In conclusion, PPGL is frequent among patients with vHL, with this frequency being higher among patients with vHL type 2 (in whom it ranges, according to the subtype, from 50 to 84%). Overall, this points to a high burden of PPGL among patients with vHL, indirectly supporting early and lifetime screening. Nevertheless, our results should be carefully interpreted on account of the observed heterogeneity and on the important methodological limitations observed in primary studies. For the future, an eventual development of an international vHL register could contribute to overcome such limitations, as it would allow for clinicians and researchers to access genotypic–phenotypic information, benefiting the individual and collective management of the vHL disease, as a day-to-day clinical tool and as a data record for future studies.
Supplementary Material
Declaration of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Funding
This work did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector.
Data sharing statement
Additional data will be available for other researchers upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
- 1.Choyke PL Glenn GM Walther MM Patronas NJ Linehan WM & Zbar B. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetic, clinical, and imaging features. Radiology 1995194629–642. ( 10.1148/radiology.194.3.7862955) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Binderup MLM Galanakis M Budtz-Jorgensen E Kosteljanetz M & Bisgaard ML. Prevalence, birth incidence, and penetrance of von Hippel-Lindau disease (vHL) in Denmark. European Journal of Human Genetics 201725301–307. ( 10.1038/ejhg.2016.173) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wachtel H & Fishbein L. Genetics of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity 202128283–290. ( 10.1097/MED.0000000000000634) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Juhlin CC.. Challenges in paragangliomas and pheochromocytomas: from histology to molecular immunohistochemistry. Endocrine Pathology 202132228–244. ( 10.1007/s12022-021-09675-0) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Prasad R Johnston LB Savage MO Martin L Perry LA & Storr HL. Pediatric endocrine screening for von Hippel-Lindau disease: benefits and the challenge of compliance. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation 201134296–299. ( 10.1007/BF03347089) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nordstrom-O’Brien M Van Der Luijt RB Van Rooijen E Van Den Ouweland AM Majoor-Krakauer DF Lolkema MP Van Brussel A Voest EE & Giles RH. Genetic analysis of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Human Mutation 201031521–537. ( 10.1002/humu.21219) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crespigio J Berbel LCL Dias MA Berbel RF Pereira SS Pignatelli D & Mazzuco TL. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: a single gene, several hereditary tumors. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation 20184121–31. ( 10.1007/s40618-017-0683-1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Feletti A, Anglani M, Scarpa B, Schiavi F, Boaretto F, Zovato S, Taschin E, Gardi M, Zanoletti E, Piermarocchi Set al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: an evaluation of natural history and functional disability. Neuro-Oncology 2016181011–1020. ( 10.1093/neuonc/nov313) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baghai M Thompson GB Young Jr WF Grant CS Michels VV & van Heerden JA. Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease: a role for laparoscopic and cortical-sparing surgery. Archives of Surgery 2002137682–688; discussion 688–689. ( 10.1001/archsurg.137.6.682) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Neumann HPH, Tsoy U, Bancos I, Amodru V, Walz MK, Tirosh A, Kaur RJ, McKenzie T, Qi X, Bandgar Tet al. Comparison of pheochromocytoma-specific morbidity and mortality among adults with bilateral pheochromocytomas undergoing total adrenalectomy vs cortical-sparing adrenalectomy. JAMA Network Open 20192 e198898. ( 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8898) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Binderup ML, Bisgaard ML, Harbud V, Moller HU, Gimsing S, Friis-Hansen L, Hansen Tv, Bagi P, Knigge U, Kosteljanetz Met al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease (vHL) National Clinical Guideline for diagnosis and surveillance in Denmark, 3rd edition. Danish Medical Journal 201360 B4763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. & PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLOS Medicine 20096 e1000097. ( 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Grebe SK, Murad MH, Naruse M, Pacak K, Young Jr WF. & Endocrine Society. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2014991915–1942. ( 10.1210/jc.2014-1498) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hoy D Brooks P Woolf A Blyth F March L Bain C Baker P Smith E & Buchbinder R. Assessing risk of bias in prevalence studies: modification of an existing tool and evidence of interrater agreement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 201265934–939. ( 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.11.014) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ciotti P Garuti A Gulli R Ballestrero A Bellone E & Mandich P. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau gene in Italian patients. European Journal of Medical Genetics 200952311–314. ( 10.1016/j.ejmg.2009.05.007) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cybulski C, Krzystolik K, Murgia A, Gorski B, Debniak T, Jakubowska A, Martella M, Kurzawski G, Prost M, Kojder Iet al. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene in patients from Poland: disease presentation in patients with deletions of the entire VHL gene. Journal of Medical Genetics 200239 E38. ( 10.1136/jmg.39.7.e38) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dollfus H, Massin P, Taupin P, Nemeth C, Amara S, Giraud S, Beroud C, Dureau P, Gaudric A, Landais Pet al. Retinal hemangioblastoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease: a clinical and molecular study. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2002433067–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Erlic Z, Ploeckinger U, Cascon A, Hoffmann MM, von Duecker L, Winter A, Kammel G, Bacher J, Sullivan M, Isermann Bet al. Systematic comparison of sporadic and syndromic pancreatic islet cell tumors. Endocrine-Related Cancer 201017875–883. ( 10.1677/ERC-10-0037) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.O’Brien FJ, Danapal M, Jairam S, Lalani AK, Cunningham J, Morrin M, McNally S, Donovan MG, Little D, Tuthill Aet al. Manifestations of Von Hippel Lindau syndrome: a retrospective national review. QJM 2014107291–296.( 10.1093/qjmed/hct249) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Frantzen C, Kruizinga RC, van Asselt SJ, Zonnenberg BA, Lenders JW, de Herder WW, Walenkamp AM, Giles RH, Hes FJ, Sluiter WJet al. Pregnancy-related hemangioblastoma progression and complications in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neurology 201279793–796. ( 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182661f3c) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gergics P, Patocs A, Toth M, Igaz P, Szucs N, Liko I, Fazakas F, Szabo I, Kovacs B, Glaz Eet al. Germline VHL gene mutations in Hungarian families with von Hippel-Lindau disease and patients with apparently sporadic unilateral pheochromocytomas. European Journal of Endocrinology 2009161495–502. ( 10.1530/EJE-09-0399) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Graziani R Mautone S Vigo M Manfredi R Opocher G & Falconi M. Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in pancreatic and other abdominal manifestations of von Hippel-Lindau disease in a series of 23 patients: a pictorial review. JOP 2014151–18. ( 10.6092/1590-8577/1757) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Losonczy G Fazakas F Pfliegler G Komaromi I Balazs E Penzes K & Berta A. Three novel germ-line VHL mutations in Hungarian von Hippel-Lindau patients, including a nonsense mutation in a fifteen-year-old boy with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Medical Genetics 2013143. ( 10.1186/1471-2350-14-3) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maher ER Yates JR Harries R Benjamin C Harris R Moore AT & Ferguson-Smith MA. Clinical features and natural history of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1990771151–1163. ( 10.1093/qjmed/77.2.1151) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stanojevic BR Lohse P Neskovic GG Damjanovic SM Novkovic TB Jovanovic-Cupic SP & Dimitrijevic BB. Germline VHL gene mutations in three Serbian families with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neoplasma 200754402–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wittstrom E Nordling M & Andreasson S. Genotype-phenotype correlations, and retinal function and structure in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Ophthalmic Genetics 20143591–106. ( 10.3109/13816810.2014.886265) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Binderup MLM.. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: diagnosis and factors influencing disease outcome. Danish Medical Journal 201865B5461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Glushkova M Dimova P Yordanova I Todorov T Tourtourikov I Mitev V & Todorova A. Molecular-genetic diagnostics of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL) in Bulgaria: first complex mutation event in the VHL gene. International Journal of Neuroscience 2018128117–124. ( 10.1080/00207454.2017.1372436) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hes FJ, van der Luijt RB, Janssen ALW, Zewald RA, De Jong GJ, Lenders JW, Links TP, Luyten GPM, Sijmons RH, Eussen HJet al. Frequency of von Hippel-Lindau germline mutations in classic and non-classic von Hippel-Lindau disease identified by DNA sequencing, Southern blot analysis and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Clinical Genetics 200772122–129. ( 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00827.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ruiz-Llorente S, Bravo J, Cebrián A, Cascón A, Pollan M, Tellería D, Letón R, Urioste M, Rodríguez-López R, De Campos JMet al. Genetic characterization and structural analysis of VHL Spanish families to define genotype-phenotype correlations. Human Mutation 200423160–169. ( 10.1002/humu.10309) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ong KR Woodward ER Killick P Lim C Macdonald F & Maher ER. Genotype-phenotype correlations in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Human Mutation 200728143–149. ( 10.1002/humu.20385) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Prasad V Tiling N Denecke T Brenner W & Plöckinger U. Potential role of 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT in screening for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2016432014–2020. ( 10.1007/s00259-016-3421-6) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vanbinst AM, Brussaard C, Vergauwen E, Van Velthoven V, Kuijpers R, Michel O, Foulon I, Jansen AC, Lefevere B, Bohler Set al. A focused 35-minute whole body MRI screening protocol for patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice 20191722. ( 10.1186/s13053-019-0121-9) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wiklund L Nordling M Wahlström J Engwall Y & Martinsson T. Novel germline mutations in Swedish von Hippel-Lindau disease patients. International Journal of Oncology 199711509–512. ( 10.3892/ijo.11.3.509) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen J Geng W Zhao Y Zhao H Wang G Huang F Liu F & Geng X. Clinical and mutation analysis of four Chinese families with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Clinical and Translational Oncology 201315391–397. ( 10.1007/s12094-012-0940-x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hattori K Teranishi J Stolle C Yoshida M Kondo K Kishida T Kanno H Baba M Kubota Y & Yao M. Detection of germline deletions using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in Japanese patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Cancer Science 200697400–405. ( 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00193.x) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hwang S Ku CR Lee JI Hur KY Lee MS Lee CH Koo KY Lee JS & Rhee Y. Germline mutation of Glu70Lys is highly frequent in Korean patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. Journal of Human Genetics 201459488–493. ( 10.1038/jhg.2014.61) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Igarashi H Ito T Nishimori I Tamura K Yamasaki I Tanaka M & Shuin T. Pancreatic involvement in Japanese patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease: results of a nationwide survey. Journal of Gastroenterology 201449511–516. ( 10.1007/s00535-013-0794-1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kwon T Jeong IG Pak S You D Song C Hong JH Ahn H & Kim CS. Renal tumor size is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 20141401171–1177. ( 10.1007/s00432-014-1654-y) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Siu WK, Ma RCW, Lam CW, Mak CM, Yuen YP, Lo FMI, Chan KW, Lam SF, Ling SC, Tong SFet al. Molecular basis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome in Chinese patients. Chinese Medical Journal 2011124237–241.( 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2011.02.016) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sriphrapradang C Choopun K Tunteeratum A & Sura T. Genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with germline mutations of VHL, RET, SDHB, and SDHD genes: Thai experience. Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes 2017101179551417705122. ( 10.1177/1179551417705122) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huang JS Huang CJ Chen SK Chien CC Chen CW & Lin CM. Associations between VHL genotype and clinical phenotype in familial von Hippel-Lindau disease. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 200737492–500. ( 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2007.01806.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim WT Ham WS Park SJ Kim SW Lee Js Lee JS Ju HJ & Choi YD. Clinical characteristics of renal cell carcinoma in Korean patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Korean Journal of Urology 200849863–867. ( 10.4111/kju.2008.49.10.863) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lee JS, Lee JH, Lee KE, Kim JH, Hong JM, Ra EK, Seo SH, Lee SJ, Kim MJ, Park SSet al. Genotype-phenotype analysis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome in Korean families: HIF-alpha binding site missense mutations elevate age-specific risk for CNS hemangioblastoma. BMC Medical Genetics 20161748. ( 10.1186/s12881-016-0306-2) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liu QL, Yuan G, Tong DL, Liu GL, Yi YT, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang LA, Wang LF, Zhang DZet al. Novel genotype-phenotype correlations in five Chinese families with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Endocrine Connections 20187870–878. ( 10.1530/EC-18-0167) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang JY, Peng SH, Li T, Ning XH, Liu SJ, Hong BA, Liu JY, Wu PJ, Zhou BW, Zhou JCet al. Risk factors for survival in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Journal of Medical Genetics 201855322–328. ( 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104995) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang Y, Liang G, Tian J, Wang X, Chen A, Liang T, Du Y, Li H, Du J, Yu Let al. Pedigree analysis, diagnosis and treatment in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome: a report of three cases. Oncology Letters 2018154882–4890. ( 10.3892/ol.2018.7957) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang J Huang YR Pan JH Liu DM Zhou LX Xue W Chen Q Dong BJ & Xuan HQ. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene in mainland Chinese families. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 20081341211–1218. ( 10.1007/s00432-008-0399-x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Aufforth RD Ramakant P Sadowski SM Mehta A Trebska-McGowan K Nilubol N Pacak K & Kebebew E. Pheochromocytoma screening initiation and frequency in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 20151004498–4504. ( 10.1210/jc.2015-3045) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bradley S Dumas N Ludman M & Wood L. Hereditary renal cell carcnoma associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease: a description of a nova Scotia cohort. Journal of the Canadian Urological Association 2009332–36.( 10.5489/cuaj.1013) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chen F Kishida T Yao M Hustad T Glavac D Dean M Gnarra JR Orcutt ML Duh FM & Glenn G. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene: correlations with phenotype. Human Mutation 1995566–75. ( 10.1002/humu.1380050109) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Salama Y, Albanyan S, Szybowska M, Bullivant G, Gallinger B, Giles RH, Asa S, Badduke C, Chiorean A, Druker Het al. Comprehensive characterization of a Canadian cohort of von Hippel-Lindau disease patients. Clinical Genetics 201996461–467. ( 10.1111/cge.13613) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chacon-Camacho OF Rodriguez-Dennen F Camacho-Molina A Rasmussen A Alonso-Vilatela E & Zenteno JC. Clinical and molecular features of familial and sporadic cases of von Hippel-Lindau disease from Mexico. Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 201038277–283. ( 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2010.02241.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rasmussen A, Alonso E, Ochoa A, De Biase I, Familiar I, Yescas P, Sosa AL, Rodriguez Y, Chavez M, Lopez-Lopez Met al. Uptake of genetic testing and long-term tumor surveillance in von Hippel-Lindau disease. BMC Medical Genetics 2010114. ( 10.1186/1471-2350-11-4) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fagundes GFC, Petenuci J, Lourenco Jr DM, Trarbach EB, Pereira MAA, Correa D’Eur JE, Hoff AO, Lerario AM, Zerbini MCN, Siqueira Set al. New insights Into pheochromocytoma surveillance of young patients with VHL missense mutations. Journal of the Endocrine Society 201931682–1692. ( 10.1210/js.2019-00225) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gomy I Molfetta GA De Andrade Barreto E Ferreira CA Zanette DL Casali-Da-Rocha JC & Silva Jr WA. Clinical and molecular characterization of Brazilian families with von Hippel-Lindau disease: a need for delineating genotype-phenotype correlation. Familial Cancer 20109635–642. ( 10.1007/s10689-010-9357-2) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.K GH Gopal RA George J Bandgar T Menon P & Shah N. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: a case series of unusual familial cancer syndrome. Endocrinologist 201020134–136. ( 10.1097/TEN.0b013e3181dfdc98) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vikkath N, Valiyaveedan S, Nampoothiri S, Radhakrishnan N, Pillai GS, Nair V, Pooleri GK, Mathew G, Menon KN, Ariyannur PSet al. Genotype–phenotype analysis of von Hippel–Lindau syndrome in fifteen Indian families. Familial Cancer 201514585–594. ( 10.1007/s10689-015-9806-z) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Abbott MA Nathanson KL Nightingale S Maher ER & Greenstein RM. The von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) germline mutation V84L manifests as early-onset bilateral pheochromocytoma. American Journal of Medical Genetics, Part A 2006140685–690. ( 10.1002/ajmg.a.31116) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Allen RC Webster AR Sui R Brown J Taylor CM & Stone EM. Molecular characterization and ophthalmic investigation of a large family with type 2A von Hippel-Lindau disease. Archives of Ophthalmology 20011191659–1665. ( 10.1001/archopht.119.11.1659) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Atuk NO Stolle C Owen Jr JA Carpenter JT & Vance ML. Pheochromocytoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease: clinical presentation and mutation analysis in a large, multigenerational kindred. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 199883117–120. ( 10.1210/jcem.83.1.4479) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bender BU, Eng C, Olschewski M, Berger DP, Laubenberger J, Altehofer C, Kirste G, Orszagh M, van Velthoven V, Miosczka Het al. VHL c.505 T>C mutation confers a high age related penetrance but no increased overall mortality. Journal of Medical Genetics 200138508–514. ( 10.1136/jmg.38.8.508) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chen F Slife L Kishida T Mulvihill J Tisherman SE & Zbar B. Genotype-phenotype correlation in von Hippel-Lindau disease: identification of a mutation associated with VHL type 2A. Journal of Medical Genetics 199633716–717. ( 10.1136/jmg.33.8.716) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Crossey PA, Richards FM, Foster K, Green JS, Prowse A, Latif F, Lerman MI, Zbar B, Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA.et al. Identification of intragenic mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene and correlation with disease phenotype. Human Molecular Genetics 199431303–1308. ( 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1303) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Curley SA Lott ST Luca JW Frazier ML & Killary AM. Surgical decision-making affected by clinical and genetic screening of a novel kindred with von Hippel-Lindau disease and pancreatic islet cell tumors. Annals of Surgery 1998227229–235. ( 10.1097/00000658-199802000-00012) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Glavac D, Neumann HP, Wittke C, Jaenig H, Masek O, Streicher T, Pausch F, Engelhardt D, Plate KH, Hofler Het al. Mutations in the VHL tumor suppressor gene and associated lesions in families with von Hippel-Lindau disease from central Europe. Human Genetics 199698271–280. ( 10.1007/s004390050206) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jalbani IK Nazim SM & Abbas F. Pheochromocytoma associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease in a Pakistani family. Urology Annals 20157120–123. ( 10.4103/0974-7796.148660) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Karsdorp N Elderson A Wittebol-Post D Hene RJ Vos J Feldberg MA van Gils AP Jansen-Schillhorn van Veen JM Vroom TM & Hoppener JW. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: new strategies in early detection and treatment. American Journal of Medicine 199497158–168. ( 10.1016/0002-9343(9490026-4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Levine E Collins DL Horton WA & Schimke RN. CT screening of the abdomen in von Hippel-Lindau disease. American Journal of Roentgenology 1982139505–510. ( 10.2214/ajr.139.3.505) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nielsen SM Rubinstein WS Thull DL Armstrong MJ Feingold E Stang MT Gnarra JR & Carty SE. Genotype-phenotype correlations of pheochromocytoma in two large von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) type 2A kindreds with different missense mutations. American Journal of Medical Genetics, Part A 2011155A168–173. ( 10.1002/ajmg.a.33760) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Nielsen SM Rubinstein WS Thull DL Armstrong MJ Feingold E Yip L Tisherman SA & Carty SE. Long-term outcomes, branch-specific expressivity, and disease-related mortality in von Hippel-Lindau type 2A. Familial Cancer 201110701–707. ( 10.1007/s10689-011-9465-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Priesemann M Davies KM Perry LA Drake WM Chew SL Monson JP Savage MO & Johnston LB. Benefits of screening in von Hippel-Lindau disease – comparison of morbidity associated with initial tumours in affected parents and children. Hormone Research 2006661–5. ( 10.1159/000093008) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pulcrano M, Camera L, Pagano L, Del Vecchio S, Ferone D, Bodei L, Murgia A, Pace L, Storto G, Paganelli Get al. Usefulness of [111In-DTPA0] octreotide scintigraphy in a family with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation 200831352–359. ( 10.1007/BF03346370) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Qi XP, Liu WT, Li JY, Dai Y, Ma JM, Zhao Y, Fei J, Li F, Shen M, Jin HYet al. P.N78S and p.R161Q germline mutations of the VHL gene are present in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome in two pedigrees. Molecular Medicine Reports 20138799–805. ( 10.3892/mmr.2013.1578) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Tong AL Zeng ZP Zhou YR Yuan T Cao CX Zhang J & Li M. Bilateral pheochromocytoma as first presentation of von Hippel-Lindau disease in a Chinese family. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal 200924197–201. ( 10.1016/s1001-9294(1060001-6) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Weirich G Klein B Wohl T Engelhardt D & Brauch H. VHL2C phenotype in a German von Hippel-Lindau family with concurrent VHL germline mutations P81S and L188V. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2002875241–5246. ( 10.1210/jc.2002-020651) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Wu P Zhang N Wang X Ning X Li T Bu D & Gong K. Family history of von Hippel-Lindau disease was uncommon in Chinese patients: suggesting the higher frequency of de novo mutations in VHL gene in these patients. Journal of Human Genetics 201257238–243. ( 10.1038/jhg.2012.10) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yoshida M, Ashida S, Kondo K, Kobayashi K, Kanno H, Shinohara N, Shitara N, Kishida T, Kawakami S, Baba Met al. Germ-line mutation analysis in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease in Japan: an extended study of 77 families. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research 200091204–212. ( 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00933.x) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Huang YL Zhou D Liu JG Zhou P Li XD & Wang Z. Germline mutations of the VHL gene in seven Chinese families with von Hippel-Lindau disease. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 20122947–52. ( 10.3892/ijmm.2011.808) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Iida K Okimura Y Takahashi K Inomata S Iguchi G Kaji H & Chihara K. A variety of phenotype with R161Q germline mutation of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in Japanese kindred. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 200413401–404. ( 10.3892/ijmm.13.3.401) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Imanaka M, Iida K, Takahashi K, Tsuji K, Nishizawa H, Fukuoka H, Takeno R, Takahashi Y, Okimura Y, Kaji Het al. The N131S mutation in the von Hippel-Lindau gene in a Japanese family with pheochromocytoma and hemangioblastomas. Endocrine Journal 200653819–827. ( 10.1507/endocrj.k06-046) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Liu P, Zhu F, Li M, Dube DA, Liu Q, Wang C, Xiao Q, Zhang L, Gao S, Li Zet al. Von Hippel-Lindau ‘Black Forest’ mutation inherited in a large Chinese family. Gland Surgery 20198343–353. ( 10.21037/gs.2019.08.03) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.André T Bossard C Gattegno B Plouin PF Benoit G & Richard S. A type 2B von Hippel-Lindau family masquerading as a metastatic sporadic renal cell carcinoma. BJU International 200391425–426. ( 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04064.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hull MT Warfel KA Muller J & Higgins JT. Familial islet cell tumors in von Hippel‐Lindau’s disease. Cancer 1979441523–1526. () [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sexton A Rawlings L McKavanagh G Simons K & Winship I. A novel von Hippel Lindau gene intronic variant and its reclassification from VUS to pathogenic: the impact on a large family. Journal of Genetic Counseling 201524882–889. ( 10.1007/s10897-015-9875-z) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhang J Wu D Ai H Bai J Dong S Yang Q Qu K Zhou L Xu X & Liu C. Epidemiological study of a von Hippel-Lindau family in northwest China. Frontiers of Medicine 20137378–385. ( 10.1007/s11684-013-0276-0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhang B Qian J Chang DH Wang YM Zhou DH & Qiao GM. VHL gene mutation analysis of a Chinese family with non-syndromic pheochromocytomas and patients with apparently sporadic pheochromocytoma. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 2015161977–1980. ( 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.5.1977) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Arıcan P Tekin BO Naldöken S Şefizade R & Berker D. A family with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome: the findings of indium-111 somatostatin receptor scintigraphy, iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy and single photon emission computerized tomography. Molecular Imaging and Radionuclide Therapy 20172638–42. ( 10.4274/mirt.70894) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bleggi-Torres LF De Noranha L Fillus Neto J Telles JE & Madalozzo LE. Von Hippel-Lindau’s disease: report of three cases and review of the literature. Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria 199553782–788. ( 10.1590/s0004-282x1995000500012) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Cruz JB Fernandes LPS Clara SA Conde SJ Perone D Kopp P & Nogueira CR. Molecular analysis of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene in a family with non-syndromic pheochromocytoma: the importance of genetic testing. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia 2007511463–1467. ( 10.1590/s0004-27302007000900008) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Cuatrecasas G Oriola J Granada ML Florensa R & Salinas I. Genetic screening in a new family with the type IIB von Hippel-Lindau disease. Medicina Clinica 1999112546–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Palmar I Vircburger M Manojlovic D Radevic B Andjelkovic Z Buric B Savicevic M & Neskovic G. The von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with pheochromocytoma. Srpski Arhiv za Celokupno Lekarstvo 2002130 (Supplement 2) 43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Mete T Berker D Yilmaz E Ozgen G Yalcin Y Tuna M Ciliz D Onen M Aydin Y & Guler S. Clinical presentation of von Hippel Lindau syndrome type 2B associated with VHL p.A149S mutation in a large Turkish family. Endocrine 201445128–135. ( 10.1007/s12020-013-9982-2) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Buffet A, Calsina B, Flores S, Giraud S, Lenglet M, Romanet P, Deflorenne E, Aller J, Bourdeau I, Bressac-de Paillerets Bet al. Germline mutations in the new E1’ cryptic exon of the VHL gene in patients with tumours of von Hippel-Lindau disease spectrum or with paraganglioma. Journal of Medical Genetics 202057752–759. ( 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106519) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.



 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a