Abstract
Aim
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and the risk of CVD increases with reductions in renal function. This study aims to investigate the potential roles of B lymphocyte populations in subclinical atherosclerosis (measured by intima-media thickness, IMT) and prognosis in elderly patients with moderate-to-severe CKD.
Methods
In this study, a total of 219 patients (143 moderate-to-severe CKD patients with stage 3–4 and 76 non-CKD controls) were recruited. B cell subsets: CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Intima-media thickness (IMT) was measured by ultrasound. Correlations between the B cell subsets with IMT and clinical outcome was analyzed.
Results
CKD patients showed increased IMT (P = 0.006). The level of CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were decreased in CKD patients. Correlation analysis showed that IMT was positively correlated with systolic blood pressure, protein/creatinine ratio and diabetes (P < 0.05), and were negatively correlated with CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes (P < 0.05). Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells had a significant independent association with IMT (P < 0.05). IMT was increased in lower level of total CD19(+) B cells (≤ 0.06 × 109 /L) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells (≤ 0.05 × 109 /L) (P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that patients with lower levels of CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells exhibited worse survival (P < 0.05). Cox regression analysis showed that patients with lower CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells counts have a higher risk of all-cause mortality (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our results showed that decreased CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes were correlated with atherosclerosis and worse survival, which indicates that B lymphocytes might involve in atherosclerosis and associated the prognosis of elderly patients with moderate-to-severe CKD.
Keywords: B cells, Atherosclerosis, Intima-media thickness, Elderly, Chronic kidney disease
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and the risk of CVD increases with reductions in renal function [1]. It is well known that CKD on hemodialysis is closely associated with accelerated atherosclerosis. However, recent studies have shown that increased atherosclerosis risk was actually observed in the early stages of CKD and remains stable thereafter [2]. Atherosclerosis is intimately interconnected with the immune system and recently, the influence of immune abnormalities on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and the possible discovery of new treatment methods have been increasingly studied [3]. Several studies have indicated that T cells promote atherosclerosis, whereas B cells may have a protective role [4, 5].
B cells can broadly be divided into 2 subsets: CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells [5]. CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells are largely fetal liver derived and considered to be elements of the innate immune system. They patrol mucosal surfaces, provide immediate defense and antigen capture, as well as modulate and systematically transport invading bacteria. CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells may have a protective effect on atherosclerosis that is largely mediated by the production of IgM antibodies. And these antibodies constitute a readily available pool of immunoglobulins for use against a variety of infections before specific high-affinity antibodies are produced [6]. CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells are bone marrow derived and differentiate into plasma cells and produce high affinity, class-switched antibodies in a T cell dependent manner that are responsible for developing an adaptive response [7].
Studies have suggested B cells may play the protective effect on atherosclerosis. Clinical studies have also reported a negative association between (IgM-producing) memory B cells and risk of CVD [8, 9]. In addition, distinct knockout mouse models targeting B cell subsets differentially have revealed the antiatherogenic potentials of CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells [10–12]. Our previous data and some other results showed that CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells exhibited a significantly negative correlation with the progression of CKD in elderly patients and patients with decreased B cell counts had a higher risk of CVD mortality [13, 14]. However, the roles of B cell subpopulations in atherosclerosis of elderly patients with CKD are unclear.
Ultrasonic measurement of the thickness of the carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) is a noninvasive and reliable tool to assess asymptomatic atherosclerosis and increased IMT is an independent predictor of future cardiovascular risk [15]. IMT is increased in CKD patients and may help to predict patients at higher risk of future CVD [16]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the potential roles of peripheral blood B lymphocyte populations in subclinical atherosclerosis (measured by IMT) and prognosis in elderly patients with moderate-to-severe CKD.
Materials and methods
Patients
A total of 143 patients with moderate-to-severe CKD (stage 3–4) aged ≥65 years were retrospectively studied in Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital from January 2010 to December 2018. CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for > 3 months. The criteria for CKD are as follows: (1) decreased GFR (for > 3 months): GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2, and/ or (2) markers of kidney damage (> 1 for > 3 months): albuminuria, electrolyte, urinary sediment abnormalities, and other abnormalities due to abnormalities detected by histology, tubular disorders, structural abnormalities detected by imaging, history of kidney transplantation. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using CKD-EPI equation, and the definition of stage 3 was eGFR from 30 to 59 ml/min/1.73 m2, stage 4 was eGFR from 15 to 29 ml/min/1.73m2. Patients with acute kidney injury, malignancy, active infection, thyroid malfunction, heart failure or on immunosuppressive drugs were excluded.
The control group (76 patients) without CKD included patients hospitalized for hypertension, prostatic hyperplasia and osteoporosis. For all patients, we recorded clinical data, including age and sex, serum creatinine (SCr), protein/creatinine ratio, serum albumin (ALB), cholesterol, triglyceride, white blood cell (WBC), lymphocytes and neutrophil levels; and comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension. SCr was measured by the enzymatic method. The study involving human participants was approved by the Ethical Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital.
Clinical outcome
Outcome of this study was all-cause mortality. All patients were followed until the date of their last visit, and the median follow-up duration was 41.5 months.
Estimation of intima–media thickness (IMT)
The IMT was measured bilaterally at the far wall over the distal 1.5-cm segment of the common carotid artery by using a high-resolution 4- to 13-MHz linear-array transducer system. For each subject, the mean IMT was computed as the average IMT on both sides.
Flow Cytometry analysis (FCM)
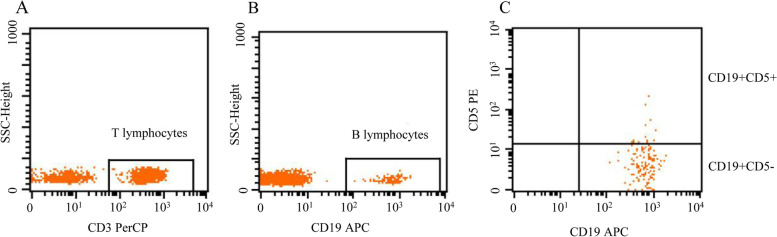
Peripheral blood lymphocyte populations (CD3(+) T lymphocytes, total CD19(+) B lymphocytes, CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes, and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Blood samples obtained by venipuncture were collected in EDTA anticoagulant. 10 μl of anti-human CD3-PerCP, CD19-APC, and CD5-PE antibodies were added to 100 μl of whole blood and incubated for 20 min at 4 °C in the dark. A total of 2 ml of red blood cell lysis buffer was added before staining to each tube, vortexed well, and incubated for 10 min at room temperature in darkness. Then, the cells were washed twice with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), and then discarded the supernatant. Last, 20,000 cells were acquired by using FACS (BD USA) and were analyzed using Cellquest-Pro analysis software to determine the subpopulation counts (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Flow cytometric analysis of lymphocytes, including T lymphocytes (CD3+) and B lymphocytes (CD19+). B cells were divided into CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 20.0 (Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous variables were analyzed by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The correlations between IMT and clinical data were performed using the Spearman’s test. Stepwise multiple regression analysis was performed to evaluate the independent predictor of IMT. The X-tile software version 3.6.1 (Yale University, New Haven, USA) was used to determine the optimal cutoff points of IMT and different B cells based on the outcome [17]. And the outcome of this study was all-cause mortality. The optimal cutoff points of IMT, total CD19(+), CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were 1.0 cm, 0.06 × 109 /L, 0.03 × 109 /L and 0.05 × 109/L, respectively.
The Kaplan–Meier survival analysis method with the log-rank test was used to compare survival times and Cox regression analysis was used for univariate and multivariate analyses. All p values were calculated two-sided and a value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Patient and demographic details
The clinical and demographic data of the study subjects are shown in Table 1. There were 219 patients entered in the final analysis: 76 control subjects and 143 patients with CKD stage 3–4. The majority of patients were males. 86.01% of the CKD patients had hypertension and 42.66% were with diabetic.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters of older patients with or without CKD
| Control subjects | CKD patients | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 76 | 143 | |
| Age, years | 80.32 ± 4.34 | 82.70 ± 4.89 | < 0.001* |
| Gender (M/F) | 60/16 | 115/28 | < 0.001* |
| Hypertension | 60.53% | 86.01% | < 0.001* |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 134.37 ± 16.78 | 143.66 ± 16.62 | < 0.001* |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 71.17 ± 9.09 | 74.66 ± 10.22 | 0.005* |
| Diabetes | 23.68% | 42.66% | 0.005* |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 77.64 ± 11.47 | 145.55 ± 50.42 | < 0.001* |
| eGFR CKD − EPI (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 78.32 ± 10.65 | 40.98 ± 13.49 | < 0.001* |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35.00 ± 33.72 | 33.72 ± 4.97 | 0.075 |
| protein/creatinine ratio (mg/g Cr) | 115.17 ± 98.40 | 776.87 ± 1587.69 | < 0.001* |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.19 ± 0.90 | 4.43 ± 1.29 | 0.401 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.12 ± 0.60 | 1.36 ± 0.89 | 0.040* |
| IMT (cm) | 0.94 ± 0.16 | 1.01 ± 0.17 | 0.006* |
| WBC (109 /L) | 6.17 ± 1.95 | 6.43 ± 1.92 | 0.247 |
| Neutrophil (109 /L) | 3.75 ± 1.51 | 4.20 ± 1.59 | 0.027* |
| T lymphocytes (109 /L) | 1.09 ± 0.44 | 0.33 ± 0.21 | 0.175 |
| Total CD19(+) B lymphocytes (109 /L) | 0.22 ± 0.36 | 0.15 ± 0.11 | 0.059 |
| CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes (109 /L) | 0.10 ± 0.33 | 0.05 ± 0.07 | 0.040* |
| CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes (109 /L) | 0.12 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.06 | 0.088 |
| Number of deaths | 9 | 46 | 0.001* |
| Follow up time | 50.37 ± 31.59 | 38.46 ± 29.56 | 0.009* |
eGFR Estimated glomerular filtration rate, SCr Serum creatinine, IMT Intima–media thickness, WBC White blood cell
Intima–media thickness and B cell subpopulations
The common carotid artery IMT was 1.01 ± 0.17 cm in CKD patients and 0.94 ± 0.16 cm in the control group (P = 0.006). Comparison of B cells in the two groups revealed remarkable differences, and the number of B lymphocyte subpopulation was decreased in CKD patients. The levels of total CD19(+), CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes in CKD patients were significantly lower than those in the control group (Table 1).
The correlation between IMT and clinical data
Spearman’s analysis showed that IMT was positively correlated with systolic blood pressure (R = 0.282, P = 0.001), protein/creatinine ratio (R = 0.253, P = 0.016) and diabetes (R = 0.267, P = 0.001). We further analyzed the association of IMT and B cells. Our data revealed that IMT was negatively correlated with total CD19(+) B lymphocytes (R = -0.209, P = 0.012), CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes (R = -0.195, P = 0.020) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes (R = -0.208, P = 0.013). In contrast, in the control group, only diabetes (R = 0.243, P = 0.034) exhibited positive correlation with IMT (Table 2). In stepwise multiple regression analysis, CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells was found to have a significant independent association with IMT (Standardized beta:-0.226, P = 0.033) (Table 3).
Table 2.
Correlation between IMT with the clinical data of older patients with or without CKD
| Variable | IMT (Control) | IMT (CKD) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | R = -0.071 | R = 0.147 |
| P = 0.545 | P = 0.080 | |
| Systolic blood pressure | R = 0.063 | R = 0.282 |
| P = 0.589 | P = 0.001* | |
| Diastolic blood pressure | R = -0.102 | R = -0.022 |
| P = 0.381 | P = 0.792 | |
| Diabetes | R = 0.243 | R = 0.267 |
| P = 0.034* | P = 0.001* | |
| SCr | R = 0.013 | R = 0.036 |
| P = 0.914 | P = 0.671 | |
| Protein/creatinine ratio | R = 0.087 | R = 0.253 |
| P = 0.593 | P = 0.016* | |
| Cholesterol | R = -0.067 | R = -0.062 |
| P = 0.565 | P = 0.460 | |
| Triglyceride | R = -0.032 | R = -0.020 |
| P = 0.783 | P = 0.815 | |
| WBC | R = 0.182 | R = 0.068 |
| P = 0.115 | P = 0.421 | |
| Neutrophil | R = 0.204 | R = 0.054 |
| P = 0.077 | P = 0.524 | |
| Total CD19(+) B lymphocytes | R = -0.087 | R = -0.209 |
| P = 0.453 | P = 0.012* | |
| CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes | R = -0.039 | R = -0.195 |
| P = 0.740 | P = 0.020* | |
| CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes | R = -0.057 | R = -0.208 |
| P = 0.628 | P = 0.013* |
IMT Intima–media thickness, CKD Chronic kidney disease, SCr Serum creatinine, WBC White blood cell
Table 3.
Stepwise multiple regression analysis showing the independent association of CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells with IMT
| Unstandardized B (SE) | Standardized beta | P value | 95% confidence interval for B | Tolerance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells (109 /L) | −0.588 (0.271) | −0.226 | 0.033 | −1.126, −0.050 | 1.000 |
Systolic blood pressure, diabetes, protein/creatinine ratio, CD19(+) B cells and CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells were also included, but they were not significantly associated with IMT. IMT, intima–media thickness
Comparison of IMT between low and high level of different B cells in the total cohort and CKD group
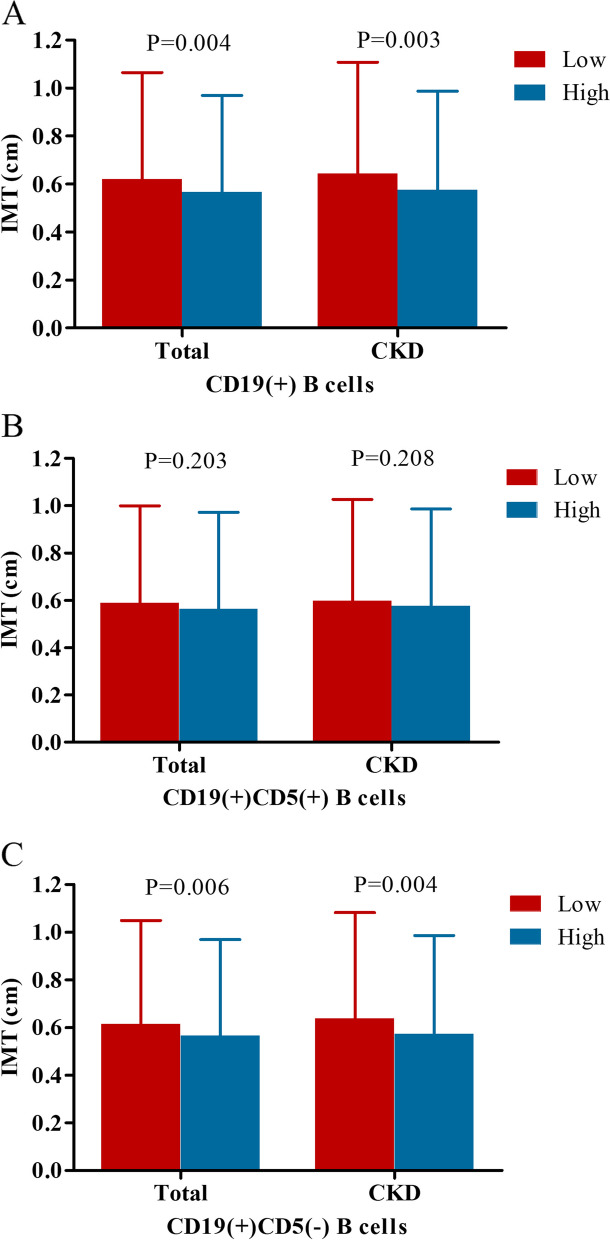
We used X-tile software to determine the optimal cutoff points of total CD19(+), CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells based on the outcome. And the cutoff points for the grouping of total CD19(+), CD19(+)CD5(+), and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were 0.06 × 109 /L, 0.03 × 109 /L and 0.05 × 109 /L, respectively. As shown in Fig. 2, IMT was increased in the lower level of total CD19(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells. IMT was increased in total CD19(+) B cells ≤0.06 × 109 /L in the total cohort (1.06 ± 0.18 vs. 0.97 ± 0.16, P = 0.004) and CKD group (1.11 ± 0.18 vs. 0.99 ± 0.16, P = 0.003). Similarly, IMT was also increased in CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells ≤0.05 × 109 /L in the total cohort (1.05 ± 0.18 vs. 0.97 ± 0.16, P = 0.006) and CKD group (1.08 ± 0.19 vs. 0.99 ± 0.16, P = 0.004). Though IMT was increased in CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells ≤0.03 × 109 /L, the difference was not significant (P > 0.05).
Fig. 2.
Comparison of intima-media thickness (IMT) between low and high level of different B cells in the total cohort and CKD group. A Total CD19(+) B cells: low: ≤0.06 × 109 /L and high: > 0.06 × 109 /L; B CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells: low: ≤0.03 × 109 /L and high: > 0.03 × 109 /L; (C) CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells: low: ≤0.05 × 109 /L and high: > 0.05 × 109 /L.
Association of IMT and different B cells with overall survival
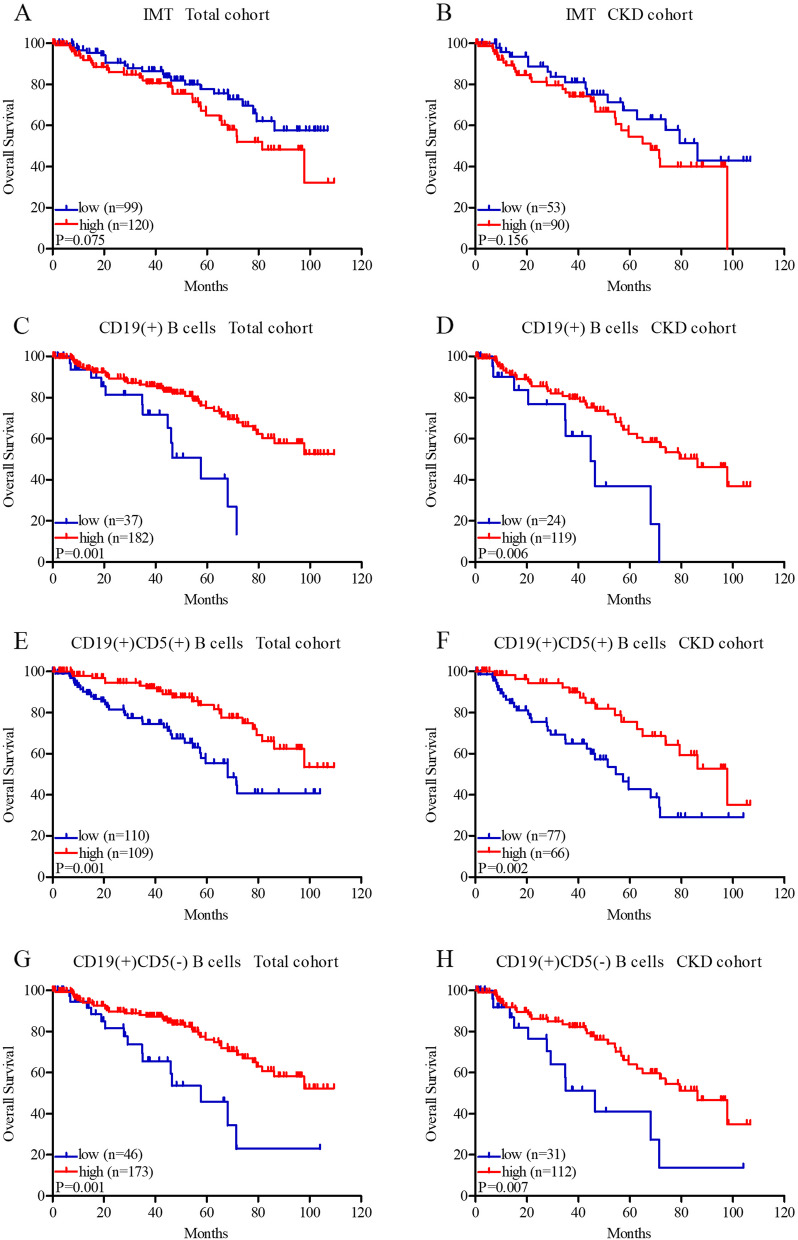
As mentioned above, patients were divided into two groups according to the optimal cutoff points, and the cutoff point of IMT was 1.0 cm. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that patients with IMT ≤1.0 cm present longer survival in the total cohort (83.92 ± 4.03 vs. 73.99 ± 4.48 months, P = 0.075, Fig. 3A) and CKD group (75.64 ± 5.83 vs. 63.35 ± 4.60, P = 0.156 months, Fig. 3B), but the difference was not statistically significant. Patients with total CD19(+) B cells > 0.06 × 109 /L showed prolonged survival in the total cohort (50.07 ± 4.53 vs. 83.51 ± 3.23 months, P = 0.001, Fig. 3C) and CKD group (45.35 ± 6.27 vs. 73.29 ± 4.12, P = 0.006 months, Fig. 3D). The group with CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells > 0.03 × 109 /L also had better survival in the total cohort (67.27 ± 4.55 vs. 89.11 ± 3.65 months, P = 0.001, Fig. 3E) and CKD group (57.83 ± 5.35 vs. 81.43 ± 4.80 months, P = 0.002, Fig. 3F). The results of CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were similar, higher levels of CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells (> 0.05 × 109 /L) exhibited better survival in the total cohort (57.57 ± 7.16 vs. 83.86 ± 3.26 months, P = 0.001, Fig. 3G) and CKD group (49.18 ± 7.98 vs. 73.73 ± 4.16 months, P = 0.007, Fig. 3H).
Fig. 3.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves of intima-media thickness (IMT), total CD19(+) B cells, CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells, and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells in the total cohort (A, C, E, G) and CKD group (B, D, F, H). IMT, total CD19(+) B cells, CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells, and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were divided into two groups (low and high) according to the optimal cutoff points, IMT: low: ≤1.0 cm and high: > 1.0 cm; total CD19(+) B cells: low: ≤0.06 × 109 /L and high: > 0.06 × 109 /L; CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells: low: ≤0.03 × 109 /L and high: > 0.03 × 109 /L; CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells: low: ≤0.05 × 109 /L and high: > 0.05 × 109 /L.
Analysis of prognostic factors
In the total cohort, univariate analysis showed that age, hypertension, systolic pressure, diabetes, SCr, CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were prognostic factors for overall survival in the total cohort, multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that age (HR = 1.100, 95%CI: 1.030–1.174, P = 0.004), systolic pressure (HR = 1.026, 95%CI: 1.007–1.046, P = 0.008), SCr (HR = 1.009, 95%CI: 1.005–1.014, P < 0.001) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells≤0.05 × 109 /L (HR = 2.821, 95%CI: 1.482–5.370, P = 0.002) were factors significantly associated with a higher risk of all-cause mortality (Table 4).
Table 4.
Univariate and multivariate analyses for all-cause mortality in the total cohort
| Variables | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Age (year) | 1.128 (1.056–1.205) | < 0.001 | 1.100 (1.030–1.174) | 0.004 |
| Female Sex | 0.951 (0.447–2.026) | 0.897 | ||
| Hypertension | 2.557 (1.091–5.991) | 0.031 | ||
| Systolic pressure (mmHg) | 1.031 (1.014–1.048) | < 0.001 | 1.026 (1.007–1.046) | 0.008 |
| Diastolic pressure (mmHg) | 1.023 (0.993–1.053) | 0.135 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.898 (1.108–3.252) | 0.020 | ||
| SCr (μmol/L) | 1.008 (1.005–1.012) | < 0.001 | 1.009 (1.005–1.014) | < 0.001 |
| Protein/creatinine ratio (mg/g Cr) | 1 | 0.161 | ||
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.132 (0.864–1.482) | 0.368 | ||
| IMT (cm) | 1.881 (0.375–9.433) | 0.442 | ||
| Neutrophil (109 /L) | 1.056 (0.918–1.215) | 0.443 | ||
| CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes (109/L) | ||||
| ≤ 0.03 | 2.472 (1.425–4.289) | 0.001 | ||
| > 0.03 | ||||
| CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes (109/L) | ||||
| ≤ 0.05 | 2.665 (1.451–4.895) | 0.002 | 2.821 (1.482–5.370) | 0.002 |
| > 0.05 | ||||
Notes: IMT Intima–media thickness, SCr Serum creatinine
In the CKD patients, univariate analysis showed that age, systolic pressure, SCr, CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells were prognostic factors for overall survival, multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that age (HR = 1.088, 95%CI: 1.015–1.166, P = 0.017), SCr (HR = 1.006, 95%CI: 1.001–1.011, P = 0.018) and CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells≤0.03 × 109 /L (HR = 2.303, 95%CI: 1.241–4.273, P = 0.008) were factors significantly associated with a higher risk of all-cause mortality (Table 5).
Table 5.
Univariate and multivariate analyses for all-cause mortality in the CKD patients
| Variables | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Age (year) | 1.080 (1.012–1.153) | 0.020 | 1.088 (1.015–1.166) | 0.017 |
| Female Sex | 0.886 (0.373–2.107) | 0.784 | ||
| Hypertension | 1.508 (0.537–4.240) | 0.436 | ||
| Systolic pressure (mmHg) | 1.020 (1.001–1.040) | 0.044 | ||
| Diastolic pressure (mmHg) | 1.005 (0.974–1.036) | 0.764 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.689 (0.928–3.074) | 0.086 | ||
| SCr (μmol/L) | 1.005 (1.000–1.010) | 0.035 | 1.006 (1.001–1.011) | 0.018 |
| Protein/creatinine ratio (mg/g Cr) | 1 | 0.556 | ||
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.000 (0.751–1.332) | 0.998 | ||
| IMT (cm) | 1.462 (0.284–7.516) | 0.649 | ||
| Neutrophil (109 /L) | 0.985 (0.833–1.164) | 0.985 | ||
| CD19(+)CD5(+) B lymphocytes (109 /L) | ||||
| ≤0.03 | 2.542 (1.376–4.699) | 0.003 | 2.303 (1.241–4.273) | 0.008 |
| > 0.03 | ||||
| CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes (109 /L) | ||||
| ≤0.05 | 2.457 (1.257–4.805) | 0.009 | ||
| > 0.05 | ||||
Notes: CKD Chronic kidney disease, IMT Intima–media thickness, SCr Serum creatinine
Discussion
In CKD subjects, cardiovascular disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, account for 40% of deaths among patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [18]. CKD accelerates atherosclerosis via augmentation of inflammation, perturbation of lipid metabolism, and other mechanisms [4]. It has been well established that the innate and adaptive immunity contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, and B cells have emerged as important modulators of inflammatory effects in atherosclerosis [5]. B lymphocytes are generated from hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Murine B cells are broadly divided into CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) subsets, CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells secrete IgM and IgA while CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells produce IgG [6]. Previous studies have shown that B lymphocytes have a protective effect on atherosclerosis [10–12]. However, few studies have analyzed the relationship between B cell subsets and atherosclerosis of moderate-to-severe CKD patients in the elderly.
In this study, we found that IMT was positively correlated with systolic blood pressure, protein/creatinine ratio and diabetes. Hypertension is a major risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis. In hypertension, changes in microcirculation can cause endothelial dysfunction, then promotes the formation of atherosclerotic plaque [19]. Atherosclerosis is the most important cause of morbidity and mortality in CKD. And Sumida et al. [20] showed that carotid artery calcification was significantly associated with proteinuria in ESRD patients. Diabetic macroangiopathy, atherosclerosis secondary to diabetes, is characterized by the alterations in vascular homeostasis due to endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction [21].
In addition, our results showed that CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes were negatively correlated IMT. B cells are divided into CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) subsets. CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells have been reported to protect from atherosclerosis by the production of IgM antibodies. IgM antibodies have the capacity to recognize apoptotic cells and Oxidized LDL (OxLDL) and limit foam cell formation and OxLDL-induced endothelial activation [5]. Gruber et al. [12] studied the Siglec-G-deficient mice and found that CD5(+) B cells derived natural IgM had an effect on decreasing levels of OxLDL and oxidation-specific epitopes, so could reduce atherosclerosis. In addition, previous studies have also showed that CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells were significant source of interleukin 10 (IL10), which also exert atheroprotection [22]. Our results showed that the levels of CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells was significantly decreased in moderate-to-severe CKD patients and IMT was increased in the lower levels of CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells, that could explain why patients with CKD exhibit accelerated development of atherosclerosis.
Moreover, our data also showed that CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes were negatively correlated IMT and IMT was significantly increased in the lower levels of CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells. Moreover, stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells had a significant independent association with IMT. Genomic data showed that the survival of CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells was mainly dependent on the B cell-activating factor (BAFF) receptor pathway [23]. Tsiantoulas et al. [24] studied Apoe−/− and Ldlr−/− mice and found that anti-BAFF antibody treatment could deplete CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells and increased atherosclerosis. In CKD patients, the uremic environment may promote resistance to BAAF-mediated signals and interfere the maturation of transitional B cells to mature B cells [25]. Therefore, decreased CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells might be associated with the uremic environment and was correlated with atherosclerosis.
Furthermore, our study showed that IMT was increased in lower levels of CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells, and moderate-to-severe CKD patients with lower levels of CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells exhibited worse survival. Cox regression analysis showed that patients with lower CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B cells counts have a higher risk of all-cause mortality. Progressive loss of renal function is associated with immune deficiency, and account for the large proportion of morbidity and mortality [26]. Molina et al. [13] showed that patients with lower levels of B cells had a higher risk of CVD and all-cause mortality. These data indicated that higher levels of B cells may play a protective role in CKD and had a potential effect of inhibiting atherosclerosis.
However, our study also had certain limitations. Firstly, this was a retrospective study. Secondly, we did not explore the mechanisms of different B lymphocytes in atherosclerosis. Further studies should be carried out to explore these results.
In conclusion, our results showed that decreased CD19(+)CD5(+) and CD19(+)CD5(−) B lymphocytes were correlated with atherosclerosis and worse clinical outcome, which indicated that B lymphocytes may be involved in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and associated with prognosis in moderate-to-severe CKD.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Statement
All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Abbreviations
- CVD
Cardiovascular diseases
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- IMT
Intima-media thickness
- eGFR
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- SCr
Serum creatinine
- ALB
Serum albumin
- WBC
White blood cell
- PBS
Phosphate buffer saline
- ESRD
End-stage renal disease
- OxLDL
Oxidized LDL
- IL10
Interleukin 10
- BAFF
B cell-activating factor
Authors’ contributions
Jieshan Lin was involved in study design, interpreting data, statistical analysis, creating tables and figures, and writing of the manuscript. Bin Tang and Wenke Hao were involved in data interpretation and statistical analysis. Zhanwu Feng took part in ultrasound analysis. Wenxue Hu designed the research and supervised the work. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF. Chronic kidney disease: effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2007;116(1):85–97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.678342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Valdivielso JM, Rodríguez-Puyol D, Pascual J, Barrios C, Bermúdez-López M, Sánchez-Niño MD, Pérez-Fernández M, Ortiz A. Atherosclerosis in chronic kidney disease: more, less, or just different? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(10):1938–1966. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Frostegård J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 2013;11:117. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gisterå A, Hansson GK. The immunology of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(6):368–380. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Upadhye A, Sturek JM, McNamara CA. 2019 Russell Ross memorial lecture in vascular biology: B lymphocyte-mediated protective immunity in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40(2):309–322. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Choi YS, Dieter JA, Rothaeusler K, Luo Z, Baumgarth N. B-1 cells in the bone marrow are a significant source of natural IgM. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(1):120–129. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gil-Borras R, García-Ballesteros C, Benet-Campos C, Catalán-Serra I, López-Chuliá F, Cuéllar C, Andreu-Ballester JC. B1a lymphocytes (CD19+CD5+) deficiency in patients with Crohn's disease and its relation with disease severity. Dig Dis. 2018;36(3):194–201. doi: 10.1159/000486893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mantani PT, Ljungcrantz I, Andersson L, Alm R, Hedblad B, Björkbacka H, Nilsson J, Fredrikson GN. Circulating CD40+ and CD86+ B cell subsets demonstrate opposing associations with risk of stroke. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(1):211–218. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Meeuwsen JAL, van Duijvenvoorde A, Gohar A, Kozma MO, van de Weg SM, Gijsberts CM, et al. High levels of (un) switched memory B cells are associated with better outcome in patients with advanced atherosclerotic disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(9):e005747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Kyaw T, Tay C, Krishnamurthi S, Kanellakis P, Agrotis A, Tipping P, Bobik A, Toh BH. B1a B lymphocytes are atheroprotective by secreting natural IgM that increases IgM deposits and reduces necrotic cores in atherosclerotic lesions. Circ Res. 2011;109(8):830–840. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.248542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Doran AC, Lipinski MJ, Oldham SN, Garmey JC, Campbell KA, Skaflen MD, et al. B-cell aortic homing and atheroprotection depend on Id3. Circ Res. 2012;110(1):e1–12. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.256438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gruber S, Hendrikx T, Tsiantoulas D, Ozsvar-Kozma M, Göderle L, Mallat Z, et al. Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like Lectin G promotes atherosclerosis and liver inflammation by suppressing the protective functions of B-1 cells. Cell Rep. 2016;14(10):2348–2361. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Molina M, Allende LM, Ramos LE, Gutiérrez E, Pleguezuelo DE, Hernández ER, et al. CD19(+) B-cells, a new biomarker of mortality in hemodialysis patients. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1221. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lin J, Tang W, Liu W, Yu F, Wu Y, Fang X, Zhou M, Hao W, Hu W. Decreased B1 and B2 lymphocytes are associated with mortality in elderly patients with chronic kidney diseases. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gepner AD, Wyman RA, Korcarz CE, Aeschlimann SE, Stein JH. An abbreviated carotid intima-media thickness scanning protocol to facilitate clinical screening for subclinical atherosclerosis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20(11):1269–1275. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2007.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hinderliter A, Padilla RL, Gillespie BW, Levin NW, Kotanko P, Kiser M, Finkelstein F, Rajagopalan S, Saran R. Association of carotid intima-media thickness with cardiovascular risk factors and patient outcomes in advanced chronic kidney disease: the RRI-CKD study. Clin Nephrol. 2015;84(1):10–20. doi: 10.5414/CN108494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(21):7252–7259. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hakeem A, Bhatti S, Chang SM. Screening and risk stratification of coronary artery disease in end-stage renal disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7(7):715–728. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Petrie JR, Guzik TJ, Touyz RM. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: clinical insights and vascular mechanisms. Can J Cardiol. 2018;34(5):575–584. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sumida Y, Nakayama M, Nagata M, Nakashita S, Suehiro T, Kaizu Y, Ikeda H, Izumaru K. Carotid artery calcification and atherosclerosis at the initiation of hemodialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Nephrol. 2010;73(5):360–369. doi: 10.5414/CNP73360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katakami N. Mechanism of development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018;25(1):27–39. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lu H, Daugherty A. Regulatory B cells, interleukin-10, and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2015;26(5):470–471. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sage AP, Tsiantoulas D, Baker L, Harrison J, Masters L, Murphy D, Loinard C, Binder CJ, Mallat Z. BAFF receptor deficiency reduces the development of atherosclerosis in mice--brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(7):1573–1576. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.244731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tsiantoulas D, Sage AP, Göderle L, Ozsvar-Kozma M, Murphy D, Porsch F, et al. B cell-activating factor neutralization aggravates atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2018;138(20):2263–2273. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vaziri ND, Pahl MV, Crum A, Norris K. Effect of uremia on structure and function of immune system. J Ren Nutr. 2012;22(1):149–156. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2011.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim KW, Chung BH, Jeon EJ, Kim BM, Choi BS, Park CW, et al. B cell-associated immune profiles in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) Exp Mol Med. 2012;44(8):465–472. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.8.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.