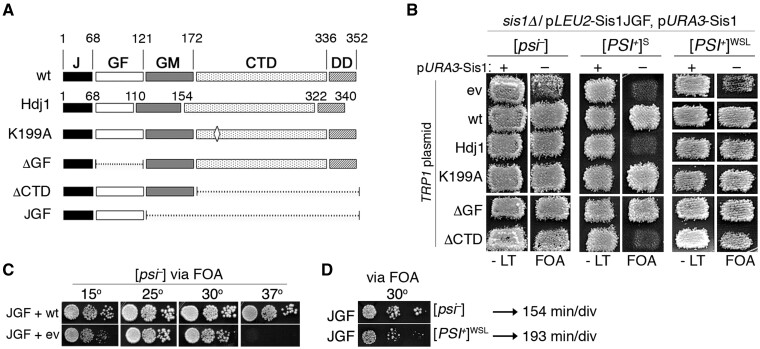
Figure 1.
Sis1JGF supports propagation of weak [PSI+]. (A) Domain structures of Sis1, Hjd1, and mutant versions of Sis1. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. The CTD (amino acids 172–336 of Sis1) is the substrate-binding domain and the J-domain (amino acids 1–68) binds and regulates Hsp70. (B) Plasmid shuffle to assess the ability of proteins to support growth and prions in place of Sis1. Strain 970L (relevant genotype at top) lacks chromosomal SIS1, expresses Sis1JGF from a LEU2 plasmid (pJE237), and wild-type Sis1 from a URA3 plasmid (pYW17). It lacks prions ([psi–]) or propagates [PSI+]S (strong) or [PSI+]WSL (weak) as indicated. Cells were transformed by a TRP1 vector encoding the versions of Sis1 or Hdj1 (pAK50) as indicated on the left (ev is empty TRP1 vector). Transformants were grown on medium lacking only leucine and tryptophan (-LT) and replica-plated to similar medium containing FOA, which kills cells that have not lost the URA3 plasmid encoding wild-type Sis1. FOA plates, which contain adenine to allow the growth of cells without prions, were incubated 2 days at 30°. All cells growing on FOA express Sis1JGF and the proteins indicated on left; those with empty TRP1 vector express only Sis1JGF. Patches are pools of 3–4 individual transformants (see text and Supplementary Figure S1). (C) Cells of [psi–] strain 970L expressing Sis1 from a TRP1 plasmid (wt, express both Sis1 and JGF) or with empty TRP1 vector (ev, express only JGF) were recovered from FOA plate in (B), grown in YPAD and dilutions were inoculated onto YPAD plates and incubated at the indicated temperatures for 3–4 days. (D) FOA-resistant [psi–] and [PSI+]WSL cells expressing Sis1JGF in place of Sis1 were recovered from FOA and grown similarly. Generation times of these two strains are 154 and 193 min/div as indicated.