ABSTRACT
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major public health concern, as drug-resistant strains increase mortality in hospital-acquired infections. We report the isolation and complete genome sequences of four lytic bacteriophages that target clinical multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa strains.
ANNOUNCEMENT
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an important nosocomial opportunistic pathogen that is able to live in a wide range of environments (1). The motile rod-shaped bacterium can cause lethal infections, such as sepsis in immunocompromised hosts and hospitalized patients (e.g., burn wounds), and infects a wide range of organs, including the lungs, urinary tract, and kidneys. Some strains of P. aeruginosa exhibit extensive drug resistance to available antibiotics, and the species has hence been listed as a priority 1 pathogen by the WHO (2, 3). Therefore, novel antibiotics or clinical therapeutic options are needed. One strategy is the use of therapeutic bacteriophages (4, 5). Here, we report the complete genome sequences of four lytic bacteriophages (Kaya, Guyu, Kopi, and TehO) that have been isolated using clinical multidrug-resistant strains of P. aeruginosa.
Water was collected in January 2020 from a river in Haining, China (120.605111°E, 30.481146°N). The water was filtered (pore size, 0.45 μm) before phage enrichment using cultures of P. aeruginosa. P. aeruginosa host strains were grown in lysogeny broth (LB) at 37°C overnight with agitation; the strains used to isolate each phage are provided in Table 1. Phages were obtained from clear single plaques and grown in the presence of the bacterial host in LB overnight. Bacterial cells were removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22-μm membrane (6). Nucleic acids were extracted using the Biomed virus rapid DNA/RNA kit (Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing libraries were prepared using the NEBNext Ultra II DNA library prep kit for Illumina, and the genomes were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq platform. The average read length obtained was 150 bp. The assembly pipeline Unicycler v0.4.8 (7) was used to conduct quality control of raw reads, assemble the genomes, and determine the completion of the assembled genomes. Genome annotation was completed using the CPT Galaxy and Web Apollo interfaces (8). tRNAs were predicted using ARAGORN v2.36 (9) and tRNA-scan-SE v2.0 (10). Open reading frames (ORFs) were predicted using GeneMarkS v4.28 (11), Glimmer v3.0 (12), and MetaGeneAnnotator v1.0 (13) and were then manually validated using BLAST v2.9.0 searches (14) against the NCBI nonredundant and Swiss-Prot databases (15). Pairwise nucleotide alignments between the phages were evaluated using NCBI blastn. Default parameters were used unless stated otherwise.
TABLE 1.
Characteristics of Pseudomonas phage genomes
| Isolate | Pseudomonas host strain | Total no. of reads (forward/reverse) | Genome coverage (×) | Genome length (bp) | GC content (%) | No. of ORFs | Accession no. |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank | SRA | |||||||
| Kaya | 2081 | 11,290,334 | 2.56 | 43,067 | 54 | 60 | MZ927745.1 | SRR16248205 |
| Guyu | 2072 | 13,776,770 | 89.19 | 43,141 | 55 | 56 | MZ927746 | SRR16248204 |
| Kopi | 2072 | 7,620,976 | 142.96 | 42,820 | 53 | 55 | OK330455.1 | SRR16248203 |
| TehO | 2081 | 8,705,734 | 86.39 | 43,015 | 54 | 56 | OK330456.1 | SRR16248202 |
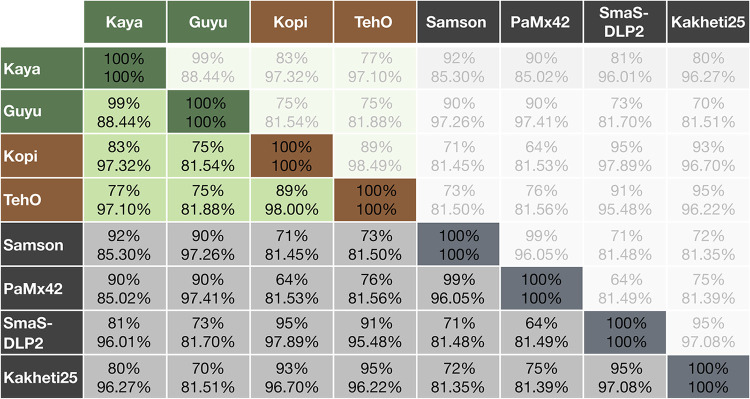
The characteristics of all four phage genomes are listed in Table 1. The phages are novel but are close relatives of each other, with their genes showing the mosaicism typical of bacterial viruses (Fig. 1). No genes were found to encode toxins or antibiotic resistance factors according to blastn searches against the Bacterial Virulence Factor Database (VFDB) (16). The phages were categorized as lytic using PhageAI (17). The most closely related phages of Kaya and Guyu are Xanthomonas phage Samson (GenBank accession number MN062187) and Pseudomonas phage PaMx42 (JQ067092), with genome coverage between 90% and 92% at sequence identities between 85% and 97%. Kopi and TehO are most closely related to Stenotrophomonas phage vB_SmaS-DLP2 (KR537871) and Pseudomonas phage vB_Pae-Kakheti25 (JQ307387), with sequence coverage between 91% and 95% at 95.48% to 97.89% sequence identity. With these sequence similarities, Kaya, Guyu, Kopi, and TehO are predicted to be Siphoviridae of the order Caudovirales.
FIG 1.
Genome sequence coverage (top number in each cell) and nucleotide identity (bottom number) of Pseudomonas phages with their closest relatives. The green and brown boxes indicate phages from this study. The gray boxes indicate phages from other studies: Samson (Xanthomonas phage; GenBank accession number MN062187), PaMx42 (Pseudomonas phage; JQ067092), SmaS-DLP2 (Stenotrophomonas phage; KR537871), and Kakheti25 (vB_Pae-Kakheti25) (Pseudomonas phage; JQ307387).
Data availability.
The sequencing data for bacteriophages Kaya, Guyu, Kopi, and TehO are available in GenBank under BioProject accession number PRJNA751744. The accession numbers for the genomes and sequencing reads are listed in Table 1.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32011530116).
Contributor Information
Belinda Loh, Email: belinda.loh@gmail.com.
Sebastian Leptihn, Email: sebastian.leptihn@ed.ac.uk.
Simon Roux, DOE Joint Genome Institute.
REFERENCES
- 1.Moradali MF, Ghods S, Rehm BH. 2017. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lifestyle: a paradigm for adaptation, survival, and persistence. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:39. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, Pulcini C, Kahlmeter G, Kluytmans J, Carmeli Y, Ouellette M, Outterson K, Patel J, Cavaleri M, Cox EM, Houchens CR, Grayson ML, Hansen P, Singh N, Theuretzbacher U, Magrini N, WHO Pathogens Priority List Working Group . 2018. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis 18:318–327. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Horcajada JP, Montero M, Oliver A, Sorlí L, Luque S, Gómez-Zorrilla S, Benito N, Grau S. 2019. Epidemiology and treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 32:e00031-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00031-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rohde C, Wittmann J, Kutter E. 2018. Bacteriophages: a therapy concept against multi-drug-resistant bacteria. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 19:737–744. doi: 10.1089/sur.2018.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Leptihn S. 2019. Welcome back to the pre-penicillin era: why we desperately need new strategies in the battle against bacterial pathogens. Infect Microbes Dis 1:33. doi: 10.1097/IM9.0000000000000009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Loh B, Wang X, Hua X, Chook HW, Ma L, Zhang L, Manohar P, Jin Y, Leptihn S. 2021. Complete genome sequence of the lytic bacteriophage Phab24, which infects clinical strains of the nosocomial pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol Resour Announc 10:e00669-21. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00669-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE. 2017. Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ramsey J, Rasche H, Maughmer C, Criscione A, Mijalis E, Liu M, Hu JC, Young R, Gill JJ. 2020. Galaxy and Apollo as a biologist-friendly interface for high-quality cooperative phage genome annotation. PLoS Comput Biol 16:e1008214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Laslett D, Canback B. 2004. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:11–16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. 1997. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M. 2001. GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2607–2618. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.12.2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL. 1999. Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res 27:4636–4641. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.23.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Noguchi H, Taniguchi T, Itoh T. 2008. MetaGeneAnnotator: detecting species-specific patterns of ribosomal binding site for precise gene prediction in anonymous prokaryotic and phage genomes. DNA Res 15:387–396. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bairoch A, Boeckmann B. 1994. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank: current status. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3578–3580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu B, Zheng D, Jin Q, Chen L, Yang J. 2019. VFDB 2019: a comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive Web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D687–D692. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tynecki P, Guziński A, Kazimierczak J, Jadczuk M, Dastych J, Onisko A. 2020. PhageAI—bacteriophage life cycle recognition with machine learning and natural language processing. bioRxiv doi: 10.1101/2020.07.11.198606. [DOI]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The sequencing data for bacteriophages Kaya, Guyu, Kopi, and TehO are available in GenBank under BioProject accession number PRJNA751744. The accession numbers for the genomes and sequencing reads are listed in Table 1.