Abstract
Aims
Naturally secreted extracellular vesicles (EVs) play important roles in stem-mediated cardioprotection. This study aimed to investigate the cardioprotective function and underlying mechanisms of EVs derived from HIF-1α engineered mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in a rat model of AMI.
Methods and results
EVs isolated from HIF-1α engineered MSCs (HIF-1α-EVs) and control MSCs (NC-EVs) were prepared. In in vitro experiments, the EVs were incubated with cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells exposed to hypoxia and serum deprivation (H/SD); in in vivo experiments, the EVs were injected in the acutely infarcted hearts of Sprague-Dawley rats. Compared with NC-EVs, HIF-1α-EVs significantly inhibited the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes and enhanced angiogenesis of endothelial cells; meanwhile, HIF-1α-EVs also significantly shrunk fibrotic area and strengthened cardiac function in infarcted rats. After treatment with EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels, we observed longer retention, higher stability in HIF-1α-EVs, and stronger cardiac function in the rats. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) displayed that miRNA-221–3p was highly expressed in HIF-1α-EVs. After miR-221–3p was inhibited in HIF-1α-EVs, the biological effects of HIF-1α EVs on apoptosis and angiogenesis were attenuated.
Conclusion
EVs released by MSCs with HIF-1α overexpression can promote the angiogenesis of endothelial cells and the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via upregulating the expression of miR-221–3p. RGD hydrogels can enhance the therapeutic efficacy of HIF-1α engineered MSCs-derived EVs.
Keywords: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α, Extracellular Vesicles, Mesenchymal stem cells, myocardial infarction
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
Ischemic heart disease is one of the leading causes of death all over the world [1]. Apoptosis of myocardial cells are the molecular and cellular basis of progressive heart failure. The damaged myocardium is usually replaced by fibrotic scar tissue due to the negligible regenerative ability of cardiomyocytes, which will eventually lead to congestive heart failure [2].
Accumulating evidence shows that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transplantation can promote tissue repair, regulate immunity and promote angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. MSCs function through releasing paracrine, especially extracellular vesicles (EVs) [3]. EVs are vesicles with a diameter of 50–200 nm, responsible for the communication between cells and cells [4]. Studies have shown that EVs derived from different types of stem cells, such as MSCs, embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, have cardioprotective effects [5]. EVs exhibited similar beneficial effects, including promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis and fibrosis, as their mother cells [6]. For example, MSCs transplantation can promote tissue repair, regulate immunity and promote angiogenesis after myocardial infarction through releasing paracrine, especially EVs [3]. MSCs-derived EVs (MSCs-EVs) can reduce cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury and protect heart function in ischemic heart disease [7]. Moreover, MSCs-EVs have been shown to have little side-effects, including immunogenicity, tumorigenicity and teratoma formation [8]. Therefore, EVs-based therapy has become one of the most promising strategies to restore cardiac function after myocardial infarction.
Our previous studies demonstrated that hypoxia-conditioned hMSCs-derived exosomes protected cardiomyocyte from apoptosis. Moreover, four weeks after intramyocardial injection of MSCs-EVs, the infarct size and number of apoptotic cells in the infarct border area were significantly reduced, and the cardiac function was improved [9]. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) regulates cells' adaptation to hypoxia through activating a variety of angiogenic factors [10]. HIF-1α-overexpressed exosomes could rescue the impaired angiogenic ability, migration, and proliferation of hypoxia-pretreated HUVECs in vitro and mediate cardioprotection by upregulating proangiogenic factors and improving neovascularization [11]. In this study, we studied the effects of HIF-1α engineered MSCs-EVs on infarcted heart and analyzed their molecular mechanism.
However, EVs functions rely on their concentrations, administration routes, retention and target tissues. EVs injected into the body will be quickly removed in the body [12]. The application of EVs in tissue repair is still restricted by its low stability and short retention. This problem can be overcome by using biomaterials, such as RGD-functionalized hydrogels [13]. Gallagher et al. reported the incorporation of the RGD peptide (arginine-glycine-aspartate, Arg-Gly-Asp) into biomaterials to promote cell adhesion to the matrix [14]. Zhang et al. also used RGD hydrogels which bind to integrins on the membrane of EVs to enhance the stability and retention of MSCs-EVs in kidney repair [12]. However, it is not clear whether it can be used to load HIF-EVs and be injected into the heart. Thus, our second hypothesis was to further improve the therapeutic ability of MSCs-EVs for heart by using RGD peptides.
Overall, the aim of our study was to evaluate whether the combinations of gene engineered MSCs-EVs and RGD peptide hydrogels could provide a promising therapy for ischemic heart diseases.
2. Methods
2.1. Human umbilical cord MSCs culture and lentiviral transduction
Human umbilical cord MSCs were obtained from healthy donors (n = 3, ages 20–25 yrs) and cultured in α-MEM with 10% FBS and 100 U/mL penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco). MSCs in passages 3–6 were used for experiments. MSCs were incubated at 37 °C in humidified air with 5% CO2.
MSCs were transduced with a HIF-1α-overexpressing lentivirus (Ubi-MCS-3FLAG-SV40-EGFP-IRES-puromycin) or a control lentivirus, named as HIF-1α-MSCs or NC-MSCs, respectively (Genechem, Shanghai, China). 72 h after transduction, these cells were further confirmed by western blot analysis and fluorescence microscope.
2.2. Culture of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and human umbilical vein endothelial cells
One-day-old (P1) S/D rats were prepared for isolation of primary cardiomyocytes. Heart ventricles were removed from neonatal pups, minced into 1-mm3 pieces, then digested with a solution containing 0.25% trypsin and 0.1% collagenase II. The dissociated cells were pre-plated at 37 °C for 1.5–2 h. Afterwards, cardiomyocytes were separated from fibroblasts through differential adhesion, followed by culture with Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Gibco, New York, USA) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, New York, USA) and 10% horse serum (HS, Gibco, New York, USA) at 37 °C in 5% CO2 air.
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured in DMEM mixed with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin and 110 mg/mL sodium pyruvate at 37 °C in 5% CO2 air.
2.3. Western blot
The experiments were performed as previously described [9]. Bradford assay (BioRad, CA, USA) was carried out to quantify the protein concentration. The antibodies used in the experiments including HIF-1α (Cell Signaling Technology, MA, USA), anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (Cell Signaling Technology, MA, USA), TSG101 (Proteintech, Chicago, USA), CD63 (Proteintech, Chicago, USA) and CD81 (Proteintech, Chicago, USA).
2.4. Isolation of EVs
EVs were prepared through differential ultracentrifugation, allowed to grow in the EV-free medium to a 70–80% confluency for 48 h. Cell debris was eliminated from the conditioned medium through centrifugation at 300g for 10 min, at 2000g for 10 min, and at 10,000g for 30 min. Then the EVs were filtrated with a 0.22 μm filter and harvested through ultracentrifugation at 100,000g for 70 min at 4 °C. Having been washed and resuspended in PBS, the EVs were ultracentrifuged at 100,000g for 2 h to eliminate the contaminated proteins. After this treatment, the EVs were resuspended in PBS and stored at −80 °C. The content of protein in the EVs was measured through a BCA protein assay kit (Promega, WI, USA). The structure of EVs was exhibited by transmission electron microscope (TEM), and their size by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA).
2.5. Internalization of EVs in vitro
The EVs were labeled by DiR (Beyotime, Nanjing, China). The cardiomyocytes and HUVECs were seeded and co-cultured with DiR-labeled EVs at different concentrations. After 24 h, the cells were washed with PBS and observed using IVIS Lumina Imaging Systems. The density of BLI signals was measured as average radiance from regions of interest (ROIs).
Moreover, the EVs were also labeled by Dil (Beyotime, Nanjing, China) and co-cultured with receptor cells at 2 time points (2 h and 24 h). Then the cells were washed with PBS and observed under fluorescence microscope.
2.6. PI staining
To assess the effects of EVs on the survival of cardiomyocytes, EVs were co-cultured with cardiomyocytes for 24 h under H/SD condition and then stained with Hoechest33342 and PI, followed by fluorescence microscopy to observe the stains of red (PI) and blue (Hoechest33342) fluorescence.
2.7. Apoptosis assays
Apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL based on TUNEL Apoptosis Detection kit (Yisheng, Shanghai, China). Samples were mounted with mounting medium containing 4′, 6′-diamidino-2- phenylindole (DAPI). The stained nuclei were counted with a Zeiss LSM510 META microscope. The percentage of apoptotic nuclei =the total number of TUNEL-stained nuclei divided/the total number of DAPI-positive nuclei. Apoptosis was also evaluated with caspase-3/7 cell apoptosis detection kit (RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Caspase-3/7 green fluorescence, PI red fluorescence and hoechst33342 blue fluorescence could distinguish apoptotic cells, dead cells and living cells, respectively [15,16].
2.8. HUVECs tube formation assay
To assess their angiogenic ability of EVs derived from MSCs, HUVECs were seeded (10,000 cells/well) in 96-well plates coated with growth-factor reduced Matrigel (BD Biosciences, CA, USA). Having been challenged with EVs or PBS for 8 h, photos of capillary-like tube formation were captured. Tube length and number of branches were measured with ImageJ software.
2.9. Animal experiments
All procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee in Nanjing Medical University. Sprague-Dawley rats (male, 8 weeks old) were subjected to AMI model after left anterior descending (LAD) coronary ligation as previously described [17]. EVs suspended in PBS or RGD hydrogels was intramyocardially injected into two sites in the border area of infarcted hearts. Each rat was injected with 50 μg EV (approximately 3.6 × 107 Particles per rat). Rats were euthanized by administration of pentobarbital at day 3 or day 28 after MI.
2.10. Echocardiography studies
At 28 days after EVs therapy, cardiac function was evaluated through transthoracic echocardiography (Ultramark 9; Soma Technology, Bloomfield, CT, USA) with broadband probe (MX 2505; frequency, 14–28 MHz), and dimensions calculated using Vevo 3100 software. Left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVEDD) and left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVESD) were measured in at least three consecutive cardiac cycles. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS) were used to evaluate the systolic function of the hearts. LVEF was calculated as [(LVEDD)3-(LVESD)3]/(LVEDD)3] × 100% and LVFS was calculated as [(LVEDD-LVESD)/LVEDD] × 100%.
2.11. Masson's trichrome and Haematoxylin-Eosin staining
Paraffin-embedded slides were stained by Masson's trichrome. Infarcted area was measured as the percentage of fibrotic area in the total left ventricular area. The thickness of infarcted cardiac wall was calculated as the mean of three equidistant measurements on each section. Fluorescence microscopy (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) was used to catch images and ImageJ software (NIH) to analyze them. The inflammation was degreed using Haematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining.
2.12. Tissue apoptosis analysis
Apoptosis was assessed with TUNEL assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA) in vivo according to related instructions.
2.13. Immunofluorescence
Immunostaining was performed with the primary antibodies including anti–α-sarcomeric actin (Sigma Aldrich, MO, US); anti–α-smooth muscle actin (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom); anti-CD31 (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom); anti-connexin43 (Cell Signaling Technology, MA, USA); wheat germ agglutinin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA). DAPI was used for nuclear counterstaining.
2.14. Injectable hydrogels
Biotin-GFFYGRGD was synthesized by Xi'an Qiyue Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The amino acids in the sequence were connected from right to left according to its molecular formula [12] using 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin as the carrier. After coupling, the resin was washed off, the polypeptide was extracted, and purified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The collected samples were identified by mass spectrometry (MS). Finally, the purified solution was lyophilized as white powder. The collected samples were stored at −20 °C for subsequent experiments.
In the mixture of Biotin-GFFYGRGD (1.14 mg) with PBS buffer (1 mL), and the pH value was adjusted to 7.4 by adding 2 μL of 1 M Na2CO3. Next, the compound in the suspension was completely dissolved at 95 °C, then cooled (as low as room temperature) till hydrogels formed. EVs were added to RGD-biotin hydrogels at mass ratios of 1:1 in animal experiments. Biotin-GFFYGRGD was observed under scanning electron microscope (SEM).
2.15. In vivo tracking of EVs
In vivo, rats were LAD-ligated. EVs were stained with DiR, encapsulated in RGD hydrogels (EV/RGD-biotin), intramyocardially injected into two sites in the border area of infarcted hearts, and tracked by Gluc signals (IVIS Lumina Imaging Systems, Xenogen Corporation) at the indicated time points. The signal density of bioluminescence imaging (BLI) was measured from ROIs.
2.16. Real-time PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed as previous described [9]. RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, USA). cDNA was synthesized with miRNA First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (by stem-loop) (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China). Stem-loop qRT-PCR was accomplished with a FastStart Essential DNA Green Master (Roche, CA, USA). The cellular expression of HIF-1α mRNA was normalized to that of GAPDH. The exosomal level of miR-221–3p was normalized to that of cel-miR-39 (C39) and calculated with the equation “relative gene expression= 2− (ΔCt sample – ΔCt control)”. The primers are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
2.17. MicroRNA-inhibitor transfection
HIF-1α engineered MSCs were allowed to grow to 70%–80% confluence, then transfected with synthetic miR-221–3p inhibitor or negative control (RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) on the system of Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, NY, USA). After a 6-h transfection, the cells were added into EV-free FBS containing α-MEM and kept for 48 h. The conditioned medium was collected and EVs isolated as HIF-1α-EV-InhibitormiR−221 and HIF-1α-EV-InhibitorNC.
2.18. Statistical analyses
The data were presented as mean ± SEM. The quantification was performed and graphs generated using GraphPad Prism 7 (La Jolla, CA, USA). One-way ANOVA was implemented for comparison among multiple groups and t-test for comparison between two groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EVs derived from HIF-1α-MSCs
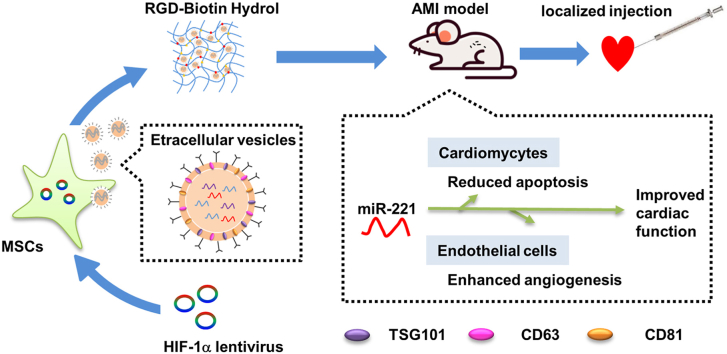
To verify the efficiency of lentiviral modification, green fluorescence was observed in both HIF-1α-MSCs or NC-MSCs (Fig. 1A). It is indicated that mRNA levels of HIF-1α was elevated in HIF-1α-MSCs compared with NC-MSCs (Supplementary Figure 1). Western blot showed that HIF-1α protein level significantly increased in HIF-1α-MSCs than in NC-MSCs (Fig. 1B). EVs were then isolated from HIF-1α-MSCs and NC-MSCs by differential centrifugation (Fig. 1C). TEM showed that the EVs from HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs had a shape of cup and a size of about 100 nm (Fig. 1D). Specific exosomal markers (TSG101, CD81 and CD63) showed positivity in HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs (Fig. 1E). The size and concentration of EVs were showed no between-group difference (Fig. 1F).
Fig. 1.
Lentiviral transduction, isolation and characterization of MSCs derived EVs. (A) Successful lentiviral transduction was confirmed by positive fluorescence signal under microscope. Scale bar = 100 μm n= 3 for each group. (B) Western blot images showed HIF-1α protein levels in HIF-1α-MSCs and NC-MSCs groups. n= 3 for each group. (C) EVs were isolated from HIF-1α-MSCs and NC-MSCs groups using a standard protocol of serial, differential centrifugation and ultracentrifugation methods. (D) TEM images of EVs derived from HIF-1α-MSCs and NC-MSCs. n= 3 for each group. Scale bar = 100 nm (E) The exosomal protein markers of TSG101, CD63, and CD81 in EVs isolated from HIF-1α-MSCs and NC-MSCs. n= 3 for each group. (F) The particle size distribution and particle concentration were analyzed by nanoparticle tracking analysis. n= 3 for each group. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. ∗∗P < 0.01.
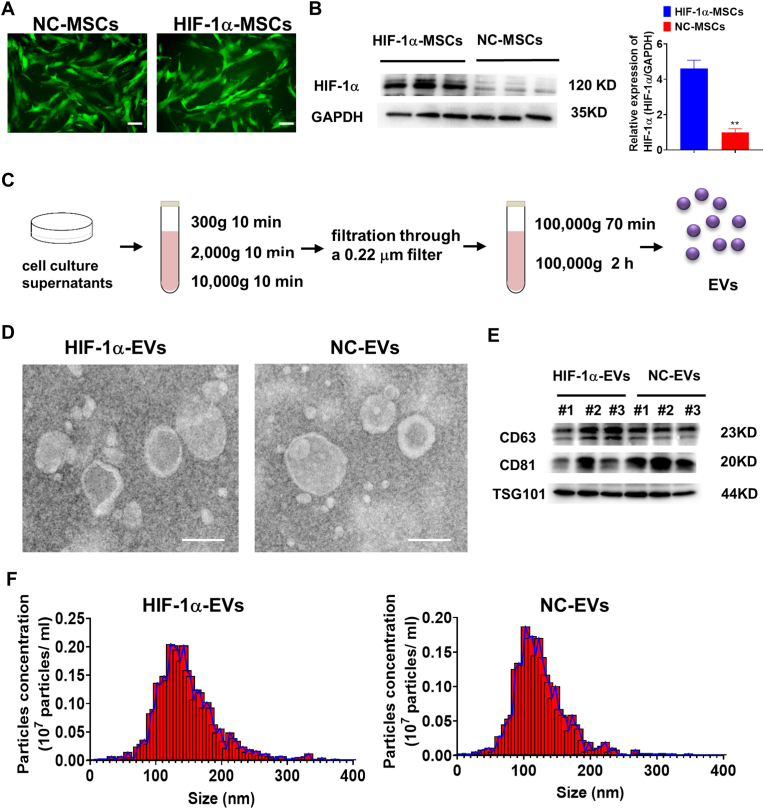
EVs were tracked in vitro after being labeled with DiR and co-cultured with cardiomyocytes and HUVECs at different concentrations. After 24 h, the calibration curves (Fig. 2A and B) presented a linear correlation between EVs level and fluorescent density.
Fig. 2.
EVs isolated from MSCs could be absorbed by cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. (A and B) DiR-labeled EVs with various concentrations was co-cultured with cardiomyocytes and internalization of EVs was detected. (C) Confocal images showed that red fluorescence of dye Dil labeled EVs were endocytosed by HUVECs and cardiomyocytes 6 h and 24 h after incubation. Scale bar = 50 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Having been labeled with Dil (10 μmol/L, 1 μL) for 24 h, the EVs were co-cultured with cardiomyocytes and HUVECs for 6 h and HUVECs for 24 h under H/SD. As shown by confocal images, cardiomyocytes and HUVECs took up labeled EVs in a time dependent manner (Fig. 2C and D).
3.2. Biofunctions of HIF-1α-EVs
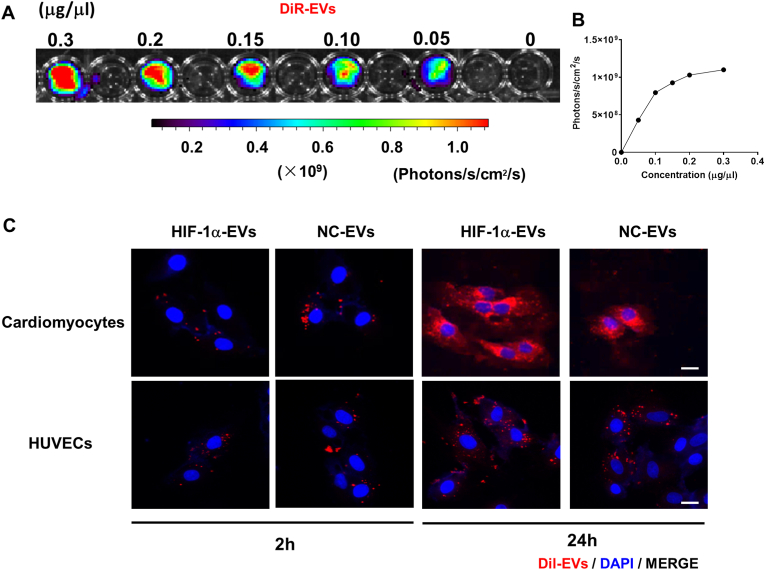
To explore whether HIF-1α in MSCs regulates the biological functions of EVs, the cytoprotective and proangiogenic effects of HIF-1α-EVs were evaluated. HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs prevented apoptosis in cardiomyocytes under H/SD condition (Fig. 3A and Fig. 3D). HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs groups also exhibited weakened caspase3 and caspase7 activity in cardiomyocytes (Fig. 3B and E). The percentages of viable cells in the HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs groups were significantly higher than that in the control group (Fig. 3C). Cardiomyocytes treated with HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs exhibited lower TUNEL-positive signals than the control cells (Fig. 3F and G). Next, the angiogenic ability of HUVECs was evaluated according to the status of microvessels, and more tubular structures developed in HUVECs as treated with HIF-1α-EVs or NC-EVs (Fig. 3H and I). Altogether, HIF-1α-EVs exhibited evident anti-apoptosis effects on cardiomyocytes and proangiogenic effects on HUVECs in vitro.
Fig. 3.
HIF-1α-EVs exhibited an anti-apoptosis effect in cardiomyocytes and a pro-angiogenesis effect in HUVECs in vitro. (A) Hoechest33342/PI double staining was used to observe the survival of cardiomyocytes treated with PBS, MSCs-EVs or HIF-1α-EVs under H/SD condition. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Caspase3/caspase7 activity of cardiomyocytes treated with PBS, MSCs-EVs or HIF-1α-EVs under H/SD condition. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) HIF-1α EVs improved cell viability of cardiomyocytes under H/SD condition. (D) Quantitative analysis of viable cells treated with PBS or EVs. (E) Quantitative analysis of caspase3/caspase7 positive cells between the three groups. (F) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells between the three groups. (G) Representative photographs showing the TUNEL-positive cells in cardiomyocytes among the different groups. Green, TUNEL-positive nuclei; red, α-actin; blue, DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bar = 100 μm. (H) Representative images showing tube formation in HUVECs treated with PBS, MSCs-EVs or HIF-1α-EVs. Scale bar = 100 μm. (I) Quantification of tube length in each group. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. ∗P< 0.05, ∗∗P< 0.01, ∗∗∗∗P< 0.0001 vs. PBS group; #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 vs. NC-EVs group; NS, not significant. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
3.3. HIF-1α-EVs protected cardiac function in a rat MI model
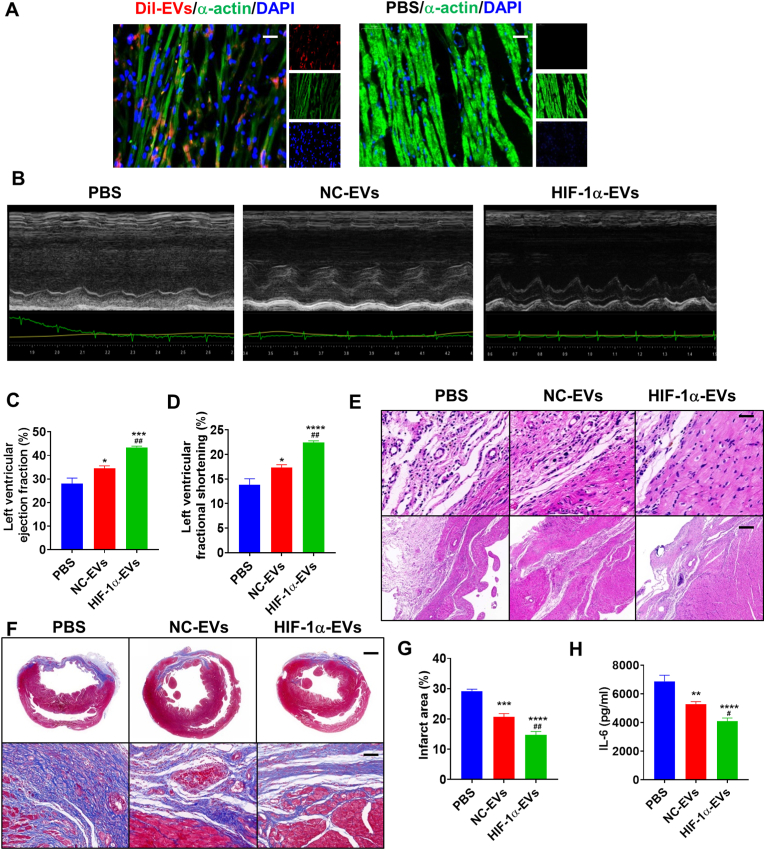
HIF-1α-EVs, NC-EVs or PBS (AMI control group) were intramyocardially injected into the border of infarcted hearts at post-MI 30 min. Distribution of Dil-labeled HIF-1α-EVs (EVs-Dil) in infarcted hearts was observed on post-MI Day 3. The area with positive EVs-Dil increased in the myocardium (Fig. 4A). In addition, HIF-1α-EVs were superior to NC-EVs in improving systolic function (Fig. 4B). On post-MI Day 28, the HIF-1α-EVs and NC-EVs groups showed significant enhancement in LVEF and LVFS, compared to the PBS group (Fig. 4C and D). Echocardiographic parameters between the three groups are listed in Supplementary Table 2. Furthermore, we observed lower level of inflammatory infiltration in the HIF-1α-EVs group than in other groups (Fig. 4E). Histological analysis exhibited smaller scars in HIF-1α-EVs group than in PBS and NC-EVs groups (Fig. 4F and G). In addition, HIF-1α-EVs inhibited the elevation of IL-6 in the peri-infarct region (Fig. 4H). These results suggested that HIF-1α overexpression in MSCs enhanced the protective effects of MSCs-derived EVs on infarcted hearts.
Fig. 4.
HIF-1α-EVs effectively preserved cardiac function in a rat MI model. (A) Dil-labeled exosomes were injected into the infarcted heart of rats for 6 h. Representative images of post-MI heart sections stained with Dil-labeled Exo (red), α-actin (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm (B) Representative echocardiogram of rat heart in different groups at 28 days post-MI. (C and D) Significantly enhanced LVEF and LVFS in rats transplanted with MSCs-EVs and HIF-1α-EVs compared with control groups. (E) HE staining at the border zone on Day 28 after MI. (F) Masson Trichrome staining at the border zone on Day 28 after MI. (G) Quantitative data for the fibrotic area. (H) Quantification of IL-6 expression level in the infarct border zone of rat heats. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. n=5–6 for each group. ∗P< 0.05, ∗∗P< 0.01, ∗∗∗P< 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P< 0.0001 vs. PBS group; #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 vs. NC-EVs group. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
3.4. HIF-1α-EVs promoted the survival and angiogenesis in cardiomyocytes
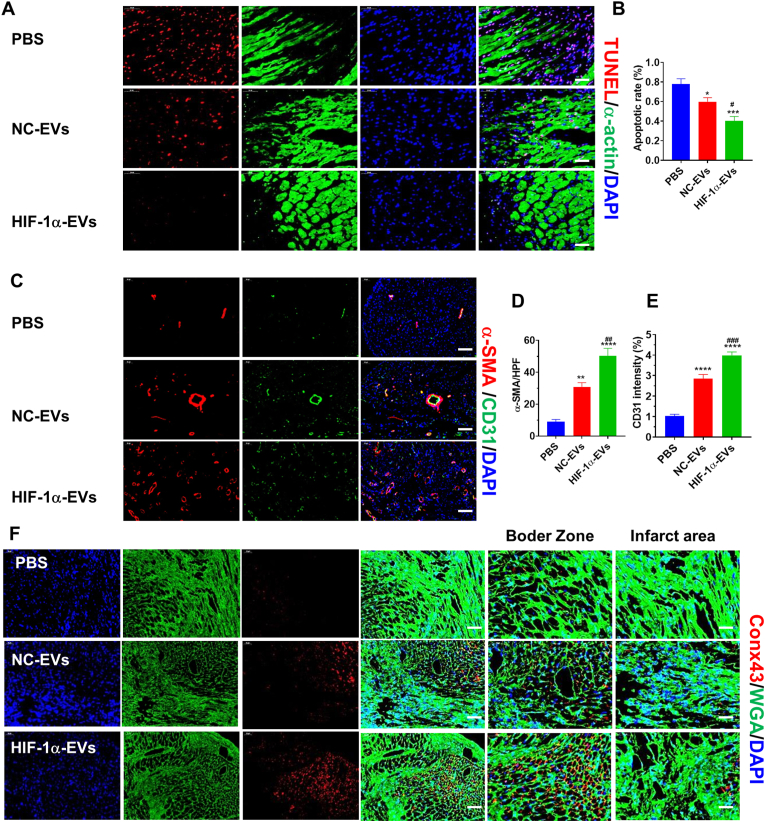
According to TUNEL results at post-MI 4 weeks, the number of apoptotic cells was lowered in the myocardial boarder zone after EVs treatment, compared to that after PBS treatment. The number of TUNEL positive cells was the lowest in the HIF-1α-EVs group (Fig. 5A and Fig. 5B). As demonstrated by immunofluorescence at 4 weeks after infarction, arteriole density was higher in the HIF-1α-EVs group than in NC-EVs and PBS groups (Fig. 5C and D). Capillary density showed similar changes (Fig. 5C and E). Conx43 expression decreased in HIF-1α-EVs group (Fig. 5F). HIF-1α-EVs played their reparative role through enhancing the angiogenesis and increasing cell survival.
Fig. 5.
HIF-1α-EVs inhibited apoptosis and promoted angiogenesis in a rat MI model. (A)TUNEL staining at the border zone on Day 28 post-MI with TUNEL-positive cells. Red, TUNEL-positive nuclei; Green, α-actin; blue, DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bar = 50 μm (B) Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells in each group. (C) Neovascularization at the border zone on Day 28 post-MI was identified by staining with a-SMA (red) and CD31 (green) and nuclei (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm (D and E) Quantification of a-SMA-positive cells, CD31-positive cells among different groups. (F) Border zone sections obtained 4 weeks after MI were immunofluorescent stained for Con43 expression. Red, Conx43; Green, α-actin; blue, DAPI-stained nuclei. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. n=5–6 for each group. ∗P< 0.05, ∗∗P< 0.01, ∗∗∗P< 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P< 0.0001 vs. PBS group; #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 vs. NC-EVs group. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
3.5. EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels increased the retention and stability of HIF-1α-EVs and improved cardiac function
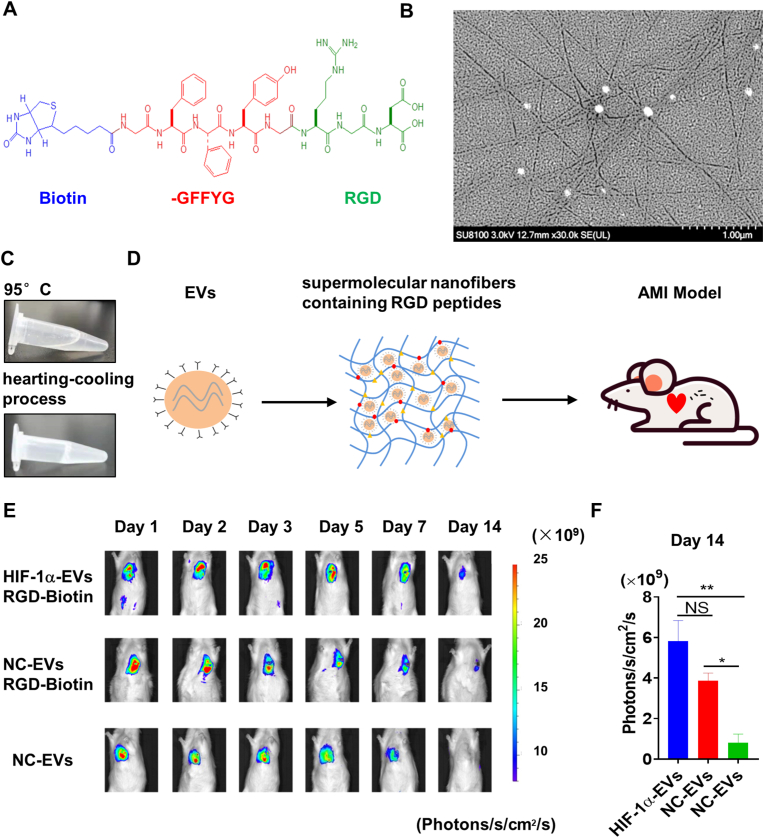
RGD-biotin molecules were generated through covalently attaching Biotin-GFFYG (Fig. 6A). HPLC analysis showed that the purity of the samples obtained was more than 95% (Supplementary Figure 2). The RGD-biotin hydrogels were identified by mass spectrometry (MS). The characteristic molecular weight of 1144.686 in MS analysis, indicated that the compound biotin-GFFYGRGD was successfully synthesized (Supplementary Figure 3). In order to further explore whether the addition of EVs had an impact on the mechanical properties of hydrogels, rheological tests were performed on hydrogels with different mass ratios (1:1, 2:1) of EVs. Rheological results showed that when the mass ratio of EVs to hydrogels was 2:1, the mechanical properties of hydrogels would be weakened (Supplementary Figure 4). SEM images of the RGD hydrogels exhibited disarranged nanofibers formed by RGD-biotin molecules (Fig. 6B). The biotin-GFFYGRGD was completely dissolved at 95 °C, till the formation of RGD hydrogels as it gradually fell to the room temperature (Fig. 6C). We also compared the properties of RGD hydrogels with those of biotin hydrogels without the integrin-targeting tripeptide RGD. Next, EVs and EVs adhered to RGD hydrogels (EV/RGD-biotin) were injected in the AMI rat model (Fig. 6D). The stability of injective EVs was then assessed. The fate of EVs in vivo was traced by bioluminescence imaging. 14 days after injection, the signal could still be detected in HIF-1α-EVs RGD-Biotin group and NC-EVs RGD-Biotin group. However, little fluorescence signal was detected in the naked EVs group 14 days after injection (Fig. 6E and F). These results indicated that EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels increased the retention and stability of EVs.
Fig. 6.
EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels enhanced the retention and stability of HIF-1α-EVs. (A) Chemical structure of the RGD-biotin molecule. (B) SEM image of RGD-biotin hydrogel revealed the formation of entangled nanofibers formed by the RGD-biotin molecule. (C) Biotin-GFFYGRGD was dissolved in PBS. After that, the suspension was heated to about 95 °C in order to dissolve the compound completely, and hydrogels formed after cooling back to room temperature. (D) EVs were incorporated in Biotin-GFFYGRGD and then injected into infarcted rat hearts. (E) The fate of EVs in vivo was tracked by bioluminescence imaging. Representative images are from rats receiving EVs incorporated in RGD hydrogels (EV/RGD-biotin) and naked EVs. (F) Quantification of bioluminescence imaging after injection. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. n=3 for each group.
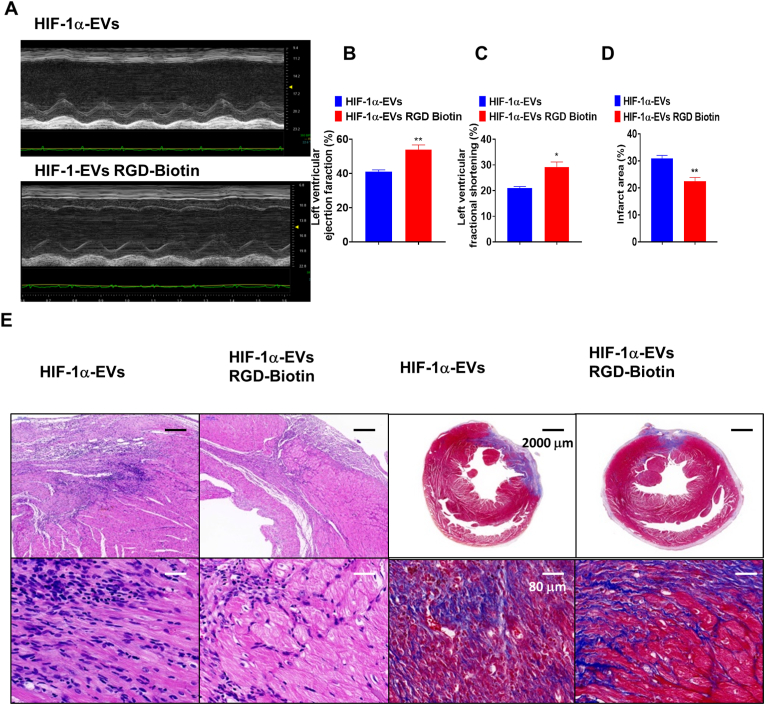
At post-AMI Day 28, LVEF and LVFS increased in the presence of RGD-Biotin in HIF-1α-EVs group (Fig. 7A–C). Echocardiographic parameters between the two groups are listed in Supplementary Table 3. The infiltration of inflammatory cells reduced in the presence of RGD-Biotin in HIF-1α-EVs group. Masson's trichrome staining also showed the attenuation in cardiac fibrosis (Fig. 7D and E). These results showed that EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels exert stronger cardiac function protection compared to EVs alone.
Fig. 7.
EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels improved Cardiac function after AMI. (A) Representative echocardiogram of rat heart between HIF-1α-EVs group and HIF-1α-EVs RGD-Biotin group at 28 days post-MI. (B and C) Significantly enhanced LVEF and LVFS in rats transplanted with MSCs-EVs and HIF-1α-EVs compared with control groups. (D) HE staining and Masson Trichrome staining at the border zone on Day 28 after MI. (E) Quantitative data for the fibrotic area. Continuous variables were described by means ± SEM. n=4–6 for each group. ∗P< 0.05, ∗∗P< 0.01.
3.6. Inhibition of miR-221–3p countered the effects of EVs on apoptosis and angiogenesis
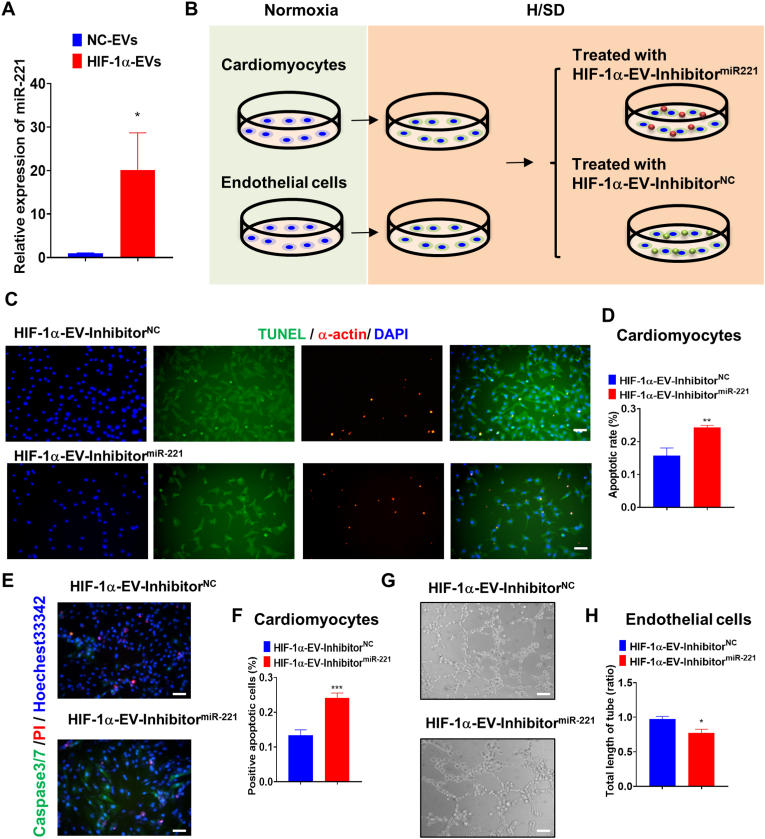
To explore the molecular mechanisms of HIF-1α-EVs, we then assessed the mRNA and protein expression in HIF-1α-EVs. We found that there were no significant differences in mRNA and protein expression between NC-EVs and HIF-1α-EVs (Supplementary Figure 5). We hypothesized that overexpression of HIF-1α in MSCs altered the ingredient of MSCs derived EVs, and therefore mediating its cardiac repair effects. It is indicated in a study that miR-221 were upregulated in exosomes derived from HIF-1α-MSCs [18]. We then evaluated the miR-221 expression in HIF-1α-EVs. As shown by qRT-PCR experiments (Fig. 8A), miRNA-221–3p was overexpressed in HIF-1α-EVs. To identify the responsible signaling pathways, miR-221–3p inhibitor and miR-221–3p inhibitor NC were transfected into HIF-1α-MSCs. Subsequently, HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 and HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC were incubated with cardiomyocytes and HUVECs under H/SD condition (Fig. 8B). The number of apoptotic cells and the activity of caspase 3/7 rose in HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 group, compared with those in HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC group (Fig. 8C–F). HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 curbed the construction of endothelial network compared with HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC, as shown by the data of endothelial tube length and branching points (Fig. 8G and H). Together, miR-221–3p inhibited the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes and boosted the angiogenesis in HUVECs. The pharmacological effects of HIF-1α-EVs were at least partly induced by miR-221–3p.
Fig. 8.
Inhibition of miR-221-3p Reversed the Protective Effects of EVs on Apoptosis and Angiogenesis. (A) Expression values for miR-221–3p in MSCs-EVs and HIF-1α-EVs by qRT-PCR. (B) Experimental design. To inhibit miR-221–3p in HIF-1α-EVs. HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 and HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC were incubated with cardiomyocytes or HUVECs under H/SD condition. (C and D) TUNEL staining at the border zone 4 weeks after MI, and quantification analysis of percentage of apoptotic cardiomyocytes between two groups. Scale bar = 100 μm (E–F) Caspase3/caspase7 activity and quantification analysis in cardiomyocytes treated with HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 and HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC under H/SD condition. Scale bar = 100 μm (G) Representative images showing tube formation in HUVECs treated with HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitormiR−221 and HIF-1α-EVs-inhibitorNC. Scale bar = 100 μm (H) Quantification of tube length in each group. Continuous variables and categorical variables were described by means ± SEM and percentages. n=6 for each group. ∗P<0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
4. Discussion
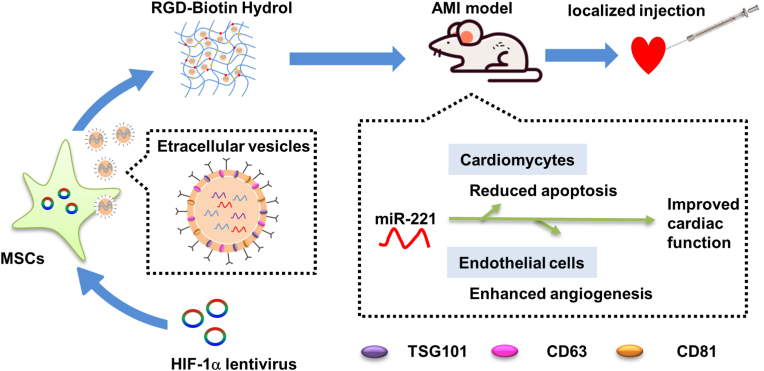
We have previously demonstrated that exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood MSCs can inhibit the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes under H/SD condition [9]. HIF-1α, always upregulated under hypoxic condition, can mediate cellular adaptation to hypoxia and trigger angiogenesis [19,20]. In the present study, we found that EVs derived from HIF-1α engineered MSCs can exert anti-apoptotic and angiogenic effects in a rat model of AMI. Moreover, we boosted the cardiac repair effects of EVs derived from HIF-1α engineered MSCs using a biocompatible and EVs-conjugating RGD hydrogel. Mechanistically, we identified miR-221–3p as a mediator in EVs of HIF-1α engineered MSCs (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9.
Schematic of the working hypothesis. EVs released by MSCs with stabilized overexpression of HIF-1α contribute to angiogenesis and anti-apoptosis in part via enhanced expression of miR-221–3p. RGD hydrogels increased the therapeutic efficacy of HIF-1α engineered MSCs-derived EVs at a functional, histopathological and molecular level.
MSCs may serve as therapeutic agents for ischemia-related diseases [[21], [22], [23], [24]]. In the present study, human umbilical cord MSCs were used for cell culture and EVs isolation. MSCs can mainly extracted from four tissue sources: bone marrow, umbilical cord, fat and amniotic membrane. There are four main reasons that we chose umbilical cord for MSCs extraction: 1) The MSCs abundance of in umbilical cord was the highest among the four. 2) Umbilical cord MSCs and amniotic MSCs had better cell proliferation ability compared with the rest two sources. 3) Compared with bone marrow MSCs, MSCs from umbilical cord, amniotic membrane and fat had better performance in immunomodulatory ability. 4) Umbilical cord, amniotic membrane and fat can be obtained easily and therefore were suitable for cell therapy and EVs therapy. As MSCs from different sources may show functional heterogeneity, we must be cautious about the results and conclusions of current study [25]. The cardiac benefits of MSCs come through their paracrine of EVs, soluble proteins, etc [26,27]. Exosomal secretion involves various environmental factors [28]. Under hypoxia, more exosomes are secreted, and HIF-1α may mediate this process [29]. In this study, we found that EVs secreted by MSCs with overexpressed HIF-1α exhibited angiogenic and anti-apoptotic function. The mechanism remains unclear; however, several strains of molecules may be responsible, including Rab proteins, SNARE complex, and ceramides [30]. HIF-1α interacts with Rab22A in the development of microvesicles, shedding light into the nature of HIF-1α-mediated secretion [31].
To explore the function of HIF-1α MSCs derived EVs on ischemic hearts, we co-cultured EVs with HUVECs and cardiomyocytes. We found that EVs could be absorbed by both HUVECs and cardiomyocytes. As compared with MSCs-EVs, HIF-1α-EVs facilitated the development of tube-like structures and prolongated the survival of cardiomyocytes. In the rat AMI model, HIF-1α-EVs quickened the recovery of cardiac functions, reduced infarcted size and inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis, as compared to MSCs-EVs. In addition, HIF-1α-EVs stimulated angiogenesis in the peri-infarct region.
The low stability and short retention have restricted the reparative abilities of MSCs-EVs. Regarding that RGD peptides are highly attachable to integrins rich on the surface of EVs [[32], [33], [34]], we used RGD hydrogels to load HIF-1α-EVs, thus enhancing their retention in the rats' hearts and improving therapeutic effects of HIF-1α-EVs. Biotin serves as a hydrogenator with biocompatibility and close interactions with cell receptors, including proteins on EV membranes [35]. Therefore, biotin can increase the stability and retention of EVs. In this study, biotin-GFFYG was covalently attached to the N-terminal of RGD to make RGD-biotin molecules (biotin-GFFYGRGD). The EVs/RGD-biotin hydrogels fortified the cardiac function after AMI.
The combined application of bioactive nanomaterials and EVs shed a light for ischemic heart diseases. A variety of other biomaterials are also reported for EVs delivery and heart regeneration application [36], such as Self-assembling peptides [37], growth hormone releasing peptides [38], gelatin [39] and so on. However, there are still some bottlenecks that need to be solved. For example, 1) How to keep more EVs in the heart tissue after injection, so as to maximize the therapeutic effects; 2) Can bioactive materials load more EVs; 3) Some bioactive materials may have adverse effects on cell proliferation; 4) Can bioactive materials safe enough for body. Some materials may have adverse effects on kidney or liver function. And such questions need to be solved in future studies.
It is indicated in a study that several miRNAs (including miR-15, miR-16, miR-17, miR-31, miR-126, miR-145, miR-221, miR-222, miR320a, and miR-424) were upregulated in exosomes derived from HIF-1α-MSCs by qRT-PCR analysis [18]. And among these miRNAs, some have been reported to be related to angiogenesis [[40], [41], [42]]. We also found that miR-221 exerted an anti-apoptic effects in cardiomyocytes [43]. Another study has verified the pro-survival effects of miR-221 in a cocktail of three miRNA mimics, on the engrafted stem cells. Therefore, we detected the expression level of miR-221 in HIF-1α-MSCs and EVs derived from HIF-1α-MSCs. However, the mechanisms remain underlying. A study has proved that miR-221 targets PUMA to protect cardiomyocytes [44]. Another study showed that overexpression of miR-221 represses autophagy through targeting the p27/mTOR pathway [45]. In our previous study, we have found that miR-221 expression level is higher in young MSCs than it in aged MSCs and therefore exosomes from young MSCs exerted a better cardioprotection effects via PTEN/akt pathway [46]. However, other molecules in HIF1α-EVs may also exert cardioprotective effects, which should be explored in future studies.
During post-MI cardiac repair, tissue regeneration is a key step. Combination of HIF-1α-EVs with cardiomyocyte inducible stem cells, or EVs with cell fate reprogramming factors, is expected to achieve this goal. Moreover, the efficacy and safety of RGD-biotin hydrogels should be validated with preclinical studies.
5. Conclusion
EVs released by MSCs with stabilized overexpression of HIF-1α can exert angiogenic and anti-apoptotic effects through increasing the expression of miR-221–3p. RGD hydrogels can strengthen the therapeutic efficacy of HIF-1α engineered MSCs-derived EVs on functional, histopathological and molecular levels.
Authors' contributions
QJW, LS, WWZ, YJ contributed to conceptualization, investigation, visualization, and writing the original article. LZ, ZQS, BYC, ALZ, LPM, JGJ contributed to data analysis, investigation, and visualization. XX contributed to synthesis of hydrogels. BYC, ALZ, LPM contributed to perform the experiments. WWZ, YJ contributed to supervision and funding acquisition. LS contributed to conceptualization, data analysis, supervision, and funding acquisition.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Animal used in this study were treated in accordance with the ethics committee guidelines at Nanjing Medical University (No. IACUC-1905024).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets and materials used in the study are available from the corresponding author.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Acknowledgements and Funding
This study was supported by grants from Changzhou Sci&Tech Program (GrantGrant No. CJ20210059), Young Talent Development Plan of Changzhou Health Commission (CZQM2020060), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81901410), Sci&Tech development fund of Nanjing Medical University (NMUB2020069), and the Major Research Plan of Changzhou Health Commission (ZD202020).
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100171.
Contributor Information
Ling Sun, Email: sunling85125@hotmail.com.
Wenwu Zhu, Email: wenwuzhu94xz@163.com.
Yuan Ji, Email: jiyuan1213@aliyun.com.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is/are the supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Roth G.A., Huffman M.D., Moran A.E., Feigin V., Mensah G.A., Naghavi M., Murray C.J. Global and regional patterns in cardiovascular mortality from 1990 to 2013. Circulation. 2015;132(17):1667–1678. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campostrini G., Windt L.M., van Meer B.J., Bellin M., Mummery C.L. Cardiac tissues from stem cells: New routes to maturation and cardiac regeneration. Circ. Res. 2021;128(6):775–801. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rani S., Ritter T. The exosome - a naturally secreted nanoparticle and its application to wound healing. Adv. Mater. 2016;28(27):5542–5552. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Raposo G., Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Orlic D., Hill J.M., Arai A.E. Stem cells for myocardial regeneration. Circ. Res. 2002;91(12):1092–1102. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000046045.00846.b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lener T., Gimona M., Aigner L., Borger V., Buzas E., Camussi G., Chaput N., Chatterjee D., Court F.A., Del Portillo H.A., O'Driscoll L., Fais S., Falcon-Perez J.M., Felderhoff-Mueser U., Fraile L., Gho Y.S., Gorgens A., Gupta R.C., Hendrix A., Hermann D.M., Hill A.F., Hochberg F., Horn P.A., de Kleijn D., Kordelas L., Kramer B.W., Kramer-Albers E.M., Laner-Plamberger S., Laitinen S., Leonardi T., Lorenowicz M.J., Lim S.K., Lotvall J., Maguire C.A., Marcilla A., Nazarenko I., Ochiya T., Patel T., Pedersen S., Pocsfalvi G., Pluchino S., Quesenberry P., Reischl I.G., Rivera F.J., Sanzenbacher R., Schallmoser K., Slaper-Cortenbach I., Strunk D., Tonn T., Vader P., van Balkom B.W., Wauben M., Andaloussi S.E., Thery C., Rohde E., Giebel B. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4:30087. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.30087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rani S., Ryan A.E., Griffin M.D., Ritter T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: toward cell-free therapeutic applications. Mol. Ther. 2015;23(5):812–823. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huang P., Wang L., Li Q., Tian X., Xu J., Xu J., Xiong Y., Chen G., Qian H., Jin C., Yu Y., Cheng K., Qian L., Yang Y. Atorvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction via up-regulating long non-coding RNA H19. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020;116(2):353–367. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sun L., Zhu W., Zhao P., Wang Q., Fan B., Zhu Y., Lu Y., Chen Q., Zhang J., Zhang F. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 from hypoxia-conditioned hMSC-derived exosomes: a novel molecular target for cardioprotection through miR-873-5p/XIAP axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):696. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02783-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sun J., Shen H., Shao L., Teng X., Chen Y., Liu X., Yang Z., Shen Z. HIF-1alpha overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mediates cardioprotection in myocardial infarction by enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020;11(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01881-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cerrada I., Ruiz-Sauri A., Carrero R., Trigueros C., Dorronsoro A., Sanchez-Puelles J.M., Diez-Juan A., Montero J.A., Sepulveda P. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha contributes to cardiac healing in mesenchymal stem cells-mediated cardiac repair. Stem Cell. Dev. 2013;22(3):501–511. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang C., Shang Y., Chen X., Midgley A.C., Wang Z., Zhu D., Wu J., Chen P., Wu L., Wang X., Zhang K., Wang H., Kong D., Yang Z., Li Z., Chen X. Supramolecular nanofibers containing arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD) peptides boost therapeutic efficacy of extracellular vesicles in kidney repair. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):12133–12147. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c05681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mauri E., Sacchetti A., Rossi F. The synthesis of RGD-functionalized hydrogels as a tool for therapeutic applications. JoVE. 2016;116 doi: 10.3791/54445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gallagher L.B., Dolan E.B., O'Sullivan J., Levey R., Cavanagh B.L., Kovarova L., Pravda M., Velebny V., Farrell T., O'Brien F.J., Duffy G.P. Pre-culture of mesenchymal stem cells within RGD-modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel improves their resilience to ischaemic conditions. Acta Biomater. 2020;107:78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xiong X., He Q., Liu J., Dai R., Zhang H., Cao Z., Liao Y., Liu B., Zhou Y., Chen J., Cheng M., Liu J. MicroRNA miR-215-5p regulates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte injury by targeting ZEB2. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021;78(4):622–629. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Killinger M., Vesela B., Prochazkova M., Matalova E., Kleparnik K. A single-cell analytical approach to quantify activated caspase-3/7 during osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021;413:5085–5093. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu W., Sun L., Zhao P., Liu Y., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Hong Y., Zhu Y., Lu Y., Zhao W., Chen X., Zhang F. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor facilitates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction through upregulating miR-133a-3p. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00808-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gonzalez-King H., Garcia N.A., Ontoria-Oviedo I., Ciria M., Montero J.A., Sepulveda P. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha potentiates jagged 1-mediated angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Stem Cell. 2017;35(7):1747–1759. doi: 10.1002/stem.2618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu Y., Luo Q., Su Z., Xing J., Wu J., Xiang L., Huang Y., Pan H., Wu X., Zhang X., Li J., Yan F., Zhang H. Suppression of myocardial hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha compromises metabolic adaptation and impairs cardiac function in patients with cyanotic congenital heart disease during puberty. Circulation. 2021;143(23):2254–2272. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pan Z., Ma G., Kong L., Du G. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1: regulatory mechanisms and drug development in stroke. Pharmacol. Res. 2021;170:105742. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guo Y., Peng Y., Zeng H., Chen G. Progress in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke. Stem Cell. Int. 2021;2021:9923566. doi: 10.1155/2021/9923566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tseng W.C., Lee P.Y., Tsai M.T., Chang F.P., Chen N.J., Chien C.T., Hung S.C., Tarng D.C. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury via enhancing renal tubular autophagy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021;12(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02374-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Razeghian-Jahromi I., Matta A.G., Canitrot R., Zibaeenezhad M.J., Razmkhah M., Safari A., Nader V., Roncalli J. Surfing the clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021;12(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02443-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pathipati P., Lecuyer M., Faustino J., Strivelli J., Phinney D.G., Vexler Z.S. Neurotherapeutics; 2021. Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC)-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Protect from Neonatal Stroke by Interacting with Microglial Cells. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wagner W. Senescence is heterogeneous in mesenchymal stromal cells: kaleidoscopes for cellular aging. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(15):2923–2924. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.15.12741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gregorius J., Wang C., Stambouli O., Hussner T., Qi Y., Tertel T., Borger V., Mohamud Yusuf A., Hagemann N., Yin D., Dittrich R., Mouloud Y., Mairinger F.D., Magraoui F.E., Popa-Wagner A., Kleinschnitz C., Doeppner T.R., Gunzer M., Meyer H.E., Giebel B., Hermann D.M. Small extracellular vesicles obtained from hypoxic mesenchymal stromal cells have unique characteristics that promote cerebral angiogenesis, brain remodeling and neurological recovery after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2021;116(1):40. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00881-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Han J., Yang S., Hao X., Zhang B., Zhang H., Xin C., Hao Y. Extracellular vesicle-derived microRNA-410 from mesenchymal stem cells protects against neonatal hypoxia-ischemia brain damage through an HDAC1-dependent EGR2/bcl2 Axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:579236. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.579236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kang X., Jiang L., Chen X., Wang X., Gu S., Wang J., Zhu Y., Xie X., Xiao H., Zhang J. Exosomes derived from hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells rescue OGD-induced injury in neural cells by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2021;405(1):112635. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guo Z., Wang X., Yang Y., Chen W., Zhang K., Teng B., Huang C., Zhao Q., Qiu Z. Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes angiogenesis via miR-96-5p/AMOTL2 in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:179–195. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bobrie A., Colombo M., Raposo G., Thery C. Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic. 2011;12(12):1659–1668. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang T., Gilkes D.M., Takano N., Xiang L., Luo W., Bishop C.J., Chaturvedi P., Green J.J., Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014;111(31):E3234–E3242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1410041111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang H., Cui J., Zheng Z., Shi Q., Sun T., Liu X., Huang Q., Fukuda T. Assembly of RGD-modified hydrogel micromodules into permeable three-dimensional hollow microtissues mimicking in vivo tissue structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;9(48):41669–41679. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b10960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zheng W., Wang Z., Song L., Zhao Q., Zhang J., Li D., Wang S., Han J., Zheng X.L., Yang Z., Kong D. Endothelialization and patency of RGD-functionalized vascular grafts in a rabbit carotid artery model. Biomaterials. 2012;33(10):2880–2891. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.12.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hoshino A., Costa-Silva B., Shen T.L., Rodrigues G., Hashimoto A., Tesic Mark M., Molina H., Kohsaka S., Di Giannatale A., Ceder S., Singh S., Williams C., Soplop N., Uryu K., Pharmer L., King T., Bojmar L., Davies A.E., Ararso Y., Zhang T., Zhang H., Hernandez J., Weiss J.M., Dumont-Cole V.D., Kramer K., Wexler L.H., Narendran A., Schwartz G.K., Healey J.H., Sandstrom P., Labori K.J., Kure E.H., Grandgenett P.M., Hollingsworth M.A., de Sousa M., Kaur S., Jain M., Mallya K., Batra S.K., Jarnagin W.R., Brady M.S., Fodstad O., Muller V., Pantel K., Minn A.J., Bissell M.J., Garcia B.A., Kang Y., Rajasekhar V.K., Ghajar C.M., Matei I., Peinado H., Bromberg J., Lyden D. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527(7578):329–335. doi: 10.1038/nature15756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bhuniya S., Park S.M., Kim B.H. Biotin-amino acid conjugates: an approach toward self-assembled hydrogelation. Org. Lett. 2005;7(9):1741–1744. doi: 10.1021/ol050300r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Murali V.P., Holmes C.A. Biomaterial-based extracellular vesicle delivery for therapeutic applications. Acta Biomater. 2021;124:88–107. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Firoozi S., Pahlavan S., Ghanian M.H., Rabbani S., Barekat M., Nazari A., Pakzad M., Shekari F., Hassani S.N., Moslem F., Lahrood F.N., Soleimani M., Baharvand H. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alone or in conjunction with a SDKP-conjugated self-assembling peptide improve a rat model of myocardial infarction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020;524(4):903–909. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Han C., Zhou J., Liang C., Liu B., Pan X., Zhang Y., Wang Y., Yan B., Xie W., Liu F., Yu X.Y., Li Y. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels promote cardiac repair. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(7):2920–2933. doi: 10.1039/c9bm00101h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Liu B., Lee B.W., Nakanishi K., Villasante A., Williamson R., Metz J., Kim J., Kanai M., Bi L., Brown K., Di Paolo G., Homma S., Sims P.A., Topkara V.K., Vunjak-Novakovic G. Cardiac recovery via extended cell-free delivery of extracellular vesicles secreted by cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2(5):293–303. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0229-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kang T., Jones T.M., Naddell C., Bacanamwo M., Calvert J.W., Thompson W.E., Bond V.C., Chen Y.E., Liu D. Adipose-derived stem cells induce angiogenesis via microvesicle transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4):440–450. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Witvrouwen I., Mannaerts D., Ratajczak J., Boeren E., Faes E., Van Craenenbroeck A.H., Jacquemyn Y., Van Craenenbroeck E.M. MicroRNAs targeting VEGF are related to vascular dysfunction in preeclampsia. Biosci. Rep. 2021;41(8) doi: 10.1042/BSR20210874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dokhanchi M., Pakravan K., Zareian S., Hussen B.M., Farid M., Razmara E., Mossahebi-Mohammadi M., Cho W.C., Babashah S. Colorectal cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles transfer miR-221-3p to promote endothelial cell angiogenesis via targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Life Sci. 2021;285:119937. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhou Y., Richards A.M., Wang P. MicroRNA-221 is cardioprotective and anti-fibrotic in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:185–197. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yu B., Gong M., Wang Y., Millard R.W., Pasha Z., Yang Y., Ashraf M., Xu M. Cardiomyocyte protection by GATA-4 gene engineered mesenchymal stem cells is partially mediated by translocation of miR-221 in microvesicles. PLoS One. 2013;8(8) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Su M., Wang J., Wang C., Wang X., Dong W., Qiu W., Wang Y., Zhao X., Zou Y., Song L., Zhang L., Hui R. MicroRNA-221 inhibits autophagy and promotes heart failure by modulating the p27/CDK2/mTOR axis. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(6):986–999. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sun L., Zhu W., Zhao P., Zhang J., Lu Y., Zhu Y., Zhao W., Liu Y., Chen Q., Zhang F. Down-regulated exosomal MicroRNA-221 - 3p derived from senescent mesenchymal stem cells impairs heart repair. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:263. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets and materials used in the study are available from the corresponding author.