Abstract
Background
There have been ongoing efforts to understand when and how data from observational studies can be applied to clinical and regulatory decision making. The objective of this review was to assess the comparability of relative treatment effects of pharmaceuticals from observational studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Methods
We searched PubMed and Embase for systematic literature reviews published between January 1, 1990, and January 31, 2020, that reported relative treatment effects of pharmaceuticals from both observational studies and RCTs. We extracted pooled relative effect estimates from observational studies and RCTs for each outcome, intervention-comparator, or indication assessed in the reviews. We calculated the ratio of the relative effect estimate from observational studies over that from RCTs, along with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) for each pair of pooled RCT and observational study estimates, and we evaluated the consistency in relative treatment effects.
Results
Thirty systematic reviews across 7 therapeutic areas were identified from the literature. We analyzed 74 pairs of pooled relative effect estimates from RCTs and observational studies from 29 reviews. There was no statistically significant difference (based on the 95% CI) in relative effect estimates between RCTs and observational studies in 79.7% of pairs. There was an extreme difference (ratio < 0.7 or > 1.43) in 43.2% of pairs, and, in 17.6% of pairs, there was a significant difference and the estimates pointed in opposite directions.
Conclusions
Overall, our review shows that while there is no significant difference in the relative risk ratios between the majority of RCTs and observational studies compared, there is significant variation in about 20% of comparisons. The source of this variation should be the subject of further inquiry to elucidate how much of the variation is due to differences in patient populations versus biased estimates arising from issues with study design or analytical/statistical methods.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12916-021-02176-1.
Keywords: Real-world evidence, Observational data, Pharmaceuticals
Background
Health care decision makers, particularly regulators but also health technology assessment agencies, have depended upon evidence from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to assess drug effectiveness and to make comparisons among treatment options. Widespread adoption of the RCT was the hallmark of progress in clinical research in the twentieth century and accelerated the development and approval of new therapeutics; confidence in RCTs derived from their experimental nature, designs to minimize bias, rigorous data quality, and analytic approaches that supported causal inference.
In the last 30 years, we have witnessed an explosion of observational real-world data (RWD) and evidence (RWE) derived from RWD that has supplemented our understanding of the benefits and risks of treatments in broader populations of patients. RWE has been largely leveraged by regulators to assess the safety of marketed products and for new drug approvals when RCTs are infeasible, such as in rare diseases, oncology, or for long-term adverse effects. RCTs often do not have sufficient sample size to detect rare adverse events or long enough follow-up to detect long-term adverse effects. In such cases, regulatory decisions are often supplemented by RWE. However, leveraging of RWE has been much more slowly embraced in comparison to the adoption of RCTs for a variety of reasons. Imputation of causality is less certain in the absence of randomization and RWD can be much sparser and often requires extensive curation before it can be analyzed. Thus, skepticism about the robustness of observational RWD studies has made decision makers cautious in relying solely upon it to render judgments about the availability and appropriate use of new therapeutics, particularly by regulatory bodies.
Moreover, observational studies examining the effectiveness of treatments in similar populations have not always provided results consistent with RCTs. Despite many studies finding similar treatment effect estimates from RCTs and RWD analyses [1–3], other analyses have documented wide variation in results from RWD analyses within the same therapeutic areas [4], including analyses using propensity score-based methods [5]. Nonetheless, public interest has grown in the routine leveraging of RWD to promote the creation of a learning healthcare system, and regulatory bodies and other decision makers are exploring ways to expand their use of RWE. This is partly due to increasing acknowledgement of the value of RWE, such as its ability to better reflect actual environments in which the interventions are used.
One promising approach to understanding the sources of variability between RCT and observational study results is to compare estimates obtained from RWD analyses that attempt to emulate the eligibility criteria, endpoints, and other features of trials as closely as possible. A small number of RWD analyses have generated findings similar to previous RCTs [6, 7], and the findings of other RWD analyses have been consistent with subsequent RCTs [8]. In a small number of cases, RCTs and RWD studies have been published simultaneously [9]. This has the advantage of not knowing the RCT estimate when conducting the RWD study. There have been disagreements between observational RWD analyses and RCTs that were based upon avoidable errors in the RWD analysis design [7, 10]. This has led to a focus on the importance of research design in observational RWD analyses attempting to draw causal inferences regarding treatment effects [11–13].Emulation studies can improve understanding of when observational studies may reliably generate results consistent with RCTs; however, not all RCTs can be feasibly emulated using RWD due to limitations in observational datasets. Existing sources of observational data, such as health insurance claims and electronic health records (EHRs), may not routinely capture the intervention, indication, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and/or endpoints used in RCTs [14].
The objective of this paper is to provide further evidence on the comparability of RCTs and observational studies when the latter use a range of study designs and were not designed to emulate RCTs. We aim to quantify the extent of the difference in treatment effect estimates between RCTs and observational studies. We go beyond previous comparisons of RCTs and observational studies, with a focus purely on pharmaceuticals, and provide a systematic landscape review of the (in)consistency between RCT and observational study treatment effect estimates. The reasons for the variation in relative treatment effects are not assessed in this review but should be the subject of further study.
Methods
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
- Study design:
- Published systematic literature reviews designed to compare relative treatment effects from observational studies with the corresponding effects from RCTs; or
- Published systematic literature reviews that reported subgroup analyses stratified by RCT and observational study design; and
- Observational studies included in these reviews have to be retrospective or prospective cohort studies, or case-control studies
Population: Human subjects
Intervention(s) and comparator(s): Any active or placebo-controlled pharmaceutical or biopharmaceutical intervention
- Outcome(s):
- Efficacy/effectiveness or safety outcomes
- Pooled relative treatment effect estimates for both observational studies and RCTs
Exclusion criteria
Systematic reviews that compared absolute outcomes, such as event rates, between non-comparative observational studies and RCTs
Non-pharmaceutical-based studies, e.g., surgical procedures, traditional medicine, vitamin/herbal supplements, etc.
Non-English language
Abstracts or conference proceedings
Search strategy
We searched PubMed and Embase to identify relevant systematic literature reviews published between January 1, 1990, and January 31, 2020. Anglemeyer et al.’s search strategy [1] was used as a template to develop the search strategy, which included a wide range of MeSH terms and relevant keywords. We updated Anglemeyer et al.’s systematic review hedge and used the more recent CADTH systematic review/meta-analysis hedge, created in 2016, in both PubMed and Embase [15]. We restricted our search to focus on pharmaceuticals only. PubMed and Embase were searched for the following concepts: pharmaceuticals, study methodology, and comparisons (filters: Humans and English language). The PubMed search strategy which was adapted for use in Embase can be found in Additional File 1.
Study selection
After removing duplicate references, three authors (JG, YH and LO) screened the titles and abstracts to identify relevant reviews. Once complete, LO verified the screening for accuracy. Following the title and abstract screen, full text articles were obtained for all potentially relevant reviews. Full text articles were then assessed to determine if they meet the selection criteria for final inclusion in the review.
Data extraction
A pilot extraction was first done by two authors (JG and YH) on a sample of three articles using a standardized extraction table. This was done to test the standardized extraction table and to ensure consistency between the authors performing the data extraction. JG and YH then independently extracted information from each review using the standardized extraction table. A third author (LO) verified the extraction for accuracy and identified any discrepancies. These discrepancies were discussed until resolved.
We focused on primary outcomes reported in the reviews and extracted information summarizing the scope of each of the identified systematic reviews. Extracted information included the following: review objective, population, disease/therapeutic area, interventions, outcome(s), number of included RCTs and observational studies, pooled relative treatment effect estimates for RCTs and observational studies along with the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI), and measures of heterogeneity.
Analysis
Based on the extracted information, we calculated the ratio of the relative treatment effect estimate from observational studies over the relative treatment effect estimate from RCTs (e.g., RRobs/RRrct), along with the corresponding 95% CI obtained via a Monte Carlo simulation for each pair of pooled RCT and observational study estimates. Outcomes for which the relative treatment effect was not expressed with a relative risk (RR), odds ratio (OR), or hazard ratio (HR) were excluded from our analysis.
We expressed differences in pooled effect estimates with the following measures: ratios that were < 1, > 1, or = 1, ratios indicating an “extreme difference” (< 0.70 or > 1.43) [16] and absence of an extreme difference. We evaluated (in)consistency between pooled RCT and observational study estimates with the following measures: presence of opposite direction of effect, RCT effect estimate outside the 95% CI of the observational study estimate, and vice versa, statistically significant difference between RCT and observational study estimates, and statistically significant difference along with opposite direction of effect. Statistically significant difference was determined by examining the 95% CI of the ratio of the relative treatment effect estimates from observational studies and RCTs derived from the Monte Carlo simulation. We examined differences in relative effect measures from observational studies and RCTs by outcome type and therapeutic area.
To test the robustness of our findings, we conducted two sensitivity analyses. As some reviews assessed more than one endpoint and contributed more than one pair of pooled relative treatment effects from RCTs and observational studies to our analysis, we repeated the analysis with one endpoint per review, i.e., a single pair of pooled relative treatment effects from RCTs and observational studies from each review, selecting the most frequently used endpoints for inclusion whenever possible. Additionally, as some studies were included in more than one review, we repeated the analysis ensuring that there is no overlap of data between the included reviews, i.e., ensuring that each study was included in only one review included in our analysis. Details on the sensitivity analyses are included in Additional File 2. All analyses were conducted using RStudio, version 1.3.1073 (©2009-2020 RStudio, PBC).
Results
Literature search
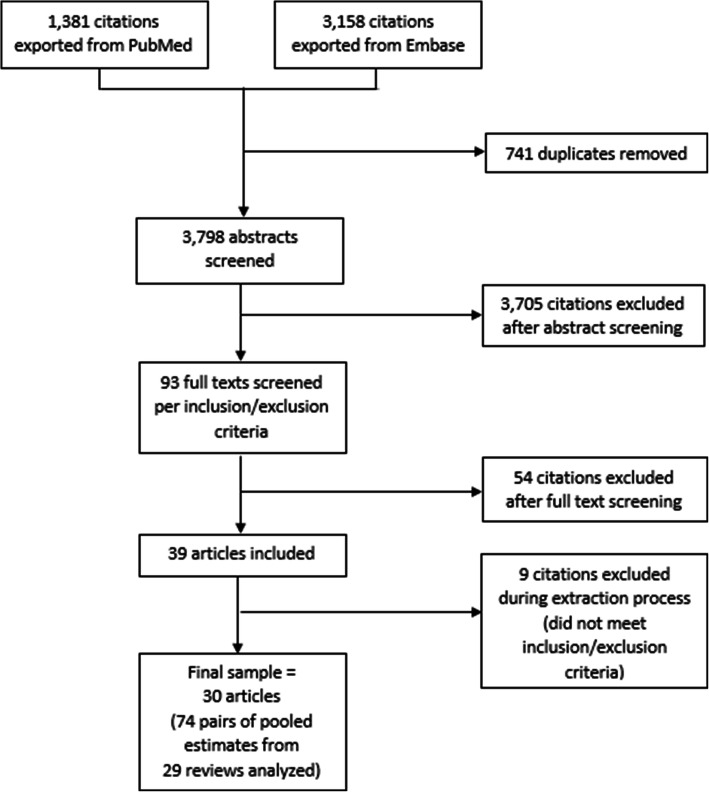
Our search on PubMed and Embase yielded 3798 unique citations after removing duplicates. After screening titles and abstracts, we identified 93 full text articles for further review. Of these, 30 reviews met our inclusion criteria (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Diagram depicting literature screening process
Included systematic reviews
The characteristics of the included reviews and the pairs of pooled relative treatment effects from RCTs and observational studies reported in the reviews are summarized in Table 1. Thirty systematic reviews across 7 therapeutic areas (cardiovascular disease [15/30], infectious disease [6/30], oncology [3/30], mental health [2/30], immune-inflammatory [1/30], metabolic disease [1/30], and other [2/30]) were identified from the literature. These reviews included 519 RCTs and observational studies and provided 79 pairs of pooled relative treatment effects from RCTs and observational studies across multiple interventions, comparators, and outcomes. Five pairs were excluded from our assessment because they concerned continuous outcomes (n = 1) or no pooled effect estimate was reported for observational studies (n = 4). As a result, 74 pairs of pooled relative treatment effects from RCTs and observational studies from 29 reviews were available for assessment of consistency.
Table 1.
Characteristics of included reviews
| Review | Disease | Treatment | Comparator | Endpoint | Number of RCTs | Number of Observational Studies | RCT pooled effect estimate (95% CI) | Observational pooled effect estimate (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abuzaid (2018) [17] | Severe aortic stenosis | Dual anti-platelet therapy (DAPT) | Single anti-platelet therapy (SAPT) | 30-day all-cause mortality | 3 | 7 | RR 1.2 (0.5–2.89) | RR 1.19 (0.74–1.91) |
| Abuzaid (2018) [17] | Severe aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | Longest reported all-cause mortality | 3 | 7 | RR 1.14 (0.54–2.42) | RR 1.06 (0.52–2.18) |
| Abuzaid (2018) [17] | Severe aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | Major bleeding | 3 | 7 | RR 1.74 (0.52–5.82) | RR 2.23 (1.36–3.65) |
| Agarwal (2019) [18] | Acute coronary syndrome (ACS), coronary artery disease (CAD) | Dual therapy | Triple therapy | Major bleeding | 3 | 3 | RR 0.53 (0.38–0.76) | RR 0.88 (0.46–1.67) |
| Agarwal (2018) [19] | CAD | DAPT | Aspirin | Primary outcome: mid- to long-term (> 30 days) composite of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or death | 8 | 4 | RR 0.43 (0.17–1.11) | RR 0.85 (0.72–1.01) |
| An (2019) [20] | Severe aortic stenosis | Antiplatelet | Anticoagulation | Mortality | 2 | 5 | RR 0.82 (0.33–2.03) | RR 0.47 (0.18–1.22) |
| An (2019) [20] | Severe aortic stenosis | Antiplatelet | Anticoagulation | Stroke/transient ischemic attack (TIA) | 2 | 5 | RR 0.9 (0.35–2.33) | RR 0.57 (0.31–1.03) |
| An (2019) [20] | Severe aortic stenosis | Antiplatelet | Anticoagulation | Thromboembolic events | 2 | 5 | RR 1.13 (0.51–2.49) | RR 0.71 (0.38–1.32) |
| An (2019) [20] | Severe aortic stenosis | Antiplatelet | Anticoagulation | Bleeding | 2 | 5 | RR 0.34 (0.11–1.04) | RR 0.34 (0.2–0.58) |
| Chien (2020)* [21] | Multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacteria (MDR-GNB) infections | Colistin | Other antibiotics | Colistin-associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKI) | 1 | 19 | OR 2.75 (0.43–17.49) | Not reported |
| Chien (2020) [21] | MDR-GNB infections | Colistin monotherapy | Colistin combination therapy | Acute kidney injury (AKI) | 3 | 6 | OR 1.77 (1.17–2.66) | OR 1.15 (0.76–1.76) |
| Chopra (2012)* [22] | Pneumonia | Statin therapy | No statin therapy | Unadjusted all-cause mortality following an episode of pneumonia | 1 | 9 | OR 0.84 (0.32–2.18) | Not reported |
| Chopra (2012) [22] | Pneumonia | Statin therapy | No statin therapy | Adjusted all-cause mortality following an episode of pneumonia | 1 | 11 | OR 0.84 (0.32–2.18) | OR 0.66 (0.55–0.79) |
| Desai (2016) [23] | Ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel diseases, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis | Adalimumab | Etanercept | Discontinuation due to adverse events | 1 | 3 | RR 0.83 (0.39–1.78) | Adjusted HR 1.67 (1.26–2.22) |
| Desai (2016) [23] | Ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel diseases, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis | Adalimumab | Infliximab | Discontinuation due to adverse events | 1 | 5 | RR 6.17 (0.78–48.71) | Adjusted HR 0.57 (0.46–0.7) |
| Gandhi (2015) [24] | Aortic stenosis | DAPT | Mono-antiplatelet therapy (MAPT). | Combined end point of 30-day major stroke, spontaneous MI, all-cause mortality, and combined lethal and major bleeding | 2 | 2 | OR 0.98 (0.46–2.11) | OR 3.02 (1.91–4.76) |
| Ge (2018) [25] | Atrial fibrillation | Novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) | Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) | Major bleeding events (Fixed effects model) | 4 | 25 | OR 0.3 (0.14–0.62) | OR 0.68 (0.48–0.95) |
| Ge (2018) [25] | Atrial fibrillation | NOACs | VKAs | Thromboembolic events (Fixed effects model) | 4 | 25 | OR 0.14 (0.01–1.3) | OR 0.91 (0.49–1.67) |
| Heffernan (2020) [26] | Serious infections | β-lactam/aminoglycoside combination therapy | β-lactam monotherapy | All-cause mortality | 2 | 4 | OR 3.18 (0.79–12.73) | OR 0.79 (0.64–0.99) |
| Ho (2013) [27] | Kidney disease (kidney transplant) | Once daily tacrolimus | Twice daily tacrolimus | Biopsy-proven acute rejection (RCT: at 6 months; Observational: mean follow-up ranges from 3 months to 672 months) | 4 | 5 | RR 1.18 (0.82–1.68) | RR 0.83 (0.39–1.78) |
| Ho (2013) [27] | Kidney disease (kidney transplant) | Once daily tacrolimus | Twice daily tacrolimus |
Biopsy-proven acute rejection (RCT: at 12 months Observational: mean follow-up ranges from 3 months to 672 months) |
2 | 5 | RR 1.24 (0.93–1.65) | RR 0.83 (0.39–1.78) |
| Ho (2013) [27] | Kidney disease (kidney transplant) |
RCT: twice daily tacrolimus Observational: once daily tacrolimus |
RCT: once daily tacrolimus Observational: twice daily tacrolimus |
Patient survival (RCT: at 6 months Observational: mean follow-up ranges from 3.5 months to 12 months) |
2 | 2 | RR 1.03 (1–1.06) | RR 1.02 (0.94–1.1) |
| Ho (2013) [27] | Kidney disease (kidney transplant) |
RCT: twice daily tacrolimus Observational: once daily tacrolimus |
RCT: once daily tacrolimus Observational: twice daily tacrolimus |
Patient survival (RCT: at 12 months Observational: mean follow-up ranges from 3.5 months to 12 months) |
3 | 2 | RR 0.99 (0.97–1.02) | RR 1.02 (0.94–1.1) |
| Khan (2019) [28] | CAD | Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) | No PPI | All-cause mortality | 3 | 24 | RR 1.35 (0.56–3.23) | RR 1.25 (1.11–1.41) |
| Kirson (2013)* [29] | Schizophrenia | Depot antipsychotics | Oral antipsychotics | Varies across studies: hospitalization, relapse, discontinuation | 5 | 8 | RR 0.89 (0.64–1.22) | Not reported |
| Land (2017) [30] | Psychiatric illnesses | Clozapine | Control drugs (other antipsychotics) | Hospitalization | 3 | 19 | RR 0.62 (0.41–0.94) | RR 0.75 (0.69–0.81) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: sulfonylurea (SU) |
Heart failure | 38 | 1 | OR 0.97 (0.61–1.56) | Unadjusted OR 0.88 (0.22–3.48) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: SU |
Heart failure | 38 | 1 | OR 0.97 (0.61–1.56) | Adjusted HR 1.10 (1.04–1.17) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes |
RCT: DPP-4 inhibitors Observational: sitagliptin |
RCT: control Observational: SU |
Heart failure | 38 | 1 | OR 0.97 (0.61–1.56) | Unadjusted OR 0.39 (0.02–6.26) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes |
RCT: DPP-4 inhibitors Observational: sitagliptin |
RCT: control Observational: no sitagliptin use |
Heart failure | 38 | 1 | OR 0.97 (0.61–1.56) | Adjusted OR 0.75 (0.38–1.46) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: active control |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 6 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted OR 0.85 (0.74–0.97) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: SU |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 3 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted HR 0.84 (0.74–0.96) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: pioglitazone |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 2 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted HR 0.67 (0.57–0.78) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors |
RCT: control Observational: other oral antidiabetics |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 1 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted OR 0.88 (0.63–1.22) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes | DPP-4 inhibitors | Control | Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 1 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted HR 0.58 (0.38–0.88) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes |
RCT: DPP-4 inhibitors Observational: sitagliptin |
RCT: control Observational: no sitagliptin use |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 2 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted OR 1.41 (0.95–2.09) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes |
RCT: DPP-4 inhibitors Observational: sitagliptin |
RCT: control Observational: no sitagliptin use |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 1 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted HR 1.21 (1.04–1.42) |
| Li (2016) [31] | Diabetes |
RCT: DPP-4 inhibitors Observational: sitagliptin |
RCT: control Observational: no sitagliptin use |
Hospital admission for heart failure | 5 | 1 | OR 1.13 (1.00–1.26) | Adjusted OR 1.84 (1.16–2.92) |
| Melloni (2015) [32] | Unstable angina/non–ST-segment–elevation myocardial infarction (UA/NSTEMI) |
RCT: omeprazole Observational: any PPI |
RCT: placebo Observational: no PPI |
Composite ischemic endpoint at ≈ 1 year | 1 | 20 | HR 0.99 (0.68–1.44) | Adjusted HR 1.35 (1.18–1.54) |
| Melloni (2015) [32] | UA/NSTEMI |
RCT: omeprazole Observational: any PPI |
RCT: placebo Observational: no PPI |
Nonfatal MI at ≈ 1 year | 1 | 10 | HR 0.92 (0.44–1.9) | HR 1.331 (1.146–1.547) |
| Miles (2019) [33] | Heart failure | Furosemide | Torsemide | All-cause mortality | 5 | 3 | OR 1.12 (0.7–1.8) | OR 0.97 (0.44–2.13) |
| Miles (2019) [33] | Heart failure | Furosemide | Torsemide | Heart failure readmissions | 4 | 1 | OR 2.04 (1.16–3.60) | OR 2.91 (0.78–10.91) |
| Miles (2019) [33] | Heart failure | Furosemide | Torsemide | New York Heart Association class improvement | 7 | 2 | OR 0.91 (0.61–1.35) | OR 0.65 (0.50–0.85) |
| Mongkhon (2019) [34] | Atrial fibrillation | OAC | Non-OAC | Risk of dementia | 1 | 4 | RR 1.31 (0.79–2.18) | RR 0.75 (0.67–0.83) |
| Mongkhon (2019) [34] | Atrial fibrillation | VKA | Non-VKA | Risk of dementia | 1 | 4 | RR 1.31 (0.79–2.18) | RR 0.71 (0.68–0.74) |
| Raheja (2018) [35] | Aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | All-cause mortality | 3 | 2 | RR 1.07 (0.48–2.41) | RR 1.34 (0.51–3.48) |
| Raheja (2018) [35] | Aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | Stroke or TIA | 3 | 2 | RR 0.93 (0.28–3.06) | RR 1.25 (0.32–4.92) |
| Raheja (2018) [35] | Aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | MI | 3 | 2 | RR 3.62 (0.60–21.76) | RR 1.18 (0.14–9.98) |
| Raheja (2018) [35] | Aortic stenosis | DAPT | SAPT | Major/life-threatening bleeding | 3 | 3 | RR 1.75 (0.88–3.50) | RR 3.24 (1.82–5.75) |
| Ramjan (2014) [36] | HIV | Fixed-dose combination (FDC) antiretroviral therapy (ART) | Separate tablet regimens | Virological suppression | 4 | 2 | RR 1.04 (0.98–1.10) | RR 1.07 (0.97–1.18) |
| Ramjan (2014) [36] | HIV | FDC ART | Separate tablet regimens | Adherence to ART | 5 | 2 | RR 1.1 (0.98–1.22) | RR 1.17 (1.07–1.28) |
| Shi (2014) [37] | Liver cancer | Statins | Placebo/non-use | Liver cancer | 1 | 11 | RR 1.06 (0.66–1.71) | RR 0.57 (0.50–0.64) |
| Teo (2014) [38] | Acute infections | Prolonged infusion, which was defined as administration of either extended infusion or continuous infusion of beta-lactam antibiotics | Identical beta-lactams that were administered as intermittent boluses (20–60 min infusion) according to the manufacturer’s package insert | All-cause in-hospital mortality | 10 | 9 | RR 0.83 (0.57–1.21) | RR 0.57 (0.43–0.76) |
| Teo (2014) [38] | Acute infections | Prolonged infusion, which was defined as administration of either extended infusion or continuous infusion of beta-lactam antibiotics. | Identical beta-lactams that were administered as intermittent boluses (20–60 min infusion) according to the manufacturer’s package insert | Clinical success (cure or improvement) | 14 | 5 | RR 1.05 (0.99–1.12) | RR 1.34 (1.02–1.76) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Total (any) cancer incidence | 3 | 7 | RR 1.01 (0.93–1.10) | OR 0.72 (0.55–0.93) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Cancer mortality | 1 | 7 | RR 1.02 (0.80–1.30) | OR 0.76 (0.59–0.97) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Colorectal cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Colorectal cancer risk | 2 | 1 | RR 0.99 (0.69–1.43) | OR 0.80 (0.68–0.94) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Lung cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Lung cancer risk | 2 | 5 | RR 1.16 (0.89–1.50) | OR 0.74 (0.43–1.28) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Breast cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Breast cancer risk | 1 | 8 | RR 2.04 (0.44–9.55) | OR 1.09 (0.87–1.37) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Bladder cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Bladder cancer risk | 2 | 2 | RR 1.07 (0.76–1.52) | OR 0.65 (0.46–0.92) |
| Vinceti (2018) [39] | Prostate cancer | Highest selenium exposure | Lowest selenium exposure | Prostate cancer risk | 4 | 21 | RR 1.01 (0.90–1.14) | OR 0.84 (0.75–0.95) |
| Wang (2019) [40] | Pneumonia | PPI | No PPI | Pneumonia | 10 | 48 | OR 1.13 (0.71–1.78) | OR 1.45 (1.32–1.59) |
| Wat (2019) [41] | Traumatic brain injury (TBI) | Antiepileptic drugs | Placebo/no treatment | Early seizures after TBI | 3 | 6 | RR 0.58 (0.20–1.72) | RR 0.42 (0.29–0.62) |
| Wong (2017)* [42] | Coronary heart disease/CAD | Macrolides | Placebo/no treatment | Short-term primary outcome (defined as cardiac mortality, cardiovascular mortality, sudden death, cardiac arrest, all-cause mortality, or composite outcomes including death and/or other cardiovascular events or procedures) | 5 | 15 | RR 0.99 (0.74–1.34) | Not reported |
| Wong (2017) [42] | Coronary heart disease/CAD | Macrolides | Placebo/no treatment | Long term primary outcome (defined as cardiac mortality, cardiovascular mortality, sudden death, cardiac arrest, all-cause mortality, or composite outcomes including death and/or other cardiovascular events or procedures) | 14 | 8 | RR 1.03 (0.96–1.10) | RR 1.05 (0.91–1.22) |
| Yang (2019)* [43] | Cancer | Epoetin alfa biosimilar drugs | Epoetin alfa drugs | Mean of hemoglobin increase | 1 | 4 | WMD -0.02 (− 0.38–0.34) | WMD 0.07 (− 0.12–0.25) |
| Yang (2019) [43] | Cancer | Epoetin alfa biosimilar drugs | Epoetin alfa drugs | Hemoglobin response | 1 | 1 | RR 1.09 (0.86–1.38) | RR 1.18 (0.87–1.60) |
| Yang (2019) [43] | Breast cancer | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) biosimilar drugs | G-CSF drugs | Febrile neutropenia in cycle 1 | 5 | 3 | RR 1.14 (0.80–1.63) | RR 1.36 (0.84–2.23) |
| Yang (2019) [43] | NHL | G-CSF biosimilar drugs | G-CSF drugs | Febrile neutropenia in cycle 1 | 1 | 1 | RR 0.54 (0.20–1.46) | RR 0.87 (0.20–3.85) |
| Yang (2019) [43] | Cancer | G-CSF biosimilar drugs (filgrastim biosimilars) | G-CSF drugs | Bone pain | 4 | 4 | RR 0.90 (0.78–1.05) | RR 0.86 (0.59–1.24) |
| Yu (2018) [44] | Non-cardiac vascular disease | Statins | Placebo/no statin treatment | All-cause mortality | 3 | 6 | OR 0.62 (0.41–0.92) | OR 0.65 (0.48–0.88) |
| Yu (2018) [44] | Non-cardiac vascular disease | Statins | Placebo/no statin treatment | Primary patency | 1 | 10 | OR 0.39 (0.09–1.65) | OR 0.77 (0.59–0.99) |
| Yu (2018) [44] | Non-cardiac vascular disease | Statins | Placebo/no statin treatment | Amputation | 1 | 10 | OR 0.47 (0.07–2.94) | OR 0.64 (0.50–0.83) |
| Yu (2018) [44] | Non-cardiac vascular disease | Statins | Placebo/no statin treatment | Cardiovascular events | 3 | 2 | OR 0.55 (0.36–0.83) | OR 0.87 (0.16–4.60) |
| Zhang (2019) [45] | Atrial fibrillation | NOAC | Non-NOAC therapy | Renal impairment | 11 | 3 | HR 0.82 (0.71–0.93) | HR 0.64 (0.58–0.69) |
| Zhao (2018) [46] | CAD | DAPT | SAPT | Any bleeding events | 5 | 8 | RR 1.25 (0.98–1.59) | RR 0.87 (0.76–1.01) |
| Zhao (2018) [46] | CAD | DAPT | SAPT | Minor bleeding events | 4 | 3 | RR 1.15 (0.73–1.81) | RR 0.84 (0.37–1.93) |
| Zhao (2018) [46] | CAD | DAPT | SAPT | Major bleeding events | 5 | 6 | RR 1.28 (0.95–1.71) | RR 0.99 (0.66–1.51) |
| Zhao (2018) [46] | CAD | DAPT | SAPT | Major bleeding events during hospitalization (random effects model) | 3 | 3 | RR 1.27 (0.91–1.78) | RR 0.50 (0.12–2.09) |
*Not included in the analysis
Ratio of relative effect measures from observational studies and RCTs
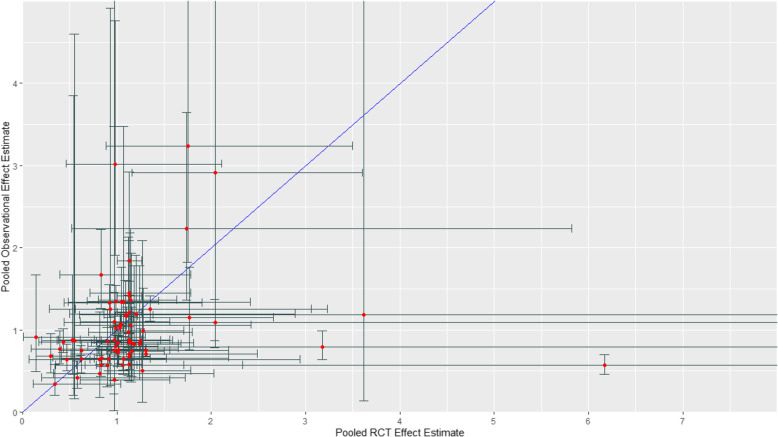
Figure 2 presents the scatterplot of relative effect measures from observational studies and RCTs across the 74 pairs of pooled relative treatment effects with the 95% CI bars. The ratio of the relative effect measure from observational studies over the corresponding relative effect measure from RCTs ranged from 0.09 to 6.50 (median = 0.92, interquartile range = 0.69–1.27). The ratio was greater than 1, i.e., the relative effect was larger in observational studies in 31 of the 74 pairs (41.9%). The ratio was less than 1, i.e., the relative effect was larger in RCTs in 42 of the 74 pairs (56.8%), and the ratio was equal to 1 in one of the 74 pairs (1.4%). The ratio was greater than 1.43 in 12 of the 74 pairs (16.2%) and less than 0.7 in 20 of the 74 pairs (27.0%) indicating an extreme difference. There was an absence of an extreme difference (0.7 ≤ ratio ≤ 1.43) in 42 of the 74 pairs (56.8%; Table 2). Sensitivity analyses including only one endpoint from each review and ensuring no overlap of data between the included reviews resulted in similar findings (Table 2). Scatterplots of relative effect measures from observational studies and RCTs by outcome type and therapeutic area can be found in Additional File 3: Figures S1 and S2.
Fig. 2.
Relative effect measures (RR, OR, HR) from observational studies (y-axis) versus corresponding relative effect measures from randomized controlled trials (x-axis) across 74 pairs of pooled relative treatment effects
Table 2.
Ratio of relative effect measures from observational studies and relative effect measures from RCTs (e.g., RRobs/RRrct): (a) among 74 pairs of pooled estimates, (b) with only one endpoint per review included, and (c) with studies reported in multiple reviews excluded
| Full sample | One endpoint per review | Studies reported in multiple reviews excluded | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion | % | Proportion | % | Proportion | % | |
| Ratio > 1*a | 31/74 | 41.9 | 12/29 | 41.4 | 24/65 | 36.9 |
| Ratio < 1*b | 42/74 | 56.8 | 17/29 | 58.6 | 40/65 | 61.5 |
| Ratio = 1* | 1/74 | 1.4 | 0/29 | 0.0 | 1/65 | 1.5 |
| Extreme difference (ratio > 1.43) | 12/74 | 16.2 | 5/29 | 17.2 | 8/65 | 12.3 |
| Extreme difference (ratio < 0.7) | 20/74 | 27.0 | 8/29 | 27.6 | 19/65 | 29.2 |
| Absence of an extreme difference (0.7 ≤ ratio ≤ 1.43) | 42/74 | 56.8 | 16/29 | 55.2 | 38/65 | 58.5 |
*Does not account for direction of effect
aRelative effect larger in observational studies
bRelative effect larger in RCTs
Consistency of relative effect measures from observational studies and RCTs
In 30 of the 74 pairs (40.5%), effect estimates from observational studies and RCTs pointed in opposite directions of effect. The RCT point estimate was outside the 95% CI of the observational study in 35 of the 74 pairs (47.3%) and the observational study point estimate was outside the 95% CI of the RCT in 27 of the 74 pairs (36.5%). There was a statistically significant difference between relative effect estimates from observational studies and RCTs in 15 of the 74 pairs (20.3%). In 13 of the 74 pairs (17.6%), there was a statistically significant difference and the effect estimates of observational studies and RCTs pointed in opposite directions (Table 3). The results remained fairly consistent when the sensitivity analyses were conducted (Table 3).
Table 3.
Consistency of relative effect measures from observational studies and relative effect measures from RCTs: (a) among 74 pairs of pooled estimates, (b) with only one endpoint per review included, and (c) with studies reported in multiple reviews excluded
| Full sample | One endpoint per review | Studies reported in multiple reviews excluded | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion | % | Proportion | % | Proportion | % | |
| Effect estimates of observational studies and RCTs in opposite directions | 30/74 | 40.5 | 11/29 | 37.9 | 26/65 | 40.0 |
| RCT effect estimate outside the observational study 95% CI | 35/74 | 47.3 | 17/29 | 58.6 | 29/65 | 44.6 |
| Observational effect estimate outside the RCT 95% CI | 27/74 | 36.5 | 11/29 | 37.9 | 25/65 | 38.5 |
| Statistically significant difference | 15/74 | 20.3 | 7/29 | 24.1 | 14/65 | 21.5 |
| Statistically significant difference and effect estimates of observational studies and RCTs in opposite directions | 13/74 | 17.6 | 6/29 | 20.7 | 12/65 | 18.5 |
Discussion
Our analysis of 29 reviews comparing results of RCTs and observational studies of pharmaceuticals showed, on average, no significant differences in their relative risk ratios across all studies, but also considerable study-by-study variability. The median ratio of the relative effect measure from observational studies to RCTs was 0.92, indicating just slightly lower effectiveness/safety estimates in observational studies than corresponding RCTs. This is in fact somewhat higher than the 0.80 ratio recently found in meta-research comparing effect estimates of randomized clinical trials that use routinely collected data (i.e., from traditional observational study sources such as registries, electronic health records, or administrative claims) for outcome ascertainment with traditional trials not using routinely collected data [47]. However, whether judging by the frequency of “extreme” differences (43.2%) or statistically significant differences in opposite directions (17.6%), one could not claim that observational study results consistently replicated RCT results on a study-by-study basis in our sample.
There are a number of reasons that any given observational study result may not replicate an RCT comparing the same treatments. First, it may not have been the intent of the observational study researchers to match a specific clinical trial—they may have intentionally studied a different treatment population, setting, or protocol in order to complement or test the RCT findings. In such cases, there would be variation in effect estimates due to estimating a different causal effect. Even if the researcher does attempt to match a specific RCT, the data may not have been available to closely match it, since patient histories, test results, etc., used for RCT inclusion criteria may not be observed, or outcomes may not be captured the same way. Even given similar data, non-randomized studies have the potential for selection/channeling bias into treatment determined by factors unobservable in either type of study, and analytic attempts to correct for such confounding may have limited success. In some cases, treatment conditions may differ enough between the RCT and real-world practice that replication of results should not be expected, e.g., due to careful safety monitoring that affects subsequent treatment in RCTs. Finally, it is possible that other pharmacoepidemiologic principles, beyond the study design considerations we already mentioned, were violated in the individual RWD studies, which could have caused disagreement between their results and the RCTs. While variation in treatment effect estimates due to estimating a different causal effect in a different study population is expected and valid, biased estimates arising from issues with study design or analytical methods may be problematic.
Details in these reviews were typically insufficient to distinguish among these possible explanations, without detailed review of the individual studies, which we did not attempt here. However, some reviews did attempt to explain the differences they found. For example, in the review by Gandhi et al. (2015) [24], which compared dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) to mono-antiplatelet therapy (MAPT) following transcatheter aortic valve implantation, there was a statistically significant difference in pooled relative treatment effect estimates from observational studies and RCTs. The primary outcome was more likely to occur in the DAPT group than in the MAPT group in the observational studies (OR 3.02; 95% CI 1.91–4.76); however, no statistically significant difference was found between DAPT and MAPT in the RCTs (OR 0.98; 95% CI 0.46–2.11). The authors explained that the RCTs (n = 2) and observational studies (n = 2) included in this review had variable patient inclusion/exclusion criteria and there were differences in the type of prosthetic aortic valve used, which may have introduced selection bias [24].
To allow for better use of individual observational studies to inform decision-making, their ability to replicate RCT results needs to become more reliable, and the “target trial” approach seems to be a path forward. Several systematic efforts using sophisticated observational data research designs to emulate multiple RCTs are underway [48, 49]. These efforts are intended to provide regulatory bodies and other decision makers with empirical evidence to support the development of a framework for assessing when and under what circumstances observational RWE can be used to support a wider range of regulatory decisions. RCT DUPLICATE is a collaboration between the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology, to replicate 30 completed Phase III or IV trials and to predict the results of seven ongoing Phase IV trials using Medicare and commercial claims data [50]. The RCT DUPLICATE team has recently reported results for its first 10 trials [51]. They report hazard ratio estimates within the 95% CI of the corresponding trial for 8 of 10 emulations.
The Multi-Regional Clinical Trials Center and OptumLabs are leading another effort called Observational Patient Evidence for Regulatory Approval and Understanding Disease (OPERAND) which extends the trial emulation activity and relaxes the inclusion/exclusion criteria of the trials to examine treatment effects in the broader patient population treated in routine care [52]. The FDA has also funded the Yale University-Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation to predict the results of three to four ongoing safety trials using OptumLabs claims data [53].
It is important to understand that clinical trials emulation efforts are being conducted solely to improve understanding of when observational studies may be expected to produce robust results. Bartlett and colleagues [14] found that in a review of 220 clinical trials published in high impact medical journals in 2017, 15% could potentially be emulated using data available from medical claims or EHRs. For example, the inclusion/exclusion criteria for many oncology trials require data on genetic markers and progression free survival unavailable in EHRs. The estimate by Bartlett and colleagues may prove to be an underestimate as the ability to link different types of observational data continues to improve. Nevertheless, it is reasonable to assume that it is not possible to emulate most trials with existing observational datasets.
These efforts are critical to advance our understanding of the strengths and limitations of observational RWE, identifying issues with study design, endpoint definition, data quality, and analytical methodology that may impact the consistency of findings between RWE and RCTs. While much attention has focused on differences in study populations between observational studies and RCTs as the reason for the inconsistency in effect estimates, emerging evidence suggests that issues with study design (e.g., establishing time zero of exposure) may be equally if not more important [7]. Therefore, the results of these efforts will not provide definitive guidance to decision makers but they emphasize how even subtle differences in study design and endpoint definition can impact absolute estimates of treatment effect. Moreover, RWE studies are answering a different question than RCTs, i.e., “Does it work?” verses “Can it Work?” The former is important to a variety of stakeholders beyond regulators. Hence, they should not be expected to provide results identical to RCTs.
Conclusions
In conclusion, although our review shows no average significant difference in the relative risk ratios between published RCTs and observational studies, there is substantial study-to-study variation. It was impractical to review all individual observational study designs and examine their potential biases, but future work should elucidate how much of the variation is due to differences in study populations versus biased estimates arising from issues with study design or analytical methods. As more target trial replication attempts are conducted and published, more systematic evidence will emerge on the reliability of this approach and on the potential for observational studies to more routinely inform healthcare decisions.
Supplementary Information
Additional File 2:. Sensitivity Analyses
Additional File 3:. Figures S1 & S2. Figure S1. Relative effect measures from observational studies versus corresponding relative effect measures from randomized controlled trials by outcome type. Figure S2. Relative effect measures from observational studies versus corresponding relative effect measures from randomized controlled trials by therapeutic area.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- CI
Confidence interval
- DAPT
Dual-antiplatelet therapy
- EHR
Electronic health record
- FDA
Food and Drug Administration
- HR
Hazard ratio
- MAPT
Mono-antiplatelet therapy
- OPERAND
Observational Patient Evidence for Regulatory Approval and Understanding Disease
- OR
Odds ratio
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- RWD
Real-world data
- RWE
Real-world evidence
- RR
Relative risk
Authors’ contributions
YH contributed to the extraction, analysis, and interpretation of the data and contributed to the drafting and revising the manuscript. JJ contributed to the design of the study, was a major contributor to the analysis and interpretation of the data, and contributed to the revision of the manuscript. JG contributed to the coordination of the study, extraction of the data, and drafting of the manuscript. MB, WC, and RW contributed to the design of the study, interpretation of the results, drafting of the manuscript, and revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. WG and CDM contributed to the design of the study, interpretation of the results, and revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. LO coordinated the study and contributed to the data extraction, interpretation of the results, drafting the manuscript, and revising the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Availability of data and materials
The data analyzed in this study are included in this published article.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Yoon Duk Hong, John Guerino, Marc L. Berger, William Crown, Richard J. Willke, Wim G. Goettsch, and Lucinda S. Orsini have no conflicts of interest to report. Jeroen P. Jansen is a part-time employee of Precision Medicine Group (PMG) (PRECISIONheor) and has stock options from Precision Medicine Group. PMG provides contracted research services to pharmaceutical and biotech industry. C. Daniel Mullins has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Incyte, Merck, Pfizer, and Takeda and has received support from Bayer and Pfizer for attending meetings and/or travel.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Anglemyer A, Horvath HT, Bero L. Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;4(4):MR000034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000034.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Concato J, Shah N, Horwitz RI. Randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and the hierarchy of research designs. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(25):1887–1892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200006223422507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Benson K, Hartz AJ. A comparison of observational studies and randomized, controlled trials. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(25):1878–1886. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200006223422506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Madigan D, Ryan P, Schuemie M, et al. Evaluating the impact of database heterogeneity on observational study results. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;178(4):645–651. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Forbes S, Dahabreh I. Benchmarking observational analyses against randomized trials: a review of studies assessing propensity score methods. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(5):1396–1404. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05713-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seeger J, Bykov K, Bartels D, Huybrechts K, Zint K, Schneeweiss S. 2015. Safety and effectiveness of dabigatran and warfarin in routine care of patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost. 2015;114(6):1277–1289. doi: 10.1160/TH15-06-0497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dickerman B, Garcia-Albeniz X, Logan R, et al. Avoidable flaws in observational analyses: an application to statins and cancer. Nat Med. 2019;25(10):1601–1606. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0597-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schneeweiss S, Seeger JD, Landon J, Walker AM. Aprotinin during coronary-artery bypass grafting and risk of death. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(8):771–783. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0707571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Noseworthy P, Gersh B, Kent D, et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation in practice: assessing CABANA generalizability. Peter A NoseworthyRobert D. and Patricia E. Kern Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery, Mayo Clinic, 200 1st St SW, Rochester, MN, USA. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(16):1257–1264. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hernán MA, Alonso A, Logan R, Grodstein F, Michels KB, Willett WC, Manson JAE, Robins JM. Observational studies analyzed like randomized experiments: an application to postmenopausal hormone therapy and coronary heart disease. Epidemiology. 2008;19(6):766–779. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181875e61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Petersen M, van der Laan M. Causal models and learning from data: integrating causal modeling and statistical estimation. Epidemiology. 2014;25(3):418–426. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goodman S, Schneeweiss S, Baiocchi M. Using design thinking to differentiate useful from misleading evidence in observational research. JAMA. 2017;317(7):705–707. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.19970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Franklin JM, Schneeweiss S. When and How can real world data analyses substitute for randomized controlled trials? Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;102(6):924–933. doi: 10.1002/cpt.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bartlett V, Dhruva S, Shah N, Ryan P, Ross J. Feasibility of using real-world data to replicate clinical trial evidence. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(10):e1912869. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Strings attached: CADTH database search filters [Internet]. Ottawa: CADTH; 2016. Available from: https://www.cadth.ca/resources/finding-evidence
- 16.Dahabreh IJ, Sheldrick RC, Paulus JK, Chung M, Varvarigou V, Jafri H, Rassen JA, Trikalinos TA, Kitsios GD. Do observational studies using propensity score methods agree with randomized trials? A systematic comparison of studies on acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(15):1893–1901. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abuzaid A, Ranjan P, Fabrizio C, et al. Single anti-platelet therapy versus dual anti-platelet therapy after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a meta-analysis. Structural Heart. 2018;2(5):408–418. doi: 10.1080/24748706.2018.1491082. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Agarwal N, Mahmoud AN, Mojadidi MK, Golwala H, Elgendy IY. Dual versus triple antithrombotic therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention-meta-analysis and meta-regression. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2019;20(12):1134–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2019.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Agarwal N, Mahmoud AN, Patel NK, Jain A, Garg J, Mojadidi MK, Agrawal S, Qamar A, Golwala H, Gupta T, Bhatia N, Anderson RD, Bhatt DL. Meta-analysis of aspirin versus dual antiplatelet therapy following coronary artery bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol. 2018;121(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.An KR, Belley-Cote EP, Um KJ, Gupta S, McClure G, Jaffer IH, Pandey A, Spence J, van der Wall S, Eikelboom JW, Whitlock RP. Antiplatelet therapy versus anticoagulation after surgical bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2019;119(2):328–339. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chien HT, Lin YC, Sheu CC, Hsieh KP, Chang JS. Is colistin-associated acute kidney injury clinically important in adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(3):105889. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chopra V, Rogers MA, Buist M, Govindan S, Lindenauer PK, Saint S, Flanders SA. Is statin use associated with reduced mortality after pneumonia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2012;125(11):1111–1123. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Desai RJ, Thaler KJ, Mahlknecht P, Gartlehner G, McDonagh MS, Mesgarpour B, Mazinanian A, Glechner A, Gopalakrishnan C, Hansen RA. Comparative risk of harm associated with the use of targeted immunomodulators: a systematic review. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(8):1078–1088. doi: 10.1002/acr.22815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gandhi S, Schwalm JD, Velianou JL, Natarajan MK, Farkouh ME. Comparison of dual-antiplatelet therapy to mono-antiplatelet therapy after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Cardiol. 2015;31(6):775–784. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ge Z, Faggioni M, Baber U, Sartori S, Sorrentino S, Farhan S, Chandrasekhar J, Vogel B, Qadeer A, Halperin J, Reddy V, Dukkipati S, Dangas G, Mehran R. Safety and efficacy of nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Ther. 2018;36(5):e12457. doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Heffernan AJ, Sime FB, Sun J, Lipman J, Kumar A, Andrews K, Ellwood D, Grimwood K, Roberts J. Beta-lactam antibiotic versus combined beta-lactam antibiotics and single daily dosing regimens of aminoglycosides for treating serious infections: a meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(3):105839. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ho ET, Wong G, Craig JC, Chapman JR. Once-daily extended-release versus twice-daily standard-release tacrolimus in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review. Transplantation. 2013;95(9):1120–1128. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318284c15b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khan SU, Lone AN, Asad ZUA, Rahman H, Khan MS, Saleem MA, Arshad A, Nawaz N, Sattur S, Kaluski E. Meta-Analysis of efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors with dual antiplatelet therapy for coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2019;20(12):1125–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2019.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kirson NY, Weiden PJ, Yermakov S, Huang W, Samuelson T, Offord SJ, Greenberg PE, Wong BJO. Efficacy and effectiveness of depot versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: synthesizing results across different research designs. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(6):568–575. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12r08167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Land R, Siskind D, McArdle P, Kisely S, Winckel K, Hollingworth SA. The impact of clozapine on hospital use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(4):296–309. doi: 10.1111/acps.12700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li L, Li S, Deng K, Liu J, Vandvik PO, Zhao P, Zhang L, Shen J, Bala MM, Sohani ZN, Wong E, Busse JW, Ebrahim S, Malaga G, Rios LP, Wang Y, Chen Q, Guyatt GH, Sun X. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and observational studies. BMJ. 2016;352:i610. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Melloni C, Washam JB, Jones WS, Halim SA, Hasselblad V, Mayer SB, Heidenfelder BL, Dolor RJ. Conflicting results between randomized trials and observational studies on the impact of proton pump inhibitors on cardiovascular events when coadministered with dual antiplatelet therapy: systematic review. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8(1):47–55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.114.001177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miles JA, Hanumanthu BK, Patel K, Chen M, Siegel RM, Kokkinidis DG. Torsemide versus furosemide and intermediate-term outcomes in patients with heart failure: an updated meta-analysis. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2019;20(6):379–388. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mongkhon P, Naser AY, Fanning L, Tse G, Lau WCY, Wong ICK, Kongkaew C. Oral anticoagulants and risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019;96:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Raheja H, Garg A, Goel S, Banerjee K, Hollander G, Shani J, Mick S, White J, Krishnaswamy A, Kapadia S. Comparison of single versus dual antiplatelet therapy after TAVR: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;92(4):783–791. doi: 10.1002/ccd.27582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ramjan R, Calmy A, Vitoria M, Mills EJ, Hill A, Cooke G, Ford N. Systematic review and meta-analysis: patient and programme impact of fixed-dose combination antiretroviral therapy. Trop Med Int Health. 2014;19(5):501–513. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shi M, Zheng H, Nie B, Gong W, Cui X. Statin use and risk of liver cancer: an update meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2014;4(9):e005399. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Teo J, Liew Y, Lee W, Kwa AL. Prolonged infusion versus intermittent boluses of Î2-lactam antibiotics for treatment of acute infections: a meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;43(5):403–411. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vinceti M, Filippini T, Del Giovane C, Dennert G, Zwahlen M, Brinkman M, Zeegers MP, Horneber M, D'Amico R, Crespi CM. Selenium for preventing cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1:CD005195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005195.pub4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang CH, Li CH, Hsieh R, Fan CY, Hsu TC, Chang WC, Hsu WT, Lin YY, Lee CC. Proton pump inhibitors therapy and the risk of pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019;18(3):163–172. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2019.1577820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wat R, Mammi M, Paredes J, Haines J, Alasmari M, Liew A, Lu VM, Arnaout O, Smith TR, Gormley WB, Aglio LS, Mekary RA, Zaidi H. The effectiveness of antiepileptic medications as prophylaxis of early seizure in patients with traumatic brain injury compared with placebo or no treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:433–440. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.11.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wong AYS, Chan EW, Anand S, Worsley AJ, Wong ICK. Managing cardiovascular risk of macrolides: systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Saf. 2017;40(8):663–677. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yang J, Yu S, Yang Z, Yan Y, Chen Y, Zeng H, Ma F, Shi Y, Shi Y, Zhang Z, Sun F. Efficacy and safety of supportive care biosimilars among cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BioDrugs. 2019;33(4):373–389. doi: 10.1007/s40259-019-00356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yu W, Wang B, Zhan B, Li Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Yan Z. Statin therapy improved long-term prognosis in patients with major non-cardiac vascular surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018;109:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang C, Gu ZC, Ding Z, Shen L, Pan MM, Zheng YL, Lin HW, Pu J. Decreased risk of renal impairment in atrial fibrillation patients receiving non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants: a pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials and real-world studies. Thromb Res. 2019;174:16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2018.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhao Y, Peng H, Li X, Qin Y, Cao F, Peng D, Liu J. Dual antiplatelet therapy after coronary artery bypass surgery: is there an increase in bleeding risk? A meta-analysis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;26(4):573–582. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivx374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.McCord KA, Ewald H, Agarwal A. Treatment effects in randomised trials using routinely collected data for outcome assessment versus traditional trials: meta-research study. BMJ. 2021;372:n450. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thompson D. Replication of randomized, controlled trials using real world data: what could go wrong? Value Health. 2021;24(1):112–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Crown W, Bierer B. Real-world evidence: understanding sources of variability through empirical analysis. Value Health. 2021;24(1):116–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.FDA Prediction Project – RCT DUPLICATE [Internet]. Available from: www.rctduplicate.org
- 51.Franklin J, Patorno E, Desai R, et al. Emulating randomized clinical trials with nonrandomized real-world evidence studies: first results from the RCT DUPLICATE initiative. Circulation. 2021;143(10):1002–1013. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Evaluating RWE from observational studies in regulatory decision-making: lessons learned from trial replication analyses. Trial Emulation Studies and OPERAND. Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy Virtual Meeting, February 16-17, 2021.
- 53.Yale School of Medicine. Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE). Current Projects. https://medicine.yale.edu/core/current_projects/cersi/research/.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional File 2:. Sensitivity Analyses
Additional File 3:. Figures S1 & S2. Figure S1. Relative effect measures from observational studies versus corresponding relative effect measures from randomized controlled trials by outcome type. Figure S2. Relative effect measures from observational studies versus corresponding relative effect measures from randomized controlled trials by therapeutic area.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed in this study are included in this published article.