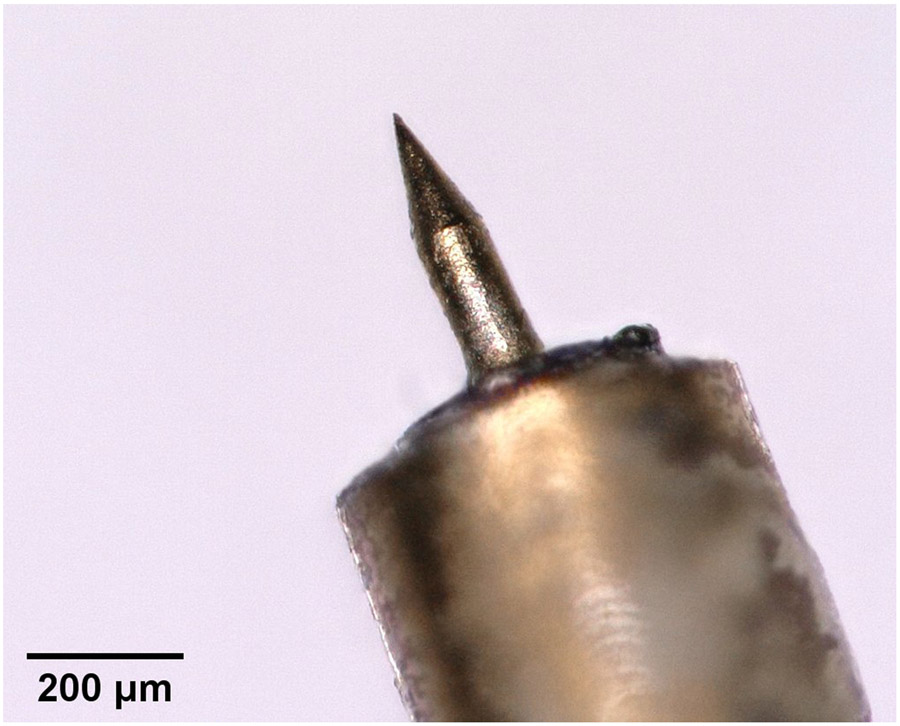
Abstract
Drug delivery into the inner ear is a significant challenge due to its inaccessibility as a fluid-filled cavity within the temporal bone of the skull. The Round Window Membrane (RWM) is the only delivery portal from the middle ear to the inner ear that does not require perforation of bone. Recent advances in microneedle fabrication enable the RWM to be perforated safely with polymeric microneedles as a means to enhance the rate of drug delivery from the middle ear to the inner ear. However the polymeric material is not biocompatible and also lacks the strength of other materials. Herein we describe the design and development of gold-coated metallic microneedles suitable for RWM perforation. When developing microneedle technology for drug delivery, we considered three important general attributes: (1) high strength & ductility material, (2) high accuracy & precision of fabrication, and (3) broad design freedom. We developed a hybrid additive manufacturing method using two-photon lithography and electrochemical deposition to fabricate ultra-sharp gold-coated copper microneedles with these attributes. We refer to the microneedle fabrication methodology as two-photon templated electrodeposition (2PTE). We demonstrate the use of these microneedles by inducing a perforation with a minimal degree of trauma in a guinea pig RWM while the microneedle itself remains undamaged. Thus this microneedle has the potential literally of opening the RWM for enhanced drug delivery into the inner ear. Finally, the 2PTE methodology can be applied to many different classes of microneedles for other drug delivery purposes as well the fabrication of small scale structures and devices for non-medical applications.
Keywords: Microneedles, Nanoscribe, Hybrid Additive Manufacturing, Inner Ear Drug Delivery, Round Window Membrane, Electrochemical Deposition, 2PTE
Graphical Abstract
Fully metallic microneedle mounted at end of 24 gauge stainless steel blunt needle tip: (left) Size of microneedle shown relative to date stamp on U.S. one-cent coin; (right) Perforation through Guinea pig Round Window Membrane introduced with microneedle.
1. Introduction
Drug delivery into the cochlea – a fluid-filled cavity within the temporal bone of the skull – is a longstanding medical challenge, yet essential to treat a variety of hearing disorders such as sudden or progressive sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus, as well as vestibular disorders such as Ménière’s disease. The challenge stems from the anatomic inaccessibility of the cochlea, which makes it difficult to deliver precise amounts of therapeutics into or to aspirate perilymph fluid from within the cochlea for diagnostic purposes [38, 57, 41]. Gaining access to the cochlea first requires gaining access to the middle ear either through the tympanic membrane or via a mastoidectomy. Once in the air-filled middle ear space, two passageways exist into the inner ear. One is the oval window (fenestra ovalis) that is covered with the oval membrane and the footplate of the stapes bone. The other is the round window (fenestra rotunda) that is covered by the Round Window Membrane, which consists of two epithelial layers surrounding a middle layer rich in collagen and elastic fibers. The Round Window Membrane (RWM) is the only pathway from the middle ear to the inner ear that does not require perforation of bone. Thus minimally invasive and reliable inner ear drug delivery and fluid sampling across the RWM is of great interest for a variety of therapeutics and treatments [45, 51, 17, 41].
Many studies have utilized injection of a drug contained within liquid or hydrogel through the tympanic membrane (i.e. ear drum) into the middle ear space; once there, a portion of the drug may diffuse across the RWM into the cochlea [40, 41]. Such intratympanic drug delivery presents several challenges, including: 1) variable rate of diffusion; 2) inability to diffuse some polar molecules; 3) inability to diffuse molecules larger than a critical size [50]. A demonstrated method to overcome these challenges is to perforate the RWM with microneedles prior to intratympanic injection into the middle ear space [57]. Another potential strategy is direct injection of a drug across the RWM into the cochlea.
Perforation of the RWM is technically challenging and also is not without risk because the RWM serves in part to protect the inner ear from the external environment [40, 41]. However recent developments in microneedle technology may mitigate these risks. Our group [1] recently reported the fabrication of ultra-sharp polymeric microneedles with a 100 μm cylindrical shaft that at its end tapers to a tip with a 500 nm radius of curvature. We demonstrated the efficacy of using the microneedles to perforate a guinea pig RWM [1]. At the initial stages of perforation, the ultra-sharp tip first penetrates through the RWM to create an initial perforation. Subsequently, the microneedle continues to perforate the RWM and gradually increases the perforation size until the microneedle shaft has fully penetrated the RWM. The resulting perforation is lens-shaped with major axis the same length as the microneedle diameter and with minor axis about 30% of the major axis. Confocal microscopy examination of the perforation demonstrates that the tapered end pushes apart the collagen and elastic fibers – rather than cutting the fibers – thus introducing the perforation with a minimal degree of damage to the RWM.
In addition, previous work from our group demonstrates the potential of delivery of therapeutics into the inner ear through perforations in the RWM [28, 52]. Furthermore, Yu et al [64] have shown that polymeric microneedles of the same size as the metallic needles used in this work are able to perforate the RWM with no long-term hearing loss. Importantly it was seen that RWM healing progressed over 24 h to 48 h and the perforation was fully closed within one week. Finally, our group [8] designed and fabricated a similar set of ultra-sharp polymeric microneedles and used them to perforate cadaveric human RWM, demonstrating their potential use in humans.
Kelso et al [28] demonstrated that the rate of diffusion of a molecule (e.g. Rhodamine B) across a guinea pig RWM is significantly enhanced by the presence of a microneedle perforation. Additionally, Santimetaneedol et al [52] showed that microperforations in a membrane can enhance the rate of diffusion irrespective of whether a molecule (again, Rhodamine B) is contained in a liquid solvent reservoir or a hydrogel such as Poloxamer 407 reservoir. Specifically, for a reservoir of liquid phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), the rate of diffusion scaled linearly with the total perforation area, independent of the number of perforations. For a reservoir of Poloxamer 407 hydrogel, the diffusion rate across one large perforation was significantly greater than the combined diffusion rate across multiple smaller perforations whose combined areas equaled the larger perforation. Thus, ultra-sharp microneedles that induce a minimal damage during RWM perforation hold great promise for drug delivery to the inner ear.
However, several challenges remain. The microneedles demonstrated by Aksit et al [1], Yu et al [64] and Chiang et al [8] were polymeric and were fabricated with two-photon polymerization (2PP) lithography, which is a 3D additive printing method with a voxel resolution of about 100 nm. While the 3D printing of a microneedle grants tremendous design freedom, the polymeric nature of the microneedles has two drawbacks. First, the polymeric material is not known to be biocompatible. Second, the polymer is not as strong as competing materials such as metals.
Herein we report the fabrication of biocompatible fully metallic microneedles with the same design and overall dimensions as those used by our group in Aksit et al [1], Yu et al [64] and Chiang et al [8]. We refer to our hybrid additive manufacturing fabrication methodology as 2-Photon Templated Electrodeposition (2PTE). Briefly, we first use 2PP photolithography to print a polymeric mold containing a negative 3D image of the desired microneedle. We then use electrodeposition to fill the negative 3D image in the mold with copper. After removing the copper microneedle from the mold, we coat the copper microneedle with a conformal layer of gold to render the surfaces biocompatible. The resulting microneedle has a 100 μm shaft diameter that at its end tapers to a tip with a 1.5 μm radius of curvature. We demonstrate that the fully metallic microneedle perforates a guinea pig RWM by separating – rather than cutting – the connective fibers.
Our 2PTE process for fabrication of biocompatible fully metallic microneedles is quite novel and has the potential to fabricate microneedles for a broad range of other potential applications beyond delivery of drugs to the cochlea. Therefore the central thrusts of this paper are the 2PTE fabrication method and the demonstration that the resulting ultra-sharp metallic microneedles perforate the RWM in the same way as ultra-sharp polymeric microneedles. In Section 2 we describe the general classes of microneedles and fabrication processes in the context of the following three attributes: 1) Design freedom; 2) Accuracy & precision; and, 3) Strength & ductility. Our 2PTE methodology is the only process that produces microneedles with all three attributes. In Section 3, we describe our novel 2PTE design and fabrication method. Section 4 describes RWM peforation experiments with the fully-metallic microneedles. The results are described in Section 5 and discussed in Section 6. We draw our conclusions in Section 7.
2. Background
Microneedles are an attractive area of research since they can enable painless and minimally invasive delivery of therapeutics or sampling of biological fluids across a number of anatomic barriers [26]. Applications of microneedles have been studied for the skin [46, 16, 43, 20], eye [31, 25, 35, 49], the mouth, the vagina, the fingernail, gastrointestinal tract, vascular wall, the anus and the scalp [14, 36, 59, 9, 58, 10, 3]. Work done by our group is presently expanding the use of microneedles into the inner ear [1, 64, 8, 28, 61].
Microneedles designed to deliver therapeutics can employ several different mechanisms including: solid needles for tissue perforation, coated solid needles, hollow needles, and dissolving needles [31]. Solid needles have been shown to greatly improve the permeability of skin for transdermal delivery of therapeutics after microneedle application, or when directly coated with the therapeutic. Hollow and dissolving microneedles have been shown to be reliable methods for painless and minimally invasive drug delivery across the skin and layers of the eye [23, 20, 15].
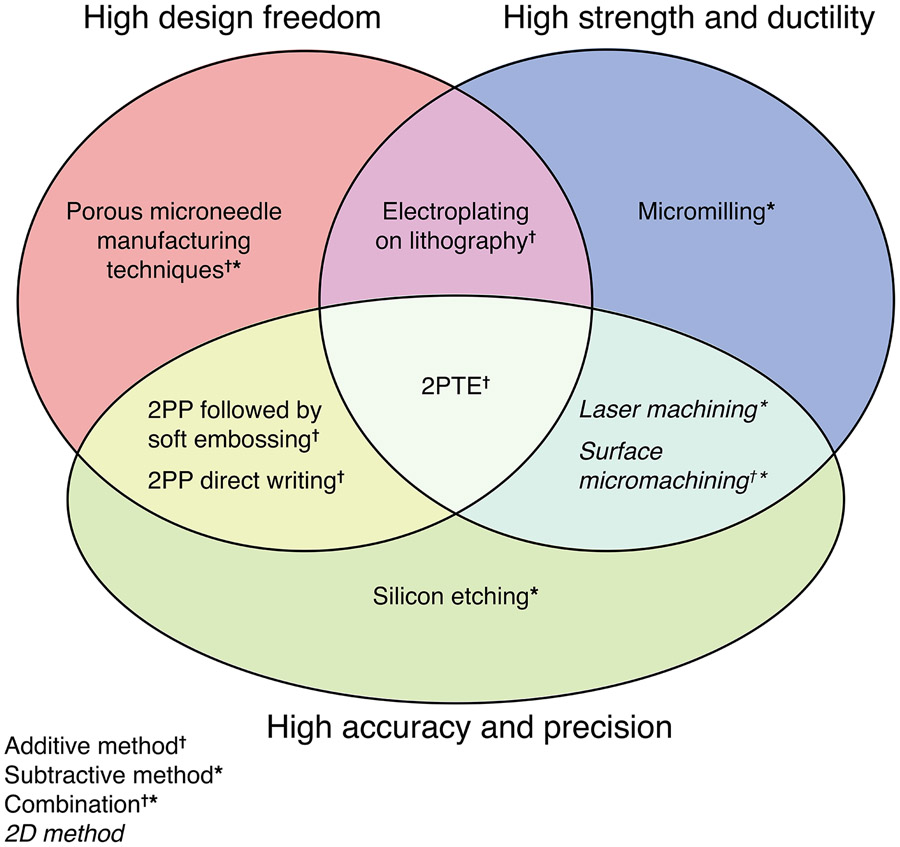
Three of the most important attributes when developing and deploying microneedle technology for meeting the most exacting requirements are: (1) high strength & ductility; (2) high accuracy & precision; and, (3) high design freedom. Figure 1 shows a Venn diagram of these qualities. Strength & ductility of a microneedle is determined primarily by the material. Ceramics and materials such as silicon generally are strong but not ductile. Polymers have a wide range of properties, but their strength is generally limited while they can be very ductile. Metals, however, can have both high strength and high ductility. Microneedles have been made out of all three classes of materials [31]. Accuracy & Precision as well as Design Freedom are determined largely by the microneedle fabrication methods, which can be categorized into either: (1) Subtractive (top-down) fabrication methods in which material is removed from a stock material to obtain the desired configuration; and, (2) Additive (bottom-up) fabrication methods in which material is added from an external source to obtain the desired configuration. Other microneedle qualities not shown in Figure 1 – such as cost, ease of fabrication, and manufacturing scalability – are important for different applications, however only the characteristics highlighted above will be considered in this paper as we establish this novel technology for the delivery of therapeutics into the inner ear.
Fig. 1.
Attributes of different microneedle manufacturing techniques
Most microneedles are fabricated using subtractive methods. For example, the etching or micromachining of silicon was the first method – and remains one of the most popular methods – of making microneedles [46]. Silicon etching played a fundamental role in the creation and development of the microneedle field, and is capable of fabricating highly accurate and precise microneedles with sub-micrometer scale features. However, silicon – while it can be quite strong – is a brittle material, and the inherent design freedom of techniques pertaining to silicon microneedles is limited [5, 4]. Other subtractive methods employ a micromilling machine or an electrical discharge machine (EDM) to fabricate fully metallic microneedles that possess high strength and ductility [19, 60]. However, the accuracy and precision are inferior to that obtainable from silicon micromachining. Laser cutting is another important subtractive fabrication method for metal microneedles that can have relatively high accuracy and precision with microscale features [37]. Overall, subtractive methods can fabricate microneedles with varying degrees of high Accuracy & Precision. When applied to metals, the resulting microneedles can have high Strength & Ductility. All microneedle fabrication methods that use only subtractive techniques have limited Design Freedom. Therefore, in Figure 1, subtractive methods populate regions denoting High Accuracy & Precision with some also classified as High Strength & Ductility.
Some microneedle manufacturing methods use a combination of subtractive and additive techniques. Metallic, porous microneedle manufacturing methods have created a unique venue in drug delivery and fluid sampling [34, 6]. The methods for creating these devices – hot embossing, sintering and metal injection molding – have significant inherent Design Freedom, but lead to less Accuracy & Precision and Strength & Ductility. Two dimensional subtractive techniques, such as laser machining and surface micromachining, combined with additive techniques such as electrochemical deposition, are successful at creating metallic microneedles with great Accuracy & Precision and Strength & Ductility, but with less Design Freedom [7, 13, 12]. Limits in their design freedom, however, makes it challenging for these needles to be used for certain applications. These methods are shown in their respective categories in Figure 1.
The newest methods, enabled by recent advances in manufacturing technology, are fully additive methods. The combination of lithography with surface electroplating has great Design Freedom and the resulting microneedles have Strength & Ductility, but with less Accuracy & Precision than competing methods [33, 30, 29]. Hollow microneedles created this way can be in a plethora of different shapes and are metallic and durable. Two-photon polymerization (2PP) lithography is a well-known technique that has recently attracted attention for micromanufacturing and has become widely commercially available. This method can be utilized to create highly complex 3-D structures with resolution approaching 100 nm [55]. Microneedles have been made with Direct Laser Writing (DLW) [1] using 2PP lithography or combined with a molding and soft embossing step to make polymeric microneedles [47]. This method combines the Accuracy & Precision of microtechnology with the Design Freedom of 3D printing. Therefore, it can be said that 2PP is a great tool to use for fabricating polymeric microneedles,[56] but the resulting microneedles are limited with regard to Strength & Ductility. These methods also are shown in their respective categories in Figure 1.
A long-standing goal has been to manufacturing microneedles with high Strength & Ductility and high Accuracy & Precision using methods that grant high Design Freedom. Fully metallic microneedles are especially desirable due to their mechanical, electrical and thermal properties, and ease of functionalization [42, 18]. Herein we report the hybrid additive fabrication of ultra-sharp solid metallic microneedles with complex architectures. This is achieved by electrochemically depositing copper into polymeric molds fabricated via 2PP lithography. We call this technique 2-Photon Templated Electrodeposition (2PTE). The resulting microneedles are the most precise fully solid metallic microneedles yet demonstrated, with a shaft diameter of 100 μm tapering to a tip radius of curvature as small as 1.5 μm.
Electrochemical deposition of metals into polymeric templates (or molds) made via 2PP lithography provides sub-micrometer resolution and results in precise, ultra-sharp, high ductility, and high strength needles that have tremendous freedom in their design. Most designs achievable via 2PP lithography can be achieved using 2PTE, including needles that are hollow or have multiple lumina through the microneedle shaft. As illustrated in Figure 1, our 2PTE fabrication methodology is currently the only method that combines the attributes of high Design Freedom and high Accuracy & Precision with the superior Strength & Ductility of metals. In the specific case of the inner ear, a high design freedom manufacturing technique to fabricate microneedles is crucial to address the complex nature and size of the middle and inner ear anatomy [38]. High accuracy and high precision are invaluable, due to the delicate nature of the tissue of interest: the Round Window Membrane [61]. Methods with these properties produce needles that are “ultra-sharp” and have smooth surfaces and can be reliably produced with repeatable dimensions and properties. Ultra-sharp needles with smooth surfaces cause minimal damage to the tissue and are conducive to healing [64]. High strength, high ductility microneedles are also important for safety purposes. High strength needles will not deform or blunt during nominal use and can be reliably used multiple times. High ductility needles, when undergoing deformation – perhaps due to accidental impact with bony tissue around the RWM during use – will yield and bend, rather than break off in a brittle manner.
3. Template Assisted Electrodeposition of Metals
Three additive manufacturing steps are used in fabricating the ultra-sharp biocompatible microneedles. First, we fabricate a mold or template for the microneedles using 2PP lithography, which can print polymeric 3D structures with spatial resolution (i.e. voxel size) approaching 100 nm. Second, we use electrodeposition to grow or deposit microneedles in the mold. Both galvanostatic and potentiostatic deposition can be used to make the microneedles, and the relationship between charge passed through the system and deposition made is consistent with Faraday’s law of electrolysis
| (1) |
where m is the mass deposited, Q is the total charge passed through the system that can be easily computed by integrating current over time, M is the molar mass of the deposited agent, F is Faraday’s constant, and z is the valency number. Third, the microneedles are coated with a thin nickel film via electroless deposition followed by a thin gold film by immersion deposition.
Galvanoforming (LIGA) is a standard method used to fabricate 2D nickel structures with constant cross-sectional area [2]. Our methodology is a significant extension to LIGA in that we are able to fabricate complex 3D structures with cross-sectional areas that vary by up to four orders of magnitude. The new methodology is made possible due to recent advances in 3D lithography such as 2PP lithography that enable the production of a variety of designs to be manufactured. These designs can be made fully metallic, and can even have controlled microstructures [22, 53, 11, 54].
3.1. Microneedle Design and Fabrication
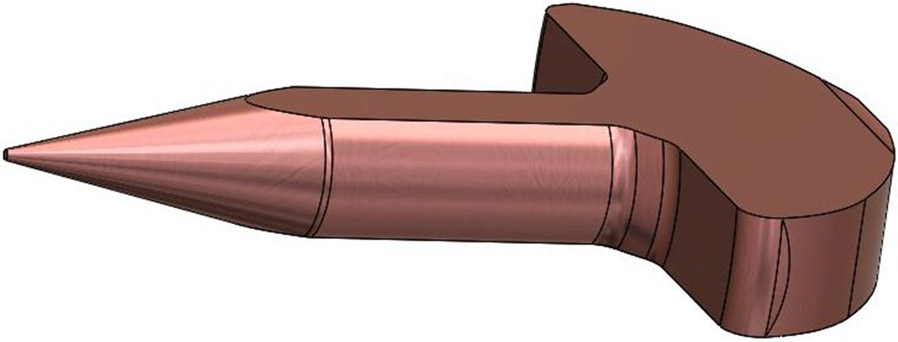
The geometric details of the mold are designed using SolidWorks (Dassault Systems SolidWorks Corporation, Concord, NH, USA) computer aided design (CAD) software to generate stereolithography (STL) files. The microneedle design is illustrated in Figure 2. The microneedle design consists of a shaft of diameter of 100 μm that tapers uniformly with an angle of 13.1° to a tip of 1.5 μm radius. The microneedle’s base section diameter is 405 μm. The entire height of the electrochemically deposited needle, including the base part and the needle part is 585 μm; we call this the total structural height. According to micro-CT imaging conducted by Watanabe et al [60], there is a 1.2 mm deep chamber behind the RWM, behind which is the basilar membrane. The needle length, which was chosen to be 430 μm, is a conservative length so that the basilar membrane is not damaged during RMW perforation.
Fig. 2.
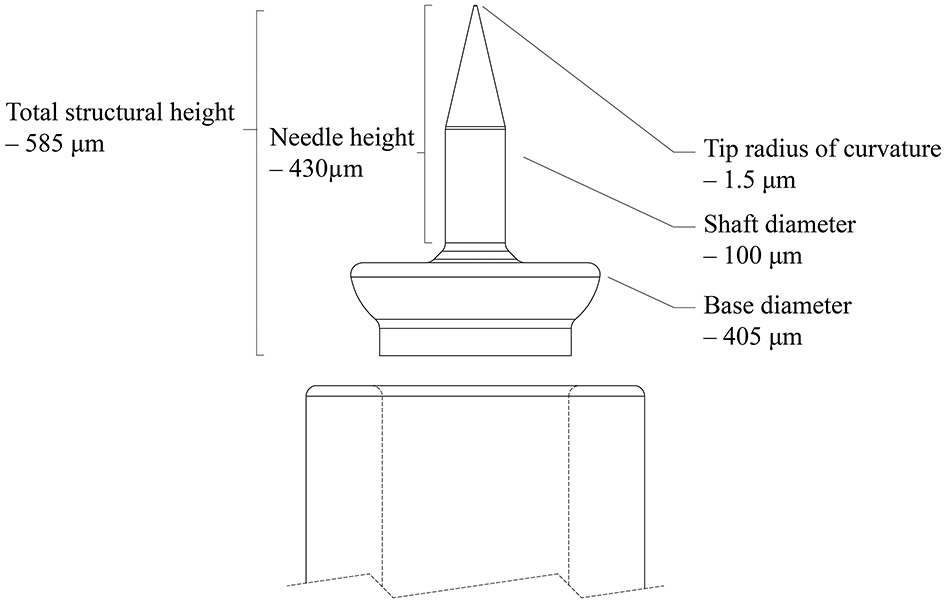
Side view of the design of the needle along with the standard 24 gauge stainless steel blunt needle tip into which it is designed to fit.
A cross-section of the mold used to electrochemically deposit the microneedles is illustrated in Figure 3. The first microneedle fabrication step is to fabricate the mold. Thin 100 nm films of titanium and gold are deposited sequentially via electron-beam evaporation (AJA Orion 8E Evaporator System) atop a (100) single crystal silicon wafer substrate. Photoresist (IP-S, Nanoscribe GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) is deposited atop the gold film via drop-casting. Subsequently, 2PP lithography (3D laser writing) is performed using the Photonic Professional GT system (Nanoscribe GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). The Dip-in Laser Lithography (DiLL) configuration is used with a 25× objective using the galvo scan mode. The 2PP process is started 2.5 μm below the substrate to ensure good anchoring. A slicing distance of 1 μm is chosen to ensure a reliable structure as well as a reasonable writing duration. The structure is divided into hexagons with 400 μm major axes, and is stitched with regions of 1 μm overlapping on the sides to ensure good stitching. After 2PP lithography is complete, the polymeric molds are soaked in a propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate (PGMEA) solution for 30 min, and are subsequently cleaned in two isopropanol alcohol (IPA) baths of length 20 min each, which completes fabrication of the molds.
Fig. 3.
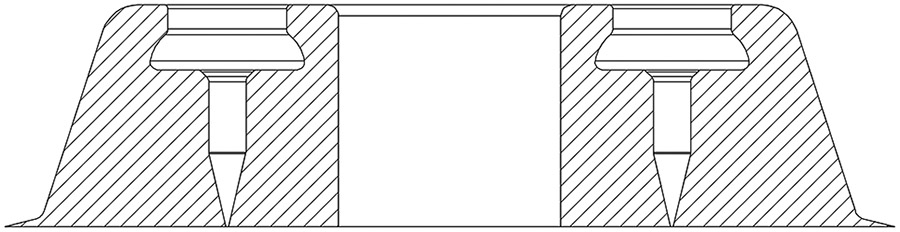
Cross-sectional view of the design of a needle mold containing a central circular current thief geometry with a diameter of 600 μm.
The fabricated molds are mounted onto a stainless steel rotating disk electrode (RDE) with a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) protector and placed in deionized (DI) water. An electrolyte (Moses Lake Industries, Moses Lake, WA, USA) is prepared containing 40 gl−1 copper, 140 gl−1 H2SO4 and 50 mgl−1 Cl−. Electrodeposition is performed using apower supply (Metrohm Autolab B.V., Utrecht, The Netherlands) that can operate either as a galvanostat or a potentiostat using a Ag/AgCl reference electrode (Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, MO, USA). Two different methods can be employed in fabricating the needles:
1. Potential controlled (potentiostatic) deposition with a stop function at a limit charge.
2. Current controlled (galvanostatic) deposition with a stop function at a limit potential.
After electrodeposition, the copper-filled mold is removed from the RDE, rinsed with DI water and rapidly dried using N2 gas or compressed air. The mold structure is dissolved away to release the needles using Technistrip NF-52 (Technic Inc., Cranston, RI, USA) that is selective against copper. The microneedles are further cleaned using Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) with 10 sccm CF4 and 50 sccm O2 (PlasmaPro NPG80 RIE, Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, United Kingdom). The copper needles are mounted on a 24 gauge stainless steel blunt hollow hypodermic needle. The microneedle surfaces are then further cleaned via electropolishing using concentrated H3PO4. Figure 4 shows an example of a copper microneedle fabricated and mounted in this manner.
Fig. 4.
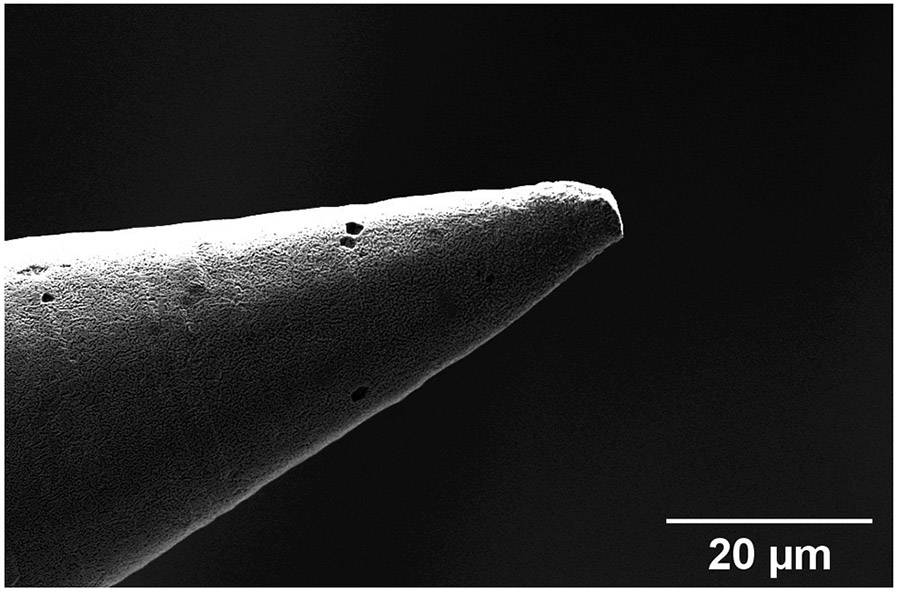
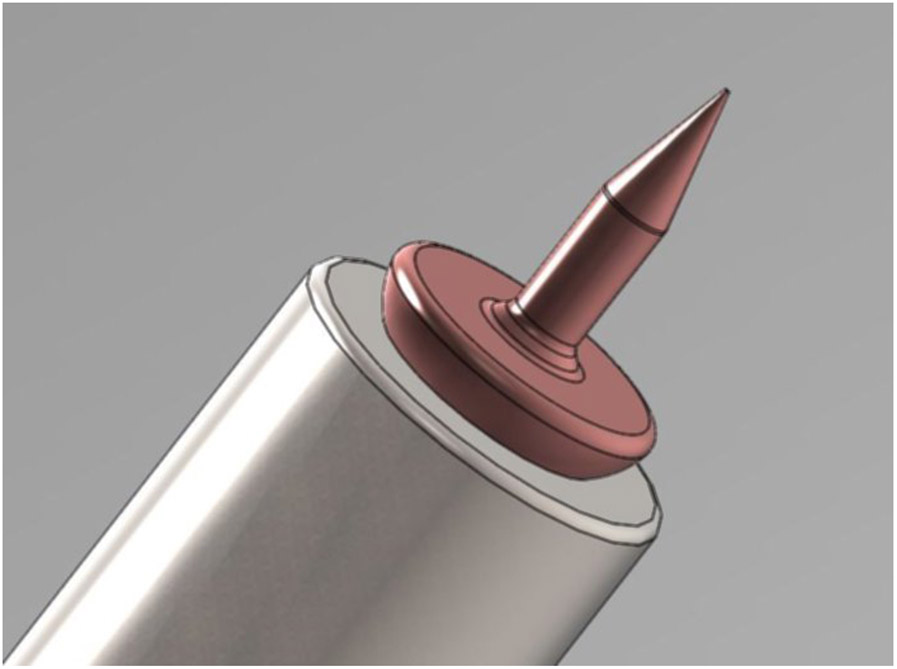
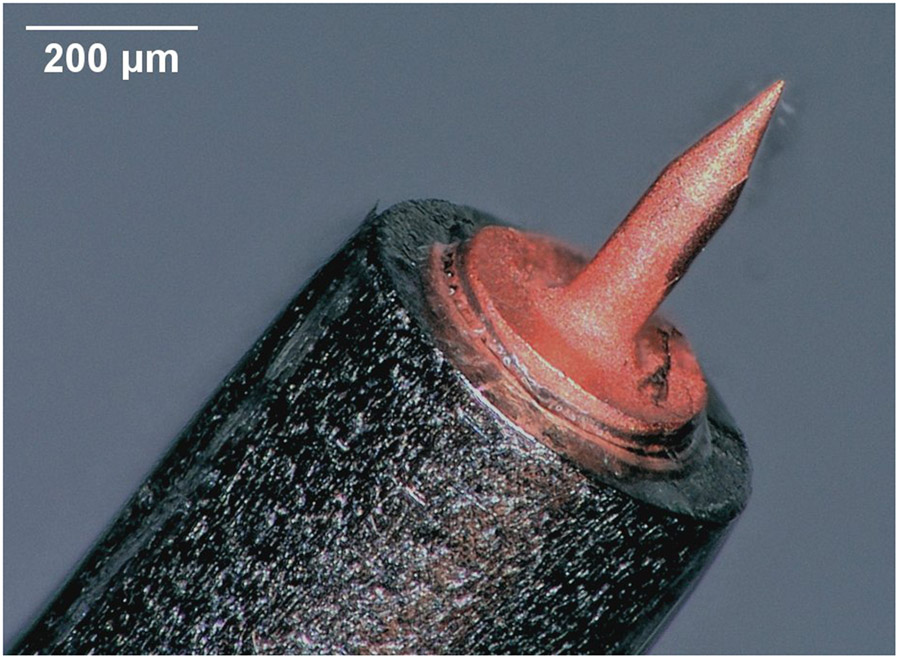
(a) Computer generated rendering of microneedle design. (b) Optical micrograph of additively manufactured copper needle (with 100 μm shaft diameter) mounted on a 24 gauge stainless steel hollow blunt needle (with nominal 565 μm outside diameter) (c) Scanning electron micrograph of a copper microneedle tip.
The microneedle can be secured to the stainless steel blunt needles with epoxy (Gorilla Epoxy Inc.). The other end of the blunt stainless steel hollow needle can be fitted with a standard Luer Lock fitting to enable connection to medical instruments.
Copper is not a biocompatible material. Hence after fabricating the microneedles, a nickel thin film (1.5 μm) is blanket coated onto the copper microneedle via electroless deposition (OMG chemicals, MN, USA). A gold thin film (30 nm to 100 nm) (based on data sheets from Technic Inc.) is then blanket coated atop the nickel film using an immersion deposition method (Technic Inc., Cranston, RI, USA). In this way the entire surface of the microneedles is coated with gold, which is a biocompatible material. The Ni interlayer between the Cu and Au prevents diffusion of Cu into the Au layer. We analyze the Ni and Au coatings using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and backscatter imaging for surface characterization. This analysis is conducted using a scanning electron microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
To allow ready analysis of the copper microstructure produced by the electrodeposition process, we fabricated microneedles with flat sides in a similar mold structure; an example of such a needle and the design are illustrated in Figure 5. These microneedles are fabricated with the same process parameters as the round microneedles. The flat microneedles are analyzed using Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) system (EDAX, NJ, USA).
Fig. 5.
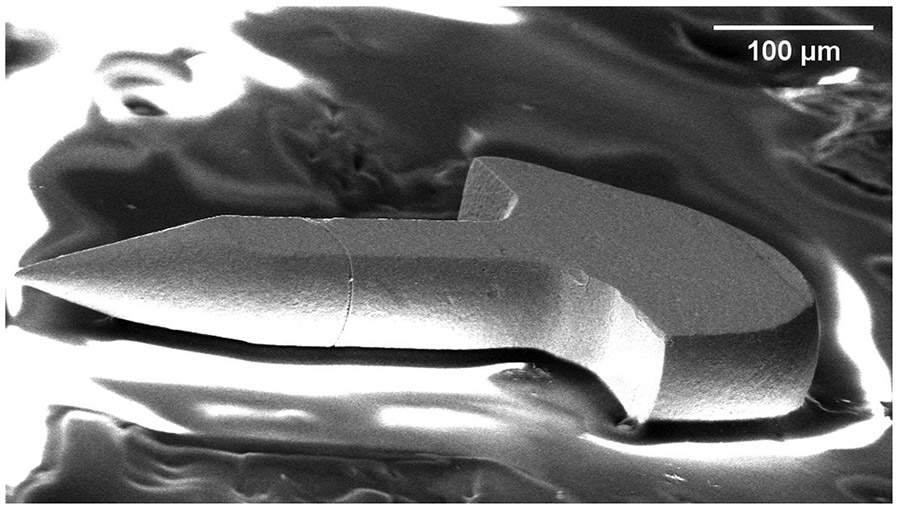
(a) Design of a flat needle for microstructural analysis. (b) Scanning electron micrograph of the flat sided needle used for analysis.
4. Perforation of Round Window Membrane using Microneedles
Previously, our group fabricated a polymeric microneedle printed directly with 2PP lithography of the same dimensions of the design in Figure 2 except that the polymeric microneedle had a 500 nm tip radius of curvature. The polymeric microneedles were used to perforate a guinea pig RWM to create perforations to enable the accurate and precise delivery of therapeutics into the inner ear [28, 1]. Our group has also demonstrated that perforation of the RWM with the polymeric microneedles does not have a lasting effect on the sense of hearing and that the resulting perforations heal progressively over 24 h to 48 h with complete closure of the perforation within one week [64]. Polymeric microneedles of the same general design but with different taper angle, 30° instead of 13.1°, have been used to perforate a human cadaveric RWM [8]. Our goal in this section is to describe the perforation of the guinea pig RWM using the fully metallic microneedles.
Hartley strain male guinea pigs were used for this study. Within 24 h after euthanasia, the intact temporal bone of the guinea pig is harvested using blunt dissection. Parts of the temporal bone were drilled away using an Osada Electric Handpiece System, (Osada, Inc., Los Angeles, California, USA) exposing a clear view of the RWM without compromising the integrity of the fluid chambers in the cochleovestibular system.
The microneedles are mounted in a custom-built micromanipulator consisting of:
Motorized stage and linear translator for moving harvested RWM into position and for translating the needle indenter vertically (Zaber Technologies Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada),
Force transducer with full scale of 98 mN for measurement of axial force exerted during indentation (Transducer Techniques, Temecula, CA, USA),
Custom 3-D printed fixture to hold the 24 gauge stainless steel needle with a Luer lock interface, that is used to align the sample and the microneedle.
We use a copper microneedle to perforate the RWM in-situ while simultaneously measuring the force and displacement (N = 4). A separate copper needle is used for each perforation. The perforated RWM is examined via confocal microscopy. The size and orientation of the perforation is recorded and the damage induced into the underlying collagen and elastic fiber matrix is examined.
5. Results
Fully metallic microneedles are fabricated with extreme precision for the goal of perforating the round window membrane. Figure 4a shows the design of the copper microneedle inserted into the 24 gauge stainless steel hyperdermic needle. Figure 4b shows the fabricated microneedle secured to the hollow stainless steel by a small amount of epoxy glue. Figure 4c is an SEM micrograph of the tip of the needle shown in Figure 4b.
Needles with altered geometries that have flat sides, shown in Figure 5, are analyzed using EBSD. The grain sizes average 3.4 μm close to the tip and 4.6 μm close to the base of the needle. A change in copper grain size, where the tip grains are significantly smaller than the base is advantageous because material hardness increases as the grain size decreases via the Hall-Petch effect [21, 44]. Thus a larger grain size is associated with greater ductility, so the copper near the base would be more ductile. A hard microneedle tip is expected to be resilient to damage and a ductile microneedle base is expected to bend rather than break in the event of unanticipated lateral forces during perforation.
Fabricated microneedles are used to perforate guinea pig round window membranes (N=4), exerting an average of 3.8 mN of perforation force, with a standard deviation of 0.35 mN. Perforation force is defined as the maximum force that is exerted on the needles during the indentation.
Perforations in the RWM made by microneedles are analyzed using confocal microscopy and are found to have major and minor axes of 75.2 μm and 22.8 μm, with standard deviations of 8.6 μm and 7.3 μm, respectively. This is similar to results from previous work [1]. It is also observed from the confocal images that the method of failure of the membrane is fiber-to-fiber decohesion, and not ripping or tearing of the collagen fibers significantly; this is consistent with our earlier study using polymeric microneedles [1]. Low magnification and high magnification confocal microscope images of a perforated RWM can be seen in Figure 6, illustrating this phenomenon visually.
Fig. 6.
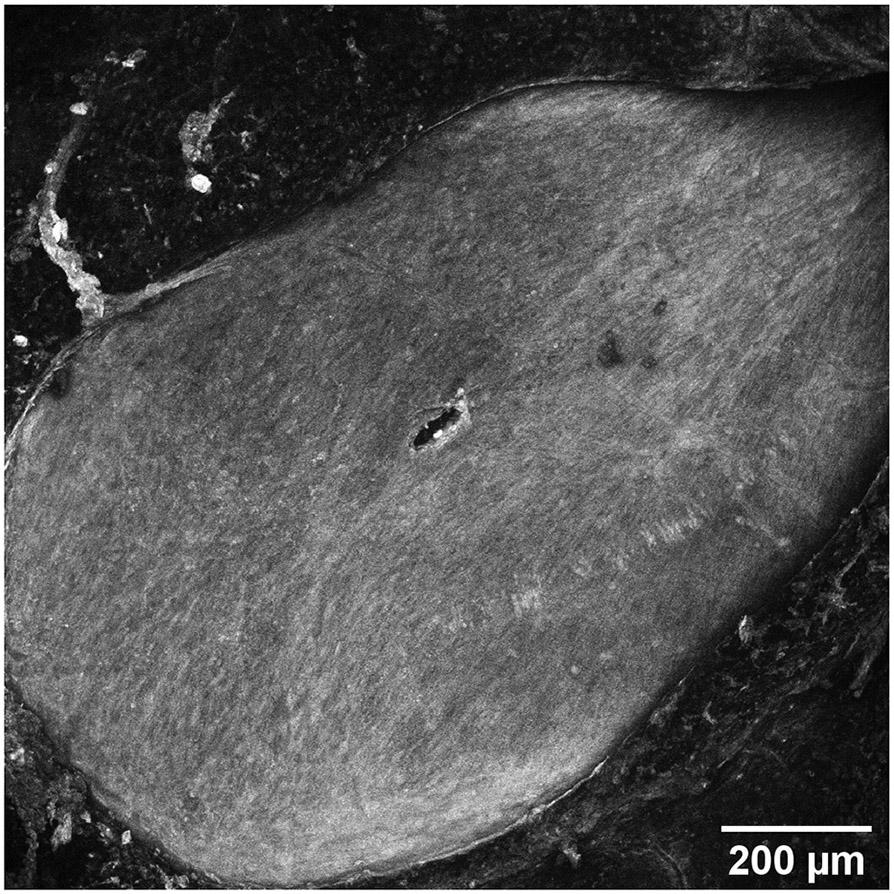
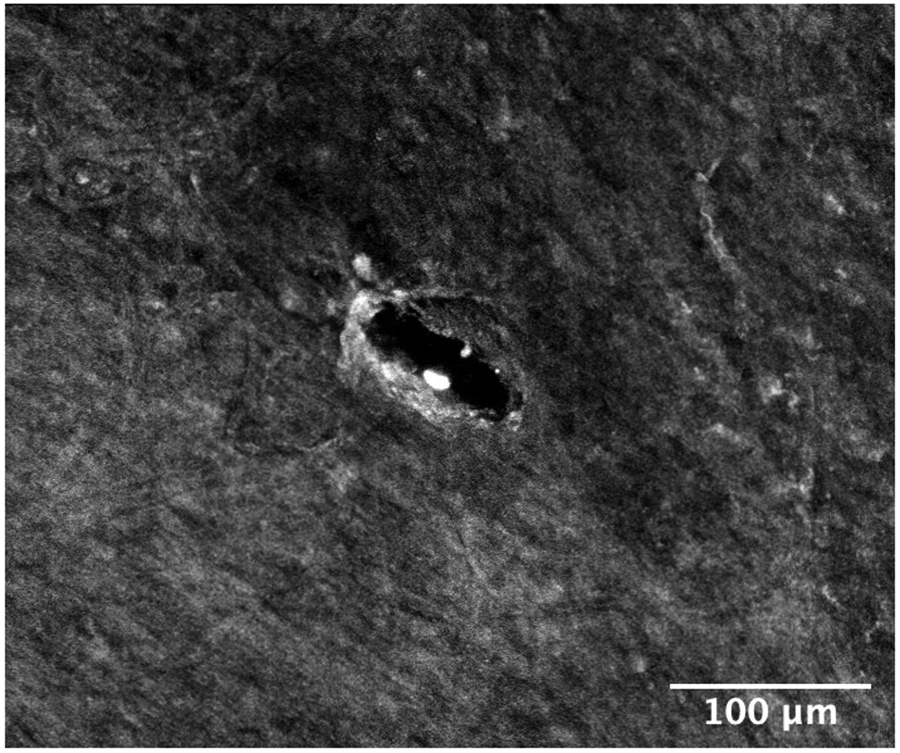
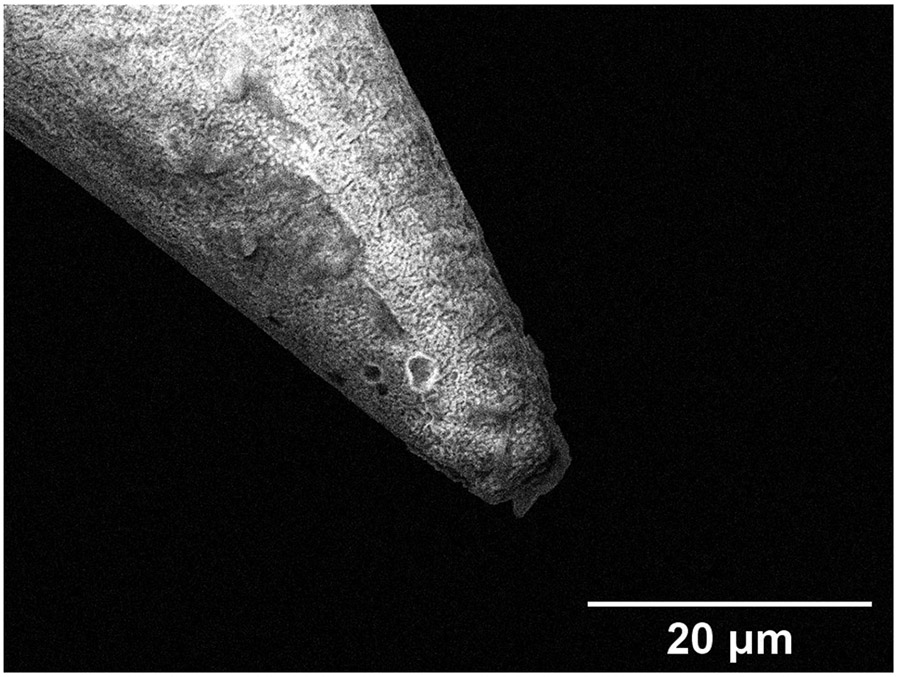
(a) Confocal micrograph of a round window membrane perforated with a metallic microneedle, 10× magnification. (b) 20× magnification of a confocal micrograph, zoomed in around the perforation to show fiber structure around the hole. (c) Scanning electron micrograph of a microneedle tip post perforation, showing no damage on the tip.
Figure 6c shows an SEM micrograph of a representative copper microneedle following perforation. There is no discernible damage to the tips of the microneedles, demonstrating the high strength at the tip does not allow the tip to deform permanently. This suggests the potential of reusability of metallic microneedles post perforation.
For the copper microneedles subsequently coated with Ni and Au, the EDS and backscatter imaging of the surface show very high and conformal coverage of the surface with Au. A digital microscope image of a gold coated needle and a SEM backscatter detection image can be seen in Figure 7b. Results of EDS from a needle can be seen in Table 1, and the gold-coated microneedle can be seen in Figure 7a.
Fig. 7.
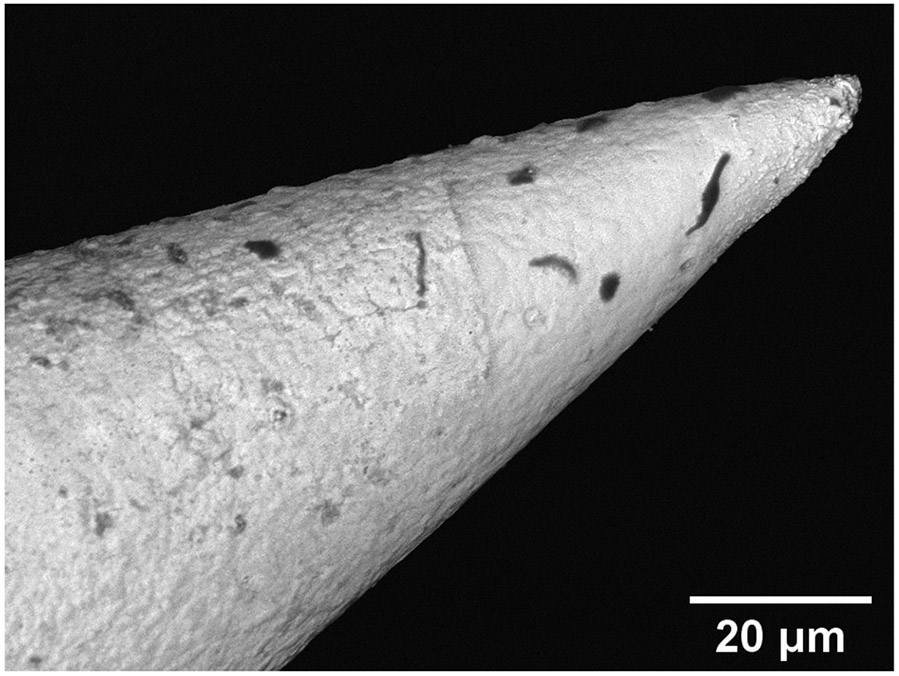
(a) Optical micrograph of a gold coated microneedle, and (b) SEM backscatter detection image showing minor dark contamination on the surface of the gold coated microneedle, possibly carbon, but an otherwise conformal coating.
Table 1.
Results from EDS analysis of the needles coated with Electroless Nickel and Immersion Gold.
| Element | Atomic No. | Mass Normalized [%] | Atomic [%] | Relative error [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | 79 | 99.06 | 97.07 | 3.76 |
| Copper | 29 | 0.72 | 2.20 | 22.89 |
| Nickel | 28 | 0.22 | 0.73 | 37.46 |
Figure 8 shows a close-up image of a copper microneedle just after the RIE cleaning step. The tip radius of curvature of the fabricated needles is on the order of 1.5 μm. The circumferential lines on the surface of the microneedle taper and shaft are a consequence of the discrete voxel size from 2PP process, leading to individual layers in the mold of the order of micrometers in thickness. These surface features are removed in the electropolishing step of our process. However, these microscale features showcase the detail that can be obtained on the manufactured needles.
Fig. 8.
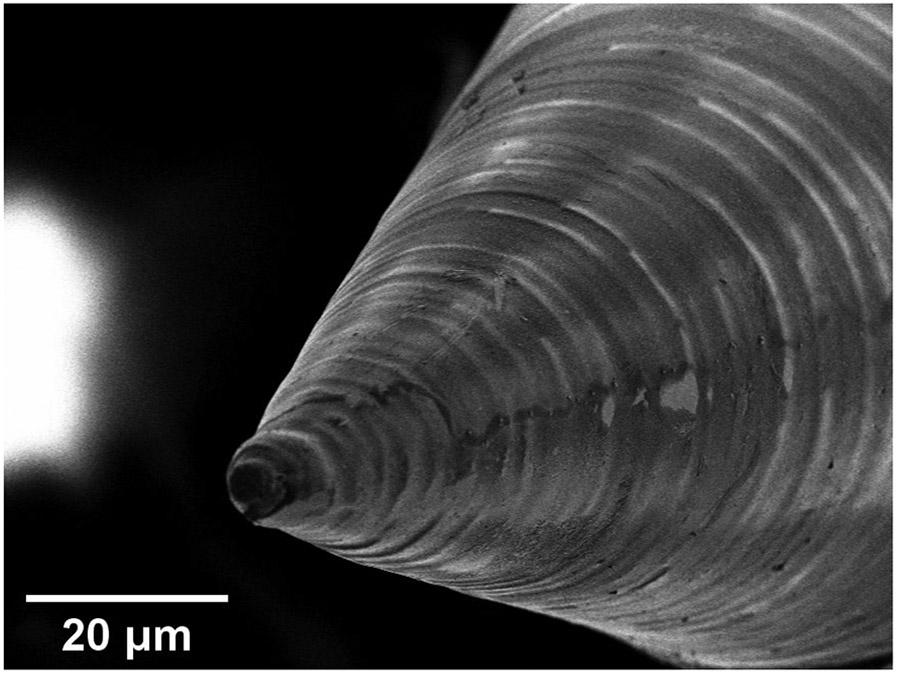
Scanning Electron Microscopy of an electrochemically deposited needle’s tip. It is possible to see the imprints of voxel lines generated during the 2PP of the molds.
6. Discussion
The work presented herein discusses the fabrication of fully metallic microneedles that can have complicated geometries and surface designs, along with a demonstration that the microneedles can be used to perforate the guinea pig RWM. It was shown that this methodology allows replication of 2PP resolution to produce fully metallic microneedles, and the voxel lines visible in Figure 8 illustrates this capability.
In previous experiments, Kelso et al [28] introduced “irregular tears” with average perforation opening area of 2500 μm2 using microneedles with a 6.25 μm radius tip into a guinea pig RWM. Subsequent diffusion experiments showed that the presence of a single such perforation increased significantly the rate of delivery of Rhodamine B across the RWM. Our ultra-sharp microneedles are able to introduce perforations by separating rather than cutting the fibers. Nonetheless, uncontrolled ripping of the RWM would occur if the microneedle shaft were too large. Therefore, we chose a microneedle shaft diameter of 100 μm because it does not introduce uncontrolled ripping of the RWM, yet introduces an average perforation area of 1700 μm2, which is a significant fraction of the mean perforation size in Kelso et al [28].
The peak force required for perforation of the guinea pig RWM with the fully-metallic microneedle is 3.8 mN. In previous work by Chiang et al [8] of our group, the median force required to perforate a human RWM with a 100 μm microneedle is 53 mN, with interquartile range of 50 mN to 60 mN. The force perception threshold for otologic surgeons (during cochlear implant surgery) is 20.4 mN [32]. This is well below the human RWM perforation force (53 mN). Thus, the surgeon may not feel the initial perforation of the RWM with the tip of the needle, but will perceive the advancement of the shaft of the needle to complete the perforation. The clinician will use the needle with either endoscopic visualization or with the aid of a microscope. Thus, there will be both visual and tactile confirmation of perforation for the surgeon. In addition, if the electrode is coated with AgCl, there can be electrical confirmation of initial perforation by using electrochemical methods described by Wazen et al [63].
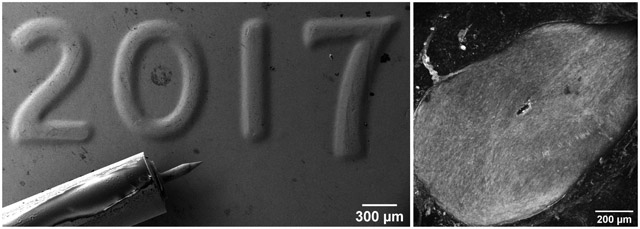
This methodology provides significant freedom in the design of needles. However, structures that can be manufactured this way have some geometric limitations. Namely, creation of protruding corners and rapidly changing cross-sectional areas (similar to what was presented in this work) require careful design and control of electrochemical deposition parameters. The realm of the designs that are feasible to produce using this methodology is not dissimilar to regular 3D printing guidelines about overhanging structures [39]. In order to illustrate the degree of accuracy along with a familiar scale, a copper microneedle mounted on a 24-gauge blunt needle has been imaged next to the 2017 date stamp of a U.S. 1 cent coin, illustrated in Figure 9.
Fig. 9.
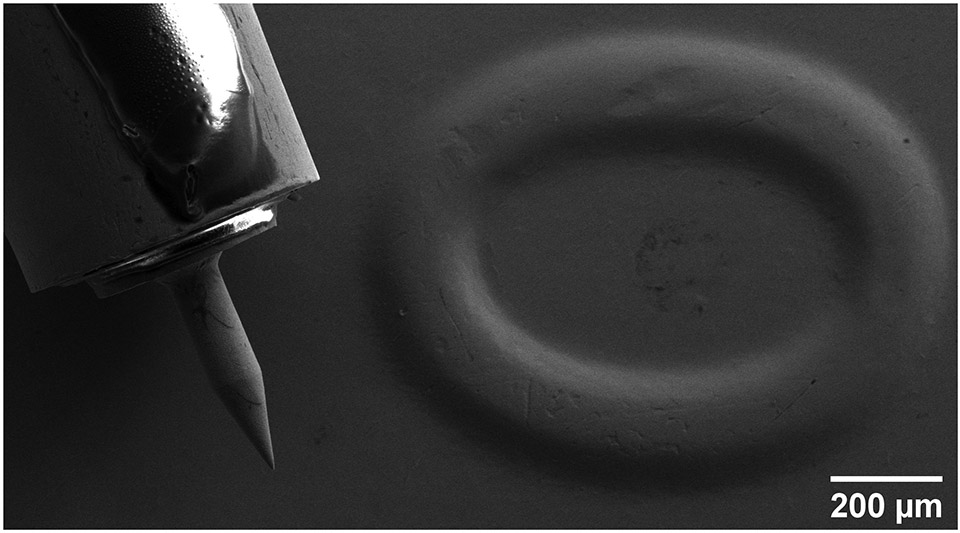

(a) High magnification and (b) Low magnification SEM image of a microneedle mounted on a blunt 24 gauge stainless steel syringe tip, next to a 2017 date stamp on a U.S. 1 cent coin.
Since the process has extensive design freedom and control over the microscale surface geometry of the microneedles, it is possible to produce a plethora of novel designs, such as hollow microneedles. One other important strength of this technique is its ability to manipulate surface topology, which can play an important role in the function of needles. Studies have been made on the effects of blade-like biomimetic protrusions from needles that can decrease insertion force [24, 35].
Two different deposition mechanisms were employed to manufacture the microneedles successfully: potential-controlled deposition and current-controlled deposition:
The potential-controlled (potentiostatic) method produces full metal needles more reliably and a charge-limit stop ensures stopping at the correct time once the base of the needles is done. However, there is little control over the current density as the deposition proceeds. The potentiostatic method allows the potential to be maintained below the threshold at which significant hydrogen evolution occurs;
In the current-controlled (galvanostatic) process, a miscalculation of the geometry – especially for complicated geometries with rapid changes in cross-sectional area or a misestimate of the current efficiency can mean that the deposition does not occur successfully due to hydrogen evolution that can obstruct the charge flow to the cathode, and increase the current density. Hence, the galvanostatic process is always used in conjunction with a potential limit, which ensures that undesirable potentials that could evolve significant amounts of hydrogen are not reached. The advantage of using the galvanostatic method is the fact that the user has complete control over the current density at every point throughout the deposition.
Using either of these methods, it is possible to change parameters of deposition, such as additive concentrations, temperature, and current density to induce an effect on the microstructure, thereby having an effect on the microneedle’s mechanical properties [27]. These effects can be experimentally verified via nanoindentation and can be visualized using EBSD. The goal would be to manipulate the microstructure of microneedles such that while the tip portion is hard and can hold an edge after many perforations, the base portion is more ductile and would bend rather than break.
Using electropolishing, only a layer of 30 nm to 50 nm of copper is estimated to be removed. This is only done to remove residue, and should not affect the needle geometry significantly. Electroless deposition of Ni and subsequent immersion coating with Au is used to make the microneedles biocompatible. Although it is shown, through EDS and backscatter imaging, that the microneedles are coated with good conformality, the strength, survivability and cytotoxicity of these coatings have not been studied at this point and will be the subject for further research.
7. Conclusion
Fully metallic single microneedles were manufactured by our 2PTE process of electrochemical deposition of copper into molds made via two-photon polymerization lithography. The needles were ultra-sharp; with a tip radius of curvature of 1.5 μm. The needles were mounted on standard blunt 24 gauge stainless steel syringe needles and coated with a thin conformal nickel film via electroless deposition, followed by gold immersion coating for biocompatibility. Success of the gold deposit was verified via EDS. Other methods have been used to fabricate ultra-sharp needles, such as in O’Mahony et al [42], Roxhed et al [48], Aksit et al [1], but those microneedles do not have all of the attributes from our 2PTE manufacturing process.
Copper microneedles successfully perforated the guinea pig round window membranes, resulting in a mean perforation force of 3.8 mN, with a standard deviation of 0.3 mN. Confocal microscopy of the membranes suggested that the method of failure of the membrane was fiber-to-fiber decohesion, which is made possible by the ultra-sharp microneedle tips. It is important to note that earlier work [28, 62] from our group showed that microneedles with a 6.25 μm radius tip introduced “irregular tears” in the guinea pig RWM rather than the lens-shaped opening obtained from the ultra-sharp microneedles.
One of the main challenges we overcame in developing the 2PTE process was to initiate the electrodeposition in a mold with a 3 μm diameter circular opening, transitioning continuously to electrodeposition of the 100 μm microneedle shaft diameter, and transitioning again to the microneedle base diameter of 405 μm. This 18000 times increase in deposition area demonstrates both the design freedom and the accuracy and precision of the 2PTE method to manufacture metallic structures with high strength and ductility, while tailoring material microstructure via varying electrodeposition parameters. This shows the promise of the 2PTE method to fabricate small structures for many other potential applications.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ryan Gusley, Jonathan Vardner, Professor Elizabeth Olson, Dr. Miguel Arriaga, Wenbin Wang, Richard Li, Dr. Dimitrios Fafalis, Chaoqun Zhou, Young Jae Ryu, Dr. Daniel N. Arteaga, Betsy Szeto, Michelle Yu, Harry Chiang and Chris Valentini for helpful discussions. This work was performed in part at the Advanced Science Research Center NanoFabrication Facility of the Graduate Center at the City University of New York. This research was supported by NIH National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01DC014547.
Footnotes
Confict of Interest Statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Compliance With Ethical Standards
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
To appear in Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2020)
References
- 1.Aksit A, Arteaga DN, Arriaga M, Wang X, Watanabe H, Kasza KE, Lalwani AK, Kysar JW (2018) In-vitro perforation of the round window membrane via direct 3-d printed microneedles. Biomedical Microdevices 20(2):47, DOI 10.1007/s10544-018-0287-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Backer E, Ehrfeld W, Münchmeyer D, Betz H, Heuberger A, Pongratz S, Glashauser W, Michel H, Siemens Rv (1982) Production of separation-nozzle systems for uranium enrichment by a combination of x-ray lithography and galvanoplastics. Naturwissenschaften 69(11):520–523 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baek C, Han M, Min J, Prausnitz MR, Park JH, Park JH (2011) Local transdermal delivery of phenylephrine to the anal sphincter muscle using microneedles. Journal of controlled release 154(2):138–147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bean KE, Runyan W (1990) Semiconductor integrated circuit processing technology. Addison-Wesley [Google Scholar]
- 5.Braybrook JH (1996) Biocompatiblity: Assessment of medical devices and materials. Biocompatiblity: Assessment of Medical Devices and Materials, by Braybrook Julian H (Editor), pp 246 ISBN 0-471-96597-9 Wiley-VCH, December 1996 p 246 [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cahill EM, Keaveney S, Stuettgen V, Eberts P, Ramos-Luna P, Zhang N, Dangol M, O’Cearbhaill ED (2018) Metallic microneedles with interconnected porosity: A scalable platform for biosensing and drug delivery. Acta Biomaterialia 80:401–411, DOI 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.007, URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1742706118305245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chandrasekaran S, Brazzle JD, Frazier AB (2003) Surface micromachined metallic microneedles. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 12(3):281–288, DOI 10.1109/JMEMS.2003.809951 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chiang H, Yu M, Aksit A, Wang W, Stern-Shavit S, Kysar JW, Lalwani AK (2020) 3d-printed microneedles create precise perforations in human round window membrane in situ. Otology & Neurotology 41(2):277–284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chiu WS, Belsey NA, Garrett NL, Moger J, Price GJ, Delgado-Charro MB, Guy RH (2015) Drug delivery into microneedle-porated nails from nanoparticle reservoirs. Journal of Controlled Release 220:98–106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Choi CK, Kim JB, Jang EH, Youn YN, Ryu WH (2012) Curved biodegradable microneedles for vascular drug delivery. Small 8(16):2483–2488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Daryadel S, Behroozfar A, Minary-Jolandan M (2019) Toward control of microstructure in microscale additive manufacturing of copper using localized electrodeposition. Advanced Engineering Materials 21(1):1800946, DOI 10.1002/adem.201800946 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Davis SP, Prausnitz MR, Allen MG (2003) Fabrication and characterization of laser micromachined hollow microneedles. In: TRANSDUCERS ’03. 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems. Digest of Technical Papers (Cat. No.03TH8664), vol 2, pp 1435–1438 vol.2, DOI 10.1109/SENSOR.2003.1217045 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Davis SP, Landis BJ, Adams ZH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2004) Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force. Journal of Biomechanics 37(8):1155–1163, DOI 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.12.010, URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021929003004731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dhurat R, Sukesh M, Avhad G, Dandale A, Pal A, Pund P (2013) A randomized evaluator blinded study of effect of microneedling in androgenetic alopecia: a pilot study. International journal of trichology 5(1):6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Donnelly RF, Singh TRR, Tunney MM, Morrow DI, McCarron PA, O’Mahony C, Woolfson AD (2009) Microneedle arrays allow lower microbial penetration than hypodermic needles in vitro. Pharmaceutical research 26(11):2513–2522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Donnelly RF, Singh TRR, Woolfson AD (2010) Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: microfabrication, drug delivery, and safety. Drug delivery 17(4):187–207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Early S, Moon IS, Bommakanti K, Hunter I, Stankovic KM (2019) A novel microneedle device for controlled and reliable liquid biopsy of the human inner ear. Hearing Research [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Forvi E, Bedoni M, Carabalona R, Soncini M, Mazzoleni P, Rizzo F, O’Mahony C, Morasso C, Cassarà DG, Gramatica F (2012) Preliminary technological assessment of microneedles-based dry electrodes for biopotential monitoring in clinical examinations. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 180:177–186 [Google Scholar]
- 19.García-López E, Siller HR, Rodríguez CA (2018) Study of the fabrication of aisi 316l microneedle arrays. Procedia Manufacturing 26:117–124, DOI 10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.014, URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S235197891830684X, 46th SME North American Manufacturing Research Conference, NAMRC 46, Texas, USA [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gardeniers HJ, Luttge R, Berenschot EJ, De Boer MJ, Yeshurun SY, Hefetz M, van’t Oever R, van den Berg A (2003) Silicon micromachined hollow microneedles for transdermal liquid transport. Journal of microelectromechanical systems 12(6):855–862 [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hall EO (1951) The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proceedings of the Physical Society Section B 64(9):747 [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hasegawa M, Yoon S, Guillonneau G, Zhang Y, Frantz C, Niederberger C, Weidenkaff A, Michler J, Philippe L (2014) The electrodeposition of fecrni stainless steel: microstructural changes induced by anode reactions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:26375–26384, DOI 10.1039/C4CP03744H, URL 10.1039/C4CP03744H [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Henry S, McAllister DV, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (1998) Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 87(8):922–925 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Izumi H, Suzuki M, Aoyagi S, Kanzaki T (2011) Realistic imitation of mosquito’s proboscis: Electrochemically etched sharp and jagged needles and their cooperative inserting motion. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 165(1):115–123 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jiang J, Moore JS, Edelhauser HF, Prausnitz MR (2009) Intrascleral drug delivery to the eye using hollow microneedles. Pharmaceutical research 26(2):395–403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaushik S, Hord AH, Denson DD, McAllister DV, Smitra S, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2001) Lack of pain associated with microfabricated microneedles. Anesthesia & Analgesia 92(2):502–504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kelly JJ, Tian C, West AC (1999) Leveling and microstructural effects of additives for copper electrodeposition. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 146(7):2540–2545 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kelso C, Watanabe H, Wazen J, Bucher T (2015) Microperforations Significantly Enhance Diffusion Across Round Window Membrane. Otology & neurotology 36(4):694–700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim K, Lee JB (2007) High aspect ratio tapered hollow metallic microneedle arrays with microfluidic interconnector. Microsystem Technologies 13(3):231–235, DOI 10.1007/s00542-006-0221-0, URL 10.1007/s00542-006-0221-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim K, Park DS, Lu HM, Che W, Kim K, Lee JB, Ahn CH (2004) A tapered hollow metallic microneedle array using backside exposure of SU-8. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 14(4):597–603, DOI 10.1088/0960-1317/14/4/021 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim YC, Park JH, Prausnitz MR (2012) Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 64(14):1547–1568, DOI 10.1016/j.addr.2012.04.005, emerging micro- and nanotechnologies for the development of novel drug delivery devices and systems [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kratchman LB, Schuster D, Deitrich MS, Labadie RF (2016) Force Perception Thresholds in Cochlear Implantation Surgery. Audiology and Neurotology 21(4):244–249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Li CG, Lee CY, Lee K, Jung H (2013) An optimized hollow microneedle for minimally invasive blood extraction. Biomedical Microdevices 15(1):17–25, DOI 10.1007/s10544-012-9683-2, URL 10.1007/s10544-012-9683-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li J, Liu B, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Jiang L, Yuan W, Liang L (2017) Fabrication of a ti porous microneedle array by metal injection molding for transdermal drug delivery. PLOS ONE 12(2):1–15, DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0172043, URL 10.1371/journal.pone.0172043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ma G, Wu C (2017) Microneedle, bio-microneedle and bio-inspired microneedle: A review. Journal of Controlled Release 251:11–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ma Y, Tao W, Krebs SJ, Sutton WF, Haigwood NL, Gill HS (2014) Vaccine delivery to the oral cavity using coated microneedles induces systemic and mucosal immunity. Pharmaceutical research 31(9):2393–2403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Martanto W, Davis SP, Holiday NR, Wang J, Gill HS, Prausnitz MR (2004) Transdermal delivery of insulin using microneedles in vivo. Pharmaceutical Research 21(6):947–952, DOI 10.1023/B:PHAM.0000029282.44140.2e, URL 10.1023/B:PHAM.0000029282.44140.2e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McCall AA, Swan EEL, Borenstein JT, Sewell WF, Kujawa SG, McKenna MJ (2010) Drug Delivery for Treatment of Inner Ear Disease: Current State of Knowledge. Ear and Hearing 31(2) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Micallef J (2015) Design Strategies for 3D Printing, Apress, Berkeley, CA, pp 175–200. DOI 10.1007/978-1-4842-0946-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Musazzi UM, Franzé S, Cilurzo F (2018) Innovative pharmaceutical approaches for the management of inner ear disorders. Drug delivery and translational research 8(2):436–449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Naples JG, Miller LE, Ramsey A, Li D (2019) Cochlear protein biomarkers as potential sites for targeted inner ear drug delivery. Drug delivery and translational research pp 1–12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.O’Mahony C, Pini F, Blake A, Webster C, O’Brien J, McCarthy KG (2012) Microneedle-based electrodes with integrated through-silicon via for biopotential recording. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 186:130–136 [Google Scholar]
- 43.Park JH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2005) Biodegradable polymer microneedles: fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery. Journal of controlled release 104(1):51–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Petch NJ (1953) The cleavage strength of polycrystals. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute 174(19):25–28 [Google Scholar]
- 45.Plontke SK, Hartsock JJ, Gill RM, Salt AN (2016) Intracochlear Drug Injections through the Round Window Membrane: Measures to Improve Drug Retention. AUDIOLOGY AND NEURO-OTOLOGY 21(2):72–79, DOI 10.1159/000442514 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Prausnitz MR (2004) Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 56(5):581–587, DOI 10.1016/j.addr.2003.10.023, breaking the Skin Barrier [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rad ZF, Nordon RE, Anthony CJ, Bilston L, Prewett PD, Arns JY, Arns CH, Zhang L, Davies GJ (2017) High-fidelity replication of thermoplastic microneedles with open microfluidic channels. Microsystems & nanoengineering 3:17034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Roxhed N, Gasser TC, Griss P, Holzapfel GA, Stemme G (2007) Penetration-enhanced ultrasharp microneedles and prediction on skin interaction for efficient transdermal drug delivery. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 16(6):1429–1440 [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rzhevskiy AS, Singh TRR, Donnelly RF, Anissimov YG (2018) Microneedles as the technique of drug delivery enhancement in diverse organs and tissues. Journal of Controlled Release 270:184–202, DOI 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.11.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Salt AN, Plontke SK (2018) Pharmacokinetic principles in the inner ear: influence of drug properties on intratympanic applications. Hearing research 368:28–40 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Salt AN, Sirjani DB, Hartsock JJ, Gill RM, Plontke SK (2007) Marker retention in the cochlea following injections through the round window membrane. Hearing Research 232(1):78–86, DOI 10.1016/j.heares.2007.06.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Santimetaneedol A, Wang Z, Arteaga D, Aksit A, Prevoteau C, Yu M, Chiang H, Fafalis D, Lalwani A, Kysar J (2019) Small molecule delivery across a perforated artificial membrane by thermoreversible hydrogel poloxamer 407. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 182:110300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schürch P, Pethö L, Schwiedrzik J, Michler J, Philippe L (2018) Additive manufacturing through galvanoforming of 3d nickel microarchitectures: Simulation-assisted synthesis. Advanced Materials Technologies 3(12):1800274, DOI 10.1002/admt.201800274 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schürch P, Ramachandramoorthy R, Pethö L, Michler J, Philippe L (2019) Additive manufacturing by template-assisted 3d electrodeposition: Nanocrystalline nickel microsprings and microspring arrays. Applied Materials Today p 100472, DOI 10.1016/j.apmt.2019.100472, URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352940719305918 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Serbin J, Egbert A, Ostendorf A, Chichkov BN, Houbertz R, Domann G, Schulz J, Cronauer C, Fröhlich L, Popall M (2003) Femtosecond laser-induced two-photon polymerization of inorganic–organic hybrid materials for applications in photonics. Opt Lett 28(5):301–303, DOI 10.1364/OL.28.000301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Suzuki M, Sawa T, Takahashi T, Aoyagi S (2015) Ultrafine three-dimensional (3d) laser lithographic fabrication of microneedle and its application to painless insertion and blood sampling inspired by mosquito. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 2748–2753, DOI 10.1109/IROS.2015.7353754 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Szeto B, Chiang H, Valentini C, Yu M, Kysar JW, Lalwani AK (2019) Inner ear delivery: Challenges and opportunities. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Traverso G, Schoellhammer CM, Schroeder A, Maa R, Lauwers GY, Polat BE, Anderson DG, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2015) Microneedles for drug delivery via the gastrointestinal tract. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 104(2):362–367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wang N, Zhen Y, Jin Y, Wang X, Li N, Jiang S, Wang T (2017) Combining different types of multifunctional liposomes loaded with ammonium bicarbonate to fabricate microneedle arrays as a vaginal mucosal vaccine adjuvant-dual delivery system (vadds). Journal of Controlled Release 246:12–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Watanabe H, Cardoso L, Lalwani AK, Kysar JW (2016) A dual wedge microneedle for sampling of perilymph solution via round window membrane. Biomedical Microdevices 18(2):24, DOI 10.1007/s10544-016-0046-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Watanabe H, Lalwani AK, Kysar JW (2016) In situ nano-indentation of round window membrane. In: Tekalur SA, Zavattieri P, Korach CS (eds) Mechanics of Biological Systems and Materials, Volume 6, Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 17–29 [Google Scholar]
- 62.Watanabe H, Lalwani AK, Kysar JW (2016) In situ NANO-indentation of round window membrane. In: Tekalur SA, Zavattieri P, Korach CS (eds) Mechanics of Biological Systems and Materials, vol 6, Springer International Publishing, Cham Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London, chap 3, pp 17–29 [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wazen JM, Stevens JP, Watanabe H, Kysar JW, Lalwani AK (2017) Silver/silver chloride microneedles can detect penetration through the round window membrane. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 105(2):307–311, DOI 10.1002/jbm.b.33557, URL https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jbm.b.33557, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jbm.b.33557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yu M, Arteaga DN, Aksit A, Chiang H, Olson ES, Kysar JW, Lalwani AK (2020) Anatomical and functional consequences of microneedle perforation of round window membrane. Otology & Neurotology 41(2):e280–e287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]