A 35-year-old male patient presented with facial and skeletal deformities since birth and no family history. He had short stature, facial deformities such as brachycephaly, flattened occiput, midfacial hypoplasia, and hypertelorism. No mental retardation was observed. He had exophthalmos, strabismus [Figure 1a], low sets of ears, beaked nose, hypoplasia of maxilla, protrusion of mandible [Figure 1b], high arched palate, double teeth line over maxilla, and crowding of teeth [Figure 2a and b]. Complete syndactyly and fused, thinned nail plates with splitting was present over bilateral hands and feet [Figure 3a-c]. Complete abduction at the shoulder joint was restricted [Figure 4]. Pure tone audiometry was suggestive of conductive hearing loss. X-rays were suggestive of these features [Figure 5a-d]. A diagnosis of Apert syndrome which is a rare type 1 acrocephalosyndactyly was made based on clinical features and X-ray findings.[1] Incidence is 1/160,000 live births.[2] It shows autosomal dominant inheritance resulting from mutation in FGFR 2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2) gene on chromosome 10.[3] Differential diagnosis includes Crouzon syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, Saethre-Chotzen syndrome[4] which are differentiated based on a constellation of symptoms. Treatment includes a multidisciplinary approach and collaboration of multiple specialists with proper psychological and genetic counseling.
Figure 1.
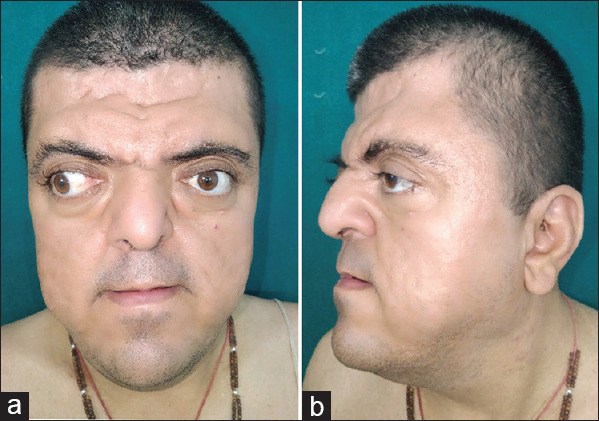
(a) Showing brachycephaly, acrocephaly, midfacial hypoplasia, hypertelorism, proptosis and strabismus. (b) Showing low sets of ears, beaked nose, maxillary hypoplasia, mandibular protrusion, flattened occiput
Figure 2.
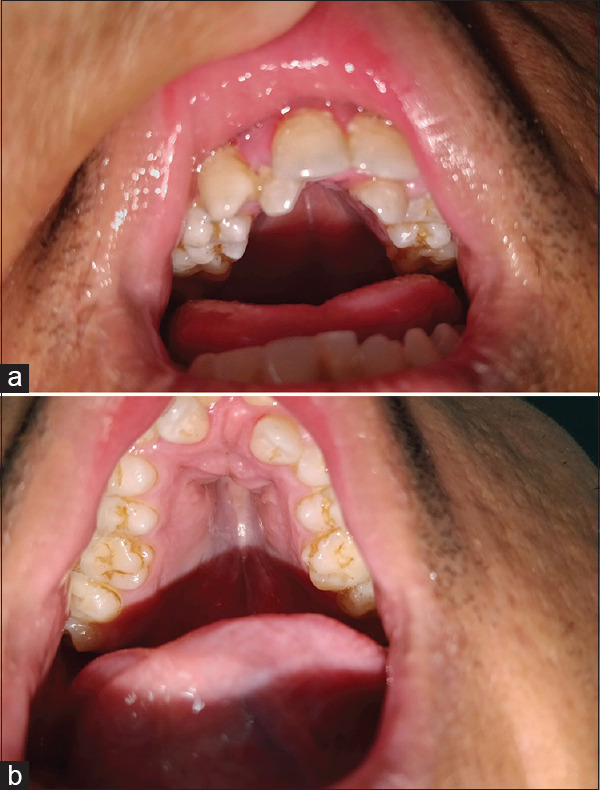
(a) Showing double teeth line and crowding of teeth of maxilla. (b) Showing high arched palate and membrane covering the bony defects
Figure 3.
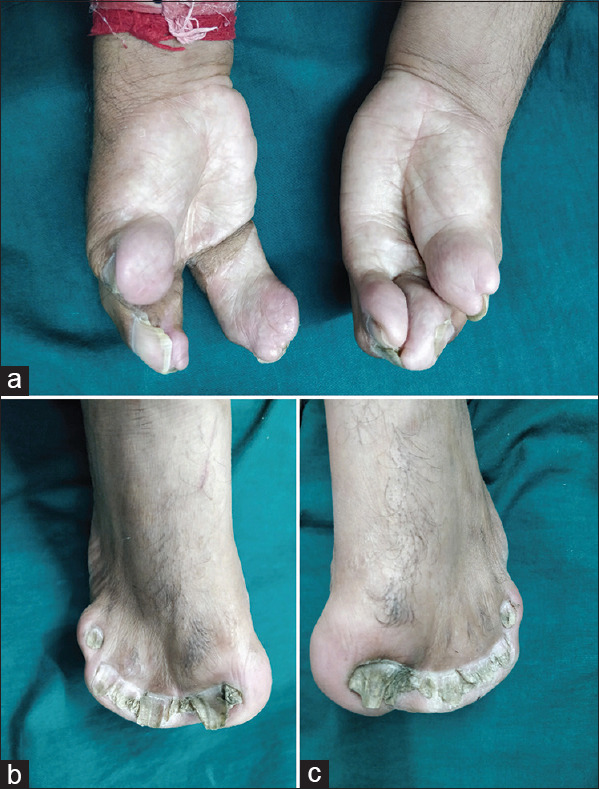
(a) Showing complete syndactyly of hands. (b) Showing complete syndactyly of right feet with fused and thinned nail plates. (c) Showing complete syndactyly of left feet with fused and thinned nail plates
Figure 4.
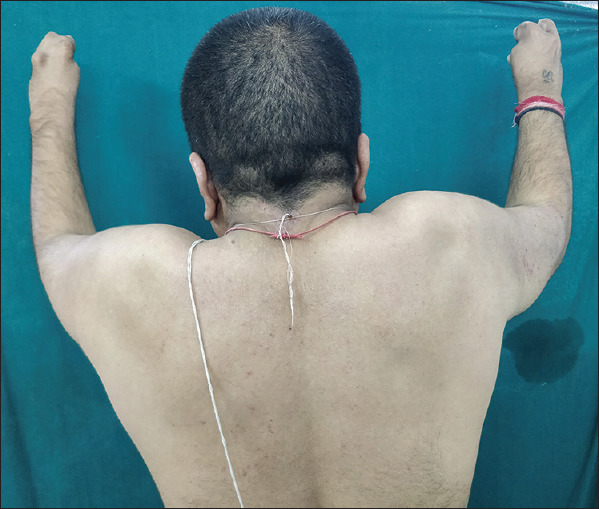
Showing restriction in complete abduction at shoulder joint
Figure 5.
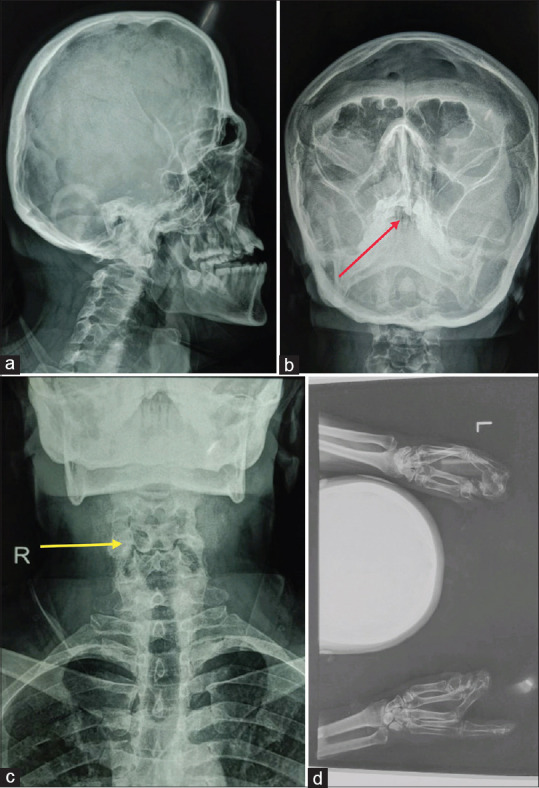
(a) X-ray skull lateral view showing brachycephaly, hypoplastic maxilla, protrusion of mandible and small orbital cavity. (b) X-ray skull paranasal sinus showing cleft palate (Red arrow). (c) X-ray cervical spine showing blocked vertebrae at C5-C6 and C6-C7 level (yellow arrow). (d) X-ray bilateral hands showing complete syndactyly of both hands
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.DeGiovanni CV, Jong C, Woollons A. What syndrome is this .Apert syndrome? Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:186–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bartlett SP, Mackay GJ. Craniosynostosis syndromes. In: Aston SJ, Beasley RW, Thorne CHM, editors. Grabb and Smith's Plastic Surgery. 5th ed. Lippincott-Raven: 1997. pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wallis-Crespo MC, Enid GB. Pathology teach and tell: Acrocephalosyndactyly type I (Apert syndrome) Fetal Pediat Pathol. 2004;23:191–7. doi: 10.1080/15227950490423160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Katzen JT, McCarthy JG. Syndromes involving craniosynostosis and midface hypoplasia. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2000;33:1257–84. doi: 10.1016/s0030-6665(05)70280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


