Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, besides Alzheimer’s Disease, characterized by multiple symptoms, including the well-known motor dysfunctions. It is well-established that there are differences in the fecal microbiota composition between Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients and control populations, but the mechanisms underlying these differences are not yet fully understood. To begin to close the gap between description and mechanism we studied the relationship between the microbiota and PD in a model organism, Drosophila melanogaster. First, fecal transfers were performed with a D. melanogaster model of PD that had a mutation in the parkin (park25) gene. Results indicate that the PD model feces had a negative effect on both pupation and eclosion in both control and park25 flies, with a greater effect in PD model flies. Analysis of the microbiota composition revealed differences between the control and park25 flies, consistent with many human studies. Conversely, gnotobiotic treatment of axenic embryos with feces-derived bacterial cultures did not affect eclosure. We speculate this result might be due to similarities in bacterial prevalence between mutant and control feces. Further, we confirmed a bacteria-potentiated impact on mutant and control fly phenotypes by measuring eclosure rate in park25 flies that were mono-associated with members of the fly microbiota. Both the fecal transfer and the mono-association results indicate a host genotype-microbiota interaction. Overall, this study concludes functional effects of the fly microbiota on PD model flies, providing support to the developing body of knowledge regarding the influence of the microbiota on PD.
Subject terms: Microbiome, Neurodegeneration, Drosophila
Introduction
Neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, create a high burden of morbidity and mortality, which is expected to increase in the next few decades1,2. Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease affecting more than ten million people worldwide2. Most cases of PD are idiopathic, while a small percentage (3–5%) is genetic in origin3. Of these genetic cases, mutation of the PRKN gene contributes to approximately 50% of all autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism4. Drosophila melanogaster (the fruit fly) has been used extensively as a model to better understand and characterize many neurodegenerative diseases5,6. Mutation of the Drosophila melanogaster ortholog of the PRKN gene, parkin (park), leads to a tenable model of PD that has many similarities to PD patients: selective loss of dopaminergic neurons, decreased motor function, loss of olfaction, reduced lifespan, mitochondrial dysfunction and others7–10. The relative ease of use of flies and powerful genetic tools available in this fly PD model has contributed greatly to the study and understanding of PD5.
Gastrointestinal (GI) dysfunctions are among the most common non-motor symptoms associated with PD, with constipation being the most common premotor symptom, affecting more than 70% of PD patients11. There have been a number studies that have demonstrated that the gut microbiota is altered in PD patients compared to healthy control individuals12 and it has been hypothesized that this altered microbiota is largely responsible for many of the GI disorders observed. Beyond this, the altered PD microbiota has been hypothesized to play a role in non-GI PD symptoms, specifically related to the gut-brain axis. In support of this, PD patient fecal transplant into germ-free PD model mice produced an increase in motor deficits compared to PD model mice with a healthy donor fecal transplant13. Taken together, the results from these previous studies prompted our investigation of the microbiota in the park mutant fly model.
Relative to humans and other mammals, the D. melanogaster microbiota is low-abundance and low-diversity, making it simpler and easier to study microbiota interactions. Laboratory and wild flies are typically colonized by 104–105 microorganisms, and the 2–5 most abundant isolates often represent > 90% of the microbial community14–16. The most represented bacteria in the gut are usually acetic acid (AAB) and lactic acid bacteria (LAB), especially members of the genera Acetobacter and Lactobacillus, respectively, and Enterobacteriaceae. Similar to mammals, the fly microbiota composition is determined by both fly genotype and diet16–19. Fly larvae possess no gut microbes upon hatching and thus obtain and develop their microbiota from both the environment and food source. Because there is no evidence of high-fidelity host-mediated acquisition or retention of specific microorganism within or across generations, the Drosophila microbiota is ‘inconstant’; although some bacterial isolates colonize and persist within the gut better than others20–22. A previous analysis of the microbiota in a PD fly model revealed differences in the diversity, but not specific taxonomic changes, between the microbiota of control and PD-model flies23. The intracellular endosymbiont Wolbachia is also a common inhabitant of the reproductive tract of Drosophila and, unlike the gut microbiota, is transmitted from mother to offspring within the egg24.
The association between Drosophila and its microbiota is experimentally tractable: bacteria-free embryos are readily derived by bleach treatment and members of the Drosophila microbiota can be isolated in pure culture in the laboratory. Inoculating bacteria-free fly embryos with a defined microbial species or community is called gnotobiotic culture and permits exquisite dissection of the contributions of individual microorganisms to specific fly phenotypes25. Adding back one or more bacterial species to the same genotype of sterile fly embryos permits the detection of the magnitude of variation in host traits that is due to the microbiota26. Unlike the gut microbiota, bleach treatment does not eliminate Wolbachia from the fly embryos.
In this study we sought to better define the relationship between the microbiota and a D. melanogaster PD model by addressing two major questions: (1) Does microbiota manipulation, including via fecal transfer, bacterial-elimination, or gnotobiotic culture affect development, an early and fundamental biologic process, in a PD-fly model? (2) Does the microbiota vary between control and PD model flies? This study aims to address these questions by measuring fly pupation, eclosion, and/or microbiota composition under a variety of conventional and gnotobiotic culture conditions.
Results
Fecal transfer from park25 flies reduces total pupation rates
To determine whether differences in the microbiome between control and park25 flies might contribute to variation in fly phenotypes we compared the pupation rate of flies that received fecal transfers from control and park25 donors. Fecal transfers were performed by allowing males to defecate on cooked but not autoclaved diet vials for 3 days before transferring fly embryos to the feces-seeded diet. The park25 feces reduced the total pupation rate of all fly genotypes when compared to the embryos that were placed on food that contained control feces (post-hoc Tukey test: P < 0.0001 for all three; Fig. 1). Each of the pupation rates are based off the 60 embryos placed on the food, such that both the park25 heterozygous and homozygous pupae numbers come from the same 60 embryos. Two-way ANOVA analysis revealed that 86% of the variation is due to genotype (P < 0.0001), which is expected given the effects of the park25 mutation. Additionally, 3.6% of the variation is due to the fecal transfer effect (P < 0.0001). When analyzing daily pupation rates, the homozygous park25 flies were the only genotype that had reduced pupation rates on two consecutive days when they received feces from park25 mutants, suggesting that the park25 homozygous flies are more susceptible to the detrimental effects of the park25 fecal transfer (Supplementary Fig. S1). Together, these results identify a negative effect on flies of multiple genotypes when they received a fecal transfer from park25 versus control flies.
Figure 1.
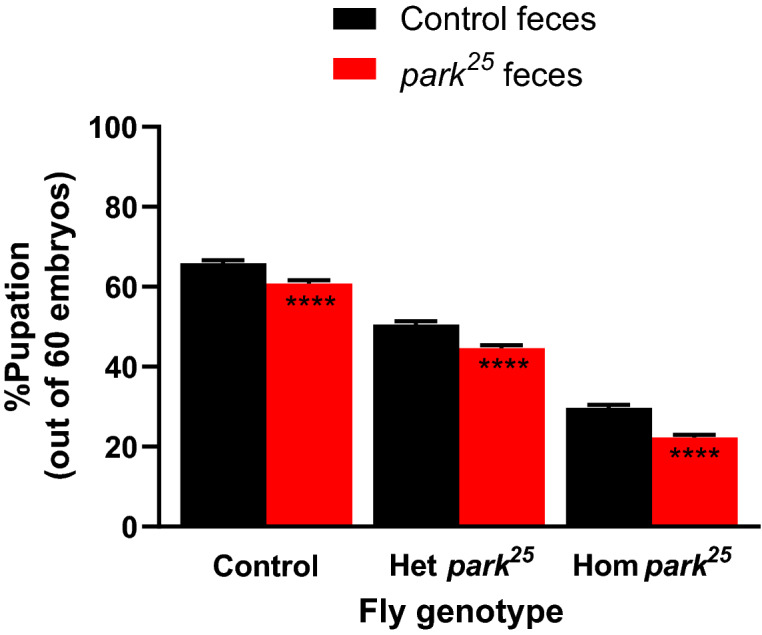
Feces from park25 flies reduces total pupation rate. Total pupation rates were calculated in control, heterozygous (Het) park25 and homozygous (Hom) park25 flies from the 60 embryos that were placed on food that had control or park25 feces present. Data are presented as mean and SEM. Asterisks represent the results of a post-hoc Sidak’s multiple comparisons test comparing the two feces groups within each fly genotype (**** = P < 0.0001). Results are from 45 separate vials in each group.
The park25 feces reduces fly eclosion rates
Eclosion rates for each fly genotype-fecal transfer combination were determined by dividing the number of flies that eclosed by the total number of pupae that had developed for that genotype. Figure 2A shows that all three fly genotypes experienced a reduced eclosion rate when placed on the park25 feces compared to the control feces (control and homozygous park25, P < 0.0001; heterozygous park25, P = 0.0101). As with pupation, the majority of variation identified was due to fly genotype (54%, P < 0.0001), which is reflected by the reduced eclosion rates of both the park25 heterozygous and homozygous flies on control feces compared to the control flies on control feces (both P < 0.0001). In agreement with pupation, a smaller amount of variation was due to the feces (11.9%, P < 0.0001) and there was also a significant interaction between the fly genotype and the feces transfer, indicating that there might be a specific effect of the fecal transfer in the park25 fly (P = 0.0042, 1.4% of variation).
Figure 2.
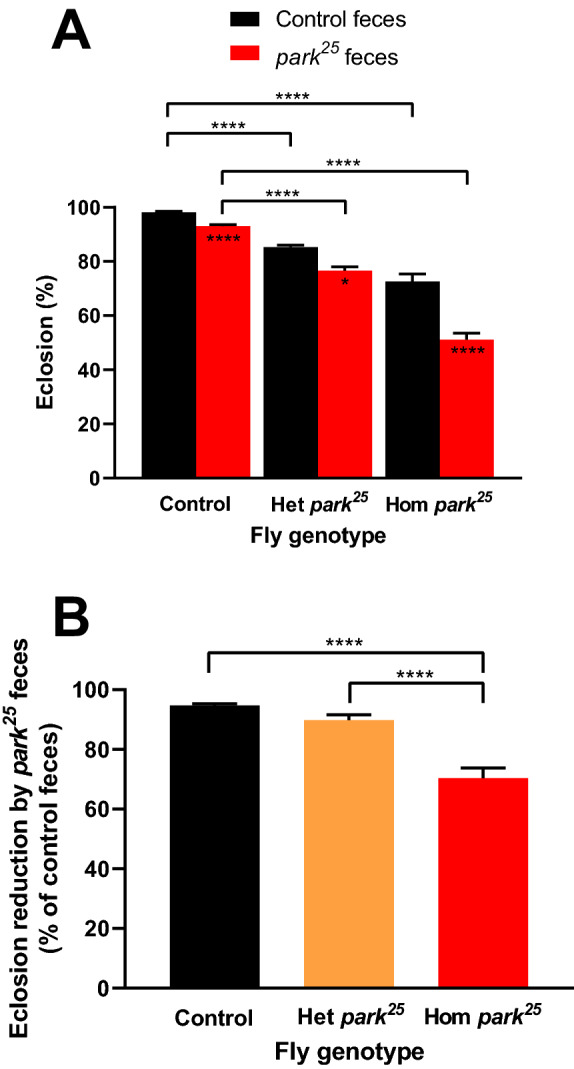
Eclosion rates are reduced in all fly genotypes but more in homozygous park25 flies with park25 feces transfer. (A) Total eclosion rates were determined in control, heterozygous (Het) park25 and homozygous (Hom) park25 flies based on the total number of pupae for each genotype. (B) The relative eclosion reduction caused by the park25 fecal transfer, calculated as a percentage of the control feces eclosion, was determined. Data are presented as mean and SEM. Asterisks represent the results of a post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Asterisks inside the bars compare the two feces groups within each fly genotype. * = P < 0.05 and **** = P < 0.0001. Results are from 45 separate vials in each group.
Regardless of the source of the fecal inoculum, both the heterozygous and homozygous park25 flies had reduced eclosion rates compared to the control flies, indicating that the park25 genotype likely has a reduced eclosion rate due to the park25 mutation (Fig. 2A). However, it appears that the park25 fecal transfer had an additional negative impact on the park25 flies. This feces-dependent differential effect, based on fly genotype, of eclosion reduction due to the park25 feces becomes more apparent when observing the number of pupae that failed to eclose. This measurement indicates that the control flies did not have an increased number of failed eclosures due to park25 feces (P = 0.1423), while the heterozygous and homozygous park25 pupae did (P = 0.0023, P < 0.0001, respectively; Supplementary Fig. S2).
Further, the detrimental effects of the park25 feces on fly eclosion were of larger magnitude for the homozygous park25 flies than other genotypes. When we calculated the percent eclosion rates of each genotype on park25 feces relative to control feces, there was no difference in the eclosion rates of the heterozygous mutants and control flies (P = 0.1211), but both genotypes had higher eclosion rates than the park25 homozygous flies (P < 0.0001 vs both, Fig. 2B). Further support of differential feces-genotype interaction is provided by observing the eclosion rate over time. Supplementary Figure S3 shows that the control flies experienced a reduction in eclosion due to park25 feces on day 10 (P < 0.0001), while heterozygous park25 flies had no significant reduction on any day in the experiment. However, homozygous park25 flies experienced a reduction in eclosion due to park25 feces on days 9, 10 and 11 (P = 0.0001, P = 0.0012, P = 0.0005, respectively).
The whole-body microbiota varies between conventional PD model and control flies
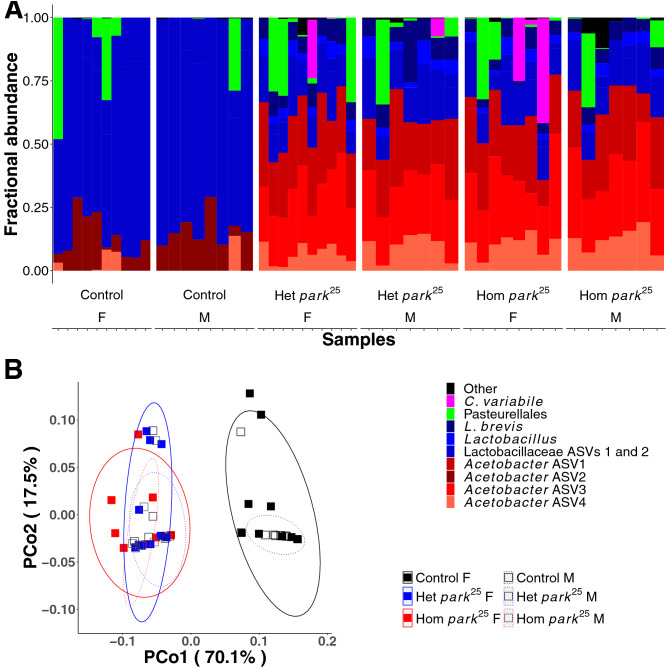
Our observations suggest that the composition of park25 and control fly microbiomes are different and cause different developmental effects on the flies tested. Thus, as an extension of these results we measured the bacterial microbiota of whole-body conventionally reared park25 and control flies. The samples for sequencing were collected at a different time than the experiments above and, because of the inconstant microbiota27, the sequencing results should not be conflated as measuring the microbiota of the flies that deposited feces in the previous experiments. Sequencing of the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene revealed significant differences in the whole-body microbial communities of our stocks. The most notable difference between the mutant and control populations was the presence of the reproductive tract endosymbiont Wolbachia in the control flies (Supplementary Fig. S4 and Supplementary Table S1); however, Wolbachia are not likely to be transferred between flies via ingestion and therefore are not likely candidates for the effects observed with fecal transfer. After Wolbachia were removed from the analysis (to focus on non-reproductive tract microorganisms), beta-diversity metrics that factor microbial abundance reported significant differences in the microbiota composition of the different fly stocks with fly genotype, but not with the sex of the flies (Fig. 3, Supplementary Fig. S5, and Table 1). Also, there was not a significant genotype-sex interaction, indicating that both males and females showed the same genotype-dependent changes in microbiota composition (Table 1). Amplicon sequence variants assigned to the LAB (more abundant in controls) and AAB (less abundant in controls) were significantly different in relative abundance between flies of different genotypes (Supplementary Fig. S6). The decreased abundance of AAB in the control flies, which also bore Wolbachia, is consistent with previous reports that Wolbachia prevalence is negatively associated with AAB abundance28. Overall, the data reveal a consistent difference in the microbiota composition of Wolbachia-discordant control and park25 mutant flies that were reared side-by-side under conventional laboratory conditions.
Figure 3.
The microbiota of control and park25 flies. (A) Taxon plot of control and park25 flies, separated by sex. Mutants of park25 were distinguished as homozygotes and heterozygotes based on the presence of the Tubby marker. Bars represent distinct ASVs. The legend shows the lowest taxonomic level that was assigned to each ASV. (B) Principal coordinates plot, showing the first two coordinates calculated from a weighted Unifrac distance matrix.
Table 1.
Genotype and sex-dependent differences in microbiota composition of control and park25 mutants.
| df | Weighted Unifrac | Unweighted Unifrac | Bray Curtis | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | MS | F | R2 | P | SS | MS | F | R2 | P | SS | MS | F | R2 | P | ||
| G | 2 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 72.18 | 0.71 | 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 6.12 | 0.21 | 0.001 | 6.71 | 3.36 | 111.90 | 0.79 | 0.001 |
| S | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.25 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 0.00 | 0.25 |
| V | 3 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 5.02 | 0.07 | 0.002 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.47 | 0.16 | 5.27 | 0.06 | 0.001 |
| GS | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.79 |
| R | 41 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 1.23 | 0.03 | 0.15 | ||||||
| T | 49 | 0.53 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 8.48 | 1.00 | |||||||||
Effects of fly genotype (G), fly sex (S), fly vial (V), and the G-S interaction (GS) are shown along with residuals (R) and totals (T) as determined by PERMANOVA. PERMANOVA values are degrees of freedom (df), sum of squares (SS), mean squares (MS), F statistic (F), R2 value (R2), and P-value (P).
Axenic preparation of park25 homozygous embryos has a dramatic effect on eclosion
To determine if the different effects of fecal transfer from park25 or control flies could be attributed to variation in the bacterial microbiota we measured eclosion rates in flies that were inoculated as sterile embryos with cultured feces from control and park25 adult flies. We observed two major differences between the different treatment approaches: fecal transfer vs fecal bacterial culture inoculation. First, the process of generating axenic embryos dramatically decreased the eclosion rates of homozygous, but not heterozygous, park25 mutants relative to controls. (Fig. 4, P < 0.0001). Second, there was no effect related to feces source (control or park25) that were used to create the bacterial cultures on eclosion rate regardless of the genotype that received the bacterial culture. These results were not due to a limited number of homozygous pupae present in the tubes, as all experimental vials with park25 pupae contained approximately 30% park25 homozygous pupae, while the axenic experimental vials had the most pupae/vial (Supplementary Table S2). The most significant source of variation was fly genotype (P < 0.0001), accounting for 65% of the variation, with the bacterial status of the fly contributing only 0.23% to variation (P = 0.0082). No difference in the eclosion rates were observed between the axenic and the two gnotobiotic treatments regardless of fly genotype (all P > 0.52). Together, these results suggest that variation in the cultured bacteria in fly feces does not contribute to the variation in the eclosion rates observed in park25 mutant and control flies when reared on fly feces-seeded vials.
Figure 4.
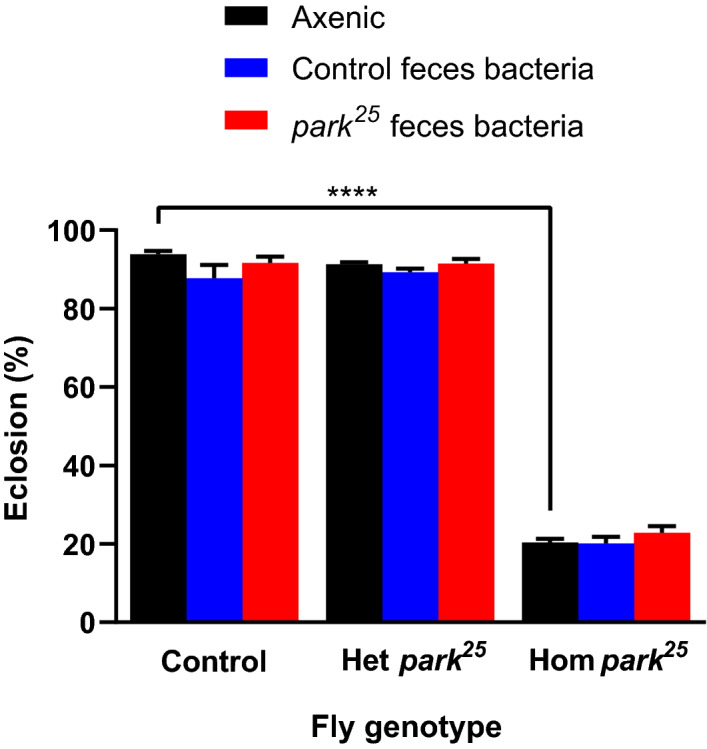
Axenic preparation of homozygous park25 embryos dramatically reduces eclosion rate. Embryos from park25 and control flies were made axenic and gnotobiotic for feces-derived bacteria from park25 or control flies. Pupae count and eclosion was recorded from each vial. Heterozygous (Het) park25 pupae were differentiated from the homozygous (Hom) park25 pupae by the presence of the Tubby marker on the TM6C balancer chromosome. Data are presented as mean and SEM. Post-hoc Tukey’s analysis results are shown: **** = P < 0.0001. Sample (number of vials) sizes: Control (axenic = 40, control feces = 41, park25 feces = 42), Het and Hom park25 (axenic = 202, control feces = 63, park25 feces = 59).
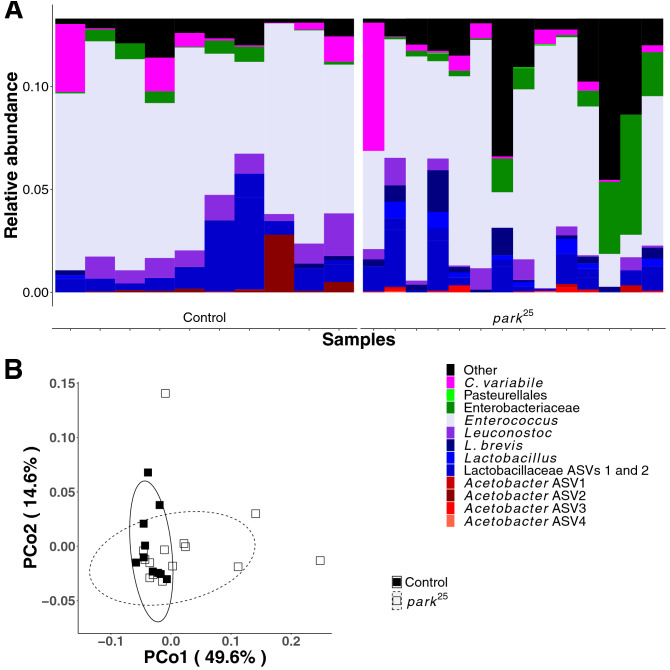
In contrast to whole-body flies, the major difference in the microbiota of fecal samples collected from park25 mutant and control flies was attributed to microbial identity, not abundance (Table 2 where unweighted Unifrac, but not weighted Unifrac or Bray–Curtis distance metrics showed significant variation in the community composition with host genotype; corresponding PCoA plots are in Fig. 5 and Supplementary Figure S7. Analyzed feces were collected from independent experiments and, because of the inconstant microbiota, the results cannot be directly compared to other experiments here. Analysis of the fecal samples and siblings of the fecal donors revealed that the microbiota composition varied with respect to both the host genotype and the sample type (fly or feces). For example, the feces was dominated by an Enterococcus ASV (Fig. 5A) and the four AAB ASVs that were most abundant in the flies (Fig. 3, Supplementary Table S3 and Supplementary Fig. S8) were detected at very low levels. The low level of AAB reads in the feces suggests that AAB DNA in living or dead cells persists poorly between the location of abundant bacterial cells in the flies and collection of < 24 h old feces. Additionally or alternatively, Enterococcus cells may grow rapidly in the feces since there is little evidence of their abundance in live flies, or Enterococcus DNA may survive gut transit well. Together, these results suggest that the role of P generation defecation in establishing the F1 adult microbiota in the flies in our study, and perhaps flies generally, is incompletely understood.
Table 2.
Genotype-dependent differences in fecal microbiota composition of control and park25 mutants.
| df | Weighted Unifrac | Unweighted Unifrac | Bray-Curtis | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | MS | F | R2 | P | SS | MS | F | R2 | P | SS | MS | F | R2 | P | ||
| G | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.34 | 0.09 | 0.061 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 2.60 | 0.10 | 0.003 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 1.82 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| V | 10 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 1.24 | 0.46 | 0.26 | 1.54 | 0.15 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 0.89 | 0.39 | 0.61 |
| R | 12 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 1.76 | 0.15 | 0.48 | 1.57 | 0.13 | 0.53 | ||||||
| T | 23 | 0.23 | 1.00 | 3.69 | 1.00 | 2.96 | 1.00 | |||||||||
Effects of fly genotype (G), fly vial (V), residuals (R), and totals (T) as determined by PERMANOVA. PERMANOVA values are degrees of freedom (df), sum of squares (SS), mean squares (MS), F statistic (F), R2 value (R2), and P-value (P).
Figure 5.
The microbiota of feces from control and park25 flies. Fecal samples were collected from male controls and a mixture of heterozygous and homozygous male park25 flies. (A) A taxon plot with bars representing distinct ASVs. The legend shows the lowest taxonomic level that was assigned to each ASV. (B) Principal coordinates plot, showing the first two coordinates calculated from a weighted Unifrac distance matrix.
Variation in the bacterial microbiota of D. melanogaster influences eclosion success in park25 mutants
To understand the extent to which bacterial microbiota of D. melanogaster influence eclosion success in homozygous and heterozygous park25 mutants, we compared eclosion rates of mono-associated flies. Previous gnotobiotic experiments provided no direct evidence that variation in the bacterial communities of the flies influenced fly eclosion in these park25 mutants. In contrast, fecal transfer experiments suggested that microbiome changes did affect fly eclosion. Similar to our results with cultured feces, we observed dramatically reduced eclosion in homozygous park25 flies compared to heterozygous park25 flies (Fig. 6). Unlike with cultured feces, there were differences in fly eclosion rates when they were axenic or colonized with a combination of four bacterial species cultured from flies in Ithaca, NY29 (heterozygous park25: P = 0.0025, homozygous park25: P < 0.0001) or individually with Acetobacter tropicalis (heterozygous park25: P = 0.0088, homozygous park25: P = 0.0456). Additionally, there was a significant fly genotype-bacterial treatment interaction (two-way ANOVA, P < 0.0001): the combination and A. tropicalis treatments led to higher eclosion survival than the axenic treatment in park25 homozygous flies; but lower survival than axenic flies for park25 heterozygous flies. Taken together, these results confirm that variation in the bacterial microbiota of park25 flies can contribute to variation in a key survival phenotype, eclosion success.
Figure 6.
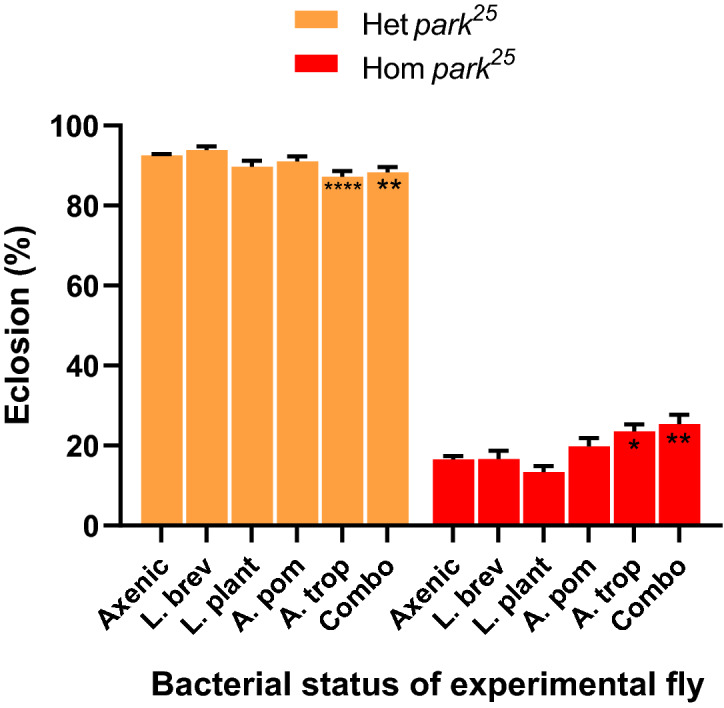
Mono-association with A. tropicalis or a combination of bacteria with park25 flies can alter eclosion rate. Embryos from park25 flies were made axenic and then mono-associated with four different laboratory bacterial strains, or inoculated with an equal CFU combination of the four strains (Combo). Pupae count and eclosion was recorded from each vial. Heterozygous (Het) park25 pupae were differentiated from the homozygous (Hom) park25 pupae by the presence of the Tubby marker on the TM6C balancer chromosome. Data are presented as mean and SEM. Post-hoc Dunnett’s analysis comparing to the axenic flies are shown: **** = P < 0.0001, ** = P < 0.01, * = P < 0.05. Axenic (n = 160), L. brev = Lactobacillus brevis (n = 24), L. plant = Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (n = 37), A. pom = Acetobacter pomorum (n = 35), and A. trop = Acetobacter tropicalis (n = 37), combination (n = 32).
Discussion
There have been many studies showing alterations in the fecal microbiota of PD patients compared to control populations (reviewed in12). To our knowledge, there has only been a single study that has looked at the microbiota in a fly PD model (PINK1B9) that also identified differences between the microbiome of the PD model and control flies23. Under condition-matched conventional rearing, our park25 PD model fly microbiota was considerably different from the control fly (Fig. 3), with significant differences in the abundance of AAB and LAB. Fly sex was not a determinant of variation in microbiota composition. Alterations in microbiota were observed in conventionally-reared flies and therefore factors such as inconstant exposure to or acquisition of distinct sets of microbes in the different vials from which samples were drawn could contribute to the observed effects; though the level of replication and matched rearing conditions of the flies suggests potential influences of host genotype on fly microbiota composition. Future experiments with gnotobiotic flies could conclusively rule out environmental effects but could be challenging because of the low survival rates of the homozygous park25 flies (Fig. 4).
Presence of the endosymbiont Wolbachia has been associated with lower counts of Acetobacter spp. in other flies30 and is positively correlated with worsening phenotypes in a fly model of Alzheimer’s disease. In agreement with this, a recent report linked Wolbachia and neurodegenerative disease severity in Drosophila by showing that administration of a Lactobacillus probiotic increased Acetobacter abundance, lowered Wolbachia titers, and ameliorated Alzheimer’s disease phenotypes31. Thus, the presence of Wolbachia could be a factor contributing to differences between the microbiota of our control and park25 flies. Our analysis identified that the Wolbachia status of our control and mutant stocks was not congruent. In consideration of the fecal transfer, it is important to recognize that Wolbachia are intracellular endosymbionts that are transmitted between generations via the germ line and not fecal transfer24. This was validated by sequence analysis which demonstrated that Wolbachia were not represented in the sequenced fecal samples, confirming their absence and irrelevance to observed functional effects of the park25 fecal transfer (Fig. 5). Our data indicate that Acetobacter spp. are reduced in our control flies both in diversity and abundance (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. S6). The data do raise the question if the differences in the eclosion of control and park25 flies is due to their discordant Wolbachia status. While some influence on eclosion is possible, Wolbachia is unlikely to be the sole contributor to this observed difference as PD phenotypes have been detected in another laboratory using the same park25 mutant and a Wolbachia-concordant control strain (8, unpublished data). The potential direct and indirect (through the microbiota) influence(s) Wolbachia has on park25 mutant development requires further analysis.
We used fecal transfers to assess whether the microbiota influences park25 mutant eclosion success. Microbiota studies typically rear dechorionated embryos free of bacteria or with a defined bacterial inoculum25, but we adopted an alternate fecal transfer approach for two reasons. First, fecal transfers have successfully identified microbiota effects in other studies (e.g., 32) and provided a straightforward method to use in initial functional explorations. Second, as shown in Figs. 4 and 6, the viability of axenic and gnotobiotic park25 flies is very low, which makes this process extremely difficult and impedes experimentation. We do not know the cause of this high mortality rate, but it appears to be related to the dechorionation process. Alternative approaches that avoid the dechorionation step are available, but these approaches also have limitations. For example, while raising axenic fly stocks for several generations after dechorionation the stocks are vulnerable to bacterial contamination, requiring the use of antibiotics which can alter but not necessarily eliminate all colonizing microorganisms. One successful recent approach fed bacteria to newly eclosed (and presumably bacteria-depleted) PINK1 mutant flies23, which might be a more high-throughput approach. Further understanding of the mechanism that determines the difference in microbiota composition between control and park25 flies may provide insight into why the microbiota composition of adult flies and fecal transfers are distinct.
The exposure of hatching larvae to park25 fly feces led to dramatically reduced fly eclosion success than did exposure to control feces. Conversely, when we inoculated flies with cultured feces there was no difference in the effect on fly eclosion. The difference in outcome between the two experiments suggests that different effectors are transmitted, or possibly diluted, when the feces is cultured first versus when it is directly deposited. We hypothesized that the fecal microbiota would largely reflect the adult fly microbiota and that culturing feces versus direct deposition would lead to similar outcomes. However, we detected no difference between the fecal microbiota of mutant and control flies even though adult mutant and control flies had a different microbiota composition. In this regard, the outcomes of the fecal transfer vs culture experiments were congruent: there was only a difference in recipient phenotypes when there was a difference in the source’s microbiota composition. Altered phenotypes following the transfer of direct but not cultured feces could be also be due to an effector that is abiotic or non-bacterial (e.g., fungal); or it may be that the culture step abates the effect. Culture in standard laboratory medium may select for certain strains in ways that does not occur in the fly diet, leading to differences in identity and abundance of key microbiota members. To address these potential limitations, the bacterial mono-association experimental approach was critical to understanding whether variation in bacterial microbiota can alter the eclosion success of park25 flies in a genotype-dependent (heterozygous vs. homozygous) manner.
We found that there is a functional consequence with the feces transfer, in that the park25 feces had a negative impact on pupation and eclosure on both the control and park25 flies; however, the homozygous park25 flies appeared to be affected the most. It is possible that homozygous park25 flies are more susceptible to park25 feces due to their general weak state. It is established that park25 flies have reduced mitochondrial function and deficiency in energy production8,10. Additionally, axenic flies have disrupted insulin-like signaling and glucose regulation compared to microbiota-colonized flies26,33,34. Therefore, axenic homozygous park25 flies may have compounding, additive deficiencies that reduce their ATP production during eclosion, which is likely a high energy-requiring process. In support of this idea, 34.9% of all axenic park25 pupae were found dead and stuck in the process of eclosing, compared to 1.6% of the axenic control flies or 3.4% of the axenic heterozygous park25 flies. Moreover, when the park25 homozygous flies had two fecal-derived gnotobiotic treatments, the rate of being stuck in eclosure reduced to 15.9% with the control bacteria and 13.4% with the park25 bacteria. This reduced rate of incomplete eclosion in the gnotobiotic populations might have masked the negative effect of the park25 bacteria on eclosure in these flies compared to the axenic controls, however, since both gnotobiotic groups had similar reductions in getting stuck, this is unlikely.
Despite the large number of studies showing an altered fecal microbiome in PD patients, there have been very few studies demonstrating that the PD microbiome has functional consequences. The most compelling functional study utilized PD model mice that had a fecal transplant from PD and healthy control patients. The PD microbiome transplant mice showed an increase in motor dysfunction and alpha-synuclein aggregation13. Our fecal transfer experiments, like another recent Drosophila PD model functional microbiome study23, did not directly manipulate the microbiome to a specifically-defined microbiota composition but we do use mono-association experiments to demonstrate species-specific influences of the associated microorganisms. Our study is the first to indicate that there might be a specific microbiota-fly genotype effect that might also be occurring with the PD microbiome and homozygous park25 flies. This type of specific microbiota-fly genotype interaction is known to happen with Wolbachia35. The current study adds to the small group of publications that indicate that the altered PD microbiome negatively affects biological processes in the host. This provides further support for research and identification of bacterial species involved in these functional effects, which has the potential to direct microbiome manipulation in PD patients that may alleviate symptoms.
Methods
Drosophila stocks and maintenance
Mutant, park25, Drosophila melanogaster were provided by Dr. Leo Pallanck at the University of Washington. This mutant stock was derived from w1118 control flies, which were obtained from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center (Indiana University). In all experiments, w1118 flies were used as the control for the park25 flies. The park25 stock in our laboratory has been backcrossed with the w1118 stock so that all chromosomes are from the w1118 background. The park25 chromosome is balanced over the TM6C balancer, allowing for identification of homozygous and heterozygous flies through use of the Tubby gene phenotype. All fly stocks were raised on standard cornmeal-molasses diet at 25 °C in a 14/10-h light cycle.
Fecal transfer
In each of three separate experiments, five separate food vials for each fly genotype were seeded with forty males of that genotype to allow flies to deposit their feces on the food. Males were used so that no embryos were laid on the food. All males were over the age of three days to ensure that they had an established microbiome36. A random mix of both homozygous and heterozygous park25 male flies were used as the fecal donors for the park25 feces. Four days post-seeding, 60 embryos of the specific genotype were placed on the feces-prepared food. The embryos were collected and counted as described below.
Embryo collection
Fly stocks (control and park25—heterozygous and homozygous) were placed in square polypropylene fly bottles with a molasses “puck” as the lid. The molasses puck was a 35 mm petri dish cover filled with a molasses-agar media (200 mL ddH2O, 6.24 g drosoagar [Genesee Scientific], 2 mL Tegosept, and 50 mL of molasses). The bottles were stored upside down, so the puck was at the bottom, while the top of the bottle had small holes for air transfer. Yeast paste was put on the inside of the bottle to help stimulate oogenesis. Flies were allowed to lay their embryos for < 24 h at 25 °C. Embryo collection was performed by wetting a paintbrush with ddH2O and carefully brushing the embryos from the molasses-agar. The embryos were then washed off the puck directly into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and were rinsed with ddH2O for a total of three washes. After washing, the embryos were pipetted into a glass spot plate in one of the three wells. Under a stereo microscope, 60 embryos were counted and placed in one of the empty wells with < 0.5 ml water. A fine-tipped paintbrush was used to paint the 60 embryos onto the surface of the fecal-prepared food. A different paintbrush was used for each fly genotype to prevent bacterial transfer between genotypes during embryo deposition. The embryos were collected for six days, with new parental fly populations being introduced every two days to produce three biological replicates with each biological replicate having two technical replicates.
Axenic and gnotobiotic experiments
We reared flies with bacteria cultured directly from fly feces beginning with axenic fly embryos. Axenic embryos were derived as described previously25. Briefly, control and park25 embryos were collected as above and suspended in a 0.6% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2.5 min. These embryos were then transferred to fresh 0.6% sodium hypochlorite solution in a sterile hood to dechorionate the embryos. The sterile, dechorionated embryos were collected with a sterile paintbrush and approximately 60 embryos were brushed onto sterile food. These embryos were either maintained as axenic or inoculated with 5 × 105 CFUs from control or park25 fecal bacterial cultures, or from individual bacterial strains, including, Lactobacillus brevis, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Acetobacter pomorum, or Acetobacter tropicalis.
To produce the fecal bacterial cultures, feces were collected from the park25 and control fly embryo collection bottles by scraping the feces off with a sterile toothpick to inoculate Luria–Bertani (LB) and modified deMan-Rogosa-Sharpe (mMRS) medium. These cultures were grown at 30 °C with aeration for 16 h. To preferentially cultivate aerotolerant microbes, separate MRS cultures were grown in loosely capped tubes with no shaking for 16 h. To generate the microbiome inoculum, each culture was normalized to 107 mL-1, combined in equivalent ratios, and 50 μl containing 5 × 105 total CFUs was used to inoculate the sterile embryos. Control axenic embryos were collected each day for four days with a minimum of eight tubes/day, while the axenic park25 embryos were collected each day for five days with a minimum of 28 tubes/day. The bacterial culture embryos were collected each day for four days with a minimum of 10 tubes/day for control embryos or 14 tubes/day for the park25 embryos.
To confirm axenic flies were truly bacteria-free, pools of five whole-body adult axenic flies from each axenic control vial were homogenized at the end of each experiment and cultured on LB and duplicate MRS plates (one incubated with standard atmospheric conditions, one in microoxic conditions in a sealed, CO2-flooded chamber) at 30 °C. If > 10 CFUs/fly were detected, those flies were deemed non-axenic and removed from the analysis.
Pupation and eclosure measurements
Newly developed pupae were counted on days 5, 6, 7 and 8 post-embryo collection. Due to the Tubby mutation on the TM6C balancer chromosome present in the heterozygous park25 flies, homozygous and heterozygous park25 flies were differentiated. Although analyzed separately, these two pupal populations account for the full 60 park25 embryos painted in the fecal transfer experiments. Individual fly eclosion was quantified on days 9, 10, 11 and 12 post-embryo collection.
16S sequencing and analysis
We prepared and analyzed DNA samples for 16S rRNA marker gene analysis as done previously28,30. Sequencing libraries were prepared by extracting DNA from pools of 10 flies using the Zymo Quick-DNA fecal/soil microbe kit (D6011, Zymo, Irvine, CA). Then, the V4 region of the extracted DNA was amplified and sequenced using a dual-barcoding method described by Kozich37, with the exception of substituting Accuprime PFX DNA polymerase reagents for Accuprime PFX Supermix. The Invitrogen SequalPrep Normalization kit was used to normalize samples into pools of 96 samples (in some cases, the samples were normalized as part of a pool with samples not published in this study). Then, fragments in the size range of 250–450 nucleotides were size-selected using a BluePippin (BYU DNA Sequencing Center). Finally, samples in this study were sequenced on partial lanes of a MiSeq using 500 cycle chemistry (paired-end 2 × 250, BioDesign Institute at Arizona State University).
Sequenced reads were analyzed using QIIME238 and R. The reads were trimmed based on quality scores, denoised and dereplicated using DADA239 to call individual amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), and taxonomy was assigned using the GreenGenes classifier40,41. To enable the calculation of Unifrac beta-diversity metrics42,43, a phylogeny of all ASVs was constructed44 based on mafft alignment45. For some analyses, Wolbachia reads were pre-filtered out so that reproductive tract symbionts were not included in the analysis. Before performing beta-diversity analyses, samples were normalized to varying read thresholds that maximized the number of reads per sample and the number of samples retained: 350 (Fig. 3), 3000 (Fig. 5), and 399 (Supplementary Fig. S8). Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) of Bray Curtis distances and of unweighted and weighted Unifrac distances were used to test for host genotype and sex-dependent variation in microbiota composition46. We also used Analysis of Composition of Microbiomes (ANCOM) to test for differences in the abundances of specific individual or groups of ASVs47.
One sample was removed from Fig. 3 analyses because it was almost exclusively enterococcus. Removing it did not change the significance of any comparisons but did reduce noise. Analyses of the data that include this sample are presented in Supplementary Figure S4.
Development statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by using One-Way and Two-Way ANOVA, with post-hoc Tukey’s, Sidak’s, or Dunnett’s tests to determine differences between the arcsin transformed percentages of each group by GraphPad Prism 9. All other data analysis was in RStudio version 1.3.1093 using R version 3.6.3 or the terminal. All graphs display the mean ± the standard error of the mean. Details on each test performed and their results are presented in the results section or legends.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
J.P.C. and Z.S.P. were supported by the Biomedical Sciences Program and G.B.C. received research support from Midwestern University.
Author contributions
Study conception and design: G.B.C.; Study supervision: G.B.C., J.M.C., and S.B.K.; Data collection: J.P.-C., D.R.H., T.B.C., Z.S.P., S.A.T.; Data and statistical analyses: G.B.C., E.M.M., and J.M.C.; Writing and revision: G.B.C., J.M.C. and S.B.K.
Data availability
The reads are publicly available at the NCBI SRA under Accession number PRJNA776269.
Code availability
The code to analyze the reads can be accessed as an R tutorial by running ‘devtools::install_github ("johnchaston/JPCparkTutorial")’ and ‘learnr::run_tutorial ("mainTutorial", "JPCparkTutorial")’ in an R console where devtools and learnR, plus other packages executed in the tutorial, are installed.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-021-02624-1.
References
- 1.Matthews KA, et al. Racial and ethnic estimates of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias in the United States (2015–2060) in adults aged >/=65 years. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;15:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Statistics - Parkinson's Foundation. <https://www.parkinson.org/Understanding-Parkinsons/Statistics> (2021).
- 3.Hernandez DG, Reed X, Singleton AB. Genetics in Parkinson disease: mendelian versus non-mendelian inheritance. J. Neurochem. 2016;139(Suppl 1):59–74. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lücking CB, et al. Association between early-onset Parkinson's disease and mutations in the parkin gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;342:1560–1567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200005253422103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hewitt VL, Whitworth AJ. Mechanisms of Parkinson's disease: lessons from Drosophila. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017;121:173–200. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yeates, C. J., Sarkar, A., Kango-Singh, M. & Singh, A. In Insights into Human Neurodegeneration: Lessons Learnt from Drosophila (eds Mousumi Mutsuddi & Ashim Mukherjee) 251–277 (Springer, new York, 2019).
- 7.Chambers RP, et al. Nicotine increases lifespan and rescues olfactory and motor deficits in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2013;253:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Greene JC, et al. Mitochondrial pathology and apoptotic muscle degeneration in Drosophila parkin mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:4078–4083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0737556100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Whitworth AJ, et al. Increased glutathione S-transferase activity rescues dopaminergic neuron loss in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:8024–8029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501078102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cackovic J, et al. Vulnerable parkin loss-of-function Drosophila dopaminergic neurons have advanced mitochondrial aging, mitochondrial network loss and transiently reduced autophagosome recruitment. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:39. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LW, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:625–639. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boertien JM, Pereira PAB, Aho VTE, Scheperjans F. Increasing comparability and utility of gut microbiome studies in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2019;9:S297–S312. doi: 10.3233/JPD-191711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sampson TR, et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson's disease. Cell. 2016;167:1469–1480.e1412. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wong CN, Ng P, Douglas AE. Low-diversity bacterial community in the gut of the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;13:1889–1900. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chandler JA, Lang JM, Bhatnagar S, Eisen JA, Kopp A. Bacterial communities of diverse Drosophila species: ecological context of a host-microbe model system. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Staubach F, Baines JF, Kunzel S, Bik EM, Petrov DA. Host species and environmental effects on bacterial communities associated with Drosophila in the laboratory and in the natural environment. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e70749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chaston JM, Dobson AJ, Newell PD, Douglas AE. Host genetic control of the microbiota mediates the Drosophila nutritional phenotype. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016;82:671–679. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03301-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carmody RN, et al. Diet dominates host genotype in shaping the murine gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17:72–84. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goodrich JK, et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell. 2014;159:789–799. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Winans NJ, et al. A genomic investigation of ecological differentiation between free-living and Drosophila-associated bacteria. Mol. Ecol. 2017;26:4536–4550. doi: 10.1111/mec.14232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pais IS, Valente RS, Sporniak M, Teixeira L. Drosophila melanogaster establishes a species-specific mutualistic interaction with stable gut-colonizing bacteria. PLoS Biol. 2018;16:e2005710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gould AL, et al. Microbiome interactions shape host fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E11951–E11960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809349115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xu Y, et al. EGCG ameliorates neuronal and behavioral defects by remodeling gut microbiota and TotM expression in Drosophila models of Parkinson's disease. FASEB J. 2020;34:5931–5950. doi: 10.1096/fj.201903125RR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Werren JH, Baldo L, Clark ME. Wolbachia: master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008;6:741–751. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Koyle ML, et al. Rearing the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster under axenic and gnotobiotic conditions. J. Visual. Exp. JoVE. 2016 doi: 10.3791/54219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shin SC, et al. Drosophila microbiome modulates host developmental and metabolic homeostasis via insulin signaling. Science. 2011;334:670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1212782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wong AC, Chaston JM, Douglas AE. The inconstant gut microbiota of Drosophila species revealed by 16S rRNA gene analysis. ISME J. 2013;7:1922–1932. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Walters AW, et al. The microbiota influences the Drosophila melanogaster life history strategy. Mol. Ecol. 2020;29:639–653. doi: 10.1111/mec.15344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Newell PD, et al. In vivo function and comparative genomic analyses of the Drosophila gut microbiota identify candidate symbiosis factors. Front. Microbiol. 2014;5:576. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rudman SM, et al. Microbiome composition shapes rapid genomic adaptation off. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:20025–20032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907787116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tan FHP, et al. Lactobacillus probiotics improved the gut microbiota profile of a Drosophila melanogaster Alzheimer's disease model and alleviated neurodegeneration in the eye. Benef. Microbes. 2020;11:79–89. doi: 10.3920/BM2019.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zare A, Johansson AM, Karlsson E, Delhomme N, Stenberg P. The gut microbiome participates in transgenerational inheritance of low-temperature responses in Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS Lett. 2018;592:4078–4086. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ridley EV, Wong AC, Westmiller S, Douglas AE. Impact of the resident microbiota on the nutritional phenotype of Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e36765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Storelli G, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum promotes Drosophila systemic growth by modulating hormonal signals through TOR-dependent nutrient sensing. Cell Metab. 2011;14:403–414. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Simhadri RK, et al. The gut commensal microbiome of Drosophila melanogaster is modified by the endosymbiont Wolbachia. mSphere. 2017 doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00287-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blum JE, Fischer CN, Miles J, Handelsman J. Frequent replenishment sustains the beneficial microbiome of Drosophila melanogaster. MBio. 2013;4:e00860–e1813. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00860-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013;79:5112–5120. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01043-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bolyen E, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019;37:852–857. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Callahan BJ, et al. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods. 2016;13:581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McDonald D, et al. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012;6:610–618. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bokulich NA, et al. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2's q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome. 2018;6:90. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0470-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lozupone C, Knight R. UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71:8228–8235. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8228-8235.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Kelley ST, Knight R. Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:1576–1585. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01996-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree 2: approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e9490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T. MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucl. Acids Res. 2002;30:3059–3066. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Oksanen, J. et al.https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (2018).
- 47.Mandal S, et al. Analysis of composition of microbiomes: a novel method for studying microbial composition. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015;26:27663. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.27663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The reads are publicly available at the NCBI SRA under Accession number PRJNA776269.
The code to analyze the reads can be accessed as an R tutorial by running ‘devtools::install_github ("johnchaston/JPCparkTutorial")’ and ‘learnr::run_tutorial ("mainTutorial", "JPCparkTutorial")’ in an R console where devtools and learnR, plus other packages executed in the tutorial, are installed.