Abstract
Introduction
Uncontrolled asthma is associated with substantial morbidity. While fast-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief from asthma symptoms, their use as rescue fails to address the underlying inflammation. Combining a short-acting beta2-agonist, such as albuterol (salbutamol), with an inhaled corticosteroid, such as budesonide, in a single inhaler as rescue therapy could help control both bronchoconstriction and inflammation, and reduce the risk of asthma exacerbations.
Methods and analysis
The Phase 3 MANDALA study was designed to determine the efficacy of albuterol in combination with budesonide (albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg or 180/80 µg, two actuations of 90/80 µg or 90/40 µg, respectively) versus albuterol (180 µg, two actuations of 90 µg) as rescue therapy in adult, adolescent and paediatric patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. This event-driven study enrolled symptomatic patients (3000 adults/adolescents and 100 children aged 4–11 years) who experienced ≥1 severe asthma exacerbation in the previous year and were receiving maintenance therapy for ≥3 months prior to study entry. The primary efficacy endpoint was time-to-first severe asthma exacerbation.
Ethics and dissemination
The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, and that are consistent with International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use and Good Clinical Practice and the applicable regulatory requirements.
Trial registration
Keywords: asthma, asthma in primary care, paediatric asthma
Introduction
Asthma is a heterogeneous inflammatory airway disease defined by a history of intermittent respiratory symptoms including wheeze and cough, and with variable expiratory airflow obstruction across all asthma severities. The global prevalence of asthma has increased in the past 60 years; it is estimated that globally over 300 million people are living with asthma, including 11.6% of children aged 6–7 years.1 2 Despite the availability of effective maintenance treatments, including inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), patients continue to suffer from periodic asthma worsenings, and the incidence of exacerbations in both paediatric and adult patients remains high.3 All patients are at risk of preventable and potentially serious exacerbations, irrespective of asthma severity.4 5
Short-acting beta2-agonists (SABA), such as albuterol (salbutamol), are often used as rescue medication for symptom relief by patients with asthma of all severities. SABA induce airway smooth muscle relaxation and provide rapid symptom relief,6 7 but do not address the underlying airway inflammation. Patients may therefore continue to experience worsening of asthma and remain at risk of exacerbations, regardless of their maintenance therapy.8 9 ICS, such as budesonide, do treat the inflammation,6 10 11 and there is evidence of a ‘window of opportunity’ during periods of worsening symptoms, in which a timely administration of ICS can prevent the symptoms developing into an exacerbation.12–14 This acute protection occurs within hours15 and may be due to reductions in the late asthmatic response following allergen inhalation, eosinophilic inflammation, bronchial hyperreactivity and/or a reduction in pulmonary blood flow, although the precise mechanism is not fully understood.15
The clinical efficacy of concomitant anti-inflammatory ICS and rapid-acting bronchodilators has been demonstrated in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma using ICS–formoterol as rescue on top of ICS–long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) maintenance. This combination reduced the relative risk of severe exacerbations by more than 30% compared with patients using ICS–LABA as maintenance and SABA as rescue.16–22 Data also show that in mild asthma, patients taking the fixed-dose combination (FDC) of budesonide–formoterol as needed have greater protection from severe exacerbations versus those taking as-needed SABA alone, with no increase in adverse effects.23–25 These results are reflected in the 2021 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) report, where as-needed ICS–formoterol is the preferred (Track 1) rescue therapy at all treatment steps in patients aged ≥12 years, and also as an alternative option for patients aged 6–11 years.6 The National Asthma Education and Prevention Program 2020 focused updates also recommend the use of as-needed combination low-dose ICS–formoterol for moderate persistent asthma in patients aged ≥4 years.7 However, despite these clinical recommendations, there is no approved ICS-containing rescue therapy available in the USA, while in Europe it is noted that ICS–formoterol is only indicated for use as rescue therapy as part of an ICS–formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy regimen, leaving those not receiving ICS–formoterol background therapy without an ICS-containing rescue option.
A novel Co-suspension Delivery Technology™ formulation26 of albuterol and budesonide in a single pressurised metered-dose inhaler (pMDI) is being developed to provide a rescue therapy alternative with the potential to be used alongside any asthma maintenance treatment for the control of acute symptoms, and to provide prevention against worsening of asthma symptoms and severe exacerbations requiring systemic steroids or hospitalisation.
The objective of this paper is to provide the rationale for, and describe the study design of, the pivotal Phase 3 MANDALA study. The study evaluated the efficacy and safety of as-needed albuterol/budesonide in an FDC pMDI as rescue therapy versus as-needed albuterol pMDI in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma receiving maintenance therapy.
Methods and analysis
Investigational product
As-needed albuterol/budesonide pMDI was formulated as micronised albuterol and budesonide, co-suspended with spray-dried porous particles in a hydrofluoroalkane propellant. This novel co-suspension formulation (administered as two actuations of albuterol/budesonide pMDI 90/80 µg or 90/40 µg) ensures that patients will receive a consistent delivery of both drugs from each inhalation of the pMDI. Albuterol pMDI was used as a comparator, administered as two inhalations of 90 µg each.
The 180 µg albuterol dose was confirmed in two clinical trials, ANTORA and ASPEN.27 Dose ranging for budesonide was conducted in study PT008001 in patients with asthma (NCT02105012). The current study included budesonide doses separately investigated in the Single inhaler Maintenance And Reliever Therapy (SMART) trials (ie, 160 µg and 80 µg) in order to provide budesonide dose ranging information for as-needed albuterol/budesonide to reduce the risk of severe asthma exacerbations.
Design, patients and treatment
MANDALA was a global Phase 3, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, event-driven asthma exacerbation study. The study compared the effect of two FDCs of albuterol/budesonide (180/160 µg and 180/80 µg, two actuations of albuterol/budesonide pMDI 90/80 µg or 90/40 µg, respectively) versus albuterol for as-needed use in response to symptoms in patients continuing to take their pre-study maintenance medication. The impact of two doses of albuterol/budesonide FDCs on severe asthma exacerbation risk (as measured by time-to-first severe asthma exacerbation) was compared with albuterol in adult, adolescent and paediatric patients with moderate-to-severe asthma receiving maintenance treatment corresponding to GINA Steps 3–5. The study recruited 1000 patients per treatment group for adults/adolescents and 50 patients per treatment group for patients aged 4–11 years (the lower dose of albuterol/budesonide and albuterol). Eligible patients were symptomatic, had experienced ≥1 severe asthma exacerbation within the 12 months prior to screening (Visit 1) and had been receiving regular-scheduled asthma maintenance therapy for ≥3 months, with stable dosing for at least the 4 weeks prior to visit 1. Other key inclusion and exclusion criteria are presented in table 1.
Table 1.
Key inclusion and exclusion criteria
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
| Female or male outpatients aged ≥4 years | Other significant lung disease (eg, COPD, emphysema, bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia) |
| Diagnosis of asthma per GINA criteria ≥1 year prior to screening | SCS use (any dose and any indication) within 6 weeks of screening |
| Background maintenance therapy of stable medium-to-high dose ICS or low-to-high dose ICS–LABA with/without one other maintenance medication (LTRA, LAMA or theophylline) for ≥3 months with stable dosing for ≥4 weeks prior to screening | Oral corticosteroid use for ≥3 weeks within 3 months of screening |
| Pre-BD FEV1 ≥40–<90% or ≥60% predicted for those aged ≥18 years and 4–17 years, respectively | Having received any marketed (benralizumab, dupilumab, mepolizumab, omalizumab or reslizumab) or investigational biologic within 3 months or 5 half-lives of screening or any other prohibited medication* |
| Reversible airway obstruction at screening, defined as an increase in FEV1 ≥12% (and ≥200 mL for patients ≥18 years) relative to baseline after inhalation of albuterol | Current or former smokers (former with either >10 pack-year history or who stopped smoking <6 months prior to screening) |
| History of ≥1 severe asthma exacerbation in the 12 months prior to screening | Completed treatment for asthma exacerbation or LRTI within 6 weeks of screening or treated unresolved URTI within 7 days of screening |
| ACQ-7 score ≥1.5 at screening and ACQ-5 score of ≥1.5 at randomisation | History of life-threatening asthma episode(s) within 5 years of screening |
| BMI <40 kg/m2 | Historical or current evidence of clinically significant disease |
| Acceptable spirometry performance (ie, meet ATS/ERS acceptability/repeatability criteria) | Pregnant, breast feeding or planned pregnancy |
| Demonstrate acceptable MDI administration technique as assessed by the investigator | Cancer not in complete remission for at least 5 years |
| Acceptable and reproducible PEF measurements | Hospitalisation for psychiatric disorder or attempted suicide within 1 year of screening |
| Use of as-needed Sponsor provided Ventolin medication due to asthma symptoms ≥3 days during the last week of the run-in period before randomisation | History of psychiatric disease, intellectual deficiency, poor motivation or other conditions if their magnitude is limiting informed consent validity |
| Significant abuse of alcohol or drugs |
*Prohibited medications included; oral, parenteral or rectal corticosteroids (except if required to treat severe asthma exacerbation); any other asthma medication except stable doses of maintenance therapy taken at entry into the study and provided by the Sponsor; inhaled disodium cromoglycate or inhaled nedocromil sodium; 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors (ie, zilueton); inhaled anticholinergics; phosphodiesterase inhibitors (ie, roflumilast); beta2-adrenergic blockers including eye-drops; systemic treatment with potent cytochrome P3A4 inhibitors (eg, ketoconazole, itraconazole and ritonavir); non-glucocorticoid-containing nasal sprays.
ACQ-5, asthma control 5-point questionnaire; ACQ-7, asthma control 7-point questionnaire; ATS, American Thoracic Society; BD, bronchodilator; BMI, body mass index; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ERS, European Respiratory Society.; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 s; GINA, Global Initiative for Asthma; ICS, Inhaled corticosteroid; LABA, long-acting beta2-agonist; LAMA, long-acting muscarinic antagonist; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection; LTRA, leukotriene receptor antagonist; MDI, metered-dose inhaler; PEF, peak expiratory flow; SCS, systemic corticosteroids; URTI, upper respiratory tract infection.
From screening through the randomised treatment period, all patients were to continue their prescribed background therapy. Required asthma maintenance therapies included medium-to-high-dose ICS with or without one additional maintenance therapy (leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRA), long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) or theophylline), or low-to-high-dose ICS in combination with LABA with or without one additional maintenance therapy (LTRA, LAMA or theophylline). Adherence to maintenance therapy and use of rescue therapies was monitored daily using an electronic patient-reported outcome device (eDiary).
Adult and adolescent patients (aged ≥12 years) meeting the eligibility criteria were randomised in a 1:1:1 ratio to as-needed rescue albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg, albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg or albuterol 180 µg. Patients aged 4–11 years were randomised 1:1 to as-needed rescue albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg, or as-needed albuterol 180 µg. The maximum daily dosage of treatment in the trial for both age groups did not exceed 12 inhalations (ie, six doses of any investigational product) per day.
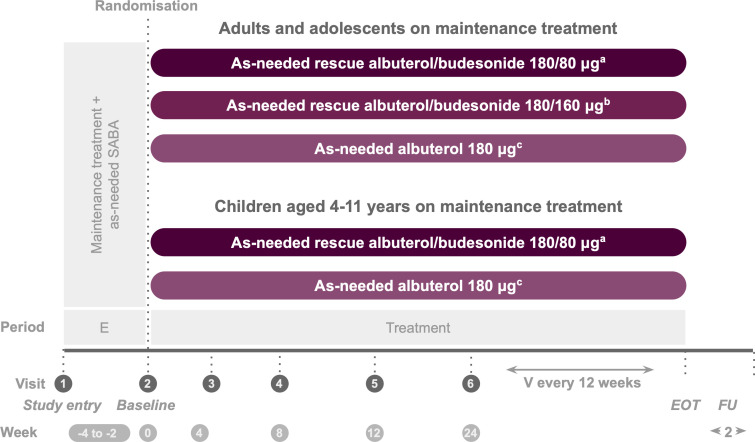
The study consisted of three phases: a screening period of 14–28 days, a treatment period of at least 24 weeks and a safety follow-up period (figure 1). At visit 1, patients discontinued their usual inhaled rescue medication and began Sponsor-provided albuterol to be used as needed in response to symptoms during the screening period only, while the investigational product (albuterol/budesonide pMDI or albuterol pMDI) was used as needed during the treatment period. The study continued until all the following conditions were satisfied: 570 first severe exacerbation events were recorded, 3100 patients had been randomised and the last enrolled patient had completed 24 weeks of treatment as well as their 2-week follow-up visit (or premature discontinuation visit; whichever occurred first). Once 570 events were recorded, patients who had reached ≥24 weeks and completed their 2-week follow-up visit ended their study participation. Patients who discontinued the investigational product early were encouraged to remain in the study for the capture of endpoints through week 24. Patients who withdrew from the treatment attended a premature discontinuation visit; any adverse events (AEs)/serious adverse events (SAEs) were followed up if medically indicated.
Figure 1.
Study design. aTwo inhalations albuterol/budesonide pMDI 90/40 µg. bTwo inhalations albuterol/budesonide pMDI 90/80 µg. cTwo inhalations albuterol pMDI 90 µg. The screening/enrolment period was 2–4 weeks except if a severe exacerbation occured during this time, in which case it was ≤9 weeks. During screening, patients discontinued their usual rescue medication and used as-needed albuterol sulfate 180 µg. E, enrolment; EOT, end of treatment; FU, follow-up; pMDI, pressurised metered-dose inhaler; SABA, short-acting beta2-agonists; V, visit.
Patient and public involvement
Neither patients or the public were involved in the study design or conduct, and will not be involved with the reporting or dissemination plans of the research.
Efficacy estimands/endpoints
The primary estimand of interest was the efficacy estimand, defined as the effect of the randomised treatment in all patients, assuming continuation of randomised treatment for the duration of the study, regardless of actual usage, and assuming that maintenance therapy was not changed. The second estimand of interest was the attributable estimand, defined as the effect of treatment in patients attributable to the randomised treatment, assuming that maintenance therapy was not changed. For this estimand, discontinuation of randomised treatment for tolerability or change in maintenance therapy for lack of asthma control was considered a negative outcome.
The primary efficacy endpoint was time-to-first severe asthma exacerbation, defined as a deterioration of asthma (worsening or new onset of symptoms) leading to at least one of the following: three or more consecutive days’ treatment with systemic corticosteroids (SCS) to treat worsening symptoms of asthma (a single depot injection was considered equivalent to a 3-day burst); an emergency room or urgent care visit for less than 24 hours requiring SCS treatment as above or an inpatient hospitalisation for at least 24 hours due to asthma.
Secondary efficacy endpoints included annualised severe exacerbation rate, total SCS exposure for the treatment of asthma over the treatment period (measured as average mg/patient), and change from baseline and responder analysis at week 24 for Asthma Control Questionnaire (ACQ-5) and Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) for patients aged ≥12 years, and Paediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (PAQLQ) for patients aged 4–11 years. ACQ-5 and AQLQ were assessed every 4 weeks up until week 24. The study also investigated exploratory endpoints, including lung function (pre-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) and peak expiratory flow (PEF)), symptoms, rescue medication (ie, investigational product) use, additional ICS exposure, change from baseline and responder analysis at week 24 for Asthma Control Test (ACT) or childhood ACT, deterioration of asthma and symptom-free days. Safety endpoints (AEs and SAEs) were also assessed from date of informed consent/assent through the safety follow-up period.
Discontinuation
Patients could discontinue study treatment or be withdrawn from the study at any time for any reason at their request, on request of the investigator or by the Sponsor. Possible reasons for treatment discontinuation included the onset of AEs, pregnancy and development of ≥3 severe exacerbations within a 3-month period or ≥5 total severe exacerbation events, or a single severe exacerbation event longer than 20 days. Discontinuation of study treatment was considered if the investigator decided that it was in the best interest of the patient. Moreover, the investigator could discontinue the patient from the study if they were non-compliant with the Clinical Study Protocol (eg, post-randomisation eligibility violation) or were lost to follow-up and no alternative contact information was available (this implied that at least two documented attempts have been made to contact the patient).
Statistical analysis
A sample size of 1000 adult and adolescent patients per treatment group and observation of the first 570 severe exacerbation events provided this study with 87% power to observe a 25% reduction in the risk of severe exacerbation in patients who received at least one dose of albuterol/budesonide versus albuterol, assuming the Hochberg procedure28 for multiple testing and a two-sided significance level of 5%.
The primary analysis was for the time-to-first severe asthma exacerbation under the efficacy estimand. A Cox proportional hazards regression model adjusted for randomisation stratification factors (age group, region) and the number of severe exacerbations in the 12 months before screening (1, >1) was applied. The primary treatment comparisons (albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg vs albuterol 180 µg; albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg vs albuterol 180 µg) were two-sided, with the 5% overall alpha level controlled using the Hochberg procedure.
The type I error was controlled for secondary endpoint treatment comparisons via a hierarchical testing procedure. The secondary comparisons were tested under the efficacy estimand in sequential order by dose (first albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg vs albuterol 180 µg, second albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg vs albuterol 180 µg) and grouped by secondary endpoint as mentioned above (annualised severe exacerbation rate, total annualised dose of SCS, ACQ-5 and AQLQ responder analysis at week 24).
Statistical tests for the secondary analyses were conducted at the 5% level of significance (two-sided). Inference for a test in the defined order was dependent on statistical significance having been achieved in the preceding tests. If this was not achieved, nominal p values were provided. As per the primary analysis, comparisons of albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg versus albuterol 180 µg excluded children (aged 4–11 years), while comparisons of albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg versus albuterol 180 µg included all ages.
Statistical significance could only be claimed on the key secondary endpoints if a statistically significant treatment effect was observed on both albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg and albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg versus albuterol 180 µg for the primary endpoint of time-to-first severe exacerbation. Annualised severe asthma exacerbation rate was analysed using a negative binomial regression model to compare treatment groups. The response variable in the model was the number of severe asthma exacerbations. The model adjusted for age group, region and number of severe exacerbations in the 12 months before screening. The total corticosteroid exposure as total annualised dose of corticosteroid (μg/year) was presented descriptively by treatment. A comparison of total annualised corticosteroid dose for albuterol/budesonide 180/160 µg versus albuterol 180 µg and albuterol/budesonide 180/80 µg versus albuterol 180 µg was analysed using a Wilcoxon rank sum test and associated p-values were presented along with the descriptive summary. Responder variables (ACQ-5 and AQLQ/PAQLQ at week 24 were analysed using a logistic regression model to compare treatment groups.
Ethics and dissemination
The study was performed in accordance with ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki and are consistent with the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use and Good Clinical Practice and applicable regulatory requirements. All patients provided written informed consent.
Discussion
The focus of long-term asthma management is on improving bronchodilation while also addressing the underlying causes of inflammation,6 but despite the availability of effective maintenance treatment, uncontrolled disease is still associated with substantial morbidity and mortality.29 SABA are still the most common rescue therapy for the majority of patients across all severities of asthma, although increased SABA use as rescue therapy may indicate less well-controlled asthma and is associated with a higher risk of exacerbations.8 9 There is, however, a ‘window of opportunity’ during periods of worsening symptoms in which ICS administered as needed at the appropriate time can prevent exacerbations.12–14 The use of a fast-acting bronchodilator/ICS combination rescue therapy, such as albuterol/ICS, within this ‘window’ can provide the required rapid symptom relief along with an added boost of anti-inflammatory therapy from the ICS to reduce the risk of asthma worsening and severe exacerbations. Albuterol/budesonide pMDI was designed to provide quick relief from symptoms while simultaneously titrating ICS to address the increasing inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of asthma symptoms progressing to exacerbation; it is intended for use as rescue treatment either alone or in addition to any maintenance therapy.
The MANDALA study was the first Phase 3 trial to compare the as-needed fast-acting bronchodilator/ICS combination therapy of albuterol/budesonide with albuterol in response to symptoms in patients with asthma. The results will provide valuable data on the efficacy and tolerability of this regimen in adults, adolescents and children with moderate-to-severe asthma. This was the first study to evaluate the effect of as-needed albuterol/budesonide when added to various ICS-containing maintenance therapies. Previous studies of rescue use of ICS in combination with a bronchodilator assessed the efficacy and safety of as-needed ICS–formoterol alone or in patients with the same concomitant ICS–LABA maintenance therapy.18 20 23 25 30–32 In mild asthma, it has also been shown that the symptom-driven use of an FDC of beclomethasone and albuterol is as effective as regular use of inhaled beclomethasone alone on the primary endpoint of morning PEF and secondary endpoint of all asthma exacerbations.33 A recent Cochrane systematic review has demonstrated that the use of combination therapy with an as-needed fast-acting beta2-agonist, including albuterol and other SABA, and an ICS significantly reduces exacerbations requiring SCS compared with SABA alone.34
Albuterol/budesonide was also developed as an alternative rescue treatment approach for younger patients with asthma (aged ≥4 years). This study is therefore important, as there is a need for further data on the effects of as-needed fast-acting bronchodilator/ICS combination in children aged 4–11 years, as rescue therapy with as-needed SABA is still the recommended treatment in these patients.7
It is anticipated that the albuterol/budesonide pivotal Phase 3 development programme, including this MANDALA exacerbation study and the DENALI (NCT03847896) lung function study, will provide the evidence needed to help change the current rescue treatment paradigm by reducing the risk of exacerbations in patients with asthma. If successful, as-needed albuterol/budesonide pMDI rescue therapy could be used irrespective of background asthma therapy, and will be the first albuterol/ICS combination inhaler available in the USA.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Andrea Maes for providing her support on statistical analysis, and Marco Emanuele Favretto and Samantha Blakemore of inScience Communications, Springer Healthcare, UK, for providing medical writing support, which was funded by AstraZeneca in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines (http://www.ismpp.org/gpp3).
Footnotes
Contributors: BEC and AP conceptualised the study, reviewed the draft versions and finalised the manuscript. CC conceptualised the study, developed the protocol, contributed to the outline of the manuscript and reviewed and finalised the draft versions. FCA, LR, EJ developed the protocol, contributed to the outline of the manuscript and reviewed and finalised the draft versions.
Funding: This study is funded by Avillion.
Competing interests: BEC is an advisor for, has received consultancy fees from, and is on the speakers’ bureau for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Regeneron and Sanofi Genzyme. FCA is an employee of Avillion. LR was an employee of Avillion when the study was conducted. EJ and CC are employees of AstraZeneca. AP reports grants, personal fees, non-financial support and other from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi Farmaceutici, TEVA, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca and Menarini, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Mundipharma, Zambon, Novartis and Sanofi/Regeneron, personal fees from Roche and Edmondpharma and grants from Fondazione Maugeri and Fondazione Chiesi, outside the submitted work.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
References
- 1.Dharmage SC, Perret JL, Custovic A. Epidemiology of asthma in children and adults. Front Pediatr 2019;7:246. 10.3389/fped.2019.00246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pearce N, Aït-Khaled N, Beasley R, et al. Worldwide trends in the prevalence of asthma symptoms: phase III of the International study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC). Thorax 2007;62:758–66. 10.1136/thx.2006.070169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Price D, Fletcher M, van der Molen T. Asthma control and management in 8,000 European patients: the REcognise Asthma and LInk to Symptoms and Experience (REALISE) survey. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med 2014;24:14009. 10.1038/npjpcrm.2014.9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McCracken JL, Veeranki SP, Ameredes BT, et al. Diagnosis and management of asthma in adults: a review. JAMA 2017;318:279–90. 10.1001/jama.2017.8372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.National Institute for Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute . Expert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma (EPR-3), 2007. Available: www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/asthma
- 6.Global Initiative for Asthma . Global strategy for asthma management and prevention, 2021. Available: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/
- 7.National Asthma Education and Prevention Program . Focused updates to the asthma management guidelines: a report from the National asthma education and prevention program coordinating Committee expert panel Working group, 2020. Available: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/all-publications-and-resources/2020-focused-updates-asthma-management-guidelines [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Bloom CI, Cabrera C, Arnetorp S, et al. Asthma-related health outcomes associated with short-acting β2-agonist inhaler use: an observational UK study as part of the SABINA global program. Adv Ther 2020;37:4190–208. 10.1007/s12325-020-01444-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nwaru BI, Ekström M, Hasvold P, et al. Overuse of short-acting β2-agonists in asthma is associated with increased risk of exacerbation and mortality: a nationwide cohort study of the global SABINA programme. Eur Respir J 2020;55. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01872-2019. [Epub ahead of print: 16 04 2020]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suissa S, Blais L, Ernst P. Patterns of increasing beta-agonist use and the risk of fatal or near-fatal asthma. Eur Respir J 1994;7:1602–9. 10.1183/09031936.94.07091602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Turner MO, Noertjojo K, Vedal S, et al. Risk factors for near-fatal asthma. a case-control study in hospitalized patients with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1804–9. 10.1164/ajrccm.157.6.9708092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Balter M, Ernst P, Watson W, FitzGerald JM, et al. Asthma worsenings: approaches to prevention and management from the asthma Worsenings Working group. Can Respir J 2008;15 Suppl B:1B–19. 10.1155/2008/973062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Larsson K, Kankaanranta H, Janson C, et al. Bringing asthma care into the twenty-first century. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med 2020;30:25. 10.1038/s41533-020-0182-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Thomas M, Bateman E. Asthma attacks: how can we reduce the risks? NPJ Prim Care Respir Med 2015;25:14105. 10.1038/npjpcrm.2014.105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Buhl R, Kuna P, Peters MJ, et al. The effect of budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy on the risk of severe asthma exacerbations following episodes of high reliever use: an exploratory analysis of two randomised, controlled studies with comparisons to standard therapy. Respir Res 2012;13:59. 10.1186/1465-9921-13-59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuna P, Peters MJ, Manjra AI, et al. Effect of budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy on asthma exacerbations. Int J Clin Pract 2007;61:725–36. 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01338.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O'Byrne PM, Bisgaard H, Godard PP, et al. Budesonide/formoterol combination therapy as both maintenance and reliever medication in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005;171:129–36. 10.1164/rccm.200407-884OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rabe KF, Atienza T, Magyar P, et al. Effect of budesonide in combination with formoterol for reliever therapy in asthma exacerbations: a randomised controlled, double-blind study. Lancet 2006;368:744–53. 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69284-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bousquet J, Boulet L-P, Peters MJ, et al. Budesonide/formoterol for maintenance and relief in uncontrolled asthma vs. high-dose salmeterol/fluticasone. Respir Med 2007;101:2437–46. 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Scicchitano R, Aalbers R, Ukena D, et al. Efficacy and safety of budesonide/formoterol single inhaler therapy versus a higher dose of budesonide in moderate to severe asthma. Curr Med Res Opin 2004;20:1403–18. 10.1185/030079904X2051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sobieraj DM, Weeda ER, Nguyen E, et al. Association of inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β-agonists as controller and quick relief therapy with exacerbations and symptom control in persistent asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2018;319:1485–96. 10.1001/jama.2018.2769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rogliani P, Ritondo BL, Ora J, et al. SMART and as-needed therapies in mild-to-severe asthma: a network meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 2020;56. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00625-2020. [Epub ahead of print: 10 09 2020]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bateman ED, Reddel HK, O'Byrne PM, et al. As-needed budesonide-formoterol versus maintenance budesonide in mild asthma. N Engl J Med 2018;378:1877–87. 10.1056/NEJMoa1715275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.O'Byrne PM, FitzGerald JM, Bateman ED, et al. Inhaled combined budesonide-formoterol as needed in mild asthma. N Engl J Med 2018;378:1865–76. 10.1056/NEJMoa1715274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Beasley R, Holliday M, Reddel HK, et al. Controlled trial of budesonide-formoterol as needed for mild asthma. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2020–30. 10.1056/NEJMoa1901963 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Usmani OS, Roche N, Jenkins M, et al. Consistent pulmonary drug delivery with whole lung deposition using the Aerosphere inhaler: a review of the evidence. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2021;16:113–24. 10.2147/COPD.S274846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cappelletti C, Maes A, Rossman K, et al. Dose-ranging and cumulative dose studies of albuterol sulfate MDI in Co-Suspension Delivery™ technology (as MDI; PT007) in patients with asthma: the ASPEN and ANTORA trials. Clin Drug Investig 2021;41:579–90. 10.1007/s40261-021-01040-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.HOCHBERG Y. A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 1988;75:800–2. 10.1093/biomet/75.4.800 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gruffydd-Jones K. Unmet needs in asthma. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2019;15:409–21. 10.2147/TCRM.S160327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hardy J, Baggott C, Fingleton J, et al. Budesonide-formoterol reliever therapy versus maintenance budesonide plus terbutaline reliever therapy in adults with mild to moderate asthma (PRACTICAL): a 52-week, open-label, multicentre, superiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019;394:919–28. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31948-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jenkins CR, Bateman ED, Sears MR, et al. What have we learnt about asthma control from trials of budesonide/formoterol as maintenance and reliever? Respirology 2020;25:804–15. 10.1111/resp.13804 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Papi A, Corradi M, Pigeon-Francisco C, et al. Beclometasone-formoterol as maintenance and reliever treatment in patients with asthma: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 2013;1:23–31. 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70012-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Papi A, Canonica GW, Maestrelli P, et al. Rescue use of beclomethasone and albuterol in a single inhaler for mild asthma. N Engl J Med 2007;356:2040–52. 10.1056/NEJMoa063861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Crossingham I, Turner S, Ramakrishnan S, et al. Combination fixed-dose β agonist and steroid inhaler as required for adults or children with mild asthma: a Cochrane systematic review. BMJ Evid Based Med 2021. doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2021-111764. [Epub ahead of print: 19 Jul 2021]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]