Misawa et al. (3) recently reported a PCR-based method for differentiating Campylobacter serotype O19 strains from non-O19 strains. In another study (2), the same investigators used restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of flaA genes and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of C. jejuni strains to conclude that all serotype O19 strains are closely related, regardless of their geographic origins, heat-labile (HL) serotype, or association with Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). In both studies, these researchers described a pair of C. jejuni isolates of Penner serotype O19 (OH4382 and OH4384) which were originally recovered from two Japanese siblings suffering from GBS (1) and characterized as HL serotype 7. The other C. jejuni serotype O19 GBS strains belonged to either serotype HL77 or HL84 (2, 3).
To understand how strains that appeared to be clonal could have different HL antigens, we further investigated the HL antigens of C. jejuni strains OH4382 and OH4384. Whereas strains OH4382 and OH4384 did not appear to agglutinate in serotyping antiserum specific for HL type 7, they both agglutinated when HL typing antisera to types 77 and 84 were tested. These slide agglutination results were confirmed with an indirect whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in which both strains reacted with anti-HL77 and anti-HL84 antisera but failed to react with anti-HL7 antiserum.
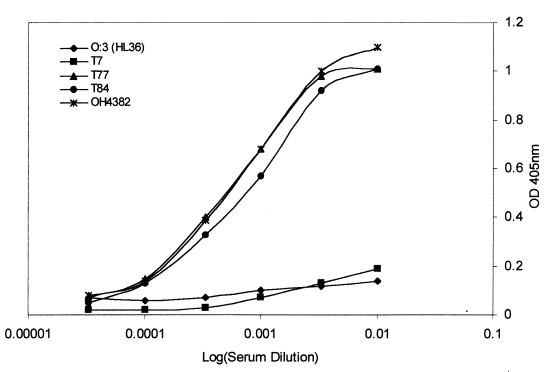
To confirm the results described above, antisera to both C. jejuni OH4382 and C. jejuni OH4384 were prepared in rabbits. After absorption of the antisera with a formalin-inactivated, whole-cell suspension of an unrelated C. jejuni standard strain (Penner O3:HL36) to remove antibodies to the common surface components on the Campylobacter organisms, we tested the absorbed antisera against HL type strains 7, 77, and 84 by an indirect whole-cell ELISA (Fig. 1). The results verified that C. jejuni strains OH4382 and OH4384 do not contain specific surface antigens related to HL type 7 but do possess surface components that induce antibodies to react specifically with HL serostrains 77 and 84.
FIG. 1.
Titration of anti-OH4382 antiserum against a homologous patient isolate (OH4382) and heterologous T7, T77, T84, and O3:HL36 serostrains by indirect whole-cell ELISA. OD, optical density.
To better understand the serological relationship of HL77 and HL84 type strains, we used a standard method (4) to determine their heat-stable (HS) O antigens. While C. jejuni HS O19 strains are not particularly common, it was surprising and unusual to observe that both the HL77 and HL84 type strains were found to possess the HS O:19 antigen. After removal of the anti-O19 antibodies by absorption with O19 lipopolysaccharide-sensitized red blood cells, anti-OH4382 and anti-OH4384 antisera still contained antibodies that reacted with the HL type strains 77 and 84, indicating the presence of HL77 and HL84 antigens on both C. jejuni OH4382 and OH4384.
Our serological studies provide further evidence that C. jejuni strains of Penner serotype O19 appear to be clonal or closely related in that they share common HS O and HL surface antigens.
REFERENCES
- 1.Aspinall G O, McDonald A G, Pang H, Kurjanczyk L A, Penner J L. Lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni serotype O19: structures of core oligosaccharide regions from serostrain and two bacterial isolates from patients with Guillain-BarréSyndrome. Biochemistry. 1994;33:241–249. doi: 10.1021/bi00167a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fujimoto S, Allos B M, Misawa N, Patton C M, Blaser M J. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from patients with Guillain-BarréSyndrome. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1105–1108. doi: 10.1086/516522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Misawa N, Allos B M, Blaser M J. Differentiation of Campylobacter jejuniserotype O19 strains from non-O19 strains by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:3567–3573. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.12.3567-3573.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Penner J L, Hennessy J N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejunion the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980;12:732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]