Abstract
Background and Aims
The impact of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) on liver function remains to be fully elucidated. This study was designed to investigate such and determine the clinical significance in determining mortality risk.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted in patients with COVID-19 from March 2020 to July 2020. Clinical details were retrieved from electronic medical records to obtain clinical characteristics, medical history, laboratory tests, therapeutic intervention, and outcome data.
Results
A total of 184 patients with COVID-19 were included (median age: 45.5 years), comprised of 62.5% men. In total, 22 (12.0%) patients had severe infection and 162 (88.0%) had mild to moderate infection. Overall, 95 (51.6%) showed abnormal liver function test (LFT) and 17 (9.2%) showed normal LFT at admission. The median age, hospital stay, and LFT were significantly higher in severe vs. non-severe infection (p<0.001). Out of 12 deaths, the majority were due to severe infection (n=11). Deaths were also due to acute respiratory distress syndrome (n=5), cardiac reasons (n=3), and sepsis with multiorgan failure (n=3). The median age, hospital stay and number of intensive care unit admissions were higher in patients having abnormal LFT compared to normal LFT. Incidence of elevated aspartate aminotransferase (42.8% and 40.4%), alanine transaminase (43.7% and 41.6%), and hypoalbuminemia (71.4% and72.7%) at admission and discharge were more common in severe infection. The mean survival was significantly lower in severe infection compared to those with non-severe disease (17.2 vs. 52.3 days; p<0.001).
Conclusions
Incidence of abnormal liver function was higher in patients with severe COVID-19 and was associated with prolonged hospital stay; mortality was associated with severity of COVID-19. For ruling out the risk of liver injury, it is crucial to vigilantly monitor the liver function parameters in patients with COVID-19 admitted to hospital.
Keywords: ALT/AST, Hospital stay, Hypoalbuminemia, Liver injury, Severe disease
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the worst pandemic seen to date worldwide, and currently India has become the second most infected country, with higher incidence of COVID-19.1 Overall, patients with severe COVID-19 are more susceptible to multiorgan failure, which may be associated with high mortality.2 Elderly patients and comorbid conditions are known predictors for increased risk of COVID-19.3,4 On the other hand, abnormal liver function has also come into the limelight as one of the important predictive risk factors for COVID-19 progression and subsequent poor outcomes.5–7
Several hospital-based studies conducted worldwide have emphasized the potential role of severe liver injury in increasing the mortality risk among COVID-19 patients.8–14 In addition, hepatic dysfunction in severe COVID-19 cases has been shown to be associated with fatal outcome.8–14 Several studies have demonstrated higher incidence of elevated levels of a alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) and hypoalbuminemia in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to patients with non-severe COVID-19.7 There might be multiple possible mechanisms for the development of abnormal liver function in these patients. These include immune-mediated inflammation, hypoxic injury due to severe pneumonia, and drug-induced inflammation leading to hepatic injury.15 The elevated load of viral infection in liver cells can also cause liver injury in patients with COVID-19.16
There are very few Indian studies that have thrown a light on the association between abnormal liver function and COVID-19.17 The present study aimed to retrospectively evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on liver function and its clinical significance in determining the mortality risk.
Methods
Study design and participant criteria
This was a retrospective study, conducted among patients with COVID-19 who were recruited during March 2020 through July 2020. Patients with COVID-19 were identified based on the World Health Organization (WHO) interim guidance and enrolled in this study. The study was conducted in accordance with ethical principles that are consistent with the Declaration of Helsinki. The inclusion criteria were patients of either sex with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19.
Severity of COVID-19
As per the national guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia and the diagnosis and treatment plan for the new coronavirus in India, all patients were classified into non-severe or severe cases based on observations from chest radiography, clinical examination, and symptoms.18 Patients with no clinical signs and symptoms (asymptomatic) and patients with mild symptoms (such as fever, cough, sore throat, headache, nasal congestion) and uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection were classified as non-severe type.
Definition
a) Mild COVID-19 was defined as symptomatic patients with uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection, mild symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, malaise, and headache, but without evidence of viral pneumonia or hypoxia.
b) Moderate COVID-19 was defined as patients (adult and child) with pneumonia with no signs of severe disease and with presence of clinical features of dyspnea and or hypoxia, fever, cough, including oxygen saturation <94% (range 90–94%) on room air, respiratory rate ≥24 breaths/m.
c) Severe COVID-19 was defined as patients either with significant respiration rate ≥30 times/m, oxygen saturation ≤93%, partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen ≤300 mmHg, or multiple organ or respiratory failure that requires intensive care unit (ICU) monitoring.
The assessment of disease severity was performed at the same time on the day of inpatient admission before treatment.18
Liver function tests
Liver function test indicators including ALT (normal range: 9–40 U/L), AST (normal range: 13–40 U/L), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), (normal range: 38–126 U/L), and serum bilirubin (normal range: 0.2–1.3 mg/dL) were analyzed.
Liver test parameters and abnormalities
Liver test abnormalities were defined as the elevation of serum levels of the following liver enzymes: ALT and AST >40 U/L, GGT >49 U/L, ALP >135 U/L, serum bilirubin >1.3 mg/dL, total protein >8.3 g/dL, albumin >5.4 g/dL, globulin >3.5 g/dL, serum creatinine >1.2 mg/dL, and blood urea nitrogen >6.7 mmol/L. Liver injury can be defined as ALT and/or AST over 3× upper limit of normal (ULN), ALP, GGT, and/or serum bilirubin over 2× ULN.7
Data collection
Computed tomography or throat swab specimens were obtained from all patients upon admission. COVID-19 was diagnosed by clinical manifestations, computed tomography scan of the lungs, or real-time polymerase chain reaction assay according to WHO interim guidance.19
Clinical report forms of all the study patients were obtained from electronic medical records to obtain clinical characteristics, medical history, laboratory tests, therapeutic intervention, and outcome data. Demographic data included age, sex, and oxygen therapy. Comorbidities, state of illness, and symptoms were obtained and evaluated. Blood samples were collected and analyzed by standard methods in the laboratory. The routine biochemical tests included ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, serum bilirubin, total protein, albumin, globulin, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen. The data collection forms were reviewed independently by experienced physicians.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for The Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Qualitative data were presented as number and percentages, while quantitative data were presented as mean (standard deviation) or median (range), depending on the normal or skewed distribution of data. Normal distribution of quantitative data was assessed by Shapiro-Wilk test. The independent sample t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for continuous variables and the chi-square test was used for categorical variables. Cox regression modeling was used to determine the correlation of mortality and liver function test. Hazards ratio and 95% confidence interval were computed. Kaplan-Meier event-free survival was computed and plotted. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline clinical characteristics
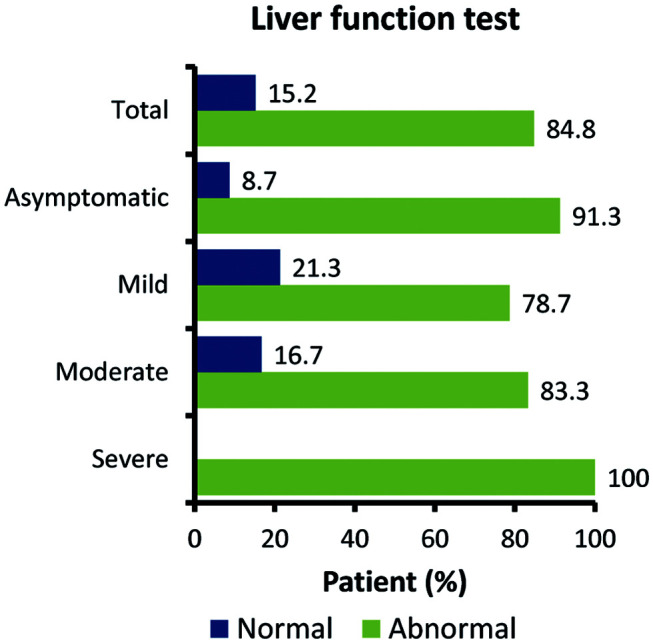
A total of 184 patients with COVID-19 were included in the analysis. Of these, 32 (17.4%), 112 (60.8%), and 18 (9.7%) patients had asymptomatic, mild, and moderate COVID-19 respectively, while 22 (11.9%) had severe COVID-19. The median age was 45.5 years and 115 (62.5%) patients were men. Hypertension (21.7%) and diabetes mellitus (16.8%) were the most common comorbidities, followed by ischemic heart disease (6.0%), chronic kidney disease (5.4%), hypothyroid (3.3%), and malignancy (2.2%). The most common symptoms at the initial stage of illness were fever (39.1%), cough (33.1%), breathlessness (18.5%), and sore throat (15.7%). While, other less common symptoms reported were generalized weakness, loss of appetite, headache, vomiting, nausea, acute weakness, unconsciousness, insomnia, loose motions, and pain in the abdomen. In the overall population, 95 (51.6%) patients showed abnormal LFT and 17 (9.2%) showed normal LFT at admission. Patients with severe and moderate COVID-19 had abnormal LFT (100% and 83.3% respectively) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Liver test abnormality during hospitalization in patients with COVID-19 by severity of disease.
Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin were given in 81.5% of patients and anticoagulant therapy administered in 10.9% of patients. Tocilizumab was prescribed in 5.4% of patients (Table 1).
Table 1. Characteristics of patients with COVID-19 by severity.
| Parameters | Total (n=184)* | Asymptomatic (n=32)** | Mild (n=112)*** | Moderate (n=18)# | Severe (n=22)## | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years, median (range) | 45.5 (13.0–86.0) | 44.1 (17.2) | 41.3 (17.3) | 55.5 (13.6) | 64.6 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.011 | |||||
| Men | 115 (62.5) | 12 (37.5) | 74 (66.1) | 14 (66.1) | 15 (68.2) | |
| Women | 69 (37.5) | 20 (62.5) | 38 (33.9) | 4 (22.2) | 7 (31.8) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| HTN | 40 (21.7) | 7 (21.9) | 17 (15.2) | 6 (33.3) | 10 (45.5) | 0.009 |
| DM | 31 (16.8) | 5 (15.6) | 11 (9.8) | 6 (33.3) | 9 (40.9) | 0.001 |
| IHD | 11 (6.0) | – | 7 (6.3) | 3 (16.7) | 1 (4.5) | – |
| CKD | 10 (5.4) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (3.6) | 1 (5.6) | 4 (18.2) | – |
| Hypothyroid | 6 (3.3) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (3.6) | – | 1 (4.5) | – |
| Malignancy | 4 (2.2) | 2 (6.3) | 1 (0.9) | – | 1 (4.5) | – |
| Others | 15 (8.2) | 2 (6.3) | 3 (2.7) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (36.4) | – |
| Hospital stay in days, median (range) | 8.0 (4.0–13.0) | 6.0 (2.0–14.0) | 8.0 (1.0–25.0) | 9.0 (1.0–53.0) | 14.5 (1.0–28.0) | 0.007 |
| ICU required | 34 (18.5) | 0 | 2 (1.8) | 10 (55.6) | 22 (100) | <0.001 |
| Oxygen | [n=36] | [n=2] | [n=15] | [n=19] | ||
| Mechanical ventilation | 14 (38.9) | – | – | 14 (73.7) | <0.001 | |
| Nasal oxygen mask | 11 (30.6) | – | 2 (100) | 9 (60.0) | – | |
| Non-rebreather facemask | 5 (13.9) | – | 2 (13.3) | 3 (15.8) | ||
| Facemask oxygen | 4 (11.1) | – | 3 (20.0) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Noninvasive ventilation | 2 (5.6) | – | 1 (6.7) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Patients on dialysis | 11 (6.0) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (3.6) | 2 (11.1) | 4 (18.2) | 0.040 |
| Result of sample | 0.033 | |||||
| Positive | 150 (81.5) | 30 (93.8) | 92 (82.1) | 12 (66.7) | 16 (72.7) | |
| Negative | 33 (17.9) | 2 (6.3) | 20 (17.9) | 6 (33.3) | 5 (22.7) | |
| Inconclusive | 1 (0.5) | – | – | – | 1 (4.5) | |
| Symptoms | ||||||
| Fever | 72 (39.1) | 1 (3.1) | 48 (42.9) | 11 (61.1) | 12 (54.5) | <0.001 |
| Cough | 61 (33.1) | 2 (6.3) | 41 (36.6) | 9 (50.0) | 9 (40.9) | 0.003 |
| Breathlessness | 34 (18.5) | – | 12 (10.7) | 7 (38.9) | 15 (68.2) | <0.001 |
| Sore throat | 29 (15.7) | – | 24 (21.4) | 2 (11.1) | 3 (13.6) | 0.028 |
| Generalized weakness | 14 (7.6) | – | 9 (8.0) | 3 (16.7) | 2 (9.1) | 0.184 |
| Fatigue | 11 (6.0) | – | 7 (6.3) | 1 (5.6) | 3 (13.6) | 0.226 |
| Loss of appetite | 5 (2.7) | – | 3 (2.7) | – | 2 (9.1) | 0.189 |
| Headache | 5 (2.7) | – | 5 (4.5) | – | – | 0.347 |
| Vomiting | 5 (2.7) | – | 4 (3.6) | – | 1 (4.5) | 0.576 |
| Nausea | 5 (2.7) | – | 5 (4.5) | – | – | 0.347 |
| Acute weakness | 4 (2.1) | – | 2 (1.8) | – | 2 (9.1) | 0.105 |
| Other | 9 (4.8) | 3 (2.7) | 6 (6.8) | – | ||
| Outcome | <0.001 | |||||
| Discharge | 172 (93.5) | 32 (100) | 112 (100) | 17 (94.4) | 11 (50.0) | |
| Death | 12 (6.5) | 0 | 0 | 1 (5.6) | 11 (50.0) | |
| Drug used | ||||||
| Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin | 150 (81.5) | 30 (93.8) | 92 (82.1) | 12 (66.7) | 16 (72.7) | 0.073 |
| Tocilizumab | 10 (5.4) | – | – | – | 10 (45.5) | <0.001 |
| Awake prone positioning | 12 (6.5) | – | 1 (0.9) | 6 (33.3) | 5 (22.7) | <0.001 |
| Anticoagulation | 20 (10.9) | – | – | 4 (22.2) | 16 (72.7) | <0.001 |
| Patients on vasopressor support | 2 (1.1) | – | – | – | 2 (9.1) | 0.002 |
| Antibiotic administration before admission | – | |||||
| Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate | 4 (2.1) | 4 (3.6) | – | – | ||
| Piperacillin and tazobactam | 4 (2.1) | – | 1 (5.6) | 3 (13.6) | – | |
| Amoxicillin, potassium clavulanate, and azithromycin | 1 (0.5) | – | – | 1 (4.5) | ||
| Ceftriaxone | 1 (0.5) | – | – | 1 (4.5) | ||
| Antibiotic administration on admission | – | – | – | |||
| Piperacillin and tazobactam | 7 (3.8) | 7 (31.8) | ||||
| Piperacillin, tazobactam, and azithromycin | 1 (0.5) | 1 (4.5) | – | |||
| Ceftriaxone | 1 (0.5) | 1 (4.5) | ||||
| Antibiotic changed to | – | – | ||||
| Meropenem | 2 (1.1) | – | – | 2 (9.1) | ||
| Meropenem and teicoplanin | 4 (2.1) | – | – | 4 (18.2) | ||
| Ceftriaxone | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.9) | – | – | ||
| Piperacillin and tazobactam | 2 (1.1) | – | 1 (5.6) | 1 (4.5) | ||
Data shown as n (%), unless otherwise specified. *n=184; **n=32; ***n=112; #n=18; ##n=22, unless otherwise specified. CKD, chronic kidney disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; IHD, ischemic heart disease. Other comorbid conditions include bronchial asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary tuberculosis, cerebrovascular accident, congestive cardiac failure, coronary artery disease, dementia, dilated cardiomyopathy, epilepsy, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, left ventricular failure, non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction, Parkinson’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. Other symptoms include unconscious, insomnia, loose motions, and pain in abdomen.
Severe vs. non-severe COVID-19
The median age was significantly higher in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to those with asymptomatic, mild, and moderate COVID-19 (64.6 vs. 44.1 vs. 41.3 vs. 55.5 years; p<0.001). The proportion of patients with presence of comorbidities was significantly higher in the severe group compared to the non-severe group (81.8% vs. 30.2%; p<0.001). The median hospital stay was two-fold longer in patients with severe COVID-19 than those with non-severe disease (14.5 vs. 7.0 days; p=0.007). Among symptoms, breathlessness was significantly higher in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to patients with non-severe COVID-19 (p<0.001). In the overall population, 12 (6.5%) patients died. A total of 11 patients had in-hospital death due to severe COVID-19, while only one patient with moderate COVID-19 was reported as an in-hospital death. The overall reasons reported for hospital deaths were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n=5), cardiac (n=3; including myocarditis with or without failure (n=2) or arrhythmia (n=1)), and sepsis with multiorgan failure (n=3). The use of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin were similar in patients from severe and non-severe groups of COVID-19. However, use of tocilizumab, anticoagulant agents, and awake prone positioning, were more common in patients with severe COVID-19. Only two patients with severe disease required vasopressor support in the total study population (Table 1).
Clinical features of patients with COVID-19 at admission
All the LFT parameters, including serum bilirubin, AST, ALT, GGT and ALP, were significantly higher in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, as compared to patients with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19 (p<0.05) (Table 2). An increasing trend was observed in median levels of serum bilirubin and AST in patients with asymptomatic to severe COVID-19 (p<0.05). The median albumin level was significantly lower in patients with severe COVID-19 (p<0.001) compared to patients from non-severe groups. The majority of the patients with moderate and severe COVID-19 had abnormal liver test results within 1–3×ULN at admission and only one patient each from the moderate and severe disease group had abnormal GGT test higher than 3×ULN, suggesting liver injury. Hypoalbuminemia was more common with increasing severity of the disease (Table 2).
Table 2. Characteristics of patients with COVID-19 at admission by laboratory tests.
| Labs | Group A Asymptomatic (n=21) | Group B Mild (n=52) | Group C Moderate (n=10) | Group D Severe (n=14) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilirubin in mg/dL | 0.3 (0.4–0.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.35 (0.3–0.6) | 0.6 (4.0–1.3) | 0.005a, 0.026b, 0.038c |
| Normal | 21 (100.0) | 52 (100.0) | 10 (100.0) | 11 (78.6) | |
| 1–2 ULN | – | – | – | 2 (14.3) | 0.005 |
| 2–3 ULN | – | – | – | 1 (7.1) | |
| AST in U/L | 18.0 (15.5–22.0) | 23.0 (20.0–29.0) | 31.5 (25.5–49.3) | 36.0 (27.7–73.0) | 0.001d, <0.001e,a,b, 0.006f |
| Normal | 21 (100.0) | 45 (86.5) | 6 (60.0) | 8 (57.1) | |
| 1–2 ULN | – | 7 (14.5) | 4 (40.0) | 4 (28.6) | 0.001 |
| 2–3 ULN | – | – | – | 2 (14.3) | |
| ALT in U/L | 15.0 (10.5–19.5) | 22.0 (14.3–35.8) | 43.0 (26.0–49.7) | 36.0 (21.3–55.0), [n=16] | 0.016d, 0.001e, <0.001a, 0.024f, 0.026b |
| Normal | 20 (95.2) | 43 (82.7) | 4 (40.0) | 9 (56.3) | 0.005 |
| 1–2 ULN | 1 (4.8) | 8 (15.4) | 6 (60.0) | 6 (37.5) | |
| 2–3 ULN | – | 1 (1.9) | – | 1 (6.3) | |
| GGT in IU/L | 17.0 (12.0–27.5) | 27.0 (16.0–43.5), [n=49] | 74.5 (38.3–121.0) | 57.0 (25.0–64.0), [n=11] | 0.010d, <0.001e,a, 0.003f, 0.025b |
| Normal | 20 (95.2) | 39 (79.6) | 3 (30.0) | 3 (27.3) | <0.001 |
| 1–2 ULN | 1 (4.8) | 8 (16.3) | 3 (30.0) | 7 (63.7) | |
| 2–3 ULN | – | 1 (2.0) | 3 (30.0) | – | |
| >3 ULN | – | 1 (2.0) | 1 (10.0) | 1 (9.0) | |
| ALP in U/L | 67.0 (56.0–86.5) | 74.5 (61.0–89.0) | 104.0 (95.0–135.3) | 76.0 (59.0–120.3) | 0.003e,f |
| Normal | 20 (95.2) | 52 (100.0) | 8 (80.0) | 12 (85.7) | 0.021 |
| 1–2 ULN | 1 (4.8) | – | 2 (20.0) | 2 (14.3) | |
| Total protein in g/dL | 7.3 (7.1–7.6) | 7.2 (6.9–7.7) | 6.7 (6.3–7.3) | 6.2 (5.9–6.3), [n=16] | <0.001a,b, 0.005c |
| Normal | 21 (100.0) | 52 (100.0) | 9 (90.0) | 15 (93.8) | 0.027 |
| Abnormal | – | – | 1 (10.0) | 1 (6.3) | |
| Albumin in g/dL | 4.2 (4.0–4.4) | 4.2 (3.9–4.5) | 3.4 (3.2–3.8) | 3.2 (3.0–3.5) | <0.001e,a,f,b |
| Normal | 20 (95.2) | 46 (88.5) | 4 (40.0) | 3 (21.4) | <0.001 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 1 (4.8) | 6 (11.5) | 6 (60.0) | 11 (78.6) | |
| Globulin in g/dL | 2.9 (2.8–3.4) | 3.1 (2.7–3.3) | 3.3 (3.1–3.6) | 3.1 (2.8–3.2) | 0.034f, 0.045c |
| Normal | 20 (95.2) | 47 (90.4) | 8 (90.4) | 13 (92.9) | 0.581 |
| Abnormal | 1 (4.8) | 5 (9.6) | 2 (20.0) | 1 (7.1) | |
| Albumin/globulin ratio | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 1.01 (0.9–1.1) | 1.1 (0.9–1.2) | <0.001e,a,f,b |
| Serum creatinine in mg/dL | 0.6 (0.5–0.9), [n=22] | 0.8 (0.6–0.8), [n=59] | 0.9 (0.7–0.1), [n=12] | 0.8 (0.7–1.8) | 0.009e, 0.036f, 0.045b |
| Normal | 21 (95.5) | 54 (91.5) | 10 (83.3) | 9 (64.3) | 0.036 |
| Abnormal | 1 (4.5) | 5 (8.5) | 2 (16.6) | 5 (35.7) | |
| BUN in mg/dL | 9.1 (7.6–10.7), [n=20] | 7.8 (6.6–9.1), [n=48] | 11.0 (7.8–22.0), [n=9] | 20.1 (11.0–24.7) | 0.001a,b, 0.036f |
| Normal | 1 (5.0) | 12 (25.0) | 1 (11.1) | – | <0.001 |
| Abnormal | 9 (95.0) | 36 (75.0) | 8 (88.9) | 14 (100.0) |
Data shown as n (%), unless otherwise specified. *n=21; **n=52; #n=10; ##n=14, unless otherwise specified. BUN, blood urea nitrogen. ; aGroup A vs. D; bGroup B vs. D; cGroup C vs. D; dGroup A vs. B; eGroup A vs. CfGroup B vs. C
Abnormal LFT vs. normal LFT
Median age was comparatively higher in patients having abnormal LFT (50.0 years) than in patients having normal LFT (37.0 years). Compared with the patients having normal LFT, the patients with abnormal LFT were more likely to have underlying comorbidities, including hypertension (30.5% vs. 17.6%) and cardiovascular disease (24.2% vs. 17.6%). The median duration of hospital stay was longer in patients having abnormal LFT compared to patients having normal LFT (10 vs. 7 days; p=0.423). Number of ICU admissions was higher in patients having abnormal LFT (n=20, 90.9%) compared to patients having normal LFT (n=2, 10.1%). All other parameters were comparable between patients with abnormal LFT and those with normal LFT. Significantly increased blood urea nitrogen was observed in more patients having abnormal LFT than in those with normal LFT (8.7 vs. 5.8; p<0.001) (Table 3).
Table 3. Characteristics of patients with COVID-19 by abnormal and normal LFT.
| Parameters | Abnormal liver function test (n=95)* | Normal liver function test (n=17)** | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years, median (range) | 50.0 (20.0–85.0) | 37.0 (17.0–80.0) | 0.106 |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Men | 61 (64.2) | 11 (64.7) | |
| Women | 34 (35.8) | 6 (35.3) | |
| Comorbidities | |||
| HTN | 29 (30.5) | 3 (17.6) | 0.387 |
| DM | 23 (24.2) | 3 (17.6) | 0.758 |
| IHD | 5 (5.3) | 1 (5.9) | – |
| CKD | 7 (7.4) | – | – |
| Hypothyroid | 6 (6.3) | – | – |
| Malignancy | 3 (3.2) | – | – |
| Others | 8 (8.4) | – | – |
| Hospital stay in days, median (range) | 10.0 (3.0–53.0) | 7.0 (1.0–25.0) | 0.423 |
| State of illness | 0.247 | ||
| Asymptomatic | 21 (22.1) | 2 (11.8) | |
| Mild | 48 (50.5) | 13 (76.5) | |
| Moderate | 10 (10.5) | 2 (11.8) | |
| Severe | 5 (5.3) | – | |
| Critical illness | 11 (11.6) | – | |
| ICU admission | 20 (21.1) | 2 (11.8) | 0.517 |
| Oxygen | [n=27] | [n=3] | 0.349 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 11 (40.7) | – | |
| Nasal oxygen mask | 6 (22.2) | 2 (66.7) | |
| Non-rebreather facemask | 4 (14.8) | 1 (33.3) | |
| Facemask oxygen | 4 (14.8) | – | |
| Noninvasive ventilation | 2 (7.4) | – | |
| Patients on dialysis | 8 (8.4) | – | 0.605 |
| Laboratory values on admission, median range | |||
| Serum bilirubin in mg/dL | 0.4 (0.2–3.0), [n=92] | 0.3 (0.2–0.9), [n=5] | 0.294 |
| AST in U/L | 23.5 (5.0–107.0), [n=92] | 22.0 (16.0–29.0), [n=5] | 0.419 |
| ALT in U/L | 21.5 (5.0–129.0), [n=94] | 21.0 (9.0–35.0), [n=5] | 0.507 |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase in IU/L | 32.5 (7.0–188.0), [n=92] | 18.0 (9.0–35.0), [n=5] | 0.098 |
| Alkaline phosphatase in U/L | 73.5 (36.0–247.0), [n=92] | 79.0 (52.0–83.0), [n=5] | 0.948 |
| Total protein level in g/dL, mean (SD) | 6.9 (0.9), [n=94] | 7.1 (0.5), [n=5] | 0.525 |
| Albumin in g/dL, mean (SD) | 3.9 (0.5), [n=92] | 4.1 (0.4), [n=5] | 0.414 |
| Globulin in g/dL, mean (SD) | 3.0 (0.5), [n=92] | 3.0 (0.2), [n=5] | 0.781 |
| Albumin to globulin ratio, mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.3), [n=92] | 1.4 (0.2), [n=5] | 0.523 |
| Serum creatinine in mg/dL | 0.8 (0.4–9.3), [n=91] | 0.7 (0.3–1.0), [n=16] | 0.125 |
| Blood urea nitrogen in mg/dL | 8.7 (2.0–48.2), [n=87] | 5.8 (4.4–6.5), [n=4] | 0.001 |
| Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin | 95 (100.0) | 16 (94.1) | 0.152 |
| Tocilizumab | 10 (10.5) | – | 0.355 |
| Awake prone positioning | 11 (11.6) | 1 (5.9) | 0.689 |
| Anticoagulation | 19 (20.0) | – | 0.072 |
| Patients on vasopressor support | 2 (2.1) | – | 1.000 |
| Outcome | 1.000 | ||
| Discharge | 90 (94.7) | 17 (100.00) | |
| Death | 5 (5.3) | – | |
Data shown as n (%), unless otherwise specified. *n=95; **n=17, unless otherwise specified. SD, standard deviation. Other comorbid conditions include bronchial asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary tuberculosis, cerebrovascular accident, congestive cardiac failure, dementia, epilepsy, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Other symptoms include unconsciousness [(n=2), injury], insomnia [(n=2), injury], loose motions [(n=1), injury], and pain in abdomen [(n=1), injury].
Table 4 summarizes the prevalence of patients with abnormal LFT markers at admission and at discharge in patients with severe and non-severe COVID-19. Incidence of elevated AST (50.0% and 33.3%) and GGT (88.9% and 50.0%) at admission and discharge were more common in patients with severe COVID-19. Incidence of hypoalbuminemia (91.7%) at discharge and elevated globulin (91.7%) at admission was common in patients with severe COVID-19. Among five patients who died, at least three LFT parameters had abnormal levels (Patient 1: AST, ALT, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, hypoalbuminemia; Patient 2: AST, ALT, GGT, ALP, globulin, blood urea nitrogen, hypoalbuminemia; Patient 3: Bilirubin, AST, ALT, GGT, BUN, hypoalbuminemia; Patient 4: ALT, GGT, blood urea nitrogen; and Patient 5: AST, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, hypoalbuminemia). Ordinal regression analysis showed that mortality was not associated with any of the parameters of LFT (Table 5).
Table 4. Prevalence of patients with abnormal LFT markers at admission and at discharge in patients with severe and non-severe COVID-19.
| Parameters | Elevated levels at | Non-severe COVID-19 (n=159) |
Severe COVID-19 (n=20) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n (%) | n | n (%) | ||
| AST in U/L | Admission | 80 | 11 (13.7) | 12 | 6 (50.0) |
| Discharge | 8 | 1 (12.5) | 9 | 3 (33.3) | |
| ALT in U/L | Admission | 80 | 16 (20.0) | 14 | 7 (50.0) |
| Discharge | 8 | 2 (25.0) | 10 | 5 (50.0) | |
| GGT in IU/L | Admission | 77 | 18 (23.4) | 9 | 8 (88.9) |
| Discharge | 7 | 4 (57.1) | 6 | 3 (50.0) | |
| ALP in U/L | Admission | 80 | 3 (3.7) | 12 | 2 (16.7) |
| Discharge | 7 | 1 (14.3) | 11 | 4 (36.3) | |
| Bilirubin in mg/dL | Admission | 80 | 0 | 12 | 3 (25.0) |
| Discharge | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 | |
| Total protein in g/dL | Admission | 80 | 1 (1.2) | 14 | 1 (7.1) |
| Discharge | 8 | 1 (12.5) | 14 | 0 | |
| Hypoalbuminemia in g/dL | Admission | 80 | 0 | 12 | 1 (8.3) |
| Discharge | 79 | 10 (12.7) | 12 | 11 (91.7) | |
| Globulin in g/dL | Admission | 80 | 7 (8.7) | 12 | 11 (91.7) |
| Discharge | 79 | 6 (7.5) | 12 | 1 (8.3) | |
Table 5. Correlation of study parameters with death.
| Parameters | Odds ratio | (95% CI); p value |
|---|---|---|
| Age in years | 0.710 | (0.055, 9.200); 0.794 |
| Serum bilirubin | 452.236 | (0.067, 3,051,506.123); 0.174 |
| AST in U/L | 0.938 | (0.702, 1.255); 0.667 |
| ALT in U/L | 1.360 | (0.723, 2.560); 0.340 |
| GGT in IU/L | 1.340 | (0.719, 2.500); 0.357 |
| ALP in U/L | 0.665 | (0.293, 1.512); 0.330 |
| Serum creatinine in mg/dL | 0.168 | (0.000, 3,651.678); 0.726 |
| BUN in mg/dL | 1.792 | (0.161, 19.892); 0.635 |
Survival analysis
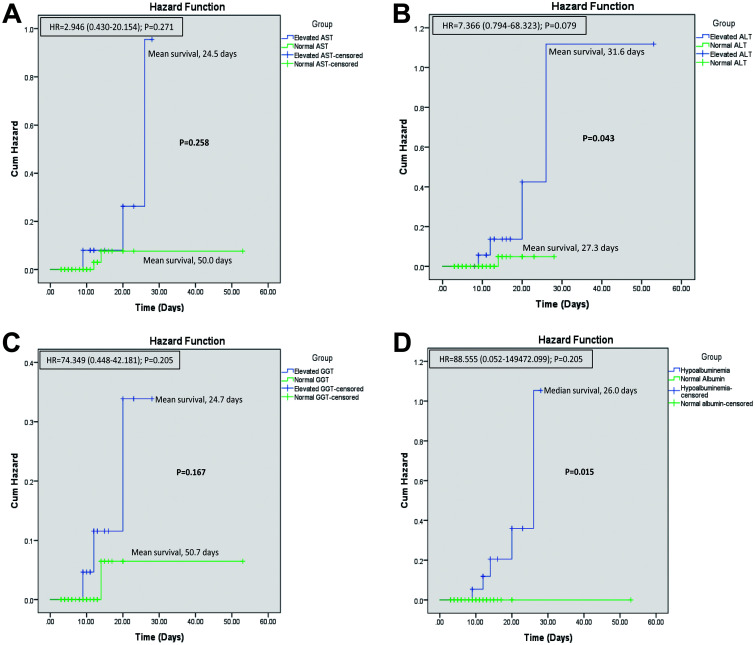
In patients with elevated AST levels, the risk of mortality were 2.946 times more compared to patients with normal AST levels. Similarly, in patients with elevated ALT, GGT and hypoalbuminemia levels, the risk of mortality were 7.366, 74.349 and 88.55 times more compared to patients with normal marker levels. However, none of these results reached the threshold for statistical significance (p>0.05).
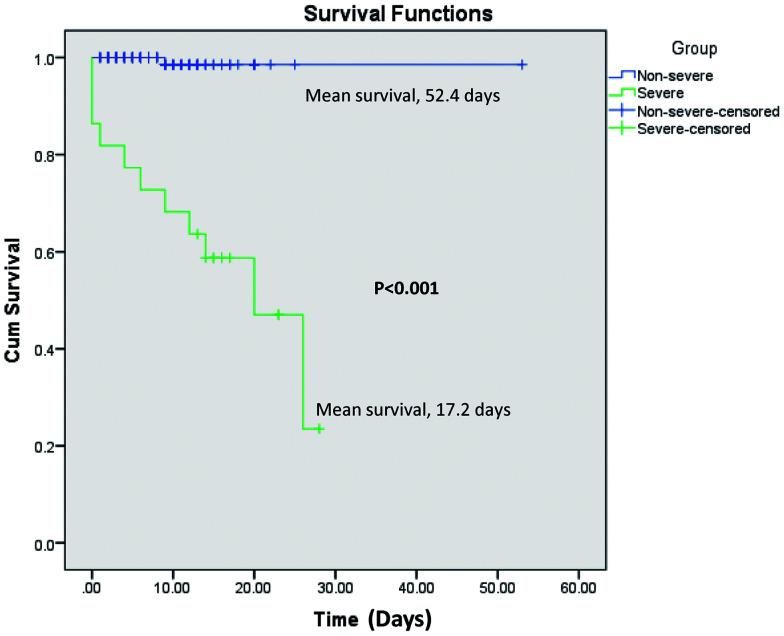
The mean survival was significantly lower in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to those with non-severe COVID-19 disease (17.2 vs. 52.3 days; p<0.001) (Fig. 2). Patients with elevated AST (24.5 vs. 50.0 days; p=0.258) and those with elevated GGT (24.7 vs. 50.7 days; p=0.167) had comparatively lower mean survival compared to those with normal levels (Fig. 3A, C). Patients with elevated ALT (31.6 vs. 27.3 days; p=0.043) had higher mean survival compared to those with normal levels (Fig. 3B). Patients with hypoalbuminemia had median survival of 26.0 days (p=0.015) and those with normal albumin levels showed 100% survival (Fig. 3D).
Fig. 2. Kaplan-Meier plots for survival severe vs. non-severe disease.
Fig. 3. Overall survival. In patients with COVID-19 and (A) elevated AST (U/L), (B) elevated ALT (U/L), (C) elevated GGT (IU/L), and (D) hypoalbuminemia (g/dL).
Discussion
The present retrospective study assessed the liver function abnormalities in patients with severe and non-severe COVID-19 to elucidate if there is any association of liver injury with mortality of patients. The key observations were: a) male preponderance in the overall study population and absence of underlying chronic liver disease as comorbidity; b) more than three-quarter of the study population had abnormal liver function test at the time of admission; c) presence of higher number of comorbidities were associated with severe COVID-19 disease; d) age and duration of hospital stay were higher in patients with severe disease and patients with abnormal liver function parameters; e) mortality was associated with severity of COVID-19 and abnormal liver function parameters; f) patients with abnormal LFT parameters were most commonly admitted to ICU; and g) incidence of elevated AST, ALT, and GGT, and hypoalbuminemia were more common in patients with severe COVID-19.
The male predominance in severe cases of COVID-19 and in patients with abnormal LFT observed in this study is in concordance with the previous studies.7,17,20 Underlying chronic liver disease can have profound effect on COVID-19 outcomes in terms of high risk of mortality and rapid progression of disease, ultimately leading to multiple organ damage and poor survival outcome.21 Evidence highlighting association between presence of underlying chronic liver disease as a comorbidity and increased risk of death have been inconsistent.4,21–23 A large-scale study that included patients with chronic liver disease and COVID-19 from 13 Asian countries suggested that COVID-19 causes significant liver injury in these patients, decompensating one-fifth of cirrhosis, and worsening the clinical status of the already decompensated.21 Further, presence of other comorbidities (diabetes and obesity) along with chronic liver disease makes them more susceptible to worse outcomes. In the present study, none of the patients had preexisting chronic liver disease.
The present study showed significantly longer duration of hospital stay in patients with severe disease and patients with abnormal liver function parameters compared to those with non-severe disease and with normal liver function parameters. These observations were in concordance with those from previous studies reported in the literature.17,20 A study by Fan et al.20 showed prevalence of abnormal liver function in more than one-third of patients admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. The authors further reported a significantly prolonged hospital stay in patients with abnormal liver function compared to those with normal function test (15.09 vs. 12.76 days; p=0.021). Therefore, all these observations suggest an association of abnormal liver function with longer hospital stay in patients with severe COVID-19.
The higher incidence of elevated levels of AST, ALT, GGT, and hypoalbuminemia among the present study patients with severe COVID-19 is in accordance with previous studies across the globe; however, these incidences are in the higher range than other reports in the literature.5,8,11,16 Similar Indian studies are few and larger studies are required to validate these higher proportions in Indian settings. Guan et al.11 reported high incidence of elevated AST levels (39.4% vs. 18.2%) and ALT levels (28.1% and 19.8%) in patients with severe disease compared to those with non-severe disease. Similarly, another study from China demonstrated higher prevalence of elevated AST and ALT levels in patients admitted to ICU (p=0.007 and p<0.001).14 A meta-analysis showed that about 80.4% of patients with abnormal liver function in COVID-19 had hypoalbuminemia, which was associated with prognosis and outcome.24 Therefore, all these lines of evidence along with the present study allude to the predominance of liver injury in severe disease rather than mild or moderate COVID-19 disease.
Previous studies suggest high incidence of hepatic dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 disease who are critically ill and hepatic dysfunction also contributes to poor outcome.25 A study by Zhang et al.16 showed that around 14–53% of patients with COVID-19 developed hepatic dysfunction, particularly those with severe COVID-19. An Indian study by Kaushik et al.17 reported more than half of the study population with abnormal LFT. A systematic meta-analysis of 107 studies showed 2.87-fold increased risk of developing severe disease in patients with COVID-19 having elevated liver chemistries (odds ratio: 2.87 [95% confidence interval: 2.29–3.6, p<0.001]) compared to those without elevated liver chemistries.4 In the present study, the elevated levels of AST, ALT, and GGT and reduced levels of total protein, albumin, and albumin to globulin ratio are associated with severe COVID-19 disease.
No statistically significant association was observed between any of the parameters of LFT and death in the present study population. Several analysis factors, such as a smaller number of deaths, relatively small sample size with all the available data, and skewed data, might be responsible for this outcome. On the contrary, other study reports have provided evidence supporting association of abnormal liver function with mortality observed in COVID-19 patients.4,9,26 Huang et al.9 demonstrated presence of an inverse relationship between the level of albumin and the risk of death in COVID-19 patients and revealed that serum albumin level <35 g/L at presentation independently increased the risk of death in COVID-19 by at least 6-fold.
The major limitations of this study are its retrospective design and unavailability of data of LFT parameters for around 40% (n=77) of patients during the data collection process from the case record forms. There was a heterogeneity in protocol maintenance and this could impact the retrospective analysis of outcome measures. The use of antibiotics can impact liver function independent of COVID-19 and hence false liver test and outcome measures might be considered. Therefore, a prospective study with a single protocol, homogenized throughout, among such specific groups as mild, moderate, severe or critically ill COVID-19 is required.
Conclusions
Overall observations suggest that incidence of abnormal liver function was higher in patients with severe COVID-19 and was associated with prolonged hospital stay; moreover, mortality was associated with severity of COVID-19. Therefore, for ruling out the risk of liver injury, it is crucial to vigilantly monitor the liver function parameters in patients with COVID-19 admitted to hospital.
Abbreviations
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- ARDS
acute respiratory distress syndrome
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- COVID-19
coronavirus disease 2019
- GGT
gamma glutamyltransferase
- ICU
intensive care unit
- LFT
liver function test
- ULN
upper limit of normal
- WHO
World Health Organization
Data sharing statement
All data are available upon request.
References
- 1. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
- 2.Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cheng Y, Luo R, Wang K, Zhang M, Wang Z, Dong L, et al. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020;97(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kulkarni AV, Kumar P, Tevethia HV, Premkumar M, Arab JP, Candia R, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52(4):584–599. doi: 10.1111/apt.15916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kumar-M P, Mishra S, Jha DK, Shukla J, Choudhury A, Mohindra R, et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the liver: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2020;14(5):711–722. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10071-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu Y, Li H, Guo X, Yoshida EM, Mendez-Sanchez N, Levi Sandri GB, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of abnormal liver biochemical tests in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2020;14(5):621–637. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10074-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cai Q, Huang D, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Su Y, et al. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J Hepatol. 2020;73(3):566–574. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tian S, Hu N, Lou J, Chen K, Kang X, Xiang Z, et al. Characteristics of COVID-19 infection in Beijing. J Infect. 2020;80(4):401–406. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang W, Cao Q, Qin L, Wang X, Cheng Z, Pan A, et al. Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19):A multi-center study in Wenzhou city, Zhejiang, China. J Infect. 2020;80(4):388–393. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang JJ, Dong X, Cao YY, Yuan YD, Yang YB, Yan YQ, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;75(7):1730–1741. doi: 10.1111/all.14238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061–1069. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li J, Fan JG. Characteristics and mechanism of liver injury in 2019 coronavirus disease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020;8(1):13–17. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang C, Shi L, Wang FS. Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(5):428–430. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30057-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kaushik A, Wani SN, Baba MA, Agarwal AK. Prevalence of abnormal liver function tests in COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care centre. J Assoc Physicians India. 2020;68(8):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Clinical management protocol: COVID-19. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19.pdf.
- 19. World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays. Interim guidance. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/334253/WHO-2019-nCoV-Antigen_Detection-2020.1-eng.pdf?sequence=1andisAllowed=y.
- 20.Fan Z, Chen L, Li J, Cheng X, Yang J, Tian C, et al. Clinical features of COVID-19-related liver functional abnormality. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(7):1561–1566. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sarin SK, Choudhury A, Lau GK, Zheng MH, Ji D, Abd-Elsalam S, et al. Pre-existing liver disease is associated with poor outcome in patients with SARS CoV2 infection; The APCOLIS Study (APASL COVID-19 Liver Injury Spectrum Study) Hepatol Int. 2020;14(5):690–700. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10072-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lenti MV, Borrelli de Andreis F, Pellegrino I, Klersy C, Merli S, Miceli E, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on liver function: results from an internal medicine unit in Northern Italy. Intern Emerg Med. 2020;15(8):1399–1407. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02425-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mantovani A, Beatrice G, Dalbeni A. Coronavirus disease 2019 and prevalence of chronic liver disease: A meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2020;40(6):1316–1320. doi: 10.1111/liv.14465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu YY, Li HY, Xu XB, Zheng KX, Qi XS, Guo XZ. Clinical features and outcome of treatment for novel coronavirus pneumonia: a meta-analysis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020;28(3):240–246. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200224-00067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jothimani D, Venugopal R, Abedin MF, Kaliamoorthy I, Rela M. COVID-19 and the liver. J Hepatol. 2020;73(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen T, Wu D, Chen H, Yan W, Yang D, Chen G, Ma K, Xu D, Yu H, Wang H, Wang T, Guo W, Chen J, Ding C, Zhang X, Huang J, Han M, Li S, Luo X, Zhao J, Ning Q. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ. 2020;368:m1091. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]