Abstract
Liver fibrosis is a life-threatening disease, with challenging morbidity and mortality for healthcare systems worldwide. It imparts an enormous economic burden to societies, making continuous research and informational updates about its pathogenesis and treatment crucial. This review′s focus is on the current knowledge about the Wnt signaling pathway, serving as an important pathway in liver fibrosis development and activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Two types of Wnt pathways are distinguished, namely the ß-catenin-dependent canonical and non-canonical Ca2+ or planar cell polarity (PCP)-dependent pathway. The dynamic balance of physiologically healthy liver and hepatocytes is disturbed by repeated liver injuries. Activation of the ß-catenin Wnt pathway prevents the regeneration of hepatocytes by the replacement of extracellular matrix (ECM), leading to the appearance of scar tissue and the formation of regenerated nodular hepatocytes, lacking the original function of healthy hepatocytes. Therefore, liver function is reduced due to the severely advanced disease. Selective inhibition of ß-catenin inhibits inflammatory processes (since chemokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines are produced during Wnt activation), reduces growth of activated HSCs and reduces collagen synthesis and angiogenesis, thereby reducing the progression of liver fibrosis in vivo. While the canonical Wnt pathway is usually inactive in a physiologically healthy liver, it shows activity during cell regeneration or renewal and in certain pathophysiological conditions, such as liver diseases and cancer. Targeted blocking of some of the basic components of the Wnt pathway is a therapeutic approach. These include the frizzled transmembrane receptor (Fz) receptors using the secreted frizzled-related protein family (sFRP), Fz-coreceptors low-density LRP 5/6 through dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) or niclosamide, glycogen kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) using SB-216763, cyclic-AMP response element-binding protein (CBP) using PRI-724 and ICG-001, the lymphoid enhancer binding factor (LEF)/T cell-specific transcription factor (TCF) system as well as Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) and miR-17-5p using pinostilbene hydrate (PSH). Significant progress has been made in inhibiting Wnt and thus stopping the progression of liver fibrosis by diminishing key components for its action. Comprehending the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in liver fibrosis may lead to discovery of novel targets in liver fibrosis therapeutic strategies’ development.
Keywords: Liver fibrosis, Wnt signaling pathway, Hepatic stellate cell, Therapeutic solutions
Graphical abstract
Introduction
Liver fibrosis represents a significant global health problem. Due to the fact that fibrosis progression leads to the development of cirrhosis and liver cancer, worldwide mortality related to this condition is 1.5 million deaths per year.1 Numerous epidemiological studies have shown important clinical implications of fibrosis staging.2 Various clinical tools have also been developed in order to better distinguish stages of liver disease and predict mortality with cirrhosis, such as the Child-Pugh score and model for end-stage liver disease score. Etiology of liver fibrosis can be divided into the following two major types of injuries: cholestatic (reduction or obstruction of the gall flow in the liver) and hepatotoxic (hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, metabolic- and alcoholic-associated steatohepatitis).3 Common pathophysiological mechanisms involved in fibrosis development, regardless of the etiology, are cytokine release and chronic inflammation, hepatocyte death, HSC activation, and disruption of the endothelial or epithelial barrier.4 Endothelial cells, HSCs and Kupffer cells have various functions, with a particularly important role in fibrosis development. Kupffer cells are liable for the production of different proinflammatory cytokines, and also act as liver macrophages. As the headspring of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) is proven to play a key role in fibrogenesis, Kupffer cells are also an important factor in the development of fibrosis.2,5 Accordingly, liver fibrogenesis represents a complex process which requires extracellular and cellular signaling.2
Recently, reactivation of several signaling pathways, such as Wnt, notch and hedgehog (Hh), has been related with liver injury and regeneration.6 The Wnt signaling pathway is a conserved signal transduction pathway included in the regulation of numerous cellular functions and controlling important aspects of development.7–10 Activation of this signaling pathway is associated to activation of HSCs and fibrogenesis, along with enhanced synthesis of ECM, transformation of epithelial cells or epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) or interaction with other profibrotic mediators. 11–13
Through this critical review, we aimed to recapitulate current lore about the Wnt signaling pathway as a part of the underlying pathophysiological mechanism in liver fibrosis development. Also, emerging data about potential molecular treatment options targeting the Wnt signaling pathway are systematically presented.
Wnt signaling pathway
Among several intracellular signaling pathways included in the pathophysiology of liver fibrosis, the Wnt signaling pathway claims a growing share.14 During its activation, it shows fibrotic effects, while poor formation of structure as well as low processes of wound healing occur during its inactivation.11 As stated above, based on the involvement of ß-catenin, the Wnt signaling pathway principally encompasses two classes: canonical and non-canonical. The correlation of these two pathways can also be expressed through the possibility that non-canonical Wnt ligands may have a negative effect on the canonical pathway.11
Canonical pathway
The key component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway is its downstream actions15 through ß-catenin, acting as a protein with dual function (as a transcription factor and an adhesion molecule).16 It is important to emphasize that in healthy liver this protein is localized in the membrane of hepatocyte,17 but in injured liver this location changes to the cytoplasm. In the adhesion cell-cell processes, binding of adhesive and transmembrane component (such as E-cadherin to actin; basically adhesive component-protein)18 within the cytoskeleton is enabled when ß-catenin is bound to the plasma membrane; the catenin acts as a bridge between cadherin and actin, as shown in Figure 1. Meanwhile, catenin is the Wnt pathway′s major transducer when localized in the cytoplasm.19 Due to the fact that ß-catenin cannot bind directly to DNA in order to make contact with target genes, it relies on coactivators and various transcription factors.19 Its own transcription factor function is mostly regulated by canonical Wnt proteins (e.g., Wnt1, Wnt3a, Wnt8), which are mainly located in the extracellular space. As extracellular signaling molecules, they bind and initiate signaling processes, leading to ß-catenin′s cascade reaction.20
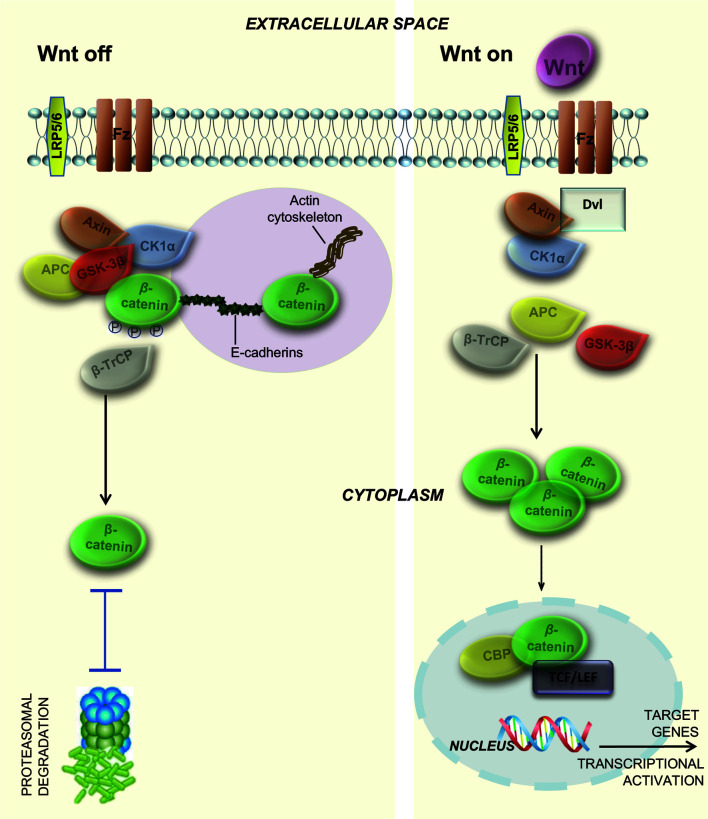
Fig. 1. Activated and inactivated canonical Wnt signaling.
In an inactivated state, β-catenin in the hepatocyte membrane forms a bridge between actin and E-cadherin. When Wnt signaling is off, β-catenin (in a multiprotein complex with GSK-3β, axin, CK1α, β-TrCP and APC) is phosphorylated by GSK-3β and CK1α and ubiquitinated by βTrCP. In the end, β-catenin is degraded by the proteosome. When Wnt signaling is on, Wnt-Fz and LRP coordinate the activation of Dvl, leading to dissociation of the multiprotein complex and resulting in the inactivation of GSK-3β (no phosphorylation anymore). Excessive free β-catenin translocates to the nucleus and binds to TCF/LEF transcription factors, resulting in a transcriptional activation of Wnt target genes. GSK-3ß, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; CK1α, casein kinase 1 alpha; ß-TrCP, beta-transducin repeat containing protein; Wnt-Fz, Wnt-Frizzled transmembrane receptor; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; Dvl, Disheveled gene; TCF/LEF, T cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer binding factor.
When Wnt signaling is off, ß-catenin is located in the cytoplasm in the low regime, where its stability is controlled by a destruction complex21 composed of protein axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), GSK-3β and casein kinase 1 alpha (CK1α).22 ß-catenin is phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK-3β and afterwards ubiquitinated by beta-transducin repeat containing protein (ß-TrCP). Final degradation by the proteasome results in insufficient levels of ß-catenin to activate the transcription process.23 Binding of canonical Wnt proteins to Fz and LRP 5/6 activates the canonical pathway.20 Relocation of Axin to LRP 5/6 due to the Fz/Disheveled (Dvl) complex leads to phosphorylation of LRP 5/6.20 As a result, GSK-3ß is inactivated24 and the destruction complex dissociated, with absence of ß-catenin phosphorylation.25,26 Subsequently, the proportion of unphosphorylated ß-catenin increases, followed by its translocation to the nucleus. Although the mechanism of ß-catenin′s translocation to nucleus is yet unknown, the main action is to become bound to lymphoid enhancer binding factor (LEF)/T cell-specific transcription factor (TCF) in order to initiate targeted genes’ transcription.27 On the molecular level, it requires engagement with either one of the two transcriptional coactivators: cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) or p300.28 Recently, Yu et al.29 demonstrated a suppressive effect on Wnt by acting through the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-associated protein 9 (CRISPR-Cas9) system as an editing system to reduce the effect of LRP 6 gene in mice with alcohol-induced liver injury.
Non-canonical pathway
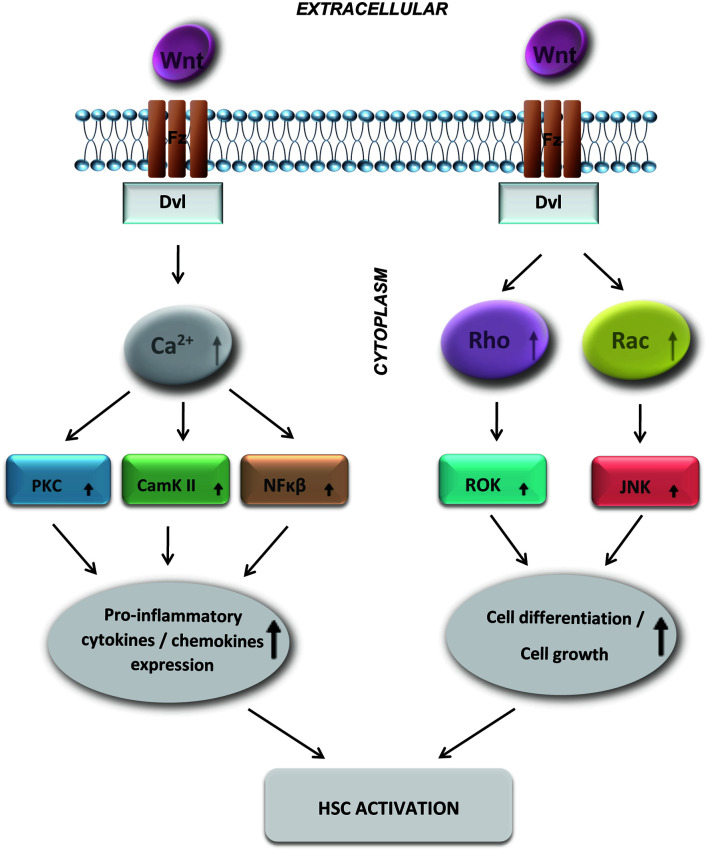
Non-canonical signaling pathways are ß-catenin-independent.20 They encompass non-the canonical Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and PCP pathway,11 as shown on Figure 2. In the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway, binding of a non-canonical Wnt protein (e.g., Wnt5a) results in activation of the cytoplasmic protein Dvl, which increases the concentration of cytoplasmatic Ca2+ and subsequently activates the protein kinase C (PKC) and calcium sensitive enzymes calmodulin kinase II (CamKII).20 It is also important to emphasize its role in increasing the activity of phospholipase C (PLC) and the nuclear factor related to T cells′ activation in transcription.11 Additionally, a study from Sen et al.30 suggested that the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway contributes to transcriptional activation of NF-κβ responsive genes, responsible for various proinflammatory cytokines’ and chemokines’ expression. The second non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway is the PCP; in the literature, it is also commonly referred to as the Wnt/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, being important in cytoskeletal organization.20 The Wnt/PCP ligands (i.e. Wnt5a, Wnt7, and Wnt11) bind to the Fz receptor encompassing Dvl-mediated stimulation of the Rho and Rac (which are small GTPases). Subsequently, activation of a kinase (such as ROK and JNK) is stimulated, which, in the end, are comprehensively involved in cellular proliferation and differentiation (including of HSCs during the process of liver fibrosis).31–33
Fig. 2. The non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways include the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and PCP pathway.
In the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway, activated Dvl increases the concentration of cytoplasmatic Ca2+, leading to activation of the Ca2+-sensitive enzymes CamKII and PKC, and NF-κβ, resulting in transcriptional activation of target genes. In the PCP pathway, Wnt proteins activate Dvl, which activates Rac and Roc and subsequently activates ROK and JNK kinase. Dvl, Disheveled gene; CamKII, calmodulin kinase II protein-1; PKC, protein kinase C; PCP, planar cell polarity; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase.
Liver fibrosis
HSCs
HSCs belong to the group of specialized liver pericytes located in the space of Disse, between endothelial sinusoidal cells and heptocytes.34,35 Their major role relates to molecular mechanisms of transdifferentiation, itself representing a key role in liver fibrosis.36 Numerous investigations have attempted to discover the key role of the Wnt signaling pathway in HSCs and liver fibrosis. Nevertheless, its role in HSC biology still remains to be fully elucidated.37
In the physiological condition, HSCs are in a quiescent state and store retinoids. Also, in the inactive stage, they synthesize glialfibrillaryacidic protein (GFAP), a component of the ECM.38 The matrix itself may be degraded by numerous different enzymes, but the matrix-degrading metalloproteinases (MMPs) have a key role in the degradation process. Due to that, ECM does not accumulate to cause fibrosis. In healthy liver, HSC’s major function is to maintain extracellular homeostasis and accumulation of retinyl esters forms of vitamin A in cytoplasmic lipid droplets.39,40
In conditions of liver damage, their transformation into myofibroblasts occurs as a part of wound healing response. If the injury is prolonged, activated HSCs stimulate the production of ECM components, while reducing their degradation and therefore becoming the major fibrogenic type of liver cell.41 Mechanical or inflammatory processes may cause liver damage and subsequent HSCs’ activation, including Wnt signaling pathway on a molecular level. As a matter of fact, activated HSCs result in increased α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagens type I and II (i.e. the ECM components). Moreover, growth regulation by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and TGF-ß1 are also increased.42 On the other hand, activation of HSCs decreases retinoids and GFAP. The profibrogenic cytokine TGF-β1 affects MMP particularly by down-regulating interstitial collagenase expression, simultaneously up-regulating expression of metallopeptidase inhibitor 1 (TIMP-1), collagen I and gelatinase A.43 Hence, the binding of TIMPs to activated MMPs causes irreversible deposition of ECM, which leads to liver fibrosis.44
For these mechanisms, it has been proposed that if HSC activation and proliferation can be hampered, or the rate of apoptosis enhanced, the progression of liver fibrosis may be inhibited as well.45
Even though HSC cell cultures have shown their potential in observation of fibrogenesis and in the estimation of complex toxicity responses, the deficiency of cultures and reliable sources of HSCs restrict their utilization.46,47 A few published findings show correlation among liver fibrosis and activation of the Wnt signaling pathway in HSCs. Antagonism of the Wnt signaling pathway with an inhibitor of interactions among β-catenin and CREB-binding protein suppresses and reverses HSC activation, resulting in attenuation of liver fibrogenesis.37,48,49 In 2008, Kordes et al.50 demonstrated that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway negatively regulates HSC activation. On the other hand, a larger number of studies have provided evidence to support a positive correlation between activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, fibrosis and the process of HSC activation.49,51,52 However, simultaneously, for non-canonical Wnt signaling, β-catenin (independent) and its components have been observed as contributors of HSC activation and as compounds of fibrotic livers.53,54
Pathophysiological mechanism of fibrosis
Pathophysiology of liver fibrosis involves a complex interplay of many mechanisms, including the intracellular signaling pathways of Wnt/ß-catenin, GAS6/Axl and TGF-ß/Smad,45 and other preserved morphogenic developmental signaling pathways, such as of notch and Hh.55 Repeated liver injuries, massive accumulation of ECM leading to cell stiffening, and the appearance of scar tissue disrupts liver homeostasis.56 In the absence of hepatocyte regeneration, the cells are replaced by ECM and the formation of regenerating nodular hepatocytes.56 The Wnt pathway has been shown to be activated in the process of liver fibrosis involving ß-catenin, Fz receptors and LRP coreceptor upregulation.55 Downregulation or selective inhibition of the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway significantly inhibits activation, differentiation, contractility and migration of HSCs in vitro, also processes of fibrosis, inflammation and angiogenesis are attenuated in vivo.55 Selective inhibition of the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway using ICG-001 inhibits HSCs activation, differentiation, contractility and migration in vitro, as well as collagen deposition and processes of fibrosis, inflammation and angiogenesis in vivo.55 It is known that activation of HSCs also results in the secretion of CXCL12, which stimulates macrophage infiltration of the liver and HSCs’ activation, thus promoting fibrosis, inflammation and angiogenesis.55 When inhibiting the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway, production of CXCL12 and the processes of fibrosis, inflammation and angiogenesis are attenuated in the liver.55
Studies have shown the connection between Wnt5a and TGF.53 When Wnt5a expression was studied in fibrotic livers of mouse and human, upregulation of the Wnt5a gene and protein was found in comparison to that in healthy livers, and the level of Wnt5a was also found to have decreased after therapeutic intervention in mice.53 In vitro studies have shown that expression of Wnt5a and Wnt receptors Fz2 and Fz8 were significantly enhanced by TGF.53 Levels of collagen type I and fibronectin in TGF-stimulated myofibroblasts are increased, along with Wnt, and decreased when Wnt5a is suppressed by antifibrotic cytokine in vitro and in vivo.53 In addition, suppression of Wnt5a in activated LX2 cells decreases production of both collagen type I and TGF-ß.53 A recent study showed that establishment of fibrosis is affected by the induction of EndMT,57 which is crucial for the production of myofibroblasts in fibrous organs and tissues.58–61 Increased TGF-ß expression increases asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and factors of inflammation, while a decrease is expected in nitric oxide secretion and nitric oxide synthase activity, as well as in dimethyl arginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 (DDAH1), Nrf2 and VE-cadherin; all, together are defined as factors for fibrosis improvement through EndMT.57 Levels of Wnt5a in serum follow hepatosteatosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).62 It is supposed that suppression of Wnt5a, as it has proinflammatory effects, can reduce NASH; based on that hypothesis, studies using celecoxib, an inhibitor of cyclooxigenase-2 (COX-2), were performed.63 In a rat model of NASH, the expression of Wnt5a, COX-2, JNK1 and NF-κB p65 were higher, as observed by levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and histologically; however, the administration of celecoxib suppressed their expression and inflammation in liver.63 It was concluded by the authors that it is possible to ameliorate NASH by suppressing the Wnt5a/JNK1 pathway.63 In another study, pharmacologically-increased Wnt3a and ß-catenin, along with suppressed Wnt5a, produced an anti-inflammatory effect in hepatosteatosis, NAFLD, and NASH.20
Hepatic fibrosis used to be considered an irreversible process, taking into account that hepatic parenchyma is destroyed and replaced with fibrotic tissue; however, laboratory and clinical studies have revealed possible reversibility of progressive Wnt signaling pathway-related liver fibrosis.64 Studies performed in vitro and in vivo have also lent support to the hypothesis that ß-catenin protects hepatocytes through the inhibition of apoptosis associated with FoxO3; importantly, such findings can be relevant for future therapeutic interventions in the field of liver injury protection, repair, and regeneration.65 A recent study confirmed that increased EMT due to Dact2 (an antagonist of ß-catenin) deficiency helps to promote healing processes in the liver.66 Dact2 inhibits binding of LEF1 to ß-catenin and promotes degradation of Dvl; by establishing re-expression of Dact2, T-cell factor 4 (its transcriptional activity) and downstream signaling of Wnt are stimulated, which is known to play a role in gene suppression.66
Therapeutic solutions
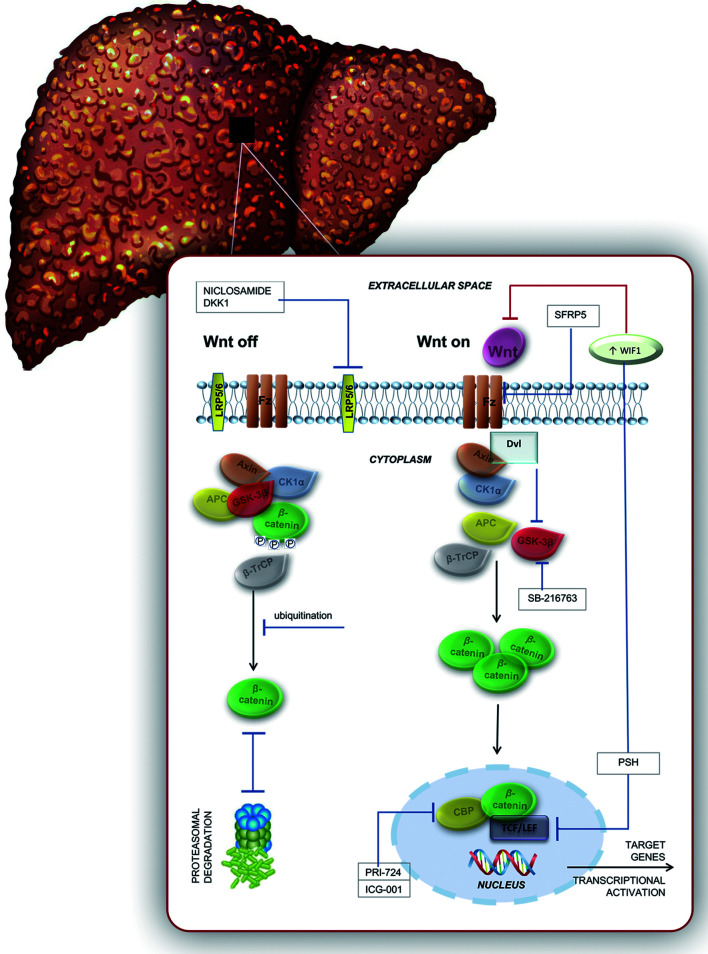
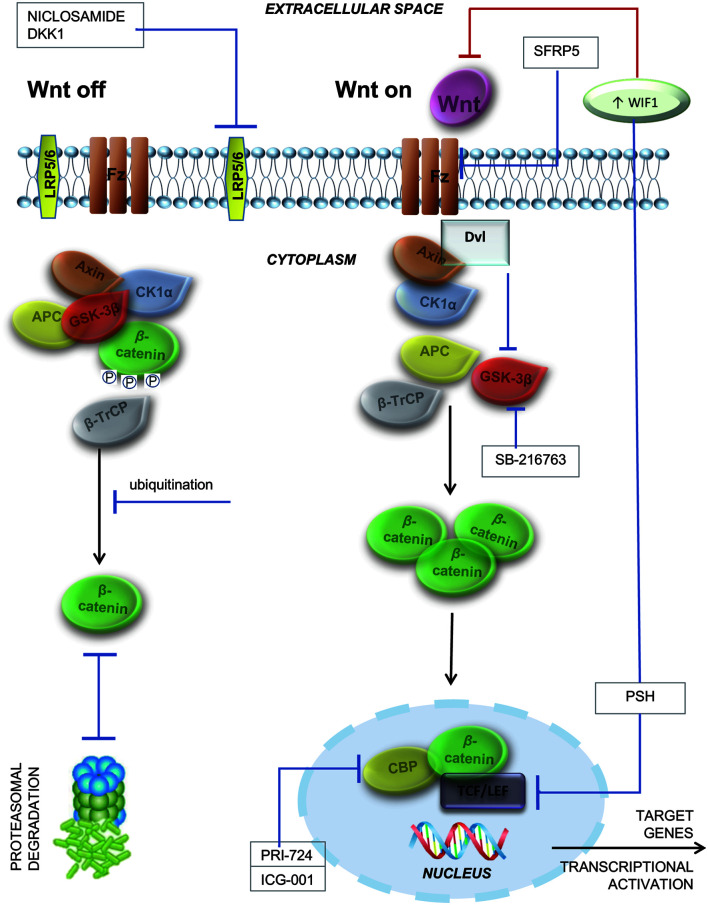
Scientists have been steadily working for years on elucidating the underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for liver fibrosis development and to develop adequate therapeutic strategies (which have to be validated in preclinical and clinical trials).67–72 Alleviation of the Wnt signaling pathway is possible, due to its members Wnt1, Wnt3a and Wnt10b, as well as Fz1 and 5; WIF is influential, in that it joins to either its ligand, sFRP family or antagonist to prevent association between the LRP coreceptor and Fz. Agents that exert inhibitory effects on the Wnt signaling pathway are being considered to have preventive or therapeutic effects in liver fibrosis; these are DKK1, niclosamide, sFRP5, SB-216763, ICG-001, PRI-724 and pinostilbene hydrate (PSH), as shown in Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Activated and inactivated canonical Wnt signaling.
When Wnt signaling is off, β-catenin (in a multiprotein complex with GSK-3β, axin, CK1α, β-TrCP and APC) is phosphorylated by GSK-3β and CK1α and ubiquitinated by β-TrCP. In the end, β-catenin is degraded by the proteosome. When Wnt signaling is on, Dvl inhibits β-catenin phosphorylation by inhibiting GSK-3β activity. The Wnt-Fz-LPR5/6 heterotrimer coordinates Dvl activation, dissociating the multiprotein complex and resulting in the inactivation of GSK-3β (no phosphorylation anymore). Unphosphorylated β-catenin increases, then migrates to the nucleus and links to TCF/LEF and CBP. The TCF/β-catenin complex links DNA and leads to transcription of Wnt target genes. Antifibrotic compounds that inhibit Wnt signaling and prevent liver fibrosis are DKK1, niclosamide, sFRP5, SB-216763, PRI-724, ICG-001, and PSH. GSK-3ß, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; CK1α, casein kinase 1 alpha; ß-TrCP, beta-transducin repeat containing protein; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; ß-TrCP; Dvl , Disheveled gene; Wnt-Fz-LPR 5/6, Wnt-Frizzled transmembrane receptor-low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; TCF/LEF, T cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer binding factor; CBP, cyclic-AMP response element-binding protein; DKK1, dickkopf-related protein 1.
DKK1
DKK1 is among the best-characterized inhibitors of the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway. It prevents binding between Wnt and the LRP5/6 component of the receptor complex,73 resulting in a disruption of Fz-LRP6 dimerization.74 DKK1 was used to prove the role of the Wnt canonical pathway in activation of HSCs as well as their quiescence and renewal of regulation (adipogenesis).75 In activated HSCs, the expression of Wnt3a and 10b (as canonical) and Wnt4 and 5a (as non-canonical) isoforms of Wnt, receptors Fz1 and 2, and LRP6 and Ryk (coreceptors) is induced, as shown by the TCF promoter-luciferase gene becoming activated. However, administration of DKK1 inhibits Wnt signaling and results in both decreasing TCF and increasing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ-trigger activity of the PPAR response element, a crucial transcriptional parameter (adipogenic).75 As demonstrated in earlier studies, PPAR is one of the major transcriptional factors in adipocyte differentiation and for the maintenance of HSC quiescence in vitro; the expression of transcriptional adipogenic factors is substantial according to its activation being associated with forfeiture of transcriptional adipogenic regulation.76 The anti-adipogenic effect of DKK1 on HSCs was shown in vitro by detection of increasing levels of PPARγ mRNA.77 By extending these findings from an animal model of cholestatic liver fibrosis, an antifibrotic effect of DKK1 has been proven.75 DKK1 can abolish epigenetic repression, return PPARγ activity and reduce fibrosis due to its inhibitory effect on Wnt signaling inhibition.42
DKK1 also showed a protective role in developing fibrosis demonstrated as attenuation of fibrosis indexes’ expression and proliferation of cells; both are induced by oxidored-nitro domain-containing protein 1 (NOR1). NOR1 locution is otherwise greater in hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhosis and hepatitis. The study by Xiang et al.76 showed induction of NOR1 locution by TGF-β1 in a dose-dependent manner and that its knockdown remarkably inhibited protein expression of fibrosis indexes, including collagen I and III and α-SMA induced by TGF-ß1. NOR1 over-locution may participate in activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in HSCs, and promote proliferation of cells as well as the locution of fibrosis indexes. Conclusively, NOR1 contributes significantly to liver fibrosis in vitro due to its activation of HSCs and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway; however, these effects may be attenuated by DKK1. Inhibitory effects on ß-catenin, Axin2, Wnt3a, α-SMA and collagen I and III were proven in human HSCs in vitro.76 Direct inhibition of inflammation and fibrogenesis78 could add DKK1 to the list as one of the most potent antifibrotic compounds.
Niclosamide
Antifibrotic effect of the Food and Drug Administration-approved antihelminthic niclosamide was recently confirmed by El Ashmawy et al.56 in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced fibrosis in mice. Niclosamide suppressed expression of TGF-β1 and the Dvl2 genes56,79 and activity of ß-catenin.56,80 Serum levels of ALT, AST, L-hydroxyproline and L-glutaminase activity and total bilirubin were significantly reduced by niclosamide and CCl4 compared to a mouse group treated with CCl4 only.56 Significant reduction of α-SMA expression, which confirmed niclosamide′s inhibitory effect of S100A481 and was responsible for induction of α-SMA,82 was also proven. Niclosamide achieved a weakened effect of autophagy-induced apoptosis,83,84 which can be explained by the fact that apoptosis may be one of the main mechanisms of liver fibrosis resolution, despite its association with exacerbated stages of fibrosis.56 Niclosamide could be established as a future antifibrotic therapeutic solution, since recently reported adverse effects of niclosamide seem to be neglectable. The latest review concluded that several shortcomings, including certain cytotoxicity, limited aqueous solubility and partial absorption from the intestinal tract, could be overcome using nano-based formulations.85 According to 2021 published results of a phase Ib trail regarding prostate cancer treatment, reformulated orally-bioavailable niclosamide was well tolerated, with diarrhea as the most common side effect.86 Only few patients experienced grade 3 adverse effects, including fatigue (n=1), abdominal pain (n=1), anemia (n=1), hypoalbuminemia (n=1), and hyperglycemia (n=1).86
sFRP5
sFRP5 is declared as an adipocytokine with anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects, that plays a regulatory role in metabolic homeostasis. In mouse models, it has been shown that sFRP5 can inhibit effects of Wnt5a/Fz2 on proliferation and migration of HSCs, and therefore ameliorate liver fibrosis.54 Lower level of sFRP in serum is associated with obesity, diabetes, and NASH.54 In studies with sFRP5 knockout mice, development of adipose inflammation and obesity is noted, while overexpression of sFRP5 via adenovirus may result in alleviating adipose inflammation, hepatosteatosis, and obesity.87 Beneficial effects of administration of recombinant sFRP5 has been shown in methionine- and choline-deprived diet-induced NASH,88 including lowered serum transaminases, reduced steatosis (intrahepatic) and inflammation scores, and inhibited activation of Kupffer cells and inflammatory factor expression of adipokines in hepatic tissues (also shown in a different NASH model).87 Intervention with recombinant sFRP5 significantly lowered levels of IL6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1),89 TNFα and IL-1β in hepatic tissue.87 The recombinant sFRP protein has so far been used in vitro and in animal models, in all showing a positive effect on fibrosis. To date, according to our knowledge, there are no literature data about the use of recombinant sFRP in humans or its side effects. However, in a recently published study, serum levels of circulating sFRP were measured in women with breast cancer. A favorable predicted survival was found, while the high levels in breast cancer tissue were found to be associated with a better outcome for patients.90
It is notable that even restored sFRP5 can also inhibit ß-catenin and the Wnt pathway by downregulation of cyclin D1 and c-myc genes.87 The observed significant effects of sFRPs in liver fibrosis could be related to its ability to bind the cysteine domain of proteins in the Wnt pathway, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are yet unknown.91
SB-216763
SB-216763 (3-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione) is a selectable and potent GSK-3ß inhibitor, capable of exerting an effective role in therapy of many diseases and currently under investigation.92 GSK-3ß has a known regulatory role in the inflammatory response and cytokine production, as well as in cellular proliferation. Over the years, GSK-3ß has gained importance among researchers, for its role in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Studies have shown that inhibition of GSK-3ß results in anti-inflammatory cytokine production. Inhibition of GSK-3ß has been studied on pulmonary fibrosis, for which administration of SB-216763 has produced beneficial effects on the inflammatory and profibrotic milieu by inhibiting the production of MCP-1 and TNFα in pulmonary macrophages; significant reduction in bleomycin-induced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells has also been noted. In vivo administration of SB-216763 to mice has been proven as safe for preventing bleomycin-induced respiratory distress syndrome, as there were no toxic effects on heart, liver or kidney, and in improving survival of treated mice. These results positioned GSK-3ß as a potential molecular target in pulmonary fibrosis treatment, and it has been further investigated in diabetes mellitus, bipolar disorder, Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and septic shock.93
It is well known that liver dysfunction can occur in cases of sepsis. Studies suggest that activation of GSK-3ß is involved in apoptosis and excessive inflammation in acute liver failure (ALF). Zhang et al.94 investigated the inhibitory effects of GSK-3ß on polymicrobial sepsis in a liver injury model (induced by cecal ligation and puncture). Inhibition of GSK-3ß in an animal model, by means of SB-216763 administration, resulted in reduction of mortality, amelioration of liver injury and suppression of hepatic apoptosis. On the molecular level, decreases in leukocyte infiltration, expression and release of inflammatory cytokines in the liver were noted. NF-κB transcriptional activity was suppressed, while CREB transcriptional activity was enhaced.94 The authors concluded that inhibition of GSK-3ß reduces inflammatory cytokine production through modulation of the NF-κB and CREB signaling pathways in macrophages simulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).94 As the studies have shown, GSK-3β was activated during ALF progression, and its inhibition mitigated inflammation of the liver and ameliorated ALF in the mouse model. In the study by Ren et al.,95 the co-injection of D-galactosamine and LPS was used to induce ALF. Inhibition of GSK-3β by administration of SB-216763 resulted in increased autophagy and decreased liver inflammation. GSK-3β inhibition by SB-216763 protected against aldosterone-induced renal and cardiac injuries by activating autophagy.96 However, for cholestatic liver disease in a mouse model, a study by Zhuang et al.97 demonstrated that SB-216763 therapy aggravated liver fibrosis.
ICG-001
ICG-001 is characterized as a selective first-generation CBP inhibitor, capable of disrupting β-catenin’s interaction with CBP and thereby reducing the mRNA and protein expression of survivin significantly; survivin is one of the inhibitors of cyclin D1 and apoptosis.28 This therapeutic solution was primarily designed for targeting colon carcinoma cells, in order to induce apoptosis; although, in physiologically normal (epithelial) colon cells, the effect was not noticed.28 There are reports on the beneficial and inhibitory effects of ICG-001 in fibrosis; meanwhile, another report indicated that mRNA levels of collagen I, Wnt3a, αSMA, LRP6 and Wnt10 stimulated with TGF-β in mouse fibroblasts and human HSCs were inhibited with this CBP inhibitor.28 Attenuation of lung fibrosis (as induced by bleomycin) in mice was observed with ICG-001 treatment, as was prevention of fibrosis when simultaneously administering bleomycin and ICG-001, which subsequently reversed the pathogenic effect at later stages of the disease and positively impacted survival rate.28 A similar outcome was achieved with renal fibrosis in mice, through suppressive effects on collagens I and III, α-SMA, fibronectin plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, Snail 1 and 2 and fibroblast-specific protein-1; this benefit also occurred with treatment applied in the late stage of fibrosis.28 Akcora et al.55 reported an inhibitory effect of ICG-001 on deposition of collagen and HSC activation, contraction and migration in in vitro models, and also attenuation of angiogenesis, fibrogenesis and inflammation in in vivo models. ICG-001 can be an inhibitor of PDGFßR, α-SMA, vimentin and collagen I; these effects were suggested by downregulated expression of the corresponding genes in in vitro models of TGF-ß-induced LX2 cells (HSCs).55 Furthermore, due to HSC migration during fibrogenesis and differentiation into myofibroblasts (contractile), scientists discovered an inhibitory effect with exactly 5 µM of ICG-001 in 24 h (then 48 h and maximum inhibition in 72 h).55 The almarBlue cell viability assay (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to confirm the absence of a relationship between migration of cells and proliferation differences.55 Confirmatory investigations of the findings from the previous study on LX2 cells (all parameters included, except vimentin) resulted in the same outcome on primary human HSCs, and ICG-001 was shown to inhibit expression of periostin.55 ICG-001-related downregulation of Axin-2 and ß-catenin was also noted in a mouse liver injury model induced by CCl4.55 The beneficial effects on fibrosis by ICG-001 were enhanced when it was used as a prototype in the development of PRI-724,98 a novel promising and effective therapeutic solution for liver fibrosis.28
PRI-724
PRI-724 is selective CBP second-generation inhibitor and influences ß-catenin interaction. It acts through HSC inhibition and disruption of the macrophage-inflammation system, exerting antifibrotic effects that have been confirmed in murine models of fibrosis.49 In a murine model of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, administration of PRI-724 showed accelerating effects on the resolution of fibrosis in liver followed by an increasing effect on MMPs in intrahepatic leukocytes. It is significant that this inhibitor reduced CCL4-induced liver fibrosis in mice without affecting levels of serum ALT and proved incoherence with reparation of hepatic fibrosis.49 Effects of C-82, an active PRI-724 metabolite, was demonstrated through a mRNA-mediated suppression of α-SMA, TIMP-1 and collagen I, as well as down-regulation of proteins such as Ki67, α-SMA and cyclin D.28 Gene expressions in activated HSCs were abrogated by PRI-724 and ECM production was inhibited, which led to antifibrotic effects.28 HCV transgenic mice are another model system used to determine effects of PRI-724 on liver fibrosis, collagen production, and levels of α-SMA.99 A study using this model showed attenuation of the previous increased collagen.99 Levels of α-SMA, reflecting HSC activation, were reported to be higher in the transgenic mice in comparison with controls and the administration of PRI-724 attenuated this effect.99 Another study showed decreased levels of TIMP-1 and elevated levels of MMP-8 as another line of evidence supporting PRI-724′s antifibrotic effect.99
A NASH mouse model was used to investigate the antifibrotic effects of PRI-724; the administration of PRI-724 inhibited hepatocyte apoptosis and hepatic fibrosis.28 PRI-724 was also used in clinical trials that included advanced stages of myeloid malignancies, pancreatic cancer and solid tumors, and according to the available literature there has been a phase I clinical trial (single-center, open-label) on the tolerance and safety of PRI-724 in HCV cirrhosis patients, in which it showed good tolerability.28 Reduction of hepatic lobule fibrosis by PRI-724 improved liver histology (in a dose-dependent manner) as well as Child-Pugh scores (in some individuals).28 In a pre-clinical study of PRI-724 administration to dogs for 28 days at the dosage of 120 mg/kg/day showed that this therapeutic solution did not yield any adverse effect; in addition, when given to 18 participants with solid tumors (dose range: 40–1,280 mg/m2/day, hyperbilirubinemia (reversed) was recorded as an event not directly correlated.100 Overall, PRI-724 has been very well tolerated, and no fatalities have been reported. Taking into account a small sample of patients (n=14 in total) in one study,98 the following side effects were noted: fatigue (n=3) and nausea (n=4), vomiting (n=2), constipation (n=2), and reaction at the injection site (n=4).98 Other less common side effects included pruritus, rash, headache, fever, vertigo, insomnia, and bleeding; the related biochemical results showed the most common to be elevations in total bilirubin and thrombocytopenia.98 Two other serious adverse events not directly related to the study were reported, namely bacillemia due to injection site infection and hemorrhage due to liver biopsy.98 However, a phase Ia/Ib clinical trial (NCT01302405) was discontinued due to low patient response. Currently, PRI-714 (new drug name: OP-724) is in a phase I clinical trial (NCT04688034) for patients with liver cirrhosis caused by human immunodeficiency virus/HCV co-infection with hemophilia.
Of note, the previous clinical studies investigating PRI-724 have included a small number of patients. As such, further and more detailed studies with larger samples are needed to gain a clearer understanding of its safety and efficacy. We hope that one of the aforementioned clinical trials will yield significant results.
PSH
PSH, a methylated derivative of resveratrol, has been previously evidenced to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic effects, and has been observed to act on reducing HSC activity. The inhibitory effect was achieved by suppressing the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway via miR-17-5p (acting as an oncogene)101 and also that it could enhance WIF1 expression. Since activation of HSCs is at the core of liver fibrosis development, it is rational to develop a therapeutic strategy that would block or limit their activation.102 MicroRNAs, as a group of non-coding RNA molecules, can significantly affect the course of liver fibrosis development, as they regulate the action of HSCs.102 A study by Yu et al.103 showed how resveratrol can reduce the progression of liver fibrosis, while one by Chao et al.104 demonstrated that the PSH, as a methylated form of resveratrol, is more stable than other forms. As previously mentioned, the imbalance between ECM synthesis and its degradation is at the core of the liver fibrosis process.102 The presence of myofibroblasts derived from HSCs form the basis for the production of ECM that contributes to the development of liver fibrosis.102 PSH’s beneficial effects involve reducing cell proliferation, collagen production and α-SMA expression, and partially inhibiting HSC activation.102 The inability of ß-catenin translocation into the nucleus and reduction of TCF activity is due to PSH along with an increased amount of APC, phosphorylated-ß-catenin, GSK-3β and WIF1 (acting as Wnt antagonist) that inhibit the Wnt ß-catenin-dependent pathway.102 This therapeutic solution needs to be further investigated in correlation in situations of liver fibrosis development and treatment; however, the potential adverse effects of resveratrol may limit its usage.
At a dose of 100 µM, resveratrol reduces the regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and inhibits the formation of major blood vessels in zebrafish; in this model, it also reduces survival and hatching rate of eggs, and causes teratogenic deformities and cardiac edema.105 Administration of resveratrol to rats at doses of 300/1,000/3,000 mg/kg/day led to hepatic impairment (confirmed by aberrant liver gene expression);106 at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg/day, it increased bilirubin levels.107 A dose of 1,000–3,000 mg/kg/day, administered for 4 weeks, induced renal toxicity.108 Guha et al.109 showed that resveratrol can delay the healing of gastric ulcers in mice. At very high doses, resveratrol has been shown to cause severe adverse effects. Lethal outcome has been reported in rats, due to acute inflammation of the pelvic region, renal tubular dilatation, papillary necrosis, severe nephropathy, and cardiac inflammation.110 In addition, increased levels of liver enzymes as well as of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine can be a significant problem.108
It is important to emphasize that resveratrol can act as a substrate for tyrosinase (an enzyme essential for the production of melanin) for the production of toxic o-quinones,111,112 which cause cytotoxicity of melanocytes (thiol protein production) and may have an adverse effect on the skin.110 The adverse effect on the skin can be explained by the fact that resveratrol is very similar to rhododendrol, which is used for whitening and lightening in cosmetics and is basically also a tyrosinase inhibitor that can increase the incidence of leukoderma skin toxicity, so a similar effect of resveratrol on the skin can be assumed.110 Resveratrol is known to exert pleotropic effects on humans,113 and so far adverse effects involving nephrotoxicity and gastrointestinal problems have been reported.114,115 Although there is little information on human clinical trials (several are awaiting publication), it is known that resveratrol can cause an increase in plasma ALT and decreases in white blood cell count and plasma IL-6 and TNF.116,117 Resveratrol at a dose of 1,000 mg/day or higher can cause significant interactions with other drugs because it activates the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP1A2 and inactivates CYP3A4, CYP2C9 and CYP2D6;104 at the same dose, an increase in markers of cardiovascular disease has been observed.118 Administration of resveratrol in high doses (2,000–5,000 mg/day) may cause nausea, hypersensitivity, anal pruritus, and episodes of diarrhea (light and mild),119 which is a more important consideration for sick persons than for healthy ones.118 The aforementioned has been confirmed by a phase II clinical trial in humans with refractory multiple myeloma, in who 5,000 mg of resveratrol was administered; one patient had lethal outcome, probably due to the adverse effects (renal toxicity, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea).120
The agents discussed above have evidenced potential therapeutic effects in liver fibrosis, acting through numerous molecular mechanisms and signaling cascades, including inflammation and fibrogenesis.
Conclusions
Liver fibrosis is a significant global health problem and economic burden, with potential to progress to liver cirrhosis and cancer. Its worldwide mortality is 1.5 million deaths per year. Regardless of etiology, the pathophysiology of fibrosis includes chronic inflammation, hepatocyte death, HSC activation, and endothelial or epithelial barrier disruption, all mediated by various proinflammatory cytokines and other chemokines, and including several signaling pathways, such as those of Wnt, notch and Hh. The Wnt signaling pathway is activated in the process of ongoing liver fibrosis. It acts through canonical and non-canonical pathways. Several agents that have shown inhibitory effects on Wnt signaling are being considered to impart preventive or therapeutic effects on liver fibrosis. These are DKK1, niclosamide, sFRP5, SB-216763, ICG-001, PRI-724 and PSH. Their validation and utility with regards to potential adverse effects has yet to be proven, but the future remains promising. In this review, the current lore about the Wnt signaling pathway, which notably participates in liver fibrosis development, was gathered and summarized. Considering the critical points of the Wnt signaling pathway in liver fibrosis, the findings on potential therapeutic targets in liver fibrosis and agents that are being considered for preventive or therapeutic effects in liver fibrosis were presented.
Abbreviations
- α-SM
alpha-smooth muscle actin
- ADMA
asymmetric dimethylarginine
- ALF
acute liver failure
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- APC
adenomatous polyposis coli
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- ß-TrCP
beta-transducin repeat containing protein
- CamKII
calmodulin kinase II
- CBP
cyclic-AMP response element-binding protein
- CCl4
carbon tetrachloride
- CK1α
casein kinase 1 alpha
- COX-2
cyclooxygenase-2
- CREB
cAMP-response element-binding protein
- CRISPR-Cas9
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-associated protein 9
- CYP
cytochrome P450
- DDAH1
dimethyl arginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1
- DKK1
dickkopf-related protein 1
- Dvl
Disheveled gene
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- EMT
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- Fz
Frizzled transmembrane receptor
- GFAP
glialfibrillaryacidic protein
- GSK-3ß
glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- HBV
hepatitis B virus
- HCV
hepatitis C virus
- Hh
hedgehog
- HSC
hepatic stellate cell
- JNK
Jun N-terminal kinase
- LEF
lymphoid enhancer binding factor
- LPS
lipopolysaccharide
- LRP 5/6
low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6
- MCP-1
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MMPs
matrix-degrading metalloproteinases
- NAFLD
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- NOR1
oxidored-nitro domain-containing protein 1
- PCP
planar cell polarity
- PDGF
platelet-derived growth factor
- PKC
protein kinase C
- PLC
phospholipase C
- PPAR
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- PSH
pinostilbene hydrate
- sFRP
secreted frizzled-related protein family
- TCF
T cell-specific transcription factor
- TGF-ß
transforming growth factor-beta
- TIMP-1
metallopeptidase inhibitor 1
- WIF1
Wnt inhibitory factor 1
References
- 1.Poynard T, Lebray P, Ingiliz P, Varaut A, Varsat B, Ngo Y, et al. Prevalence of liver fibrosis and risk factors in a general population using non-invasive biomarkers (FibroTest) BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berumen J, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T, Mekeel K. Liver fibrosis: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2021;13(1):e1499. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(2):209–218. doi: 10.1172/JCI24282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dhar D, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2020;245(2):96–108. doi: 10.1177/1535370219898141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dooley S, ten Dijke P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347(1):245–256. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1246-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tsukamoto H, Zhu NL, Wang J, Asahina K, Machida K. Morphogens and hepatic stellate cell fate regulation in chronic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(Suppl 2):94–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ng LF, Kaur P, Bunnag N, Suresh J, Sung ICH, Tan QH, et al. WNT signaling in disease. Cells. 2019;8(8):826. doi: 10.3390/cells8080826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gruber J, Yee Z, Tolwinski NS. Developmental drift and the role of Wnt signaling in aging. Cancers (Basel) 2016;8(8):73. doi: 10.3390/cancers8080073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Eisenmann DM. WormBook. 2005. Wnt signaling; pp. 1–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kaur P, Jin HJ, Lusk JB, Tolwinski NS. Modeling the role of Wnt signaling in human and drosophila stem cells. Genes (Basel) 2018;9(2):101. doi: 10.3390/genes9020101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hu HH, Cao G, Wu XQ, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY. Wnt signaling pathway in aging-related tissue fibrosis and therapies. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;60:101063. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Herrera J, Henke CA, Bitterman PB. Extracellular matrix as a driver of progressive fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(1):45–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI93557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Monga SP. β-Catenin signaling and roles in liver homeostasis, injury, and tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(7):1294–1310. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rajasekaran MR, Kanoo S, Fu J, Nguyen ML, Bhargava V, Mittal RK. Age-related external anal sphincter muscle dysfunction and fibrosis: possible role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;313(6):G581–G588. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00209.2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pradhan-Sundd T, Kosar K, Saggi H, Zhang R, Vats R, Cornuet P, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays a protective role in the Mdr2 knockout murine model of cholestatic liver disease. Hepatology. 2020;71(5):1732–1749. doi: 10.1002/hep.30927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xu W, Kimelman D. Mechanistic insights from structural studies of beta-catenin and its binding partners. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 19):3337–3344. doi: 10.1242/jcs.013771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang F, Wang F, He J, Lian N, Wang Z, Shao J, et al. Reregulation of hepatic stellate cell contraction and cirrhotic portal hypertension by Wnt/β-catenin signaling via interaction with Gli1. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(11):2246–2265. doi: 10.1111/bph.15289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Niessen CM, Gottardi CJ. Molecular components of the adherens junction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778(3):562–571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.12.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Perugorria MJ, Olaizola P, Labiano I, Esparza-Baquer A, Marzioni M, Marin JJG, et al. Wnt-β-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16(2):121–136. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang JN, Li L, Li LY, Yan Q, Li J, Xu T. Emerging role and therapeutic implication of Wnt signaling pathways in liver fibrosis. Gene. 2018;674:57–69. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yang K, Wang X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Nan G, Li Y, et al. The evolving roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis: implications in targeted cancer therapies. Lab Invest. 2016;96(2):116–136. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stamos JL, Weis WI. The β-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(1):a007898. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kühl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, et al. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382(6592):638–642. doi: 10.1038/382638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, Spokony R, Liu C, Katsuyama Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature. 2000;407(6803):530–535. doi: 10.1038/35035117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17(1):9–26. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wei J, Melichian D, Komura K, Hinchcliff M, Lam AP, Lafyatis R, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling induces skin fibrosis and subcutaneous lipoatrophy: a novel mouse model for scleroderma? Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(6):1707–1717. doi: 10.1002/art.30312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nejak-Bowen KN, Monga SP. Beta-catenin signaling, liver regeneration and hepatocellular cancer: sorting the good from the bad. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011;21(1):44–58. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nishikawa K, Osawa Y, Kimura K. Wnt/β-catenin signaling as a potential target for the treatment of liver cirrhosis using antifibrotic drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):3103. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yu L, Wang L, Yi H, Wu X. Beneficial effects of LRP6-CRISPR on prevention of alcohol-related liver injury surpassed fecal microbiota transplant in a rat model. Gut Microbes. 2020;11(4):1015–1029. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1736457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sen M. Wnt signalling in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005;44(6):708–713. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Beier F, Loeser RF. Biology and pathology of Rho GTPase, PI-3 kinase-Akt, and MAP kinase signaling pathways in chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110(3):573–580. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang L, et al. Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2326–2335. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Woods A, Wang G, Beier F. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by the actin cytoskeleton and adhesive interactions. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Seo W, Jeong WI. Hepatic non-parenchymal cells: Master regulators of alcoholic liver disease? World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(4):1348–1356. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kostallari E, Shah VH. Pericytes in the liver. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1122:153–167. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11093-2_9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Duong TE, Hagood JS. Epigenetic regulation of myofibroblast phenotypes in fibrosis. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2018;6(1):79–96. doi: 10.1007/s40139-018-0155-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang R, Kikuchi AT, Nakao T, Russell JO, Preziosi ME, Poddar M, et al. Elimination of Wnt secretion from stellate cells is dispensable for zonation and development of liver fibrosis following hepatobiliary injury. Gene Expr. 2019;19(2):121–136. doi: 10.3727/105221618X15373858350141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Carmona R, Barrena S, Muñoz-Chápuli R. Retinoids in stellate cells: development, repair, and regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2019;7(2):10. doi: 10.3390/jdb7020010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bonnans C, Chou J, Werb Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):786–801. doi: 10.1038/nrm3904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Khomich O, Ivanov AV, Bartosch B. Metabolic hallmarks of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Cells. 2019;9(1):24. doi: 10.3390/cells9010024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee UE, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;25(2):195–206. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2011.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Higashi T, Friedman SL, Hoshida Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;121:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Elpek G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: an update. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(23):7260–7276. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Robert S, Gicquel T, Victoni T, Valença S, Barreto E, Bailly-Maître B, et al. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inflammasome pathway in molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(4):e00360. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang CY, Yuan WG, He P, Lei JH, Wang CX. Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(48):10512–10522. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Coll M, Perea L, Boon R, Leite SB, Vallverdú J, Mannaerts I, et al. Generation of hepatic stellate cells from human pluripotent stem cells enables in vitro modeling of liver fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23(1):101–113.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Leite SB, Roosens T, El Taghdouini A, Mannaerts I, Smout AJ, Najimi M, et al. Novel human hepatic organoid model enables testing of drug-induced liver fibrosis in vitro. Biomaterials. 2016;78:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li W, Zhu C, Li Y, Wu Q, Gao R. Mest attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Gut Liver. 2014;8(3):282–291. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2014.8.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Osawa Y, Oboki K, Imamura J, Kojika E, Hayashi Y, Hishima T, et al. Inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP)/β-catenin reduces liver fibrosis in mice. EBioMedicine. 2015;2(11):1751–1758. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.10.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kordes C, Sawitza I, Häussinger D. Canonical Wnt signaling maintains the quiescent stage of hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yin X, Yi H, Wang L, Wu W, Wu X, Yu L. RSPOs facilitated HSC activation and promoted hepatic fibrogenesis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(39):63767–63778. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yin X, Yi H, Wu W, Shu J, Wu X, Yu L. R-spondin2 activates hepatic stellate cells and promotes liver fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59(10):2452–2461. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Beljaars L, Daliri S, Dijkhuizen C, Poelstra K, Gosens R. WNT-5A regulates TGF-β-related activities in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;312(3):G219–G227. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00160.2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chatani N, Kamada Y, Kizu T, Ogura S, Furuta K, Egawa M, et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 (Sfrp5) decreases hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. Liver Int. 2015;35(8):2017–2026. doi: 10.1111/liv.12757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Akcora B, Storm G, Bansal R. Inhibition of canonical WNT signaling pathway by β-catenin/CBP inhibitor ICG-001 ameliorates liver fibrosis in vivo through suppression of stromal CXCL12. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(3):804–818. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.El-Ashmawy NE, Al-Ashmawy GM, Fakher HE, Khedr NF. The role of WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway and glutamine metabolism in the pathogenesis of CCl. Cytokine. 2020;136:155250. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K, Zarrin V, Moghadam ER, Hashemi F, et al. Toward regulatory effects of curcumin on transforming growth factor-beta across different diseases: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:585413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13(8):952–961. doi: 10.1038/nm1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H, Zeisberg M, Kalluri R. Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(12):2282–2287. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008050513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Li J, Qu X, Bertram JF. Endothelial-myofibroblast transition contributes to the early development of diabetic renal interstitial fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Am J Pathol. 2009;175(4):1380–1388. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Potenta S, Zeisberg E, Kalluri R. The role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(9):1375–1379. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Du J, Ren W, Zhang Q, Fu N, Han F, Cui P, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 suppresses Wnt signaling pathway in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related liver fibrosis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:4910601. doi: 10.1155/2020/4910601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tian F, Zhang YJ, Li Y, Xie Y. Celecoxib ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in type 2 diabetic rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway expression. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e83819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gutiérrez-Ruiz MC, Gómez-Quiroz LE. Liver fibrosis: searching for cell model answers. Liver Int. 2007;27(4):434–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Tao GZ, Lehwald N, Jang KY, Baek J, Xu B, Omary MB, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling protects mouse liver against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the inhibition of forkhead transcription factor FoxO3. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(24):17214–17224. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim DH, Kim EJ, Park SW. Dact2 is involved in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524(1):190–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Friedman SL, Sheppard D, Duffield JS, Violette S. Therapy for fibrotic diseases: nearing the starting line. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(167):167sr1. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Schuppan D, Kim YO. Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(5):1887–1901. doi: 10.1172/JCI66028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Torok NJ, Dranoff JA, Schuppan D, Friedman SL. Strategies and endpoints of antifibrotic drug trials: Summary and recommendations from the AASLD Emerging Trends Conference, Chicago, June 2014. Hepatology. 2015;62(2):627–634. doi: 10.1002/hep.27720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Mehal WZ, Schuppan D. Antifibrotic therapies in the liver. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35(2):184–198. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1550055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J Hepatol. 2015;62(1 Suppl):S15–S24. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Schuppan D, Surabattula R, Wang XY. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J Hepatol. 2018;68(2):238–250. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2002;417(6889):664–667. doi: 10.1038/nature756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Liang L, He H, Lv R, Zhang M, Huang H, An Z, et al. Preliminary mechanism on the methylation modification of Dkk-1 and Dkk-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(2):1245–1250. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2750-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cheng JH, She H, Han YP, Wang J, Xiong S, Asahina K, et al. Wnt antagonism inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294(1):G39–49. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00263.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Xiang T, Zhang S, Cheng N, Ge S, Wen J, Xiao J, et al. Oxidored-nitro domain-containing protein 1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):5050–5054. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.She H, Xiong S, Hazra S, Tsukamoto H. Adipogenic transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(6):4959–4967. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410078200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kawakami T, Ren S, Duffield JS. Wnt signalling in kidney diseases: dual roles in renal injury and repair. J Pathol. 2013;229(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/path.4121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Osada T, Chen M, Yang XY, Spasojevic I, Vandeusen JB, Hsu D, et al. Antihelminth compound niclosamide downregulates Wnt signaling and elicits antitumor responses in tumors with activating APC mutations. Cancer Res. 2011;71(12):4172–4182. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Gangrade A, Katre AA, Kurpad C, Li Y, et al. Niclosamide and its analogs are potent inhibitors of Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR and STAT3 signaling in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(52):86803–86815. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Burock S, Daum S, Keilholz U, Neumann K, Walther W, Stein U. Phase II trial to investigate the safety and efficacy of orally applied niclosamide in patients with metachronous or sychronous metastases of a colorectal cancer progressing after therapy: the NIKOLO trial. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4197-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Zhang W, Ohno S, Steer B, Klee S, Staab-Weijnitz CA, Wagner D, et al. S100a4 is secreted by alternatively activated alveolar macrophages and promotes activation of lung fibroblasts in pulmonary fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1216. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wang C, Zhou X, Xu H, Shi X, Zhao J, Yang M, et al. Niclosamide inhibits cell growth and enhances drug sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2018;9(22):4150–4155. doi: 10.7150/jca.26948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zhang LX, Zhao HJ, Sun DL, Gao SL, Zhang HM, Ding XG. Niclosamide attenuates inflammatory cytokines via the autophagy pathway leading to improved outcomes in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(2):1810–1816. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Xu J, Shi PY, Li H, Zhou J. Broad spectrum antiviral agent niclosamide and its therapeutic potential. ACS Infect Dis. 2020;6(5):909–915. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Parikh M, Liu C, Wu CY, Evans CP, Dall’Era M, Robles D, et al. Phase Ib trial of reformulated niclosamide with abiraterone/prednisone in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):6377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85969-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Chen L, Zhao X, Liang G, Sun J, Lin Z, Hu R, et al. Recombinant SFRP5 protein significantly alleviated intrahepatic inflammation of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2017;14:56. doi: 10.1186/s12986-017-0208-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Bruno S, Pasquino C, Herrera Sanchez MB, Tapparo M, Figliolini F, Grange C, et al. HLSC-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate liver fibrosis and inflammation in a murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol Ther. 2020;28(2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.10.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Baeck C, Wehr A, Karlmark KR, Heymann F, Vucur M, Gassler N, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut. 2012;61(3):416–426. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Zhou W, Ye C, Li L, Liu L, Wang F, Yu L, et al. Adipocyte-derived SFRP5 inhibits breast cancer cells migration and invasion through Wnt and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathways. Chin J Cancer Res. 2020;32(3):347–360. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.03.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bovolenta P, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Cisneros E, Lopez-Rios J. Beyond Wnt inhibition: new functions of secreted Frizzled-related proteins in development and disease. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 6):737–746. doi: 10.1242/jcs.026096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Phukan S, Babu VS, Kannoji A, Hariharan R, Balaji VN. GSK3beta: role in therapeutic landscape and development of modulators. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160(1):1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gurrieri C, Piazza F, Gnoato M, Montini B, Biasutto L, Gattazzo C, et al. 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione (SB216763), a glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor, displays therapeutic properties in a mouse model of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;332(3):785–794. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.153049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Zhang H, Wang W, Fang H, Yang Y, Li X, He J, et al. GSK-3β inhibition attenuates CLP-induced liver injury by reducing inflammation and hepatic cell apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:629507. doi: 10.1155/2014/629507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ren F, Zhang L, Zhang X, Shi H, Wen T, Bai L, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes autophagy to protect mice from acute liver failure mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2151. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Zhang YD, Ding XJ, Dai HY, Peng WS, Guo NF, Zhang Y, et al. SB-216763, a GSK-3β inhibitor, protects against aldosterone-induced cardiac, and renal injury by activating autophagy. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(7):5934–5943. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Zhuang S, Hua X, He K, Zhou T, Zhang J, Wu H, et al. Inhibition of GSK-3β induces AP-1-mediated osteopontin expression to promote cholestatic liver fibrosis. FASEB J. 2018;32(8):4494–4503. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701137R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kimura K, Ikoma A, Shibakawa M, Shimoda S, Harada K, Saio M, et al. Safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of the anti-fibrotic small molecule PRI-724, a CBP/β-catenin inhibitor, in patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis: a single-center, open-label, dose escalation phase 1 trial. EBioMedicine. 2017;23:79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Tokunaga Y, Osawa Y, Ohtsuki T, Hayashi Y, Yamaji K, Yamane D, et al. Selective inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin/CBP signaling ameliorates hepatitis C virus-induced liver fibrosis in mouse model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):325. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00282-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Lenz HJ, Kahn M. Safely targeting cancer stem cells via selective catenin coactivator antagonism. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(9):1087–1092. doi: 10.1111/cas.12471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Zhu Y, Gu J, Li Y, Peng C, Shi M, Wang X, et al. MiR-17-5p enhances pancreatic cancer proliferation by altering cell cycle profiles via disruption of RBL2/E2F4-repressing complexes. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Zhou G, Li C, Zhan Y, Zhang R, Lv B, Geng W, et al. Pinostilbene hydrate suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of miR-17-5p-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Phytomedicine. 2020;79:153321. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Yu B, Qin SY, Hu BL, Qin QY, Jiang HX, Luo W. Resveratrol improves CCL4-induced liver fibrosis in mouse by upregulating endogenous IL-10 to reprogramme macrophages phenotype from M(LPS) to M(IL-4) Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109110. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chao J, Li H, Cheng KW, Yu MS, Chang RC, Wang M. Protective effects of pinostilbene, a resveratrol methylated derivative, against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2010;21(6):482–489. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Nathan JR, Antony B, Ragunathan M. Resveratrol suppresses angiogenesis by down-regulating Vegf/Vegfr2 in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2014;6(12):892–899. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hebbar V, Shen G, Hu R, Kim BR, Chen C, Korytko PJ, et al. Toxicogenomics of resveratrol in rat liver. Life Sci. 2005;76(20):2299–2314. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.10.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Johnson WD, Morrissey RL, Usborne AL, Kapetanovic I, Crowell JA, Muzzio M, et al. Subchronic oral toxicity and cardiovascular safety pharmacology studies of resveratrol, a naturally occurring polyphenol with cancer preventive activity. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011;49(12):3319–3327. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.08.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Crowell JA, Korytko PJ, Morrissey RL, Booth TD, Levine BS. Resveratrol-associated renal toxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2004;82(2):614–619. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Guha P, Dey A, Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay SK. Pro-ulcer effects of resveratrol in mice with indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers are reversed by L-arginine. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(3):726–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Shaito A, Posadino AM, Younes N, Hasan H, Halabi S, Alhababi D, et al. Potential adverse effects of resveratrol: a literature review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2084. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Ito S, Fujiki Y, Matsui N, Ojika M, Wakamatsu K. Tyrosinase-catalyzed oxidation of resveratrol produces a highly reactive ortho-quinone: implications for melanocyte toxicity. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2019;32(6):766–776. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, Kwon SH, Park KC. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):956. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ramírez-Garza SL, Laveriano-Santos EP, Marhuenda-Muñoz M, Storniolo CE, Tresserra-Rimbau A, Vallverdú-Queralt A, et al. Health effects of resveratrol: results from human intervention trials. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1892. doi: 10.3390/nu10121892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Howells LM, Berry DP, Elliott PJ, Jacobson EW, Hoffmann E, Hegarty B, et al. Phase I randomized, double-blind pilot study of micronized resveratrol (SRT501) in patients with hepatic metastases—safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2011;4(9):1419–1425. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Poulsen MM, Vestergaard PF, Clasen BF, Radko Y, Christensen LP, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, et al. High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men: an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1186–1195. doi: 10.2337/db12-0975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Atmaca N, Yıldırım E, Güner B, Kabakçı R, Bilmen FS. Effect of resveratrol on hematological and biochemical alterations in rats exposed to fluoride. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:698628. doi: 10.1155/2014/698628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Wang Y, Cui H, Niu F, Liu SL, Li Y, Zhang LM, et al. Effect of resveratrol on blood rheological properties in LPS-challenged rats. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1202. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Mankowski RT, You L, Buford TW, Leeuwenburgh C, Manini TM, Schneider S, et al. Higher dose of resveratrol elevated cardiovascular disease risk biomarker levels in overweight older adults - a pilot study. Exp Gerontol. 2020;131:110821. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.110821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Muñoz, O MR, Bustamante S. Pharmacological properties of resveratrol. a pre-clinical and clinical review. Biochem Pharmacol (Los Angel) 2015;4(5):1000184. doi: 10.4173/2167-0501.1000184. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Popat R, Plesner T, Davies F, Cook G, Cook M, Elliott P, et al. A phase 2 study of SRT501 (resveratrol) with bortezomib for patients with relapsed and or refractory multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2013;160(5):714–717. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]