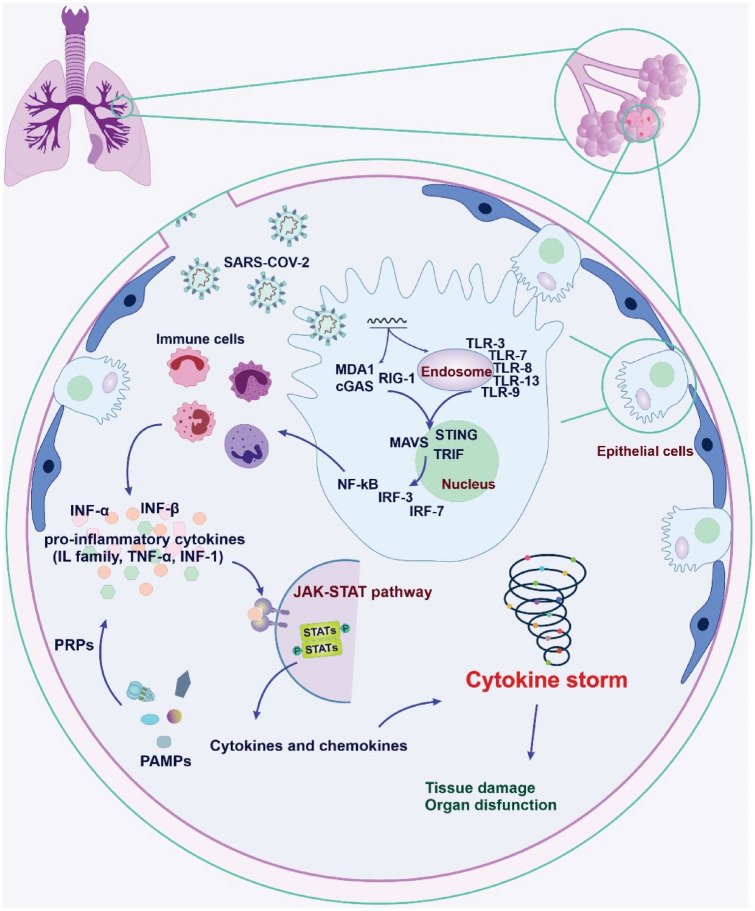
Fig. 2.
Schematic depicting the cytokine storm (CS) mechanisms in severe COVID-19 patients. The pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect and respond to the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are expressed by immune and non-immune cells. Retinoid acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I), cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA-5) are receptors for detecting the viral genome in the cytoplasm. The activation of these sensors leads to an increase of TIR-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon β (TRIF), stimulation of interferon genes (STINGs), and mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS). The activation of interferon regulatory factor-3, 7 (IRF-3, IRF-7), and nuclear factor-kappa (NF-κB) initiate a subcellular signaling cascade, induce interferons (INFs) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, subsequently leading to CS phenomena