Abstract
Background
Acute radiation dermatitis (ARD) is the most common acute response after adjuvant radiotherapy in breast cancer patients and negatively affects patients’ quality of life. Some studies have reported several risk factors that can predict breast cancer patients who are at a high risk of ARD. This study aimed to identify patient- and treatment-related risk factors associated with ARD.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and WanFang literature databases were searched for studies exploring the risk factors in breast cancer patients. The pooled effect sizes, relative risks (RRs), and 95% CIs were calculated using the random-effects model. Potential heterogeneity and sensitivity analyses by study design, ARD evaluation scale, and regions were also performed.
Results
A total of 38 studies composed of 15,623 breast cancer patients were included in the analysis. Of the seven available patient-related risk factors, four factors were significantly associated with ARD: body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2 (RR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.06–1.16, I 2 = 57.1%), large breast volume (RR = 1.02, 95% CI = 1.01–1.03, I 2 = 93.2%), smoking habits (RR = 1.70, 95% CI = 1.24–2.34, I 2 = 50.7%), and diabetes (RR = 2.24, 95% CI = 1.53–3.27, I 2 = 0%). Of the seven treatment-related risk factors, we found that hypofractionated radiotherapy reduced the risk of ARD in patients with breast cancer compared with that in conventional fractionated radiotherapy (RR = 0.28, 95% CI = 0.19–0.43, I 2 = 84.5%). Sequential boost and bolus use was significantly associated with ARD (boost, RR = 1.91, 95% CI = 1.34–2.72, I 2 = 92.5%; bolus, RR = 1.94, 95% CI = 1.82–4.76, I 2 = 23.8%). However, chemotherapy regimen (RR = 1.17, 95% CI = 0.95–1.45, I 2 = 57.2%), hormone therapy (RR = 1.35, 95% CI = 0.94–1.93, I 2 = 77.1%), trastuzumab therapy (RR = 1.56, 95% CI = 0.18–1.76, I 2 = 91.9%), and nodal irradiation (RR = 1.57, 95% CI = 0.98–2.53, I 2 = 72.5%) were not correlated with ARD. Sensitivity analysis results showed that BMI was consistently associated with ARD, while smoking, breast volume, and boost administration were associated with ARD depending on study design, country of study, and toxicity evaluation scale used. Hypofractionation was consistently shown as protective. The differences between study design, toxicity evaluation scale, and regions might explain a little of the sources of heterogeneity.
Conclusion
The results of this systematic review and meta-analysis indicated that BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 was a significant predictor of ARD and that hypofractionation was consistently protective. Depending on country of study, study design, and toxicity scale used, breast volume, smoking habit, diabetes, and sequential boost and bolus use were also predictive of ARD.
Keywords: acute radiation dermatitis, breast cancer, radiotherapy, risk factor, meta-analysis
1 Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women (1, 2). Due to advances in earlier screening and treatment, breast cancer mortality has greatly reduced over the past few decades (2). Adjuvant radiation therapy (RT) for patients with early-stage breast cancer undergoing breast-conserving surgery or locally advanced breast cancer with positive lymph nodes undergoing modified radical mastectomy (MRM) has become the standard treatment to reduce the local recurrence and death rates of breast cancer (3, 4).
RT targets tumor cells and induces double-stranded DNA breaks, resulting in cell damage and death, as well as damage to the surrounding normal tissue (5). Due to the rapid turnover of skin tissue, the skin is particularly sensitive to the damaging effects of radiation. Acute radiation dermatitis (ARD) is one of the most common side effects, ranging from mild erythema to wet desquamation reactions; ulcers and necrosis can occur in severe cases (6). ARD may occur 2–3 weeks after the start of RT and may last up to 4 weeks after the treatment ends. ARD can cause pain/discomfort and negatively impact patients’ quality of life, increasing the incidence of depression and anxiety in patients with breast cancer (7–9). If severe ARD occurs, the RT schedule will be changed or even terminated. Therefore, exploring the risk factors of ARD is an important priority in preventing ARD and caring for patients with breast cancer undergoing RT. According to present research reports, the development or severity of ARD is affected by several risk factors, including patient-related factors (e.g., smoking, bra size, age, ethnic origin, coexisting diseases, hormonal status, tumor site, and genetic factors) and treatment factors (e.g., beam energy, total dose of radiation, treatment techniques, volume and fraction of radiation, chemotherapy, and tamoxifen therapy) (10–19). However, inconsistencies still exist between different radiotherapy centers worldwide.
Consequently, we believe that a high-quality systematic review and meta-analysis is needed to summarize currently available data to obtain an exact conclusion. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the risk factors that are significantly associated with acute ARD in women with breast cancer and provide more evidence for the prevention and management of ARD.
2 Materials and Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The study protocol was registered in PROSPERO (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021250289) (20). The PRISMA 2020 checklist is shown in Supplementary Table 1 .
2.1 Search Strategy
Articles in three English databases (PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library) and two Chinese databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure and WanFang databases) were searched from January 2000 to May 2021. A manual search of the reference lists of the identified literature and systematic reviews was also conducted. Only articles published in English or Chinese were included. Based on a combination of MeSH terms and keywords, the following research terms were used: “breast cancer,” “radiotherapy,” and “radiation dermatitis.” The search strategy is shown in Supplementary Table 2 .
2.2 Selection Criteria
The included study needed to meet the following criteria: 1) the research participants were breast cancer patients aged 18 years and older undergoing radiotherapy; 2) the purpose of the study was to assess patients’ skin toxicity reactions and tumor- and treatment-related factors that increase the risk of radiation-induced acute skin toxicity in breast cancer patients; 3) the study outcomes were the prevalence, incidence, and severity of acute skin reactions (radiation dermatitis and erythema) induced by radiotherapy; 4) the study design was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) or observational study design, including cohort and case–control studies; and 5) relative risks (RRs), odds ratios (ORs), and hazard ratios (HRs) were used as measures of effect.
Studies were excluded if they were books, reviews, case reports, experimental laboratory articles, conference abstracts, opinion articles, commentaries, and editorial reviews.
2.3 Data Extraction
Study selection and data extraction were performed by two independent authors using the PRISMA flow diagram. Dissent was resolved by discussion or consultation with a third author. When data were incomplete, the original authors were contacted.
The following data were extracted for each article: first author, country, publication year, study design, study period, patient characteristics, follow-up duration, sample size of participants, all risk factors investigated, and outcome measured. Finally, the adjusted OR, RR, and HR, and 95% CIs and p-values were also gathered.
2.4 Risk of Bias Assessment
The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews was used to assess the quality of RCTs. Quality scoring of the observational study was performed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. Funnel plots and Egger’s tests were performed to assess publication bias, in which Egger’s regression test (21) was performed where the number of included studies was 10 or more (22).
2.5 Strategy for Data Synthesis
To determine the risk factors associated with ARD, the Stata version 16 software was used for data synthesis. The RR and 95% CI of the outcome variables were calculated. The pooled effect sizes of the studies were visualized using a forest plot. The random-effects model was applied to calculate the pooled RR and its 95% CI if significant heterogeneity among studies was found. Otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. Sensitivity analysis of the study design (RCT and cohort), ARD assessment scale (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE)), and area (Europe, North America, Asia, and Africa) was performed. Cochran’s Q test and I 2 statistics were conducted to assess the potential heterogeneity between individual studies, with values of the latter above 75% being regarded as indicating high levels of heterogeneity. A sensitivity analysis was also carried out using the “leave-one-out” method.
3 Results
3.1 Study Selection and Characteristics
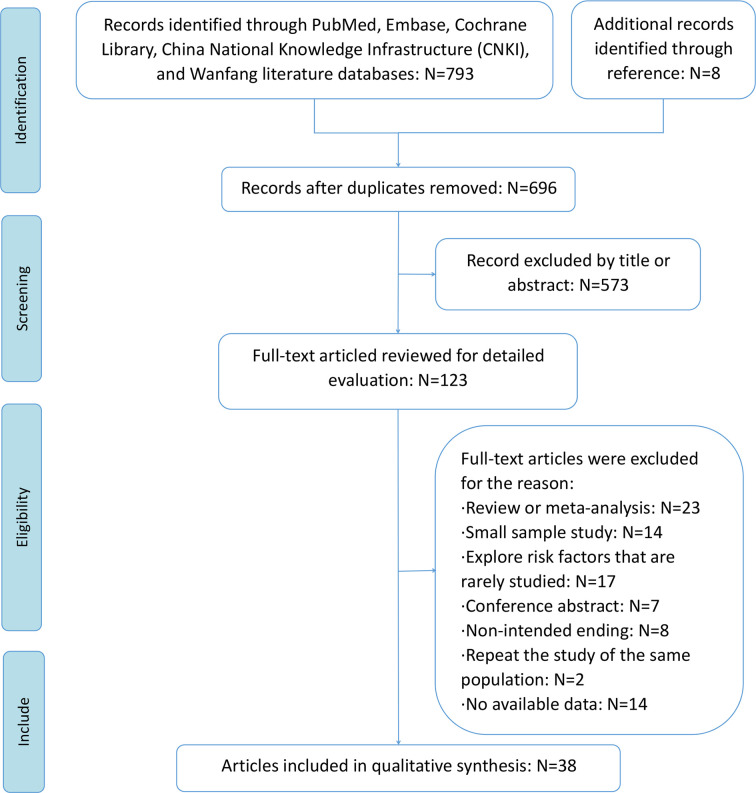
A total of 793 articles were initially identified through database searches after removing 105 duplicate articles. The abstracts and titles of 606 articles were reviewed, and 573 articles were excluded. The remaining 123 articles were read and screened in full texts for further assessment of eligibility. A total of 85 articles were further excluded for the following reasons: review or meta-analysis, small sample study, risk factors that are rarely studied, conference abstracts, non-intended endings, study being repeated on the same population, and lack of available data. Finally, 38 studies were included in this meta-analysis, of which five studies were RCTs, nine studies were retrospective designs, and 24 studies were prospective design (10–12, 14–17, 23–53). Except for one study from the WanFang database (40), all other included studies were indexed in PubMed. A flowchart of the literature search is shown in Figure 1 .
Figure 1.
The flowchart of the literature search.
The characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. The total number of patients was 15,623, ranging from 75 to 2,309 patients per study. Most patients had stage I–III breast cancer and were treated with breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer or MRM with positive lymph nodes for advanced breast cancer. None of the patients received breast reconstruction [except for some patients in the study by Aoulad et al. (36)]. The National Cancer Institute CTCAE (NCI CTCAE) and the RTOG were the most common scales used to evaluate ARD ( Supplementary Table 3 ). Most centers used three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (n = 18) or intensity-modulated RT (n = 13) technique for radiotherapy. The dose and fractionation schedule of radiotherapy used in all studies was conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT), defined as a total of 50 Gy in 25 fractions over 5 weeks, or hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT), defined as a total dose ranging from 40 to 45.05 Gy, with a single dose of 2.3–2.9 Gy given over 13–17 fractions. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale is shown in Supplementary Table 4 .
Table 1.
The characteristic of included studies.
| Study ID | Study design | Country | Evaluation criterion | Total patients | The proportion of ARD with ≥2 Grade | Period | Age (range, years) | RT technique | RT dose, F and time | Boost | Risk factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pasquier, D.2021 (10) | PS | France | CTCAE v4.0 | 288 | 36.8% | NA | 55 (32–82) | IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Smoking; chemotherapy |
| Joseph, K.2021 (23) | RCT | Canada | CTCAE v3.0 | 177 | FiF-IMRT: 61%; HT-IMRT: 37% | 2008–2012 | 58 (41–82) | FiF-IMRT; HT-IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | No | Breast volume; chemotherapy; hormone treatment |
| Abdeltawab, A. A.2021 (11) | PS | Egypt | RTOG/EORTC | 75 | 16% | 2015–2018 | 59.47 (44–80) | 2D-RT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Using of trastuzumab; boost |
| Zygogianni, A.2020 (24) | RS | Greece | RTOG/EORTC | 134 | NA | 2004–2012 | 75 | HF RT | Group A: 42.75 Gy/15 F/5 w; group B: 45.05 Gy/17 F | Yes | Age; treatment group: two hypofractionated radiation schedules |
| Rattay, T.2020 (12) | PS | UK | RTOG/CTCAE | 2285 | LeN: 27.1%, ISE: 74.9%, Cam: 38.9% | LeN: 2008–2010, ISE: 1998–2001, Cam2003–2007 | LeN: 59, ISE: 61, Cam: 59 | 3D-CRT; IMRT | LeN: 50 Gy/25 F, ISE: 50 Gy/25 F, Cam: 40 Gy/15 F | Yes | BMI; breast size; HFRT; boost; smoking |
| Chen, C. H.2020 (14) | RS | China | RTOG | 308 | 17.3% | 2012–2018 | 54 (24–88) | 3D-CRT; IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F; 42.56 Gy/16 F | NA | Surgery type; nodal irradiation; BMI; RT technique: IMRT vs. 3D-CRT |
| Wang, S. L.2019 (15) | RCT | China | CTCAE v3.0 | 810 | CFRT: 8%; HRT: 3% | 2008–2016 | 49 (24–74) | 2D-RT, 3D-CRT, IMRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 43.5 Gy/15 F/3 w | Yes | Treatment group: CFRT vs. HFRT |
| Pasquier, D.2019 (16) | PS | France | CTCAE v4.0 | 114 | 42% | 2014–2016 | 56 (32–83) | NA | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | BMI; chemotherapy |
| Palumbo, I.2019 (25) | PS | Italy | CTCAE v4.03 | 219 | NA | 2014–2015 | 62 (34–88) | WBRT | HFRT: 42.4 Gy/16 F | Yes | Boost; chemotherapy |
| Kawaguchi, H.2019 (26) | PS | Japan | CTCAE v3.0. | 348 | HF-WBI: 13.8%; CF-WBI: 29.4% | 2009–2013 | 58 (26–81) | CF-WBI; HF-WBI | CF-WBI: 50 Gy/25 F; HF-WBI: 41.6 Gy/16 F | Yes | CF-WBI vs. HF-WBI; chemotherapy; hormone treatment |
| Butler-Xu, Y. S.2019 (17) | RS | USA | RTOG | 114 | CFRT: 76%, HFRT: 28% | 2012–2015 | NA | 3D-CRT | HFRT: 40.05 Gy/15 F; CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Boost; CFRT vs. HFRT |
| Yap, M. L.2018 (27) | PS | Canada | NA | 314 | 16.60% | 2004–2009 | 53.2 (27–86) | 3D CRT; IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Bolus |
| Rastogi, K.2018 (28) | PS | India | RTOG | 100 | NA | NA | 48 (21–79) | 3D-CRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 42.72 Gy/16 F/3-3.5 w | No | Treatment group: HFRT vs. CFRT |
| Parekh, A.2018 (29) | RS | India | CTCAE | 280 | 31.40% | 2008–2015 | 60 | 3D-CRT | CFRT, HFRT | No | Black race; BMI; treatment group: HFRT; chemotherapy; regional nodal irradiation |
| Lin, J. C.2018 (30) | RS | China | CTCAE v3.0 | 458 | IMRT: 26.80%, IGRT: 14.10% | 2012–2014 | 20–85 | TOMO, IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Age; treatment group: IGRT vs. IMRT; smoking |
| Guttmann, D. M.2018 (31) | RS | USA | CTCAE v4.03 | 413 | NA | 2011–2015 | 56 | 3D planning or IMRT | CFRT: 50–50.4 Gy/25 F/5 F. HFRT: 4,256 cGy/266 cGy daily | Yes | IMRT vs. FiF3D; treatment group: HFRT vs. CFRT; boost |
| De Santis, M. C.2018 (33) | PS | Italy | RTOG | 727 | 21.9%–28.4% | 2009–2016 | 74 (47–92) | Hypo-RT | NA | Yes | Chemotherapy; boost; trastuzumab |
| Das, Pabitra.2018 (34) | RCT | India | RTOG | 108 | CFRT: 24.5%; HFRT: 23.6% | 2013–2015 | 49 | 2D-RT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 42.56 Gy/16 F/3.1 w | No | Treatment group: HFRT vs. CFRT |
| Fatma M. F.2018 (32) | RCT | Egypt | RTOG | 100 | HFRT: 16%, CFRT: 26% | 2015–2017 | 31–68 | 3D-CRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 40 Gy/15 F/3 w | Yes | Treatment group: HFRT vs. CFRT |
| De Felice, F.2017 (35) | PS | Italy | CTCAE v4.0 | 120 | HFRT: 26.5%, CFRT: 73.5% | 2012–2015 | 58 (39–82) | NA | CFRT: 50 Gy/2 Gy daily; HFRT: 42.5 Gy/2.66 Gy daily | Yes | Chemotherapy |
| Aoulad, N.2017 (36) | RS | France | CTCAE v4.0 | 292 | 24.6% | 2010–2014 | NA | IMRT | Conservative surgery: 52.2-63.8 Gy/29 F; mastectomy: 50 Gy/25 F | NA | BMI |
| Wright, J. L.2016 (37) | PS | USA | CTCAE v3.0 | 392 | 52% | 2008–2014 | 56.2 (27–85) | Field-in-field technique | CFRT: 50 Gy/2 Gy daily; HFRT: 42.4 Gy/2.65 Gy daily | Yes | Age; race; BMI; treatment group: CRT vs. HFRT; breast volume. |
| Linares, I.2016 (38) | PS | Spain | CTCAE v4.0 | 143 | 9.8% | 2006–2011 | 73 (50–86) | 3D-CRT | HFRT: 42.4 Gy/16 F/2.65 Gy daily | Yes | RT volume; simultaneous boost (SIB) vs. none; boost: not simultaneous boost vs. none |
| Córdoba, E. E.2016 (39) | PS | USA | RTOG | 80 | 40% | NA | 59 (26–79) | 3D-CRT | CFRT: 50–50.4 Gy/1.8–2 Gy daily | Yes | BMI; breast size |
| Zhang, S. K.2015 (40) | PS | China | CTCAE v4.03 | 786 | 12.9% | 2009–2014 | NA | 3D-CRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | NA | Diabetes; BMI; neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| Pignol, J. P.2015 (41) | PS | Canada | CTCAE v3.0 | 257 | 28.4% | 2005–2007 | 51 (24–80) | Photon beams or direct electron field and photon tangent fields | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Smoking; chemotherapy; bolus frequency |
| Jagsi, R.2015 (42) | PS | USA | CTCAE v4.0 | 2309 | CFRT: 62.6%; HFRT: 27.4% | 2011–2014 | 61.2 | NA | NA | Yes | Treatment group: CFRT vs. HFRT |
| Wright, J. L.2014 (43) | PS | USA | CTCAE v3.0 | 110 | NA | 2010–2013 | 51.9 (28–75) | NA | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | NA | Age; ethnicity; race; BMI; smoking; chemotherapy |
| Park, H.2014 (44) | PS | Korea | RTOG | 213 | 27% | NA | 42 (21–71) | NA | 50–65 Gy/1.8–2 Gy daily | Yes | Age; BMI; breast volume; diabetes; hypertension; chemotherapy; hormone therapy |
| De Langhe, S.2014 (45) | PS | Belgium | CTCAE v3.0 | 377 | 58% | NA | 58 (30–82) | IMRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 40 Gy/15 F/3 w | Yes | BMI; breast size; smoking; HFRT vs. CFRT; hormone therapy; chemotherapy; trastuzumab |
| Ciammella, P.2014 (46) | PS | Italy | RTOG | 212 | 15% | 2009–2012 | 63 (39–88) | 3D-CRT | HFRT: 40.05/15 F/2.67 Gy daily | Yes | Breast volume; boost |
| Tortorelli, G.2013 (47) | RS | Italy | RTOG | 339 | CFRT: 55%; HFRT: 37.5% | 2007–2010 | 60 (22–86) | 3D-CRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w; HFRT: 44 Gy/16 F/2.75 Gy daily | Yes | Chemotherapy; hormone therapy; fractionation schedule; age; breast volume |
| Sharp, L.2013 (48) | PS | Sweden | RTOG/EORTC | 390 | 21% | 2010–2011 | 59 (29–86) | NA | 50 Gy/2.0 Gy daily; 42.56 Gy/2.66 Gy daily | Yes | Age; BMI; smoking; surgery: chemotherapy; endocrine therapy |
| Terrazzino, S.2012 (49) | PS | Italy | RTOG | 286 | 31.1% | 2009–2011 | 60.8 | 3D-CRT | CFRT: 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Breast size; boost; BMI |
| Freedman, G. M.2009 (51) | RS | USA | CTCAE v3.0 | 804 | Conventional: 75%, IMRT: 52% | 2001–2006 | NA | Wedged photon tangents and IMRT | 46–50 Gy | Yes | CRT vs. IMRT; breast size; chemotherapy; hormone therapy |
| Morganti, A. G.2009 (50) | PS | Italy | NA | 332 | CG: 33.6%, MARA-1: 13.1%, MARA-2: 45.1% | NA | 57.5 | 3D-CRT | MARA-1: HFRT; 40 Gy/2.5 Gy daily; MARA-2: CFRT: 50 Gy/2 Gy daily | Yes | HFRT vs. CFRT; hypertension; diabetes; smoke; hemoglobin; age; hormone therapy; chemotherapy |
| Pignol, J. P.2008 (52) | RCT | Canada | CTCAE v2.0 | 331 | IMRT: 31.2%, standard treatment: 47.8% | 2003–2005 | 57 | Standard wedge missing tissue or IMRT | 50 Gy/25 F/5 w | Yes | Treatment group: BIMRT technique Breast size; boost |
| Back, M.2004 (53) | PS | Germany | CTCAE | 478 | 17.5% | 1998–2001 | NA | NA | 50 Gy/2 Gy/F; 50.4 Gy/1.8 Gy daily | Yes | Radiotherapy of lymph nodes; hormone therapy; age; BMI; smoking |
PS, prospective study; RS, retrospective study; RCT, randomized controlled trial; HFRT, hypofractionated radiotherapy; CFRT, conventional fractionated radiotherapy; FiF-IMRT; field-in-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy; HT-IMRT; helical tomotherapy intensity-modulated radiotherapy; CTCAE, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; RTOG, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group; F, fractions; w, weeks; 2D-RT, two-dimensional radiotherapy; 3D-CRT, three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy; IMRT, intensity-modulated radio therapy; AA, African-American; BMI, body mass index; LeN, LeND cohort; ISE, ISE cohort; Cam, Cambridge cohort; EORTC, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer; WBRT, whole brain radiotherapy; HF-WBI, hypofractionated whole-breast irradiation; CF-WBI, conventionally fractionated whole-breast irradiation; IGRT, image-guided radiation therapy; TOMO, tomotherapy.
3.2 Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors
3.2.1 Patient-Related Risk Factors
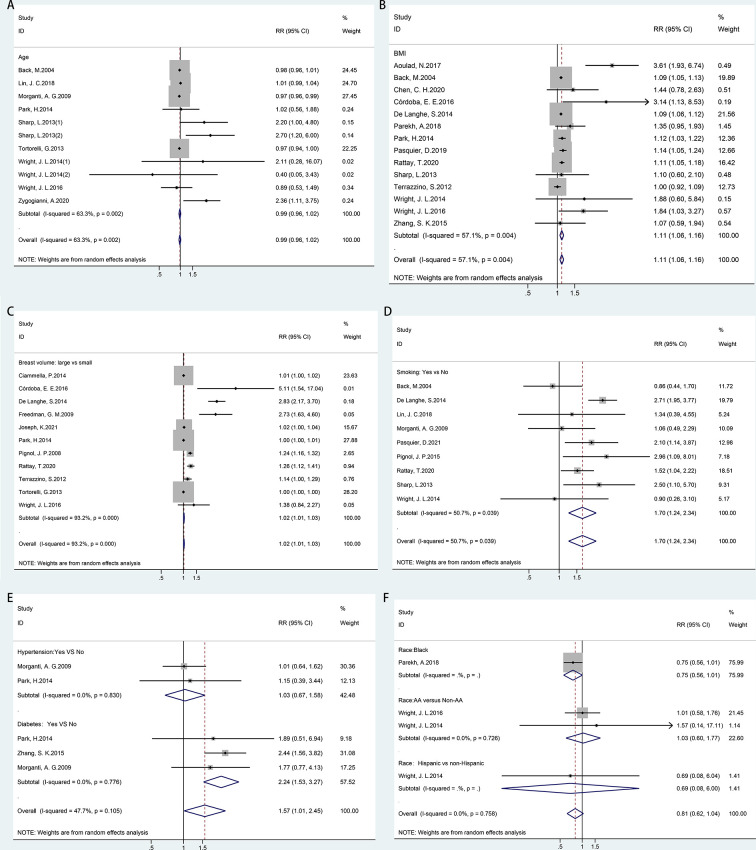
Random-effects meta-analyses were conducted for patient-related risk factors, including age, body mass index (BMI), breast volume, smoking, race, hypertension, and diabetes, as shown in Figure 2. It was found that patients with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 (RR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.06–1.16), large breast volume (RR = 1.02, 95% CI = 1.01–1.03), smoking habits (RR = 1.70, 95% CI = 1.24–2.34), or diabetes (RR = 2.24, 95% CI = 1.53–3.27) had significantly higher risks of ARD than their counterparts. However, a significantly increased risk was not observed with increasing age (RR = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.96–1.02), hypertension (RR = 1.03, 95% CI = 0.67–1.58), or race (RR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.62–1.04).
Figure 2.
Forest plot of studies among patient-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Age. (B) Body mass index (BMI). (C) Breast volume. (D) Smoking. (E) Chronic disease (hypertension/diabetes). (F) Race.
According to Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistics, a substantially large inconsistency (p = 0.000, I 2 = 93.2%) was found for significant heterogeneity among studies regarding the breast volume. BMI (p = 0.004, I 2 = 57.1%) and smoking habits (p = 0.039, I 2 = 50.7%) showed moderate inconsistency with significant heterogeneity in each meta-analysis. No heterogeneity was found for hypertension, diabetes, or race. There was no indication of publication bias, as implied by the funnel plot and Egger’s tests for the risk factors of age (p = 0.084) and smoking habits (p = 0.284). However, funnel plots and Egger’s test indicated potential publication bias for BMI (p = 0.016) and breast volume (p = 0.001) ( Supplementary Figure 1 ).
3.2.2 Treatment-Related Risk Factors
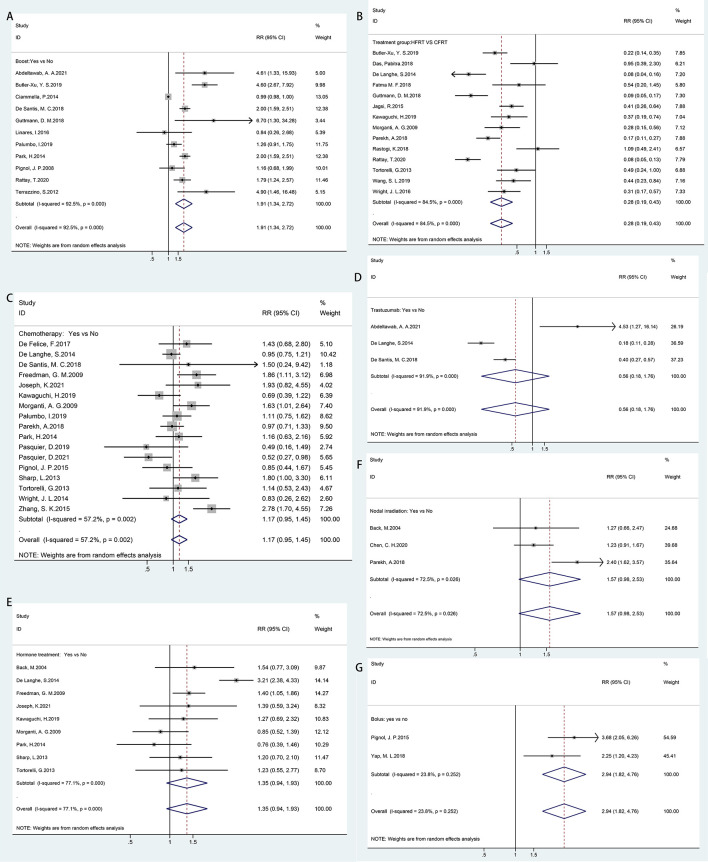
In Figure 3, all treatment-related risk factors available for meta-analyses were performed on sequential boost (boost vs. non-boost), chemotherapy regimen (yes vs. no), hormone therapy (yes vs. no), trastuzumab therapy (yes vs. no), HFRT versus CFRT, bolus (yes vs. no), and nodal irradiation (yes vs. no). Our results indicated that HFRT reduced the risk of ARD in breast cancer patients as compared with CFRT (RR = 0.28, 95% CI = 0.19–0.43). Sequential boost and bolus use was significantly associated with ARD (boost, RR = 1.91, 95% CI = 1.34–2.72; bolus, RR = 1.94, 95% CI = 1.82–4.76). However, chemotherapy regimen (RR = 1.17, 95% CI = 0.95–1.45), hormone therapy (RR = 1.35, 95% CI = 0.94–1.93), trastuzumab therapy (RR = 1.56, 95% CI = 0.18–1.76), and nodal irradiation (RR = 1.57, 95% CI = 0.98–2.53) were not correlated with ARD.
Figure 3.
Forest plot of studies among treatment-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Boost. (B) Hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT) vs. conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT). (C) Chemotherapy regimen. (D) Trastuzumab therapy. (E) Hormone therapy. (F) Nodal irradiation. (G) Bolus.
Considerable heterogeneity was observed among the risk estimates for chemotherapy (p = 0.002, I 2 = 57.2%), sequential boost (p = 0.000, I 2 = 92.5%), hormone therapy (p = 0.000, I 2 = 77.1%), HFRT versus CFRT (p = 0.000, I 2 = 84.5%), trastuzumab therapy (p = 0.000, I 2 = 91.9%), and nodal irradiation (p = 0.026, I 2 = 72.5%). No statistically significant heterogeneity was detected for bolus (p = 0.252, I 2 = 23.8%). No evidence of asymmetry in the funnel plot was found, and Egger’s tests also showed no significant evidence of publication bias for chemotherapy (p = 0.676), hormone therapy (p = 0.152), or HFRT versus CFRT (p = 0.07). However, a potential publication bias was observed for boosts in the funnel plot and Egger’s test (p = 0.002) ( Supplementary Figure 2 ).
3.3 Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis by study design, ARD assessment scale, and regions was performed on the risk factors that more than 10 studies reported and included. As shown in Table 2, in each subgroup, the results of the risk factors (age, BMI, chemotherapy, and HFRT vs. CFRT) did not change significantly; however, the results of heterogeneity were slightly improved. BMI was consistently associated with ARD. Hypofractionation is consistently shown as a protective factor. The results of studies from European countries showed that smoking was a risk factor for ARD; however, studies in North America and Asia indicated that smoking was not associated with ARD. The combined results of three studies from North American countries also suggested that a boost was not related to ARD. For the two risk factors of breast volume and boost, the RCT results suggested no statistical significance, but the results of the prospective cohort study were significant. These contradictory results may be because only one or two related RCT studies were included in the meta-analysis, but such results also proved the heterogeneous results of the study design. In addition, our results showed that when the CTCAE was used to assess ARD, large breast volume increased the risk, but an irrelevant association was observed when the RTOG criteria were used. Inconsistent results were also observed between the boost and ARD according to the different assessment criteria. The difference between the CTCAE scale (which incorporates inframammary desquamation in grade 2) and RTOG criteria may explain a little of the sources of heterogeneity. Besides, after removing one study every time, the significance of the results remained consistent, which indicated that our results were stable ( Supplementary Figures 3, 4).
Table 2.
Sensitivity analysis by study design, acute radiation dermatitis evaluation scale and area.
| Factors | All | Area | Study design | Evaluation scale | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | North America | Asia | Africa | Prospective study | Retrospective study | RCT | RTOG | CTCAE | ||
| RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | RR (95% CI) | |
| Age | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) | 0.98 (0.94–1.02) | 0.99 (0.55–1.46) | 1.01 (0.99–1.04) | 0.98 (0.94–1.01) | 1.00 (0.94–1.07) | 1.57 (0.97–2.57) | 1.00 (0.98–1.01) | ||
| BMI | 1.11 (1.06–1.16) | 1.09 (1.05–1.14) | 2.06 (1.30–3.26) | 1.13 (1.04–1.23) | 1.09 (1.06–1.13) | 1.85 (1.03–3.31) | 1.09 (1.01–1.18) | 1.13 (1.06–1.20) | ||
| Smoking | 1.70 (1.24–2.34) | 1.71 (1.18–2.47) | 1.73 (0.54–5.53) | 1.34 (0.39–4.58) | 1.72 (1.23–2.41) | 1.34 (0.39–4.58) | 1.70 (1.13–2.54) | 1.75 (1.11–2.78) | ||
| Breast volume | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | 1.32 (1.08–1.62) | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 1.06 (1.02–1.10) | 1.60 (0.60–4.26) | 1.12 (0.93–1.35) | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 1.55 (1.22–1.97) | |
| Chemotherapy | 1.17 (0.95–1.45) | 1.10 (0.85–1.42) | 1.35 (0.85–2.14) | 1.22 (0.69–2.14) | 1.12 (0.86–1.46) | 1.24 (0.80–1.91) | 1.93 (0.82–4.55) | 1.38 (0.96–1.99) | 1.09 (0.84–1.42) | |
| Hormone treatment | 1.35 (0.94–1.93) | 1.47 (0.81–2.69) | 1.40 (1.07–1.83) | 1.00 (0.60–1.65) | 1.33 (0.77–2.29) | 1.38 (1.05–1.81) | 1.39 (0.59–3.26) | 1.04 (0.72–1.51) | 1.72 (1.09–2.71) | |
| Boost | 1.91 (1.34–2.72) | 1.51 (1.02–2.24) | 2.94 (0.94–9.14) | 2.00 (1.59–2.51) | 4.61 (1.33–15.95) | 1.70 (1.17–2.47) | 4.78 (2.85–8.00) | 1.16 (0.68–1.99) | 2.24 (1.41–3.57) | 1.30 (0.86–1.96) |
| HFRT vs. CFRT | 0.28 (0.19–0.43) | 0.17 (0.07–0.40) | 0.23 (0.12–0.42) | 0.47 (0.23–0.96) | 0.54 (0.20–1.45) | 0.26 (0.13–0.51) | 0.20 (0.11–0.35) | 0.57 (0.36–0.90) | 0.39 (0.17–0.93) | 0.22 (0.13–0.37) |
RCT, randomized controlled trial; HFRT, hypofractionated radiotherapy; CFRT, conventional fractionated radiotherapy; CTCAE, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; RTOG, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group; BMI, body mass index; RR, relative risk.
4 Discussion
The proportion of patients with ARD of grade 2 or higher after radiotherapy ranged from 9.8% to 76%, with an average of 34.3% and a median of 28.4%, across the 38 included studies. This study aimed to identify the risk factors associated with ARD so that clinicians could assess the risk of toxicity at the time of breast cancer diagnosis and before planning any treatment, as well as adjust treatment decisions and take preventive measures in advance. Our results indicated that several variables, including BMI, breast volume, smoking habits, diabetes, boost and bolus use, and hypofractionation (protective), were related to ARD. Age, hypertension, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, trastuzumab therapy, and nodal irradiation were not associated with radiation dermatitis.
The 10-year follow-up of the UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) trials confirmed that appropriately dosed HFRT was safe and effective in patients with early breast cancer (54–57). Normal tissue effects (breast induration, shrinkage, telangiectasia, and breast edema) were significantly less common in the HFRT group than that in the CFRT group (54, 55). Another randomized, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial reported that the HFRT (43.5 Gy over 15 fractions in 3 weeks) and CFRT groups (50 Gy over 25 fractions in 5 weeks) had equivalent efficacy in the 5-year locoregional recurrence, overall survival, and disease-free survival in patients with high-risk breast cancer (15). This trial did not find a significant difference in the incidence of acute or late toxicities, but there were fewer patients who experienced grade 3 acute skin toxicity in the HFRT group than that in the CFRT group (14 [3%] of 401 patients vs. 32 [8%] of 409 patients, p < 0.0001) (15). A meta-analysis based on large randomized trials also indicated that HFRT and CFRT were equally effective with respect to overall survival, disease-free survival, locoregional recurrence, and distant metastasis after breast MRM and had similar toxic side effects (58). Another meta-analysis concluded that no difference was found between CFRT and HFRT in terms of efficacy; however, HFRT showed a lower incidence of breast edema, telangiectasia, and acute skin radiation toxicity compared with that in CFRT (59). A large multicenter cohort found that HFRT not only improved the convenience of patients but also reduced acute pain, fatigue, and dermatitis in patients with breast cancer (42). Consistent with these studies, our results also suggest that HFRT could reduce the risk of radiation dermatitis compared with that in CFRT. Recruitment bias cannot be eliminated in nonrandomized trials, such as the hypofractionation proposed for smaller breast volumes. Therefore, we conducted a subgroup analysis according to the study design, and the results showed that HFRT could reduce the risk of ARD compared with that in CFRT according to three randomized trials. In addition, studies from the United States and Asia have reported that HFRT could reduce the treatment cost of patients by approximately 1/3 (60, 61). HFRT not only reduces the occurrence of ARD but also helps shorten the treatment cycle, reduce the length of hospital stay, save medical resources, and mitigate financial pressure, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Therefore, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, England’s Health Technology Assessment agency, recommends HFRT as a standard practice in patients with early-stage breast cancer who underwent breast-conserving surgery or MRM (62).
To improve the local control rate, it is necessary to administer a localized dose escalation (boost) to the tumor bed. However, as our results show, sequential application of a boost increases the risk of ARD. Therefore, it is urgent to find a suitable boost administration method that reduces the risk of side effects without compromising local control. A study found that patients with simultaneous integrated boost had lower toxicity than those receiving a sequential boost or no boost (38). Two reviews concluded that simultaneous integrated boost is a feasible approach with acceptable risk and severity of adverse events (63, 64). The Phase III trial (RTOG 1005 trial) of the North American Radiotherapy Oncology Group is currently in clinical trials, which compare the therapeutic and side effects of hypofractionated whole breast RT with a concurrent tumor bed boost versus standard daily RT with a sequential boost. We look forward to the results of the trial, which could improve the acceptance, shorten the overall treatment time, and broaden the applicability of HFRT in patients with breast cancer (65).
Our results showed that nodal irradiation was not associated with ARD, but nodal irradiation resulted in a larger irradiated volume. Regarding the dose distribution of the target volume and skin and the occurrence of skin toxicity, existing data are sparse. One prospective study found that subclavian skin volume is correlated with medium-term skin toxicity (16). Two other authors stated that dose inhomogeneities within the target volume have a significant impact on the incidence of skin reactions (47, 66). As hot spots often occur close to the skin, a more homogenous dose distribution will result in a lower incidence of skin toxicity. Therefore, it is suggested that treatment planning techniques with a more homogenous dose distribution, such as intensity-modulated RT, are shown to result in lower rates of severe skin toxicity (51, 67).
Patient-related risk factors, such as BMI, breast volume, smoking habits, and diabetes, were found to be risk factors for ARD. Large breast volume and high BMI have been most frequently reported to increase the risk of ARD. BMI is strongly related to breast volume (68). Breast volume has been used as a surrogate indicator of radiotherapy dose inhomogeneity, which may be one of the reasons for the increased ARD. However, two randomized clinical trials have highlighted breast volume as a stand-alone predictor of ARD independent of dose inhomogeneity (52, 69). It is necessary to consider that the association between a larger breast volume and the risk of ARD is likely due to the abrasive effect of friction within skin folds and the bolus effect in the inframammary, skin folds, and axillary regions. In fact, it is difficult for obese people to lose weight in a short period of time. In addition, weight changes during RT planning and radiotherapy will obviously change the treatment area; hence, weight loss is not recommended at this point. We recommend that breast cancer patients keep their skin dry and avoid friction at the skin folds during radiotherapy. Smoking increases the risk of radiation dermatitis; therefore, quitting smoking during radiotherapy is one of the best decisions that patients can make to reduce the risk of ARD. It was found that diabetic patients have a higher risk of ARD, but this result was obtained from three prospective studies only. Whether diabetes is related to radiation dermatitis and the repair mechanism of radiation damage caused by abnormal metabolism in the skin requires further research.
It was necessary to investigate potential sources of heterogeneity. First, the type of research design included in the study is different, resulting in substantial heterogeneity. Therefore, a sensitivity analysis was conducted according to the type of study (prospective cohort study, retrospective cohort, and RCT). For the two risk factors of breast volume and boost, the results of the prospective cohort study and RCT were conflicting, proving the heterogeneous results of the study design. Second, acute toxicity was evaluated using the most common tools: the NCI CTCAE or RTOG scale. One study found a high concordance between the RTOG and CTCAE criteria (correlation coefficients >0.9) (70). Nevertheless, differences still exist between the two assessment tools, such as the CTCAE scale incorporating inframammary desquamation in grade 2, leading to inconsistent assessment results of radiation dermatitis. The sensitivity analysis found that large breast volume increased the risk by the CTCAE scale, but an irrelevant association was observed when the RTOG criteria were used. Inconsistent results were also observed between the boost and ARD according to the different assessment criteria. In addition, skin toxicity was assessed at different time points, such as at the completion of the last RT, 2 weeks after the end of RT, or when the toxicity was the most serious, which caused differences in outcome reporting. Third, the use of different radiotherapy techniques inevitably caused partial heterogeneity. Several studies have demonstrated that, compared with 3D and 2D conformal radiotherapies, intensity-modulated RT provides better dose homogeneity with lower volumes of OAR receiving high doses and reduced acute and late breast toxicity (16, 52, 71, 72). Finally, heterogeneity may be partly due to ethnic differences. Similar to the sensitivity of radiotherapy, the tissue actions produced by radiotherapy are complex processes involving multiple genes in multiple biological pathways (73–76). One study reported that African-American patients with breast cancer were more likely to suffer from skin toxicity (77).
In addition to the large heterogeneity of our results, there are other shortcomings that need to be considered. First, the number of included studies was limited, especially for some risk factors (diabetes, hypertension, trastuzumab therapy, and bolus users); therefore, it is insufficient for statistical analyses, and the results should be interpreted with caution. Second, cohort studies are the main part of the included studies and carry inevitable inherent biases. Cohort studies do not use randomization; therefore, the groups may not be comparable, leading to selection bias. In addition, not all studies adjusted for confounding factors and recall bias due to selective reports, or the presentation of incomplete result data may affect the results of the analysis. These are potential deviations that may affect the validity of the research results. Third, this article only studied the risk factors of ARD; other side effects of radiotherapy, such as late radiation dermatitis, radiation pneumonitis, and radiation esophagitis, still need to be further explored. Finally, studies have reported that genetic analysis can predict patients who are at a higher risk of ARD (75, 76). However, they were single-center, small-sample studies, and each study focused on different genes. Therefore, a meta-analysis could not be performed to obtain a relevant and precise conclusion. Given the heterogeneity and shortcomings, this study should be interpreted carefully.
In conclusion, BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 was a significant predictor of ARD, and hypofractionation was consistently protective. Depending on country of study, study design, and toxicity scale used, breast volume, smoking habit, diabetes, and sequential boost and bolus use were also predictive of ARD. On the basis of this study, doctors could predict patients with breast cancer at high risk of ARD at the outset of treatment options, adjust treatment plans, and take necessary precautions. In the future, more accurate predictions, such as genetic markers, are expected.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: YX and JC contributed to the conception and design of the research. YX and QW extracted the data and performed the analyses. YX, QW, and TH interpreted the evidence and wrote the manuscript. RC, JW, and HC revised the article. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of our study team for their whole-hearted cooperation and the original authors of the included studies for their wonderful results.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.738851/full#supplementary-material
Begg’s funnel plot of patients-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Age; (B) BMI; (C) breast volume; (D) smoking.
Begg’s funnel plot of treatment-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) boost; (B) hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT) vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT); (C) chemotherapy regimen; (D) hormone therapy.
Sensitivity analysis of the effect of patients-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Age; (B) BMI; (C) breast volume; (D) smoking.
Sensitivity analysis of the effect of treatment-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) boost; (B) hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT) vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT); (C) chemotherapy regimen; (D) hormone therapy.
The PRISMA 2020 checklist.
The search strategy.
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) or The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) toxicity scales for acute radiation dermatitis.
Quality assessment of eligible studies by Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS).
Results of individual studies: summary statistics for each group and an effect estimate.
References
- 1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin (2021) 71(3):209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin (2021) 71(1):7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, Clarke M, et al. Effect of Radiotherapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery on 10-Year Recurrence and 15-Year Breast Cancer Death: Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data for 10,801 Women in 17 Randomised Trials. Lancet (2011) 378(9804):1707–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61629-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Holli K, Hietanen P, Saaristo R, Huhtala H, Hakama M, Joensuu H. Radiotherapy After Segmental Resection of Breast Cancer With Favorable Prognostic Features: 12-Year Follow-Up Results of a Randomized Trial. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol (2009) 27(6):927–32. doi: 10.1200/jco.2008.19.7129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Leventhal J, Young MR. Radiation Dermatitis: Recognition, Prevention, and Management. Oncol (Williston Park) (2017) 31(12):885–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ramseier JY, Ferreira MN, Leventhal JS. Dermatologic Toxicities Associated With Radiation Therapy in Women With Breast Cancer[Formula Presented. Int J women's Dermatol (2020) 6(5):349–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.07.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hauth F, De-Colle C, Weidner N, Heinrich V, Zips D, Gani C. Quality of Life and Fatigue Before and After Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Strahlenther und Onkologie Organ der Dtsch Rontgengesellschaft (2021) 197(4):281–7. doi: 10.1007/s00066-020-01700-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Fuzissaki MA, Paiva CE, Oliveira MA, Lajolo Canto PP, Paiva Maia YC. The Impact of Radiodermatitis on Breast Cancer Patients' Quality of Life During Radiotherapy: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Pain symptom Manage (2019) 58(1):92–9.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Yee C, Wang K, Asthana R, Drost L, Lam H, Lee J, et al. Radiation-Induced Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Trials. Clin Breast Cancer (2018) 18(5):e825–40. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.06.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Pasquier D, Bataille B, Le Tinier F, Bennadji R, Langin H, Escande A, et al. Correlation Between Toxicity and Dosimetric Parameters for Adjuvant Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy of Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study. Sci Rep (2021) 11(1):3626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83159-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Abdeltawab AA, Ali SA, Mostafa HG, Hassan MA. Predictive Factors Increasing the Risk of Radiation Toxicity in Patients With Early Breast Cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP (2021) 22(1):145–9. doi: 10.31557/apjcp.2021.22.1.145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Rattay T, Seibold P, Aguado-Barrera ME, Altabas M, Azria D, Barnett GC, et al. External Validation of a Predictive Model for Acute Skin Radiation Toxicity in the REQUITE Breast Cohort. Front Oncol (2020) 10:575909. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.575909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Choi KH, Ahn SJ, Jeong JU, Yu M, Kim JH, Jeong BK, et al. Postoperative Radiotherapy With Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Versus 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy in Early Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial of KROG 15-03. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol (2020) 154:179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.09.043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chen CH, Hsieh CC, Chang CS. Chen MF. A Retrospective Analysis of Dose Distribution and Toxicity in Patients With Left Breast Cancer Treated With Adjuvant Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy: Comparison With Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy. Cancer Manage Res (2020) 12:9173–82. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S269893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Wang SL, Fang H, Song YW, Wang WH, Hu C, Liu YP, et al. Hypofractionated Versus Conventional Fractionated Postmastectomy Radiotherapy for Patients With High-Risk Breast Cancer: A Randomised, Non-Inferiority, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol (2019) 20(3):352–60. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(18)30813-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Pasquier D, Le Tinier F, Bennadji R, Jouin A, Horn S, Escande A, et al. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy With Simultaneous Integrated Boost for Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study on Toxicity and Quality of Life. Sci Rep (2019) 9(1):2759. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39469-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Butler-Xu YS, Marietta M, Zahra A, TenNapel M, Mitchell M. The Effect of Breast Volume on Toxicity Using Hypofractionated Regimens for Early Stage Breast Cancer for Patients. Adv Radiat Oncol (2019) 4(2):261–7. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.10.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. De Ruyck K, Van Eijkeren M, Claes K, Morthier R, De Paepe A, Vral A, et al. Radiation-Induced Damage to Normal Tissues After Radiotherapy in Patients Treated for Gynecologic Tumors: Association With Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in XRCC1, XRCC3, and OGG1 Genes and In Vitro Chromosomal Radiosensitivity in Lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2005) 62(4):1140–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.12.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Porock D. Factors Influencing the Severity of Radiation Skin and Oral Mucosal Reactions: Development of a Conceptual Framework. Eur J Cancer Care (2002) 11(1):33–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ (1997) 315(7109):629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for Examining and Interpreting Funnel Plot Asymmetry in Meta-Analyses of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ (2011) 343:d4002. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Joseph K, Vos LJ, Gabos Z, Pervez N, Chafe S, Tankel K, et al. Skin Toxicity in Early Breast Cancer Patients Treated With Field-In-Field Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Versus Helical Inverse Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy: Results of a Phase III Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin Oncol (Royal Coll Radiologists (Great Britain)) (2021) 33(1):30–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2020.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Zygogianni A, Gogalis J, Georgakopoulos I, Nikoloudi S, Liakouli Z, Kougioumtzopoulou A, et al. Two Hypofractionated Schedules for Early Stage Breast Cancer: Comparative Retrospective Analysis for Acute and Late Radiation Induced Dermatitis. J BUON (2020) 25(3):1315–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Palumbo I, Mariucci C, Falcinelli L, Perrucci E, Lancellotta V, Podlesko AM, et al. Hypofractionated Whole Breast Radiotherapy With or Without Hypofractionated Boost in Early Stage Breast Cancer Patients: A Mono-Institutional Analysis of Skin and Subcutaneous Toxicity. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan) (2019) 26(3):290–304. doi: 10.1007/s12282-018-0923-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Kawaguchi H, Tsujino K, Miki M, Matsumoto Y, Ota Y, Hirokaga K, et al. Patient Preference Study Comparing Hypofractionated Versus Conventionally Fractionated Whole-Breast Irradiation After Breast-Conserving Surgery. Japanese J Clin Oncol (2019) 49(6):545–53. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Yap ML, Tieu M, Sappiatzer J, Panzarella T, Cuartero J, McCready D, et al. Outcomes in Patients Treated With Post-Mastectomy Chest Wall Radiotherapy Without the Routine Use of Bolus. Clin Oncol (Royal Coll Radiologists (Great Britain)) (2018) 30(7):427–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2018.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Rastogi K, Jain S, Bhatnagar AR, Bhaskar S, Gupta S. Sharma N. A Comparative Study of Hypofractionated and Conventional Radiotherapy in Postmastectomy Breast Cancer Patients. Asia-Pacific J Oncol Nurs (2018) 5(1):107–13. doi: 10.4103/apjon.apjon_46_17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Parekh A, Dholakia AD, Zabranksy DJ, Asrari F, Camp M, Habibi M, et al. Predictors of Radiation-Induced Acute Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer at a Single Institution: Role of Fractionation and Treatment Volume. Adv Radiat Oncol (2018) 3(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2017.10.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Lin JC, Tsai JT, Chou YC, Li MH, Liu WH. Compared With Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Image-Guided Radiotherapy Reduces Severity of Acute Radiation-Induced Skin Toxicity During Radiotherapy in Patients With Breast Cancer. Cancer Med (2018) 7(8):3622–9. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Guttmann DM, Gabriel P, Kennedy C, Rate W, Grizos W, Nagda S, et al. Comparison of Acute Toxicities Between Contemporary Forward-Planned 3D Conformal Radiotherapy and Inverse-Planned Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Whole Breast Radiation. Breast J (2018) 24(2):128–32. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12857 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Akl FFM, Khater A. Hypofractionated Versus Conventionally Fractionated Radiotherapy in Post-Mastectomy Breast Cancer Patients. J Cancer Ther (2018) 09(11):941–54. doi: 10.4236/jct.2018.911078 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33. De Santis MC, Bonfantini F, Di Salvo F, Fiorentino A, Riboldi VM, Di Cosimo S, et al. Trastuzumab and Hypofractionated Whole Breast Radiotherapy: A Victorious Combination? Clin Breast Cancer (2018) 18(3):e363–71. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.08.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Das P, Das T, Jana A, Gupta P, Gupta P, Das S. Comparison of Result and Outcome of Conventional and Hypofractionated Radiotherapy in Post-Operative Breast Cancer Patients. Int J Med Sci Public Health (2018) 7(6):452–6. doi: 10.5455/ijmsph.2018.0102010032018 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35. De Felice F, Ranalli T, Musio D, Lisi R, Rea F, Caiazzo R, et al. Relation Between Hypofractionated Radiotherapy, Toxicity and Outcome in Early Breast Cancer. Breast J (2017) 23(5):563–8. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Aoulad N, Massabeau C, de Lafontan B, Vieillevigne L, Hangard G, Ciprian C, et al. Acute Toxicity of Breast Cancer Irradiation With Modulated Intensity by Tomotherapy. Cancer Radiotherapie J la Societe Francaise Radiotherapie Oncologique (2017) 21(3):180–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2016.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wright JL, Takita C, Reis IM, Zhao W, Lee E, Nelson OL, et al. Prospective Evaluation of Radiation-Induced Skin Toxicity in a Race/Ethnically Diverse Breast Cancer Population. Cancer Med (2016) 5(3):454–64. doi: 10.1002/cam4.608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Linares I, Tovar MI, Zurita M, Guerrero R, Expósito M, Del Moral R. Hypofractionated Breast Radiation: Shorter Scheme, Lower Toxicity. Clin Breast Cancer (2016) 16(4):262–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2015.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Córdoba EE, Abba MC, Lacunza E, Fernánde E, Güerci AM. Polymorphic Variants in Oxidative Stress Genes and Acute Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat (2016) 48(3):948–54. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Zhang SK, Chen G. Analysis of Risk Factors of Incidence of Radiation Dermatitis on Chest Wall of Patients Underwent Postmastectomy Radiotherapy. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Med Sci) (2015) 35(7):1034–9. [Google Scholar]
- 41. Pignol JP, Vu TT, Mitera G, Bosnic S, Verkooijen HM, Truong P. Prospective Evaluation of Severe Skin Toxicity and Pain During Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2015) 91(1):157–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.09.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Jagsi R, Griffith KA, Boike TP, Walker E, Nurushev T, Grills IS, et al. Differences in the Acute Toxic Effects of Breast Radiotherapy by Fractionation Schedule: Comparative Analysis of Physician-Assessed and Patient-Reported Outcomes in a Large Multicenter Cohort. JAMA Oncol (2015) 1(7):918–30. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.2590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Wright JL, Takita C, Reis IM, Zhao W, Lee E, Hu JJ. Racial Variations in Radiation-Induced Skin Toxicity Severity: Data From a Prospective Cohort Receiving Postmastectomy Radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2014) 90(2):335–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.06.042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Park H, Choi DH, Noh JM, Huh SJ, Park W, Nam SJ, et al. Acute Skin Toxicity in Korean Breast Cancer Patients Carrying BRCA Mutations. Int J Radiat Biol (2014) 90(1):90–4. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.835504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. De Langhe S, Mulliez T, Veldeman L, Remouchamps V, van Greveling A, Gilsoul M, et al. Factors Modifying the Risk for Developing Acute Skin Toxicity After Whole-Breast Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy. BMC Cancer (2014) 14:711. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Ciammella P, Podgornii A, Galeandro M, Micera R, Ramundo D, Palmieri T, et al. Toxicity and Cosmetic Outcome of Hypofractionated Whole-Breast Radiotherapy: Predictive Clinical and Dosimetric Factors. Radiat Oncol (London England) (2014) 9:97. doi: 10.1186/1748-717x-9-97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Tortorelli G, Di Murro L, Barbarino R, Cicchetti S, di Cristino D, Falco MD, et al. Standard or Hypofractionated Radiotherapy in the Postoperative Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis of Acute Skin Toxicity and Dose Inhomogeneities. BMC Cancer (2013) 13:230. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Sharp L, Johansson H, Hatschek T, Bergenmar M. Smoking as an Independent Risk Factor for Severe Skin Reactions Due to Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer. Breast (Edinburgh Scotland) (2013) 22(5):634–8. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Terrazzino S, La Mattina P, Masini L, Caltavuturo T, Gambaro G, Canonico PL, et al. Common Variants of eNOS and XRCC1 Genes may Predict Acute Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy After Breast Conserving Surgery. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol (2012) 103(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2011.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Morganti AG, Cilla S, Valentini V, Digesu C, Macchia G, Deodato F, et al. Phase I-II Studies on Accelerated IMRT in Breast Carcinoma: Technical Comparison and Acute Toxicity in 332 Patients. Radiother Oncol (2009) 90(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2008.10.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Freedman GM, Li T, Nicolaou N, Chen Y, Ma CCM, Anderson PR. Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Reduces Time Spent With Acute Dermatitis for Women of All Breast Sizes During Radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2009) 74(3):689–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Pignol JP, Olivotto I, Rakovitch E, Gardner S, Sixel K, Beckham W, et al. A Multicenter Randomized Trial of Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy to Reduce Acute Radiation Dermatitis. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol (2008) 26(13):2085–92. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Back M, Guerrieri M, Wratten C, Steigler A. Impact of Radiation Therapy on Acute Toxicity in Breast Conservation Therapy for Early Breast Cancer. Clin Oncol (Royal Coll Radiologists (Great Britain)) (2004) 16(1):12–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2003.08.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Haviland JS, Owen JR, Dewar JA, Agrawal RK, Barrett J, Barrett-Lee PJ, et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) Trials of Radiotherapy Hypofractionation for Treatment of Early Breast Cancer: 10-Year Follow-Up Results of Two Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet Oncol (2013) 14(11):1086–94. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70386-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Hopwood P, Haviland JS, Sumo G, Mills J, Bliss JM, Yarnold JR. Comparison of Patient-Reported Breast, Arm, and Shoulder Symptoms and Body Image After Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: 5-Year Follow-Up in the Randomised Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) Trials. Lancet Oncol (2010) 11(3):231–40. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70382-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bentzen SM, Agrawal RK, Aird EG, Barrett JM, Barrett-Lee PJ, Bliss JM, et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) Trial A of Radiotherapy Hypofractionation for Treatment of Early Breast Cancer: A Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol (2008) 9(4):331–41. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70077-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Bentzen SM, Agrawal RK, Aird EG, Barrett JM, Barrett-Lee PJ, Bentzen SM, et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) Trial B of Radiotherapy Hypofractionation for Treatment of Early Breast Cancer: A Randomised Trial. Lancet (2008) 371(9618):1098–107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60348-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Liu L, Yang Y, Guo Q, Ren B, Peng Q, Zou L, et al. Comparing Hypofractionated to Conventional Fractionated Radiotherapy in Postmastectomy Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Radiat Oncol (London England) (2020) 15(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-1463-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Andrade TRM, Fonseca MCM, Segreto HRC, Segreto RA, Martella E, Nazário ACP. Meta-Analysis of Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Hypofractionated Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Early Breast Cancer. Breast (Edinburgh Scotland) (2019) 48:24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Karasawa K, Kunogi H, Hirai T, Hojo H, Hirowatari H, Izawa H, et al. Comparison of Hypofractionated and Conventionally Fractionated Whole-Breast Irradiation for Early Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Institute Study of 1,098 Patients. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan) (2014) 21(4):402–8. doi: 10.1007/s12282-012-0406-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Greenup RA, Camp MS, Taghian AG, Buckley J, Coopey SB, Gadd M, et al. Cost Comparison of Radiation Treatment Options After Lumpectomy for Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol (2012) 19(10):3275–81. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2546-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. NICE . Early and Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Diagnosis and Management (2018). Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng101/chapter/Recommendations#radiotherapy.
- 63. Hamilton DG, Bale R, Jones C, Fitzgerald E, Khor R, Knight K, et al. Impact of Tumour Bed Boost Integration on Acute and Late Toxicity in Patients With Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Breast (Edinburgh Scotland) (2016) 27:126–35. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Franco P, Cante D, Sciacero P, Girelli G, La Porta MR, Ricardi U. Tumor Bed Boost Integration During Whole Breast Radiotherapy: A Review of the Current Evidence. Breast Care (Basel Switzerland) (2015) 10(1):44–9. doi: 10.1159/000369845 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. RTOG . Higher Per Daily Treatment-Dose Radiation Therapy or Standard Per Daily Treatment Radiation Therapy in Treating Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer That was Removed by Surgery (2011). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01349322.
- 66. Chen MF, Chen WC, Lai CH, Hung CH, Liu KC, Cheng YH. Predictive Factors of Radiation-Induced Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients. BMC Cancer (2010) 10:508. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-508 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Harsolia A, Kestin L, Grills I, Wallace M, Jolly S, Jones C, et al. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Results in Significant Decrease in Clinical Toxicities Compared With Conventional Wedge-Based Breast Radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2007) 68(5):1375–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.02.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Steele JR, Coltman CE, McGhee DE. Effects of Obesity on Breast Size, Thoracic Spine Structure and Function, Upper Torso Musculoskeletal Pain and Physical Activity in Women. J Sport Health Sci (2020) 9(2):140–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2019.05.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Barnett GC, Wilkinson JS, Moody AM, Wilson CB, Twyman N, Wishart GC, et al. The Cambridge Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Trial: Patient- and Treatment-Related Factors That Influence Late Toxicity. Clin Oncol (Royal Coll Radiologists (Great Britain)) (2011) 23(10):662–73. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2011.04.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Huang CJ, Hou MF, Luo KH, Wei SY, Huang MY, Su SJ, et al. RTOG, CTCAE and WHO Criteria for Acute Radiation Dermatitis Correlate With Cutaneous Blood Flow Measurements. Breast (Edinburgh Scotland) (2015) 24(3):230–6. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Dayes I, Rumble RB, Bowen J, Dixon P, Warde P. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Clin Oncol (Royal Coll Radiologists (Great Britain)) (2012) 24(7):488–98. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2012.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Barnett GC, Wilkinson JS, Moody AM, Wilson CB, Twyman N, Wishart GC, et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of Forward-Planned Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: Interim Results at 2 Years. Int J Radiat oncol biol Phys (2012) 82(2):715–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Lee E, Eum SY, Slifer SH, Martin ER, Takita C, Wright JL, et al. Association Between Polymorphisms in DNA Damage Repair Genes and Radiation Therapy–Induced Early Adverse Skin Reactions in a Breast Cancer Population: A Polygenic Risk Score Approach. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2020) 106(5):948–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Mumbrekar KD, Bola Sadashiva SR, Kabekkodu SP, Fernandes DJ, Vadhiraja BM, Suga T, et al. Genetic Variants in CD44 and MAT1A Confer Susceptibility to Acute Skin Reaction in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2017) 97(1):118–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.09.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Kerns SL, Ostrer H, Rosenstein BS. Radiogenomics: Using Genetics to Identify Cancer Patients at Risk for Development of Adverse Effects Following Radiotherapy. Cancer Discovery (2014) 4(2):155–65. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-13-0197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Tanteles GA, Murray RJ, Mills J, Barwell J, Chakraborti P, Chan S, et al. Variation in Telangiectasia Predisposing Genes Is Associated With Overall Radiation Toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2012) 84(4):1031–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Hu JJ, Urbanic JJ, Case LD, Takita C, Wright JL, Brown DR, et al. Association Between Inflammatory Biomarker C-Reactive Protein and Radiotherapy-Induced Early Adverse Skin Reactions in a Multiracial/Ethnic Breast Cancer Population. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol (2018) 36(24):2473–82. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.77.1790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Begg’s funnel plot of patients-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Age; (B) BMI; (C) breast volume; (D) smoking.
Begg’s funnel plot of treatment-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) boost; (B) hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT) vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT); (C) chemotherapy regimen; (D) hormone therapy.
Sensitivity analysis of the effect of patients-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) Age; (B) BMI; (C) breast volume; (D) smoking.
Sensitivity analysis of the effect of treatment-related risk factors associated with acute radiation dermatitis. (A) boost; (B) hypofractionated radiotherapy (HFRT) vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT); (C) chemotherapy regimen; (D) hormone therapy.
The PRISMA 2020 checklist.
The search strategy.
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) or The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) toxicity scales for acute radiation dermatitis.
Quality assessment of eligible studies by Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS).
Results of individual studies: summary statistics for each group and an effect estimate.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.