SUMMARY
Objective
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic inflammatory disease. There are no markers that can be used to identify the risk of a malignant transformation of OLP to oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods
Immunohistochemical staining was performed among 56 patients with OLP and 66 patients with OSCC for p53, HSP90 and E-cadherin expression and presence of HPV16/18.
Results
Significant differences in p53 and HSP90 expression between OLP and OSCC were found (p = 0.01 and p = 0.006, respectively). A positive correlation between HSP90 and p53 expression was seen in OLP (p = 0.017). Univariate analysis identified HSP90 expression and HPV16/18 presence as prognostic factors for overall survival time (OS) (p < 0.05). In multivariate analysis, only HSP90 expression was an independent prediction factor for shorter OS of OSCC patients (p = 0.016).
Conclusions
The present study suggests that cooperation between p53 and HSP90 as well as between HPV16/18 and HSP90 exists in OLP and may affect the biological behaviour of OLP. The observed expression of HSP90 and p53 in OLP and their increase in OSCC suggests that these proteins participate in the malignant transformation of OLP. HSP90 may be a potential independent prognostic biomarker that can predict poor prognosis in OSCC.
KEY WORDS: OLP, OSCC, biomarkers, HPV, immunohistochemistry
RIASSUNTO
Obiettivo
Il lichen planus orale (OLP) è una malattia cronica infiammatoria. Non ci sono marcatori predittivi del rischio di trasformazione di OLP nel carcinoma a cellule squamose del cavo orale (OSCC).
Metodi
Con il metodo immunoistochimico è stata valutata la presenza di p53, HSP90, E-caderina, HPV in 56 pazienti affetti da OLP e 66 da OSCC.
Risultati
Sono state rilevate le differenze, statisticamente significative, nell’occorrenza di p53 e HSP90 nell’OLP e OSCC (p = 0,01; p = 0,006; rispettivamente). La correlazione positiva tra l’occorrenza di HSP90 e p53 è stata notata in OLP (p = 0,017). L’analisi monovariata ha evidenziato che HSP90 e HPV costituiscono i fattori prognostici per il tempo di sopravvivenza dei malati (OS) di OSCC (p < 0,05). L’analisi multivariata ha evidenziato che HSP90 è un fattore prognostico indipendente correlato ad una OS più breve negli OSCC (p = 0,016).
Conclusioni
Questo studio suggerisce che esiste una correlazione fra interazione di p53 e HSP90 e di HSP90 ed HPV ed il comportamento biologico di OLP. L’accertamento della presenza di p53 e HSP90 in OLP e l’aumento della loro espressione in OSCC indica che queste proteine possono partecipare al processo di trasformazione di OLP. I rapporti evidenziati tra la presenza di HSP90 e il tempo di OS di OSCC indica che HSP90 è un fattore prognostico indipendente in OSCC.
PAROLE CHIAVE: OLP, OSCC, biomarcatori, HPV, immunoistochimica
Introduction
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic disorder that affects the oral mucosa of 1-2% of adult population 1,2. The lesions appear symmetrically and bilaterally, and are white or red-white in colour. There are five subtypes of OLP lesions, i.e., reticular, plaque, atrophic, erosive, and bullous 3. The aetiology and pathogenesis of OLP is still unclear and has not been fully explained 3,4. There are conflicting data concerning the rate of OLP malignant transformation into oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), which is estimated at 0.4-5.0% over a four-to-five-year period 3,5,6. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the mechanism of malignant transformation of OLP 3,6. A potential mechanism leading to the neoplastic transformation of OLP is associated with the genetic mutation or overexpression of the p53 protein, heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and E-cadherin 1,4,6-8. It was found that human papillomavirus 16 and 18 (HPV16/18) infection in OLP may increase the risk of the malignant transformation to OSCC 5. There are no prognostic biomarkers that can identify OLP lesions with a high risk of developing into malignant lesions 4. Some biomarkers expressed in OSCC can also be observed in OLP 1,2,4,6,7. One such biomarker is the p53 protein, which plays an important role in cell cycle control and apoptosis 1,2,4. The loss of the suppressive function of the p53 protein due to a mutation in the TP53 gene leads to abnormal cell proliferation, resulting in the development of cancer 2,4,9. It was found that p53 overexpression was associated with an increased risk of OLP malignancy 1,3,9,10. E-cadherin and HSP90, which are frequently observed in oral carcinoma, are also present in the OLP tissue, but their role is unknown 11,12. E-cadherin is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily found in human and animal epithelial cells; the mediated junctions between cells play an important role in tumorigenesis and the invasion of tumor cells 10,12. Studies revealed that E-cadherin may be associated with the pathological features and biological behaviour of tumours 12. The downregulation of mRNA E-cadherin levels in OSCC suggests that it is likely to be an early factor in tumour growth 13. Only a few studies concerning E-cadherin expression in OLP have been published 6,12. The focal loss of E-cadherin expression in OLP lesions may increase their growth and cause malignancy 8,12. HSP90 is a molecular chaperone that is crucial for cell growth, communication, protein degradation and signal transduction 11. Some studies note that HSP90 may be involved in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory process, which can be observed in OLP 8,11. It was suggested that HSP90 overexpression in OLP may be associated with the persistence or chronicity of the disease 11. Significantly higher HSP90 expression in OSCC samples, in comparison to the normal epithelium tissue, suggests their potential as prognostic biomarkers 8,14. Some researchers have found a strong correlation between HPV16/18 infection and oral premalignant lesions, particularly in OLP 15. However, epidemiologic studies on HPV infection in OSCC and OLP have shown some discrepancies 5,16. The prevalence of HPV in OLP has been reported to range from 0.5 to 2.5%, depending on the geographic location 16. The risk of progression to malignancy was approximately 0.5% for non-erosive OLP, compared to at least 3.5-4.0% for erosive OLP over similar follow-up periods 16. Recent data suggest that HPV is a risk factor for OSCC development, especially OSCC occurring in the oropharynx, which includes the base of the tongue and tonsils 17,18. To understand the biological behaviour of OLP and its transformation into a malignant lesion, a comparative analysis of molecular changes in both OLP and OSCC is needed. As of today, there are no studies analysing the relationship between the presence of p53, E-cadherin, HSP90 and HPV in OLP and OSCC lesions to determine their impact on the possibility of an OLP malignant transformation. We assumed that a comparison of p53, HSP90 and E-cadherin expression and HPV16/18 presence in precancerous and cancerous lesions would allow us to discover their role in the risk of OSCC development.
The study aimed to assess p53 protein, HSP90 and E-cadherin expression and presence of HPV16/18 in two subtypes of OLP in comparison to their expression in OSCC to reveal the role of these proteins in the progressive growth of OLP and OSCC as part of an analysis of their clinical behaviour.
Materials and methods
Patients
Fifty-six patients with OLP and 66 patients with OSCC took part in the study between 2012 and 2017. Biopsy specimens of OLP and surgical specimens of OSCC were obtained from the Department of Pathomorphology and Oncological Cytology of the Wroclaw Medical University, Poland. Tissue specimens were formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded. The OLP group consisted of 21 men and 35 women, whereas the OSCC group consisted of 44 men and 22 women. OLP biopsy specimens were verified histopathologically. The fifty-six samples of two subtypes of OLP included 43 cases of reticular OLP and 13 cases of erosive OLP. Five-micron sections from paraffin blocks were prepared and stained using haematoxylin-eosin. Microscopic slides were examined to verify the subtype of oral OLP (reticular and erosive). The tissue specimens were classified as the reticular subtype, with clinical characteristics of Wickham striae without atrophic-erosive areas and with specific histological features, e.g., the hydropic degeneration of basal cells. The tissue samples were classified as the erosive subtype, with the clinical characteristic of Wickham striae at the periphery with the presence of atrophic-erosive areas and apparent hydropic degeneration of basal cells. Sixty-six tissue samples of primary OSCC collected from the tongue, the floor of the mouth, and buccal mucosa were included in the study. Tissue specimens from the primary OSCC were histologically verified to confirm the diagnosis, histological type and tumour grade. The clinicopathological features of patients with OLP and patients with OSCC are presented in Table I. Approval of the Ethics Committee of Wroclaw Medical University to perform this study was obtained (decision number KB230/2016).
Table I.
Clinicopathological parameters of patients with oral lichen planus (OLP) and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
| Parameter | OLP n = 56 (%) |
OSCC n = 66 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| < 60 years | 17 (30.4) | 24 (36.4) |
| ≥ 60 years | 39 (69.6) | 42 (63.6) |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 35 (62.5) | 22 (33.3) |
| Male | 21 (37.5) | 44 (66.7) |
| Duration | ||
| ≤ 37 months | 37 (66.0) | - |
| > 37 months | 19 (34.0) | - |
| Clinical type | ||
| Reticular | 43 (76.8) | - |
| Erosive | 13 (23.2) | - |
| Tumour grade | ||
| G1 | - | 23 (34.9) |
| G2 | - | 35 (53.0) |
| G3 | - | 8 (12.1) |
| Tumour site | ||
| Tongue | - | 30 (45.5) |
| Floor of the mouth | - | 18 (27.3) |
| Buccal mucosa | 27 (48.2) | 18 (27.3) |
| General involvement | 25 (44.6) | - |
| Other | 4 (7.2) | - |
| T classification | ||
| T1/T2 | - | 29 (43.9) |
| T3/T4 | - | 37 (56.1) |
| N classification | ||
| N0 | - | 37 (56.1) |
| N1/N2/N3 | - | 29 (43.9) |
| Clinical stage | ||
| I/II | - | 21 (32.0) |
| III/IV | - | 45 (68.0) |
| Survival | ||
| Alive | - | 20 (30.0) |
| Dead | - | 46 (70.0) |
Antibodies
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using the following antibodies: mouse monoclonal antibody DO-7 (clone DO-7), which reacts with both wild- and mutant-type of the unphosphorylated human p53 protein (Novocastra, Newcastle, UK), anti-HSP90 protein which recognises the protein corresponding to the 306 amino acids of the C-terminus of the HSP90 molecule (clone JPB24, Novocastra), anti-human cadherin (clone NCH-38) which recognises the 120 kD mature form of E-cadherin (Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) and anti-HPV16 E6 + HVP18 E6 [C1P5] which reacts with the E6 protein (Abcam, USA).
Immunohistochemical staining (IHC)
Proteins were stained immunohistochemically on paraffin-embedded OLP and OSCC tissue specimens using the Universal Dako REAL EnVision Detection System, Peroxidase/DAB+, Rabbit/Mouse (Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. OLP and OSCC specimens were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. After washing of specimens with 0.1 M Tris buffer, pH = 7.4 (TBS), they were incubated with Dako REAL EnVision/HRP, Rabbit/Mouse (Dako) for 30 minutes at room temperature. The antigen-antibody reaction was visualised with DAB (3,3-diaminobenzidine) (Dako) as a chromogen. The sections were counterstained with haematoxylin and mounted. The incubation buffer (TBS) without the primary antibodies was used as a negative control. Positive controls for each antibody were performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Interpretation of immunohistochemical staining
Protein expression in OLP and OSCC tissues was assessed semiquantitatively, taking into account the intensity of immunostaining and the number of cells showing immunoreactivity for the analysed proteins. The number of cells exhibiting staining for p53 protein and HPV16/18 was assessed by counting 1000 cells in 10-15 randomly selected high-power fields. The proportion of p53 and HPV16/18 positive cells in tissue was assessed as follows: 0 = (0-10%), 1 = (> 10-30%), 2 = (31-50%), 3 = (> 50%).
E-cadherin and HSP90 expression was analysed based on the intensity of membrane or cytoplasmic immunostaining and the percentage of stained tumour cells. The frequency of E-cadherin and HSP90 positive cells in tissue areas was scored as follows: 0% (no reaction-10%), 1 = (> 10-25%), 2 = (26-60%), 3 = (> 61%). The colour of the IHC stain was used to evaluate its intensity as follows: negative (-, no colour), weak (+, light brown colour), moderate (++, dark brown colour), and strong (+++, very dark brown colour). In cases where no immunostaining or variable weak positivity occurred, negative scores were given for all protein expressions (< 10% of cells).
Statistical analysis
In all statistical analyses, p53, HPV16/18, E-cadherin and HSP90 immunoreactivity was divided into two groups: negative or limited to 10% of tumour cells versus > 10% of positive cells. Associations between p53, HSP90, E-cadherin, and HPV16/18 expression and clinicopathological parameters were evaluated using the Chi2, Mann-Whitney, and Kruskal-Wallis tests. Correlations between proteins were analysed using Spearman’s rank correlation. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the number of months from surgery until death of patients with OSCC. Cox-regression analyses were used to identify prognostic factors for OSCC patients. Differences were considered significant for p < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using the STATISTICA v13.0 software (Statsoft, Krakow, Poland).
Results
HSP90, p53 protein and E-cadherin expression and HPV 16/18 infection in OLP and OSCC
As shown in Table II, in OLP specimens HSP90, p53 protein and E-cadherin expression and HPV type 16/18 were observed in 28/56 (50.0%), 18/56 (32.1%), 35/56 (62.5%) and 4/56 (7.1%) cases, respectively. A higher number of cells stained for p53 and HSP90 was observed in erosive OLP (expression of p53, 20-50%, and HSP90, 20-70%, of the positive tissue) compared to non-erosive OLP (expression of p53, 10-15%, HSP90, 10-50%, of the positive tissue). Percentage of E-cadherin staining was similar (10-50% of the positive tissue) in both OLP types. Conversely, HPV16/18 was limited to small (10-15%) tissue areas (Fig. 1A-H). OSCC specimens revealed HSP90, p53 protein and E-cadherin expression and HPV type 16/18 in 49/66 (74.2%), 30/66 (45.5%), 42/66 (63.6%) and 11/66 (16.7%) cases, respectively (Tab. III). A marked heterogeneity of protein expression was observed in OLP and OSCC. HSP90, p53 and E-cadherin expression in OSCC was stronger (10-90% of positive tissue) than in OLP specimens (10-60% of the positive tissue) (Fig. 1A-D). In the majority of OSCC samples, HPV16/18 was restricted to 10-20% of tumour cells, but in some individual cases, HPV16/18 was found in 30-40% of the OSCC tissue (Fig. 1G-H). A comparative analysis of OLP and OSCC for the expression of p53 and HSP90 proteins and HPV16/18 presence between OLP and OSCC specimens revealed differences. A significant increase in HSP90 and p53 expression was observed in OSCC compared to OLP lesions (p = 0.006; p = 0.01, respectively) (Fig. 2). A positive correlation between HSP90 and p53 expression (p = 0.017) and a low positive correlation tendency between HSP90 and HPV16/18 expression was found in OLP (p = 0.088, Tab. IV). No significant association between the biomarkers analysed and HPV16/18 infection was found in OSCC samples (p > 0.05, Tab. IV).
Table II.
Correlation between clinicopathological parameters and immunoreactivity for HSP90, p53, E-cadherin and HPV in oral lichen planus.
| Parameter | HSP90, n (%) | p53, n (%) | E-cadherin, n (%) | HPV16/18, n (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | |
| Age | ||||||||||||
| < 60 years | 9 (52.9) |
8 (47.1) |
0.771a | 13 (76.5) |
4 (23.5) |
0.362a | 6 (35.3) |
11 (64.7) |
0.822a | 17 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) |
0.171a |
| ≥ 60 years | 19 (48.7) |
20 (51.3) |
25 (64.1) |
14 (35.9) |
15 (38.5) |
24 (61.5) |
35 (89.7) |
4 (10.3) |
||||
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Female | 15 (42.9) |
20 (57.1) |
0.084b | 21 (60.0) |
14 (40.0) |
0.104a | 16 (45.7) |
19 (54.2) |
0.036 b | 31 (88.6) |
4 (11.4) |
0.108a |
| Male | 13 (61.9) |
8 (38.9) |
17 (81.0) |
4 (19.0) |
5 (23.8) |
16 (76.2) |
21 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) |
||||
| Duration | ||||||||||||
| ≤ 37 months | 23 (62.2) |
14 (37.8) |
0.011 a | 26 (70.3) |
11 (29.7) |
0.589a | 18 (48.6) |
19 (51.4) |
0.016 a | 36 (97.3) |
1 (2.7) |
0.072a |
| > 37 months | 5 (26.3) |
14 (73.7) |
12 (63.2) |
7 (36.8) |
3 (15.8) |
16 (84.2) |
16 (84.2) |
3 (15.8) |
||||
| Tumour site | ||||||||||||
| Buccal mucosa |
12 (44.4) |
15 (55.6) |
0.503a | 22 (81.5) |
5 (18.5) |
0.025 c | 13 (48.1) |
14 (51.9) |
0.282a | 26 (96.3) |
1 (3.7) |
0.432a |
| General involvement |
13 (52.0) |
12 (48.0) |
13 (52.0) |
12 (48.0) |
7 (28.0) |
18 (72.0) |
22 (88.0) |
3 (12.0) |
||||
| Other | 3 (75.0) |
1 (25.0) |
3 (75.0) |
1 (25.0) |
1 (25.0) |
3 (75.0) |
4 (100.0) |
0 (0.0) |
||||
| Clinical type | ||||||||||||
| White striae | 21 (48.8) |
22 (51.2) |
0.752a | 27 (62.8) |
16 (37.2) |
0.140a | 18 (41.9) |
25 (58.1) |
0.220a | 40 (93.0) |
3 (7.0) |
0.930a |
| Erosive | 7 (53.8) |
6 (46.2) |
11 (84.6) |
2 (15.4) |
3 (23.1) |
10 (76.9) |
12 (92.3) |
1 (7.7) |
||||
| Total OLP | 28 (50.0) | 28 (50.0) | 38 (67.9) | 18 (32.1) | 21 (37.5) | 35 (62.5) | 52 (92.9) | 4 (7.1) | ||||
a Chi-square test;
b Mann-Whitney U-test;
c Kruskal-Wallis test.
Bold values indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05).
Figure 1.
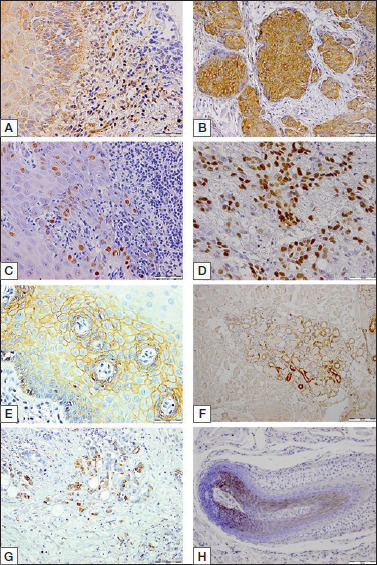
Representative immunostaining of HSP90, p53, E-cadherin and presence of HPV16/18 in OLP and OSCC cases. (A) HSP90 cytoplasmic immunostaining observed in basal and superbasal epithelial cells of OLP; (B) HSP90 membrane/cytoplasmic strong immunostaining observed in a high percentage of the OSCC tissue; (C) p53 protein expression limited to small OLP tissue areas; (D) a high number of cells showed strong p53 expression in the OSCC tissue; (E) membrane/diffuse E-cadherin expression in superficial and deep layers of the epithelial tissue of OLP; (F) low E-cadherin expression restricted to a small tissue area of OSCC; (G) HPV16/18 infection detected in a low number of cell nuclei in OLP; (H) HPV16/18 presence in malignant cells forming gland in OSCC tissue (EnVision technique). Figure 1A,C,D,E,F scale bar = 50 μm, Figure 1B,G,H scale bar = 100 μm.
Table III.
Correlation between clinicopathological parameters and immunoreactivity for HSP90, p53, E-cadherin and HPV in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
| Parameter | HSP90, n (%) | p53, n (%) | E-cadherin, n (%) | HPV16/18, n (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | Negative | Positive | p-value | |
| Age | ||||||||||||
| < 60 years | 6 (25.0) |
18 (75.0) |
0.915a | 15 (62.5) |
9 (37.5) |
0.327a | 8 (33.3) |
16 (66.7) |
0.699a | 19 (79.2) |
5 (20.8) |
0.492a |
| ≥ 60 years | 11 (26.2) |
31 (73.8) |
21 (50.0) |
21 (50.0) |
16 (38.1) |
26 (61.9) |
36 (85.7) |
6 (14.3) |
||||
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Female | 7 (31.8) |
15 (68.2) |
0.426a | 14 (63.6) |
8 (36.4) |
0.294a | 8 (36.4) |
14 (63.6) |
1.000a | 19 (86.4) |
3 (13.6) |
0.640a |
| Male | 10 (22.7) |
34 (77.3) |
22 (50.0) |
22 (50.0) |
16 (36.4) |
28 (63.6) |
36 (81.8) |
8 (18.2) |
||||
| Tumour grade | ||||||||||||
| G1 | 6 (26.1) |
17 (73.9) |
0.186a | 15 (65.2) |
8 (34.8) |
0.032 a | 8 (34.8) |
15 (65.2) |
0.268a | 21 (91.3) |
2 (8.7) |
0.347a |
| G2 | 11 (31.4) |
24 (68.6) |
20 (57.1) |
15 (42.9) |
15 (42.9) |
20 (57.1) |
27 (77.1) |
8 (22.9) |
||||
| G3 | 0 (0.0) |
8 (100.0) |
1 (12.5) |
7 (87.5) |
1 (12.5) |
7 (87.5) |
7 (87.5) |
1 (12.5) |
||||
| Tumour site | ||||||||||||
| Tongue | 8 (26.7) |
22 (73.3) |
0.919a | 13 (43.3) |
17 (56.7) |
0.234a | 10 (33.3) |
20 (66.7) |
0.897a | 26 (86.7) |
4 (13.3) |
0.726a |
| Floor of the mouth | 4 (22.2) |
14 (77.8) |
12 (66.7) |
6 (33.3) |
7 (38.9) |
11 (61.1) |
14 (77.8) |
4 (22.2) |
||||
| Buccal mucosa | 5 (27.8) |
13 (72.2) |
11 (61.1) |
7 (38.9) |
7 (38.9) |
11 (61.1) |
15 (83.3) |
3 (16.7) |
||||
| T classification | ||||||||||||
| T1/T2 | 11 (37.9) |
18 (62.1) |
0.045 a | 17 (58.6) |
12 (41.4) |
0.556a | 10 (34.5) |
19 (65.5) |
0.779a | 27 (93.1) |
2 (6.9) |
0.059a |
| T3/T4 | 6 (16.2) |
31 (83.8) |
19 (51.4) |
18 (48.6) |
14 (37.8) |
23 (62.2) |
28 (75.7) |
9 (24.3) |
||||
| N classification | ||||||||||||
| N0 | 7 (18.9) |
30 (81.1) |
0.151a | 20 (54.1) |
17 (45.9) |
0.928a | 10 (27.0) |
27 (73.0) |
0.043 b | 34 (91.9) |
3 (8.1) |
0.035 a |
| N1/N2/N3 | 10 (34.5) |
19 (65.5) |
16 (55.2) |
13 (44.8) |
14 (48.2) |
15 (51.7) |
21 (72.4) |
8 (27.6) |
||||
| Clinical stage | ||||||||||||
| I/II | 7 (33.3) |
14 (66.7) |
0.067b | 13 (61.9) |
8 (38.1) |
0.412a | 6 (28.6) |
15 (71.4) |
0.369a | 19 (90.5) |
2 (9.5) |
0.288a |
| III/IV | 10 (22.2) |
35 (77.8) |
23 (51.1) |
22 (48.9) |
18 (40.0) |
27 (60.0) |
36 (80.0) |
9 (20.0) |
||||
| Survival | ||||||||||||
| Alive | 9 (45.0) |
11 (55.0) |
0.018 a | 12 (60.0) |
8 (40.0) |
0.558a | 6 (30.0) |
14 (70.0) |
0.479a | 19 (95.0) |
1 (5.0) |
0.089b |
| Dead | 8 (17.4) |
38 (82.6) |
24 (52.2) |
22 (47.8) |
18 (39.1) |
28 (60.9) |
36 (78.3) |
10 (21.7) |
||||
| Total OSCC | 17 (25.8) |
49 (74.2) |
36 (54.5) |
30 (45.5) |
24 (36.4) |
42 (63.6) |
55 (83.3) |
11 (16.7) |
||||
a Chi-square test;
b Mann-Whitney U-test;
Bold values indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05).
Figure 2.
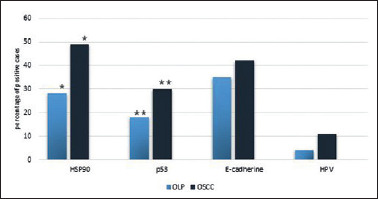
Comparison of HSP90 and p53 protein expression in OLP and OSCC. Significant differences in HSP90 and p53 expression between OLP and OSCC were found (*p = 0.006 and **p = 0.01, respectively).
Table IV.
Spearman’s rank correlation between immunoreactivity for HSP90, p53, E-cadherin and HPV in oral lichen planus (OLP) and oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC).
| OLP | HSP90 | p53 | E-cadherin | HPV16/18 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-value | r | p-value | r | p-value | r | p-value | |
| HSP90 | 0.318 | 0.017 | 0.184 | 0.175 | 0.230 | 0.088 | ||
| p53 | 0.318 | 0.017 | 0.068 | 0.618 | 0.197 | 0.146 | ||
| E-cadherin | 0.184 | 0.175 | 0.068 | 0.618 | 0.156 | 0.254 | ||
| HPV16/18 | 0.230 | 0.088 | 0.197 | 0.146 | 0.156 | 0.254 | ||
| OSCC | ||||||||
| HSP90 | 0.095 | 0.449 | 0.181 | 0.146 | -0.116 | 0.352 | ||
| p53 | 0.095 | 0.449 | 0.100 | 0.423 | 0.117 | 0.350 | ||
| E-cadherin | 0.181 | 0.146 | 0.100 | 0.423 | -0.120 | 0.337 | ||
| HPV16/18 | -0.116 | 0.352 | 0.117 | 0.350 | -0.120 | 0.337 | ||
Bold values indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05). r: Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient.
Clinicopathological features correlated to HSP90, p53, E-cadherin and HPV16/18 expression in OLP and OSCC
The relation between clinical parameters and expression of biomarkers revealed correlations between HSP90 expression and longer duration of OLP (p = 0.011), p53 protein and general involvement of oral mucosa (p = 0.025), E-cadherin and male gender (p = 0.036) and longer disease duration (p = 0. 016). The differences between HPV16/18 infection and duration were borderline significant (p = 0.072, Tab. II).
Analysis between the clinicopathological parameters of OSCCs and biomarker expression revealed that HSP90 expression correlated with an advanced tumour stage and short survival time (p = 0.045 and p = 0.018, respectively), while p53 protein correlated with a high tumour grade (p = 0.032). E-cadherin expression correlated with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.043). HPV16/18 infection correlated with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.035) and showed a correlation trend with survival time (p = 0.088, Tab. III).
Univariate and multivariate analyses (Tab. V) were conducted based on the clinicopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of the OSCC patient cohorts to determine prognostic factors. Univariate analysis identified tumour grade (p = 0.036), T classification (p < 0.001), clinical stage (p = 0.005), lymph node involvement (p = 0.004), HSP90 expression (p = 0.021), and HPV16/18 presence (p = 0.032) as prognostic factors for the OS of OSCC patients. As part of multivariate analysis, it was determined that tumour grade (HR 2.30, p = 0.016), T classification (HR 1.77, p = 0.001), lymph node involvement (HR 2.14, p = 0.021) and HSP90 expression (HR 2.78, p = 0.016) were independent factors associated with the shorter OS of OSCC patients.
Table V.
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of overall survival in patients with oral squamous carcinoma.
| Parameter | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female/male | 0.50 (0.25-0.98) | 0.045 | ||
| Tumour grade | ||||
| G1/G2+G3 | 2.00 (1.05-3.81) | 0.036 | 2.30 (1.17-4.52) | 0.016 |
| T classification | ||||
| T1+T2/T3+T4 | 1.97 (1.42-2.74) | < 0.001 | 1.77 (1.25-2.51) | 0.001 |
| N classification | ||||
| N0/N1+N2+N3 | 2.38 (1.32-4.29) | 0.004 | 2.14 (1.12-4.08) | 0.021 |
| Clinical stage | ||||
| I+II/III+IV | 1.66 (1.17-2.37) | 0.005 | ||
| HSP90 expression | ||||
| Positive/negative | 2.47 (1.14-5.33) | 0.021 | 2.78 (1.21-6.40) | 0.016 |
| p53 expression | ||||
| Positive/negative | 1.00 (0.96-1.04) | 0.918 | ||
| E-cadherin expression | ||||
| Positive/negative | 0.74 (0.41-1.33) | 0.311 | ||
| HPV16/18 expression | ||||
| Positive/negative | 2.18 (1.07-4.44) | 0.032 | ||
HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval. Bold values indicate statistical significance.
Discussion
Several attempts have been made to identify biomarkers that may be useful in examining the biological characteristics of OLP and make it possible to predict clinical outcomes for OLP patients 5,8,17. Several reports analysing the role of p53, HSP90, E-cadherin and HPV16/18 in malignant transformation of OLP towards OSCC have been published 1,5-7,11. However, the role of these biomarkers in this process is still a controversial topic 5,10,18,19. Nonetheless, many biomarkers expressed in OLP are also overexpressed in OSCC 8,20. The correlation between HSP90 expression, low E-cadherin expression and disease duration for OLP patients observed in this study are partly consistent with previous reports, which suggests that in cases of long disease duration, the risk of genetic changes may be increased 6,7,20. In our study, HSP90 expression was more frequently observed in non-erosive OLP, but it was limited to small tissue areas, and this type of OLP is associated with longer disease duration. There are reports which define the HSP90 protein as a marker associated with the malignant transformation of OLP 11. As a chaperone protein, HSP90 is involved in the stabilisation and maturation of a large number of proteins, including the p53 protein, which contributes to the aggressive behaviour of tumours 11,21. We found that low E-cadherin expression is associated with shorter OLP duration. These results indicate that cell-cell contact is distorted at an early stage of OLP development 20. The association between the p53 protein and the areas of oral mucosa observed in non-erosive OLP in this study is in line with the observations of Shiva et al. 22, who observed p53 protein expression in non-erosive OLP. The results of this study, which show increased p53 and HSP90 expression and lower E-cadherin expression in OSCC in comparison to OLP are in line with other data indicating that dysfunctions of these proteins may lead to malignant lesions in some cases 6,7,10,11. The impact of these proteins on the aggressive biological behaviour of OLP lesions is reflected in our data, which shows their increased expression in OSCC, as well as a correlation with worse clinical and pathological features of tumours. Similar data were presented by other authors, who found a correlation between p53, E-cadherin and HSP90 protein expression and worse OSCC clinical parameters, and suggests that these proteins are involved in the progressive growth of tumours 8,9,13,18,23. Moreover, our observation of significant differences in p53 and HSP90 expression between OLP and OSCC may reflect genetic alterations or protein structural changes occurring as part of the malignancy process 3,7,10. In this study, we were unable to reveal the prognostic value of p53 and HSP90 expression due to the short observation time of OLP patients. Nevertheless, the results obtained by Giuliani et al. 2, who described the overall malignant transformation in 1.4% of cases, including 1.37% for OLP, concluded that p53 expression may cause the progression from healthy oral tissue to malignancy. The lack of differences in E-cadherin expression between OLP and OSCC found in this study is in line with the previous results, which showed downregulation of E-cadherin in the early stage of OSCC development that did not significantly change during tumour progression 13. The topic of the oncogenic potential of HPV infection in OLP and OSCC is controversial 5,16. As with the earlier reports, in our study HPV16/18 infection was detected in a small percentage of OLP, but the number of HPV16/18 positive cases increased in OSCC and was associated with worse clinical outcomes of patients with HPV positive tumours 16,18. According to published data, our results indicate that the HPV16/18 infection may contribute to the malignant transformation of OLP and generate the HPV16/18 positive subtype of OSCC with aggressive growth 5,15,18. To our knowledge, this is the first study that had revealed a positive correlation between HSP90 and p53 protein, and between HSP90 and HPV16/18 infection in OLP, but not in OSCC. These findings suggest that as a chaperone protein HSP90 is crucial for the stability of the p53 protein; and although the interaction between HSP90 and the E6/E7 proteins expressed by HPV16/18 is not fully described, it was found that HSP90β induces the stability of E6/E7 proteins 24,25. Nevertheless, the observed interaction between HSP90 and p53 and HPV16/18 E6 and E7 proteins indicates that HSP90 may prolong the presence of p53 and E6/E7 proteins in cells. On the other hand, we may consider that the constant expression of E6/E7 oncoproteins may interfere with the p53 signaling pathway, leading to the p53 protein degradation and causing loss of suppressive function and increase the possibility of malignant transformation 18,25. The progressive character of these proteins in OLP was confirmed in this study through univariate analysis of HSP90, p53 and E-cadherin expression and presence of HPV16/18 as independent factors in OSCC, but only HSP90 expression in multivariate analysis showed a prognostic value in OSCC. The results reveal that the progressive growth of OSCC requires complex changes in various molecules, which may occur in premalignant lesions as indicators of OLP malignancy 10.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our data suggest that a positive correlation between HSP90 and p53 protein expression, as well as between HSP90 and HPV16/18 in OLP, indicates that cooperation between these proteins exists in OLP. Moreover, we can propose that the network between the host cell proteins and E6/E7 proteins indicates that this interaction can modulate the differential profile of the expression of host cell proteins, affecting the biological behaviour of OLP. The observation of HSP90 and p53 expression in OLP and their increase in OSCC may suggest that these proteins participate in the malignant transformation of OLP. HSP90 may be a potential independent prognostic biomarker and effectively predict poor prognosis in OSCC.
Figures and tables
References
- 1.Farhadi S, Shahsavari F, Alf K. Comparison of expression of p53 and bcl-2 markers in oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci 2018;2:37-45. https://doi.org/10.29252/jrdms.3.2.37 10.29252/jrdms.3.2.37 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Giuliani M, Troiano G, Cordaro M, et al. Rate of malignant transformation of oral lichen planus: a systematic review. Oral Dis 2019;25:693-709. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12885 10.1111/odi.12885 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aghbari SMH, Abushouk AI, Attia A, et al. Malignant transformation of oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: a meta-analysis of 20095 patient data. Oral Oncol 2017;68:92-102. https://doi.org/10/1016/j.oraloncology.2017.03.012 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hadzi-Mihailovic M, Petrovic R, Raybaud H, et al. Expression and role p53 in oral lichen planus patients. J BUON 2017;22:1278-1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu T, Zhang H, Yang X, et al. Study on expression of p16 and human papillomavirus 16 and 18 (E6) in OLP and its malignant transformation. Pathol Res Pract 2017;214:296-302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.014 10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sargolzaei S, Mohamadian F. Immunohistochemical comparison of E-cadherin expression in oral lichen planus with and without dysplasia. J Dental School 2017;1:26-31. https://doi.org/10.22037/jds.v35i1.24627 10.22037/jds.v35i1.24627 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sanketh DS, Kumari K, Rao RS, et al. Expression of Ki-67, p53, α -SMA, and COX-2 in lichen planus and related lesions: a pilot study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 2019; 9:230-235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2018.02.003 10.1016/j.jobcr.2018.02.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang WC, Tsai P-T, Lin C-K, et al. Expression pattern of heat shock protein 90 in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma in northern Taiwan, Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017;55:281-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.01.008 10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hashmi AA, Hussan ZF, Hashmi SK, et al. Immunohistochemical over expression of p53 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: clinical and prognostic significance. BMC Res Notes 2018;11:433. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3547-7 10.1186/s13104-018-3547-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tampa M, Caruntu C, Mitran M, et al. Markers of oral lichen planus malignant transformation. Dis Markers 2018;2018:1959506. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1959506 10.1155/2018/1959506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Soumya A, Malathi N, Prathiba D, et al. Role of HSP 90 alpha in oral lichen planus: an immunohistochemical evaluation. International Journal Recent Trends Science and Technology 2015;15:510-514. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yong D, Haobo L. Expression of E-cadherin in oral lichen planus. Exp Ther Med 2015;10:1544-1548. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2654 10.3892/etm.2015.2654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.López-Verdín S, Martínez-Fierro ML, Garza-Veloz I, et al. E-Cadherin gene expression in oral cancer: clinical and prospective data. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2019;24:E444-E451. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.23029 10.4317/medoral.23029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ono K, Eguchi T, Sogawa C, et al. HSP-enriched properties of extracellular vesicles involve survival of metastatic oral cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 2018;119:7350-7362. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27039 10.1002/jcb.27039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Poulopoulos A, Hempel M, Karakitsos G, et al. Assessment of HPV screening methods and sample in oral planus lesions. Transl Res Oral Oncol 2017;2:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1177/2057178X17727674 10.1177/2057178X17727674 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ma J, Zhang J, Zhang Y, et al. The magnitude of the association between human papillomavirus and oral lichen planus: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2016;11:e0161339. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161339 10.1371/journal.pone.0161339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jiang S, Dong Y. Human papillomavirus and oral squamous cell carcinoma: a review of HPV-positive oral squamous cell carcinoma and possible strategies for future. Curr Probl Cancer 2017;41:323-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2017.02.006 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2017.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Palve V, Bagwan J, Krishnam NM, et al. Detection of high-risk human paplillomavirous in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma using multiple analytes and their role in patients survival. J Glob Oncol 2018;4. https://doi.org/10.1200/JGO.18.00058 10.1200/JGO.18.00058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kang BH, Shu CW, Chao JK, et al. HSPD1 repressed E-cadherin expression to promote cell invasion and migration for poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 2019;9:8932. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45489-1 10.1038/s41598-019-45489-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fan CC, Wang TY, Cheng YA, et al. Expression of E-cadherin, twist, and p53 and their prognostic value in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:1735-1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1499-9 10.1007/s00432-013-1499-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tojyo I, Shinatani Y, Nakanish T, et al. PD-L1 expression correlated with p53 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2019;41:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-o19-0239-8 10.1186/s40902-o19-0239-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shiva A, Zamanian A, Arab S, et al. Immunohistochemical study of p53 expression in patients with erosive and non-erosive oral lichen planus. J Dent (Shiraz) 2018;19:118-123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kushwaha S, Joshi KS, Arora KS, et al. Correlation of E- cadherin immunohistochemical expression with histopathological grading of squamous cell carcinoma. Contemp Clin Dent 2019;10:232-238. https://doi.org/10.4103/ccd.ccd_624_18 10.4103/ccd.ccd_624_18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jafari A, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Farhadihosseinabadi B, et al. HSP90 and co-chaperones: impact on tumor progression and prospects for molecular-targeted cancer therapy. Cancer Invest 2020;38:310-328. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2020.1752227 10.1080/07357907.2020.1752227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Olmedo-Nieva L, Munzo-Bell JO, Contreras-Paredes A, et al. The role of E6 spliced isoforms (E6*) in human papillomaviruses-induced carcinogenesis. Viruses 2018;10:45. https:// doi.org/10.3390/v10010045 10.3390/v10010045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


