Abstract
Two novel lathyrane-type diterpenoids, the Euphorbia factors L2a (1) and L2b (2), and their stereoisomer Euphorbia factor L2 (3) were obtained from seeds of Euphorbia lathyris. Both Euphorbia factors L2a and L2b possess an unprecedented trans-gem-dimethylcyclopropane as structural feature. Also, the Euphorbia factor L2a is the first example of a lathyrane diterpenoid with an endocyclic 12(Z)-double bond. The structures of the molecules and their absolute configurations were elucidated by comprehensive spectroscopic analyses, Cu-Kα radiation X-ray diffraction, and comparison with calculated electronic circular dichroism (ECD) data. The Euphorbia factor L2b exhibited an inhibitory effect against U937 cell line with an IC50 value of 0.87 μM.
Two novel lathyrane-type diterpenoids, which possess a trans-gem-dimethylcyclopropane were obtained from seeds of Euphorbia lathyris. The Euphorbia factor L2b exhibited an inhibitory effect against U937 cell line with an IC50 value of 0.87 μM.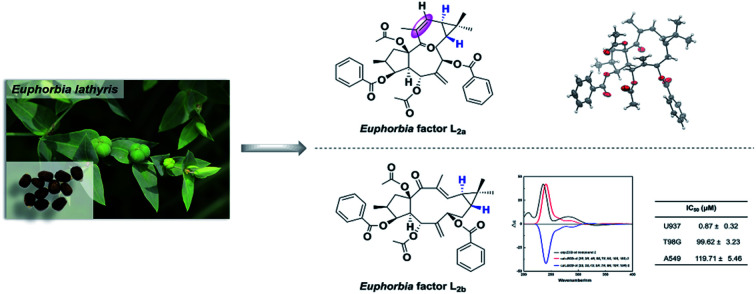
Introduction
Lathyrane diterpenoids, a group of macrocyclic diterpenoids based on a 5/11/3-tricyclic skeleton, have been found exclusively in the family Euphorbiaceae.1 These diterpenoids contain a cis-fused gem-dimethylcyclopropane unit and are generally substituted with a variety of acyl groups.2 Several studies have been conducted to investigate lathyrane diterpenoids for their anticancer,3,4 multidrug resistance modulation (MDR),5–7 and anti-inflammatory activities.8,9 The existing structure–activity relationship (SAR) analyses showed that the configuration of the molecule's structure as well as the nature of the acyl side chains influence the bioactivities of lathyrane diterpenoids.4,6,10 However, whether the configuration of the gem-dimethylcyclopropane influences the bioactivity of lathyrane diterpenoids has never been studied.
Euphorbia lathyris is native to the Mediterranean and has been introduced to many other parts of the world. A characteristic of the plant's constituents is the abundance of lathyrane-type diterpenoids. Up to now, 46 lathyrane-type diterpenoids, most of them containing an endocyclic 12(E)-double bond, have been identified.7,8,11–14 As part of our ongoing search for bioactive natural products,15–18 two novel lathyrane diterpenoids, the Euphorbia factor L2a (1) and L2b (2) along with the Euphorbia factor L2 (3)19 were isolated from the seeds of E. lathyris. The compounds 1–3 share the presence of similar planar structures, but the configuration of the gem-dimethylcyclopropanes and the endocyclic 12-double bonds differ. Herein, we describe the isolation, structural elucidation, and the cytotoxicity evaluation of the isolated compounds. The results indicate that the cytotoxicity of lathyrane-type diterpenoids is dependent on the configuration of the gem-dimethylcyclopropane and the endocyclic double bond.
Results and discussion
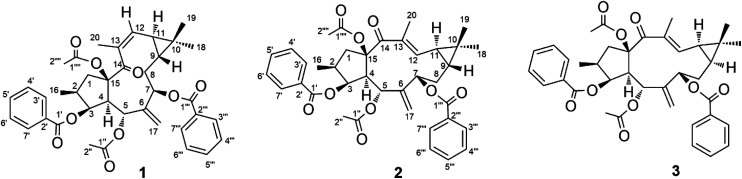
Seeds of E. lathyris (12 kg) were extracted with 95% aqueous ethanol. The extract was rotary-evaporated, reconstituted with H2O and successively partitioned with petroleum ether, dichloromethane, and ethyl acetate. The petroleum ether-soluble fraction was re-extracted with acetonitrile. Then the acetonitrile fraction was subjected to separation by column chromatography on silica gel and (recycling) semipreparative HPLC to obtain compound 1 (45 mg), compound 2 (20 mg), and compound 3 (120 mg) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Chemical structures of compounds 1–3.
Structural elucidation of Euphorbia factors L2a (1)
Compound 1, obtained as colorless crystals, showed a specific optical rotation value of [α]D +20.9 [c 0.50, methanol/CH2Cl2 (95 : 5, v/v)]. The molecular formula of C38H42O9 was determined by the pseudo-molecular ion peak at m/z 665.2720 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C38H42O9Na, 665.2721) in positive HR-ESI-MS. The 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and DEPT spectra of 1 (Table 1) exhibited signals for a ketone group, two acetyl groups, two benzoyl groups, two double bonds (one exocyclic and one trisubstituted), four methyls, two methylenes, seven methines (three oxygenated), and two quaternary carbons (one oxygenated). The interpretation of the above-mentioned spectra data suggested that compound 1 is an isomer of Euphorbia factor L2 (3), a major diterpenoid of the plant with a 7-hydroxy-lathyrol type macrocyclic scaffold. A further comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR data of 1 with those of 3 revealed identical functional groups but with differences regarding their chemical shifts. We observed upfield shifts for C-7 (δC 70.8, δH 5.48), C-9 (δC 24.4, δH 0.91), C-12 (δC 130.4, δH 5.77), and C-18 (δC 21.5, δH 1.09) and downfield shifts for C-19 (δC 21.7) and C-20 (δC 23.8, δH 2.05), indicating structural changes in the cyclopropyl enone of 1. Consequently, two-dimensional NMR experiments (COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and ROESY) were used to determine the structure of 1.
1H and 13C NMR spectral data of compounds 1–3 in CDCl3.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ H a (mult JHH) | δ C b | δ H a (mult JHH) | δ C b | δ H a (mult JHH) | δ C b | |
| 1α | 3.17 (dd, 6.6, 14.9) | 46.4 | 2.81 (dd, 8.9, 14.6) | 44.5 | 3.40 (dd, 8.2, 14.3) | 47.8 |
| 1β | 2.08–2.17 (m) | 2.06–2.13 (m) | 1.78 (m) | |||
| 2 | 2.24 (m) | 38.2 | 2.44 (m) | 36.0 | 2.36 (m) | 37.6 |
| 3 | 5.84 (t, 3.6) | 78.0 | 5.80 (t, 3.7) | 75.9 | 5.77 (t, 3.4) | 79.5 |
| 4 | 3.28 (dd, 3.6, 10.8) | 49.2 | 2.97 (dd, 3.7, 8.1) | 52.0 | 2.92 (dd, 3.4, 7.9) | 52.9 |
| 5 | 6.02 (d, 10.8) | 72.5 | 6.00 (d, 7.5) | 72.4 | 6.37 (d, 7.9) | 64.3 |
| 6 | 138.9 | 148.0 | 142.2 | |||
| 7 | 5.48 (dd, 3.9, 10.1) | 70.8 | 5.11 (dd, 3.2, 9.2) | 74.1 | 5.53 (dd, 3.1, 8.9) | 78.5 |
| 8α | 2.16–2.20 (m) | 28.7 | 1.61 (m) | 36.5 | 2.33 (m) | 28.7 |
| 8β | 1.61 (m) | 2.38 (m) | 2.21 (m) | |||
| 9 | 0.91 (m) | 24.4 | 1.58 (m) | 34.1 | 1.34 (m) | 31.6 |
| 10 | 21.5 | 30.1 | 24.6 | |||
| 11 | 0.98 (m) | 30.4 | 1.28 (m) | 35.1 | 1.50 (dd, 11.0, 8.3) | 27.8 |
| 12 | 5.77 (d, 5.6) | 130.4 | 6.02 (d, 11.2) | 136.1 | 6.51 (d, 11.2) | 142.5 |
| 13 | 136.5 | 131.9 | 135.6 | |||
| 14 | 201.9 | 202.1 | 197.5 | |||
| 15 | 91.0 | 91.4 | 92.0 | |||
| 16 | 0.99 (d, 6.5) | 13.7 | 1.07 (d, 6.7) | 14.2 | 0.94 (d, 6.7) | 14.1 |
| 17a | 5.76 (s) | 121.1 | 5.41 (s) | 111.8 | 5.50 (s) | 119.4 |
| 17b | 5.61 (s) | 5.00 (s) | 5.22 (s) | |||
| 18 | 1.09 (s) | 21.5 | 1.26 (s) | 22.8 | 1.26 (s) | 28.8 |
| 19 | 1.00 (s) | 21.7 | 1.17 (s) | 21.2 | 1.19 (s) | 16.6 |
| 20 | 2.05 (s) | 23.8 | 2.11 (s) | 15.7 | 1.81 (s) | 12.7 |
| 1′ | 165.9 | 166.0 | 166.0 | |||
| 2′ | 130.4 | 130.4 | 130.4 | |||
| 3′, 7′ | 7.96 (2H, d, 7.4) | 130.0 | 8.16 (2H, d, 7.2) | 129.7 | 8.06 (2H, d, 7.2) | 129.7 |
| 4′, 6′ | 7.43 (2H, t, 7.7) | 128.6 | 7.45 (2H, t, 7.8) | 128.3 | 7.45 (2H, t, 7.8) | 128.3 |
| 5′ | 7.56 (1H, t, 7.4) | 133.4 | 7.58 (1H, t, 7.5) | 133.1 | 7.58 (1H, t, 7.5) | 133.1 |
| 1′′ | 169.1 | 169.5 | 169.3 | |||
| 2′′ | 1.48 (3H, s) | 20.6 | 1.45 (3H, s) | 20.5 | 1.29 (3H, s) | 20.9 |
| 1′′′ | 165.9 | 165.6 | 165.6 | |||
| 2′′′ | 130.4 | 130.2 | 130.2 | |||
| 3′′′, 7′′′ | 7.93 (2H, d, 7.5) | 129.7 | 8.07 (2H, d, 7.2) | 129.6 | 7.93 (2H, d, 7.2) | 129.6 |
| 4′′′, 6′′′ | 7.38 (2H, t, 7.8) | 128.6 | 7.44 (2H, t, 7.8) | 128.3 | 7.35 (2H, t, 7.8) | 128.3 |
| 5′′′ | 7.50 (1H, t, 7.4) | 133.2 | 7.55 (1H, t, 7.5) | 133.1 | 7.50 (1H, t, 7.5) | 133.1 |
| 1′′′′ | 169.2 | 170.0 | 169.7 | |||
| 2′′′′ | 2.30 (3H, s) | 21.6 | 2.07 (3H, s) | 21.2 | 2.21 (3H, s) | 21.8 |
Recorded at 500 MHz.
Recorded at 125 MHz.
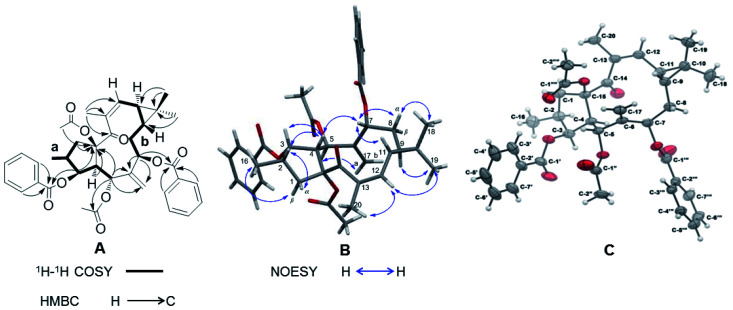
Correlations in the 1H–1H COSY spectrum of 1 confirmed the presence of two spin systems C-1 to C-5 and C-16 and C-7 to C-12, while HMBC correlations from H-1β (δH 2.08–2.17), H-3 (δH 5.84), H-4 (δH 3.28), and H-5 (δH 6.02) to C-15 (δC 91.0) revealed the presence of a five-membered ring in 1 (Fig. 2A). The correlations from H-5 and H-7 (δH 5.48) to C-6 (δC 138.9) and C-17 (δC 121.1) were characteristic for the presence of the exocyclic olefinic methylene group at C-6. Further HMBC correlations from H3-18 (δH 1.09) and H3-19 (δH 1.00) to C-9 (δC 24.4), C-10 (δC 21.5), and C-11 (δC 30.4) established a gem-dimethyl-substituted cyclopropane ring at C-9 and C-11. The assignments of the trisubstituted Δ12 double bond and the keto group at C-14 were determined by the correlations from H-20 (δH 2.05) to C-12 (δC 130.4), C-13 (δC 136.5), and C-14 (δC 201.9). The two acetyl groups at C-5 and C-15 were determined by the correlations from H-5 (δH 6.02) to C-1′′ (δC 169.1) and from H3-2′′′′ (δH 2.30) to C-15. The HMBC correlations from H-3′/7′ (δH 7.96) and H-3 to C-1′ (δC 165.9) and from H-3′′′/7′′′ (δH 7.93) and H-7 to C-1′′′ (δC 165.9) showed that the two benzoyl groups were attached to C-3 and C-7 respectively.
Fig. 2. (A) 1H–1H COSY (black thick lines) and key HMBC correlations (black arrows). (B) Important NOESY correlations (blue arrows). (C) X-ray ORTEP drawing of compound 1 (displacement ellipsoids were drawn at the 30% probability level.).
The relative configuration of 1 was deduced by analysis of its 13C NMR and NOESY data (Fig. 2B). The trans-linked cyclopentane ring and the β-oriented O-acetyl-15, CH3-16, and O-benzoyl-3 groups were deduced from the NOESY correlations between H-1β and H3-16 (δH 0.99) and between H-1α (δH 3.17), H-2 (δH 2.24), H-3, and H-4 (Fig. 2B). The NOESY correlations between H-4 and H-7 and between H-5 and H-17a (δH 5.76) revealed that the O-acetyl group at C-5 was α-oriented while the O-benzoyl at C-7 was in β-orientation. Further NOESY correlations between H-7, H-8α (δH 2.16–2.20), and H-11 (δH 0.98) and between H-9 (δH 0.91) and H3-19 indicated a trans-fused cyclopropane ring with a β-oriented H-9 and an α-oriented H-11. This assumption was also corroborated by the absence of a NOESY cross peak between H-9 and H-11. The (E)/(Z) double-bond geometry has a significant effect on the NMR chemical shifts of the olefinic carbons and also on the substituted carbons connected to the double bond.20,21 In 1 the 12, 13-double bond has a (Z) geometry as it is indicated by an upfield-shifted carbon signal of C-12 (δC 130.4) and a downfield-shifted carbon signal of C-20 (δC 23.8). In contrast, the double bond in the Euphorbia factor L2 (3) has the opposite (E) geometry. The NOESY correlation between H-12 (δH 5.77), H3-20, and H3-19 indicated furthermore the (Z) configuration of the trisubstituted double bond in 1. A single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis with Cu-Kα radiation [flack parameter at 0.00(8)] (Fig. 2C) unambiguously assigned the absolute configuration of 1 as 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R, 7R, 9R, 11S and 15R. Thus, 1 was given the trivial name Euphorbia factor L2a, and its systematic name is (2S, 3S, 4R, 5R, 7R, 9R, 11S, 15R)-5,15-diacetoxy-3,7-dibenzoyloxy-14-oxolathyra-6(17),12(13) Z-diene. The two specific structural characteristics of 1, namely the (Z) geometry of the 12,13-double bond and the trans-fused cyclopropane ring at C-9/C-11 were here firstly described for the lathyrane skeleton.
Structural elucidation of Euphorbia factors L2b (2)
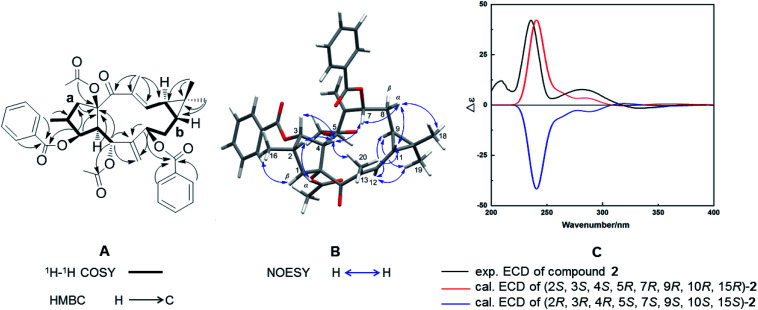
Compound 2, with a specific optical rotation of [α]D +62.5 [c 0.46, methanol/CH2Cl2 (95 : 5, v/v)], had the same molecular composition as 1. The analysis of its NMR spectroscopical data suggested that 2 was a derivative of 1 and 3 (Fig. 3A). In comparison with the 13C NMR data of 1 (Table 1), the downfield-shifted carbon signal of C-12 (δC 136.1) and the upfield-shifted carbon signals of C-20 (δC 15.7) and C-13 (δC 131.9) suggested an (E)-geometry for the 12,13-double bond in 2. The NOESY correlation of H-12 (δH 6.02) with H-9 (δH 1.58) supported the above assignment for the 12,13-double bond. The NOESY correlations H-1α (δH 2.81)/H-2 (δH 2.44), H-2/H-4 (δH 2.97), H-4/H-3 (δH 5.80), H-4/H3-20, H-4/H-7 (δH 5.11), H-7/H-8α (δH 1.61), H-8α/H3-18 (δH 1.26), H-8α/H-11, and H-11/H3-20 determined these hydrogens and methyl groups as cofacial and α-oriented (Fig. 3B). Further NOE correlations of H-9 (δH 1.58)/H-12 (δH 6.02), H-9/H3-19 (δH 1.17), H-12/H3-19, and H-1β (δH 2.11)/H3-16 (δH 1.07) confirmed the β-orientation of H-9, H-12, H3-16, and H3-19. As a result, the cyclopropane ring was revealed to be trans-fused to the 11-membered ring at the positions C-9 and C-11. The relative configuration of 2 was therefore determined as (2S*, 3S*, 4S*, 5R*, 7R*, 9R*, 10R*, 15R*), resulting in a molecular structure as shown in Fig. 3B. For the absolute stereochemical determination of 2 the circular dichroism spectrum was measured and compared to the result of calculated quantum chemical electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra (ECD was simulated at TD-DFT/CAM-B3LYP/TZVP level). The calculated ECD curve for (2S, 3S, 4S, 5R, 7R, 9R, 10R, 15R)-2 was in good accordance to the sign and intensity of the experimentally determined positive cotton effect (CE) at 236 and 283 nm and the negative CE at 333 nm. The calculated ECD spectrum for (2R, 3R, 4R, 5S, 7S, 9S, 10S, 15S)-2 showed a mirror image to the experimental curve of compound 2 (Fig. 3C). Therefore, the absolute configuration of 2 was assigned to (2S, 3S, 4S, 5R, 7R, 9R, 10R, 15R). As a result, the trivial name Euphorbia factor L2b was given to compound 2, and its systematic description is (2S, 3S, 4S, 5R, 7R, 9R, 10R, 15R)-5, 15-diacetoxy-3,7-dibenzoyloxy-14-oxolathyra-6(17),12(13) E-diene.
Fig. 3. (A) 1H–1H COSY (black thick lines) and key HMBC correlations (black arrows). (B) Important NOESY correlations (blue arrows). (C) Experimentally determined and calculated ECD curves of compound 2.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway
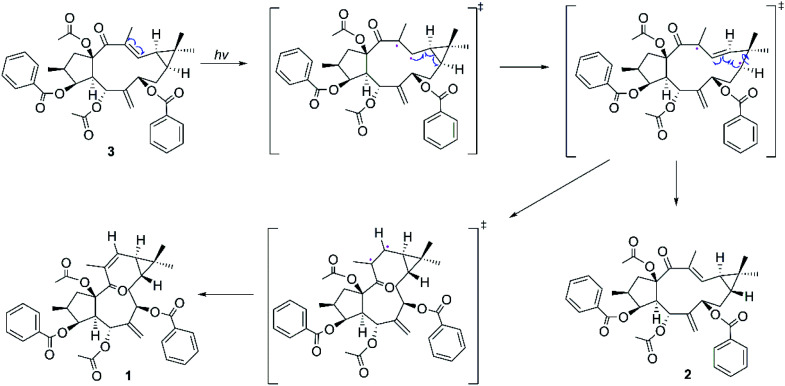
Considering the structural similarities of the compounds 1–3, these compounds may have a close biogenic relationship. We propose that Euphorbia factor L2 (3) is the biosynthetic precursor of 1 and 2. A plausible biosynthetic pathway for 1 and 2, which Euphorbia factor L2 triggered by light and then the formation of trans-gem-dimethylcyclopropane isomers (compounds 1 and 2) through free radical intermediate, is proposed in Scheme 1.
Scheme 1. Proposed biosynthetic pathway of compounds 1–2.
Antitumor assay
Compounds 1–3 were tested for their in vitro cytotoxicity against human lung carcinoma (A549), human glioblastoma (T98G), and human leukemic monocyte lymphoma (U937) cell lines using the MTT assay. The results indicated that 1 and 3 were inactive against the above-mentioned cancer cell lines [50% effective dose of clonal inhibition (IC50) > 200 μM], while 2 showed moderate cytotoxicity against U937 (IC50: 0.87 ± 0.32 μM) (Table 2). It is suggested that the cytotoxicity of lathyrane-type diterpenoids is determined by the geometry of the C-12/C-13 double bond and the configuration of the cyclopropane ring in the molecule. The differential inhibitory effects against the U937 cell line of the three stereoisomers 1–3 may attract the interest of other researchers for further investigation.
Effect of compounds 1–3 on the proliferation of T98G, A549, and U937 cells.
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| T98G | A549 | U937 | |
| 1 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 2 | 119.71 ± 5.46 | 99.62 ± 3.23 | 0.87 ± 0.32 |
| 3 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| Camptothecin | 1.03 ± 0.14 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
Experimental
General experimental procedures
Column chromatography (CC) was performed on silica gel (200–300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Inc., China). Semi-preparative HPLC separations were conducted on a Shimadzu HPLC system (LC-20AR, Shimadzu, Japan) with a Shim-pack GIS C18 column (5 μm, 250 × 20 mm, Shimadzu, Japan). For conducting recycling preparative separations, the Shimadzu LC-20AR instrument equipped with a SPD-20A detector and an Inertsil ODS-3 column (5 μm, 150 × 10 mm, Shimadzu, Japan) was used. LC-HRMS spectra were obtained on an Agilent 6530 Q-TOF mass spectrometer coupled to an Agilent 1260 HPLC (Agilent Technologies GmbH, Waldbronn, Germany). Specific optical rotation values were measured using a Jasco P-1020 polarimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). Electronic circular dichroism spectrum was measured using a JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) at 25 °C in spectroscopy grade methanol. NMR data were obtained using (operating at 500.13 MHz for 1H NMR and 125.75 MHz for 13C NMR) (Bruker Biospin GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). CDCl3 was used as solvent and tetramethylsilane (TMS) was used as an internal standard. The X-ray crystallographic data were collected on a Bruker Smart Apex-II CCD diffractometer using graphite monochromated Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å) at 296 K. SHELXT-2014 (ref. 22) was used for structure solution; SHELXL-2018 (ref. 23) for cell refinement and Mercury 4.1 (ref. 24) for the visualization of the structure.
Plant materials
The seeds of E. lathyris were collected from Jiaozuo in Henan Province of China in June 2016. The plants were taxonomically identified by Changqi Yuan, professor at the Institute of Botany, Jiangsu Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences. A voucher specimen (accession number 201609-EL) was deposited at the Department of Natural Product Chemistry, Institute of Botany, Jiangsu Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Extraction and isolation
The dried E. lathyris seeds (12 kg) were extracted with 95% aqueous ethanol (50 L × 3 times × 2 hours) under reflux to give crude extracts. The combined crude extracts were evaporated under reduced pressure to yield a brown residue (5.1 kg) which was suspended in distilled H2O (12 L) and partitioned sequentially with petroleum ether, CH2Cl2, and EtOAc. After evaporation of the solvent, the petroleum ether fraction (730 g) was re-extracted repeatedly with acetonitrile. The acetonitrile extract (145 g) was subjected to normal-phase silica gel CC and eluted with a petroleum ether–EtOAc gradient (1 : 0, 20 : 1, 10 : 1, 4 : 1, 2 : 1, 0 : 1, v/v) to obtain six fractions (Fr.1–Fr.6). Fraction 2 was further separated using a silica gel CC and eluted with a step-gradient (petroleum ether–EtOAc, 80 : 1, 70 : 1, 60 : 1, 50 : 1, 40 : 1, 30 : 1, 20 : 1, 10 : 1, v/v) resulting in eight subfractions (Fr.2-1–Fr.2-8). Fr.2-3 (21 g) was separated by semipreparative HPLC followed by recycling semipreparative HPLC (MeOH–H2O, 85 : 15, v/v, 4 mL min−1) to yield 1 (45 mg), 2 (20 mg) and 3 (120 mg). Recrystallization of 1 from petroleum ether–EtOAc (4 : 1) gave colorless crystals.
LC-HRMS measurements
Zorbax C18 column (3.5 μm; 150 × 4.6 mm; Agilent, St Louis, MO, USA) with a constant flow rate of 500 μL min−1 at 35 °C, binary solvent system of H2O (solvent A) and MeOH (0.1% (v/v) formic acid, solvent B). 0–20 min, isocratic, 85% B; 20–30 min, isocratic, 100% B; 30–40 min, isocratic, 85% B.
Euphorbia factor L2a (1)
Colorless crystals; [α]D +20.9 [c 0.50, methanol/CH2Cl2 (95 : 5, ν/ν)]; HPLC-PDA-HRMS tR 9.23 min; UV (MeOH–H2O) λmax 200, 235, 280 nm; NMR data see Table 1; HRESIMS (m/z): 665.2720 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C38H42O9Na, 665.2721). 1 was re-crystallized from petroleum ether–EtOAc (4 : 1). A single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis using Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å) was carried out to obtain the structure. M = 642.71, triclinic, P1̄, a = 9.1400(4) Å, b = 9.3542(4) Å, c = 10.6916(5) Å, α = 104.278(2)°, β = 90.570(2)°, γ = 91.630(2), V = 885.37(7) Å3, Z = 1, Dc = 1.378 mg mm−3, T = 296(2) K, Flack (abs) = 0.00(8).
Euphorbia factor L2b (2)
Colorless crystals; [α]D +62.5 [c 0.50, methanol/CH2Cl2 (95 : 5, v/v)]; HPLC-PDA-HRMS tR 8.21 min; UV (MeOH–H2O) λmax 200, 232, 280 nm; ECD (methanol) λ(∼Δε) 236 (+), 283 (+), 333 (−) nm; NMR data see Table 1; HRESIMS (m/z): 665.2716 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C38H42O9Na, 665.2721).
Computational details
The conformational search for a pair of enantiomers of 2 ((2S*, 3S*, 4S*, 5R*, 7R*, 9R*, 10R*, 15R*)-2) was performed using Spartan 14 (ref. 25) with MMFF molecular mechanics force field. After surveying the conformational space, the conformers within a 5 kcal mol−1 energy window were preliminarily optimized at B3LYP level using 6-31G+(d) basis set. The frequency calculation was then conducted for the previously optimized conformers to obtain the corresponding their relative Gibbs free energies (ΔG). Boltzmann weighting factors (Pi%) for each conformer were determined on the basis of ΔG to eliminate the conformers which possess inappreciable contribution. Subsequently, the conformers selected for ECD calculation were re-optimized by DFT calculations at CAM-B3LYP/TZVP level. Then, the 20 lowest electronic transitions were calculated using time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) method at CAM-B3LYP/TZVP level, and with methanol as solvent employing the PCM model. All quantum chemical calculations were conducted using Gaussian 09 program package.26 ECD curves were generated with SpecDis27 at a half bandwidth of 0.30 eV and 11 nm red-shift UV correction.
Biological assay
The human cancer cell lines A549, T98G, and U937 were cultured in Nutrient Mixture F-12 Ham (Sigma, USA), Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Gibco, USA), and Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 Medium (Gibco, USA) respectively, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 100 μg mL−1 penicillin, and 100 μg mL−1 streptomycin. All cells were cultivated in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 air at 37 °C. The cytotoxicity of compounds 1–3 against the above-mentioned three cell lines were evaluated using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay, which was carried out according to protocols described previously.28 Camptothecin was used as a positive control.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the two specific structural characteristics of the stereoisomers 1 and 2, the (Z)-geometry for the C-12/C-13 double bond in 1 as well as the trans-fused cyclopropane ring at C-9/C-11 in 1 and 2, are firstly found in the lathyrane skeleton. The different inhibitory effect against U937 cell lines among the three stereoisomers 1–3 may attract interest from researchers for further investigation.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770383, 31970375), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180311, BK20200287) and the Jiangsu Key Laboratory for the Research and Utilization of Plant Resources (JSPKLB201836). The theoretical calculations were conducted on the ScGrid and Deepcomp7000 the Supercomputing Center, Computer Network Information Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: HR-HPLC-ESI-MS, 1H and 13C NMR, 13C-DEPT, 1H–13C HSQC, 1H–13C HMBC, 1H–1H COSY, 1H–1H NOESY data of compounds 1–3, the DFT-optimized 3D structures of relative stable conformers of compound 2 and their Boltzmann weighting factors. CCDC 2010124 for the crystal structure of 1. The CCDC contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d0ra10724g
Notes and references
- Vasas A. Hohmann J. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:8579–8612. doi: 10.1021/cr400541j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran-Pena M. J. Botubol Ares J. M. Collado I. G. Hernandez-Galan R. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014;31:940–952. doi: 10.1039/C4NP00008K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng Y. N. Wang Y. Hsu P. L. Xin G. Zhang Y. Morris-Natschke S. L. Goto M. Lee K. H. Phytomedicine. 2018;41:62–66. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis M. A. Ahmed O. B. Spengler G. Molnar J. Lage H. Ferreira M. U. J. Nat. Prod. 2017;80:1411–1420. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b01084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao W. Dong W. Li Z. Deng M. Lu R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009;17:4786–4792. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao W. Wan Z. Chen S. Lu R. Chen X. Fang D. Wang J. Pu S. Huang X. Gao H. Shao H. J. Med. Chem. 2015;58:3720–3738. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. Wang S. Li H. Zhao Q. Yan S. Dong M. Liu D. Chen X. Li R. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020;121:109663. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. G. Li Z. L. Bai J. Meng D. L. Li N. Pei Y. H. Zhao F. Hua H. M. J. Nat. Prod. 2014;77:792–799. doi: 10.1021/np400873v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. Wu Y. Li C. Yang Y. Li X. Li H. Chen L. Chem. Biodivers. 2020;17:e1900531. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201900531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monico A. Nim S. Duarte N. Rawal M. K. Prasad R. Di Pietro A. Ferreira M. U. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017;25:3278–3284. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu A. Zhang T. Wang Q. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018;227:41–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. X. Wang Q. Zhen Y. Q. Zhao S. M. Gao F. Zhou X. L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018;66:674–677. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c17-00946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. Zhen Y. Q. Gao F. Huang S. Zhou X. L. Chem. Biodivers. 2018;15:e1800386. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. W. Jin Q. Jang H. Kim J. G. Lee D. Kim Y. Hong J. T. Lee M. K. Hwang B. Y. Chem. Biodivers. 2018;15:e1800144. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. Zhao X. Liu F. Cao Y. Wang B. Wang X. Yin M. Wang Q. Feng X. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018;74:2716–2723. doi: 10.1002/ps.5091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyu H. Liu W. Bai B. Shan Y. Paetz C. Feng X. Chen Y. Molecules. 2019;24:4276. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. Wang B. Li L. Zhou Q. Tian M. Zhao X. Peng J. Liu F. Chen Y. Xu Y. Feng X. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020;163:108–116. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Paetz C. Menezes R. C. Schneider B. Phytochemistry. 2016;128:95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appendino G. Tron G. C. Cravotto G. Palmisano G. Jakupovic J. J. Nat. Prod. 1999;62:76–79. doi: 10.1021/np980218n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevesi L. Nagy J. B. Krief A. Derouane E. G. Org. Magn. Reson. 1977;10:14–19. doi: 10.1002/mrc.1270100105. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chukovskaya E. C. Dostovalova V. I. Vasil'Eva T. T. Freidlina R. K. Org. Magn. Reson. 1976;8:229–232. doi: 10.1002/mrc.1270080502. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick G., SHELXTL-2014, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2014 [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick G., SHELXL-2018, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2018 [Google Scholar]
- Macrae C. F. Edgington P. R. McCabe P. Pidcock E. Shields G. P. Taylor R. Towler M. Streek J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006;39:453–457. doi: 10.1107/S002188980600731X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Deppmeier B., Driessen A., Hehre T., Hehre W., Johnson J., Klunzinger P., Leonard J., Pham I., Pietro W. and Yu J., Spartan 14, Wavefunction Inc., 2014 [Google Scholar]
- Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery Jr J. A., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J. and Fox D. J., GAUSSIAN 09 (Revision A.1), Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2009 [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn T. Schaumlöffel A. Hemberger Y. Bringmann G. Chirality. 2013;25:243–249. doi: 10.1002/chir.22138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley M. C. Scudiero D. A. Monks A. Hursey M. L. Czerwinski M. J. Fine D. L. Abbott B. J. Mayo J. G. Shoemaker R. H. Boyd M. R. Cancer Res. 1998;48:589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.