Abstract
The genetic diversity of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 (HIV-1) has been characterized mainly by analysis of the env and gag genes. Information on the vpu genes in the HIV sequence database is very limited. In the present study, the nucleotide sequences of the vpu genes were analyzed, and the genetic subtypes determined by analysis of the vpu gene were compared with those previously determined by analysis of the gag and env genes. The vpu genes were amplified by nested PCR of proviral DNA extracted from 363 HIV-1-infected individuals and were sequenced directly by use of the PCR products. HIV-1 subtypes were determined by sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis with reference strains. The strains in all except one of the samples analyzed could be classified as subtype A, B, C, E, or G. The vpu subtype of one strain could not be determined. Of the strains analyzed, genetic subtypes of 247 (68.0%) were also determined by analysis of the env or gag gene. The genetic subtypes determined by vpu gene analysis were, in general, consistent with those determined by gag and/or env gene analysis except for those for two AG recombinant strains. All the strains that clustered with a Thailand subtype E strain in the vpu phylogenetic analyses were subtype E by env gene analysis and subtype A by gag gene analysis. In summary, our genetic typing revealed that subtype B strains, which constituted 73.8% of all strains analyzed, were most prevalent in Taiwan. While subtype E strains constituted about one-quarter of the viruses, they were prevalent at a higher proportion in the group infected by heterosexual transmission. Genetic analysis of vpu may provide an alternate method for determination of HIV-1 subtypes for most of the strains, excluding those in which intersubtype recombination has occurred.
Prominent genomic heterogeneity is found among different human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 (HIV-1) isolates. Phylogenetic analyses of env gene sequences from different isolates obtained worldwide have identified at least 10 genetic subtypes (subtypes A to J) in the major (M) group and sets of strains in the outlier (O) and new (N) groups (8, 14, 17, 19, 20, 24). The genetic diversity of HIV-1 is generated by accumulation of point mutations and by recombination (9, 15).
In addition to gag, pol, and env, the HIV-1 genome contains six accessory genes (18). One of them is the vpu gene, which is located in the middle part of the genome. vpu encodes a small phosphorylated protein, Vpu, which is composed of the N-terminal transmembrane domain and the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. The cytoplasmic domain contains two highly conserved serine residues that are phosphorylated (25). Structure-function studies of Vpu revealed that the transmembrane domain is critical for virus release and that the cytoplasmic domain is required for degradation of CD4 (25). The 3′ one-third (83 bp for most of the HIV-1 reference strains) of the vpu gene overlaps the env gene.
Information on the genetic subtypes of HIV-1 is important for understanding of the global evolution of HIV-1 and for vaccine development. Genetic subtypes may also have an impact on drug susceptibility, as well as on the determination of drug resistance mutations and the measurement of viral loads (5, 7, 23). The genetic diversity of HIV-1 has mainly been characterized by analysis of the env and gag genes (17, 22). Information on the sequence variation and the subtypes of the vpu gene is still very limited. In the study described here, the nucleotide sequences of the vpu genes were analyzed. The genetic subtypes of HIV-1 determined by analysis of the vpu gene were compared with those previously determined by analysis of the gag and env genes (C. N. Lee, M. Y. Chen, C. L. Kao, H. S. Lin, M. C. Lee, S. J. Twu, R. Y. Lin, M. C. Sheng, and C. Y. Chuang, Program Abstr. 4th Int. Conf. AIDS, abstr. V8, p. 22, 1996). The prevalence of HIV-1 subtypes among different risk groups in Taiwan was also determined on the basis of vpu sequence analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Samples.
HIV-1-positive blood samples have been collected since 1990 at the Taipei Municipal Venereal Disease Center and National Taiwan University Hospital. Blood samples were collected in sterile EDTA-containing tubes. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were separated by incorporating a Ficoll-Hypaque gradient (21). For each HIV-1-infected individual, information including gender, age, race, sexual orientation, risk factors, etc., was obtained through a questionnaire, and the risk factors were rechecked by counseling with medical personnel. The risk groups were categorized into hemophiliac, intravenous drug user, and sexual transmission groups. The sexual transmission group was further divided into female and male heterosexual, homosexual, and bisexual groups. The differences in the prevalence of HIV-1 subtypes between different groups were analyzed by the χ2 test.
Genomic DNA isolation.
PBMCs were first treated with erythrocyte lysis buffer (0.32 M sucrose, 10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 5 mM MgCl2, 1% Triton X-100). The supernatant was discarded after centrifugation. The pelleted cells were treated with proteinase K (100 μg/ml) in a solution containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 50 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.45% Nonidet P-40, and 0.45% Tween 20 at 55°C for 1 h. The DNA was then phenol-chloroform extracted, ethanol precipitated, and quantitated by measuring the optical density at 260 nm.
PCR.
The vpu genes were amplified by nested PCR. One to 1.5 μg of genomic DNA extracted from PBMCs was used as the template for the first round of PCR. The reaction mixture contained 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 9.0), 50 mM KCl, 0.1% (wt/vol) gelatin, 1.5 mM MgCl2, each of the deoxynucleoside triphosphates at a concentration of 200 μM, 15 pmol of each of the primers, and 1 U of Super Taq DNA polymerase (HT Biotechnology, Cambridge, England). A close examination of the sequences available in the HIV sequence database was carried out to identify highly conserved regions that flank the vpu gene. Primer pairs that covered the conserved regions were thus designed. They were TAT-1 (5′-CCTAAACTAGAGCCCTGGAACCATCC-3′; positions in SF2, nucleotides 5855 to 5880) and EN70 (5′-GGTACACAGGCATGTGTGGCCC-3′; nucleotides 6435 to 6456) for the first-round PCR. The amplification conditions were 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 50°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 30 s and a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The formulation for the second-round PCR was identical to that for the first-round PCR, and the second-round PCR was performed in a manner identical to that for the first-round PCR. A 1-μl aliquot of the first-round PCR product was applied. The primers used in the second-round PCR were 154.1 (5′-CTTAGGCATCTCCTATGGCAGGAAGAAG-3′; nucleotides 5965 to 5992) and KPN (5′-ACACAGGTACCCCATAATAGACTGT-3′; nucleotides 6338 to 6362). To avoid contamination and the resultant false-positive results, standard precautions recommended for PCR were taken during the amplification (11).
Purification of PCR product.
Five microliters of the final PCR product for each sample was first checked in a 1% agarose gel. Then, the amplified 398-bp fragments were purified through a QIAquick silica gel membrane (QIAGEN, Chatsworth, Calif.).
DNA sequencing.
The purified PCR product was sequenced by using the sequencing kit with fluorescent dye terminators (Perkin-Elmer, Foster City, Calif.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The PCR primers were also used for sequencing. The thermal cycling reactions were 96°C for 30 s, 50°C for 15 s, and 60°C for 4 min for 25 cycles. The products were purified by ethanol precipitation and were then resuspended in the loading buffer (formamide and 25 mM EDTA [5:1]). The samples were heated at 90°C for 2 min and were loaded onto a 4.75% polyacrylamide gel. The sequence data were collected with an autosequencer (ABI-373A; Perkin-Elmer).
Analysis of sequences.
The full-length vpu genes were aligned with the vpu genes of selected reference strains that represented various HIV-1 subtypes from the Los Alamos HIV database. The sequence data were analyzed with GeneWorks software (IntelliGenetics, Mountain View, Calif.). The phylogenetic relationships of the vpu genes among HIV-1 strains were analyzed by the neighbor-joining method and the Kimura 2-parameter distance matrix listed in the MEGA (molecular evolutionary genetic analysis) analytical package (10). The sequences of following reference strains (with their subtypes, GenBank accession numbers given in parentheses) were used for comparison: U455 (A, M62320), UG273 (A, L22957), UG275 (A, L22951), 92UG037 (A, U51190), SF2 (B, K02007), MN (B, M17449), JRFL (B, U63632), ETH2220 (C, U46016), 92BR025 (C, U52953), NDK (D, M27323), Z2Z6 (D, M22639), CM240X (AE, U54771), BZ126A (F, L22082), BZ163A (F, L22085), HH8793 (G, AF061641), SE6165 (G, AF061642), 92NG083 (AG, U88826), IBNG (AG, L39106), 90CR056 (H, AF005496), ANT70 (group O, L20587), and MVP5180 (group O, L20571).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The vpu gene sequences determined in this study were deposited in the GenBank sequence database. The accession numbers are AF143901 to AF143903 for TWA strains, AF220462 to AF220471 for TWB strains, AF220472 to AF220475 for TWC strains, AF220476 to AF220485 for TWE strains, and AF220486 to AF220489 for TWG strains.
RESULTS
Determination of vpu subtypes.
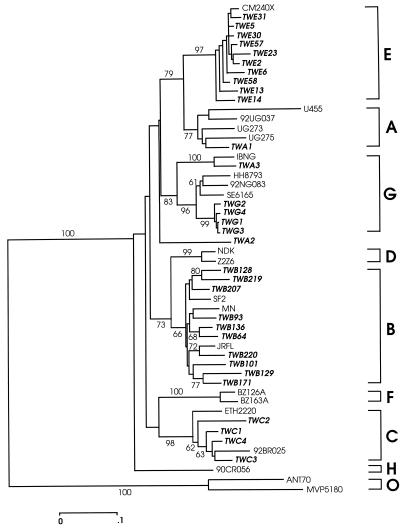
The vpu genes of HIV-1 strains from 363 infected individuals in Taiwan were amplified by PCR and completely sequenced. The nucleotide sequences were aligned with reference strains of subtypes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H and were subjected to phylogenetic analysis. The genetic subtypes of the vpu genes were thus determined on the basis of the alignments and the phylogenetic trees. A typical phylogenetic tree with some of the strains is shown in Fig. 1. These Taiwanese strains were designated “TW,” followed by characters that indicate the env subtype. An env subtype A variant, TWA1, clustered with subtype A reference strains U455, UG273, UG275, and 92UG037 (Fig. 1). Strains TWB64, TWB93, TWB101, TWB128, TWB129, TWB136, TWB171, TWB207, TWB219, and TWB220 clustered with subtype B reference strains SF2, MN, and JRFL. Strains TWC1 to TWC4 clustered with subtype C reference strains 92BR025 and ETH2220. Strains TWE2, TWE5, TWE6, TWE13, TWE14, TWE23, TWE30, TWE31, TWE57, and TWE58 clustered with subtype E reference strain CM240X. Strains TWG1 to TWG4 and TWA3 formed a cluster with subtype G reference strains HH8793 and SE6165 and with AG recombinants IBNG and 92NG083. It should be noted that the subtype E strains form a distinct group, although this group is also closely related to subtype A strains (Fig. 1). The vpu subtype of one strain, TWA2, could not be determined, since it did not cluster with any of the strains analyzed.
FIG. 1.
Scaled vpu gene neighbor-joining phylogeny of 31 Taiwanese strains and 19 reference sequences from various HIV-1 subtypes, with ANT70 and MVP5180 as the outliers. The Taiwanese strains are indicated by boldface italic type. The Taiwanese strains were designated according to the env subtype, which is indicated by the characters that follow “TW.” Bootstrap values above 60% are indicated at the branch nodes. A branch length nucleotide difference of 10% is indicated at the bottom.
Sequence analysis of vpu genes.
Sequence analysis of the vpu genes of three previously reported Taiwanese env subtype A variants (12), TWA1, TWA2, and TWA3, revealed that the sequence divergences among them were greater than 20%. The results of the sequence comparisons of the vpu genes of these env subtype A variants and some of the Taiwanese strains of different subtypes are summarized in Table 1. The nucleotide sequence divergences among strains of each of the env subtypes B, C, E, and G were less than 14%, whereas the divergences among strains of different env subtypes were generally greater than 17%. The vpu gene of TWA3 was classified as subtype G in the phylogenetic analysis, but it varied from those of the other four Taiwanese subtype G strains that were epidemiologically linked (13) (divergence range, 13.4 to 14.6%). TWA1 did not show a high degree of similarity to the other Taiwanese strains. However, its vpu gene was closely related to those of subtype A reference strains U455, UG273, UG275, and 92UG037, with similarities ranging from 85.8 to 90.7%. This was consistent with the classification of TWA1 as vpu subtype A in the phylogenetic analysis. As for the strain with an undetermined vpu subtype, TWA2, its nucleotide sequence did not show a high degree of similarity to that of any Taiwanese strain or to those of any of the subtype reference strains analyzed (Table 1 and Table 2).
TABLE 1.
Percent divergence among the vpu genes from Taiwanese HIV-1 strains
| Strain | % Divergencea
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWA1 | TWA2 | TWA3 | TWB64 | TWB93 | TWB128 | TWB129 | TWB207 | TWC1 | TWC2 | TWC3 | TWC4 | TWE5 | TWE13 | TWE14 | TWE23 | TWE31 | TWG1 | TWG2 | TWG3 | TWG4 | |
| TWA1 | 34.6 | 29.7 | 35.8 | 30.9 | 29.7 | 35.8 | 29.6 | 32.9 | 32.9 | 31.7 | 31.7 | 27.2 | 28.4 | 29.7 | 32.1 | 29.6 | 32.1 | 33.3 | 32.1 | 32.1 | |
| TWA2 | 24.0 | 35.8 | 37.0 | 34.6 | 29.7 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 33.3 | 38.3 | 38.3 | 35.8 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 25.9 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 27.2 | |
| TWA3 | 22.4 | 22.8 | 29.7 | 30.9 | 32.1 | 33.3 | 32.1 | 37.0 | 43.0 | 39.5 | 35.8 | 32.1 | 33.3 | 35.8 | 35.8 | 32.1 | 19.8 | 23.5 | 21.0 | 21.0 | |
| TWB64 | 23.6 | 23.6 | 19.5 | 19.8 | 21.0 | 19.8 | 13.6 | 38.3 | 43.2 | 42.0 | 39.5 | 35.8 | 39.5 | 35.8 | 39.5 | 39.0 | 29.6 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | |
| TWB93 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 19.1 | 8.9 | 18.5 | 18.5 | 14.8 | 37.0 | 44.4 | 39.5 | 39.5 | 30.9 | 34.6 | 32.1 | 38.3 | 33.3 | 30.9 | 32.1 | 32.1 | 32.1 | |
| TWB128 | 19.9 | 21.5 | 22.4 | 11.4 | 10.6 | 21.0 | 13.6 | 30.9 | 40.7 | 33.3 | 31.7 | 29.7 | 31.7 | 28.4 | 34.6 | 29.6 | 32.1 | 29.7 | 32.1 | 30.9 | |
| TWB129 | 25.2 | 23.2 | 25.2 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 13.8 | 18.5 | 34.6 | 39.5 | 33.3 | 35.8 | 32.1 | 34.6 | 32.1 | 38.3 | 34.6 | 29.7 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | |
| TWB207 | 21.1 | 21.1 | 21.5 | 8.1 | 8.9 | 7.7 | 11.8 | 33.4 | 38.3 | 34.6 | 34.6 | 29.6 | 30.9 | 29.6 | 35.8 | 30.9 | 32.1 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 32.1 | |
| TWC1 | 21.5 | 21.1 | 24.8 | 22.4 | 20.7 | 19.9 | 22.0 | 21.1 | 17.1 | 12.2 | 8.5 | 40.7 | 43.2 | 40.7 | 45.7 | 42.0 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | |
| TWC2 | 21.5 | 25.6 | 28.0 | 29.2 | 25.6 | 24.8 | 26.4 | 24.8 | 11.6 | 17.4 | 21.0 | 39.5 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 44.5 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | |
| TWC3 | 22.8 | 23.2 | 26.4 | 24.4 | 21.5 | 22.4 | 24.4 | 22.8 | 6.0 | 10.3 | 8.5 | 37.0 | 39.5 | 37.0 | 42.0 | 38.3 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | 40.7 | |
| TWC4 | 21.1 | 23.2 | 24.8 | 23.6 | 22.0 | 20.3 | 24.0 | 22.4 | 4.4 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 39.5 | 40.7 | 39.5 | 42.0 | 40.7 | 38.3 | 40.7 | 38.3 | 38.3 | |
| TWE5 | 17.1 | 20.3 | 24.0 | 25.6 | 22.8 | 21.1 | 24.4 | 21.1 | 23.6 | 26.4 | 25.6 | 27.6 | 13.6 | 11.1 | 9.9 | 4.9 | 22.2 | 21.0 | 22.2 | 22.2 | |
| TWE13 | 17.1 | 21.1 | 24.0 | 25.2 | 23.2 | 21.5 | 24.0 | 20.3 | 24.8 | 26.4 | 25.2 | 24.4 | 5.7 | 17.3 | 17.3 | 14.8 | 24.7 | 22.2 | 23.5 | 24.7 | |
| TWE14 | 17.9 | 20.3 | 24.4 | 24.8 | 22.4 | 21.5 | 24.4 | 21.5 | 24.0 | 25.6 | 24.0 | 23.6 | 4.9 | 7.3 | 9.9 | 12.3 | 25.9 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 24.7 | |
| TWE23 | 18.3 | 22.4 | 26.4 | 27.2 | 25.2 | 24.0 | 27.2 | 24.0 | 26.8 | 28.5 | 27.6 | 25.6 | 4.5 | 7.7 | 5.3 | 12.3 | 25.9 | 25.9 | 25.9 | 25.9 | |
| TWE31 | 18.3 | 20.4 | 23.6 | 26.4 | 24.0 | 22.0 | 25.2 | 22.0 | 24.8 | 27.2 | 26.8 | 25.2 | 3.3 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 22.2 | 19.8 | 22.2 | 22.2 | |
| TWG1 | 21.5 | 18.3 | 13.4 | 18.7 | 18.3 | 19.9 | 20.7 | 19.9 | 25.2 | 27.6 | 26.8 | 25.6 | 17.5 | 18.3 | 17.5 | 19.5 | 17.1 | 3.7 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| TWG2 | 22.8 | 19.1 | 14.6 | 19.1 | 18.7 | 19.5 | 20.7 | 19.5 | 25.2 | 28.5 | 27.6 | 27.2 | 16.3 | 16.7 | 16.3 | 19.1 | 15.9 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.7 | |
| TWG3 | 21.5 | 18.7 | 13.8 | 19.1 | 18.7 | 19.9 | 21.1 | 19.5 | 25.6 | 28.0 | 27.2 | 26.0 | 17.5 | 17.9 | 17.5 | 19.5 | 17.1 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| TWG4 | 21.5 | 18.7 | 13.8 | 19.1 | 18.7 | 19.5 | 21.1 | 19.9 | 25.2 | 27.6 | 26.8 | 25.6 | 17.5 | 18.3 | 17.5 | 19.5 | 17.1 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 0.8 | |
The Taiwanese strains were designated “TW,” followed by characters that indicate their env subtype. The divergence was calculated after excluding the insertion or deletion sequences and is shown as the percentage of deviant positions. The divergence between the nucleotide sequences is shown below the diagonal; the divergence between deduced amino acid sequences is shown above the diagonal. Boldface numbers indicate the comparisons between strains of the same env subtype.
TABLE 2.
Comparison of vpu gene of Taiwanese env subtype A variant TWA2 with those of reference strains
| vpu subtype | Reference strain | % Similarity to TWA2a
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full length | 5′ two-thirds | 3′ one-third | ||
| A | U455 | 75.6 | 71.8 | 83.1 |
| UG273 | 76.8 | 73.6 | 83.1 | |
| UG275 | 76.8 | 72.4 | 85.5 | |
| 92UG037 | 75.6 | 75.5 | 75.9 | |
| B | JRFL | 77.6 | 79.1 | 74.7 |
| C | ETH2220 | 72.1 | 76.7 | 75.9 |
| D | NDK | 79.3 | 79.1 | 79.5 |
| E | CM240X | 78.9 | 71.8 | 92.8 |
| F | BZ126A | 79.5 | 77.9 | 80.7 |
| G | HH8793 | 79.3 | 73.0 | 91.6 |
| SE6165 | 83.3 | 78.5 | 92.8 | |
| 92NG083 | 79.3 | 77.8 | 91.6 | |
| H | 90CR056 | 76.0 | 76.3 | 74.7 |
The values represents percent similarity in the nucleotide sequence. The similarity was calculated after excluding the insertion or deletion sequences. For most of the strains in the comparison, the regions of the full-length, 5′ two-thirds, and 3′ one-third of the vpu gene compared contain 246, 163, and 83 nucleotides, respectively.
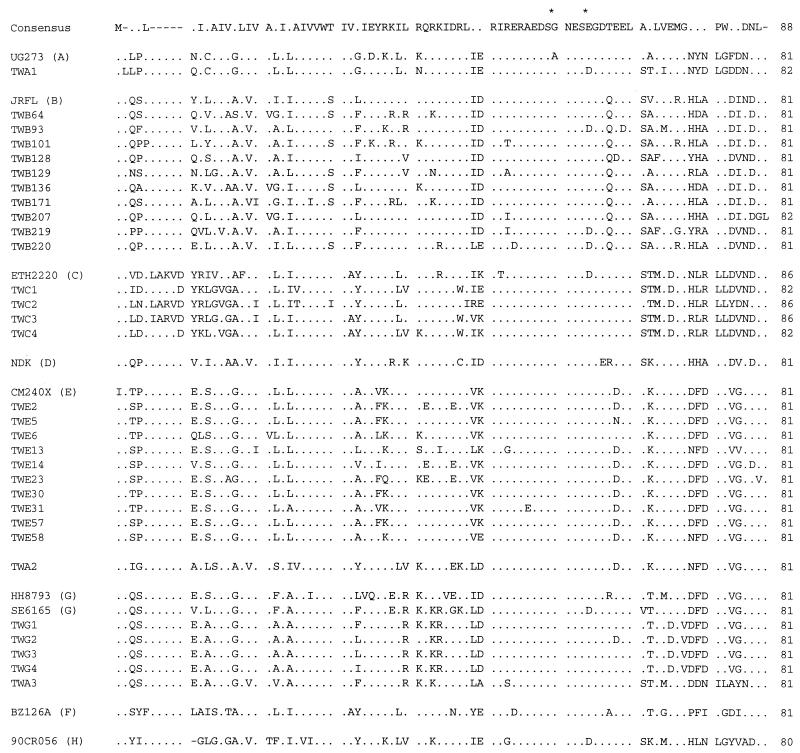
The deduced amino acid sequences of the vpu gene were also aligned and analyzed. As shown in Fig. 2, two serine residues were retained by all of the strains analyzed. In addition, charged residues were highly conserved at 11 positions. The strains of the same subtype were more similar in terms of the deduced amino acid sequences of Vpu. Of note was the fact that the sequence of the C-terminal one-third of TWA2 was similar to those of CM240X, HH8793, and SE6165. In particular, of the 27 amino acid residues in this region (from residue N55 to residue L81), TWA2 was identical to CM240X at 26 positions. Since the C-terminal one-third but not the N-terminal portion of the Vpu amino acid sequence of TWA2 was very similar to those of some of the reference strains, the nucleotide sequence similarity between TWA2 and the subtype reference strains was reexamined by dividing the sequence into two portions: the 5′ two-thirds and 3′ one-third. As shown in Table 2, the 3′ one-third of TWA2 had 91.6% or greater similarity to the 3′ one-third of HH8793, SE6165, 92NG083, and CM240X, whereas the similarity of the 5′ two-thirds of TWA2 to the 5′ two-thirds of any of the strains analyzed was less than 80% (Table 2).
FIG. 2.
Deduced amino acid alignment of Vpu for the 31 Taiwanese strains and 9 reference strains. The vpu subtypes of the reference strains are indicated in parentheses. The alignment was constructed with GeneWorks software (IntelliGenetics, San Jose, Calif.). The consensus sequence inferred from the 40 sequences is shown at the top of the alignment. Dots indicate identity with the consensus sequence. Dashes denote gaps generated during the alignment. Conserved serine residues are indicated by asterisks.
Comparison of HIV-1 subtypes determined by different genes.
The genetic subtypes determined by vpu gene analysis were compared with those previously determined by env and gag gene analysis (Lee et al., Program Abstr. 4th Int. Conf. AIDS). Table 3 summarizes the results of the comparison for the strains in 247 samples. Of the strains in these samples, both the env and gag subtypes were determined for 69 strains, only the env subtype was determined for 143 strains, and only the gag subtype was determined for 35 strains. As shown in Table 3, the genetic subtypes determined by vpu gene analysis were generally in agreement with those determined by env and/or gag gene analysis. Of the 212 strains for which both vpu and env subtypes were available, 210 were of the same subtype. Of the 104 strains for which both vpu and gag subtypes were available, 65 were of the same subtype but 37 were of subtype E by vpu analysis and subtype A by gag analysis. The 37 subtype E vpu strains were actually AE recombinants which contain subtype E env and subtype A gag.
TABLE 3.
Comparison of HIV-1 subtypes determined by genetic analysis of vpu, env, and gag genes
| Subtype determined by analysis of the following gene:
|
No. of strains | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| vpu | env | gag | |
| A | A | A | 1 |
| B | B | B | 25 |
| B | —a | B | 35 |
| B | B | — | 143 |
| C | C | C | 4 |
| E | E | A | 37 |
| G | A | A | 1 |
| Unclassified | A | G | 1 |
| Total | 247 | ||
—, subtyping with the specific gene was not done.
vpu subtypes of the HIV-1 strains among different risk groups in Taiwan.
Of the 363 samples collected from HIV-1-infected individuals, the strains in 268 (73.8%) were classified as subtype B, the strains in 84 (23.1%) were classified as subtype E, the strains in 5 (1.4%) were classified as subtype G, the strains in 4 (1.1%) were classified as subtype C, the strain in 1 (0.3%) was classified as subtype A, and the strain in 1 was unclassified (0.3%). The prevalence of HIV-1 subtypes among different risk groups in Taiwan was further analyzed and is summarized in Table 4. Eleven HIV-1-seropositive hemophiliacs who had received coagulation factors were all infected with subtype B viruses. Of the 10 intravenous drug users, 7 were infected with subtype B viruses and 3 were infected with subtype E viruses. Of the 35 strains collected from women who were not intravenous drug users and who were infected through heterosexual contact, 10 (28.6%) were subtype B, 21 (60.0%) were subtype E, 3 (8.6%) were subtype G, and 1 (2.9%) was unclassified. The group of men who were not intravenous drug users but who were infected with HIV-1 by sexual transmission included 307 individuals. Two hundred forty (78.2%) were infected with subtype B viruses and 60 (19.5%) were infected with subtype E viruses. Among the individuals in this risk group, all 78 homosexual men were infected with subtype B viruses. Of the 136 heterosexual men, 82 (60.3%) were found to be infected with subtype B virus, 47 (34.6%) were infected with subtype E virus, and the rest of them were infected with either subtype A, subtype C, or subtype G virus. These results indicated that while subtype B infection was predominant in the whole study population as well as in most of the risk groups, subtype E viruses constituted a significant proportion of the viruses in the heterosexual transmission risk group. Compared with the prevalence of subtype E infection in homosexual and bisexual men, the prevalence of subtype E infection in heterosexual men was much higher (P < 0.005 by the χ2 test). Furthermore, subtype E infection was prevalent at a significantly higher proportion in the women, who were infected primarily through heterosexual contacts, than in the men (P < 0.0001 by the χ2 test).
TABLE 4.
vpu subtypes of the HIV-1 strains recovered from people in different risk groups in Taiwan
| Risk group | No. (%) of individuals infected with HIV-1 subtype:
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | E | G | Unclassified | Total | |
| Hemophiliac | 0 (0) | 11 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 11 |
| Intravenous drug user | 0 (0) | 7 (70.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (30.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 10 |
| Sexual transmission | |||||||
| Women | 0 (0) | 10 (28.6) | 0 (0) | 21 (60.0)a | 3 (8.6) | 1 (2.9) | 35 |
| Men | |||||||
| Homosexual | 0 (0) | 78 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 78 |
| Heterosexual | 1 (0.7) | 82 (60.3) | 4 (2.9) | 47 (34.6)b | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | 136 |
| Bisexual | 0 (0) | 52 (89.7) | 0 (0) | 6 (10.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 58 |
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 28 (80.0) | 0 (0) | 7 (20.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 35 |
| Subtotal | 1 (0.3) | 240 (78.2) | 4 (1.3) | 60 (19.5) | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 307 |
| Total | 1 (0.3) | 268 (73.8) | 4 (1.1) | 84 (23.1) | 5 (1.4) | 1 (0.3) | 363 |
In the sexual transmission group, subtype E infection was prevalent at a significantly higher proportion in the women than in the men (P < 0.0001 by the χ2 test).
Subtype E infection was prevalent at a significantly higher proportion in heterosexual men than in the homosexual and bisexual men (P < 0.005 by the χ2 test).
DISCUSSION
We have used vpu gene sequencing analyses to subtype 363 HIV-1-positive samples. Only one strain could not be subtyped in this manner. The possibility of coinfection with two subtypes of HIV-1 in one individual was remote, since direct sequencing of each PCR product as described in this study revealed no evidence that indicated the coexistence of two distinct sequences. Furthermore, the vpu subtypes were generally in agreement with those determined by analysis of the env or gag gene. There was one exception, in which the subtype determined by vpu gene analysis was different from the subtype determined by env and gag gene analyses. This strain (TWA3), which was subtype A by gag and env gene analyses, as identified previously, was found in this study to be of subtype G by vpu gene analysis (12). Therefore, TWA3 was an AG recombinant.
The one strain (TWA2) that had an undetermined vpu subtype in this study was previously characterized as an intersubtype (AG) recombinant with subtype G by gag gene analysis and subtype A by env gene analysis (12). TWA2 did not show a high degree of similarity to any subtype reference strains analyzed. However, the 3′ one-third of the vpu gene of TWA2 had a higher degree of similarity to those of subtype G and subtype E strains than to those of strains of other subtypes. These observations suggest that part of the vpu gene of TWA2 can be classified as subtype G. Of note is that CM240X, an AE recombinant from Thailand, is closely related to subtype G strains in the 3′ one-third of vpu, as revealed by nucleotide sequence alignment (with 91.6% similarity) and by phylogenetic analysis (data not shown). CM240X was known to have a subtype A gag gene and a subtype E env gene (1). The 3′ one-third of vpu is the region of vpu that overlaps env. Although the reason for the clustering of subtype E and subtype G in this region remains unclear, the close relationship between subtype E and subtype G has also been described for the cytoplasmic domain of gp41, and subtype E and subtype G strains form a single cluster in the coding region for the cytoplasmic domain of gp41 by phylogenetic analysis. (2).
The vpu genes of the Taiwanese env subtype E strains were closely associated with that of CM240X by phylogenetic analysis. These subtype E strains form a distinct group which was close to the subtype A strains in the phylogenetic tree. While the similarities of the vpu genes of these subtype E strains to those of subtype A strains U455, UG273, UG275, and 92UG037 ranged from 81.7 to 85.0%, the similarity of the vpu genes of these strains to that of CM240X was in the range of 93.9 to 98.0%. Therefore, the vpu genes of the subtype E strains could easily be distinguished from those of the subtype A strains.
The epidemic of HIV-1 infection in Taiwan began at about the same time that HIV-1 was introduced into Asia (16, 26). The first case of HIV-1 infection in Taiwan was reported in 1985. Since 1991, the seroprevalence rates have increased rapidly. As the end of November 1999, 2,375 cumulative HIV-1 infections had been reported to the Department of Health (Center for Disease Control, Department of Health, Taiwan, Republic of China, http://www.cdc.gov.tw/e/aids). Among them, 982 were among individuals in the risk category of heterosexual transmission, 664 were among homosexual men, and 383 were among bisexual men (Center for Disease Control, Department of Health). Although the main risk factor has been reported to shift from homosexual to heterosexual contact in 1992 (3), an extraordinary male-to-female ratio of 12:1 was noted.
The spread of subtype B HIV-1 in Taiwan was first found in the homosexual male population through contact with foreigners. Later, subtype E virus was introduced into Taiwan through travelers who had heterosexual contact with commercial sex workers in Thailand. This study revealed that subtype B was the most prevalent subtype in Taiwan, whereas subtype E viruses constituted a significant proportion of the HIV-1 strains that infected those in the heterosexual transmission risk group. These results were generally in agreement with the findings of a previous study which determined the subtypes by the peptide serotyping method (4). However, that study showed a much higher proportion of subtype E virus in the homosexual male population (20.8%). This discrepancy could partially be explained by the cross-reactivity by the peptide serotyping method and by the limited number of samples selected. To clarify this, more samples need to be studied in the future.
The genetic variability of HIV-1 has been a problem for PCR amplification. It is difficult to design a single primer set in the env and gag regions suitable for detection of all HIV-1 strains. Multiple primer pairs and different amplification conditions are commonly used to achieve the optimal results (6). However, PCR amplification of the vpu gene with the primers and the conditions reported in this study was rather satisfactory. This was probably due to the conservation of the sequences that flank the vpu gene. In addition, the specificities of the primers were validated by the findings that each positive PCR product was completely sequenced and was found to be a vpu sequence. Furthermore, the vpu gene of the virus in each sample occupied a distinct position in the phylogenetic tree, suggesting that cross-contamination between samples was unlikely to have occurred. The sensitivity of the PCR protocol described here was good, since the detection limit was estimated to be four copies of HIV-1 DNA spiked in genomic DNA extracted from seronegative PBMCs (data not shown). PCR amplification of vpu was promising at least for our local circulating strains of subtypes A, B, C, E, and G. vpu gene analysis may provide additional information and an alternate method from traditional gag and env analysis for determination of the subtypes of most of the HIV-1 strains, excluding those in which intersubtype recombination has occurred.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the staff of Taipei Municipal Venereal Disease Control Institute for the collection of samples, Hui-Shiuh Lin and Shih-Hsiang Chien for technical assistance, and Chin-Der Lee for data analysis.
This work was supported by grants from the National Taiwan University Hospital (grants NTUH-85209-B01 and NTUH-87S1522) and the Department of Health (grant DOH87-TD-1038) of Taiwan, Republic of China.
REFERENCES
- 1.Carr J K, Salminen M O, Koch C, Gotte D, Artenstein A W, Hegerich P A, St. Louis D, Burke D S, McCutchan F E. Full-length sequence and mosaic structure of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate from Thailand. J Virol. 1996;70:5935–5943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.9.5935-5943.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carr J K, Salminen M O, Albert J, Sanders-Buell E, Gotte D, Birx D L, McCutchan F E. Full genome sequences of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes G and A/G intersubtype recombinants. Virology. 1998;247:22–31. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen M Y, Wang G R, Chuang C Y, Shih Y T. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in Taiwan, 1984 to 1994. J Formos Med Assoc. 1994;93:901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen Y M A, Lee C M, Lin R Y, Chang H J. Molecular epidemiology and trends of HIV-1 subtypes in Taiwan. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1998;19:393–402. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199812010-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Debyser Z, Van Wijngaerden E, Van Laethem K, Beuselinck K, Reynders M, De Clercq E, Desmyter J, Vandamme A. Failure to quantify viral load with two of the three commercial methods in a pregnant woman harboring an HIV type 1 subtype G strain. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1998;14:453–459. doi: 10.1089/aid.1998.14.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Engelbrecht S, van Rensburg E J. Detection of Southern African human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes by polymerase chain reaction: evaluation of different primer pairs and conditions. J Virol Methods. 1995;55:391–400. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(95)00088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hammond J, Larder B A, Schinazi R F, Mellors J W. Human retroviruses and AIDS 1997: a compilation and analysis of nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Los Alamos, N.Mex: Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1997. Mutations in retroviral gene associated with drug resistance. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hu D J, Dondero T J, Rayfield M A, George J R, Schochetman G, Jaffe H W, Luo C C, Kalish M L, Weniger B G, Pau C P, Schable C A, Curran J W. The emerging genetic diversity of HIV: the importance of global surveillance for diagnostics, research, and prevention. JAMA. 1996;275:210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hu W S, Temin H M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990;250:1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetic analysis, version 1.01. University Park: The Pennsylvania State University; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kwok S, Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989;339:237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee C N, Chen M Y, Lin H S, Lee M C, Luo C C, Twu S J, Lin R Y, Chuang C Y. HIV type 1 env subtype A variants in Taiwan. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1998;9:807–809. doi: 10.1089/aid.1998.14.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee C N, Chen M Y, Fan W S, Twu S J, Lin R Y. Domestic transmission of HIV type 1 subtype G strains in Taiwan. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1999;15:1137–1140. doi: 10.1089/088922299310421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leitner T. Human retroviruses and AIDS 1996: a compilation and analysis of nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Los Alamos, N.Mex: Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1996. Genetic subtypes of HIV-1. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li W H, Tanimura M, Sharp P M. Rates and dates of divergence between AIDS virus nucleotide sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1988;5:313–330. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin K T, Huang S H, Kao C L, Huang K M, Yu J C, Hung T P, Chou M Y, Liu W T, Fang C T, Kuo Y T. An autopsy-proved case of AIDS in Taiwan. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 1987;5:25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Louwagie J, McCutchan F E, Peeters M, Brennan T P, Sanders-Buell E, Eddy G A, van der Groen G, Fransen K, Gershy-Damet G-M, Deleys R, Burke D S. Phylogenetic analysis of gag genes from 70 international HIV-1 isolates provides evidence for multiple genotypes. AIDS. 1993;7:769–780. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199306000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Luciw P A. Human immunodeficiency viruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, Chanock R M, Melnick J L, Monath T P, Roizman B, Straus S E, editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1996. pp. 1881–1952. [Google Scholar]
- 19.McCutchan F E, Salminen M O, Carr J K, Burke D S. HIV-1 genetic diversity. AIDS. 1996;10:S13–S20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Myers G. Assimilating HIV sequences. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1993;9:697–702. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ou C Y, Kwok S, Mitchell S W, Mack D H, Sninsky J J, Krebs J W, Feorino P, Warfield D, Schochetman G. DNA amplification for direct detection of HIV-1 in DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Science. 1988;239:295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3336784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ou C Y, Takebe Y, Weniger B G, Luo C C, Kalish M L, Auwanit W, Yamazaki S, Gayle H D, Young N L, Schochetman G. Independent introduction of two major HIV-1 genotypes into distinct high-risk populations in Thailand. Lancet. 1993;341:1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Palmer S, Alaeus A, Albert J, Cox S. Drug susceptibility of subtypes A, B, C, D, and E human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1998;14:157–162. doi: 10.1089/aid.1998.14.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Simon F, Mauclere P, Roques P, Loussert-Ajaka I, Muller-Trutwin M C, Saragosti S, Georges-Courbot M C, Barre-Sinoussi F, Brun-Vezinet F. Identification of a new human immunodeficiency virus type 1 distinct from group M and group O. Nat Med. 1998;4:1032–1037. doi: 10.1038/2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Strebel K. Human retroviruses and AIDS 1996: a compilation and analysis of nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Los Alamos, N.Mex: Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1996. Structure and function of HIV-1 Vpu. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Weniger B G, Limpakarnjanarat K, Ungchusak K, Thanprasertsuk S, Choopanya K, Vanichseni S, Uneklabh T, Thongcharoen P, Wasi C. The epidemiology of HIV infection and AIDS in Thailand. AIDS. 1991;5:S71–S85. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101001-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]