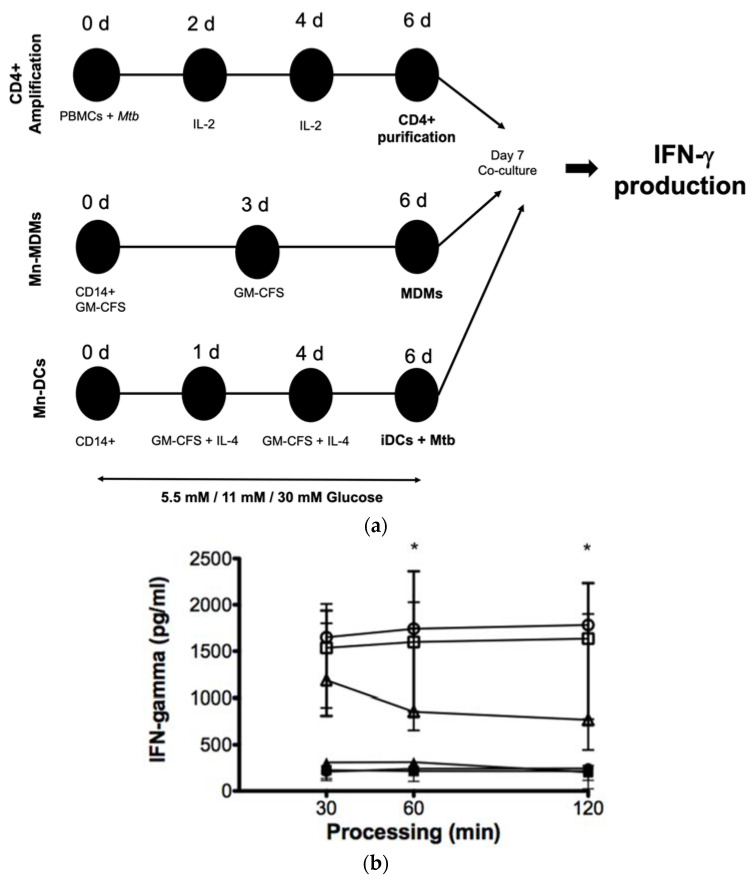
Figure 6.
Effect of high glucose concentrations on the processing and presentation of M. tuberculosis antigens by MDMs. (a) PBMCs isolated from healthy donors were infected with the nonvirulent laboratory strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mtb H37Ra at a MOI 1:10 at day 0, and IL-2 was added as indicated to amplify specific CD 4+ T cell clones. Mtb specific CD4+ T cells were purified by negative selection at day 6. CD14+ cells purified from the same donors at day 0 were differentiated for 6 days to MDMs and DCs as described. MDMs and DCs were cultured in 5.5 mM, 11 mM, 30 mM of glucose and infected with Mtb H37Ra at a MOI 1:10 for 1 h and co-cultivated with autologous CD4+ specific T cells for 4 h. Cells and supernatants were collected and IFN-𝛾 production was analyzed by ELISA. (b) Concentration of IFN-γ in the supernatants of co-cultured CD4+ T cells in the presence of 5.5 (open circles), 11 (open squares), and 30 mM (open triangles) of glucose for 6 days infected with and without Mtb infection in 5.5 (filled circles), 11 (filled squares), and 30 mM (filled triangles) of glucose, assayed by ELISA. Data were analyzed using the Friedman test. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Differences were considered significant when * p < 0.01; from five independent experiments.