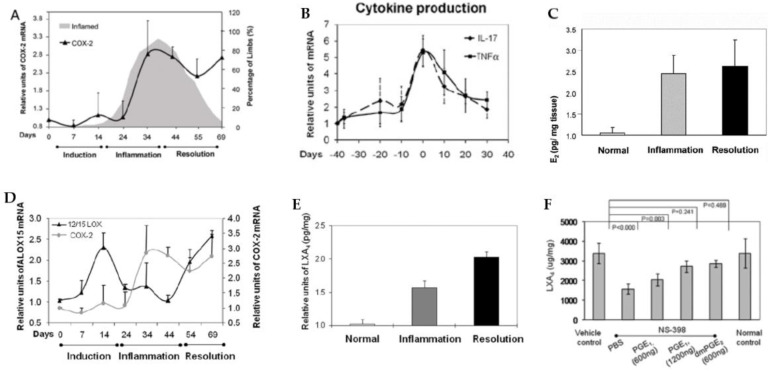
Figure 8.
Changes in the expression of COX-2 and cytokines (IL-17 and TNF-α) in a murine model of autoimmune arthritis. (A,B) PGE2 levels, (C) expression of LOX-15, (D) changes in the concentration of LXA4, and (E) effect of various concentrations of PGE2 on LXA4 production (F) in the joints of murine autoimmune arthritis model (see reference [36]). These data were taken from reference [36] and modified. It is evident from this data that, during the acute inflammation stage, there is enhanced expression of COX-2, increased production of IL-17 and TNF-α, augmentation in the production of PGE2, and relatively less production of LXA4 and 12-15-LOX expression. During the phase of resolution of inflammation, the expression of COX-2 (A) and PGE2 (C) production remains high, whereas 12-15-LOX expression is decreased (D) and LXA4 production is elevated (E) with concomitant decrease in IL-17 and TNF-α production (B) that results in resolution of joint inflammation. Both PGE1 and PGE2 enhanced the production of LXA4 (PGE2 > PGE1) (F) by enhancing the expression of ALX, the receptor of LXA4.