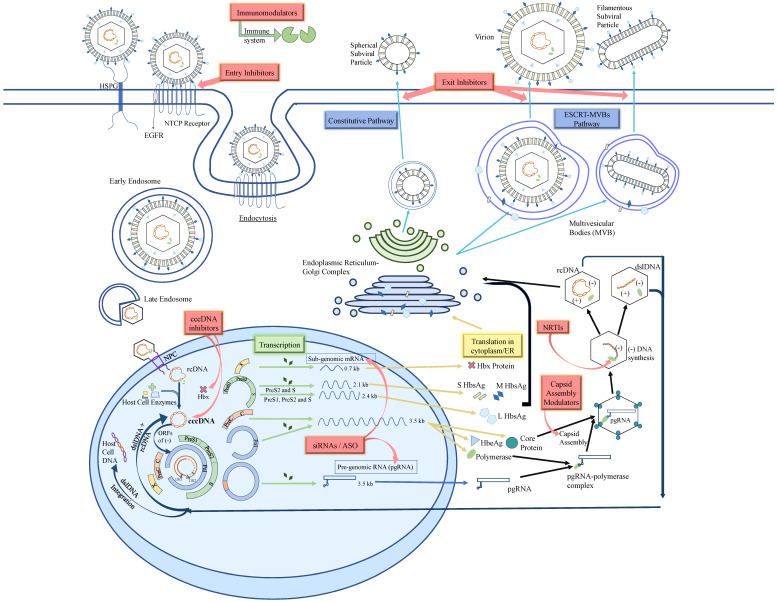
Figure 2.
HBV life cycle in a hepatocyte. Entry inhibitors target the NTCP receptor on hepatocytes and hence prevent the entry of virion into the cell altogether. cccDNA inhibitors either act by targeting the HBx protein which leads to smc5/6 degrading cccDNA or by using the CRISPR/Cas9 nucleases system to break apart the cccDNA. Silencing RNAs (siRNAs) play a role in the destruction of newly formed RNAs. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) work against the mRNAs and stop them from reaching the translation step. Capsid assembly modulators cause the production of defected or empty nucleocapsids which fail to further produce new cccDNA or virions. Nucleic acid polymers (NAPs) block the assembly and the secretion of spherical SVP. The release of subviral filaments and virions is not affected [12]. Immunomodulators boost the immune system to attack the virus. HSPG: Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans, NTCP: Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide, EGFR: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, NPS: Nuclear Pore Complex, rcDNA: relaxed circular DNA, cccDNA: covalently closed circular DNA, ORFs: Open Reading Frames, dslDNA: double-stranded linear DNA, siRNAs: small interfering RNA, ASO: Anti-sense Oligonucleotide, S, M, L HBsAg: Small, Medium, Large HBsAg, ER: Endoplasmic Reticulum, ESCRT-MVBs pathway: Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport.