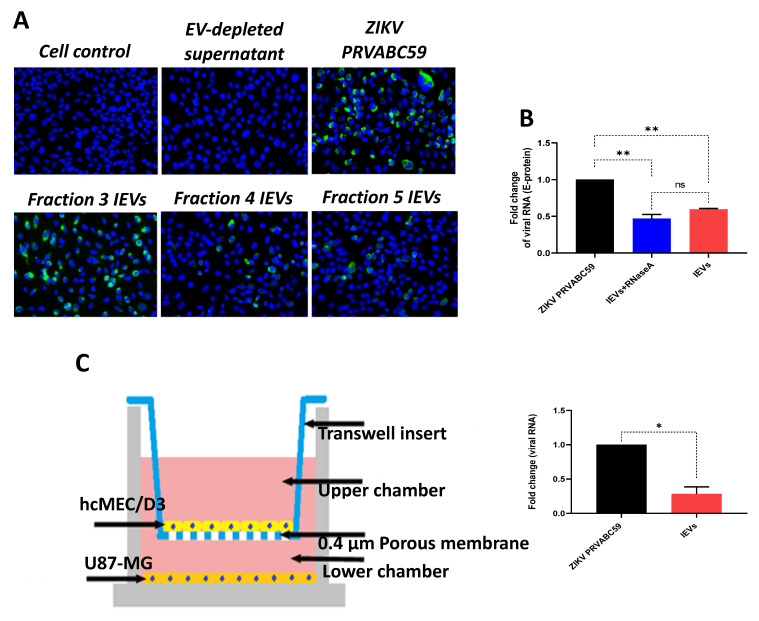
Figure 2.
ZIKV-infected cell-derived EVs (IEVs) are able to transfer viral material to naïve cells. (A) Detection of ZIKV envelope protein (green) in hcMEC/D3 cells after their inoculation (72 h) with different IEV fractions (20× objective). Positive (ZIKV-infected cells) and negative (EV-depleted supernatant) controls are also included. (B) Fold change in viral RNA levels (detection of E-protein) among ZIKV- (black), IEVs-pretreated with RNase A (blue), and IEVs- (red) infected hcMEC/D3 cells. Pretreatment of IEVs with RNase A shows no differences in viral RNA levels with untreated IEVs, indicating that most of the RNA resides inside the vesicles. (C) Representation of the Transwell assay setup to demonstrate that IEVs (colored spheres), isolated from ZIKV-infected hcMEC/D3 cells, can transfer viral RNA to glioblastoma cells (U87-MG, lower chamber) (6 days post-infection). ZIKV virions (virus stock) was also included in the assay. Significant difference is also indicated between ZIKV- and IEV-treated cells and calculated based on p-values; ns: p > 0.05, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005. Data are acquired from two independent experiments.