ABSTRACT
Diphtheria is one of the most well studied of all the bacterial infectious diseases. These milestone studies of toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae along with its primary virulence determinant, diphtheria toxin, have established the paradigm for the study of other related bacterial protein toxins. This review highlights those studies that have contributed to our current understanding of the structure-function relationships of diphtheria toxin, the molecular mechanism of its entry into the eukaryotic cell cytosol, the regulation of diphtheria tox expression by holo-DtxR, and the molecular basis of transition metal ion activation of apo-DtxR itself. These seminal studies have laid the foundation for the protein engineering of diphtheria toxin and the development of highly potent eukaryotic cell-surface receptor-targeted fusion protein toxins for the treatment of human diseases that range from T cell malignancies to steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease to metastatic melanoma. This deeper scientific understanding of diphtheria toxin and the regulation of its expression have metamorphosed the third-most-potent bacterial toxin known into a life-saving targeted protein therapeutic, thereby at least partially fulfilling Paul Erlich’s concept of a magic bullet—“a chemical that binds to and specifically kills microbes or tumor cells.”
INTRODUCTION
Over the past 4 decades, perhaps no other infectious disease has been as successfully studied as diphtheria (1, 2). Indeed, the study of diphtheria toxin established the structure-function paradigm for the study of other toxins in the bacterial protein toxin field. Moreover, when coupled with the molecular genetic study of the iron-activated regulatory element, DtxR, that controls the expression of diphtheria toxin, we now have a detailed understanding of the entire tox genetic system, from the regulation of expression to the molecular mechanism of diphtheria toxin action. In this article, we review the development of our current understanding of diphtheria toxin, from its structure-function relationships to its mechanism of entry into the eukaryotic cell cytosol, the molecular mechanism of transition metal ion activation of DtxR and its regulation of tox expression, and finally, the protein engineering of diphtheria toxin for the development of highly potent and selective cell-surface receptor-targeted fusion protein toxins for the treatment of human diseases.
It is well known that to cause clinical disease, the etiologic agent of diphtheria, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, must first be infected with one of a closely related family of bacteriophages that carry the structural gene for the toxin. Humans are the only natural host for diphtheria, and disease is readily spread through close contact and aerosolized droplets. While clinical diphtheria remains prevalent in tropical developing countries where immunization with diphtheria toxoid remains sporadic, diphtheria is almost nonexistent in industrialized countries that have continued to maintain a comprehensive immunization program with diphtheria toxoid. Since diphtheria toxin is secreted into the culture medium, the high-yield-producing Park-Williams 8 strain of C. diphtheriae has been used almost worldwide to produce diphtheria toxin in sufficient yields to produce diphtheria toxoid (3). Once purified from the spent culture medium, native diphtheria toxin is then treated with formalin at 30 to 38°C for several weeks to produce the nontoxic toxoid. To produce the vaccine, diphtheria toxoid is absorbed to alumina, which acts as an adjuvant, and it is then combined with tetanus toxoid and either heat-killed Bordetella pertussis to produce the DPT vaccine or purified pertussis antigens to produce the diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis vaccine.
Along with botulinum, tetanus, and Shiga, diphtheria toxin is one of the most potent bacterial protein toxins known. In humans the 50% lethal dose for diphtheria toxin was found to be approximately 100 ng/kg. This value was determined after a catastrophic accident in Kyoto, Japan, in 1948. Shortly after the end of World War II, a mass immunization program against diphtheria was initiated in Japan. After the production of diphtheria toxin and its distribution into vials for formalin detoxification in the preparation of toxoid, one vial of toxin was either inadvertently not treated or reverted to full toxicity after formalin treatment and was sent into the community as part of the program to immunize children. Of 606 children that were “immunized” from this vial, 68 children, mostly between the ages of 1 and 2, died of diphtheria intoxication (4, 5). Since the concentration of toxin in the vial, the dose that was administered, and the body weight of the children were all known, the human 50% lethal dose for diphtheria toxin could be calculated.
While diphtheria toxoid as a vaccine was available as early as the 1920s, investigations into the development of a simplified medium for toxin production led Alwin M. Pappenheimer, Jr., to make one of the earliest observations that the concentration of iron in the growth medium was critical to obtain maximal yields of the toxin (6). In 1935, Pappenheimer, then a Bradford Fellow at the Harvard Medical School, started his laboratory at the Massachusetts Antitoxin and Vaccine Laboratory to work on diphtheria toxin production. At that time Pyrex glassware was newly available, and he used Pyrex flasks in his first attempts to produce toxin. While he followed established protocols for medium preparation and incubation temperature and time for maximal yields, Pappenheimer was able to produce only half as much toxin as that reported by his predecessors who used the older soft glassware flasks in the laboratory. The question was obvious: Why did the glassware make a difference in toxin production? Pappenheimer’s experiment to address the question was equally obvious: He broke a flask made of soft glass and ground it into a powder. He then added varying amounts of powdered glass to the Pyrex flasks he was using and determined its effect on toxin production. Remarkably, Pappenheimer found that the addition of as little as 300 μg powdered soft glass resulted in a stimulation of both C. diphtheriae growth and toxin yield. Equally importantly, he found that the addition of 5 or 10 mg of powdered glass resulted in the almost complete inhibition of toxin production without a change in the growth of the diphtheria bacillus. The irony (pun intended) of this story is that Pappenheimer wrote his Ph.D. dissertation at Harvard College on the effect of organic bases on the oxidation potential of heme. It is no surprise then that his first experiments were focused on the effect of adding increasing amounts of inorganic iron to the growth medium as a function of diphtheria toxin yield. As shown in his classic 1936 paper (6), the stimulation and subsequent inhibition of toxin production following the addition of either powdered glass or iron salts to the media were superimposable. The ability to produce a maximal yield of diphtheria toxin in the soft glass resulted from the leaching of small levels of iron from the glass into the culture medium. We now know that maximal yields of diphtheria toxin are produced only when iron becomes the growth-rate-limiting substrate. So, as early as 1936, it was realized that with respect to iron, an essential nutrient for the growth of the bacillus, the physiologic state of toxigenic C. diphtheriae was a determining factor in the production of diphtheria toxin.
TEMPERATE CORYNEBACTERIOPHAGES CARRY THE STRUCTURAL GENE FOR DIPHTHERIA TOXIN, tox, IN LYSOGENIC C. DIPHTHERIAE
While it had been known since the earliest observations of C. diphtheriae that there were both virulent and nonvirulent strains that could be isolated from healthy individuals, it was not until the remarkable discovery by Freeman (7) that one could isolate diphtheria toxin-producing strains following the exposure of nontoxigenic strains to corynebacteriophages. Thus, it became clear that not only the physiologic state of C. diphtheriae with respect to the concentration of iron in the growth medium but also its lysogenic state determined the ability of a given isolate to produce diphtheria toxin. As important as Freeman’s observation was, the question of whether it was the host bacterium or the lysogenic phage that carried the structural gene for the toxin still remained.
Twenty years after Freeman’s initial report, Uchida et al. (8) described the isolation of corynebacteriophage β mutant lysogens of C. diphtheriae that produced nontoxic proteins that were serologically related to diphtheria toxin. The discovery of these mutant serologically related cross-reacting materials (CRMs) was extremely important because they not only demonstrated that the structural gene for diphtheria toxin, tox, was carried by β-phage, but the isolation of CRMs that were the result of both nonsense (e.g., CRM45) and missense (e.g., CRM197) mutations established both the genetic orientation of the toxin, N- to C-terminal, and began to give both biochemical and genetic definition to its structural-functional domains.
While corynebacteriophage β has not been nearly as well studied as coliphage λ, it is a temperate phage and, as such, may either enter a vegetative lytic cycle or lysogenize a sensitive host (e.g., the nontoxigenic, nonlysogenic C7s(–)tox– strain of C. diphtheriae) and convert it from a tox– to a tox+ phenotype. Both genetic and molecular genetic evidence suggest that the linear β-genome circularizes by ligation of its cohesive ends (cos) and integrates into the host chromosome as a prophage in a manner that corresponds to that for the integration of λ-phage into the Escherichia coli genome (9–11). It has been shown that the prophage map is a circular permutation of the vegetative map and that the imm marker is positioned at one end of the β-genome and tox is at the other end (Fig. 1). The Cs7(–)tox– genome carries two separate attB sites, attB1 and attB2, and as a result, β-phage can integrate and form single lysogens, double lysogens, and in rare instances, triple lysogens (12). In its lysogenic state, most β-phage genes appear to be repressed, and the lysogen is immune to superinfection by homoimmune corynebacteriophages. While triple lysogens are unstable and revert to stable double lysogens, under iron-limiting conditions, the final yield of diphtheria toxin that may be produced is directly related to the number of integrated prophage genomes (12).
FIGURE 1.
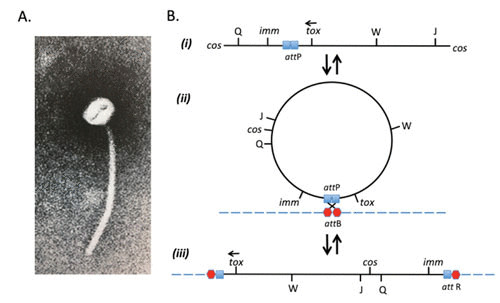
(A) Electron micrograph of corynebacteriophage β, which has a polyhedral head ∼52 nm in diameter and a 270 nm long tail. (B) Genetic map of β-phage in its (i) vegetative phase, (ii) circularized form, and (iii) prophage state. (Modified from reference 9.)
CORYNEBACTERIAL DETERMINED DtxR REGULATES EXPRESSION OF THE CORYNEBACTERIOPHAGE tox GENE
As noted above, the discovery by Uchida et al. (8) that the structural gene encoding diphtheria toxin was carried by corynebacteriophage β raised the question of whether the iron-sensitive regulation of tox expression was mediated by either a corynebacteriophage or corynebacterial determinant. To address that question, Murphy et al. (13) used S-30 extracts of E. coli in a coupled transcription-translation system programmed with β-phage DNA to synthesize diphtheria toxin in vitro. In this system, diphtheria toxin was expressed in good yield, and remarkably, the in vitro synthesis of the toxin was not inhibited by the addition of iron. In contrast, the addition of cell-free extracts of the nontoxigenic, nonlysogenic C7s(–)tox– strain of C. diphtheriae to the E. coli system resulted in the inhibition of tox expression but not that of other phage gene products. These results clearly suggested that the inhibitory effect of iron was mediated through a bacterial host-determined factor. Furthermore, the subsequent isolation of C. diphtheriae mutants which when lysogenized by β-phage constitutively expressed diphtheria toxin in the presence of excess iron (14), as well as the isolation of phage mutants which constitutively expressed diphtheria toxin when lysogenized in wild-type C. diphtheriae (15, 16), ultimately led to a hypothetical model for the regulation of tox expression (Fig. 2).
FIGURE 2.
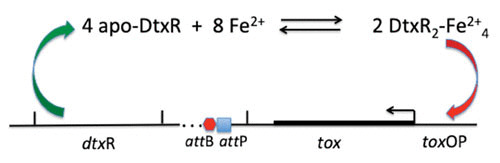
Schematic representation of Fe2+ activation of apo-DtxR and the binding of two dimers to the tox operator, thereby repressing expression of the diphtheria toxin structural gene, tox.
DNA sequence analysis of the structural gene for diphtheria toxin revealed a 27-bp interrupted palindromic sequence that overlapped the putative –10 region of the tox promoter (17–20). Based on these observations, this upstream region of the gene encoding diphtheria toxin was then designated the tox promoter-operator, toxPO. In 1989, Fourel et al. (21) used DNase protection assays to show that an element(s) found in crude cell-free extracts of C. diphtheriae specifically bound to toxO. Mutant strains of C. diphtheriae that are cis-dominant for toxin production were later found to carry mutations only in the tox operator (22–24).
To clone the trans-acting putative tox repressor, Boyd et al. (25) screened genomic libraries of the C7s(–)tox– strain of C. diphtheriae in recombinant E. coli that carried a transcriptional fusion between toxPO and lacZ. This work led to the isolation of the structural gene for the diphtheria tox repressor, dtxR, which encoded a 226-amino acid protein. DtxR was shown to repress the expression of β-galactosidase from the toxPO-lacZ fusion in E. coli in an iron-dependent fashion. Schmitt and Holmes (23) subsequently demonstrated the functional activity of DtxR in C. diphtheriae by showing that expression of wild-type dtxR in the iron-insensitive host-mutant C7hm723(βtox+) strain resulted in conversion to the wild-type iron-sensitive phenotype.
TRANSITION METAL IONS ACTIVATE DtxR BINDING TO THE tox OPERATOR
By using gel mobility shift assays, Tao et al. (26) demonstrated that the activation of apo-DtxR and its subsequent binding to a [32P]-labeled toxO probe required the addition of divalent transition metal ions to both the binding reaction mixture and the gel matrix. Since binding of DtxR to the labeled toxO probe was blocked by the addition of excess unlabeled probe, anti-DtxR antibodies, or the chelator 2,2′-dipyridyl, DtxR binding was specific and dependent on metal ion activation. Both Tao and Murphy (27) and Schmitt and Holmes (28) demonstrated that the addition of Co2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, or Mn2+ activated apo-DtxR and resulted in the protection of the toxPO probe in DNase protection assays. Zinc was found to be only a weak activator of apo-DtxR, and Cu2+ failed to activate repressor activity.
While apo-DtxR could be activated by a number of divalent transition metal ions, Tao and Murphy (29) demonstrated that the activated DtxR could also bind to a number of closely related DNA target sequences. To determine the consensus operator sequence for DtxR binding, Tao and Murphy used a gel electrophoresis mobility-shift assay and PCR amplification for in vitro affinity selection of randomized DNA sequences from a universe of >6 × 1010 variants. After 10 rounds of in vitro selection, each with 30 cycles of PCR amplification, a family of DNA sequences that functioned as DtxR-responsive elements both in vitro and in vivo was isolated and characterized. The consensus sequence for DtxR binding was found to be as follows: T.AGGTTAGC/GCTAACCT.A. Moreover, since this family of related target sequences was found to bind DtxR with the same apparent affinity as the 27-bp tox operator, it was clear that the iron-activated repressor was most likely to function as a global regulatory element in the regulation of iron-sensitive genes in C. diphtheriae. Indeed, a number of genes which have upstream DtxR-binding sites, including the operon essential for the expression of siderophores for iron acquisition, have been isolated and characterized (23, 28).
Since the cloning and characterization of DtxR from C. diphtheriae, homologous metal ion-activated repressors have been identified in a number of other Gram-positive prokaryotes. IdeR (iron-dependent regulator) which has been found in several species of Mycobacterium and is 78% identical and 90% homologous has been isolated and characterized (30). Remarkably, expression of the C. diphtheriae hyperactive repressor, DtxR(E175K), in merodiploid strains of both Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Staphylococcus aureus has been shown to attenuate virulence in vivo, presumably by repression of iron-sensitive genes (31–33). These results clearly suggest that there is a high degree of both function and DNA sequence target specificity between DtxR and IdeR. In addition, DtxR homologs have been identified in a number of genera, including the species Enterococcus faecalis (34), Streptococcus mutans (35), S. aureus (36), Streptomyces pilosus (37), and Rhodococcus equi (38). It is of interest to note that both M. tuberculosis and C. diphtheriae also express additional DtxR-like proteins which are likely to be activated by different transition metal ions and have different DNA target sequences (39), including the MntR protein in C. diphtheriae, which is responsive to Mn2+.
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF TRANSITION METAL ION ACTIVATION OF DtxR REPRESSOR ACTIVITY
As noted above, DtxR is a 226-amino acid protein. DNA sequence analysis revealed a single cysteine residue, Cys102, and disulfide-linked dimers are inactive. The substitution of Cys102 with all 20 amino acids, except for Asp, by site-directed mutagenesis results in the complete loss of repressor activity. Further characterization of the wild type and individual mutants demonstrated that Cys102 plays an essential role in the coordination of Fe2+ in the activation of apo-DtxR (40). In addition, Wang et al. (24) used bisulfite mutagenesis to inactivate DtxR and found that a high percentage of mutations were found in regions of DtxR that exhibited homology with other repressors. In addition, a number of mutations were also isolated in a predicted α-helical region with the sequence of His98-Cys102-His106 that resembled metal ion-binding motifs in other proteins.
A more complete understanding of the structural basis of metal ion-activated DtxR repressor activity was revealed by the solution of the crystal structures of apo-DtxR and holo-DtxR in complex with toxPO (41–44). As shown in Fig. 3, the structure of the C-terminal end of DtxR was found to fold into a SRC homology 3 (SH3)-like domain (45). The SH3 domain was first described as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk but has also been found to be present in phospholipases and the cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases, Abl and Src. In general, SH3 domains are found in proteins that either interact with other proteins or mediate the formation of specific protein complexes by binding to proline-rich peptide sequences.
FIGURE 3.
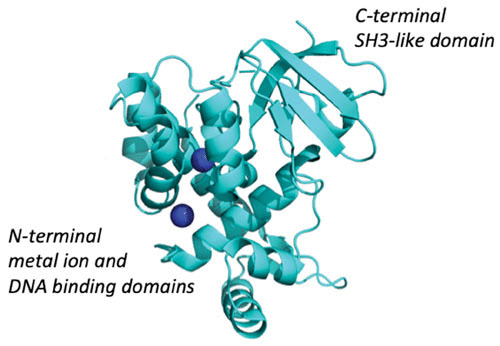
X-ray crystal structure of Co2+-activated DtxR showing its N-terminal metal ion and DNA-binding domain and the C-terminal SH3-like domain. (Modified from reference 45 [Protein Data Bank ID 1C0W].)
DtxR contains a total of eight α-helices, six of which are contained in the N-terminal two-thirds of the protein. Helices B and C and the loop connecting them form the helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif. Interestingly, Ni2+-activated DtxR was shown to bind to the toxPO oligonucleotide as two pairs of dimers (44). In this instance, each DtxR dimer was found to bind to almost opposite faces of the palindromic toxO sequence (Fig. 4). As one would anticipate, the solution of the X-ray structures of DtxR and the ternary complex that forms with its binding to toxO confirms and extends the earlier observation that its footprint compasses a region of 30 bp immediately upstream of the transcription initiation signal (46).
FIGURE 4.
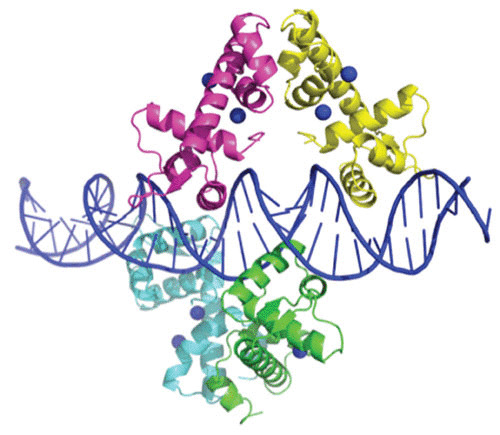
X-ray crystal structure of Ni2+-activated DtxR(C102D) bound to the tox operator. Due to high thermal values, the C-terminal SH3-like domain is not shown in this Ni2+ activated structure. (Modified from reference 44 [Protein Data Bank ID 1DDN].)
While the overall mechanism of DtxR binding to toxO is similar to that of other prokaryotic repressors, there are some unique interactions that should be noted. The C-helix of DtxR is responsible for most interactions with DNA and inserts into the major groove of the DNA double helix. Each helix-turn-helix in the dimer makes a total of nine interactions with backbone phosphate groups. In addition, the guanidinium group of Arg60 binds in the minor groove of DNA and thereby makes a bridge to additional phosphate groups. Since there is a structural rearrangement of activated DtxR upon binding to the tox operator, Thr7 in helix A also interacts with a backbone phosphate group, and Ser37 and Pro39 contact methyl groups on thymine bases in the tox operator through van der Waals interactions (47).
While saturation and equilibrium dialysis experiments suggested that DtxR contained a single metal ion-binding site with an apparent dissociation constant of 2 × 10–6 to 9 × 10–7 M (46), X-ray crystallographic analysis of transition metal ion-DtxR complexes clearly revealed two metal ions bound to each monomer (41, 43). Using site-directed mutagenesis, Ding et al. (48) demonstrated that the primary metal ion-binding site of DtxR is composed of Met10, Cys102, Glu105, His106, and a water molecule form an octahedral coordination center. The second metal ion-binding site, or ancillary site, is composed of five residues: His79, His98, Glu83, Glu170, and Gln173 (41, 43, 49). The role played by the ancillary metal ion-binding site was elucidated through the analysis of DtxR(E175K), a hyperactive mutant that remained active in vivo even in the presence of the chelator 2,2′dipyridyl (50). In vitro studies with purified apo-DtxR(E175K) demonstrated that this mutant required very low levels of metal ion to transit from an inactive apo- to the active form of the repressor. Love et al. (51) demonstrated that the hyperactive phenotype of DtxR(E175K) was dependent on an intact ancillary metal ion-binding site and that this site facilitated the conversion of the inactive apo-repressor to its active toxO binding conformation.
Nuclear magnetic resonance solution structures combined with other biophysical studies have suggested that apo-DtxR exists in a partially unstructured molten globule, which upon coordination with divalent transition metal ions undergoes a structural conversion to a discrete ordered tertiary structure that both dimerizes and is able to bind to the tox operator (52). As shown schematically in Fig. 5, in its inactive molten globule apo-form, the SH3-like domain forms an intramolecular complex with a proline-rich peptide segment of the repressor and, in doing so, destabilizes the ancillary metal ion-binding site of the repressor, and this leads to the complete inactivation of the repressor. Upon metal ion-binding to the primary site, the SH3-like domain disassociates from this proline-rich region, thereby allowing a structural conversion and stabilization of the ancillary metal ion-binding site. The resulting conformational changes then allow the binding of the second metal ion to the ancillary site and subsequent dimerization of DtxR and the formation of an active repressor (53).
FIGURE 5.
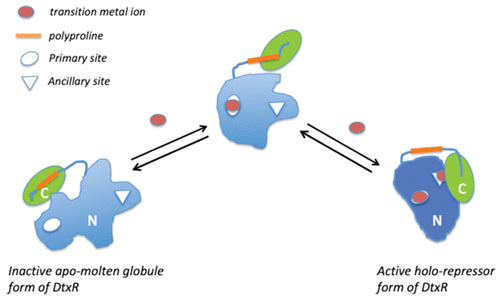
DtxR is a two-domain protein that is composed of the N-terminal [blue] and C-terminal SH3-like [green] regions and functionally distinct transition metal ion-binding sites (primary and ancillary). An activating transition metal ion first binds to the primary site. This binding event orients the DNA-binding helices and begins to induce the folding of the disordered N-terminal domain. Subsequent binding of a second metal ion to the ancillary site disassociates and reorients the SH3-like domain away from the poly-proline region of the repressor and completes the folding of the N-terminal domain, resulting in the formation of the dimer interface of the active holo-repressor. (Modified from reference 52.)
STRUCTURE-FUNCTION RELATIONSHIPS OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN AND THE MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF ITS ACTION
Diphtheria toxin is expressed and secreted into the culture medium as a single polypeptide chain of 62 kDa by C. diphtheriae. The toxin is readily purified from the spent culture supernatant by ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by ion exchange chromatography on a diethylaminoethyl matrix. While the intact toxin is enzymatically inactive, exposure of purified toxin to trypsin or other serine proteases results in “nicking” of the protein and the subsequent activation of adenosine diphosphate ribosyl (ADPR) transferase. Under reducing and denaturing conditions, nicked diphtheria toxin may be separated into an enzymatically active N-terminal 24-kDa fragment A and its 38-kDa C-terminal fragment B (54, 55). Honjo et al. (56) and Gill et al. (57) demonstrated that nicked diphtheria toxin and fragment A were enzymatically active in catalyzing the following reaction:
Yamaizumi et al. (58), in a series of elegant experiments, loaded erythrocyte ghosts with various concentrations of purified fragment A and a known concentration of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled bovine serum albumin. These preloaded red cell ghosts were then fused to diphtheria toxin-resistant mouse L-cells by Sendai virus. Using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter, L-cells that fused with a single red cell ghost were then isolated and grown for 7 days. Careful analysis of the colony-forming ability of the recipient cells compared to the control cells clearly demonstrated that the delivery of a single molecule of fragment A to the cytosol was sufficient to kill that cell.
Comparison of the nontoxic mutants CRM197 and CRM45 revealed that the C-terminal 38 kDa fragment B of diphtheria toxin carried two functional domains: a hydrophobic domain (59), which under denaturing conditions behaved like an integral membrane protein, and the native receptor-binding domain. As such, it was realized through biochemical and genetic analyses that native diphtheria toxin was a protein with at least three structural-functional domains: (i) catalytic, (ii) transmembrane or translocation, and (iii) receptor-binding domains. As shown in Fig. 2, this prediction proved to be correct with the determination of the crystal structure of diphtheria toxin (60, 61). While DNA sequence analysis of the tox structural gene revealed the presence of a 21-amino acid signal sequence (18–20), the mature form of diphtheria toxin is a 535-amino acid polypeptide. The N-terminal catalytic domain consists of amino acids Gly1 to Cys186 and is composed of eight β-strands that form two β-sheets forming a core structure that is surrounded by seven short α-helices. The β-sheets that form the central core also form the active site cleft. The catalytic domain is connected to the centrally positioned translocation domain by a 14-amino acid loop that is subtended by a disulfide bond between Cys186 and Cys201. This exposed loop carries an ArgArgValArg protease recognition site for either furin or other trypsin-like proteases. The proteolytic cleavage of this site is essential for the release of the catalytic domain into the eukaryotic cell cytosol (62). The translocation domain encompasses amino acids Cys186 to K385 and is composed of nine α-helices and their connecting loops. The translocation domain plays an essential role in the intoxication process by forming an 18- to 22-Å channel, or pore, through which the catalytic domain is threaded from the lumen of acidified endocytic vesicles into the cytosol. This channel is formed by translocation helices 5 to 7 and 8 to 9, which are highly hydrophobic and form two membrane-soluble “daggers” (61). The loops connecting translocation helices 8 to 9 and 5 to 6 are highly acidic and carry a total of six Asp and Glu residues. Upon internalization of the toxin into an endosomal compartment and the acidification of the vesicle lumen by the vacuolar ATPase, the carboxylic acid groups on these Asp and Glu residues become protonated and lose their respective charges, allowing for membrane insertion and channel formation.
Ratts et al. (3) developed an in vitro assay system composed of partially purified endosomes that were preloaded with either diphtheria toxin or the fusion protein toxin DAB389IL-2 in the presence of the vacuolar ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 to probe the requirements necessary for catalytic domain translocation from the endosomal lumen to the external medium. Upon removal of bafilomycin A1 and addition of ATP, the endosomal lumen becomes rapidly acidified; however, catalytic domain translocation to the external medium was shown to require the addition of eukaryotic cytosolic fractions to the assay mixture. Using this assay system, Ratts et al. (3) demonstrated that both coatomer complex 1 (COPI) and thioredoxin reductase were essential for in vitro translocation of the catalytic domain. Ratts et al. (63) also described a highly conserved motif, T1, in translocation helix 1 of diphtheria toxin that played an essential role in the delivery of the catalytic domain to the cytosol. In 2010, Trujillo et al. (64) used both site-directed mutagenesis and a COPI complex precipitation assay to demonstrate that the interaction(s) between at least three lysine residues in the T1 motif are essential for both COPI binding and delivery of the catalytic domain to the eukaryotic cell cytosol. Further, Trujillo et al. (64) demonstrated that substitution of the lysine-rich region in translocation helix 1 with the COPI binding portion of the p23 adaptor cytoplasmic tail results in a mutant form of toxin that displays full wild-type activity against sensitive eukaryotic cells.
The above-described studies demonstrate that diphtheria toxin has evolved to become an extremely efficient nano-machine in which all of its structural domains play an essential role in the intoxication of sensitive eukaryotic cells. The molecular mechanisms leading toward intoxication require at least the following steps: (i) binding of the toxin to its cell surface receptor, the heparin-binding epidermal growth factor precursor, (ii) furin-mediated nicking of the protease-sensitive RVRR site in the 14-amino acid exposed loop between the catalytic and translocation domains, (iii) internalization of toxin into an endosomal compartment that becomes acidified through the action of its vacuolar ATPase, (iv) insertion of translocation helical loops formed by TH5-7 and TH8-9 into a vesicle membrane forming a channel or pore, (v) the insertion of the disulfide-linked C-terminal end of the catalytic domain and N-terminal end of the translocation domain into the channel, (vi) protein::protein interactions between the dibasic KXKXX signatures in translocation helix 1 with COPI, which facilitates the threading and translocation of the catalytic domain through the channel, (vii) reduction of the disulfide bond between the catalytic and translocation domains by thioredoxin reductase, (viii) the release and refolding of the catalytic domain into an enzymatically active ADP-ribosyltransferase, and (ix) the NAD+-dependent ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2, which results in the cessation of protein synthesis and death of the cell (65).
MOLECULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY OF DIPHTHERIA AND DtxR
Outbreaks of clinical diphtheria almost always occur in individuals who have not been immunized with either the DPT or diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis vaccine and who have been exposed to a “carrier” (a person who carries a toxigenic strain of C. diphtheriae as part of their normal flora) who has recently traveled to a country where mass immunization against diphtheria is not performed and disease is still prevalent. C. diphtheriae is usually transmitted via the aerosol route; close contact with an individual presenting with cutaneous diphtheria may also result in transmission. While colonization of a susceptible individual with a toxigenic strain certainly plays a role in pathogenesis, Pappenheimer and Murphy (66) demonstrated that transmission of toxigenicity may also occur by in situ lysogenic conversion of an autochthonous nontoxigenic strain of C. diphtheriae to toxigenicity. It is remarkable that immunization with diphtheria toxoid results in the production of neutralizing antibodies that not only block diphtheria toxin from binding to its cell surface receptor, but also protects against clinical disease (67, 68). It is well known that mass immunization of populations with diphtheria toxoid has led to a dramatic decrease in the incidence of clinical disease (69). For example, in 1958, before mass immunization with diphtheria toxoid in Romania, only 60% of the population was immune to diphtheria toxin, whereas by 1979, the percentage dramatically increased to 97%. At the same time, diphtheria morbidity dropped from ca. 600 per 100,000 in 1958 to only 1 per 100,000 in 1972 (67, 70).
The consequence of either stopping or dramatically reducing a mass immunization program against diphtheria is also known. During the 1990s, the Newly Independent States (NIS) of the former Soviet Union experienced a sweeping epidemic of clinical diphtheria. With the breakup of the Soviet Union, public health immunization programs were dramatically affected and by 1990 only 68% of Russian children had received the appropriate vaccination regimen (71). As a result, by 1995 the incidence of clinical diphtheria in the NIS peaked at over 50,000 cases. From the onset of the diphtheria outbreak in 1990 through 1999, more than 157,000 cases and 5,000 deaths were reported.
Given the increased incidence of clinical diphtheria in the NIS, Kolodkina et al. (72) characterized 129-bp single-strand conformational polymorphism DNA fragments that contained the toxPO region from 81 strains of C. diphtheriae. From this group, only two strains had mutations. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed T to C mutations in positions –54 and –184 of the tox operon. The –54 mutation was found in the 9-bp interrupted palindromic sequence of toxPO, and these two strains had the highest level of toxin production out of the 81 strains characterized. In addition, these investigators also analyzed the nucleotide sequence of the dtxR gene. Fifteen strains in this collection were found to carry two missense mutations in DtxR, A147V and L214I in the C-terminal region of the repressor. Interestingly, the dtxR alleles in the two strains that expressed the highest levels of diphtheria toxin were not found to carry a nucleotide substitution. This initial study was extended by Kombarova et al. (73), who found seven point mutations in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin. While most of these mutations did not result in an amino acid substitution, two strains from the Otchakov ribotype carried a G393R mutation in the native receptor-binding domain of the toxin. In contrast, 16 point mutations in dtxR were found. Of these, the A147V mutation is characteristic of the epidemic clonal group Sankt-Peterburg/Rossija, which was the dominant strain isolated in the Russian diphtheria epidemic in the 1990s.
It is remarkable that the amino acid sequence of diphtheria toxin encoded by the omega-phage in the Park-Williams strain of C. diphtheriae, PW8, which was isolated in 1896 (74), is identical to the amino acid sequence of the toxin produced by all but two of the clinical isolates carrying the G393R mutation that have been characterized from the NIS diphtheria epidemic. While several missense mutations within the tox gene have been described, they encode the same amino acid as found in the PW8 allele. It is interesting to note that in the single exception, the G393R substitution falls early on in the toxin’s receptor-binding domain and is far removed from the region of that domain which interacts with the toxin’s eukaryotic cell surface receptor-binding region. This extraordinary conservation of amino acid sequence strongly suggests the highly evolved nature of the toxin’s structure-function relationships. This conservation of amino acid sequence for at least 100 years suggests that the evolution of new tox alleles that might encode a toxin sufficiently different to avoid neutralization by antitoxoid antibodies is highly unlikely.
In contrast, this high degree of conservation does not hold for DtxR. In the case of this metal ion-activated repressor, the N-terminal region of dtxR was found to carry several missense mutations that did not give rise to an amino acid substitution. In contrast, missense mutations in the C-terminal region of the repressor were often found to encode amino acid substitutions that appeared to subtly affect DtxR activity (51, 75–77).
TURNING THE SWORD OF DIPHTHERIA INTO THE PLOWSHARE OF TARGETED THERAPEUTICS
Shortly after Köhler and Milstein (78) described the methodology to produce monoclonal antibodies, many in the bacterial protein toxin field seized on this technology in an attempt to fulfill Paul Ehrlich’s idea of developing “magic bullets,” therapeutic compounds that were selectively targeted toward a disease-causing organism or cell (79). In an early series of experiments, Gilliland et al. (50) independently coupled ricin A chain and diphtheria toxin fragment A to monoclonal antibodies directed against a cell surface antigen on colorectal carcinoma cells. While the ricin A chain-coupled immunotoxin was highly potent (i.e., the half maximal inhibitory concentration [IC50] < 10–12 M), the diphtheria toxin fragment A immunotoxin, surprisingly, was found to be at least 1,000-fold less potent (i.e., IC50 ∼ 5 × 10–9 M). These results prompted Bacha et al. (80) to ask whether fragment A alone contained sufficient structural information to deliver the catalytic domain across the endocytic vesicle membrane. Since Boquet et al. (59) had previously demonstrated that under denaturing conditions, the hydrophobic domain in the B fragment of CRM45 displayed properties of an integral membrane protein, Bacha et al. (80) independently coupled fragment A (CRM26) and CRM45 to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and assessed their relative cytotoxic potency against GH3 rat pituitary cells. While the fragment A-TRH construct was nontoxic even at concentrations of 10–7 M, the CRM45-TRH construct was highly active (IC50 ∼ 3 × 10–9 M). These results clearly demonstrated that fragment B translocation domain sequences were required to facilitate the delivery of fragment A, the catalytic domain, into the eukaryotic cell cytosol.
Since additional preparations of CRM45-TRH varied by greater than 10-fold in cytotoxic potency, Murphy et al. (81) turned to recombinant DNA and protein engineering methods to redesign native diphtheria toxin by receptor-binding domain substitution. The hypothesis was that by choosing a surrogate receptor-binding domain that bound to a cell surface receptor that was both limited in distribution and was internalized into an endosomal compartment that became acidified, it might be possible to develop a family of fusion protein toxins that could potentially serve as a new class of targeted toxins for the treatment of human diseases. Moreover, we reasoned that, if successful, these genetically engineered proteins would constitute a unique family of reagents to deplete discrete subsets of cells and to study the molecular process by which the diphtheria toxin catalytic domain was delivered to the cytosol of targeted eukaryotic cells.
To begin to test this hypothesis, Leong et al. (82, 83) demonstrated that cloned fragment A of diphtheria toxin was expressed and secreted by the SecA apparatus in recombinant E. coli. Despite the controversial nature of deliberately designing and constructing a recombinant gene that encoded a toxic protein that the world had not seen previously, in 1985, we were finally granted approval to genetically construct, express, and evaluate the biosafety of the first fusion protein toxin under biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) containment. Murphy et al. (81) described the assembly of a fusion gene that was composed of a portion of diphtheria tox that encoded first 486 amino acids of diphtheria toxin and a synthetic gene encoding the 13-amino acid polypeptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). While this fusion protein was expressed and secreted into the periplasmic space of recombinant E. coli, the yield of full-length fusion protein toxin was extremely low due to proteolytic degradation. Since this degradation appeared to have occurred close to the fusion junction between diphtheria and α-MSH sequences, we reasoned that increasing the molecular size of the substitute receptor-binding domain with a larger polypeptide might at least partially solve the degradation problem by stearic hindrance. In 1987, Williams et al. (84) described the genetic construction and properties of a fusion protein toxin in which the 133-amino acid sequence of human interleukin-2 (IL-2) was genetically fused to amino acid 486 of diphtheria toxin. Surprisingly, DAB486IL-2 was expressed, and full-length fusion protein toxin was secreted into the periplasmic space in good yield.
Since the DAB486IL-2 construct used a naturally occurring SphI restriction endonuclease site in the tox gene as the fusion junction between diphtheria toxin and IL-2 sequences, we then asked how much fragment B sequence was required to deliver the catalytic domain of the fusion protein into the target cell cytosol. Williams et al. (85) constructed a series of in-frame deletion mutants and found that the removal of 97 amino acids from Thr387 to His485 increased both the cytotoxic potency and the apparent dissociation constant of the resulting fusion toxin, DAB389IL-2, for cells that expressed the high-affinity IL-2 receptors (IL-2R). Upon the subsequent solution of the diphtheria toxin X-ray structure (Fig. 6), we realized that quite by chance our internal in-frame deletion of 97 amino acids resulted in an almost perfect receptor-binding domain substitution (Fig. 7). Since that time, more than a dozen diphtheria-based fusion protein toxins have been constructed and characterized using amino acid 388 or 389 as the junction between diphtheria toxin and surrogate receptor-binding domain polypeptides.
FIGURE 6.
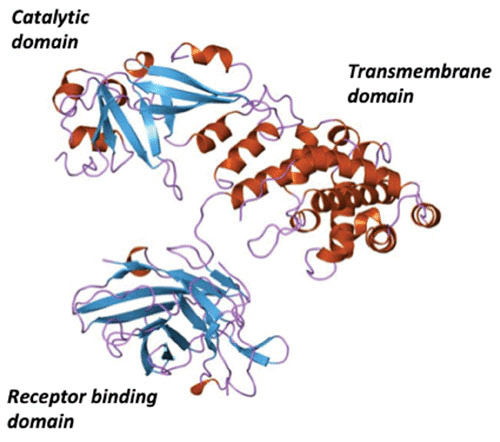
X-ray structure of native diphtheria toxin showing its catalytic, translocation, and receptor-binding domains.
FIGURE 7.
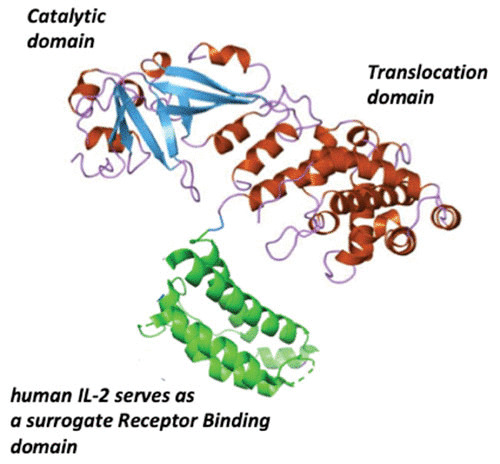
Molecular model of denileukin diftitox (Ontak, DAB389IL-2). The catalytic and translocation domains are composed of amino acids Gly1 through Thr387 of native diphtheria toxin, to which the 133-amino acid polypeptide of human IL-2 is genetically fused. The additional two amino acids in the construct are the result of the introduction of a unique SphI restriction endonuclease site at the fusion junction between diphtheria toxin and human (h)IL-2 sequences.
In 1999, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved denileukin diftitox (Ontak; DAB389IL-2) for the treatment of refractory cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), making it the first-in-class recombinant targeted biologic to achieve approval. Phase III trials conducted with CTCL patients who had failed other therapeutic interventions demonstrated that 30% of the total number of patients had a 50% or greater reduction in their tumor burden for at least 6 weeks following treatment (86, 87). In the case of peripheral T cell lymphomas, an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with a median overall survival of 5.5 months, Ontak has been used both as a monotherapy and in combination with traditional chemotherapy (88). Both Fuentes et al. (89) and Wong et al. (90) reported individual cases where Ontak therapy, when used as a long-term maintenance therapy over a span of 1 to 2 years, resulted in sustained remissions of 9 and 4 years that are ongoing. In addition to its effective use in T cell malignancies, Ontak has also been successfully used in the treatment of steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease. Ho et al. (91) conducted a phase I trial of Ontak in 30 patients presenting with steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease and reported that 50% of the patients responded with complete resolution, and an additional 21% of the total number of patients responded with partial resolution of their disease.
While Ontak selectively targets the high and intermediate IL-2R on malignant T cells in both CTCL and peripheral T cell lymphomas, as well as on activated T effector cells in graft-versus-host disease, in recent years it has also shown promise as an immunotherapeutic in the transient depletion of T regulatory cells in solid tumors. Both phase I (92) and phase II (93) studies have shown that Ontak is also effective as an immunotherapeutic as a monotherapy in patients presenting with unresectable stage IV malignant melanoma. In these instances, Ontak was shown to transiently deplete T regulatory cells and, as such, apparently break tolerance and allow for a more robust host-mounted T-effector cell antitumor response.
Despite its clinical effectiveness, Ontak was placed on clinical hold in 2011 because of the presence of drug aggregates, contaminating DNA, varying concentrations of Tween20, and batch-to-batch variations in its final formulation. Since Ontak was expressed as inclusion bodies in recombinant E. coli, the agent had to be completely denatured and refolded into a biologically active conformation. During the refolding process, it was necessary to add Tween20 to partially prevent the formation of insoluble drug aggregates and allow for refolding of the drug into a biologically active conformation.
We (94) recently solved the production issues associated with refolding of the drug by recloning the structural gene for Ontak, DAB389IL-2, in an E. coli-C. diphtheriae shuttle vector. Furthermore, we modified the gene by adding back the native tox signal sequence so that the fusion protein toxin would be secreted into the culture medium. Finally, we introduced mutations into the downstream half of the palindromic tox operator so that expression was constitutive even in medium with high iron concentrations. Thus, this second-generation Ontak, s-DAB389IL-2, is expressed and secreted from recombinant C. diphtheriae in good yield as a fully folded monomeric protein that may be readily isolated and purified from the culture medium. Cheung et al. (94) also demonstrated that s-DAB389IL2 has great potential when used in a sequential combination regimen with anti-PD-1 in the treatment of B16F10 melanoma in the mouse. In these studies, either s-DAB389IL-2 or s-DAB389IL-2(V6A), a vascular leak motif modified mutant, was first used to transiently deplete T regulatory cells, thereby removing one of the immune suppression signals that dampen a T effector cell antitumor response. Anti-PD-1 was then administered to block the PDL-1–PD-1 interaction between the tumor and the immune system, thereby blocking a second suppressive signal to the T effector arm of the immune system. The combined effect of this sequential therapeutic regimen was found to be at least additive and perhaps synergistic in the treatment of this aggressive murine melanoma. These results are encouraging and prestage the use of s-DAB389IL2(V6A) in clinical medicine in a sequential checkpoint inhibitor blockade for the treatment of solid tumors.
Ontak (denileukin diftitox, DAB389IL-2) and the second-generation form of the biologic, s-DAB389IL-2(V6A), while not magic and certainly not bullets, have shown remarkable efficacy in the treatment of human malignancies and in murine models of melanoma and colon and renal cell carcinomas, both as a targeted monotherapy against the tumor itself and as an immunotherapeutic to reset immunologic balance by transient depletion of T regulatory cells. In the latter instance, the transient depletion of T regulatory cells appears to break tolerance and thereby allows a robust patient-mounted antitumor response. Thus, through the biochemical and biochemical genetic study of diphtheria toxin, the diphtheria tox operon, and the iron-activated repressor DtxR, which regulates expression, and through modern molecular biologic methods, one of nature’s most potent bacterial protein toxins has been tamed. Diphtheria toxin, once the primary virulence determinant of a dreaded infectious disease of children, has now been retargeted to selectively eliminate specific disease-causing cells as a protein therapeutic, thereby at least partially fulfilling Paul Erlich’s magic bullet concept of a “chemical that binds to and specifically kills microbes or tumor cells” (79).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Pankaj Kumar for his critical review of the manuscript and very helpful comments.
We also acknowledge financial support from the National Institutes of Health (grants R21 AI130595, RO1 AI36973, RO1 AI137856, and RO1 HL133190), Maryland TEDCO (project 0916-006), the Abell Foundation, and the Cigarette Restitution Fund.
REFERENCES
- 1.Pappenheimer AM, Jr. 1977. Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem 46:69–94 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pappenheimer AM, Jr. 1993. The story of a toxic protein, 1888-1992. Protein Sci 2:292–298 10.1002/pro.5560020218. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ratts R, Zeng H, Berg EA, Blue C, McComb ME, Costello CE, vanderSpek JC, Murphy JR. 2003. The cytosolic entry of diphtheria toxin catalytic domain requires a host cell cytosolic translocation factor complex. J Cell Biol 160:1139–1150 10.1083/jcb.200210028. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barksdale L, Garmise L, Horibata K. 1960. Virulence, toxinogeny, and lysogeny in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Ann N Y Acad Sci 88:1093–1108 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20099.x. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kurokawa M, Murata R. 1961. On the toxicity of the “toxoid” preparation responsible for the Kyoto catastrophe in 1948. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 14:249–256 10.7883/yoken1952.14.249. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pappenheimer AM, Jr, Johnson S. 1936. Studies in diphtheria toxin production. I. The effect of iron and copper. Br J Exp Pathol 17:335–341. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Freeman VJ. 1951. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol 61:675–688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Uchida T, Gill DM, Pappenheimer, AM Jr. 1971. Mutation in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by temperate phage. Nat New Biol 233:8–11 10.1038/newbio233008a0. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Buck GA, Groman NB. 1981. Physical mapping of beta-converting and gamma-nonconverting corynebacteriophage genomes. J Bacteriol 148:131–142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Laird W, Groman N. 1976. Prophage map of converting corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol 19:208–219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Michel JL, Rappuoli R, Murphy JR, Pappenheimer AM Jr. 1982. Restriction endonuclease map of the nontoxigenic corynephage gamma c and its relationship to the toxigenic corynephage beta c. J Virol 42:510–518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rappuoli R, Michel JL, Murphy JR. 1983. Integration of corynebacteriophages beta tox+, omega tox+, and gamma tox- into two attachment sites on the Corynebacterium diphtheriae chromosome. J Bacteriol 153:1202–1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Murphy JR, Pappenheimer AM, Jr, de Borms ST. 1974. Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:11–15 10.1073/pnas.71.1.11. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kanei C, Uchida T, Yoneda M. 1977. Isolation from Corynebacterium diphtheriae C7(beta) of bacterial mutants that produce toxin in medium with excess iron. Infect Immun 18:203–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Murphy JR, Skiver J, McBride G. 1976. Isolation and partial characterization of a corynebacteriophage beta, tox operator constitutive-like mutant lysogen of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol 18:235–244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Welkos SL, Holmes RK. 1981. Regulation of toxinogenesis in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Mutations in bacteriophage beta that alter the effects of iron on toxin production. J Virol 37:936–945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boyd J, Murphy JR. 1988. Analysis of the diphtheria tox promoter by site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 170:5949–5952 10.1128/jb.170.12.5949-5952.1988. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Greenfield L, Bjorn MJ, Horn G, Fong D, Buck GA, Collier RJ, Kaplan DA. 1983. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by corynebacteriophage beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6853–6857 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6853. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kaczorek M, Delpeyroux F, Chenciner N, Streeck RE, Murphy JR, Boquet P, Tiollais P. 1983. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the diphtheria tox228 gene in Escherichia coli. Science 221:855–858 10.1126/science.6348945. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ratti G, Rappuoli R, Giannini G. 1983. The complete nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for diphtheria toxin in the corynephage omega (tox+) genome. Nucleic Acids Res 11:6589–6595 10.1093/nar/11.19.6589. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fourel G, Phalipon A, Kaczorek M. 1989. Evidence for direct regulation of diphtheria toxin gene transcription by an Fe2+-dependent DNA-binding repressor, DtoxR, in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun 57:3221–3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Krafft AE, Tai SP, Coker C, Holmes RK. 1992. Transcription analysis and nucleotide sequence of tox promoter/operator mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. Microb Pathog 13:85–92 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90069-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schmitt MP, Holmes RK. 1991. Characterization of a defective diphtheria toxin repressor (dtxR) allele and analysis of dtxR transcription in wild-type and mutant strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun 59:3903–3908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang Z, Schmitt MP, Holmes RK. 1994. Characterization of mutations that inactivate the diphtheria toxin repressor gene (dtxR). Infect Immun 62:1600–1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boyd J, Oza MN, Murphy JR. 1990. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a diphtheria tox iron-dependent regulatory element (dtxR) from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5968–5972 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5968. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tao X, Boyd J, Murphy JR. 1992. Specific binding of the diphtheria tox regulatory element DtxR to the tox operator requires divalent heavy metal ions and a 9-base-pair interrupted palindromic sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5897–5901 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5897. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tao X, Murphy JR. 1992. Binding of the metalloregulatory protein DtxR to the diphtheria tox operator requires a divalent heavy metal ion and protects the palindromic sequence from DNase I digestion. J Biol Chem 267:21761–21764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schmitt MP, Holmes RK. 1994. Cloning, sequence, and footprint analysis of two promoter/operators from Corynebacterium diphtheriae that are regulated by the diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) and iron. J Bacteriol 176:1141–1149 10.1128/jb.176.4.1141-1149.1994. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tao X, Murphy JR. 1994. Determination of the minimal essential nucleotide sequence for diphtheria tox repressor binding by in vitro affinity selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9646–9650 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9646. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Doukhan L, Predich M, Nair G, Dussurget O, Mandic-Mulec I, Cole ST, Smith DR, Smith I. 1995. Genomic organization of the mycobacterial sigma gene cluster. Gene 165:67–70 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ando M, Manabe YC, Converse PJ, Miyazaki E, Harrison R, Murphy JR, Bishai WR. 2003. Characterization of the role of the divalent metal ion-dependent transcriptional repressor MntR in the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 71:2584–2590 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2584-2590.2003. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Manabe YC, Saviola BJ, Sun L, Murphy JR, Bishai WR. 1999. Attenuation of virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis expressing a constitutively active iron repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12844–12848 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12844. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Manabe YC, Hatem CL, Kesavan AK, Durack J, Murphy JR. 2005. Both Corynebacterium diphtheriae DtxR(E175K) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis IdeR(D177K) are dominant positive repressors of IdeR-regulated genes in M. tuberculosis. Infect Immun 73:5988–5994 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5988-5994.2005. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Low YL, Jakubovics NS, Flatman JC, Jenkinson HF, Smith AW. 2003. Manganese-dependent regulation of the endocarditis-associated virulence factor EfaA of Enterococcus faecalis. J Med Microbiol 52:113–119 10.1099/jmm.0.05039-0. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kitten T, Munro CL, Michalek SM, Macrina FL. 2000. Genetic characterization of a Streptococcus mutans LraI family operon and role in virulence. Infect Immun 68:4441–4451 10.1128/IAI.68.8.4441-4451.2000. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Horsburgh MJ, Wharton SJ, Cox AG, Ingham E, Peacock S, Foster SJ. 2002. MntR modulates expression of the PerR regulon and superoxide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus through control of manganese uptake. Mol Microbiol 44:1269–1286 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02944.x. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Günter-Seeboth K, Schupp T. 1995. Cloning and sequence analysis of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae dtxR homologue from Streptomyces lividans and S. pilosus encoding a putative iron repressor protein. Gene 166:117–119 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00628-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Boland CA, Meijer WG. 2000. The iron dependent regulatory protein IdeR (DtxR) of Rhodococcus equi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 191:1–5 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schmitt MP, Predich M, Doukhan L, Smith I, Holmes RK. 1995. Characterization of an iron-dependent regulatory protein (IdeR) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as a functional homolog of the diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun 63:4284–4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tao X, Murphy JR. 1993. Cysteine-102 is positioned in the metal binding activation site of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae regulatory element DtxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8524–8528 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8524. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Qiu X, Verlinde CL, Zhang S, Schmitt MP, Holmes RK, Hol WG. 1995. Three-dimensional structure of the diphtheria toxin repressor in complex with divalent cation co-repressors. Structure 3:87–100 10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00137-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schiering N, Tao X, Murphy JR, Petsko GA, Ringe D. 1994. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of the diphtheria Tox repressor from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Mol Biol 244:654–656 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1760. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schiering N, Tao X, Zeng H, Murphy JR, Petsko GA, Ringe D. 1995. Structures of the apo- and the metal ion-activated forms of the diphtheria tox repressor from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9843–9850 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9843. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.White A, Ding X, vanderSpek JC, Murphy JR, Ringe D. 1998. Structure of the metal-ion-activated diphtheria toxin repressor/tox operator complex. Nature 394:502–506 10.1038/28893. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pohl E, Holmes RK, Hol WG. 1999. Crystal structure of a cobalt-activated diphtheria toxin repressor-DNA complex reveals a metal-binding SH3-like domain. J Mol Biol 292:653–667 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3073. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tao X, Zeng HY, Murphy JR. 1995. Transition metal ion activation of DNA binding by the diphtheria tox repressor requires the formation of stable homodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6803–6807 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6803. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen CS, White A, Love J, Murphy JR, Ringe D. 2000. Methyl groups of thymine bases are important for nucleic acid recognition by DtxR. Biochemistry 39:10397–10407 10.1021/bi0009284. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ding X, Zeng H, Schiering N, Ringe D, Murphy JR. 1996. Identification of the primary metal ion-activation sites of the diphtheria tox repressor by X-ray crystallography and site-directed mutational analysis. Nat Struct Biol 3:382–387 10.1038/nsb0496-382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Qiu X, Pohl E, Holmes RK, Hol WG. 1996. High-resolution structure of the diphtheria toxin repressor complexed with cobalt and manganese reveals an SH3-like third domain and suggests a possible role of phosphate as co-corepressor. Biochemistry 35:12292–12302 10.1021/bi960861d. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gilliland DG, Steplewski Z, Collier RJ, Mitchell KF, Chang TH, Koprowski H. 1980. Antibody-directed cytotoxic agents: use of monoclonal antibody to direct the action of toxin A chains to colorectal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:4539–4543 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4539. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Love JF, vanderSpek JC, Marin V, Guerrero L, Logan TM, Murphy JR. 2004. Genetic and biophysical studies of diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) and the hyperactive mutant DtxR(E175K) support a multistep model of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2506–2511 10.1073/pnas.0303794101. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rangachari V, Marin V, Bienkiewicz EA, Semavina M, Guerrero L, Love JF, Murphy JR, Logan TM. 2005. Sequence of ligand binding and structure change in the diphtheria toxin repressor upon activation by divalent transition metals. Biochemistry 44:5672–5682 10.1021/bi047825w. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Love JF, VanderSpek JC, Murphy JR. 2003. The src homology 3-like domain of the diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) modulates repressor activation through interaction with the ancillary metal ion-binding site. J Bacteriol 185:2251–2258 10.1128/JB.185.7.2251-2258.2003. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Collier RJ, Kandel J. 1971. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem 246:1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gill DM, Pappenheimer AM, Jr. 1971. Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem 246:1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Honjo T, Nishizuka Y, Hayaishi O. 1968. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem 243:3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gill DM, Pappenheimer AM, Jr, Brown R, Kurnick JT. 1969. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VII. Toxin-stimulated hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in mammalian cell extracts. J Exp Med 129:1–21 10.1084/jem.129.1.1. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yamaizumi M, Mekada E, Uchida T, Okada Y. 1978. One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell 15:245–250 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Boquet P, Silverman MS, Pappenheimer AM, Jr, Vernon WB. 1976. Binding of triton X-100 to diphtheria toxin, crossreacting material 45, and their fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:4449–4453 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4449. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bennett MJ, Choe S, Eisenberg D. 1994. Domain swapping: entangling alliances between proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3127–3131 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3127. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Choe S, Bennett MJ, Fujii G, Curmi PM, Kantardjieff KA, Collier RJ, Eisenberg D. 1992. The crystal structure of diphtheria toxin. Nature 357:216–222 10.1038/357216a0. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Williams DP, Wen Z, Watson RS, Boyd J, Strom TB, Murphy JR. 1990. Cellular processing of the interleukin-2 fusion toxin DAB486-IL-2 and efficient delivery of diphtheria fragment A to the cytosol of target cells requires Arg194. J Biol Chem 265:20673–20677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ratts R, Trujillo C, Bharti A, vanderSpek J, Harrison R, Murphy JR. 2005. A conserved motif in transmembrane helix 1 of diphtheria toxin mediates catalytic domain delivery to the cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15635–15640 10.1073/pnas.0504937102. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Trujillo C, Taylor-Parker J, Harrison R, Murphy JR. 2010. Essential lysine residues within transmembrane helix 1 of diphtheria toxin facilitate COPI binding and catalytic domain entry. Mol Microbiol 76:1010–1019 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07159.x. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kochi SK, Collier RJ. 1993. DNA fragmentation and cytolysis in U937 cells treated with diphtheria toxin or other inhibitors of protein synthesis. Exp Cell Res 208:296–302 10.1006/excr.1993.1249. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pappenheimer AM, Jr, Murphy JR. 1983. Studies on the molecular epidemiology of diphtheria. Lancet 2:923–926 10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90449-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pappenheimer AM, Jr. 1980. Diphtheria: studies on the biology of an infectious disease. Harvey Lect 76:45–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zucker DR, Murphy JR. 1984. Monoclonal antibody analysis of diphtheria toxin. I. Localization of epitopes and neutralization of cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol 21:785–793 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Dixon JMS. 1984. Diphtheria in North America. J Hyg (Lond) 93:419–432 10.1017/S0022172400065013. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Saragea A, Maximescu P, Meitert E. 1979. Corynebacterium diphtheriae: microbiological methods used in clinical and epidemiological investigations. Methods Microbiol 13:161–176 10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70374-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Maurice J. 1995. Russian chaos breeds diphtheria outbreak. Science 267:1416–1417 10.1126/science.7878458. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kolodkina VL, Titov LP, Sharapa TN, Drozhzhina ON. 2007. Point mutations in tox promoter/operator and diphtheria toxin repressor (DTXR) gene associated with the level of toxin production by Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains isolated in Belarus. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol 1:22–29. (In Russian.) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kombarova S, Borisova O, Melnikov VG, Gubina NI, Loseva LV, Mazurova IK. 2009. Polymorphism of tox and dtxR gene in circulating strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 1:7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Park WH, Williams AW. 1896. The production of diphtheria toxin. J Exp Med 1:164–185 10.1084/jem.1.1.164. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Nakao H, Mazurova IK, Glushkevich T, Popovic T. 1997. Analysis of heterogeneity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae toxin gene, tox, and its regulatory element, dtxR, by direct sequencing. Res Microbiol 148:45–54 10.1016/S0923-2508(97)81899-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nakao H, Pruckler JM, Mazurova IK, Narvskaia OV, Glushkevich T, Marijevski VF, Kravetz AN, Fields BS, Wachsmuth IK, Popovic T. 1996. Heterogeneity of diphtheria toxin gene, tox, and its regulatory element, dtxR, in Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains causing epidemic diphtheria in Russia and Ukraine. J Clin Microbiol 34:1711–1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Love JF, Murphy JR. 2002. Design and development of a novel genetic probe for the analysis of repressor-operator interactions. J Microbiol Methods 51:63–72 10.1016/S0167-7012(02)00058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Köhler G, Milstein C. 1975. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–497 10.1038/256495a0. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Schwartz RS. 2004. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullets. N Engl J Med 350:1079–1080 10.1056/NEJMp048021. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bacha P, Murphy JR, Reichlin S. 1983. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-diphtheria toxin-related polypeptide conjugates. Potential role of the hydrophobic domain in toxin entry. J Biol Chem 258:1565–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Murphy JR, Bishai W, Borowski M, Miyanohara A, Boyd J, Nagle S. 1986. Genetic construction, expression, and melanoma-selective cytotoxicity of a diphtheria toxin-related alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8258–8262 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8258. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Leong D, Coleman KD, Murphy JR. 1983a. Cloned fragment A of diphtheria toxin is expressed and secreted into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli K12. Science 220:515–517 10.1126/science.6403984. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Leong D, Coleman KD, Murphy JR. 1983. Cloned diphtheria toxin fragment A is expressed from the tox promoter and exported to the periplasm by the SecA apparatus of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem 258:15016–15020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Williams DP, Parker K, Bacha P, Bishai W, Borowski M, Genbauffe F, Strom TB, Murphy JR. 1987. Diphtheria toxin receptor binding domain substitution with interleukin-2: genetic construction and properties of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin-2 fusion protein. Protein Eng 1:493–498 10.1093/protein/1.6.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Williams DP, Snider CE, Strom TB, Murphy JR. 1990. Structure/function analysis of interleukin-2-toxin (DAB486-IL-2). Fragment B sequences required for the delivery of fragment A to the cytosol of target cells. J Biol Chem 265:11885–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Duvic M, Kuzel TM, Olsen EA, Martin AG, Foss FM, Kim YH, Heald PW, Bacha P, Nichols J, Liepa A. 2002. Quality-of-life improvements in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients treated with denileukin diftitox (ONTAK). Clin Lymphoma 2:222–228 10.3816/CLM.2002.n.003. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Foss F. 2006. Clinical experience with denileukin diftitox (ONTAK). Semin Oncol 33(Suppl 3):S11–S16 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.12.017. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Foss FM, Sjak-Shie N, Goy A, Jacobsen E, Advani R, Smith MR, Komrokji R, Pendergrass K, Bolejack V. 2013. A multicenter phase II trial to determine the safety and efficacy of combination therapy with denileukin diftitox and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone in untreated peripheral T-cell lymphoma: the CONCEPT study. Leuk Lymphoma 54:1373–1379 10.3109/10428194.2012.742521. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Fuentes AC, Szwed E, Spears CD, Thaper S, Dang LH, Dang NH. 2015. Denileukin diftitox (Ontak) as maintenance therapy for peripheral T-cell lymphomas: three cases with sustained remissions. Case Rep Oncol Med 2015:123756 10.1155/2015/123756. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wong BY, Ma Y, Fitzwilson R, Dang NH. 2008. De novo maintenance therapy with denileukin diftitox (Ontak) in a patient with peripheral T-cell lymphoma is associated with prolonged remission. Am J Hematol 83:596–598 10.1002/ajh.21177. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ho VT, Zahrieh D, Hochberg E, Micale E, Levin J, Reynolds C, Steckel S, Cutler C, Fisher DC, Lee SJ, Alyea EP, Ritz J, Soiffer RJ, Antin JH. 2004. Safety and efficacy of denileukin diftitox in patients with steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 104:1224–1226 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0028. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rasku MA, Clem AL, Telang S, Taft B, Gettings K, Gragg H, Cramer D, Lear SC, McMasters KM, Miller DM, Chesney J. 2008. Transient T cell depletion causes regression of melanoma metastases. J Transl Med 6:12 10.1186/1479-5876-6-12. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Telang S, Rasku MA, Clem AL, Carter K, Klarer AC, Badger WR, Milam RA, Rai SN, Pan J, Gragg H, Clem BF, McMasters KM, Miller DM, Chesney J. 2011. Phase II trial of the regulatory T cell-depleting agent, denileukin diftitox, in patients with unresectable stage IV melanoma. BMC Cancer 11:515 10.1186/1471-2407-11-515. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Cheung LS, Fu J, Kumar P, Kumar A, Urbanowski ME, Ihms EA, Parveen S, Bullen CK, Patrick GJ, Harrison R, Murphy JR, Pardoll DM, Bishai WR. 2019. Second-generation IL-2 receptor-targeted diphtheria fusion toxin exhibits antitumor activity and synergy with anti-PD-1 in melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:3100–3105 10.1073/pnas.1815087116. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


