Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease with memory loss and cognitive decline. Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) formed by hyperphosphorylated Tau protein are one of the pathological hallmarks of several neurodegenerative diseases including AD. Heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 (HSPB1) is a molecular chaperone that promotes the correct folding of other proteins in response to environmental stress. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 (NRF2), a redox-regulated transcription factor, is the master regulator of the cellular response to excess reactive oxygen species. Tropomyosin-related kinase B (TRKB) is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon binding brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), phosphorylates itself to initiate downstream signaling for neuronal survival and axonal growth. In this study, four natural flavones such as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF), wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin were evaluated for Tau aggregation inhibitory activity and neuroprotection in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma. Among the tested flavones, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin reduced Tau aggregation, oxidative stress, and caspase-1 activity as well as improved neurite outgrowth in SH-SY5Y cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed folding reporter. Treatments with 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin rescued the reduced HSPB1 and NRF2 and activated TRKB-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling to upregulate cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) and its downstream antiapoptotic BCL2 apoptosis regulator (BCL2). Knockdown of TRKB attenuated the neuroprotective effects of these three flavones. Our results suggest 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin targeting HSPB1, NRF2, and TRKB to reduce Tau aggregation and protect cells against Tau neurotoxicity and may provide new treatment strategies for AD.
Keywords: Tau; Alzheimer’s disease; quercetin; apigenin; TRKB agonist; 7,8-dihydroxyflavone
Introduction
Neurodegenerative disorders tauopathies, including the most common Alzheimer’s disease (AD), are characterized by abnormal hyperphosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein Tau that leads to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and causes gain of toxic function (Iqbal et al., 2005). Tau is mainly expressed in neuronal axons, where it promotes assembly and bundling of microtubules, thereby regulating vesicular transport and apoptosis (Lee et al., 2001). Phosphorylation of Tau has been proposed as the link between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and synaptic failure during early stages of AD (Mondragón-Rodríguez et al., 2013). In retinal ganglion cells of human P301S Tau transgenic mice with early tauopathy, the impairment of tropomyosin-related kinase B (TRKB) signaling is triggered by Tau pathology and mediates the Tau-induced dysfunction of visual response (Mazzaro et al., 2016). In addition, the accumulated asparagine endopeptidase-cleaved N368 Tau N-terminal fragment binds the TRKB receptor on its C terminus and antagonizes neurotrophic signaling to trigger neuronal apoptosis (Xiang et al., 2019).
Tropomyosin-related kinase B, a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase family, is a high-affinity receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Soppet et al., 1991). Upon BDNF binding, TRKB phosphorylates itself and members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway initiate intracellular signaling cascades (Levine et al., 1996). TRKB is highly expressed in adult hippocampus (Nakagawara et al., 1995), an area of the brain involved in learning and memory. Rapid activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), a member of the MAPK family, by BDNF/TRKB signaling induces phosphorylation of cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) (Bonni et al., 1999) to stimulate expression of antiapoptotic BCL2 apoptosis regulator (BCL2) (Riccio et al., 1999) for neuronal survival. As a significant risk factor for AD (Coppola et al., 2012), p.A152T Tau variant alters Tau function and toxicity via impairing retrograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicles (Butler et al., 2019). As retrograde axonal transport of endosomes mediated by TRKB signaling is essential for dendrite growth of cortical neurons (Zhou et al., 2012), BDNF/TRKB potentiation would be protective in AD.
Structurally, Tau is a prototypical natively unfolded protein (Schweers et al., 1994). Tau binds microtubules through C-terminal highly conserved 18-amino acid repeat domains (TauRD), which reside at the core of paired helical filaments of NFT (Goedert et al., 1989). The TauRD with the deletion mutation ΔK280 is highly prone to spontaneous aggregation (Khlistunova et al., 2006). Heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 (HSPB1) can prevent pathological misfolding of Tau by altering the conformation of hyperphosphorylated Tau and rescue hyperphosphorylated Tau-mediated cell death (Shimura et al., 2004). Accumulation of misfolded proteins can cause oxidative stress and compromise nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 (NRF2) to incur early events in the pathogenesis of AD (Mota et al., 2015). NRF2 activators have therapeutic effects in AD animal models and in cultured human cells that express the pathology of AD (Bahn and Jo, 2019).
Flavones, common in fruits and vegetables, are a class of flavonoids consisting of a benzene A ring condensed with an oxygenated heterocyclic C ring and phenyl B ring. Flavones are plant secondary metabolites with wide range of biological activity including antioxidant, anti-inflammation, and neuroprotective activity (Kumar and Pandey, 2013; Singh et al., 2014). 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF), the first reported BDNF-mimetic compound, binds with high affinity and specificity to the TRKB receptor (Jang et al., 2010). In addition to improve memory consolidation processes in rats and mice (Bollen et al., 2013), 7,8-DHF activates TRKB signaling to rescue amyloid-beta (Aβ)-induced neurotoxicity and synaptic dysfunction in transgenic mice expressing five familial AD-linked amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 (PS1) mutations [5 × familial Alzheimer’s disease (FAD)] (Devi and Ohno, 2012; Zhang et al., 2014). Furthermore, an optimized 7,8-DHF prodrug R13 alleviates Aβ deposition, attenuates the loss of hippocampal synapse, and ameliorates memory deficits in 5 × FAD mice (Chen et al., 2018). We have previously shown neuroprotective effects of 7,8-DHF on neurite length and branch in mouse hippocampal primary neurons under Aβ toxicity and 7,8-DHF-mediated upregulation of neuronal nuclei, p-ERK, and p-CREB in the immunohistochemical staining of mice with oligomeric Aβ injection into hippocampal cornu ammonis area 1 subregion (Fan et al., 2020). In addition, wogonin (5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone), a novel inhibitor for mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, strengthens the autophagy to effectively clear Aβ and suppresses Tau protein phosphorylation (Zhu and Wang, 2015). Quercetin (3,3′,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone) decreases β-amyloidosis and tauopathy and protects the cognitive function in APP, PS1, and Tau triple-transgenic AD mouse model (3 × Tg-AD mice) (Sabogal-Guáqueta et al., 2015; Pérez-Corredor et al., 2019). Studies have shown that apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone) ameliorates learning and memory impairment through relieving Aβ burden, suppressing amyloidogenic process, and restoring ERK/CREB/BDNF pathway in APP and PS1 double transgenic AD mice (Zhao et al., 2013). Wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin provide neuroprotection in AD through potentiating HSPB1, NRF2, and TRKB signaling that are not clear. Previously, we have generated human neuroblastoma cells overexpressing ΔK280 TauRD and used to screen agents that prevent the aggregation and degeneration of cells (Chang et al., 2017). Using this cell model, we demonstrate that 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin target HSPB1, NRF2, and TRKB to reduce Tau aggregation and protect cells against Tau neurotoxicity, providing new treatment strategies for AD.
Materials and Methods
Test Compounds and Biochemical Analysis of Tau Aggregation Inhibition
7,8-dihydroxyflavone, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States. Congo red (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States), known to bind to the cross β-sheet structure of amyloid fibrils (Sipe and Cohen, 2000), was included for comparison. For biochemical Tau aggregation inhibition test, bacterial expressed proaggregator ΔK280 TauRD (Gln244–Glu372 of 441-residue human Tau) was prepared as described (Lin et al., 2020). ΔK280 TauRD protein (20 μM in final 50 μl) was incubated with tested compounds (5–10 μM in 150 mM sodium chloride (NaCl) and 20 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-hydrochloride (Tris–HCl), pH 8.0) at 37°C for 48 h. Then, thioflavin T (5 μM final concentration; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States), a dye exhibiting enhanced fluorescence upon binding to diverse types of amyloid fibrils (Biancalana and Koide, 2010), was added and incubated for 25 min at room temperature. The formed aggregates reflected by thioflavin T fluorescence intensity was recorded at excitation 420 nm and emission 485 nm by using the FLx800 Fluorescence Microplate Reader (BioTek Instruments Incorporation, Winooski, VT, United States). Half maximal effective concentration (EC50) was calculated using the interpolation method.
1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl Radical Scavenging Assay
1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States), a common stable free radical for antioxidant assay (Li et al., 2008), was used to examine the radical scavenging activity of the studied flavones. DPPH solution (100 μM) was prepared in 95% ethanol. After adding test compounds (10–80 μM), the mixture was vortexed for 15 s and allowed to stand for 30 min at room temperature. Subsequently, the mixture was measured spectrophotometrically at 517 nm (Multiskan GO Microplate Spectrophotometer; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The free radical scavenging activity was calculated as the percentage of DPPH discoloration using the formula 1 − (absorbance of sample/absorbance of control) × 100%, with EC50 calculated using the interpolation method.
Docking Computation
7,8-dihydroxyflavone is a known potent and selective small-molecule agonist of TRKB (Jang et al., 2010). Using GOLD docking program (Nissink et al., 2002; Verdonk et al., 2003), protein structure of TRKB-d5 domain (pdb code: 1HCF) (Banfield et al., 2001) was utilized to perform docking computation for 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin. In addition to be used to determine the specificity of neurotrophin receptors experimentally (Urfer et al., 1995), the d5 domain was predicted to be the binding site by docking computation (Chitranshi et al., 2015). In docking computations, 10,000, 20,000, 40,000, and 80,000 operations were performed to ensure convergence of the calculated results.
Cells and Culture
Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y-derived ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed cells (Chang et al., 2017) were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM)/F12 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States), with 5 μg/ml blasticidin and 100 μg/ml hygromycin (InvivoGen, San Diego, CA, United States) added to the growth medium. Retinoic acid (10 μM; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) and doxycycline (2 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) were used to induce neuronal differentiation and ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression, respectively.
High Content Analyses of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed Fluorescence and Oxidative Stress
On day 1, ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were seeded into a 96-well plate (2.5 × 104/well), with retinoic acid (10 μM) added to induce neuronal differentiation (Påhlman et al., 1984). On day 2, cells were pretreated with Congo red, 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, or apigenin (2.5–10 μM) for 8 h, followed by inducing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression with doxycycline. On day 8, cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 (0.1 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) for 30 min and cell images were automatically recorded at excitation/emission wavelengths of 543/593 nm (ImageXpress Micro Confocal High-Content Imaging System; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, United States) and analyzed (MetaXpress High-Content Image Acquisition and Analysis Software; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, United States).
For reactive oxygen species (ROS) measurement, dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) (10 μM; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), a fluorogenic dye that measures hydroxyl, peroxyl, and other ROS activity within cells (Aranda et al., 2013), was added to the cells on day 8 and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. ROS in cells was measured using the High-Content Imaging System, with excitation/emission wavelengths at 482/536 nm.
Real-Time PCR Analysis
As described, ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were seeded on a 6-well plate (5 × 105/well), with retinoic acid addition on day 1, treated with tested compounds (5 or 10 μM), and induced ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression with doxycycline on day 2. On day 8, cells were collected and total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). The RNA was reverse-transcribed using the SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using 50 ng complementary DNA (cDNA) with the customized Assays-by-Design probe for DsRed (Chang et al., 2017) and the TaqMan fluorogenic probe for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1) (4326321E) using the StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, United States). Fold change was calculated using the formula 2ΔCt, ΔCT = CT (HPRT1) − CT (DsRed), in which CT indicates cycle threshold.
Neurite Outgrowth Analysis
As described, ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were seeded on a 24-well plate (5 × 104 cells/well), with induced neuronal differentiation on day 1, treated with test compounds (5 or 10 μM), and induced ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression on day 2. After 7 days, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min. After being permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 min and blocked with 3% bovine serum albumin in PBS for 20 min, cells were stained with tubulin beta 3 class III (TUBB3) primary antibody (1:1,000; Covance, Princeton, NJ, United States) at 4°C overnight, followed by goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor ®555 secondary antibody (1:1,000; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States) at room temperature for 3 h. After nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (0.1 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) for 30 min, neuronal images from at least 60 individual fields (150–250 neurons per field) per experiment were captured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 531/593 nm using the ImageXpress Micro Confocal High-Content Imaging System (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, United States). Neurite total length (μm), process (the number of primary neurites defined as the segments originating from the cell body of a neuron), and branch (the number of secondary neurites extending from primary neurites) were analyzed using the MetaXpress Neurite Outgrowth Application Module (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, United States). For each sample, around 6,000 cells were analyzed in each of 3 independent experiments.
Caspase-1, Lactate Dehydrogenase, and Acetylcholinesterase Assays
ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were seeded in a 6-well plate (5 × 105/well) and treated with retinoic acid, test compound, and doxycycline as described. On day 8, cells were collected and lysates were prepared by 6 freeze/thaw cycles. After centrifugation to collect supernatant, caspase-1 activity in 50 μg cell extracts was measured using the ICE Fluorometric Assay Kit (BioVision, Milpitas, CA, United States). The mixture was incubated for 2 h at 37°C and caspase-1 activity was measured with excitation/emission wavelengths at 400/505 nm (FLx800 Fluorescence Microplate Reader; BioTek Instruments Incorporation, Winooski, VT, United States). In addition, the collected cells were lysed by sonication. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in supernatant was determined using AChE Activity Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) with 10 μg cell extracts. The mixture was incubated for 2–10 min at room temperature and absorbance at 412 nm was measured using the Multiskan GO Microplate Spectrophotometer Reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in culture medium was examined by using the LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit (Cayman, Ann Arbor, MI, United States). The absorbance was read at 490 nm with the Multiskan GO Microplate Spectrophotometer Reader.
Ribonucleic Acid Interference
For TRKB knockdown in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells, lentivirus carrying TRKB-targeting (TRCN0000002243, TRCN0000002245, and TRCN0000002246) and negative control scrambled (TRC2.Void) short hairpin RNA (shRNA) were obtained from the National RNAi Core Facility, institute of molecular biology/genomic research center, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan. On day 1, cells were plated on 24-well plates in the presence of retinoic acid as described. On day 2, the cells were infected with lentivirus (3 multiplicity of infection for each shRNA) in medium with polybrene (8 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States). On day 3, the culture medium was changed and the cells were pretreated with Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM) for 8 h, followed by induction of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression. On day 9, the cells were collected for TRKB protein analysis or analyzed for neurite outgrowth as described.
Protein Blot Analysis
Total proteins from ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were prepared using lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid pH 8.0, 1 mM ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)tetraacetic acid pH 8.0, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 1% Triton X-100, and protease (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) and phosphatase (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, United States) inhibitor cocktails. After quantitation using a protein assay kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, United States), proteins (20 μg) were separated on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mosby, MO, United States) by reverse electrophoresis. After blocking, the membrane was probed with antibody against DsRed (1:500; BioVision #3994, Milpitas, CA, United States); HSPB1 (1:500; Abcam #ab137748, Cambridge, MA, United States); NRF2 (1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, United States #sc-365949); TRKB (1:500; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States #4603); p-TRKB (Y817) (1:500; Millipore #ABN1381, Billerica, MA, United States); ERK (1:500; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States #9102); p-ERK (T202/Y204) (1:500; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States #9101); CREB (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, United States #sc-186); p-CREB (S133) (1:1,000; Millipore #06-519, Billerica, MA, United States); BCL2 (1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, United States #sc-7382), BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) (1:500; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States #2772); or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (as a loading control) (1:1,000; MDBio #30000002, Taipei, Taiwan). The immune complexes were detected by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat antimouse (#GTX213111-01) or goat antirabbit (#GTX213110-01) immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody (1:5,000, GeneTex Incorporation, Irvine, CA, United States) and chemiluminescent substrate (Millipore, Billerica, MA, United States).
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SD. 3 independent tests in 2 or 3 biological replicates were performed in each experiment. Differences between groups were evaluated using the two-tailed Student’s t-test or the one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test where appropriate. p < 0.05 indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Tested Flavones, Radical Scavenging, and Biochemical Tau Aggregation Inhibition
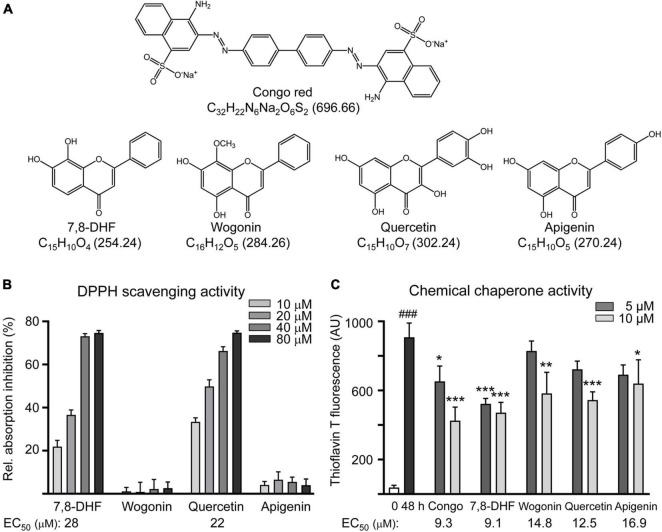
Natural flavones such as 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin (Figure 1A) were examined. Oxidative stress has been recognized as a contributing factor to the progression of AD and preventing oxidative stress is considered as a treatment approach for AD (Poprac et al., 2017). Therefore, the radical scavenging activity of the three flavones (10–80 μM) was first examined. While wogonin and apigenin displayed no radical scavenging activity, 7,8-DHF and quercetin had EC50 values of 24 and 25 μM, respectively (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
Tested compounds. (A) Structure, formula, and molecular weight of Congo red (as a positive control), 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF), wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin. (B) Radical-scavenging activity of tested flavones (10–80 μM) on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) (n = 3). Shown below are the EC50 values. (C) ΔK280 TauRD aggregation inhibition of tested compounds (5–10 μM) by the thioflavin T assay (n = 3). p-values: comparisons between 0-h and 48-h incubation (###p < 0.001) or between with and without compound addition (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001) (one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test). Shown below are the EC50 values.
The inhibition of Tau aggregation was measured by measuring thioflavin T binding to Escherichia coli-derived 14.7 kDa ΔK280 TauRD protein using Congo red as a control. EC50 values of Congo red, 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin for Tau aggregation inhibition were: 9.3, 9.1, 14.8, 12.5, and 16.9 μM, respectively (Figure 1C).
Tropomyosin-Related Kinase B Binding Prediction
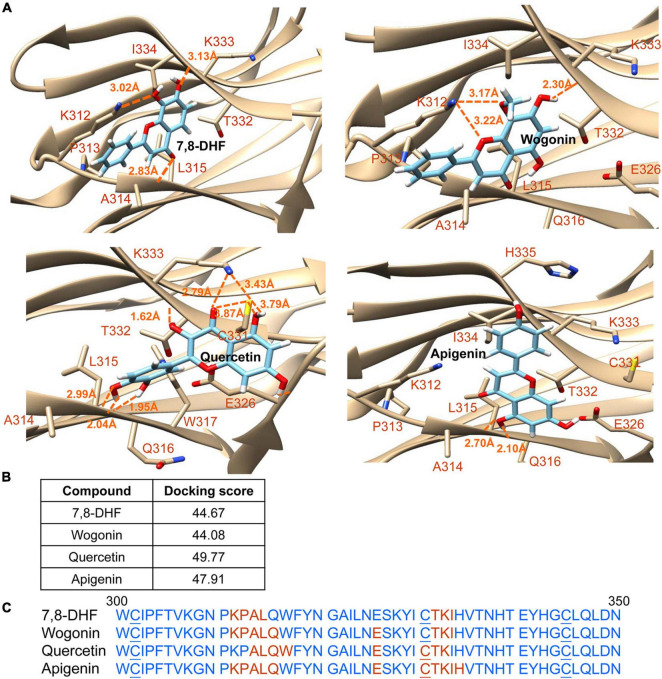
The strengths and conformation of wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin binding with neurotrophin-binding domain d5 of TRKB were calculated using 7,8-DHF as a control. As shown in Figure 2, the computations predicted docking scores of 44.67, 44.08, 49.77, and 47.91 for 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin, respectively. Quercetin had the top interacting docking score with TRKB receptor among the 3 flavones examined.
FIGURE 2.
Docking computations of 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin. (A) The docking conformations of tested flavones binding to d5 domain (the second immunoglobulin-like domain, 250–340 amino acid residues) of extracellular domain of tropomyosin-related kinase B (TRKB) receptor. The TRKB-d5 domain (ribbon structures) is colored in beige and the wire-frame structures denote the compounds. The labeled amino acids were within 10 Å radii of examined compounds. Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms of compounds or side chains of surrounding amino acids are shown in light blue, red, white, and blue, respectively. The dotted orange lines indicate hydrogen bond interactions between compounds and proteins. (B) The docking scores of 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, and apigenin calculated by the GOLD program. (C) Amino acid residues 301–350 of d5 domain. The amino acids within 10 Å radii of examined compounds are colored in red; the cysteines involved in disulfide linkage are underlined.
Cellular Tau Aggregation Inhibition and Oxidative Stress Reduction in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-Expressing SH-SY5Y Cells
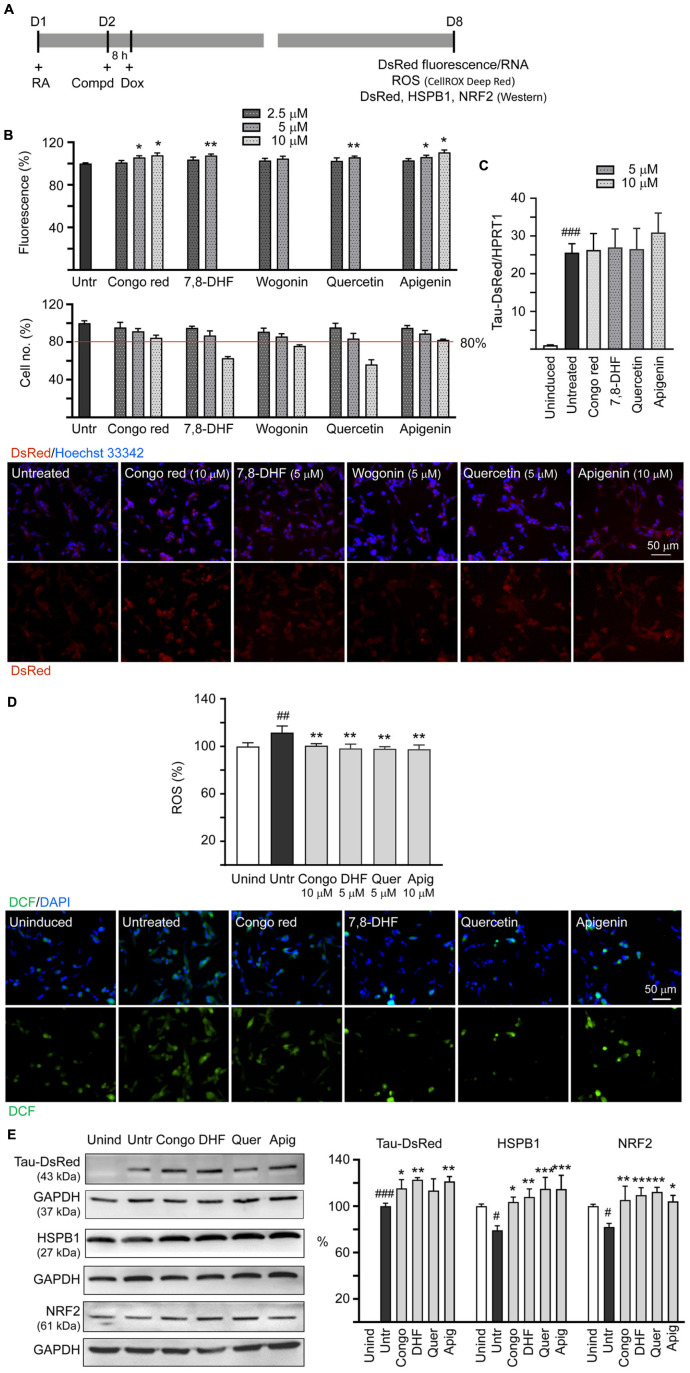
Neuronal differentiated human SH-SY5Y cells were used to evaluate the effects of tested flavones on ΔK280 TauRD aggregation inhibition, ROS reduction, and HSPB1 and NRF2 expression changes (Figure 3A). In these cells, the misfolded ΔK280 TauRD adversely affected the folding of fused DsRed to decrease DsRed fluorescence (Chang et al., 2017). DsRed fluorescence was measured in wells containing at least 80% cells remained compared to untreated cells. Congo red, known to attenuate amyloid-like aggregates of neuronal Tau induced by formaldehyde (Nie et al., 2007), was included for comparison. As shown in Figure 3B, after normalization of DsRed fluorescence with cell number counted, treatment with Congo red at 5–10 μM (106–108%; p = 0.018–0.017), 7,8-DHF at 5 μM (108%; p = 0.004), quercetin at 5 μM (106%; p = 0.004), or apigenin at 5–10 μM (106–110%; p = 0.016–0.010) increased the DsRed fluorescence intensity significantly compared with untreated cells (100%), but treatment with wogonin did not increase the DsRed fluorescence intensity. Under circumstance of over 80% cells remained, treatment of 10 μM Congo red, 5 μM 7,8-DHF, 5 μM quercetin, or 10 μM apigenin did not altered Tau-DsRed RNA level significantly (26.3–30.9-folds, p > 0.05) compared with untreated cells (25.6-fold) (Figure 3C). Given that wogonin did not show aggregation-inhibiting and free radical scavenging effects, only Congo red, apigenin at 10 μM and 7,8-DHF, quercetin at 5 μM were adopted in the subsequent experiments.
FIGURE 3.
Tau aggregation inhibition and reactive oxygen species (ROS) reduction in SH-SY5Y cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, cells were plated with retinoic acid (RA) (10 μM) added to the culture medium. On day 2, Congo red (as a positive control), 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, or apigenin was added to the cells for 8 h, followed by inducing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression with doxycycline (Dox) (2 μg/ml) for 6 days. On day 8, ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed fluorescence/RNA, ROS dichlorofluorescein (DCF stain), as well as DsRed, heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 (HSPB1), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 (NRF2) protein levels were measured. (B) Top: Assessment of DsRed fluorescence with Congo red, 7,8-DHF, wogonin, quercetin, or apigenin (2.5–10 μM) treatment and cell number (obtained by counting Hoechst 33342 stained cell nuclei) analyzed (n = 3). The relative DsRed fluorescence/cell number of untreated cells (Untr) was normalized as 100%. p-values: comparisons between with and without compound addition (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; two-tailed Student’s t-test). Bottom: Fluorescent images of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed cells with or without Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), wogonin (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM) treatment. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). (C) Real-time PCR analysis of TauRD-DsRed RNA in SH-SY5Y cells uninduced, untreated, or treated with 5 or 10 μM compound (n = 3). HPRT1 was used as an endogenous control to normalize between samples. (D) Top: Quantitation of ROS (n = 3) and images of DCF stain (green) of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed cells uninduced, untreated, or treated with Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM). The relative ROS of uninduced cells was normalized as 100%. Bottom: Images of DCF (green) assay of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed cells uninduced, untreated, or treated with Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM). Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). (E) Immunoblot analysis of TauRD-DsRed, HSPB1, and NRF2 proteins in SH-SY5Y cells uninduced, untreated, or treated with 5 or 10 μM compound (n = 3). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. To normalize, the HSPB1 or NRF2 expression level in uninduced (Unind) cells was set at 100%. For TauRD-DsRed, the soluble level in untreated cells (Untr) cells was set at 100%. (D,E) p-values: comparisons between untreated vs. uninduced cells (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001) or compound-treated vs. untreated cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) (one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test).
Misfolded Tau may increase the production of ROS (Cente et al., 2006). Thus, we evaluated antioxidative effects of 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin using DCFH-DA. Induced ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression elevated the ROS level in these cells (112%; p = 0.005) and Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM) effectively reduced the ROS level associated with ΔK280 TauRD overexpression (from 112 to 101–98%; p = 0.008–0.001) (Figure 3D).
We also examined if Congo red, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin upregulate HSPB1 and NRF2 expression in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells. As shown in Figure 3E, addition of Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM) increased soluble ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed (from 100 to 113–123%; p = 0.098–0.003) and HSPB1 (from 79 to 104–115%; p = 0.016– < 0.001) levels. In addition, addition of Congo red or tested flavones (5 or 10 μM) increased NRF2 protein level (from 82 to 104–112%; p = 0.010– < 0.001), which is essential for defense against ROS.
Caspase-1, AChE Reduction, and Neurite Outgrowth Promotion in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-Expressing SH-SY5Y Cells
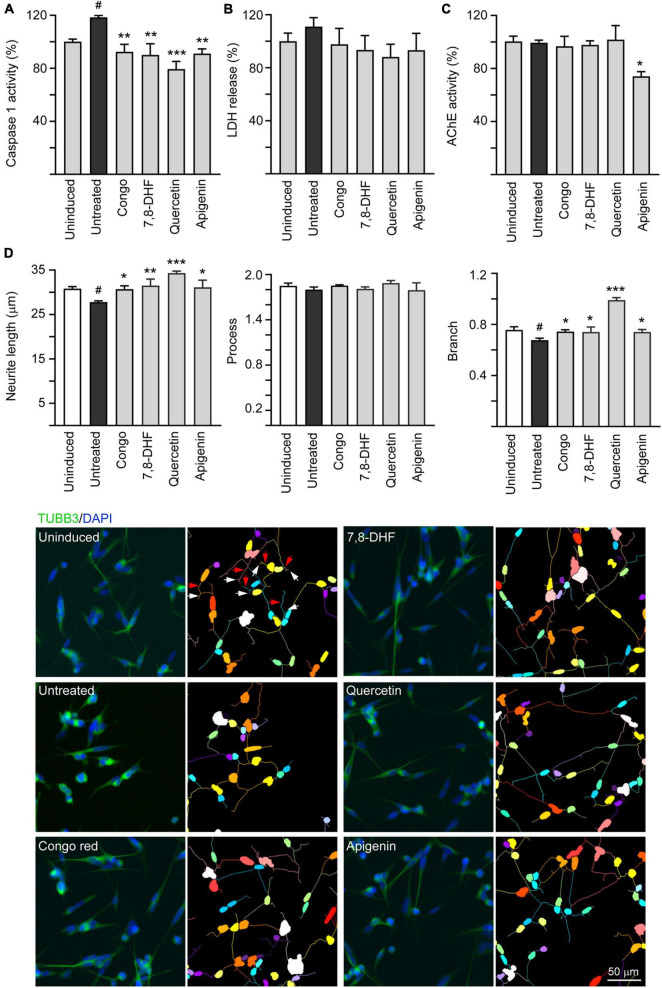
In the brains of patients with AD, cholinergic neurons were selectively impaired (Davies and Maloney, 1976) and AChE inhibitors have been used as standard treatment of AD (Citron, 2010). In addition, caspase-1 activation is associated with brain pathology of AD (Heneka et al., 2013) and caspase-1 inhibition alleviates cognitive impairment and neuropathology (Flores et al., 2018) in AD mouse models. Therefore, caspase-1 and AChE activities in compound-treated cells were also evaluated. The overexpression of ΔK280 TauRD significantly increased caspase-1 activity (118%; p = 0.020) and treatment with Congo red, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin (5 or 10 μM) reduced the caspase-1 activity (from 118 to 92–79%; p = 0.002– < 0.001) (Figure 4A). Similar changing trend of LDH release was also observed (from 111 to 98–88%), although not significant (p > 0.05) (Figure 4B). In SH-SY5Y cells, ΔK280 TauRD overexpression did not increased AChE activity, but treatment with apigenin (10 μM) reduced AChE activity (from 99 to 74%; p = 0.016) compared to no treatment (Figure 4C).
FIGURE 4.
Caspase-1, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) reduction, and neurite outgrowth promotion of 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin in SH-SY5Y cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed. As described, cells were seeded with RA, treated with Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM), and induced ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression with doxycycline for 6 days. On day 8, (A) caspase-1 activity, (B) lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, (C) AChE activity, and (D) neurite length, process, and branch were analyzed (n = 3). To normalize, the relative caspase-1, LDH release, or AChE activity of uninduced cells (Dox -) was set as 100%. Shown on the bottom half of panel (D), there were images of TUBB3 (green)-stained cells, with nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue) and segmented images with multicolored mask to assign each outgrowth to a cell body for neurite outgrowth quantification. Process and branches in uninduced cells were marked with red and white arrows, respectively. p-values: comparisons between induced vs. uninduced cells (#p < 0.05) or compound-treated vs. untreated cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) (one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test).
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that plays a role in mediating neurite outgrowth (Johnson and Stoothoff, 2004). Calpain-cleaved neurotoxic Tau45–230 fragment modifies the composition of the neuronal cytoskeleton and impairs neurite elongation in neurons undergoing degeneration (Afreen and Ferreira, 2019). The neurite outgrowth-promoting effect of tested compounds including total neurite length, number of processes, and number of branch points was evaluated. As shown in Figure 4C, overexpression of ΔK280 TauRD significantly decreased neurite length (from 30.8 to 27.8 μm; p = 0.026) and branch (from 0.76 to 0.67; p = 0.010). Treatment with Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), and apigenin (10 μM) rescued the impairment of neurite length (from 27.8 to 30.7–34.3 μm; p = 0.035– < 0.001) and branch (from 0.67 to 0.74–0.99; p = 0.034– < 0.001).
Molecular Targets of 7,8-DHF, Quercetin, and Apigenin in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-Expressing SH-SY5Y Cells
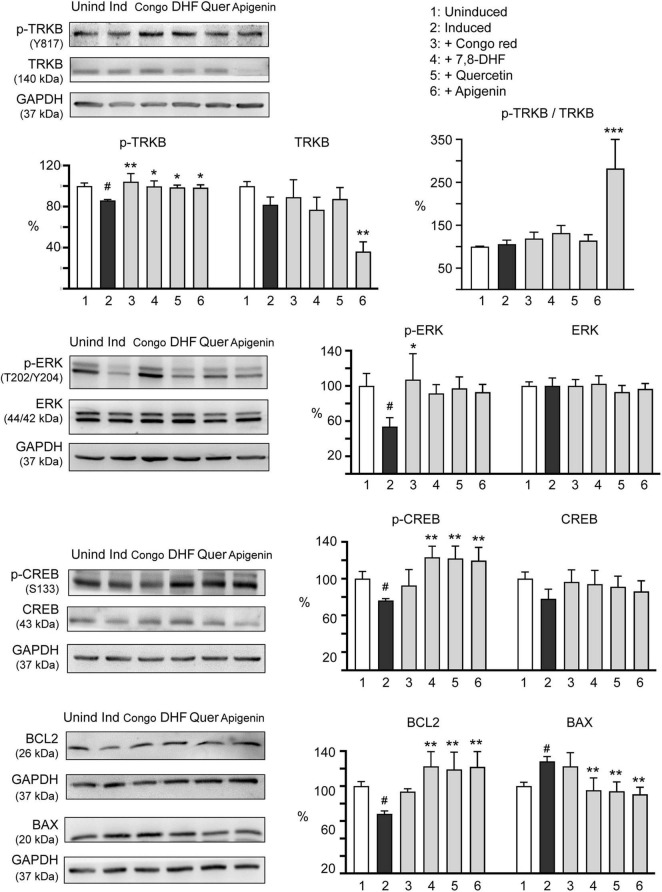
Tropomyosin-related kinase B is highly expressed in the hippocampus and plays a critical role in memory processes (Kang et al., 1997). Phosphorylation of TRKB at the most C-terminal tyrosine, Y817, leads to activation of ERK and CREB and transcription of BCL2 to promote cell survival (Hausott et al., 2009). The effects of Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), and apigenin (10 μM) on expression levels of TRKB, ERK, CREB, and BCL2 in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-expressing SH-SY5Y cells were examined (Figure 5). Addition of tested flavones increased p-TRKB (Y817) (from 86 to 99–100%; p = 0.039–0.022), p-ERK (T202/Y204) (from 54 to 92–97%; p = 0.105–0.052), p-CREB (S133) (from 76 to 120–123%; p = 0.003–0.001), and downstream BCL2 (from 68 to 119–123%; p = 0.002–0.001) protein levels. In response to the antiapoptotic BCL2 change, addition of tested flavones significantly reduced the expression of proapoptotic BAX (from 128 to 95–91%; p = 0.003–0.002). Although Congo red treatment increased p-TRKB (Y817) (104%; p = 0.003) and p-ERK (T202/Y204) (107%; p = 0.014), changes of p-CREB (S133) (92 vs. 76%), BCL2 (94 vs. 68%), and BAX (122 vs. 128%) were not significant (p > 0.05) in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-expressing SH-SY5Y cells. Due to reduction of the total amount of TRKB (36%; p = 0.001), apigenin induced a significant hyperphosphorylation of TRKB in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-expressing SH-SY5Y cells (p-TRKB/TRKB: 282%; p < 0.001). The reason for observed reduced TRKB level in apigenin-treated cells is not clear.
FIGURE 5.
Molecular targets of 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin in SH-SY5Y cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed. Congo red (10 μM) was included as a negative control. Relative TRKB, p-TRKB (Y817), p-TRKB/TRKB, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p-ERK (T202/Y204), cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), p-CREB (S133), BCL2 apoptosis regulator (BCL2), and BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) protein levels were analyzed through immunoblotting using specific antibodies (n = 3). GAPDH was used as a loading control. Relative protein levels are shown on the right side of the representative western blot images. To normalize, the relative protein level in uninduced cells (Dox -) was set as 100%. p-values: comparisons between induced and uninduced cells (#p < 0.05) or between treated and untreated cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) (one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test).
Tropomyosin-Related Kinase B Knockdown in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed-Expressing SH-SY5Y Cells
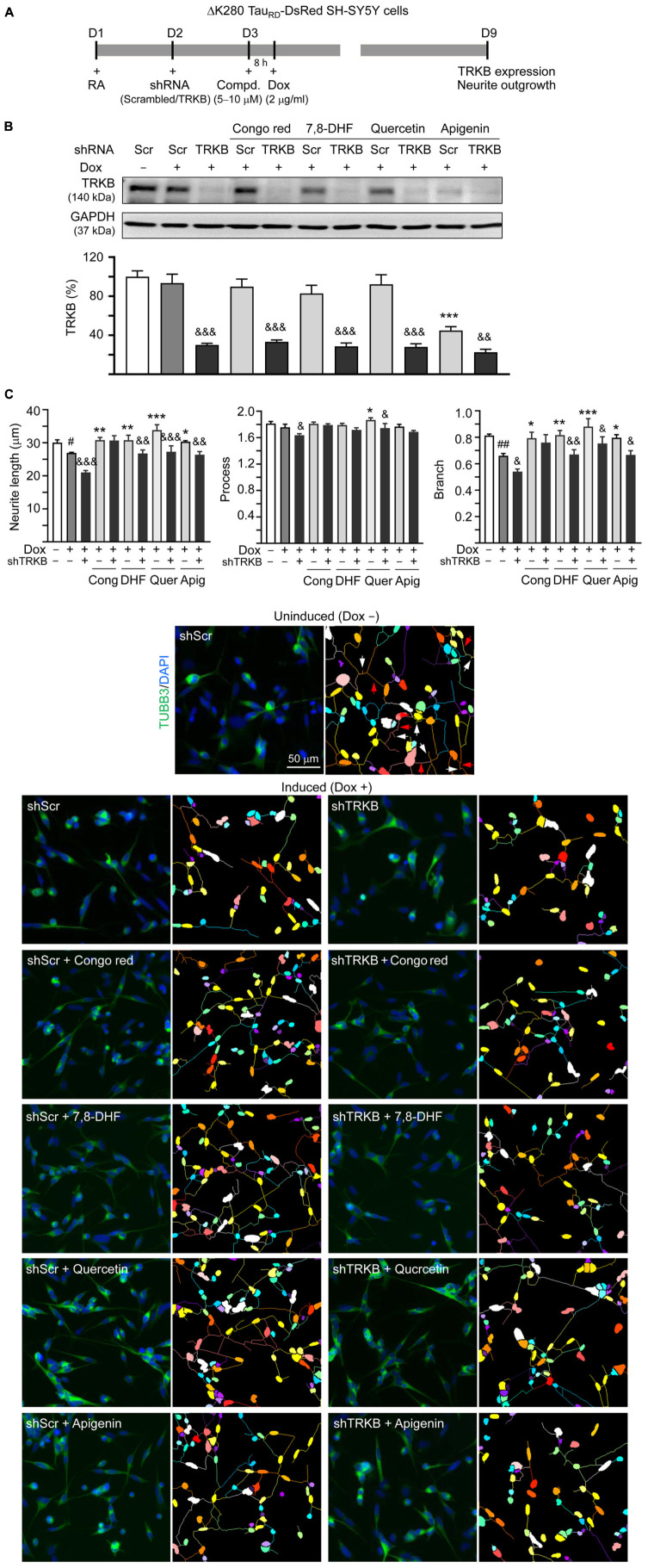
Since the studied compounds displayed potential to activate TRKB signaling, we knocked down TRKB expression through lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells to examine if TRKB was the therapeutic target of 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin (Figure 6A). As shown in Figure 6B, no significant change of TRKB level (93 vs. 100%; p > 0.05) was observed in scrambled shRNA-infected cells with or without inducing ΔK280 TauRD expression. While apigenin reduced TRKB level (from 93 to 45%; p < 0.001), addition of Congo red, 7,8-DHF, or quercetin did not affect TRKB level in scrambled shRNA-infected cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD (83–92 vs. 93%; p > 0.05). However, TRKB-specific shRNA significantly reduced TRKB in ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells treated without (from 93 to 30%, p < 0.001) or with (from 92–45 to 33–23%, p = 0.007– < 0.001) compound.
FIGURE 6.
TRKB RNA interference of SH-SY5Y cells expressing ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed SH-SY5Y cells were plated with RA (10 μM). On day 2, the cells were infected with lentivirus-expressing TRKB-specific or scrambled shRNA. At 24 h postinfection, Congo red (10 μM), 7,8-DHF (5 μM), quercetin (5 μM), or apigenin (10 μM) was added to the cells for 8 h, followed by induction of ΔK280 TauRD-DsRed expression (Dox, 2 μg/ml) for 6 days. On day 9, the cells were collected for (B) TRKB protein (GAPDH as a loading control) and (C) neurite outgrowth analyses (n = 3). To normalize, the relative TRKB protein of uninduced cells (Dox -) was set as 100%. Shown on the bottom half of panel (C), there were images of TUBB3 (green)-stained cells, with nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue) and segmented images with multicolored mask to assign each outgrowth to a cell body for neurite outgrowth quantification. Processes and branches in scrambled shRNA-infected uninduced cells were marked with red and white arrows, respectively. p-values: comparisons between induced (Dox +) vs. uninduced (Dox -) cells (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01) between compound-treated vs. untreated cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) or between TRKB shRNA-treated vs. scrambled shRNA-treated cells (&p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01, &&&p < 0.001) (one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey’s test).
For neurite outgrowth analysis (Figure 6C), neurite length (from 30.0 to 26.9 μm; p = 0.030) and branch (from 0.81 to 0.66; p = 0.006) were reduced upon induction of ΔK280 TauRD expression in scrambled shRNA-infected cells. Congo red, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, or apigenin increased neurite length (from 26.9 to 30.3–33.8 μm; p = 0.013– < 0.001) and branch (from 0.66 to 0.79–0.88; p = 0.022– < 0.001). In line with TRKB knockdown, TRKB-specific shRNA significantly reduced neurite length and branch without (length: from 26.9 to 21.0 μm, p < 0.001; branch: from 0.66 to 0.54, p = 0.049) or with (length: from 30.3–33.8 to 26.4–27.6 μm, p = 0.003– < 0.001; branch: from 0.81–0.88 to 0.67–0.76, p = 0.033–0.009) 7,8-DHF, quercetin, or apigenin addition, but not with Congo red addition (length: 30.7 vs. 30.8 μm, branch: 0.76 vs. 0.79; p > 0.05). These results suggested that 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin improved neurite outgrowth phonotype by upregulating TRKB signaling.
Discussion
Effective treatments to slow neurodegeneration of AD are still unavailable. BDNF, a well-characterized member of the nerve growth factor family, is expressed in whole brain (Jones and Reichardt, 1990). Binding of BDNF to TRKB receptor activates downstream signaling pathways to promote neuronal growth, survival, and neural plasticity as well as enhance memory formation and storage (Nagahara and Tuszynski, 2011; Lu et al., 2013). The expanding role of BDNF suggests a valuable therapeutic target for AD. However, BDNF has a poor biostability such as the very short plasma half-life and the limited diffusion crossing blood–brain barrier (BBB) (Dittrich et al., 1996). Small compounds that mimic neurotrophic signaling and overcome the pharmacokinetic barrier of BDNF may have greater therapeutic potential (Zeng et al., 2013). In human SH-SY5Y cells expressing proaggregator Tau, we found protective potentials of three natural flavones, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin, including reduction of Tau aggregation, ROS and caspase-1, as well as promotion of neurite outgrowth (Figures 3, 4). Similarly, promotion of neurite outgrowth by quercetin in Figure 4 has been reported in pheochromocytoma cell line (Katebi et al., 2019). TRKB silencing counteracted the neuroprotective effects of these flavones against toxicity of proaggregator Tau (Figure 6), demonstrating that the neuroprotective effects of three natural flavones against Tau toxicity were mechanically mediated by increasing p-TRKB (Y817) (Figure 5) to enhance TRKB signaling, in addition to directly interfering with Tau aggregate formation (Figure 1). As knockdown of TRKB is not complete, the added flavones may still exert a modest neuroprotective effect by binding to the remained TRKB, so that the flavone-treated cells with TRKB knockdown still displayed improved neurite outgrowth compared to those without flavone treatment (Figure 6). The mechanism is supported by the high docking scores of the tested compounds binding to the neurotrophin-binding domain d5 of TRKB predicted by the computations (Figure 2). The observed neuroprotective effect under the knockdown of TRKB by these flavones may be also attributed to the increased NRF2 to promote neurite outgrowth (Yang et al., 2015).
Various natural flavones display antioxidant activity (Pietta, 2000). The majority of neurodegenerative diseases are speculated to originate from cumulative oxidative stress caused by deposition of abnormal aggregated proteins (Grimm et al., 2011). There is clear evidence that ROS is highly upregulated in the brain of tauopathies of the patients and ROS also directly promotes Tau modifications (Haque et al., 2019). Compounds with antioxidative potential may directly serve as chemical chaperone to suppress protein aggregates or quench free oxygen radicals. All the three flavones displayed some degree of chemical chaperone activity to enhance the folding and/or stability of proaggregator Tau (Figure 1C). Structural requirements of flavonoids for appreciable radical scavenging activity have been established (Seyoum et al., 2006). Without o-dihydroxy group (catechol structure) in the benzene ring, apigenin has poor antioxidant capacity for scavenging free radicals as assessed using stable radical DPPH (Figure 1B).
An alternative way to decrease cellular ROS is by enhancing antioxidative signaling such as NRF2 pathway. Stabilized following oxidative stress, NRF2 induces the expression of antioxidants as well as cytoprotective genes (Vomund et al., 2017). Reduced nuclear levels of NRF2 are observed in postmortem brains of patients with AD (Ramsey et al., 2007) and NRF2 inducer carnosic acid improves learning and memory in 3 × Tg-AD mice (Lipton et al., 2016). In this study, all the three flavones enhanced the expression of NRF2 (Figure 3E), supporting the role of 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin in activating the adaptive response to reduce oxidative stress. The NRF2 expression can be upregulated by AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT), which is one of the downstream proteins of TRKB activation (Yoo et al., 2017). Therefore, the NRF2 in the ΔK280 TauRD cell model treated with the three flavones may be increased through TRKB activation, at least partially.
Heat-shock proteins such as HSP90, HSP40, and HSPB1 had been speculated to function as regulators of soluble Tau protein levels (Sahara et al., 2007). As all the three flavones enhanced the expression of HSPB1 for chaperoning misfolded Tau (Figure 3E), 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin may also reduce the Tau-associated ROS through eliminating the misfolded Tau deposits. HSPB1 is transcriptionally upregulated by heat shock transcription factor 1 that can be enhanced by NRF2 (Paul et al., 2018). The HSPB1 expression in the ΔK280 TauRD cell model treated with the tested compounds may be activated by increased NRF2. However, further studies are required to consolidate the assumption.
Reactive oxygen species-associated neuroinflammation has been well known to be involved in caspase-1 activation and cleavage of proinflammatory cytokines (Howley and Fearnhead, 2008). Oxidative stress may also directly activate caspase-1 involved in inflammasome (Bai et al., 2020). Active caspase-1 induces caspase-6 activation that leads to axonal and neuronal degeneration in human primary central nervous system (CNS) cultures (Kaushal et al., 2015). Both the quercetin and apigenin have been reported to suppress inflammasome activation and downstream effector caspase-1 in human diseases induced by inflammatory responses (Yi, 2018). In this study, 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin counteract increased caspase-1 activity induced by proaggregator Tau (Figure 4B), which may be attributed to their free radical-scavenging (Figure 1B) or NRF2-enhancing activity (Figure 3E) to reduce ROS.
Acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, is a feasible therapeutic target for treatment of AD (Akıncıoğlu and Gülçin, 2020). Currently AChE inhibitors such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine are commonly used to increase the level and duration of acetylcholine and facilitate cholinergic transmission in AD (Marucci et al., 2021). It has been shown that AChE activity as well as choline acetyltransferase is reduced in the cerebral cortex of patients with AD and tauopathy, indicating degenerated cholinergic neurons in both the diseases (Shinotoh et al., 2000; Hirano et al., 2006, 2018). However, the AChE activity is increased in frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 human tau transgenic mice (Silveyra et al., 2012). The findings of AChE activity in human tauopathy and the mouse model are not consistent. Our cell model that did not show significant changes in AChE activity may indicate that AChE activity is still preserved or partially impaired in this model and that inhibiting AChE activity may rescue acetylcholine levels. Among the three flavones examined, only apigenin reduced AChE activity in SH-SY5Y cells expressing proaggregator Tau (Figure 4C). Studies have shown that oxidative stress may induce AChE activity (Wang et al., 2019). However, given that all the three flavones in this study can reduce ROS, the reduced AChE activity only by apigenin may be attributed to some unknown mechanism. In the past years, intensive study efforts have been made for developing multitarget anti-Alzheimer compounds that hit several key pathogenic factors of the disease. Hybrid compounds combining a unit of potent and selective AChE inhibitor huprine Y with the 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylpentanone moiety of natural antioxidant 6-shogaol have been documented (Pérez-Areales et al., 2014). In addition, herbal formulations with anticholinesterase and antioxidant activity could be benefit to memory enhancement (Nwidu et al., 2018). Being a dual antioxidant and anticholinesterase agent with tau antiaggregating property (Figures 1, 3, 4), apigenin emerges as an interesting multitarget anti-AD agent.
Upon BDNF binding, TRKB dimerized and phosphorylated to initiate intracellular signaling such as ERK, leading to activation of transcription factor CREB and downstream antiapoptotic BCL2 for neuronal survival (Walton and Dragunow, 2000). The level of phosphorylated CREB is decreased in the hippocampus of old rats with spatial memory deficits (Kudo et al., 2005; Williams et al., 2008; Xu et al., 2010). BCL2 binds to and inactivates BAX, thereby inhibiting apoptosis (Jonas, 2009). In 3 × Tg-AD mice, Tau provokes downregulation of BCL2 and increases level of BAX to lead to degeneration of cochlear spiral ganglion neurons (Wang and Wu, 2021). In our SH-SY5Y cell model, induction of proaggregated ΔK280 TauRD expression downregulated BCL2 and upregulated BAX, whereas 7,8-DHF, quercetin, and apigenin rescued changes in these gene expression (Figure 4). Although Congo red was used as a control, it did not rescue changes of p-CREB, BCL2, and BAX, which is probably due to its modest neuroprotection effect. In contrast, under the same condition, the tested flavones showed significant improvements in p-CREB, BCL2, and BAX, suggesting their promising therapeutic potential. As crosstalk between pathological Tau phosphorylation and mitochondrial dysfunction exists (Guha et al., 2020) and BCL2 counteracts the mitochondria dysfunction-mediated apoptosis, investigation of mitochondria-related apoptotic pathways through caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation may shed light on the mechanism of how quercetin and apigenin provide antiapoptotic effect on ΔK280 TauRD cells. There are still other TRKB downstream pathways such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mTOR. In the future, investigating if PI3K/AKT/mTOR is also involved in the neuroprotective mechanism of these flavones is warranted. Besides, although our previous study has shown the neuroprotection effects of 7,8-DHF in the primary hippocampal primary neurons and mouse models induced by Aβ (Fan et al., 2020), whether the other two flavones apigenin and quercetin also provide the similar effects either in primary neurons and mouse models should be examined in the future.
In conclusion, our results show that, in addition to 7,8-DHF, quercetin and apigenin activate TRKB signaling to upregulate downstream CREB and BCL2 expressions. In the proaggregator Tau AD cell model, these flavones improve neurite outgrowth, reduce caspase-1 and/or AChE activities by activating TRKB, as well as ameliorating ROS. As multiple pathogenic pathways are involved in AD, the potential of these flavones targeting multiple pathways may have a significant perspective for developing anti-AD drug. The effect of quercetin and apigenin as TRKB agonists should be validated in AD animal models. Assays of mitochondrial function, especially in the light of increased BCL2 expression, would provide a better connection between the reported signaling mechanisms and resulting changes in cell physiology. Also, binding of quercetin and apigenin to the TRKB receptor should be measured using surface plasmon resonance to consolidate the action as agonists of TRKB.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
N-NC, T-HL, and Y-ST contributed to the execution of experiments, data analysis, and interpretation. Y-CS, K-HC, C-YL, HH-L, and M-TS contributed to review and editing. C-MC and G-JL-C contributed to the concept and design, data analysis and interpretation, obtained funding, and wrote and finalized the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the draft of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Molecular Imaging Core Facility of National Taiwan Normal University for the technical assistance. We would like to acknowledge computing resources provided by the National Center of High-Performance Computing to facilitate this study. We would also like to thank the National RNAi Core Facility, Academia Sinica, for technical support.
Funding
This study was supported by the grants 108-2320-B-003-001 and 108-2320-B-182A-001 from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
References
- Afreen S., Ferreira A. (2019). Altered cytoskeletal composition and delayed neurite elongation in tau45-230-expressing hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 412 1–15. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.05.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akıncıoğlu H., Gülçin İ. (2020). Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 20 703–715. 10.2174/1389557520666200103100521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aranda A., Sequedo L., Tolosa L., Quintas G., Burello E., Castell J. V., et al. (2013). Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay: a quantitative method for oxidative stress assessment of nanoparticle-treated cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 27 954–963. 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.01.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahn G., Jo D. G. (2019). Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease through modulation of NRF2. Neuromolecular Med. 21 1–11. 10.1007/s12017-018-08523-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai B., Yang Y., Wang Q., Li M., Tian C., Liu Y., et al. (2020). NLRP3 inflammasome in endothelial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 11:776. 10.1038/s41419-020-02985-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfield M. J., Naylor R. L., Robertson A. G., Allen S. J., Dawbarn D., Brady R. L. (2001). Specificity in Trk receptor:neurotrophin interactions: the crystal structure of TrkB-d5 in complex with neurotrophin-4/5. Structure 9 1191–1199. 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00681-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biancalana M., Koide S. (2010). Molecular mechanism of Thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804 1405–1412. 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.04.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen E., Vanmierlo T., Akkerman S., Wouters C., Steinbusch H. M., Prickaerts J. (2013). 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone improves memory consolidation processes in rats and mice. Behav. Brain Res. 257 8–12. 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.09.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Brunet A., West A. E., Datta S. R., Takasu M. A., Greenberg M. E. (1999). Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 286 1358–1362. 10.1126/science.286.5443.1358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. J., Salazar D. A., Soriano-Castell D., Alves-Ferreira M., Dennissen F. J. A., Vohra M., et al. (2019). Tau/MAPT disease-associated variant A152T alters tau function and toxicity via impaired retrograde axonal transport. Hum. Mol. Genet. 28 1498–1514. 10.1093/hmg/ddy442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cente M., Filipcik P., Pevalova M., Novak M. (2006). Expression of a truncated tau protein induces oxidative stress in a rodent model of tauopathy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24 1085–1090. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04986.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Lin C. H., Chen H. C., Huang H. Y., Chen S. L., Lin T. H., et al. (2017). The potential of indole/indolylquinoline compounds in tau misfolding reduction by enhancement of HSPB1. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 23 4–56. 10.1111/cns.12592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Wang Z., Zhang Z., Liu X., Kang S. S., Zhang Y., et al. (2018). The prodrug of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone development and therapeutic efficacy for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115 578–583. 10.1073/pnas.1718683115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitranshi N., Gupta V., Kumar S., Graham S. L. (2015). Exploring the molecular interactions of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone and its derivatives with TrkB and VEGFR2 proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 21087–21108. 10.3390/ijms160921087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M. (2010). Alzheimer’s disease: strategies for disease modification. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9 387–398. 10.1038/nrd2896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola G., Chinnathambi S., Lee J. J., Dombroski B. A., Baker M. C., Soto-Ortolaza A. I., et al. (2012). Evidence for a role of the rare p.A152T variant in MAPT in increasing the risk for FTD-spectrum and Alzheimer’s diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21 3500–3512. 10.1093/hmg/dds161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Maloney A. J. (1976). Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2:1403. 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91936-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi L., Ohno M. (2012). 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule TrkB agonist, reverses memory deficits and BACE1 elevation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 37 434–444. 10.1038/npp.2011.191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich F., Ochs G., Grosse-Wilde A., Berweiler U., Yan Q., Miller J. A., et al. (1996). Pharmacokinetics of intrathecally applied BDNF and effects on spinal motoneurons. Exp. Neurol. 141 225–239. 10.1006/exnr.1996.0157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. H., Lin C. W., Huang H. J., Lee-Chen G. J., Sun Y. C., Lin W., et al. (2020). LMDS-1, a potential TrkB receptor agonist provides a safe and neurotrophic effect for early-phase Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 237 3173–3190. 10.1007/s00213-020-05602-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Noël A., Foveau B., Lynham J., Lecrux C., LeBlanc A. C. (2018). Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates cognitive impairment and neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Nat. Commun. 9:3916. 10.1038/s41467-018-06449-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. (1989). Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 8 393–399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Hoehn A., Davies K. J., Grune T. (2011). Protein oxidative modifications in the ageing brain: consequence for the onset of neurodegenerative disease. Free Radic. Res. 45 73–88. 10.3109/10715762.2010.512040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha S., Johnson G. V. W., Nehrke K. (2020). The crosstalk between pathological Tau phosphorylation and mitochondrial dysfunction as a key to understanding and treating Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 57 5103–5120. 10.1007/s12035-020-02084-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque M. M., Murale D. P., Kim Y. K., Lee J. S. (2019). Crosstalk between oxidative stress and tauopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1959. 10.3390/ijms20081959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausott B., Kurnaz I., Gajovic S., Klimaschewski L. (2009). Signaling by neuronal tyrosine kinase receptors: relevance for development and regeneration. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 292 1976–1985. 10.1002/ar.20964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heneka M. T., Kummer M. P., Stutz A., Delekate A., Schwartz S., Vieira-Saecker A., et al. (2013). NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493 674–678. 10.1038/nature11729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Shinotoh H., Kobayashi T., Tsuboi Y., Wszolek Z. K., Aotsuka A., et al. (2006). Brain acetylcholinesterase activity in FTDP-17 studied by PET. Neurology 66 1276–1277. 10.1212/01.wnl.0000208515.50924.94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Shinotoh H., Shimada H., Ota T., Sato K., Tanaka N., et al. (2018). Voxel-based acetylcholinesterase PET study in early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 62 1539–1548. 10.3233/JAD-170749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley B., Fearnhead H. O. (2008). Caspases as therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12 1502–1516. 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00292.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Alonso Adel C., Chen S., Chohan M. O., El-Akkad E., Gong C. X., et al. (2005). Tau pathology in Alzheimer disease and other tauopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1739 198–210. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. W., Liu X., Yepes M., Shepherd K. R., Miller G. W., Liu Y., et al. (2010). A selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 2687–2692. 10.1073/pnas.0913572107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. V., Stoothoff W. H. (2004). Tau phosphorylation in neuronal cell function and dysfunction. J. Cell Sci. 117 5721–5729. 10.1242/jcs.01558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas E. A. (2009). Molecular participants in mitochondrial cell death channel formation during neuronal ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 218 203–212. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.03.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. (1990). Molecular cloning of a human gene that is a member of the nerve growth factor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 8060–8064. 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H. J., Welcher A. A., Shelton D., Schuman E. M. (1997). Neurotrophins and time: different roles for TrkB signaling in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuron 19 653–664. 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80378-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katebi S., Esmaeili A., Ghaedi K., Zarrabi A. (2019). Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles combined with NGF and quercetin promote neuronal branching morphogenesis of PC12 cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14 2157–2169. 10.2147/IJN.S191878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal V., Dye R., Pakavathkumar P., Foveau B., Flores J., Hyman B., et al. (2015). Neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome activation of Caspase-1 coordinately regulates inflammatory interleukin-1-beta production and axonal degeneration-associated Caspase-6 activation. Cell Death Differ. 22 1676–1686. 10.1038/cdd.2015.16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khlistunova I., Biernat J., Wang Y., Pickhardt M., von Bergen M., Gazova Z., et al. (2006). Inducible expression of Tau repeat domain in cell models of tauopathy: aggregation is toxic to cells but can be reversed by inhibitor drugs. J. Biol. Chem. 281 1205–1214. 10.1074/jbc.M507753200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo K., Wati H., Qiao C., Arita J., Kanba S. (2005). Age-related disturbance of memory and CREB phosphorylation in CA1 area of hippocampus of rats. Brain Res. 1054 30–37. 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.06.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Pandey A. K. (2013). Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. Sci. World J. 2013:162750. 10.1155/2013/162750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Goedert M., Trojanowski J. Q. (2001). Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24 1121–1159. 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. S., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B., Plummer M. R. (1996). Selective role for trkB neurotrophin receptors in rapid modulation of hippocampal synaptic transmission. Mol. Brain Res. 38 300–303. 10.1016/0169-328x(96)00025-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Liu J. H., Zhang J., Yu B. Y. (2008). Comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity and antioxidative activity of 20 flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56 3876–3883. 10.1021/jf073520n [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. H., Chiu Y. J., Lin C. H., Lin C. Y., Chao C. Y., Chen Y. C., et al. (2020). Exploration of multi-target effects of 3-benzoyl-5-hydroxychromen-2-one in Alzheimer’s disease cell and mouse models. Aging Cell 19:e13169. 10.1111/acel.13169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Rezaie T., Nutter A., Lopez K. M., Parker J., Kosaka K., et al. (2016). Therapeutic advantage of pro-electrophilic drugs to activate the Nrf2/ARE pathway in Alzheimer’s disease models. Cell Death Dis. 7:e2499. 10.1038/cddis.2016.389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Nagappan G., Guan X., Nathan P. J., Wren P. (2013). BDNF-based synaptic repair as a disease-modifying strategy for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14 401–416. 10.1038/nrn3505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marucci G., Buccioni M., Ben D. D., Lambertucci C., Volpini R., Amenta F. (2021). Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 190:108352. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro N., Barini E., Spillantini M. G., Goedert M., Medini P., Gasparini L. (2016). Tau-driven neuronal and neurotrophic dysfunction in a mouse model of early tauopathy. J. Neurosci. 36 2086–2100. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0774-15.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondragón-Rodríguez S., Perry G., Zhu X., Moreira P. I., Acevedo-Aquino M. C., Williams S. (2013). Phosphorylation of tau protein as the link between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and connectivity failure: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013:940603. 10.1155/2013/940603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota S. I., Costa R. O., Ferreira I. L., Santana I., Caldeira G. L., Padovano C., et al. (2015). Oxidative stress involving changes in Nrf2 and ER stress in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1852 1428–1441. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.03.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahara A. H., Tuszynski M. H. (2011). Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10 209–219. 10.1038/nrd3366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Liu X. G., Ikegaki N., White P. S., Yamashiro D. J., Nycum L. M., et al. (1995). Cloning and chromosomal localization of the human TRK-B tyrosine kinase receptor gene (NTRK2). Genomics 25 538–546. 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80055-q [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nie C. L., Wang X. S., Liu Y., Perrett S., He R. Q. (2007). Amyloid-like aggregates of neuronal tau induced by formaldehyde promote apoptosis of neuronal cells. BMC Neurosci. 8:9. 10.1186/1471-2202-8-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissink J. W., Murray C., Hartshorn M., Verdonk M. L., Cole J. C., Taylor R. (2002). A new test set for validating predictions of protein-ligand interaction. Proteins 49 457–471. 10.1002/prot.10232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwidu L. L., Elmorsy E., Carter W. G. (2018). In vitro anti-cholinesterase and anti-oxidant activity of three standardised polyherbal products used for memory enhancing in ethnomedicine of South-East Nigeria. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 25 27–39. 10.21315/mjms2018.25.2.4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Påhlman S., Ruusala A. I., Abrahamsson L., Mattsson M. E., Esscher T. (1984). Retinoic acid-induced differentiation of cultured human neuroblastoma cells: a comparison with phorbolester-induced differentiation. Cell Differ. 14 135–144. 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90038-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S., Ghosh S., Mandal S., Sau S., Pal M. (2018). NRF2 transcriptionally activates the heat shock factor 1 promoter under oxidative stress and affects survival and migration potential of MCF7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 293 19303–19316. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Areales F. J., Pietro O. D., Espargaró A., Vallverdú-Queralt A., Galdeano C., Ragusa I. M., et al. (2014). Shogaol-huprine hybrids: dual antioxidant and anticholinesterase agents with β-amyloid and tau anti-aggregating properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 22 5298–5307. 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.07.053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Corredor P., Sabogal-Guáqueta A. M., Carrillo-Hormaza L., Cardona-Gómez G. P. (2019). Preventive effect of quercetin in a triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice model. Molecules 24:2287. 10.3390/molecules24122287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietta P. G. (2000). Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 63 1035–1042. 10.1021/np9904509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poprac P., Jomova K., Simunkova M., Kollar V., Rhodes C. J., Valko M. (2017). Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38 592–607. 10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey C. P., Glass C. A., Montgomery M. B., Lindl K. A., Ritson G. P., Chia L. A., et al. (2007). Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 66 75–85. 10.1097/nen.0b013e31802d6da9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A., Ahn S., Davenport C. M., Blendy J. A., Ginty D. D. (1999). Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286 2358–2361. 10.1126/science.286.5448.2358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta A. M., Muñoz-manco J. I., Ramírez J. R., Lamprea-rodriguez M., Osorio E., Cardona-gómez G. P. (2015). The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology 93 134–145. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahara N., Maeda S., Yoshiike Y., Mizoroki T., Yamashita S., Murayama M., et al. (2007). Molecular chaperone-mediated tau protein metabolism counteracts the formation of granular tau oligomers in human brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 85 3098–3108. 10.1002/jnr.21417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweers O., Schonbrunnhanebeck E., Marx A., Mandelkow E. (1994). Structural studies of tau-protein and Alzheimer paired helical filaments show no evidence for β-structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1269 24290–24297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyoum A., Asres K., El-Fiky F. K. (2006). Structure-radical scavenging activity relationships of flavonoids. Phytochemistry 67 2058–2070. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura H., Miura-Shimura Y., Kosik K. S. (2004). Binding of tau to heat shock protein 27 leads to decreased concentration of hyperphosphorylated tau and enhanced cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 279 17957–17962. 10.1074/jbc.M400351200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinotoh H., Namba H., Fukushi K., Nagatsuka S., Tanaka N., Aotsuka A., et al. (2000). Brain acetylcholinesterase activity in Alzheimer disease measured by positron emission tomography. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 14(Suppl. 1) S114–S118. 10.1097/00002093-200000001-00017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silveyra M. X., García-Ayllón M. S., de Barreda E. G., Small D. H., Martínez S., Avila J., et al. (2012). Altered expression of brain acetylcholinesterase in FTDP-17 human tau transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Aging 33 624.e23–e34. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Kaur M., Silakari O. (2014). Flavones: an important scaffold for medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 84 206–239. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Cohen A. S. (2000). Review: history of the amyloid fibril. J. Struct. Biol. 130 88–98. 10.1006/jsbi.2000.4221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., et al. (1991). The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell 65 895–903. 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urfer R., Tsoulfas P., O’Connell L., Shelton D. L., Parada L. F., Presta L. G. (1995). An immunoglobulin-like domain determines the specificity of neurotrophin receptors. EMBO J. 14 2795–2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonk M. L., Cole J. C., Hartshorn M. J., Murray C. W., Taylor R. D. (2003). Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 52 609–623. 10.1002/prot.10465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vomund S., Schäfer A., Parnham M. J., Brüne B., von Knethen A. (2017). Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:2772. 10.3390/ijms18122772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton M. R., Dragunow M. (2000). Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 23 48–53. 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01500-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. E., Wu C. H. (2021). Tau phosphorylation and cochlear apoptosis cause hearing loss in 3Tg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin. J. Physiol. 64 61–71. 10.4103/CJP.CJP_79_20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Li P., Ding Q., Wu C., Zhang W., Tang B. (2019). Observation of acetylcholinesterase in stress-induced depression phenotypes by two-photon fluorescence imaging in the mouse brain. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141 2061–2068. 10.1021/jacs.8b11414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. M., El Mohsen M. A., Vauzour D., Rendeiro C., Butler L. T., Ellis J. A., et al. (2008). Blueberry-induced changes in spatial working memory correlate with changes in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 45 295–305. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang J., Wang Z. H., Ahn E. H., Liu X., Yu S. P., Manfredsson F. P., et al. (2019). Delta-secretase-cleaved Tau antagonizes TrkB neurotrophic signalings, mediating Alzheimer’s disease pathologies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116 9094–9102. 10.1073/pnas.1901348116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Rong S., Xie B., Sun Z., Deng Q., Wu H., et al. (2010). Memory impairment in cognitively impaired aged rats associated with decreased hippocampal CREB phosphorylation: reversal by procyanidins extracted from the lotus seedpod. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 65 933–940. 10.1093/gerona/glq094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Cheng Y., Zhao J., Rong J. (2015). Releasing Nrf2 to promote neurite outgrowth. Neural Regen. Res. 10 1934–1935. 10.4103/1673-5374.169618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi Y. S. (2018). Regulatory roles of flavonoids on inflammasome activation during inflammatory responses. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62:e1800147. 10.1002/mnfr.201800147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo J. M., Lee B. D., Sok D. E., Ma J. Y., Kim M. R. (2017). Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells. Redox Biol. 11 592–599. 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Y., Wang X., Wang Q., Liu S., Hu X., McClintock S. M. (2013). Small molecules activating TrkB receptor for treating a variety of CNS disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 12 1066–1077. 10.2174/18715273113129990089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Liu X., Schroeder J. P., Chan C. B., Song M., Yu S. P., et al. (2014). 7,8-dihydroxyflavone prevents synaptic loss and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 39 638–650. 10.1038/npp.2013.243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L., Wang J. L., Liu R., Li X. X., Li J. F., Zhang L. (2013). Neuroprotective, anti-amyloidogenic and neurotrophic effects of apigenin in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Molecules 18 9949–9965. 10.3390/molecules18089949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou B., Cai Q., Xie Y., Sheng Z. H. (2012). Snapin recruits dynein to BDNF-TrkB signaling endosomes for retrograde axonal transport and is essential for dendrite growth of cortical neurons. Cell Rep. 2 42–51. 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.06.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Wang J. (2015). Wogonin increases β-amyloid clearance and inhibits tau phosphorylation via inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin: potential drug to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 36 1181–1188. 10.1007/s10072-015-2070-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.