Abstract
The number of mitochondria in the oocyte along with their functions (e.g., energy production, scavenger activity) decline with age progression. Such multifaceted functions support several processes during oocyte maturation, ranging from energy supply to synthesis of the steroid hormones. Hence, it is hardly surprising that their impairment has been reported in both physiological and premature ovarian aging, wherein they are crucial players in the apoptotic processes that arise in aged ovaries. In any form, ovarian aging implies the progressive damage of the mitochondrial structure and activities as regards to ovarian germ and somatic cells. The imbalance in the circulating hormones and peptides (e.g., gonadotropins, estrogens, AMH, activins, and inhibins), active along the pituitary-ovarian axis, represents the biochemical sign of ovarian aging. Despite the progress accomplished in determining the key role of the mitochondria in preserving ovarian follicular number and health, their modulation by the hormonal signalling pathways involved in ovarian aging has been poorly and randomly explored. Yet characterizing this mechanism is pivotal to molecularly define the implication of mitochondrial dysfunction in physiological and premature ovarian aging, respectively. However, it is fairly difficult considering that the pathways associated with ovarian aging might affect mitochondria directly or by altering the activity, stability and localization of proteins controlling mitochondrial dynamics and functions, either unbalancing other cellular mediators, released by the mitochondria, such as non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). We will focus on the mitochondrial ncRNAs (i.e., mitomiRs and mtlncRNAs), that retranslocate from the mitochondria to the nucleus, as active players in aging and describe their role in the nuclear-mitochondrial crosstalk and its modulation by the pituitary-ovarian hormone dependent pathways. In this review, we will illustrate mitochondria as targets of the signaling pathways dependent on hormones and peptides active along the pituitary/ovarian axis and as transducers, with a particular focus on the molecules retrieved in the mitochondria, mainly ncRNAs. Given their regulatory function in cellular activities we propose them as potential diagnostic markers and/or therapeutic targets.
Keywords: ncRNA, mitochondria, ovarian aging, estrogens, FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), LncRNA - long noncoding RNA, miRNA - microRNA, MitomiRs
Introduction
The physiological and the premature ovarian aging are often asymptomatic. Both include the decline in the number of the follicles. The number of follicles is established in early life and they mature later in life. Genetic and environmental factors co-contribute to the establishment of the ovarian reserve (OR) and its following decrease, which is promoted by different mechanisms. The imbalance of the hormonal asset, required for the preservation and maturation of the ovarian follicles, is among them and it can lastly lead to their premature aging and/or death (1). Ovarian follicle maturation is a complex process, defined folliculogenesis, organized in different phases to generate a species dependent number of mature oocytes. The oocyte maturation equally involves changes in the ovarian somatic cells, such as Granulosa Cells (GCs) and Theca Cells (TCs), surrounding the oocytes and supporting its maturation. These cells also will undergo an highly differentiation process involving multiple paracrine interactions, important for the maintenance of normal follicular development (2–4).
The decline in the number of follicles throughout the life is known as follicular atresia, consisting in the apoptosis of the oocytes and of the surrounding follicular cells (5). It is not surprising that mitochondria play a central role in follicular atresia, since they are central executors of the apoptosis (6–10). Recently, it has been shown that mitochondrial biogenesis is among the pathways determining the size of the follicular pool which, as said, is established in early life (11, 12). Furthermore, mitochondria are among the determinants of the cytoplasmic quality of the oocytes that, with nuclear integrity, defines the oocyte quality and competence. Indeed, transfer of mitochondria to oocytes prevents their apoptosis (13, 14). Quality of mitochondria in GCs influences the oocyte since these cells supply them with energy substrates (15).
Mitochondrial quantity is generally reduced in physiological aging, decreasing their ability to supply adenosine triphosphate (ATP) along with their mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenger activities (16–23). These concepts are widely accepted however the recent genome-wide association studies conducted to identify genomic loci that influence age at menopause do not evidence its association with gene codifying mitochondrial proteins (24). This finding suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction described in ovarian aging might be primarily due to environmental factors. In fact, diet and chemical toxins, capable of reducing OR, impact on processes leading to follicular atrophy such as control of the oxidative stress (OS), inflammation, hormone secretion and, finally, modulation of the cellular content of the non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) involved in ovarian aging (25–27). These latter modulate ovarian lifespan and health-span in vertebrates, including mammals, regulating signaling pathways playing pivotal role in follicular atresia as PI3K-AKT, mTOR and estrogen signaling pathways, among the others (28, 29).
Here, we will discuss the literature on the role of pituitary-ovarian hormones in regulating ovarian mitochondrial activity and dynamics associated with ovarian aging. Furthermore, we will discuss the role of ncRNAs as executors of such activities pointing out the role of mitochondrial associated miRNAs (mitomiRNAs, mitolncRNAs).
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Ovarian Aging
Mitochondria are unique organelles in animal cells since they contain a genome (mtDNA) and the enzymes to duplicate and transcribe it. Since DNA-repairing enzymes are not present in mitochondria, mutations are frequently found in mtDNA. They affects mtDNA replication and transcription and increase with aging (30). Impairment in mitochondrial number and function in oocytes and ovarian somatic cells has been associated with ovarian aging and infertility (31). The increase of mitochondrial number characterizes the oogenesis and stops when oocytes are fully mature. In fact, the number of mitochondria is approximately ten-hundred in the human Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) and becomes about several hundred-thousand in the mature oocyte (32). This suggests that mitochondria could be targets of the hormonal asset controlling this process, as we will discuss later. Since they do not further replicate during the post-fertilization cleavage process, they are distributed amongst the dividing cells and their number has been proposed as a biomarker of embryo viability (33–35). Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a major role in ovarian aging since this organelle contributes to the energetic needs of the oocyte and protect DNA with its ROS-scavenger activity (36). The ROS are produced in the cells as a result of their metabolic activity, including ATP production. Their increase induces a cascade of events at the level of the mitochondrion that, if left unchecked, will promote mtDNA, mutations and accumulation of misfolded proteins (UPRmt), causing cellular damage and death (37–39). Noteworthy, mitochondrial dysfunction promotes an increased oxidative stress that, in turns, impairs the energy production required to sustain the metabolic needs during oogenesis and follicle maturation (40).
The ability of ovarian cells to neutralize the OS diminishes with age, resulting in a steady decline in oocyte quality (41–43). In humans, increased production of ROS within the ovarian cells correlate with follicular atresia, poor oocyte quality and infertility (44). The aged GCs exhibit an increase of OS that promotes their apoptosis and senescence. Indeed, OS induces shortening of telomeres, a process described in ovarian aging (45, 46). Several studies have been conducted in mice to investigate how changes in the redox state can damage the oocytes and GCs. Gene expression profiling of aged oocytes revealed a down-regulation of mRNAs codifying mitochondrial antioxidant proteins such as peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3) and thioredoxin 2 (TXN2), in addition to cytosolic antioxidant proteins (47–49). Their imbalance affects directly mitochondrial activity, including the ovarian steroidogenesis as shown in SOD-2 deficient mice, due to an impairment in the cholesterol transport to mitochondria following the reduction of mitochondrial content of STAR protein (50). The reduction of these “protective proteins” makes the oocytes far more susceptible to damage induced by changes in the oxidative state.
Moreover, the damage of mitochondrial dynamics has been described in women affected from premature and physiological ovarian aging. As we will discuss here, this might result from the imbalance of the hormones active along the pituitary-ovarian axis (51).
Mitochondrion-Nucleus Crosstalk: A Focus on ncRNAs Acting as Anterograde and Retrograde Signals
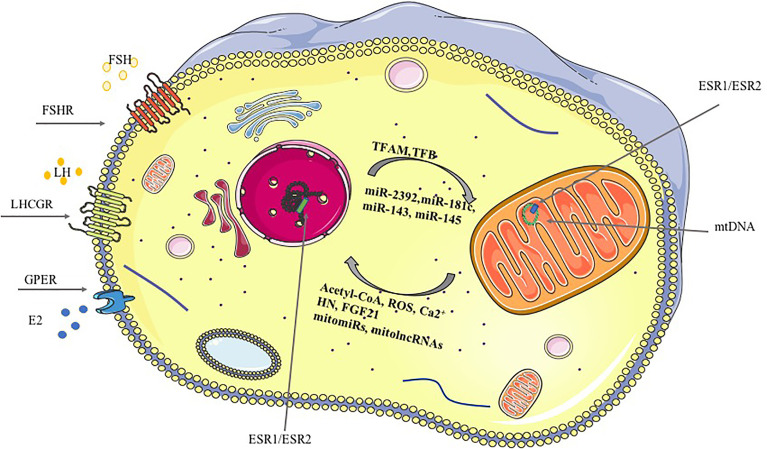
An extensive bidirectional communication network between mitochondria and the nucleus has been characterized (52). The anterograde (nucleus to- mitochondria) signals have been extensively described whereas more recently the retrograde (mitochondria-to-nucleus) pathway components, including Acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA), ROS and ncRNAs, have been described ( Figure 1 ). The retrograde signals, ROS and intracellular calcium (Ca2+) increase or/and reduction of Acetyl-CoA or ATP, disarrange the activity of several cellular signaling pathways impairing the cellular content of Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (NRF1), a protein regulating the mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) and, finally, the mitochondrial gene transcription (54, 55). Furthermore, proteins secreted by the mitochondria under stress condition, defined mitokines, might act as retrograde signals (56). Humanin (HN) and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) are among them (57, 58). Interestingly, mitochondrial HN has been recognized as a protective factor for GCs (59). Indeed, its inactivation through gene targeting modified ovarian organization and promoted the apoptosis of GCs. Such effects were confirmed in vitro in granulosa tumor cell line (KGN) which were more viable, when treated with exogenous humanin. Concordantly, its level in follicular fluids positively correlates with the ovarian reserve (60).
Figure 1.
Mitochondria-nucleus crosstalk, anterograde and retrograde signaling. Gonadotropins and ovarian hormones signaling pathways regulating mitochondrial dynamics and function are reported in the figure underlining the cellular comportment involved. Anterograde and retrograde signals are reported for the mitochondrion-nucleus crosstalk. Anterograde signals (nucleus to mitochondria) include: the nuclear-encoded transcription factors (TFs, TFAM and TFB that bind the mtDNA, nuclear receptors (NRs) and ncRNAs, among the others. Retrograde signals (mitochondria-nucleus) include: Ca2+, ROS, mitomiRs, mitolncRNAs, among the others (53).
Non-coding RNAs control numerous cellular functions by modulating specific signaling pathways, also involved in ovarian aging (26). Several classes of ncRNAs may impact directly and/or indirectly on mitochondrial biology (61). They are considered mediators of the anterograde and retrograde mitochondrion-nucleus crosstalk, controlling several cellular activities at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Mitochondria-localized miRNAs and lncRNAs, termed mitomiRs and mt-lncRNAs respectively, directly regulate mitochondrial gene expression. Their uptake by the mitochondria as well their transcription from mtDNA has been suggested (62). Certainly, it is still ambiguous whether mitochondrial ncRNAs (mt-ncRNAs) are transcribed inside the mitochondria or the nuclei, as result of mitochondrial genes integrated into the nuclear genome (63). The former suggestion is not entirely surprising since mitochondria contain genomes and can produce mitochondrial-specific nucleic acids and proteins. Some studies have indicated the presence of RNA interference components in the mitochondria implying their functional importance (64). MitomiRs are short single stranded RNA molecules with a unique size ~17-25, with no 5’ cap, short 3’ overhangs, and with specific thermodynamic features as opposed to canonical miRNAs. It has been speculated that some of these characteristics might facilitate their entry into mitochondria. However, it is still challenging to accurately characterize the mechanisms determining their localization because of the technical difficulties in separating isolated and uncontaminated organelles.
However, mt-ncRNAs are among the molecules used by mitochondria to communicate with the nucleus to ensure cellular homeostasis since they control rapid cell stress responses, energy balance and apoptosis controlling the cellular content of proteins both at transcriptional and translational levels (65, 66). Although mt-ncRNAs have not been investigated in ovary, we will discuss them here because they modulate mitochondrial processes involved in ovarian aging, such as abundance, metabolism, and scavenger activity ( Table 1 ). For instance, miR-2392, together with Argonaute 2 (Ago2), has been reported to partially inhibit mtDNA transcription in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells (TSCC), resulting in down-regulation of oxidative phosphorylation and up-regulation of glycolysis (67). At the translational level, it has been shown that miR-181c in concert with Ago2 can repress the translation of the mitochondrial cyclooxygenase (Cox1) mRNA, determining a remodeling of complex IV in cardiac dysfunction (68, 69, 78, 79). Noteworthy, Cox1 transcript is among the transcripts induced during oocyte maturation (80). Similarly, miR-378 can inhibit the mitochondrial expression of Atp6 (71) that modulates mouse follicle development and oocyte maturation as well as aromatase levels (70). Furthermore, miR-378 modulates Cyp450 in non-human primates ovaries (72). Furthermore, miR-378 is included in a network of miRNAs regulating follicular atresia. On the other hand, mitomiRs can enhance mitochondrial translation (81, 82). For example, same miRNA has been suggested to mobilize ND1 and Cox1 mRNAs to mitochondrial ribosomes through Ago2. Furthermore, the growth arrest specific 5 (GAS5) a lncRNA diminished in physiological and environmentally promoted ovarian aging, has been reported as mt-lncRNA and involved in the modulation of mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid flux (26, 83). The results above summarized suggest the role of the mitomiRs in ovarian aging although the mode of action remains largely unexplored and enigmatic.
Table 1.
miRNAs and lncRNAs and their targets for mitochondrial function in ovarian aging.
| miRNAs | Target | Tissue | Model/Cell lines | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-2392 | mtDNA/AGO2 | Oral and maxillofacual region | TSCC | (67) |
| miR-181c | Cox1/GRP78 | Heart/Ovary | In vivo Rats/A2780, SKOV3 and human tissues | (68, 69) |
| miR-378 | Aromatase, Atp6, Cyp450 | Ovary, Heart, Ovary | Porcine ovaries, HL-1, Cynomolgus macaques | (70–72) |
| miR-143 | KRAS | Ovary | Granulosa cells/ovaries from mouse | (73) |
| miR-145 | ARL5B | Ovary | SKOV3 | (74) |
| lncRNAs | ||||
| lncND5, lncND6, lncCYT b | ND5, ND6 and Cyt b | Ovary | Granulosa cells (mouse) | (66) |
| MDL1,MDL1AS | mitoepigenetic processes | Ovary | Germinal Vesicle Oocytes | (75) |
| GAS5 | mTOR | Ovary | Ovaries from mouse | (76) |
| lncH19 | STAT3 | Ovary | KGN | (77) |
Additionally, cytoplasmic miRNAs impact a variety of mitochondrial processes, including energy metabolism, fusion and fission. The present work origins from our belief that the impairment of some ncRNAs (miR-143, miR-145, GAS5, etc.) could damage mitochondrial function and dynamics accelerating the ovarian aging (76). For instance, miR-145, shown to be overexpressed in ovaries from middle aged mice as well as in follicular fluids from Diminished Ovarian Reserve (DOR) patients, has been associated with poor mitochondrial function in ovarian cancer cells marked by decreased mtDNA copy numbers, ATP production, membrane potential and, finally, the expression levels of mitochondrial markers (74). In vivo and in vitro studies showed that follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) significantly decreased miR-143 expression, found deregulated in ovarian aging by our and other studies. It has been shown that miR-143 inhibits estradiol production, and proliferation of GCs regulating the cell cycle-related genes expression by targeting KRAS (73). Lastly, it has been reported that its increase promoted mitochondrial damage in myocardial infarction (84). Unfortunately, this has not been verified in the ovarian follicles.
Additionally, lncRNAs have been reported as modulators of mitochondrial function (66, 79). They are ncRNAs, long more than 200 nucleotides, and have a characteristic structure containing domains for RNA, protein and possibly DNA binding. Their structural flexibility and plasticity contribute to the regulation of several cellular processes. LncRNAs have been detected in different cell compartments, including mitochondria (79). Their biological activities depend on their localization in the cell and comprise transcriptional regulation, post-transcriptional activity, metabolic function, and chromosome remodeling. Increasing evidence suggests that lncRNAs can be encoded by nuclear and mitochondrial DNA and some of them have been outlined to regulate mitochondrial biology directly or indirectly (61). The ones retrieved in mitochondria are known as mt-lncRNAs and might work as retrograde signals. For instance, a sense ncRNA (SncmtRNA) and two antisense ncRNAs (ASncmtRNas-1, -2) can be transported in the nucleus from the mitochondria and act as mediator of the crosstalk between these organelles. The mitochondrial transcripts ND5, ND6, and Cyt b are target of three mt-lncRNAs, lncND5, lncND6, and lncCyt b. These last are complementary to their respective mRNAs and the duplex formation increases the mRNAs stability (66, 85). Since ND5, ND6, and Cyt b are components of the NADH-deidrogenase, it is easily conceivable the role that these mt-lncRNAs might have in establishing mitochondrial activity and dynamics. Only one paper explored their function in reproductive tissue using in vitro models. Experiments performed in vitro with culture of GCs in medium supplemented or not with FSH, showed that FSH induced mitochondrial activity, verified by evaluation of membrane potential, ATP content, and of mt-ND6 proteins (86).
Other mt-lncRNAs have been identified as Long Intergenic noncoding RNA predicting CARdiac remodelling (LIPCAR), Mitochondrial D-Loop 1 (MDL1) and Mitochondrial D-Loop 1 antisense (MDL1AS) in tissues other than ovaries (87). The last two have been suggested as executor of mitoepigenetic processes whose dynamic nature has been shown in oocytes and GCs (75). It is well established that mitochondria import various nuclear-encoded lncRNAs. An example is SRA1, a steroid receptor RNA activator, that is downregulated in cumulus cells from old females and upregulated in steroid hormone-responsive tumors, including ovarian cancers. It can recruit co-repressors modulating nuclear receptors activity because of the interaction with SLIRP (SRA stem-loop interacting RNA-binding protein) (88, 89). Interestingly, Slirp-knockout females are sub-fertile whereas males have defects in sperm motility and mitochondrial morphology (88, 89). Another example is the RNA component of the RNA processing endoribonuclease (RMRP) transported by RNA binding proteins such as GRSF1 localized in RNA granules. In spite of the fact that it has not been investigated in follicle maturation and/or aging, it has been shown increased in platin-resistant ovarian cancers (90). In other tissues, it is described as p53 inhibitor (91). Finally, some lncRNAs can affect indirectly mitochondrial biology by modulating mitochondrial key pathways. For instance, GAS5 can induce growth-arrest after inhibition of mTOR, known to regulate mitochondrial function. This suggests its potential ability to impact mTOR activity in the mitochondria. In our study, previously mentioned, we showed downregulation of GAS5 in ovaries from middle aged mice suggesting yet again that mitochondrial dysfunction can promote ovarian aging which is consistent with the derangement of the AKT pathway prediction by the IPA analysis (76). Noteworthy as reported above, GAS5 has been also described as mt-lncRNA that alters tricarboxylic acid cycle disrupting metabolic enzyme tandem association of fumarate hydratase, malate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase (83).
Pituitary Gonadotropins Modulate Ovarian Mitochondrial Morphology, Dynamics, and Steroidogenic Activity
As discussed above, mitochondria play a central role in follicular atresia. It is well established that the oocyte relies largely on mitochondria to acquire competence for fertilization (92, 93). Additionally, early embryonic development depends on their number and quality in the oocytes (94, 95). Furthermore, mitochondria control proliferation, differentiation and activity of GCs along with their apoptosis (96). Therefore, mitochondria might be regarded as targets of the signaling pathways determining the follicle number, quality and surviving, which are adversely affected by aging (51). Pituitary gonadotropins are survival factors for the ovarian follicular cells. Their imbalance characterizes the physiological and premature ovarian aging because they activate survival pathways in the follicle that will determine its growth or death. Although mitochondria are key compartments in this decision, the role of pituitary gonadotropins and of their intracellular mediators in controlling mitochondrial dynamics and activity is largely undefined in ovarian aging.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is the most efficient gonadotropin in preventing follicular atresia and GCs apoptosis under different conditions, including hypoxic or oxidative stress exposure. Few studies have addressed if FSH could modulate mitochondrial activity and biogenesis through ncRNAs. For instance, it has been reported that FSH modulates the expression of several miRNAs in the ovaries (97). These miRNAs modulate mitochondrial ROS-scavenger activity in other tissues and cell types. An example is miR-143 which has been shown to inhibit mitochondrial activity in human colon cancer cells (HCT116). Particularly, the superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) was downregulated by stable expression of miR-143 that increased the ROS production in cells treated with oxaliplatin (98). Noteworthy, miR-143 is negatively regulated by FSH and its increase has been associated with ovarian aging. Taken together, the data suggest that its increase in aged ovaries translates into a less efficient ROS-scavenger activity. No other papers have directly addressed this point, neither characterized other miRNAs nor lncRNAs regulated by FSH and involved in such processes.
Some reports have described the mitochondria as direct targets of FSH under stress conditions. In particular, under hypoxic conditions FSH stimulates the mitochondrial biogenesis in GCs by a process suggestive of its involvement in the degradation of the damaged organelles as well as of their regeneration (99). This finding is in agreement with previously published results obtained in GCs exposed to H2O2 to induce oxidative stress (100). FSH has a major role in preserving mitochondrial integrity under stress conditions in ovary and it is defined as an active factor in reducing mitophagy induced by oxidative stress and in preventing the death of GCs. Such an effect results from the inhibition of the PINK1-Parkin pathway activated under oxidative stress conditions. Indeed, FSH suppresses Pink1, promotes the dissociation of Parkin from mitochondria and, consequently, it increases the resistance of the GCs to oxidative stress. Noteworthy, Pink1 translation is limited by lncH19 resulting in a reduced mitophagy (101). The reduction of lncH19 expression in GCs results in inhibition of proliferation and increased apoptosis of GCs (77).
GCs are the major site of synthesis of steroid hormones that is strictly controlled by FSH. Mitochondria play a critical role in steroid synthesis and FSH modulates this mitochondrial activity (102, 103). Such aspect has been investigated and molecularly characterized in rat primary GCs showing that prohibitin (PHB) was a FSH responsive transcript. The mitochondrial increase of PHB levels correlated with the stimulation of the steroidogenesis, specifically of the estrogens and progesterone. Furthermore, it has been shown that FSH stimulation promoted PHB phosphorylation by the activation of the ERK1/2 pathway (104). PHB also mediated the pro-survival activity of the FSH in GCs regulating the expression of the anti-apoptotic genes (105). Lastly, PHB maintained the mitochondrial morphology, particularly of the cristae by modulating the processing of mitochondrial dynamin like GTPase (OPA1) (106, 107). This role in preserving mitochondrial fusion and cristae morphogenesis has been firstly evidenced in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and, then, in rat immature GCs overexpressing PHB (108–110). Again, the evaluation of the role of the PHB-OPA1 axis in this model points to mitophagy as a target of the FSH signaling pathway. Finally, other reports showed the role of mTOR pathway in FSH-modulated mitophagy during follicular development. The reported data evidenced that FSH treatment increased the levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) promoting the autophagy. Interestingly, FSH induced autophagy correlated with an incomplete mitophagy process. Indeed, the Authors reported that the FSH-mediated autophagy increased the mitochondrial membrane potential that was abolished in presence of the autophagy inhibitors due to the PINK1-Parkin pathway (111).
Reduced levels of the luteinizing hormone (LH) characterize both physiological and premature ovarian aging (112, 113). Although suggested since 1975, LH role in modulating mitochondrial function and dynamics has been poorly investigated in ovarian aging. At that time, Robinson and co-authors observed that LH, administrated subcutaneously, increased the rates of cholesterol translocation and the rates of ovarian mitochondrial cholesterol side-chain cleavage in immature rats (114). Recently, more insights have been provided in a study assessing the effects of LH in cultured GCs from infertile women having low (L), medium (M), and high (H) LH serum levels during ovarian stimulation. The bioinformatic analyses of the data suggested an impairment of the mitochondrial activity, involving the mitochondrial dehydrogenase, associated with both insufficient (L) and excessive (H) recombinant LH (rLH) treatment. Morphologically GCs from the L and H groups had an increased number of autophagosomes. Furthermore, swollen and rounder mitochondria were detected with excessive rLH whereas reduced levels of LH promoted the appearance of forked mitochondria (115). Another study specifically addressed the point of the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by LH in the luteal cells. Plewes and co-authors demonstrated that Dynamin-Related Protein 1 (DRP1), a key mediator of mitochondrial fission, is regulated by LH via PKA (116). The LH stimulation decreased the association of DRP1 with the mitochondria indicating that DRP1 was required for optimal LH-induced progesterone biosynthesis. Taken together, these findings place DRP1 as an important target downstream of PKA in steroidogenic luteal cells. LH also is a modulator of the retrograde signaling since it modulates the expression of humanin in luteal cells (117). Although luteal cells do not seem to have a role in ovarian aging, this mechanism has been here discussed since they derive from GCs and TCs. However, it is has been shown that LH acts directly on GCs (118–120).
The discussed data suggest that mitochondria are targets of the main pituitary gonadotropins. FSH-mediated mitophagy, via activation of different pathways, is an important mechanism of FSH mediated follicular growth and development other than survival. However, the relationship between FSH, mitophagy and apoptosis remains elusive in GCs and more studies are needed to evaluate the role of FSH-mediated mitochondrial integrity, mitophagic flux and the survival of fully functional GCs. This is even more needed for LH, since very little mechanistic data are available despite the reorganization of mitochondrial network during the luteal phase (121). Overall, this indicates the LH signaling pathway as a modulator of the mitochondrial steroidogenic activity and dynamics.
Ovarian Steroid Hormones and Peptides Controlling Mitochondrial Dynamics and Activity
The number and maturation of the follicles is strictly controlled by ovarian endocrine hormones (estradiol, progesterone, etc.) and intra-ovarian regulators. While the formers are synthetized by GCs and TCs, the latter include proteins secreted by oocytes (Growth Differentiation Factor 9, GDF9, bone morphogenetic protein 15, BMP15) and somatic cells (Anti-Mullerian Hormone, AMH, inhibins, activins, etc). These lasts are defined “ovarian peptides” and play an important role in ovarian aging so that they are used in evaluation of the ovarian reserve (122–125). As factors controlling the follicular atresia, we looked for reports investigating their role in regulation of mitochondria activity and dynamics (5, 126). We did not retrieve reports describing their direct role either exerted by ncRNAs. In summary, we emphazise the need to direct future research in understanding the mechanisms by which the decline in these “ovarian peptides” promote follicular atresia altering mitochondrial activity (127, 128).
Ovarian somatic cells play a major role in deciding the fate of follicles since serving other molecules essential for their growth and maintenance as estrogens and other steroid hormones. Steroids affect the mitochondrial function directly and/or indirectly: estrogens (E) and testosterone (T) are directly active in the mitochondria. Their receptors (ERs, AR), localized also in the organelle, might directly regulate DNA-encoded mitochondrial proteins (129, 130). They might exert an indirect activity affecting the nuclear transcription of proteins controlling the expression of mtDNA-encoded proteins (131).
Estrogens withdrawal characterizes the physiological and premature ovarian aging. Mitochondria are involved in synthesis of E and are also their targets. Indeed, mitochondrial function including mitochondrial bioenergetics, calcium homeostasis, and ROS-scavenger and their dynamics are regulated by E (38, 131). Indeed, glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and Mn-superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) are directly regulated by binding of activated ERα and ERβ to their promoters (132). Despite that, the role of estrogens as modulator of mitochondrial activity and dynamics has been scarcely addressed in ovary. The studies discussed below have been conducted mainly in other tissues and cell types and have been included since they involve molecular players non cell specific. Although some mitochondrial transcripts are directly regulated by estradiol (E2) like E2-ERs complexes (TFAM, ATP5PB, mtATP6, etc.), E2 controls their expression primarily through modulation of NRF1 mRNA, a major transcriptional regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis (133). ERα and Erβ bind to a non-consensus ERE in the 5’ promoter of the human NRF1, regulating its transcription (134). It has been demonstrated that NRF1 plays a critical role in integrating nucleus-mitochondrial interactions by initiating transcription of nuclear-encoded mtDNA-specific transcription factors including TFAM, TFB1M, and TFB2M (135). NRF1 was shown to bind and increase transcription of all ten nuclear-encoded mouse Cox genes (136). Additional target genes of NRF1 include TFAM, TFB1M, TFB2M, SURF1, VDAC, and TOM20 genes (137–140). TFAM, TFB1 and TFB2 increase transcription of mtDNA and increase mitochondrial biogenesis regulating other key transcription factors including NRF2 and PGC-lα. These lasts play master roles in mitobiogenesis, whereas E and ERs are key “directors” for the entire pathway. Alteration of the mitochondrial number compromises cellular metabolism and leads to an uncontrolled ROS production (141). Estradiol up-regulates the cellular levels of antioxidant enzymes (GPX and Mn-SOD). However, the mechanism by which E2 up-regulates those enzymes remains unidentified, but they may have implications for gender differences in lifespan (132). Estrogens withdrawal promotes a ROS scavenger activity reduction and the following ROS increase leads to a Ca2+ overload in the mitochondrial matrix. This last event induces the permeabilization of the inner mitochondrial membrane and the dissipation of the proton electrochemical gradient (ΔΨm) resulting in ATP depletion, further ROS production, and ultimately swelling and rupture of the organelle (142–145). Mitochondrial ERβ functions as a mitochondrial vulnerability factor because it is involved in ΔΨm maintenance, potentially through a mitochondrial transcription dependent mechanism (146). Furthermore, E2 controls mitochondrial dynamics modulating DRP1 phosphorylation via AKT pathways. Additionally, other proteins (MFN1, MFN2, OPA1) involved in control of mitochondrial dynamics are targets of E2 signaling pathways, moving from the membrane bound estrogen receptor (GPER) (147). It has been shown that GPER1 overexpression induces the levels of mitofusion 1 (MFN1), mitofusion 2 (MFN2) and Parkin (PRKN) mRNAs whereas mitochondrial fission 1 (FIS1) mRNA is reduced. Therefore, it controls mitochondrial fission/fusion and mitophagy, that is increased (148). Although E modulates the expression of several ncRNAs we did not retrieve papers highlighting their modulation as a mechanism of estrogen regulation of mitochondrial dynamics and activity.
Androgens are also steroids retrieved in the ovary and their role in follicle maturation and atresia is known since time (149). Their deficiency is likely to have a negative impact on fertility whereas their excess is a hallmark of polycystic ovary syndrome. Androgens contribute to the antral follicle formation (150). The absence of androgen receptor (AR−/−) induces abnormal ovarian function due to the promotion of preantral follicle growth and prevention of follicular atresia (151). The AR signaling modulates transcriptionally the mitochondrial metabolism regulating the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC). MPC inhibition results into a considerable disruption of the metabolic homeostasis, affecting ATP and antioxidant content (152). NRF1 is also a major mediator of androgen signaling pathway. It has been shown that AR reduction led to a significant decrease in the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) co-activator 1-β (PGC1-β) and of its downstream genes, including NRF1 and TFAM. Therefore, the mitochondrial biogenesis is affected also by androgens.
In summary, estrogens and androgens protect mitochondria stimulating their ROS-scavenger activity resulting in a reduction of mitochondrial stress and mitochondrial misfolded proteins. The accumulation of the latter in the inner mitochondrial membrane space activates the unfolded protein response (UPRmt), finally initiating the mitochondrial-nuclear retrograde signaling. Noteworthy, mtUPR activates ERα promoting its phosphorylation by AKT whereas E2-ERα modulates mtUPR (54, 153–155).
Conclusion
Despite the well-characterized role of the mitochondria in follicular maturation and atresia, less is known on how their dynamics and activity is modulated by the signaling pathways dependent on pituitary-ovarian axis hormones and how the latter influence the nucleus-mitochondrial crosstalk ( Figure 1 ). The data summarized here suggest pituitary-ovarian hormones as modulator of the anterograde signaling, from nucleus to mitochondria. Among the hormones produced in the ovary, the estrogens are well-characterized regulators of mitochondrial activity and their role have been analyzed also in ovarian aging. Their absence is a marker in the ovarian aging. They are anterograde signals since their classic receptors have been localized in the mitochondria, where they modulate the expression of several genes and control different mitochondrial activity including the mtUPR. Furthermore, they modulate the expression of NRF1 a key anterograde signal. The effects of the other ovarian steroids, such as progesterone and androgens, on ovarian aging have barely been reported. Their ability to control mitochondrial dynamics and activity in ovary has been evidenced in patients suffering from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), whose discussion is behind the scope of this work (156). The follicle is also site of synthesis of the so-called ovarian peptides, key modulators of ovarian aging as AMH, activins and inhibins. To our knowledge no data are available on the modulation of mitochondrial activity and dynamics by their signaling pathways.
Focusing on pituitary gonadotropins, the reported data showed a better characterization of the molecular mechanisms regulating mitochondrial dynamics and activity only for FSH that might act on anterograde signaling modulating the PINK1-Parkin pathway or via modulation of prohibitin level. However, these studies are not numerous. The LH signaling pathway has been far less investigated, and few papers suggested the mitochondrial dynamics is targeted by LH targets in luteal cells. Ovarian and pituitary hormones can regulate nucleus-mitochondria crosstalk also modulating the cellular content of ncRNAs involved in ovarian aging. MiR-143 is an example since it is regulated by FSH.
The molecules involved in the retrograde signaling between the two organelles, different from ATP, Acetyl-CoA and ROS among the others, are almost an unexplored during follicular maturation and atresia. Very few proteins, mitokines (humanin and FGF21), have been described as retrograde signals, which are mainly represented by ncRNAs. Despite that, it has been shown that humanin levels in follicular fluids positively associates with ovarian reserve (60). The role of the ncRNAs associated with the mitochondria (mitomiRNAs and mt-lncRNAs) has been discussed here. Given that this issue is almost unexplored in ovaries, we were surprised to find among them GAS5, a lncRNA that we and other researchers have associated with ovarian aging, which seems to be active as retrograde signal. Our unpublished data evidence that GAS5 and miR-143 have similar regulation in a context of physiological aging in testes, suggesting the need to evaluate their role as modulator of nucleus-mitochondria crosstalk in both gonads. Indeed, an imbalance of the pituitary-testes hormones occurs in physiological aging of spermatozoa and mitochondria play a major role in this process. To our surprise, in testicular somatic and germ cells they have been rarely investigated as targets of these signaling pathways but mainly as biosynthetic sites of androgens.
In conclusion, we believe that more efforts are needed to characterize the mitochondria-nucleus reciprocal crosstalk during follicle maturation and during their physiological and premature aging and how it might be targeted by the hormones active along the pituitary-ovary axis. Furthermore, considering the role that pituitary-testis hormones have on spermatozoa maturation and health.
Perspective
Mitochondria and their crosstalk with the nucleus have been proposed as a therapeutic target for neurological diseases. Considering the role that bidirectional mitochondrial-nuclear crosstalk have in senescence and aging, we suggest it as a potential valid therapeutic target also in ovarian aging (157). Since mitochondria are main executors of the apoptosis and of the depletion mechanisms of OR, the exploitation of the molecular mechanisms underlying their regulation by the signaling pathways dependent on pituitary and ovarian hormones and peptides is needed to identify their mediators that can be targeted to preserve the ovarian health. Among them, ncRNAs, acting as anterograde and retrograde signals in nuclear-mitochondrial crosstalk, could represent an innovative therapeutic approach already suggested for several other diseases. What we consider evident is how far we are from this goal although such mediators, proteins and ncRNAs, might represent “druggable pathways” in ovarian aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, CA and MF. Investigation, MC and DC. Writing-original draft preparation, CA, MC, DC, TP, IF, and MM. Writing-review and editing, CA, MC, and DC. Visualization, MC. Supervision, CA, MM, and MF. Project administration, CA. Funding acquisition, CA. MC and DC have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by: The Italian Workers’ Compensation Authority 571 (grant no 12010), Sensor Regione Campania (grant no 23), Goodwater Regione 572 Campania (POR Campania FESR 2014/2020 O.S. 1.1 Az. 1.1.3 E 1.1.4—CUP 573 B63D18000150007), POR FESR 2014-2020- Projects (RARE PLATNET, SATIN and 574 COEPICA) Regione Campania and “Legge Regionale 5”- Annualità 2008.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank University of Sannio, Goodwater Regione 572 Campania (POR Campania FESR 2014/2020 O.S. 1.1 Az. 1.1.3 E 1.1.4—CUP 573 B63D18000150007) and “Legge Regionale 5”- Annualità 2008 for support.
References
- 1. Colella M, Cuomo D, Giacco A, Mallardo M, De Felice M, Ambrosino C. Thyroid Hormones and Functional Ovarian Reserve: Systemic vs. Peripheral Dysfunctions. J Clin Med (2020) 9:1679. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061679 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Hirshfield AN. Development of Follicles in the Mammalian Ovary. Int Rev Cytol (1991) 124:43–101. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)61524-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Edson MA, Nagaraja AK, Matzuk MM. The Mammalian Ovary From Genesis to Revelation. Endocr Rev (2009) 30:624–712. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Richards JS, Pangas SA. The Ovary: Basic Biology and Clinical Implications. J Clin Invest (2010) 120:963–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI41350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hussein MR. Apoptosis in the Ovary: Molecular Mechanisms. Hum Reprod Update (2005) 11:162–78. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmi001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ratts VS, Flaws JA, Kolp R, Sorenson CM, Tilly J. Ablation of Bcl-2 Gene Expression Decreases the Numbers of Oocytes and Primordial Follicles Established in the Post-Natal Female Mouse Gonad. Endocrinology (1995) 136:3665–8. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.8.7628407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hsu SY, Lai RJM, Finegold M, Hsueh AJW. Targeted Overexpression of Bcl-2 in Ovaries of Transgenic Mice Leads to Decreased Follicle Apoptosis, Enhanced Folliculogenesis, and Increased Germ Cell Tumorigenesis. Endocrinology (1996) 137:4837–43. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.11.8895354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR. The BCL-2 Family Reunion. Mol Cell (2010) 37:299–310. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Tait SWG, Green DR. Mitochondria and Cell Death: Outer Membrane Permeabilization and Beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2010) 11:621–32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ene AC, Park S, Edelmann W, Taketo T. Caspase 9 Is Constitutively Activated in Mouse Oocytes and Plays a Key Role in Oocyte Elimination During Meiotic Prophase Progression. Dev Biol (2013) 377:213–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.01.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Aiken CE, Tarry-Adkins JL, Penfold NC, Dearden L, Ozanne SE. Decreased Ovarian Reserve, Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis, and Increased Lipid Peroxidation in Female Mouse Offspring Exposed to an Obesogenic Maternal Diet. FASEB J (2016) 30:1548–56. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-280800 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kirillova A, Smitz JEJ, Sukhikh GT, Mazunin I. The Role of Mitochondria in Oocyte Maturation. Cells (2021) 10:2484. doi: 10.3390/cells10092484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Perez GI, Trbovich AM, Gosden RG, Tilly JL. Mitochondria and the Death of Oocyte. Nature (2000) 403:500–1. doi: 10.1038/35000651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Cagnone GLM, Tsai TS, Makanji Y, Matthews P, Gould J, Bonkowski MS, et al. Restoration of Normal Embryogenesis by Mitochondrial Supplementation in Pig Oocytes Exhibiting Mitochondrial DNA Deficiency. Sci Rep (2016) 6. doi: 10.1038/srep23229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Orisaka M, Tajima K, Tsang BK, Kotsuji F. Oocyte-Granulosa-Theca Cell Interactions During Preantral Follicular Development. J Ovarian Res (2009) 2. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-2-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Athanasiou V, Stefanidis K, Stavrou D, Vaxevanoglou T, Chronopoulou M. Influence of Advanced Age on the Blastocyst Development Rate and Pregnancy Rate Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril (1999) 71:1144–46. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00121-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bartmann AK, Romão GS, Ramos EDS, Ferriani RA. Why do Older Women Have Poor Implantation Rates? A Possible Role of the Mitochondria. J Assist Reprod Genet (2004) 21:79–83. doi: 10.1023/B:JARG.0000027018.02425.15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Iwata H, Goto H, Tanaka H, Sakaguchi Y, Kimura K, Kuwayama T, et al. Effect of Maternal Age on Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number, ATP Content and IVF Outcome of Bovine Oocytes. Reprod Fertil Dev (2011) 23:424–32. doi: 10.1071/RD10133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Simsek-Duran F, Li F, Ford W, Swanson RJ, Jones HW, Castora FJ. Age-Associated Metabolic and Morphologic Changes in Mitochondria of Individual Mouse and Hamster Oocytes. PLoS One (2013) 8. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tilly JL, Sinclair DA. Germline Energetics, Aging, and Female Infertility. Cell Metab (2013) 17:838–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Rambags BPB, van Boxtel DCJ, Tharasanit T, Lenstra JA, Colenbrander B, Stout TAE. Advancing Maternal Age Predisposes to Mitochondrial Damage and Loss During Maturation of Equine Oocytes Invitro. Theriogenology (2014) 81:959–65. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.01.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kansaku K, Takeo S, Itami N, Kin A, Shirasuna K, Kuwayama T, et al. Maternal Aging Affects Oocyte Resilience to Carbonyl Cyanide-M-Chlorophenylhydrazone -Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cows. PLoS One (2017) 12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Masciangelo R, Chiti MC, Camboni A, Amorim CA, Donnez J, Dolmans MM. Mitochondrial Content, Activity, and Morphology in Prepubertal and Adult Human Ovaries. J Assist Reprod Genet (2021) 38:2581–90. doi: 10.1007/s10815-021-02282-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ruth KS, Day FR, Hussain J, Martínez-Marchal A, Aiken CE, Azad A, et al. Genetic Insights Into Biological Mechanisms Governing Human Ovarian Ageing. Nature (2021) 596:393–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03779-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Moslehi N, Mirmiran P, Tehrani FR, Azizi F. Current Evidence on Associations of Nutritional Factors With Ovarian Reserve and Timing of Menopause: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr (2017) 8:597–612. doi: 10.3945/an.116.014647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Cuomo D, Ambrosino C. Non-Coding RNAs as Integrators of the Effects of Age, Genes, and Environment on Ovarian Aging. Cell Death Dis (2019) 10. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1334-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Gebremedhn S, Ali A, Hossain M, Hoelker M, Salilew-Wondim D, Anthony RV, et al. MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Regulatory Mechanisms in Mammalian Female Reproductive Health. Int J Mol Sci (2021) 22:938. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Zayed Y, Qi X, Peng C. Identification of Novel MicroRNAs and Characterization of MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Zebrafish Ovarian Follicular Cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2019) 10:518. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Pan Y, Yang S, Cheng J, Lv Q, Xing Q, Zhang R, et al. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of LncRNAs Mediated ceRNA Regulation in Granulosa Cells Isolated From Healthy and Atresia Follicles of Chinese Buffalo. Front Vet Sci (2021) 8:680182. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.680182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Wang T, Zhang M, Jiang Z, Seli E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Ovarian Aging. Am J Reprod Immunol (2017) 77:i. doi: 10.1111/aji.12651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Kasapoğlu I, Seli E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Ovarian Aging. Endocrinol (United States) (2020) 161. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Shoubridge EA, Wai T. The Mitochondrion in the Germline and Early Development. Elsevier Science Publishing Co Inc. (2007). [Google Scholar]
- 33. May-Panloup P, Chrétien MF, Jacques C, Vasseur C, Malthièry Y, Reynier P. Low Oocyte Mitochondrial DNA Content in Ovarian Insufficiency. Hum Reprod (2005) 20:593–7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Seli E. Mitochondrial DNA as a Biomarker for in-Vitro Fertilization Outcome. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol (2016) 28:158–63. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Ravichandran K, McCaffrey C, Grifo J, Morales A, Perloe M, Munne S, et al. Mitochondrial DNA Quantification as a Tool for Embryo Viability Assessment: Retrospective Analysis of Data From Single Euploid Blastocyst Transfers. Hum Reprod (2017) 32:1282–92. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Wang S, He G, Chen M, Zuo T, Xu W, Liu X. The Role of Antioxidant Enzymes in the Ovaries. Oxid Med Cell Longev (2017) 2017. doi: 10.1155/2017/4371714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Liu Y, Fiskum G, Schubert D. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species by the Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain. J Neurochem (2002) 80:780–7. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2002.00744.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Klinge CM. Estrogens Regulate Life and Death in Mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr (2017) 49:307–24. doi: 10.1007/s10863-017-9704-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Almansa-Ordonez A, Bellido R, Vassena R, Barragan M, Zambelli F. Oxidative Stress in Reproduction: A Mitochondrial Perspective. Biol (Basel) (2020) 9:269. doi: 10.3390/biology9090269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional Paradigms in Mammalian Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function. Physiol Rev (2008) 88:611–38. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kujoth CC, Hiona A, Pugh TD, Someya S, Panzer K, Wohlgemuth SE, et al. Medicine: Mitochondrial DNA Mutations, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis in Mammalian Aging. Science (2005) 309:481–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1112125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Van Blerkom J. Mitochondrial Function in the Human Oocyte and Embryo and Their Role in Developmental Competence. Mitochondrion (2011) 11:797–813. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2010.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Kauppila TES, Kauppila JHK, Larsson NG. Mammalian Mitochondria and Aging: An Update. Cell Metab (2017) 25:57–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Ávila J, González-Fernández R, Rotoli D, Hernández J, Palumbo A. Oxidative Stress in Granulosa-Lutein Cells From In-Vitro Fertilization Patients. Reprod Sci (2016) 23:1656–61. doi: 10.1177/1933719116674077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kalmbach KH, Fontes Antunes DM, Dracxler RC, Knier TW, Seth-Smith ML, Wang F, et al. Telomeres and Human Reproduction. Fertil Steril (2013) 99:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.11.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Keefe DL. Telomeres, Reproductive Aging, and Genomic Instability During Early Development. Reprod Sci (2016) 23:1612–5. doi: 10.1177/1933719116676397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Hamatani T, Falco G, Carter MG, Akutsu H, Stagg CA, Sharov AA, et al. Age-Associated Alteration of Gene Expression Patterns in Mouse Oocytes. Hum Mol Genet (2004) 13:2263–78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Lim J, Luderer U. Oxidative Damage Increases and Antioxidant Gene Expression Decreases With Aging in the Mouse Ovary. Biol Reprod (2011) 84:775–82. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.088583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Sasaki H, Hamatani T, Kamijo S, Iwai M, Kobanawa M, Ogawa S, et al. Impact of Oxidative Stress on Age-Associated Decline in Oocyte Developmental Competence. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2019) 10:811. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Zaidi SK, Shen WJ, Cortez Y, Bittner S, Bittner A, Arshad S, et al. SOD2 Deficiency-Induced Oxidative Stress Attenuates Steroidogenesis in Mouse Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2021) 519. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. May-Panloup P, Boucret L, de la Barca JMC, Desquiret-Dumas V, Ferré-L’Hotellier1 V, Morinière C, et al. Ovarian Ageing: The Role of Mitochondria in Oocytes and Follicles. Hum Reprod Update (2016) 22:725–43. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Giordani C, Silvestrini A, Giuliani A, Olivieri F, Rippo MR. MicroRNAs as Factors in Bidirectional Crosstalk Between Mitochondria and the Nucleus During Cellular Senescence. Front Physiol (2021) 12:734976. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.734976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. LesLaboratories Servier SAS . SMART Servier Medical Art. SMART Servier Med Art (2020). [Google Scholar]
- 54. Horan MP, Cooper DN. The Emergence of the Mitochondrial Genome as a Partial Regulator of Nuclear Function is Providing New Insights Into the Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Age-Related Complex Disease. Hum Genet (2014) 133:438–58. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1402-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Barchiesi A, Vascotto C. Transcription, Processing, and Decay of Mitochondrial RNA in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20:2221. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bárcena C, Mayoral P, Quirós PM. Mitohormesis, an Antiaging Paradigm. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol (2018) 340:35–77. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Bourdon G, Froment P, Ducluzeau PH. How a Metabolic Hormone, FGF21 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 21) Impacts Reproduction. Medecine/Sciences (2021) 37:265–70. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2021012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Lei H, Rao M. The Role of Humanin in the Regulation of Reproduction. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gen Subj (2022) 1866:130023. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2021.130023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Marvaldi C, Martin D, Conte JG, Gottardo MF, Pidre ML, Imsen M, et al. Mitochondrial Humanin Peptide Acts as a Cytoprotective Factor in Granulosa Cell Survival. Reproduction (2021) 161:581–91. doi: 10.1530/REP-20-0197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Rao M, Zhou F, Tang L, Zeng Z, Hu S, Wang Y, et al. Follicular Fluid Humanin Concentration is Related to Ovarian Reserve Markers and Clinical Pregnancy After IVF–ICSI: A Pilot Study. Reprod Biomed Online (2019) 38:108–17. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Vendramin R, Marine J, Leucci E. Non-Coding RNA s: The Dark Side of Nuclear–Mitochondrial Communication. EMBO J (2017) 36:1123–33. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Bandiera S, Rüberg S, Girard M, Cagnard N, Hanein S, Chrétien D, et al. Nuclear Outsourcing of RNA Interference Components to Human Mitochondria. PLoS One (2011) 6. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020746 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Noh JH, Kim KM, Abdelmohsen K, Yoon JH, Panda AC, Munk R, et al. HuR and GRSF1 Modulate the Nuclear Export and Mitochondrial Localization of the lncRNA RMRP. Genes Dev (2016) 30:1224–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.276022.115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Barrey E, Saint-Auret G, Bonnamy B, Damas D, Boyer O, Gidrol X. Pre-microRNA and Mature microRNA in Human Mitochondria. PLoS One (2011) 6. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Quirós PM, Mottis A, Auwerx J. Mitonuclear Communication in Homeostasis and Stress. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2016) 17:213–26. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Dong Y, Yoshitomi T, Hu JF, Cui J. Long Noncoding RNAs Coordinate Functions Between Mitochondria and the Nucleus. Epigenet Chromatin (2017) 10. doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0149-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Fan S, Tian T, Chen W, Lv X, Lei X, Zhang H, et al. Mitochondrial miRNA Determines Chemoresistance by Reprogramming Metabolism and Regulating Mitochondrial Transcription. Cancer Res (2019) 79:1069–84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2505 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Das S, Bedja D, Campbell N, Dunkerly B, Chenna V, Maitra A, et al. miR-181c Regulates the Mitochondrial Genome, Bioenergetics, and Propensity for Heart Failure In Vivo . PLoS One (2014) 9. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Yao L, Wang L, Li F, Gao X, Wei X, Liu Z. MiR181c Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Metastasis and Progression by Targeting PRKCD Expression. Int J Clin Exp Med (2015) 8:15198–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Xu S, Linher-Melville K, Yang BB, Wu D, Li J. Micro-RNA378 (miR-378) Regulates Ovarian Estradiol Production by Targeting Aromatase. Endocrinology (2011) 152:3941–51. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Jagannathan R, Thapa D, Nichols CE, Shepherd DL, Stricker JC, Croston TL, et al. Translational Regulation of the Mitochondrial Genome Following Redistribution of Mitochondrial MicroRNA in the Diabetic Heart. Circ Cardiovasc Genet (2015) 8:785–802. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.115.001067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Uno Y, Yamazaki H. Expression Levels of microRNAs That Are Potential Cytochrome P450 Regulators in Cynomolgus Macaques. Xenobiotica (2020) 50:747–52. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2019.1688423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Zhang L, Zhang XX, Zhang X, Lu Y, Li L, Cui S. MiRNA-143 Mediates the Proliferative Signaling Pathway of FSH and Regulates Estradiol Production. J Endocrinol (2017) 234:1.14. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Zhao S, Zhang Y, Pei M, Wu L, Li J. miR-145 Inhibits Mitochondrial Function of Ovarian Cancer by Targeting ARL5B. J Ovarian Res (2021) 14. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00762-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Sirard MA. Distribution and Dynamics of Mitochondrial DNA Methylation in Oocytes, Embryos and Granulosa Cells. Sci Rep (2019) 9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48422-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Cuomo D, Porreca I, Ceccarelli M, Threadgill DW, Barrington WT, Petriella A, et al. Transcriptional Landscape of Mouse-Aged Ovaries Reveals a Unique Set of Non-Coding RNAs Associated With Physiological and Environmental Ovarian Dysfunctions. Cell Death Discov (2018) 4. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0121-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Li L, Wei J, Hei J, Ren Y, Li H. Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Regulates Proliferation of Ovarian Granulosa Cells via STAT3 in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Arch Med Sci (2021) 17:785–91. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.89254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Das SS, Das S, Byram PK, Rahaman M, Dolai TK, Chatterjee A, et al. MicroRNA Expression Patterns in HbE/β-Thalassemia Patients: The Passwords to Unlock Fetal Hemoglobin Expression in β-Hemoglobinopathies. Blood Cells Mol Dis (2021) 87. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Gusic M, Prokisch H. ncRNAs: New Players in Mitochondrial Health and Disease? Front Genet (2020) 11:95. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Yang CX, Wu ZW, Liu XM, Liang H, Gao ZR, Wang Y, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals mRNAs and lncRNAs Important for Oocytes In Vitro Matured in Pigs. Reprod Domest Anim (2021) 56:642–57. doi: 10.1111/rda.13901 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Donadeu FX, Mohammed BT, Ioannidis J. A miRNA Target Network Putatively Involved in Follicular Atresia. Domest Anim Endocrinol (2017) 58:76–83. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2016.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Sun XF, Li YP, Pan B, Wang YF, Li J, Shen W. Molecular Regulation of miR-378 on the Development of Mouse Follicle and the Maturation of Oocyte In Vivo . Cell Cycle (2018) 17:2230–42. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1520557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Sang L, Ju H, Yang Z, Ge Q, Zhang Z, Liu F, et al. Mitochondrial Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 Tunes TCA Metabolism in Response to Nutrient Stress. Nat Metab (2021) 3. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00325-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Hong H, Tao T, Chen S, Liang C, Qiu Y, Zhou Y, et al. MicroRNA-143 Promotes Cardiac Ischemia-Mediated Mitochondrial Impairment by the Inhibition of Protein Kinase Cepsilon. Basic Res Cardiol (2017) 112. doi: 10.1007/s00395-017-0649-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Rackham O, Shearwood AMJ, Mercer TR, Davies SMK, Mattick JS, Filipovska A. Long Noncoding RNAs Are Generated From the Mitochondrial Genome and Regulated by Nuclear-Encoded Proteins. RNA (2011) 17:2085–93. doi: 10.1261/rna.029405.111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Hoque SAM, Kawai T, Zhu Z, Shimada M. Mitochondrial Protein Turnover is Critical for Granulosa Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in Antral Follicles. J Endocr Soc (2019) 3:324–39. doi: 10.1210/js.2018-00329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Klinge CM. Non-Coding RNAs: Long Non-Coding RNAs and microRNAs in Endocrine-Related Cancers. Endocr Relat Cancer (2018) 25:R259–82. doi: 10.1530/ERC-17-0548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Shi Y, Downes M, Xie W, Kao HY, Ordentlich P, Tsai CC, et al. Sharp, an Inducible Cofactor That Integrates Nuclear Receptor Repression and Activation. Genes Dev (2001) 15:1140–51. doi: 10.1101/gad.871201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Hatchell EC, Colley SM, Beveridge DJ, Epis MR, Stuart LM, Giles KM, et al. SLIRP, a Small SRA Binding Protein, Is a Nuclear Receptor Corepressor. Mol Cell (2006) 22:657–68. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Bi F, An Y, Sun T, You Y, Yang Q. PHGDH Is Upregulated at Translational Level and Implicated in Platin-Resistant in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Front Oncol (2021) 11:643129. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Chen Y, Hao Q, Wang S, Cao M, Huang Y, Weng X, et al. Inactivation of the Tumor Suppressor P53 by Long Noncoding RNA RMRP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2021) 118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026813118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Babayev E, Seli E. Oocyte Mitochondrial Function and Reproduction. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol (2015) 27:175–81. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Ferreira AF, Soares M, Reis SA, Ramalho-Santos J, Sousa AP, Almeida-Santos T. Does Supplementation With Mitochondria Improve Oocyte Competence? A Systematic Review. Reproduction (2021) 161:269–87. doi: 10.1530/REP-20-0351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Harvey AJ. Mitochondria in Early Development: Linking the Microenvironment, Metabolism and the Epigenome. Reproduction (2019) 157:R159–79. doi: 10.1530/REP-18-0431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. May-Panloup P, Boguenet M, Hachem H, Bouet PE, Reynier P. Embryo and its Mitochondria. Antioxidants (2021) 10:139. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Urs DBS, Wu WH, Komrskova K, Postlerova P, Lin YF, Tzeng CR, et al. Mitochondrial Function in Modulating Human Granulosa Cell Steroidogenesis and Female Fertility. Int J Mol Sci (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Yao N, Lu CL, Zhao JJ, Xia HF, Sun DG, Shi XQ, et al. A Network of miRNAs Expressed in the Ovary are Regulated by FSH. Front Biosci (2009) 14. doi: 10.2735/3447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Gomes SE, Pereira DM, Roma-Rodrigues C, Fernandes AR, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CMP. Convergence of MIR-143 Overexpression, Oxidative Stress and Cell Death in HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells. PLoS One (2018) 13. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Li C, Zhou J, Liu Z, Zhou J, Yao W, Tao J, et al. FSH Prevents Porcine Granulosa Cells From Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis via Activating Mitophagy Through the HIF-1α-PINK1-Parkin Pathway. FASEB J (2020) 34:3631–45. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901808RRR [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Shen M, Jiang Y, Guan Z, Cao Y, Sun SC, Liu H. FSH Protects Mouse Granulosa Cells From Oxidative Damage by Repressing Mitophagy. Sci Rep (2016) 6. doi: 10.1038/srep38090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Wang SH, Zhu XL, Wang F, Chen SX, Chen ZT, Qiu Q, et al. LncRNA H19 Governs Mitophagy and Restores Mitochondrial Respiration in the Heart Through Pink1/Parkin Signaling During Obesity. Cell Death Dis (2021) 12. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03821-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Walther TC, Farese RV. The Life of Lipid Droplets. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Biol Lipids (2009) 1791:459–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.10.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Miller WL, Bose HS. Early Steps in Steroidogenesis: Intracellular Cholesterol Trafficking. J Lipid Res (2011) 52:2111–35. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R016675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Chowdhury I, Thomas K, Zeleznik A, Thompson WE. Prohibitin Regulates the Fsh Signaling Pathway in Rat Granulosa Cell Differentiation. J Mol Endocrinol (2016) 56:325–36. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Chowdhury I, Thompson WE, Thomas K. Prohibitins Role in Cellular Survival Through Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK Pathway. J Cell Physiol (2014) 229:998–1004. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Merkwirth C, Dargazanli S, Tatsuta T, Geimer S, Löwer B, Wunderlich FT, et al. Prohibitins Control Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis by Regulating OPA1-Dependent Cristae Morphogenesis in Mitochondria. Genes Dev (2008) 22:476–88. doi: 10.1101/gad.460708 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Osman C, Merkwirth C, Langer T. Prohibitins and the Functional Compartmentalization of Mitochondrial Membranes. J Cell Sci (2009) 122:3823–30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.037655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Ishihara N, Fujita Y, Oka T, Mihara K. Regulation of Mitochondrial Morphology Through Proteolytic Cleavage of OPA1. EMBO J (2006) 25:2966–77. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Song Z, Chen H, Fiket M, Alexander C, Chan DC. OPA1 Processing Controls Mitochondrial Fusion and Is Regulated by mRNA Splicing, Membrane Potential, and Yme1L. J Cell Biol (2007) 178:749–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200704110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Chowdhury I, Thompson WE, Welch C, Thomas K, Matthews R. Prohibitin (PHB) Inhibits Apoptosis in Rat Granulosa Cells (GCs) Through the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and the Bcl Family of Proteins. Apoptosis (2013) 18:1513–25. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0901-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Zhou J, Yao W, Li C, Wu W, Li Q, Liu H. Administration of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Induces Autophagy via Upregulation of Hif-1α in Mouse Granulosa Cells. Cell Death Dis (2017) 8. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Lambalk CB, van Disseldorp J, de Koning CH, Broekmans FJ. Testing Ovarian Reserve to Predict Age at Menopause. Maturitas (2009) 63:280–91. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Bosch E, Alviggi C, Lispi M, Conforti A, Hanyaloglu AC, Chuderland D, et al. Reduced FSH and LH Action: Implications for Medically Assisted Reproduction. Hum Reprod (2021) 36:1469–80. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Robinson J, Stevenson PM, Boyd GS, Armstrong DT. Acute In Vivo Effects of HCG and LH on Ovarian Mitochondrial Cholesterol Utilization. Mol Cell Endocrinol (1975) 2:149–55. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(75)90001-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Wan YT, Liu S, Zhao SK, Luo YY, Lv YS, Qu DN, et al. Effect of Luteinizing Hormone Concentration on Transcriptome and Subcellular Organelle Phenotype of Ovarian Granulosa Cells. J Assist Reprod Genet (2021) 38:809–24. doi: 10.1007/s10815-021-02066-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Plewes MR, Hou X, Talbott HA, Zhang P, Wood JR, Cupp AS, et al. Luteinizing Hormone Regulates the Phosphorylation and Localization of the Mitochondrial Effector Dynamin-Related Protein-1 (DRP1) and Steroidogenesis in the Bovine Corpus Luteum. FASEB J (2020) 34:5299–316. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902958R [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Yadav VK, Muraly P, Medhamurthy R. Identification of Novel Genes Regulated by LH in the Primate Corpus Luteum: Insight Into Their Regulation During the Late Luteal Phase. Mol Hum Reprod (2004) 10:629–39. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gah089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Duffy DM, Stouffer RL. Luteinizing Hormone Acts Directly at Granulosa Cells to Stimulate Periovulatory Processes: Modulation of Luteinizing Hormone Effects by Prostaglandins. Endocrine (2003) 22:249–56. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:22:3:249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Hummitzsch K, Anderson RA, Wilhelm D, Wu J, Telfer EE, Russell DL, et al. Stem Cells, Progenitor Cells, and Lineage Decisions in the Ovary. Endocr Rev (2015) 36:65–91. doi: 10.1210/er.2014-1079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Liu C, Peng J, Matzuk MM, Yao HHC. Lineage Specification of Ovarian Theca Cells Requires Multicellular Interactions via Oocyte and Granulosa Cells. Nat Commun (2015) 6. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Przygrodzka E, Plewes MR, Davis JS. Luteinizing Hormone Regulation of Inter-Organelle Communication and Fate of the Corpus Luteum. Int J Mol Sci (2021) 22:9972. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Mather JP, Moore A, Li RH. Activins, Inhibins, and Follistatins: Further Thoughts on a Growing Family of Regulators. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med (1997) 215:209–22. doi: 10.3181/00379727-215-44130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Chapman SC, Kenny HA, Woodruff TK. “Activin, Inhibin, and Follistatin in Ovarian Physiology”. In: The Ovary, 2nd ed. Elsevier Science Publishing Co Inc. (2004). doi: 10.1016/B978-012444562-8/50017-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Moolhuijsen LME, Visser JA. Anti-Müllerian Hormone and Ovarian Reserve: Update on Assessing Ovarian Function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2020) 105:3361–73. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa513 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Park MJ, Ahn JW, Kim KH, Bang J, Kim SC, Jeong JY, et al. Prediction of Ovarian Aging Using Ovarian Expression of BMP15, GDF9, and C-KIT. Exp Biol Med (2020) 245. doi: 10.1177/1535370220915826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Seifer DB, Merhi Z. Is AMH a Regulator of Follicular Atresia? J Assist Reprod Genet (2014) 31:1403–7. doi: 10.1007/s10815-014-0328-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Hurwitz JM, Santoro N. Inhibins, Activins, and Follistatin in the Aging Female and Male. Semin Reprod Med (2004) 22:209–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-831896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Reame NE, Lukacs JL, Olton P, Ansbacher R, Padmanabhan V. Differential Effects of Aging on Activin A and Its Binding Protein, Follistatin, Across the Menopause Transition. Fertil Steril (2007) 88:1003–5. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.12.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Klinge CM. Estrogenic Control of Mitochondrial Function and Biogenesis. J Cell Biochem (2008) 105:1342–51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Bajpai P, Koc E, Sonpavde G, Singh R, Singh KK. Mitochondrial Localization, Import, and Mitochondrial Function of the Androgen Receptor. J Biol Chem (2019) 294:6621–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Klinge CM. Estrogenic Control of Mitochondrial Function. Redox Biol (2020) 31. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Borrás C, Gambini J, Gómez-Cabrera MC, Sastre J, Pallardó FV, Mann GE, et al. 17β-Oestradiol Up-Regulates Longevity-Related, Antioxidant Enzyme Expression via the ERK1 and ERK2[MAPK]/Nfκb Cascade. Aging Cell (2005) 4:113–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00151.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Chen JQ, Yager JD, Russo J. Regulation of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Structure and Function by Estrogens/Estrogen Receptors and Potential Physiological/Pathophysiological Implications. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res (2005) 1746:1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Mattingly KA, Ivanova MM, Riggs KA, Wickramasinghe NS, Barch MJ, Klinge CM. Estradiol Stimulates Transcription of Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1 and Increases Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Mol Endocrinol (2008) 22:609–22. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Scarpulla RC. Nuclear Control of Respiratory Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells. J Cell Biochem (2006) 97:673–83. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Dhar SS, Ongwijitwat S, Wong-Riley MTT. Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 Regulates All Ten Nuclear-Encoded Subunits of Cytochrome C Oxidase in Neurons. J Biol Chem (2008) 283:3120–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707587200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Evans MJ, Scarpulla RC. Interaction of Nuclear Factors With Multiple Sites in the Somatic Cytochrome C Promoter. Characterization of Upstream NRF-1, ATF, and Intron Sp1 Recognition Sequences. J Biol Chem (1989) 264:P14361–8. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)71686-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Scarpulla RC. Nuclear Activators and Coactivators in Mammalian Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gene Struct Expr (2002) 1576:1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4781(02)00343-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Kelly DP, Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional Regulatory Circuits Controlling Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function. Genes Dev (2004) 18:357–68. doi: 10.1101/gad.1177604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Gleyzer N, Vercauteren K, Scarpulla RC. Control of Mitochondrial Transcription Specificity Factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by Nuclear Respiratory Factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 Family Coactivators. Mol Cell Biol (2005) 25:1354–66. doi: 10.1128/mcb.25.4.1354-1366.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Circu ML, Aw TY. Reactive Oxygen Species, Cellular Redox Systems, and Apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med (2010) 48:749–62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.12.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Bernardi P, Krauskopf A, Basso E, Petronilli V, Blalchy-Dyson E, Di Lisa F, et al. The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition From In Vitro Artifact to Disease Target. FEBS J (2006) 273:277–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05213.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial Membrane Permeabilization in Cell Death. Physiol Rev (2007) 87:99–163. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Leung AWC, Halestrap AP. Recent Progress in Elucidating the Molecular Mechanism of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore. Biochim Biophys Acta - Bioenerg (2008) 1777:946–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Murphy E, Steenbergen C. Mechanisms Underlying Acute Protection From Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Physiol Rev (2008) 88:581–609. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00024.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Yang SH, Sarkar SN, Liu R, Perez EJ, Wang X, Wen Y, et al. Estrogen Receptor β as a Mitochondrial Vulnerability Factor. J Biol Chem (2009) 284:9540–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808246200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Sastre-Serra J, Nadal-Serrano M, Pons DG, Roca P, Oliver J. Mitochondrial Dynamics Is Affected by 17β-Estradiol in the MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Effects on Fusion and Fission Related Genes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol (2012) 44:1901–5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.07.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Wegner MS, Gruber L, Schömel N, Trautmann S, Brachtendorf S, Fuhrmann D, et al. GPER1 Influences Cellular Homeostasis and Cytostatic Drug Resistance via Influencing Long Chain Ceramide Synthesis in Breast Cancer Cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol (2019) 112:95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Hillier SG, Tetsuka M. Role of Androgens in Follicle Maturation and Atresia. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol (1997) 11:249–60. doi: 10.1016/S0950-3552(97)80036-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Lebbe M, Woodruff TK. Involvement of Androgens in Ovarian Health and Disease. Mol Hum Reprod (2013) 19:828–37. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gat065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Prizant H, Gleicher N, Sen A. Androgen Actions in the Ovary: Balance Is Key. J Endocrinol (2014) 222:R141–51. doi: 10.1530/JOE-14-0296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Stone L. Mitochondrial Metabolism: A Target in AR-Driven Disease. Nat Rev Urol (2019) 16. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0132-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Papa L, Germain D. Estrogen Receptor Mediates a Distinct Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response. J Cell Sci (2011) 124:1396–402. doi: 10.1242/jcs.078220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Jovaisaite V, Mouchiroud L, Auwerx J. The Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response, a Conserved Stress Response Pathway With Implications in Health and Disease. J Exp Biol (2014) 217:137–43. doi: 10.1242/jeb.090738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Germain D. Sirtuins and the Estrogen Receptor as Regulators of the Mammalian Mitochondrial UPR in Cancer and Aging. Adv Cancer Res (2016) 130:211–56. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2016.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Zhang J, Bao Y, Zhou X, Zheng L. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol (2019) 17. doi: 10.1186/s12958-019-0509-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Vizioli MG, Liu T, Miller KN, Robertson NA, Gilroy K, Lagnado AB, et al. Mitochondria-To-Nucleus Retrograde Signaling Drives Formation of Cytoplasmic Chromatin and Inflammation in Senescence. Genes Dev (2020) 34:428–45. doi: 10.1101/gad.331272.119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]