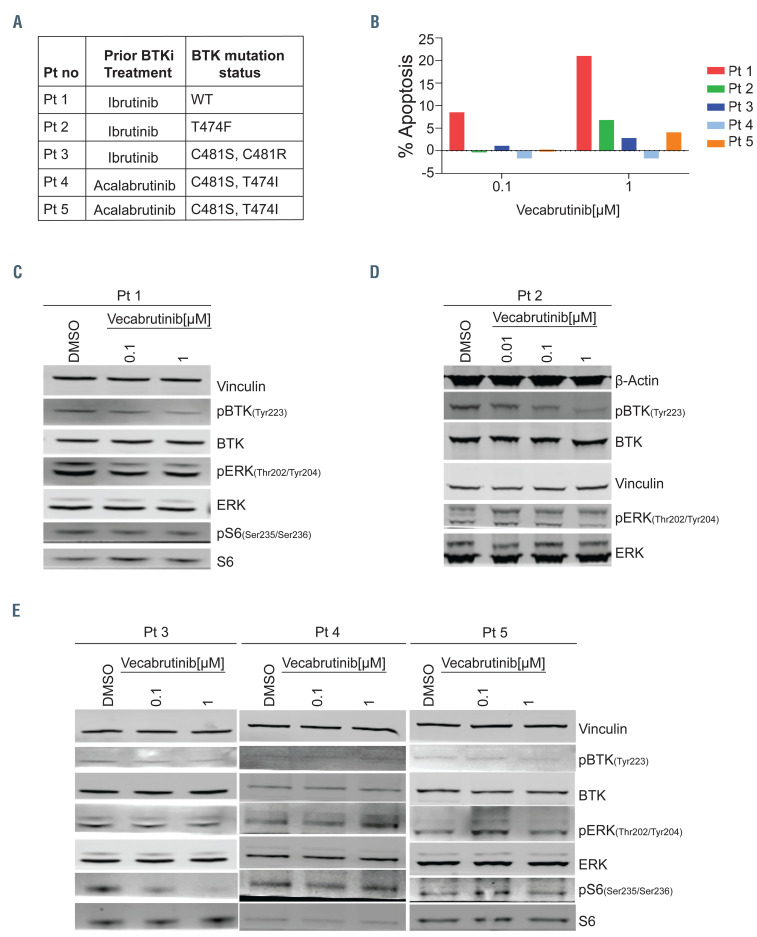
Figure 3.
Inhibition of the B-cell receptor pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells from patients with wild-type or mutant BTK. For blood sample collections, patients (n=5) provided written informed consent for the protocol, which was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Blood samples were collected into Vacutainer glass green-top blood collection tubes and cells were isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque density centrifugation and incubated with vecabrutinib at two or three concentrations (0.01, 0.1, and 1 mM) for 24 h. (A) Table presenting the patients’ numbers and BTK mutation status for five patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). BTK mutations were identified in patients’ samples using End CLL or End Lymphoma panels that included C481F, C481R, C481S, L528W, T474I, and T474F mutations. The same patients’ numbers are used in Figure 3B-E. (B) Apoptotic cell death in primary CLL lymphocytes of five patients. Freshly isolated cells (patients 1-3) or cryopreserved cells (patients 4 and 5) were incubated for 24 h with indicated concentrations of vecabrutinib. Cells were stained with annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) and apoptotic cells were determined with flow cytometry. Cell death in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)-treated samples was subtracted from that of treated samples. Percent apoptosis in DMSO was 14.6, 0.3, 3.3, 73, and 41.9 in patients 1 to 5, respectively. (C-E) Effect of vecabrutinib on B-cell receptor pathway proteins. Protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot assays to determine levels of phospho-BTK (Y223), BTK, phospho-ERK (T202/Y204), ERK, phospho-S6 (Ser235/236), and S6. (C, D) Patients with BTKWT or BTKT474F mutant CLL cells, (E) Patients with BTKC481S and BTKC481R variants.