Abstract
During endochondral bone development, a complex process that leads to the formation of the majority of skeletal elements, mesenchymal cells condense, differentiating into chondrocytes and producing the foetal growth plate. Chondrocytes progressively hypertrophy, induce angiogenesis and are then gradually replaced by bone. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), one of many growth factors, is the prototype of the EGF-ligand family, which comprises several proteins involved in cell proliferation, migration and survival. In bone, EGF pathway signalling finely tunes the first steps of chondrogenesis by maintaining mesenchymal cells in an undifferentiated stage, and by promoting hypertrophic cartilage replacement. Moreover, EGF signalling modulates bone homeostasis by stimulating osteoblast and osteoclast proliferation, and by regulating osteoblast differentiation under specific spatial and temporal conditions. This evidence-based narrative review describes the EGF pathway in bone metabolism and endochondral bone development. This comprehensive description may be useful in light of possible clinical applications in orthopaedic practice. A deeper knowledge of the role of EGF in bone may be useful in musculoskeletal conditions which may benefit from the modulation of this signalling pathway.
Key messages
The EGF pathway is involved in bone metabolism.
EGF signalling is essential in the very early stages of limb development by maintaining cells in an undifferentiated stage.
EGF pathway positively regulates chondrocyte proliferation, negatively modulates hypertrophy, and favours cartilage replacement by bone.
EGF and EGF-like proteins finely tune the proliferation and differentiation of bone tissue cells, and they also regulate the initial phases of endochondral ossification.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor, bone development, endochondral ossification
Introduction
Endochondral bone development
Bones form through two complex processes: intramembranous or endochondral ossification. During the former, mesenchymal cells directly differentiate in osteoblasts by activating the RUNX-2 pathway. This process occurs in most of the calvarial bones and in the clavicle [1]. Endochondral ossification is more complex, and it involves an initial cartilage anlage, which is then replaced by bone [1]. Mesenchymal progenitors first condensate and then start differentiating into chondrocytes. These latter cells pile up in columns, exit the cell cycle, and secrete an osteogenic matrix and pro-angiogenic factors, such as Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) [2,3]. Subsequently, perichondrial cells surrounding the primary cartilage anlage invade the template together with blood vessels, and they differentiate into osteoblasts, forming the primary ossification centre. Subsequently, chondrocytes form the growth plate at both ends of the primary ossification centre [4].
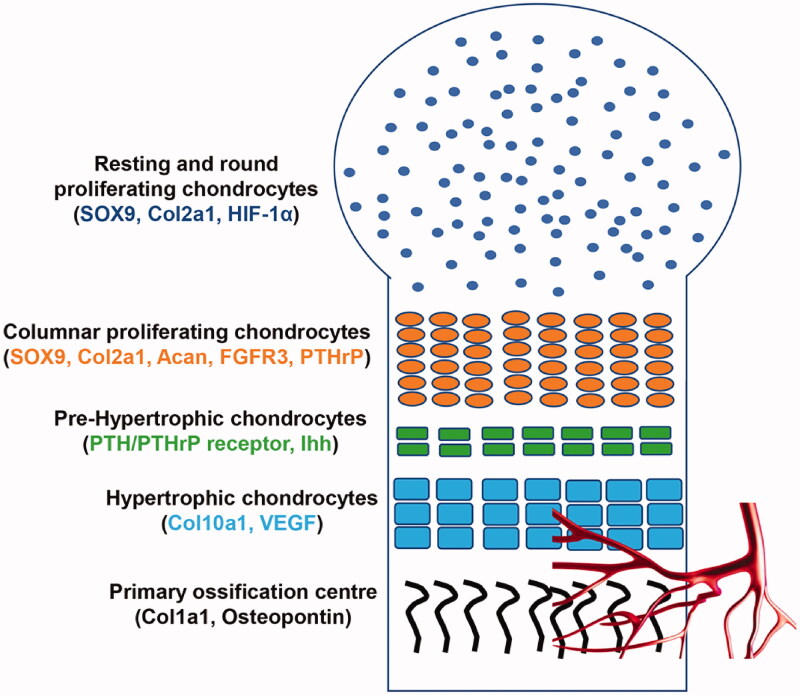
The growth plate is composed of different layers, each representing a distinct stage of cell differentiation (Figure 1). In the resting zone, chondrocytes have a round shape, are still in an undifferentiated phase and divide asymmetrically: some of them remain as “stem cells,” and the others differentiate into proliferative chondrocytes, which form the proliferating layer. In this layer, chondrocytes assume a cuboidal shape, they floridly proliferate, and progressively pile up in columns, forming the proliferating columnar layer. Gradually, columnar chondrocytes exit the cell cycle, stop proliferating and they first become pre-hypertrophic cells, which then terminally differentiate into hypertrophic chondrocytes [4].
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the formation of the growth plate during endochondral bone development. In the resting zone, chondrocytes have a round shape and they mainly express SOX9, Col2a1 and HIF-1α. In the proliferating layer, chondrocytes express SOX9, Acan, Col2a1, PTHrP, FGFR3; they assume a cuboidal shape, progressively pile up in columns. Columnar chondrocytes stop proliferating and they firstly become pre-hypertrophic cells, which express PTHrP receptor and Ihh. These cells terminally differentiate into hypertrophic cells, which express Col10a1 and VEGF; thus promoting angiogenesis. Lastly, hypertrophic cells are progressively replaced by osteoblasts expressing Col1a1 and osteopontin.
Most of these latter cells undergo apoptosis and are resorbed by osteoclasts. Conversely, some of these cells directly transdifferentiate into osteoblasts [5]. Thus, both stem cells from the resting zone and hypertrophic chondrocytes maintain their osteogenic potential [5]. During this process, the cartilage template progressively enlarges, allowing for bone growth.
In the growth plate, cell gene expression varies depending on the layer, and this influences cell fate and differentiation. Mesenchymal progenitors express Sox-9, a master transcription factor for chondrocytes differentiation [6–8]. Upon Sox-9 pathway activation, chondrocytes in the proliferating zone largely express type II collagen alpha 1 (Col2a1), the main component of the cartilaginous matrix, aggrecan (Acan), fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) and Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP). Conversely, pre-hypertrophic cells express PTH/PTHrP receptor and Indian hedgehog (Ihh) mRNA, and hypertrophic chondrocytes are characterised by an abundant expression of type X collagen alpha 1 (Col10a1); thus, they contribute to the secretion of osteogenic matrix [4].
The foetal growth plate is highly hypoxic. Thus, the activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway is crucial for chondrocyte survival and differentiation [9–11]. Moreover, this pathway also initiates blood invasion at the level of the primary ossification centre through the activation of the Vascular Endothelial Factor (VEGF) [12]. Many other growth factors play an important role in endochondral bone development, such as FGFR3 [13,14]. For example, gain-of-function mutations of this molecule cause achondroplasia, a genetic bone dysplasia [15].
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling pathway
Recently, the role of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) in bone development has gained interest, as it is involved in multiple steps of this process [16]. EGF is a single-chain polypeptide consisting of 53 amino acids, with three intramolecular disulphide bonds, which are essential for its function [17,18]. EGF is the prototype of the EGF-ligand family which includes other EGF-like proteins, such as Heparin-Binding (HB-EGF), betacellulin (BTC), Transforming Growth Factor-α (TGF-α), Epigen (EPGN), amphiregulin (AREG), epiregulin (EREG) and neuregulins (NRG1-4) [19,20]. These molecules share a high affinity for the EGF receptor, a similar response in cells and a typical 35–40 amino acid sequence spaced by 6 conserved cysteines in this order: CX7CX3–5CX10–12CXCX5GXRC (C: cysteine, G: glycine, R: arginine, X: other amino acids). The six cysteines form the three disulphide bonds, which are the hallmark of the EGF-ligand family [21,22].
The EGF receptor (EGFR or ErbB1) has a typical transmembrane structure: an extracellular domain and a tyrosine kinase cytoplasmic domain. EGFR is activated either through an autocrine mechanism, where different stimuli lead to the synthesis of EGFR ligands or through an intra-cellular transactivation process [23].
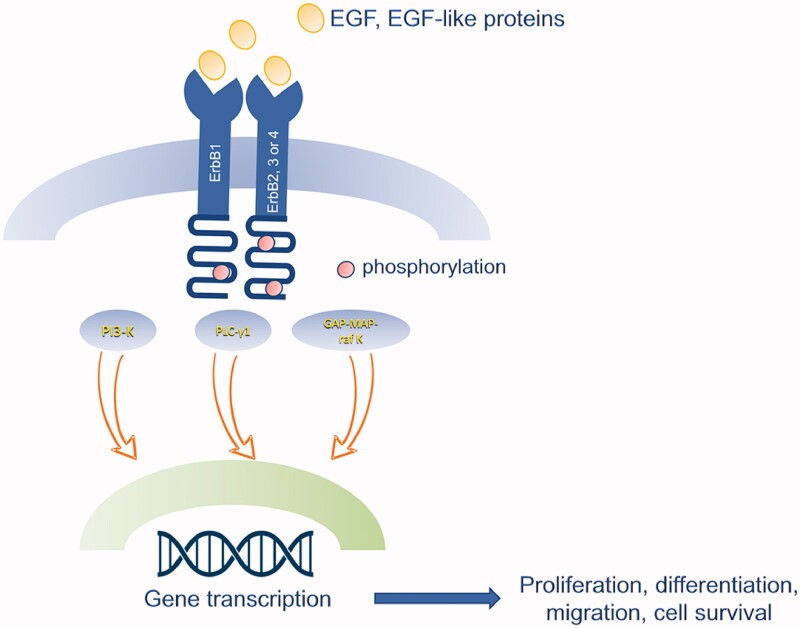
The binding of EGF or EGF-like proteins induces oligomerization of EGFR with ErbB2/c-neu, ErbB3, and ErbB4, and subsequent phosphorylation of the receptor, leading to the transduction of different pathways: PLC-γ1, PI-3 Kinase, GAP-MAP-raf kinase. These pathways are involved in several functions, such as cell proliferation, migration and survival. PI-3 and MAP kinase transduction are also mainly involved in endothelial cells migration and vessel formation in several tissues; thus, they promote angiogenesis (Figure 2) [24,25].
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of EGF signalling pathway. The binding of EGF or EGF-like proteins induces oligomerization of EGFR (ErbB1) with ErbB2/c-neu, ErbB3, and ErbB4, and subsequent phosphorylation of the receptor, leading to the transduction of different pathways: PLC-γ1, PI-3 Kinase, GAP-MAP-raf kinase. These pathways are involved in several functions, such as cell proliferation, migration and survival.
EGFR ligands can be divided into three groups based on the affinity for the different subunits of the receptor. EGF, TGF-α and AREG can only activate ErbB1; NRG1-4 can bind ErbB3 and ErbB4; and finally HB-EGF, BTC and EREG activate both ErbB1 and ErbB4. ErbB2 does not directly bind any ligand but it can dimerise with all the other subunits [23].
The EGF signalling pathway is involved in several tissues at different stages of development. Indeed, EGF stimulates blastocyst formation and embryo implantation [22]. Postnatally, it is required for a proper formation of the gastrointestinal tract, for lactation and for regulation of body mass [24].
EGF also plays a central role in wound healing; exogenous application of EGF associated with several scaffolds represents a valid tool in wound healing [22]. In bone, the EGF signalling pathway has also been involved both in oncological and inflammatory pathologies, as briefly described in the next two sections.
EGF signalling pathway in bone tumours
EGF is implicated in cancer: its tyrosine kinase activity is responsible for tumour survival, growth and metastatization [26]. EGF favours epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and it maintains cancer stemness [27,28]. In bone, this pathway is involved both in primary malignant tumours and in the process of metastases formation. In osteosarcoma, EGF activates the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways, thus leading to cytoskeleton reorganisation, which in turn causes cell proliferation and migration [29,30]. Moreover, EGFR is expressed in osteosarcoma cells, it is associated with a worse prognosis, and it is related to local recurrences and metastatization [31–33]. EGFR activity is also linked to chemotherapy resistance and cell survival under stress conditions, suggesting that the inhibition of EGFR associated with antineoplastic drugs might exert a synergistic effect on tumour progression [31].
In osteolytic bone metastasis, tumour cells secrete osteoclastogenic factors (i.e. RANKL, interleukin-6, PTHrP), which activate osteoclasts. The release of growth factors by the resorbed bone further stimulates cancer cells, thus leading to a vicious cycle [34]. EGF signalling may further sustain this vicious cycle by downregulating the RANKL-antagonist Osteoprotegerin (OPG), ultimately increasing osteoclast activity [34,35].
EGF signalling pathway in osteoarthritis
EGFR activity is also present in the superficial layer of healthy articular cartilage, and it is greatly diminished in osteoarthritic samples [36–38]. This evidence point to the role of the EGF pathway in osteoarthritis (OA), as confirmed by several knockout murine models. Reduced EGFR activity in a murine model increased chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix degradation [39].
Moreover, mice lacking EGFR activity in chondrocytes (EGFR-Col2-Cre) display defective articular cartilage, and they quickly develop OA [40]. EGFR activity promotes chondrocyte proliferation of the superficial layer, it maintains joint lubrication and preserves the mechanical functions of cartilage [40]. Consistent with these findings, the deficiency of Mig6, an inhibitor of EGFR, led to an increased number and thickness of the superficial chondrocytes [38,41,42]. Conditional overexpression of EGFR enhances the pool of chondroprogenitor cells and it delays the process of osteoarthritic degeneration [43].
In contrast, EGFR activity was overexpressed in a subpopulation of OA patients, and in vitro cultures of chondrocytes with EGFR induction demonstrated a role of this pathway in the loss of cartilage homeostasis [44]. The intra-articular application of gefitinib, a specific EGFR inhibitor, ameliorated the OA phenotype in a mouse model [44].
Thus, the EGF signalling pathway has a contradictory role in OA. It is possible that EGFR activity may promote joint degeneration only in a specific subpopulation of OA patients. A different spatial and temporal activation of this pathway may also explain these conflicting results.
These findings open the road for novel therapeutic strategies targeting OA. Intra-articular injections of stabilised TGF-α in OA knees slows down the process of joint degeneration by reducing the catabolic activity, subchondral bone sclerosis and synovitis [43]. On the other hand, gefitinib-mediated EGFR inactivation may improve cartilage homeostasis in a specific subpopulation of OA patients.
EGF is therefore linked to several physiological and pathological bone conditions. In this review, we focussed on the EGF signalling pathway in the first steps of bone formation. We analyse the expression and function of EGF in bone homeostasis, and particularly in the endochondral development of bone.
Materials and methods
We used the string EGF AND endochondral ossification or EGF AND osteogenesis to search the Pubmed and Web of Science databases to identify articles on the role of this growth factor in bone development. We divided these articles based on topics: role of EGF in cell proliferation or differentiation of bone tissue, the role of EGF in endochondral ossification.
Results
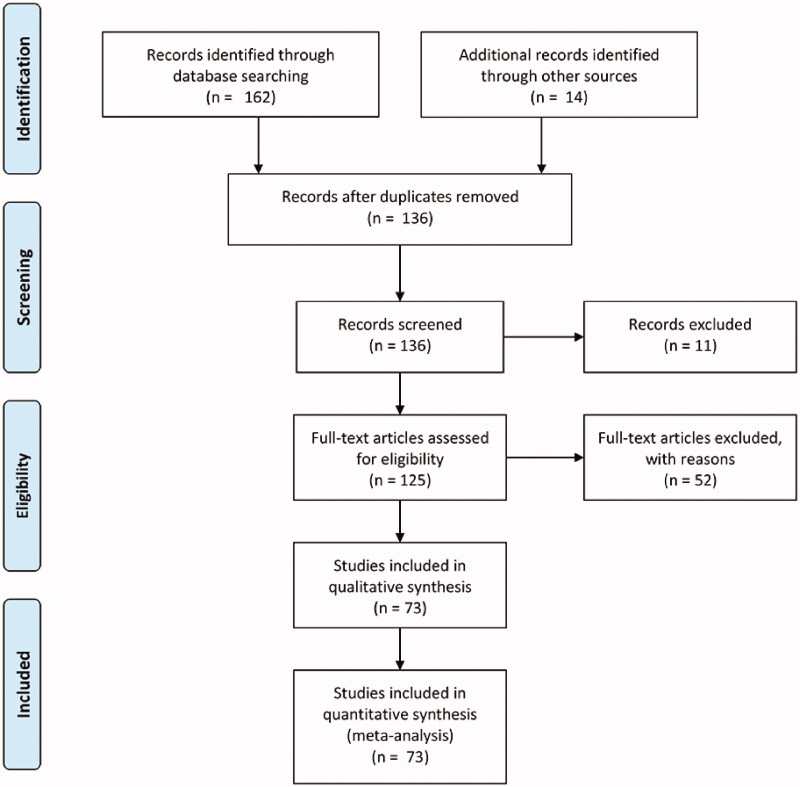
We retrieved 162 articles: 73 manuscripts were included, 11 articles were excluded for the absence of full text, 52 articles were excluded because they studied unrelated topics. The selected manuscripts were divided into two main groups: projects on the role of EGF in proliferation and/or osteogenic differentiation (n = 46), and articles on the role of EGF in endochondral ossification (n = 13). Studies were mainly focused on the role of EGF in proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in vitro (n = 43). Only a few articles specifically analysed the EGF signalling pathway in endochondral ossification (n = 13). We identified additional 14 investigations from the reference lists of those articles to better understand the function of EGF in this developmental process (Figure 3). Based on the analysis of the articles identified, we describe the EGF signalling pathway in bone and in endochondral ossification (Tables 1 and 2).
Figure 3.
PRISMA flow diagram of the present systematic review.
Table 1.
EGF in bone metabolism database.
| Authors | Year | Type of study | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ng, K.W., et al. | 1983 | In vitro, rat osteosarcoma cells | EGF promotes cell proliferation |
| Ng, K.W., et al. | 1983 | In vitro, rat osteosarcoma cells | EGFR is expressed in osteogenic cells |
| Takahashi, N., et al. | 1986 | In vitro, human marrow cultures | TGF-α stimulates osteoclast formation |
| Ibbotson, K.J., et al. | 1986 | In vitro, rat long bones and neonatal mouse calvariae | TGF-α and EGF promote bone resorption |
| Nakayama, Y., et al. | 1990 | In vitro, mouse MC3T3-E1 cells | EGF stimulates proliferation and inhibits differentiation |
| Joos, U.E., et al. | 1992 | In vitro, rat mesenchymal and osteoblast cells | EGF promotes osteogenesis in combination with TGFβ |
| Satomura, K., et al. | 1998 | In vitro, human BMSCs | EGFR is expressed in osteoprogenitors cells |
| Beech, D., et al. | 1998 | In vitro, human soft tissue sarcoma cells | EGF promotes cell proliferation and mitogenesis |
| Yarram, S.J., et al. | 2004 | In vitro, human osteoblast cell line MG63 | EGF and calcitriol promote osteogenic differentiation |
| Lin, H.T., et al. | 2005 | In vitro, human BMSCs | EGF promotes proliferation |
| Qin, L., et al. | 2005 | In vitro, rat osteosarcoma cell line | AREG is expressed in osteoblasts and it is regulated by PTH |
| Tamama K., et al. | 2006 | In vitro, human and rat BMSCs | EGF promotes proliferation of human BMSCs |
| Elabd, C., et al | 2007 | In vitro, human ADSCs | EGF promotes osteogenic differentiation |
| Ozaki Y., et al. | 2007 | In vitro, rabbit and human MSCs | EGF and HB-EGF promote cell migration |
| Grasser, W.A., et al. | 2007 | In vitro, in vivo, human osteoblasts, mouse | EGF and IGF-1 promote osteogenic differentiation upon BMP-6 stimulus |
| Zhu, J., et al. | 2007 | In vitro, mouse osteoblastic cell line | EGF-like ligands stimulate osteoclastogenesis by acting on osteoblastic cells |
| Cheon S.J., et al. | 2008 | In vitro, human ADSCs | EGF and nsulin-transferrin-selenium (ITS) promote proliferation |
| McCarty, R.C., et al. | 2009 | In vitro, in vivo, ovine BMSCs, mouse | TGF-α promotes proliferation |
| Marcantonio, N.A., et al. | 2009 | In vitro, human BMSCs | Tethered EGF stimulates osteogenic differentiation |
| Platt, M.O., et al. | 2009 | In vitro, human BMSCs | Tethered EGF induces osteogenesis |
| Solmesky, L., et al. | 2010 | In vitro, human BMSCs | EGF and bFGF stimulate cell proliferation and migration |
| Laflamme, C., et al. | 2010 | In vitro, osteoblast-like cell line from human osteosarcoma | EGF has a synergistic effect with BMPs on cell proliferation |
| Tamama, K., et al. | 2010 | Review | Role of EGF In MSC proliferation and differentiation |
| Chieregato, K., et al. | 2011 | In vitro, human ADSCs | Combination of EGF, bFGF and PRP supports cell expansion |
| Zhu, J., et al. | 2011 | In vitro, mouse osteoblastic cell line | EGF-ligands suppress osteoblast differentiation and EGFR signalling downregulates Rux-2 and Osterix |
| Zhu, J., et al. | 2012 | In vitro, human and rat BMSCs | AREG stimulates mesenchymal cell migration towards PTH-stimulated osteoblasts |
| Nickerson, N.K., et al. | 2012 | In vitro, in vivo, breast and osteoblast cancer cell lines, mouse | Inhibition of EGFR signalling decreases tumour growth and metastatization |
| Yu, S., et al. | 2013 | In vitro, C2C12/Runx2Dox cells | Runx2 induces osteogenesis by downregulating HB-EGF |
| Keeve, P.L., et al. | 2013 | In vitro, human periodontal and palate cells (pdSCs and paldSCs) | EGF promotes cell migration during osteogenesis |
| Hu, F., et al. | 2013 | In vitro, rat ADSCs | Low concentrations of EGF and bFGF limit osteogenic differentiation |
| Lim, K.T., et al. | 2013 | In vitro, human ABMSC | Fluid shear stress enhances EGF expression during osteogenic differentiation |
| Liu, X., et al. | 2013 | In vitro, in vivo, HEK293, C2C12 and C3H10T1/2 cell lines, mouse foetal limbs, mouse | EGF enhances BMP-9 induced osteogenesis of MSCs |
| Felthaus, O., et al. | 2014 | In vitro, dental follicle cells (DFCs) | EGF does not induce osteogenic differentiation |
| Yang, M., et al. | 2014 | In vitro, MC3T3-E1 cell line, mouse BMSCs and osteoblasts | miR-96 promotes osteogenic differentiation by inhibiting HB-EGF |
| Lee, H.L., et al. | 2014 | In vitro, C2C12 mouse cell line | Smurf1 mediates the inhibitory effect of EGF on BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation |
| Tanaka, U., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, multipotent clonal human periodontal cell line | Spry2 combined with bFGF and EGF stimulation reduced cell migration and proliferation |
| Boonanantanasarn, K., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, HEK293T and C2C12 cell lines | EGF/Smurf1 inhibits Wnt/b catenin induced osteogenic differentiation |
| Del Angel-Mosqueda, C., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) | EGF promotes osteogenic differentiation |
| Lee, J.H., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, in vivo, human MSCs, rat calvarial defects | Combination of EGF and rhBMP-2 enhances bone formation |
| Lee, J.H., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, in vivo, human MSCs, rabbit tibial defects | Combination of EGF and rhBMP-2 enhances bone formation in an orthotopic model |
| Kuek V., et al. | 2016 | In vitro, primary murine osteoblasts | NPNT is expressed in osteoblasts and favours angiogenesis |
| Ai, G., et al. | 2017 | In vitro, human ADSCs | EGF promotes cell proliferation |
| Go, Y.Y., et al. | 2017 | In vitro, MG-63 cell line, human BMSCs | EGF negatively regulates osteogenic differentiation |
| Sun, Y., et al. | 2018 | Review | NPNT, a novel EGF-ligand, is involved in angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling |
| Wang, J., et al. | 2020 | In vitro, murine-macrophage cell line RAW 264.7, human MSCS | Ca-P ceramics increases EGF expression during osteogenic differentiation |
| Zou, W., et al. | 2020 | In vivo, mouse | Modulation of BMP signalling together with short-term EGF receptor activation increase bone mass |
Table 2.
EGF and endochondral ossification database.
| Authors | Year | Type of study | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chenevix-Trench, G., et al. | 1992 | In vivo, human | Cleft palate associated with polymorphism in TGFA gene |
| Threadgill, D.W., et al. | 1995 | In vivo, mouse | EGFR null mice have prenatal and postnatal defects and growth retardation based on the genetic background |
| Miettinen, P.J., et al. | 1995 | In vivo, mouse | EGFR null mice have epithelial alterations and dysfunctions in several tissues and growth retardation |
| Monsonego E., et al. | 1995 | In vitro, avian epiphyseal chondrocytes | EGF and GH increase cell proliferation |
| Huang, L., et al. | 1996 | In vitro, rat micromass culture | TGF-α prevents chondrocyte differentiation |
| Bonassar, L.J., et al. | 1997 | In vitro, rabbit | EGF interacts with IGF-1 in skeletal growth |
| Dealy, C.N., et al. | 1998 | In vitro, embryonic chick limb | Exogenous TGF-a and EGF inhibit chondrogenesis and myogenesis of limb mesenchyme |
| Miettinen, P.J., et al. | 1999 | In vivo, mouse | EGFR null mice have impaired craniofacial development |
| Yoon, Y.M., et al. | 2000 | In vitro, micromass culture of chick limb bud | EGF negatively regulates chondrogenesis by modulating PKC, Erk-1, p38 MAPK |
| Chan, S.Y., et al. | 2000 | In vivo, mouse | Overexpression of human EGF impairs endochondral development |
| Sibilia, M., et al. | 2003–2016 | In vivo, mouse | Mice humanised for EGFS display growth retardation |
| Wang, K., et al. | 2004 | In vivo, mouse | EGFR-deficient mice have delayed primary endochondral ossification |
| Schneider, M.R., et al. | 2005 | In vivo, mouse | BTC overexpressing mice display growth retardation and reduced bone dimensions |
| Fisher, M.C., et al. | 2007 | In vivo, mouse | Inhibition of EGF signalling causes delayed endochondral ossification and impaired chondrocyte and osteoblast proliferation |
| Schneider, M.R., et al. | 2009 | In vivo, mouse | BTC overexpressing mice display increased BMD and bone cortical mass |
| Genetos, D.C., et al. | 2010 | In vitro, human MSCs | BTC promotes proliferation but it inhibits differentiation upon HIF-1α regulation |
| Zhang, X., et al. | 2011 | In vivo, mouse | EGFR conditional knockout in pre-osteoblasts causes reduced trabecular and cortical volume |
| Usmani S.E., et al. | 2012 | In vivo, mouse | TGF-α knockout model shows impaired endochondral development ut to 10 weeks postnatally |
| Hall, K.C., et al., | 2013 | In vivo, in vitro, mouse | ADAM17 conditional knockout in chondrocytes displays a significant expansion of hypertrophic chondrocytes |
| Saito K., et al. | 2013 | In vivo, mouse | TACE conditional knockout in chondrocytes delays hypertrophy through EGFR signalling |
| Pruvot B., et al. | 2014 | In vivo, zebrafish | Inhibition of EGF signalling impairs Meckel’s cartilage development |
| Chim, S.M., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, in vivo, mouse | EGFL7 regulates angiogenesis in bone microenvironment |
| Lin, Y.C., et al. | 2015 | In vitro, in vivo, mouse | Scube2 knockout impairs Ihh-dependent endochondral ossification |
| Wolf, C.J., et al. | 2018 | In vitro, organoids from human umbilical MSCs | EGF promotes proliferation during palate development |
| Li P., et al. | 2019 | In vitro, in vivo, mouse BMSCs, mouse | HB_EGF overexpression in osteoprogenitor cells causes chondrodysplasia, chondromas and sorter long bones |
| Fang, R., et al. | 2020 | In vivo, mouse | iRhoms 1 and 2 conditional knockout in chondrocytes impairs endochondral ossification |
| Lin, Y.C., et al. | 2021 | In vitro, In vivo, mouse, human | Scube3 loss of function causes growth disorders by impairing BMP signalling |
Role of EGF signalling pathway in cell proliferation and differentiation of bone tissue
EGF, EGF-like genes and EGF-R are abundantly expressed in bone tissue, where they play a crucial role in cell proliferation, differentiation and in the coupling osteogenesis-angiogenesis [17,45,46]. Genes encoding for EGF signalling proteins are present in mesenchymal cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and endothelial cells. For example, activation of this pathway stimulates periodontal cell proliferation and inhibits differentiation [47,48].
EGF stimulates the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells [47,49–52]. In rat osteosarcoma cells, EGF induces the expression of Egr-1 mRNA, thus increasing mitogenesis [53]. In addition, a combination of EGF and Bone Morphogenic Proteins, namely BMP-2 and −7, further stimulates cell proliferation in the early differentiation stage, while inhibiting late osteoblast differentiation [53]. EGF also promotes proliferation and migration of mesenchymal cells from different origins (bone marrow, adipose tissue, Human Alveolar Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells, periodontium-derived stem cells) [54–64].
Furthermore, EGF-like proteins are involved in bone metabolism [65]; in particular, amphiregulin (AREG) is highly expressed in preosteoblasts, where it strongly promotes proliferation upon Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulation [66]. The secretion of AREG from osteoblasts and osteocytes stimulates mesenchymal cell chemotaxis and recruitment, thus favouring the anabolic function of PTH in bone [67].
All the EGF-like proteins strongly suppress osteogenesis in different cell lines in vitro [68,69]; EGFR mediates this effect by activating Smurf1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which in turn inhibits Wnt/βcatenin osteogenic differentiation downregulating the master transcription factors of osteoblastogenesis, Runx2 and Osterix [69–75].
Conversely, the EGF signalling pathway has been also involved in osteoblast differentiation [76–81]; in MG63 immature osteoblasts, the combination of calcitriol and EGF leads to an increase in alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin protein expression in a dose-dependent manner [82]. This synergistic effect is mediated by Protein Kinase C (PKC) activation. Furthermore, EGF mediates osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells [83]. In vivo, EGF displayed a synergistic effect with human recombined BMP-2 (hrBMP-2) on bone formation in rat calvarial defects and in tibial defects of rabbits [84,85].
EGF plays a role in signalling in osteoclastogenesis. EGF and TGF-α enhance osteoclast formation in cultures of human marrow, and they promote bone resorption in organ cultures of rat long bones and calvarial bones [86,87]. Moreover, osteoclast proliferation is regulated by EGF-dependent regulation of Osteoprotegerin (OPG) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) expression in osteoblasts [88]. Overall, these studies demonstrate a clear involvement of the EGF pathway in bone metabolism. However, EGF can regulate bone metabolism positively or negatively.
This apparently contradictory effect of the EGF signalling pathway on osteogenesis may be explained by the different experimental conditions, such as the combination of several growth factors or different cell cultures, but also by the different EGF concentrations and temporal distribution. Indeed, strong and continuous signalling from EGF promotes MSC osteogenic differentiation, whereas weak and alternating signalling inhibits differentiation [78,89,90].
Overview
EGF and EGF-like proteins clearly promote cell proliferation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. However, the function of EGF signalling pathway in osteoblast differentiation is still controversial given the differences in the experimental settings. It is highly possible that EGF can differently modulate osteogenesis in vivo depending on the environmental background.
Role of EGF signalling pathway in endochondral bone development
EGF signalling is also greatly implicated in postnatal growth [91]. This pathway regulates mammary gland development and lactation, thus favouring postnatal maturity [24]. Moreover, EGF-R knockout mice die before birth or they present different degrees of growth retardation. Over the years, EGF signalling in limb development has been extensively studied. Cell culture of avian growth plate chondrocytes showed that EGF in combination with Growth Hormone (GH) significantly increase proliferation [92].
Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridisation analyses have shown that TGF-α and TGF-α mRNA are uniformly distributed in the limb-forming mesoderm of embryonic chicks at very early stages of differentiation, whereas they are almost absent in non-limb forming areas [93]. At later stages, neither TGF-α nor EGF are present in cartilage or muscle. Moreover, in limb-bud explants in vitro cultures, exogenous TGF-α or EGF dramatically increase proliferation but inhibit in vitro chondrogenesis. Micromass in vitro cultures of mesenchymal cells confirmed these findings, as TGF-α or EGF addition prevents chondrocytes differentiation [93]. In particular, the addition of TGF-α to micro masses of rat limb buds decreases cartilage nodule formation up to 50% in a dose-dependent manner [94]. EGF signalling pathway acts on mesenchymal cells by downregulating PKCα, which in turn leads to ERK-1 phosphorylation, and ultimately to inhibition of chondrogenesis [95]. EGF also performs its action by inhibiting the p38 MAP kinase. Therefore, EGF plays an important role in preventing pre-cartilage condensation. In vitro EGF interacts with IGF-1, an important growth factor in skeletal development, by increasing IGF-1 receptors’ number and responsiveness to signals [96].
Interestingly, BTC promotes the proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells and pre-osteoblasts but it inhibits differentiation. This effect is mediated by Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α), which is essential for endochondral bone development [10,11,97]. These findings further prove that endochondral ossification is finely tuned by the EGF signalling pathway.
More recently, in vivo models have been analysed to confirm the essential role of the EGF pathway in bone growth. EGFR knockout mice were stillbirth or lived only up to 6–8 days, displaying epithelial alterations and dysfunctions in several tissues, such as lungs and intestine. Interestingly, up to one-third of those mice had cleft palates, from retardation in skeletal development [98,99]. In humans, the cleft palate has been associated with polymorphism in TGFA gene, encoding for TGF-α, thus linking this condition to the EGF pathway [100]. Palate growth requires a correct development of the mandibular Meckel’s cartilage, and palate explants of Egfr-\- mice showed a decrease in the dimensions of Meckel’s cartilage, with the presence of undifferentiated cells with lower content of proteoglycans, consistent with an EGF-dependent modulation of chondrogenesis [101]. MMPs, downstream targets of EGF, mediate this phenotype [101]. Moreover, in vitro culture of palate organoids with human MSCs from the umbilical cord demonstrated that EGF significantly promoted proliferation, further proving its involvement in osteogenesis [102]. EGF-like protein signalling has also been associated with other human conditions characterised by growth retardation and skeletal abnormalities from impaired endochondral ossification [103,104].
To better understand the role of EGF signalling in postnatal growth, a rescue experiment was performed [105,106]. In this study, a conditional knock-in mouse model for human EGFR was bred with Egfr-\- mice to analyse the effects of lower levels of EGFR in different tissues, as the rescue was only partial. In long developing bones, the hypertrophic chondrocyte layer was expanded, probably from a delay in the formation of the primary ossification centre. Moreover, the culture of primary osteoblasts was characterised by decreased proliferation; conversely, differentiation was promoted [105,106].
Further in vivo studies have been performed to better clarify whether postnatal growth delay was EGF-dependent. Transgenic mice overexpressing human EGF were characterised by a significant decrease in body weight at birth and by alterations in endochondral development [107]. Namely, hEGF was detected in some proliferating and in all hypertrophic chondrocytes and its expression lead to a delay of hypertrophy. Moreover, an abnormal accumulation of osteoblasts was found both at the periosteum and at the endosteum of long bones, associated with a decrease in cortical bone thickness [107].
As mentioned above, the EGFR signalling is involved both in bone deposition and resorption [108,109]. Indeed, EGFR mRNA was detected in vitro in osteoclasts. Moreover, a significantly decreased number of TRAP + cells, namely pre-osteoclasts, were detected in Egfr-\- mice at E16.5; these cells in wild type mice were mainly distributed inside the calcifying cartilage, whereas in Egfr-\- mice these cells lie at the periphery of the hypertrophic layer. This phenotype was then rescued at E18.5 and at birth. E18.5 Egfr-\- mice were also characterised both by an enlargement of the hypertrophic layer and by the presence of very few bone trabeculae, probably from a delay in the initial recruitment of osteoblasts, as indicated by the altered distribution of these cells in the primary ossification centre [108]. Also, trabecular bone mass was reduced up to birth in these knockout mice, possibly from impaired cell proliferation [49,50].
Modulation of EGF-like proteins produces similar phenotypes. TGF-α newborn knockout mice displayed shorter limbs, enlarged hypertrophic layer, and delayed secondary ossification; interestingly, the phenotype was rescued after 10 weeks [110].
Transgenic mice overexpressing BTC displayed growth retardation and reduced bone dimensions [111]. Histomorphometric analyses of transgenic bones showed a significant increase in bone mineral density (BMD) of femora but not in vertebrae, probably from a different spatial expression of the transgene. Moreover, cortical thickness was significantly higher in those mice compared to controls, and the number and thickness of trabeculae were also increased; lastly, the hypertrophic layer of the growth plate was reduced. These phenotypes were EGFR-dependent, consistently with previous findings [111,112].
However, whole knockout models do not allow for a clear definition of the role of a molecule or a pathway in a specific tissue; thus, conditional knockouts have been recently developed to overcome this issue. Related to the EGF signalling pathway, a limb bud specific knockout mouse model has been analysed; in these animals, a negative regulator of ErbB2 (Herstatin) has been activated under the control of Prx1 promoter, which is expressed in the limb bud mesenchyme. Embryos displayed several alterations in endochondral development: shorter limbs, an enlarged hypertrophic layer, and a delayed primary ossification centre. Moreover, chondrocyte proliferation was impaired and expression of osteocalcin in primary osteoblasts was reduced. Interestingly, the phenotype was completely rescued by day 18.5 [113]. Conditional knockout of ADAM17, an essential disintegrin for the EGF signalling pathway, and of its regulators (Rhomboids 1 and 2) in chondrocytes confirmed these findings, as transgenic mice displayed a significant expansion of the hypertrophic layer, probably from an alteration in bone remodelling [114–116].
Moreover, conditional knockout of EGFR in preosteoblasts and osteoblasts caused shorter limbs in adult mice, and histomorphometric analyses confirmed a striking bone phenotype characterised by reduced trabecular bone volume from reduced trabecular number and thickness, and reduced cortical area, thus proving an alteration in bone formation [117]. These findings were also confirmed by the significant reduction in mesenchymal cell and osteoblast number [117].
In the end, the inhibition of EGF signalling affects several stages of endochondral bone development. This pathway positively regulates chondrocyte proliferation, negatively modulates hypertrophy and favours cartilage replacement by bone. Also, overexpression of HB-EGF in osteoprogenitor cells leads to postnatal chondrodysplasia, chondromas and shorter long bones from increased cell proliferation associated with inhibition of osteogenic differentiation [118].
Overall, these in vitro and in vivo results suggest that EGF signalling is essential in the very early stages of limb development by maintaining cells in an undifferentiated stage; thus, the decrease of EGF expression is critically important to promote the first phases of chondrogenesis.
Overview
EGF and EGF-like proteins are expressed in the limb bud mesenchyme. This pathway contributes to mesenchymal cell proliferation, thus favouring the first proliferative phase of endochondral bone development. Negative modulation of its expression is then critical to support the next phases of endochondral ossification.
Future and outlook
This comprehensive review of the literature highlights the function of EGF in bone development. This pathway is clearly involved in the first phases of endochondral ossification and in bone homeostasis. However, some points are still controversial and should be further investigated. A better knowledge of the in vivo modulation of this pathway in osteogenesis is desirable. As reported above, the spatial and temporal distribution of EGF activity is critical to determine the final effect on bone cells. Moreover, a deeper understanding of the role of EGF in the fine balance between bone formation and bone resorption would allow to plan novel therapeutic approaches to bone pathologies.
Discussion
EGF and EGF-like proteins finely tune the proliferation and differentiation of bone tissue cells, and they also regulate the initial phases of endochondral ossification. These findings are crucial in light of possible clinical applications. Indeed, several orthopaedic conditions may benefit from the activation of the EGF signalling pathway. For example, EGF or EGF-like proteins together with other stimuli (i.e. BMP-2) may favour the first phases of fracture healing, which recapitulate endochondral bone development [84,85]. In particular, the use of AREG in combination with scaffolds may stimulate MSC migration, thus favouring osteogenesis in the early phases of nonunions [67].
Thus, the EGF signalling pathway may enhance bone restoration in nonunions, characterised by a delay in fracture healing from poor vascularisation or from a lack of mechanical stability at the site of fracture [119,120]. Moreover, EGF may be combined with osteogenic scaffolds to fill large bone losses caused by traumas or tumours [47,121–124].
Further in vitro and in vivo investigations are necessary to better define the ideal conditions for bone restoration. As mentioned above, different experimental conditions, such as spatial and temporal distribution of the molecule or cell type, can lead to seemingly contrasting results, with EGF promoting or inhibiting cell proliferation and differentiation.
Furthermore, the EGF pathway is clearly involved in several malignancies [26]; thus, preclinical studies in vitro and in animal models are required to evaluate the possible long-term oncogenic effects arising from an enhancement of EGF signalling.
Disclosure statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Data availability statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
References
- 1.Galea GL, et al. Making and shaping endochondral and intramembranous bones. Dev Dyn. 2021;250(3):414–449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maes C, Carmeliet P, Moermans K, et al. Impaired angiogenesis and endochondral bone formation in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Mech Dev. 2002;111(1–2):61–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zelzer E, McLean W, Ng Y-S, et al. Skeletal defects in VEGF(120/120) mice reveal multiple roles for VEGF in skeletogenesis. Development. 2002;129(8):1893–1904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Provot S, Schipani E.. Molecular mechanisms of endochondral bone development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3):658–665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matsushita Y, Ono W, Ono N.. Growth plate skeletal stem cells and their transition from cartilage to bone. Bone. 2020;136:115359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Akiyama H, Chaboissier M-C, Martin JF, et al. The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 2002;16(21):2813–2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Akiyama H, Lyons JP, Mori-Akiyama Y, et al. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004;18(9):1072–1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dy P, Wang W, Bhattaram P, et al. Sox9 directs hypertrophic maturation and blocks osteoblast differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes. Dev Cell. 2012;22(3):597–609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mangiavini L, Merceron C, Araldi E, et al. Loss of VHL in mesenchymal progenitors of the limb bud alters multiple steps of endochondral bone development. Dev Biol. 2014;393(1):124–136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schipani E, Mangiavini L, Merceron C.. HIF-1α and growth plate development: what we really know. Bonekey Rep. 2015;4:730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schipani E, Ryan HE, Didrickson S, et al. Hypoxia in cartilage: HIF-1alpha is essential for chondrocyte growth arrest and survival. Genes Dev. 2001;15(21):2865–2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zelzer E, Mamluk R, Ferrara N, et al. VEGFA is necessary for chondrocyte survival during bone development. Development. 2004;131(9):2161–2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Karsenty G, Wagner EF.. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev Cell. 2002;2(4):389–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kronenberg HM. Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature. 2003;423(6937):332–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ornitz DM, Marie PJ.. FGF signaling pathways in endochondral and intramembranous bone development and human genetic disease. Genes Dev. 2002;16(12):1446–1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang X, Siclari VA, Lan S, et al. The critical role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in endochondral ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(11):2622–2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, et al. Angiogenic factors in bone local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24(3):297–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cohen S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harris RC, Chung E, Coffey RJ.. EGF receptor ligands. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284(1):2–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Carpenter G, Zendegui JG.. Epidermal growth factor, its receptor, and related proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1986;164(1):1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Savage CR, Jr., Hash JH, Cohen S.. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zeng F, Harris RC.. Epidermal growth factor, from gene organization to bedside. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;28:2–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wong RW. Transgenic and knock-out mice for deciphering the roles of EGFR ligands. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(1):113–118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xian CJ. Roles of epidermal growth factor family in the regulation of postnatal somatic growth. Endocr Rev. 2007;28(3):284–296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zanetti-Domingues LC, Bonner SE, Martin-Fernandez ML, et al. Mechanisms of action of EGFR tyrosine kinase receptor incorporated in extracellular vesicles. Cells. 2020;9(11):2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gomez GG, Wykosky J, Zanca C, et al. Therapeutic resistance in cancer: microRNA regulation of EGFR signaling networks. Cancer Biol Med. 2013;10(4):192–205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vergara D, Merlot B, Lucot J-P, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010;291(1):59–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kfoury Y, Scadden DT.. Mesenchymal cell contributions to the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):239–253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang J, et al. Rho a regulates epidermal growth factor-induced human osteosarcoma MG63 cell migration. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;1;19(5):1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li D, et al. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-Dependent Protein Kinase II Blocks Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Induced Biological Effects on Osteosarcoma Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:1997–2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sevelda F, et al. EGFR is not a major driver for osteosarcoma cell growth in vitro but contributes to starvation and chemotherapy resistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34:134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lee JA, Ko Y, Kim DH, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor: is it a feasible target for the treatment of osteosarcoma? Cancer Res Treat. 2012;44(3):202–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wen YH, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor in osteosarcoma: expression and mutational analysis. Hum Pathol. 2007;38(8):1184–1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lu X, Kang Y.. Epidermal growth factor signalling and bone metastasis. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(3):457–461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lu X, et al. ADAMTS1 and MMP1 proteolytically engage EGF-like ligands in an osteolytic signaling Cascade for bone metastasis. Genes Dev. 2009;23(16):1882–1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Citri A, Yarden Y.. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(7):505–516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Appleton CT, et al. Transforming growth factor alpha suppression of articular chondrocyte phenotype and Sox9 expression in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3693–3705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Staal B, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of mig-6 results in osteoarthritis-like disorder with excessive articular chondrocyte proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(7):2590–2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang X, Zhu J, Liu F, et al. Reduced EGFR signaling enhances cartilage destruction in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Bone Res. 2014;2:14015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jia H, Ma X, Tong W, et al. EGFR signaling is critical for maintaining the superficial layer of articular cartilage and preventing osteoarthritis initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(50):14360–14365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pest MA, Russell BA, Zhang Y-W, et al. Disturbed cartilage and joint homeostasis resulting from a loss of mitogen-inducible gene 6 in a mouse model of joint dysfunction. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(10):2816–2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shepard JB, Jeong J-W, Maihle NJ, et al. Transient anabolic effects accompany epidermal growth factor receptor signal activation in articular cartilage in vivo. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(3):R60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wei Y, et al. Targeting cartilage EGFR pathway for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(576):eabb3946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sun H, Wu Y, Pan Z, et al. Gefitinib for epidermal growth factor receptor activated osteoarthritis subpopulation treatment. EBioMedicine. 2018;32:223–233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nickerson NK, Mohammad KS, Gilmore JL, et al. Decreased autocrine EGFR signaling in metastatic breast cancer cells inhibits tumor growth in bone and mammary fat pad. PLOS One. 2012;7(1):e30255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nakayama Y, Takahashi K, Noji S, et al. Functional modes of retinoic acid in mouse osteoblastic clone MC3T3-E1, proved as a target cell for retinoic acid. FEBS Lett. 1990;261(1):93–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang J, Chen X, Yang X, et al. Positive role of calcium phosphate ceramics regulated inflammation in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(6):1305–1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tanaka U, Sanui T, Fukuda T, et al. Sprouty2 inhibition promotes proliferation and migration of periodontal ligament cells. Oral Dis. 2015;21(8):977–986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ng KW, Partridge NC, Niall M, et al. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor in osteoblast-like cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1983;35(4–5):624–628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ng KW, Partridge NC, Niall M, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptors in clonal lines of a rat osteogenic sarcoma and in osteoblast-rich rat bone cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1983;35(3):298–303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Satomura K, Derubeis AR, Fedarko NS, et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase expression in human bone marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 1998;177(3):426–438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Beech D, Pollock RE, Tsan R, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor expression and function in human soft-tissue sarcoma cells. Int J Oncol. 1998;12(2):329–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Laflamme C, Curt S, Rouabhia M.. Epidermal growth factor and bone morphogenetic proteins upregulate osteoblast proliferation and osteoblastic markers and inhibit bone nodule formation. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(9):689–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hu F, Wang X, Liang G, et al. Effects of epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and osteogenic and neural differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2013;15(3):224–232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lim K-T, Kim J, Seonwoo H, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of human alveolar bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells for tooth tissue engineering using fluid shear stress in a rocking culture method. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19(2):128–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Keeve PL, Dittmar T, Gassmann G, et al. Characterization and analysis of migration patterns of dentospheres derived from periodontal tissue and the palate. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(3):276–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chieregato K, Castegnaro S, Madeo D, et al. Epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor-bb can substitute for fetal bovine serum and compete with human platelet-rich plasma in the ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from adipose tissue. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8):933–943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Solmesky L, Lefler S, Jacob-Hirsch J, et al. Serum free cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as a platform to characterize the effects of specific molecules. PLOS One. 2010;5(9):e12689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ai G, Shao X, Meng M, et al. Epidermal growth factor promotes proliferation and maintains multipotency of continuous cultured adipose stem cells via activating STAT signal pathway in vitro. Medicine. 2017;96(30):e7607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Felthaus O, Gosau M, Ettl T, et al. Migration of human dental follicle cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2014;49(2):205–212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lin H-T, Tarng Y-W, Chen Y-C, et al. Using human plasma supplemented medium to cultivate human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell and evaluation of its multiple-lineage potential. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(10):4504–4505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tamama K, Fan VH, Griffith LG, et al. Epidermal growth factor as a candidate for ex vivo expansion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):686–695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ozaki Y, Nishimura M, Sekiya K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of chemotactic factors for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16(1):119–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cheon SJ, Kim JI, Lee JS.. Effects of growth factors and kinase inhibitors on the properties of human adipose-stromal cells in different culture conditions. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(7):784–791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.McCarty RC, Gronthos S, Zannettino AC, et al. Characterisation and developmental potential of ovine bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(2):324–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Qin L, Partridge NC.. Stimulation of amphiregulin expression in osteoblastic cells by parathyroid hormone requires the protein kinase a and cAMP response element-binding protein signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2005;96(3):632–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhu J, Siclari VA, Liu F, et al. Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling mediates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors toward PTH-stimulated osteoblasts and osteocytes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kuek V, Yang Z, Chim SM, et al. NPNT is expressed by osteoblasts and mediates angiogenesis via the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sun Y, Kuek V, Qiu H, et al. The emerging role of NPNT in tissue injury repair and bone homeostasis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3):1887–1894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhu J, Shimizu E, Zhang X, et al. EGFR signaling suppresses osteoblast differentiation and inhibits expression of master osteoblastic transcription factors Runx2 and osterix. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7):1749–1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yu S, Geng Q, Ma J, et al. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor and miR-1192 exert opposite effect on Runx2-induced osteogenic differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lee H-L, Park H-J, Kwon A, et al. Smurf1 plays a role in EGF inhibition of BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2014;323(2):276–287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Boonanantanasarn K, Lee H-L, Baek K, et al. EGF inhibits Wnt/β-catenin-induced osteoblast differentiation by promoting β-catenin degradation. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(12):2849–2857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Go YY, Kim SE, Cho GJ, et al. Differential effects of amnion and chorion membrane extracts on osteoblast-like cells due to the different growth factor composition of the extracts. PLOS One. 2017;12(8):e0182716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Yang M, Pan Y, Zhou Y.. miR-96 promotes osteogenic differentiation by suppressing HBEGF-EGFR signaling in osteoblastic cells. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(24):4761–4768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zou W, Rohatgi N, Brestoff JR, et al. Ablation of fat cells in adult mice induces massive bone gain. Cell Metab. 2020;32(5):801–813 e6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Liu X, Qin J, Luo Q, et al. Cross-talk between EGF and BMP9 signalling pathways regulates the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(9):1160–1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Platt MO, Roman AJ, Wells A, et al. Sustained epidermal growth factor receptor levels and activation by tethered ligand binding enhances osteogenic differentiation of multi-potent marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;221(2):306–317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Grasser WA, Orlic I, Borovecki F, et al. BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect through activation of IGF-I and EGF pathways. Int Orthop. 2007;31(6):759–765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Joos UE, Fehrenbach E, Hogh-Janovsky K, et al. Effects of a new bone-inducing biomaterial on mesenchymal cells in vitro. Artif Organs. 1992;16(4):354–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Elabd C, Chiellini C, Massoudi A, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived multipotent stem cells differentiate in vitro and in vivo into osteocyte-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(2):342–348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yarram SJ, Tasman C, Gidley J, et al. Epidermal growth factor and calcitriol synergistically induce osteoblast maturation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;220(1–2):9–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Del Angel-Mosqueda C, Gutiérrez-Puente Y, López-Lozano AP, et al. Epidermal growth factor enhances osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells in vitro. Head Face Med. 2015;11:29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lee JH, Jang S-J, Baek H-R, et al. Synergistic induction of early stage of bone formation by combination of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and epidermal growth factor. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(4):447–459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lee JH, Baek H-R, Lee KM, et al. Enhanced osteoinductivity of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in combination with epidermal growth factor in a rabbit tibial defect model. Growth Factors. 2015;33(1):31–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Takahashi N, MacDonald BR, Hon J, et al. Recombinant human transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells in long-term human marrow cultures. J Clin Invest. 1986;78(4):894–898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ibbotson KJ, Harrod J, Gowen M, et al. Human recombinant transforming growth factor alpha stimulates bone resorption and inhibits formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83(7):2228–2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhu J, Jia X, Xiao G, et al. EGF-like ligands stimulate osteoclastogenesis by regulating expression of osteoclast regulatory factors by osteoblasts: implications for osteolytic bone metastases. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):26656–26664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Marcantonio NA, Boehm CA, Rozic RJ, et al. The influence of tethered epidermal growth factor on connective tissue progenitor colony formation. Biomaterials. 2009;30(27):4629–4638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tamama K, Kawasaki H, Wells A.. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) treatment on multipotential stromal cells (MSCs). possible enhancement of therapeutic potential of MSC. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:795385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Pruvot B, Curé Y, Djiotsa J, et al. Developmental defects in zebrafish for classification of EGF pathway inhibitors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;274(2):339–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Monsonego E, Halevy O, Gertler A, et al. Growth hormone inhibits differentiation of avian epiphyseal growth-plate chondrocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1995;114(1–2):35–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Dealy CN, Scranton V, Cheng HC.. Roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor in chick limb development. Dev Biol. 1998;202(1):43–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Huang L, Solursh M, Sandra A.. The role of transforming growth factor alpha in rat craniofacial development and chondrogenesis. J Anat. 1996;189(Pt 1):73–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yoon YM, Oh CD, Kim DY, et al. Epidermal growth factor negatively regulates chondrogenesis of mesenchymal cells by modulating the protein kinase C-alpha, erk-1, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(16):12353–12359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bonassar LJ, Trippel SB.. Interaction of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-I in the regulation of growth plate chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1997;234(1):1–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Genetos DC, Rao RR, Vidal MA.. Betacellulin inhibits osteogenic differentiation and stimulates proliferation through HIF-1alpha. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;340(1):81–89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Miettinen PJ, Berger JE, Meneses J, et al. Epithelial immaturity and multiorgan failure in mice lacking epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1995;376(6538):337–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Threadgill DW, Dlugosz AA, Hansen LA, et al. Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science. 1995;269(5221):230–234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chenevix-Trench G, Jones K, Green AC, et al. Cleft lip with or without cleft palate: associations with transforming growth factor alpha and retinoic acid receptor loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1992;51(6):1377–1385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Miettinen PJ, Chin JR, Shum L, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor function is necessary for normal craniofacial development and palate closure. Nat Genet. 1999;22(1):69–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wolf CJ, Belair DG, Becker CM, et al. Development of an organotypic stem cell model for the study of human embryonic palatal fusion. Birth Defects Res. 2018;110(17):1322–1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Lin Y-C, Niceta M, Muto V, et al. SCUBE3 loss-of-function causes a recognizable recessive developmental disorder due to defective bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108(1):115–133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lin Y-C, Roffler SR, Yan Y-T, et al. Disruption of Scube2 impairs endochondral bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(7):1255–1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Sibilia M, Wagner B, Hoebertz A, et al. Correction: Mice humanised for the EGF receptor display hypomorphic phenotypes in skin, bone and heart. Development. 2016;143(24):4755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sibilia M, Wagner B, Hoebertz A, et al. Mice humanised for the EGF receptor display hypomorphic phenotypes in skin, bone and heart. Development. 2003;130(19):4515–4525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Chan SY, Wong RW.. Expression of epidermal growth factor in transgenic mice causes growth retardation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(49):38693–38698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Wang K, Yamamoto H, Chin JR, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-deficient mice have delayed primary endochondral ossification because of defective osteoclast recruitment. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(51):53848–53856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chim SM, Kuek V, Chow ST, et al. EGFL7 is expressed in bone microenvironment and promotes angiogenesis via ERK, STAT3, and integrin signaling Cascades. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(1):82–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Usmani SE, Pest MA, Kim G, et al. Transforming growth factor alpha controls the transition from hypertrophic cartilage to bone during endochondral bone growth. Bone. 2012;51(1):131–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Schneider MR, Dahlhoff M, Herbach N, et al. Betacellulin overexpression in transgenic mice causes disproportionate growth, pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome, and complex eye pathology. Endocrinology. 2005;146(12):5237–5246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Schneider MR, Mayer-Roenne B, Dahlhoff M, et al. High cortical bone mass phenotype in betacellulin transgenic mice is EGFR dependent. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(3):455–467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fisher MC, Clinton GM, Maihle NJ, et al. Requirement for ErbB2/ErbB signaling in developing cartilage and bone. Dev Growth Differ. 2007;49(6):503–513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hall KC, Hill D, Otero M, et al. ADAM17 controls endochondral ossification by regulating terminal differentiation of chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(16):3077–3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Fang R, Haxaire C, Otero M, et al. Role of iRhoms 1 and 2 in endochondral ossification. IJMS. 2020;21(22):8732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Saito K, Horiuchi K, Kimura T, et al. Conditional inactivation of TNFα-converting enzyme in chondrocytes results in an elongated growth plate and shorter long bones. PLOS One. 2013;8(1):e54853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Zhang X, Tamasi J, Lu X, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor plays an anabolic role in bone metabolism in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(5):1022–1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Li P, Deng Q, Liu J, et al. Roles for HB-EGF in mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation and differentiation during skeletal growth. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(2):295–309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Rodriguez-Merchan EC. A review of recent developments in the molecular mechanisms of bone healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Forriol F.. Nonunion: general principles and experimental data. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;419:4–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.El-Fiqi A, Mandakhbayar N, Jo SB, et al. Nanotherapeutics for regeneration of degenerated tissue infected by bacteria through the multiple delivery of bioactive ions and growth factor with antibacterial/angiogenic and osteogenic/odontogenic capacity. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):123–136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Liu L, Chen Y, Song D, et al. BMP9 is a potential therapeutic agent for use in oral and maxillofacial bone tissue engineering. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020;48(3):1269–1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Mishra R, Sefcik RS, Bishop TJ, et al. Growth factor dose tuning for bone progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation on resorbable poly(propylene fumarate) scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(9):904–913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Eyckmans J, Roberts SJ, Bolander J, et al. Mapping calcium phosphate activated gene networks as a strategy for targeted osteoinduction of human progenitors. Biomaterials. 2013;34(19):4612–4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.