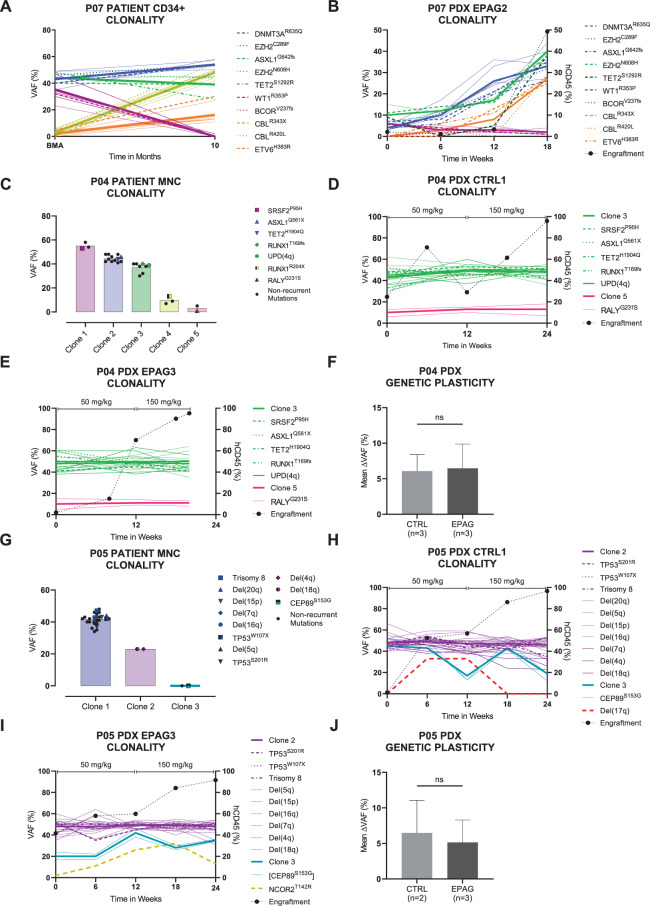
Fig. 6. EPAG treatment does not affect clonal evolution in MDS patient-derived xenografts compared to vehicle control.
Bone marrow clonality of patients and exemplary xenografts during 18–24 weeks of experiment reconstructed by clustering of variant allele frequencies (VAFs) using the bioinformatic tool SciClone. Mutations within the same clone are equally colored. Thicker lines represent the mean clonal VAF. Non-synonymous mutations are displayed with superscripted amino acid change. Dotted black line describes the course of human engraftment. See also Supplementary Fig. S8A–Z for additional data. A, B VAFs of patient P07’s CD34+ cells in the course of 10 months and human CD45+ (hCD45+) cells from EPAG2. C–E VAFs of patient P04’s mononuclear cells (MNCs) and hCD45+ cells from CTRL1 and EPAG3. Dose was escalated after 12 weeks from 50 to 150 mg/kg. EPAG3 had to be eliminated after 20 weeks due to excessive weight loss. F Total mean deltaVAF of P04’s n = 3 CTRL and n = 3 EPAG xenografts. G–I VAFs of patient P05’s MNCs and hCD45+ cells from CTRL1 and EPAG3. Dose was escalated after 12 weeks from 50 to 150 mg/kg. J Total mean deltaVAF of P05’s n = 2 CTRL and n = 3 EPAG xenografts. Data in F and J were analyzed using unpaired, two-tailed t-test and is represented as mean ± SD. ns, not significant; EPAG, eltrombopag; BMA, bone marrow aspiration.