Abstract
Several radiopharmaceuticals targeting fibroblast activation protein (FAP) based on the highly potent FAP inhibitor UAMC1110 are currently under investigation. Pre-clinical as well as clinical research exhibited the potential of these imaging agents. However, the monomeric small molecules seemed to have a short retention time in the tumor in combination with fast renal clearance. Therefore, our strategy was to develop homodimeric systems having two FAP inhibitors to improve residence time and tumor accumulation. The homodimers with two squaramide coupled FAP inhibitor conjugates DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 and DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 were synthesized and radiochemically evaluated with gallium-68. [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was tested for its in vitro stability, lipophilicity and affinity properties. In addition, human PET/CT scans were performed for [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 with a head-to-head comparison with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [18F]FDG. Labeling with gallium-68 demonstrated high radiochemical yields. Inhibition measurements revealed excellent affinity and selectivity with low nanomolar IC50 values for FAP. In PET/CT human studies, significantly higher tumor uptake as well as longer tumor retention could be observed for [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 compared to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi. Therefore, the introduction of the dimer led to an advance in human PET imaging indicated by increased tumor accumulation and prolonged retention times in vivo and thus, the use of dimeric structures could be the next step towards prolonged uptake of FAP inhibitors resulting in radiotherapeutic analogs of FAP inhibitors.
Keywords: Fibroblast activation protein, homodimer, gallium-68, lutetium-177, DOTA, DOTAGA, squaric acid, squaramide
Introduction
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a member of the S9 family of serine proteases. In addition to FAP, this S9 family includes other closely related proline-specific serine proteases, such as prolyl oligopeptidase (PREP) and the dipeptidyl peptidases 4, 8, and 9 (DPP4, DPP8, and DPP9) [1]. FAP, a specific marker of myofibroblasts, has become a target of great interest, especially in the field of cancer diagnostics. Many radiotracers based on the highly selective FAP inhibitor UAMC1110 were developed and already used in different (pre-)clinical trials [2-9]. Recently, our group reported FAP inhibitor (FAPi) PET tracers containing squaramide (SA) as a linker moiety coupled to bifunctional DOTA and DATA5m chelators [10]. These precursors and their non-radioactive metal (natGa and natLu) complexes demonstrated very potent in vitro inhibition of FAP in combination with a high selectivity with respect to prolyl endopeptidase (PREP). A preclinical µPET study and ex vivo biodistribution indicated high accumulation in tumor and overall, very low background activity at 1 h p.i. in HT-29 colon cancer tumor-bearing mice. Both [68Ga]Ga-DATA5m.SA.FAPi and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi were examined in clinical PET/CT studies. Kreppel et al. showed specific uptake of [68Ga]Ga-DATA5m.SA.FAPi in focal nodular hyperplasia [11]. Ballal and Yadav et al. executed clinical trials with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi in patients holding various end-stage cancer types [12]. The same authors have performed a first theranostic approach of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT and [177Lu]Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi radiotherapy in an end-stage breast cancer patient [13]. Yet, prolongation of residence times in stroma tissue appears to be one of the key challenges to turn FAP inhibitors into radiotherapeutics.
An approach to improve tumor accumulation as well as retention time is the formation of dimeric derivatives. Already in 2009 our group reported DOTA-based homodimers containing two separated tyrosine units [14,15]. Later, Chauhan et al. published bivalent chalcones bound to DTPA to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease [16]. This homodimeric PET tracer displayed high affinity towards Aβ aggregates and high brain uptake in vivo. Later, the same group also published another chalcone-containing homodimeric tracer labeled with carbon-11. A higher binding affinity and higher brain uptake were observed for the latter compared to the corresponding monomeric tracer [17]. Liolios et al. observed comparable in vivo behavior and slightly better in vitro cell binding for dimeric HBED-CC coupled bombesin GRPR-antagonists, when compared to the monomeric analogs [18]. In 2019, Zia et al. published PSMA targeting mono- and bivalent PET tracers equipped with a sarcophagine chelator. They reported significantly increased tumor uptake with low background and retention for a homodimeric, copper-64 complexed structure than the corresponding monomeric analogue [19].
These desirable effects of bivalent structures with regard to the increased tumor accumulation and prolonged tumor retention time have led us to develop the two homodimeric structures DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 and DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 with squaramide-conjugated FAP inhibitors (Figure 1). The SA.FAPi moieties are connected via a central, bifunctional DOTA or DOTAGA chelator, respectively. As common substructure, they contain the SA.FAPi monomer that we reported earlier [10]. Non-radioactive complexes [natGa]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2, [natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 were synthesized and tested in vitro for their inhibitory potential to FAP and their selectivity against the DPPs and PREP. Radiolabeling and stability tests were determined with gallium-68 for DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 and DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2. Lipophilicity comparison was determined with [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and the monomer [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi. Furthermore, clinical investigations were carried out including a head-to-head comparison with the DOTA.SA.FAPi monomer and the homodimer DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 addressing both absolute tumor accumulation and kinetics uptake.
Figure 1.
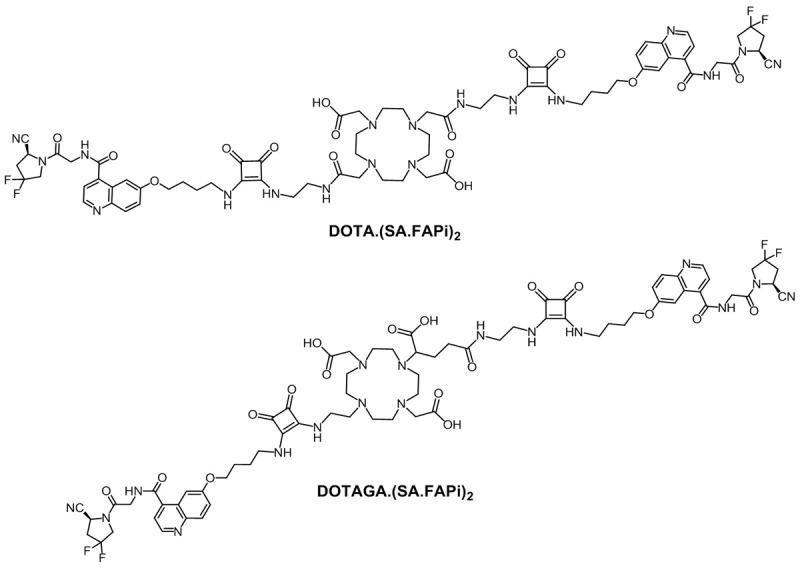
DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 and DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2.
Materials and methods
General reagents and instrumentations
All basic chemicals were bought from Acros Organics (Schwerte, Germany), Alfa Aesar, Thermo Fisher Scientific (Kandel, Germany), Merck and Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany), TCI (Eschborn, Germany) ABCR (Karlsruhe, Germany) and VWR (Bruchsal, Germany) and used without further purification. Dry solvents were purchased from Merck and VWR and deuterated solvents from Deutero (Kastellaun, Germany). The chelators 2,2’-(4,10-bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclodo-decane-1,7-diyl)diacetic acid [DOTA-di(tBu)ester] and 5-benzyl-1-tert-butyl-2-(4,10-bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-yl)pentanedioate [DO2A(tBu)-GABz] were acquired from CheMatech (Dijon, France). (S)-6-(4-aminobutoxy)-N-(2-(2-cyano-4,4-difluoro-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-quinoline-4-carboxamide [NH2-FAPi] was purchased from KE Biochem Co. (Shanghai, China). Reaction controls and determination of the product masses were measured on an Agilent Technologies (Waldbronn, Germany) 1220 Infinity LC System connected to an Agilent Technologies 6130B Single Quadrupole LC/MS system. Thin layer chromatography plates coated with silica gel 60 F254 were acquired from Merck. All analysis controls were detected with a UV lamp (254 nm) and by staining with potassium permanganate. For column chromatography, silica gel 60 (0.063 nm-0.200 nm) from Macherey-Nagel (Düren, Germany) was used. Semi-preparative HPLC was performed on a Hitachi LaChrom 7000 series with a Phenomenex (Aschaffenburg, Germany) Synergi C18 (250×10 mm, 4 µ) column. Characterization of compounds were performed by 1H NMR on a Brucker Avance III HD 300 spectrometer (300 MHz, 5 mm BBFO probe head with z-gradient and ATM and BACS 60 sample changer) and an Avance II 400 spectrometer (400 MHz, 5 mm BBFO sample head with z-gradient and ATM and SampleXPress 60-sample changer).
Organic synthesis
Synthesis of DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2
Di-tert-butyl-2,2’-(4,10-bis(2-((2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl)diacetate [DOTA-(COOtBu)2(N-Boc-en)2] (2)
Commercially available DOTA-di(tBu)ester (1) (75.2 mg, 0.15 mmol), HATU (84.3 mg, 0.22 mmol), DIPEA (74 µL, 0.44 mmol) and HOBt (29.2 mg, 0.22 mmol) were dissolved in dry MeCN (2 mL). After 30 min at RT, tert-butyl-N-(2-aminoethyl)carbamate (60 µL, 0.38 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred for 24 h at RT. Afterwards, tert-butyl-N-(2-aminoethyl)carbamate (85 µL, 0.54 mmol), HATU (54.2 mg, 0.14 mmol), DIPEA (25 µL, 0.14 mmol) and HOBt (19.1 mg, 0.14 mmol) were added in portions and the mixture was stirred for 24 h at RT. After the reaction was completed, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue purified by column chromatography (CHCl3: MeOH/20:1, Rf =0.3). Compound (2) (83.7 mg, 0.10 mmol, 72%) was obtained as yellowish oil. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ [ppm] =3.44-3.28 (m, 16H), 1.47-1.43 (m, 36H), 1.42-1.39 (m, 10H), 1.33-1.21 (m, 3H), 0.92-0.83 (m, 3H). MS (ESI+): m/z=802 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C38H72N8O10: 800.5.
2,2’-(4,10-bis(2-((2-((2-ethoxy-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl)diacetic acid [DOTA.(SA)2] (4)
(2) (75.2 mg, 0.09 mmol) was dissolved in dry DCM (500 µL) and TFA (500 µL) was added. Under RT, the solution was stirred overnight and the solvents were removed at reduced pressure. Deprotected intermediate (3) was obtained as a yellowish oil and used without further purification processing. MS (ESI+): m/z=489 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C20H40N8O6: 488.3. The intermediate (3) was dissolved in 0.5 M Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 phosphate buffer (pH 7, 1 mL). Afterwards, 3,4-diethoxycyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione (SADE) (26 µL, 0.18 mmol) was added and the pH value was adjusted with 1 M NaOH to 7 again. The reaction was stirred for 24 h at RT and then the solvent was removed by lyophilization. The colorless product (4) was processed without any further purification. MS (ESI+): m/z=737 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C32H48N8O12: 736.3.
2,2’-(4,10-bis(2-((2-((2-((4-((4-((2-((S)-2-cyano-4,4-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)carbamoyl)-quinolin-6-yl)oxy)butyl)amino)-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl) diacetic acid [DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2] (5)
(4) was suspended in 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH 9 (500 µL). NH2-FAPi (25.8 mg, 0.06 mmol) was then added and the pH adjusted with 1 M NaOH to pH 9. After 24 h at RT, the solvent was removed by lyophilization and the product was purified via HPLC purification (Phenomenex® Synergi® 10 µm C18(2) 100 Å), flow rate 5 mL/min, H2O (+0.1% TFA)/MeCN (+0.1% TFA) with a linear gradient condition of 20-24% MeCN in 20 min. The final ligand (5) (11.6 mg, 0.01 mmol, 17%) could be obtained as a yellowish powder. MS (ESI+): m/z=754 [M+2H]2+, calculated Mmi for C70H82F4N18O16: 1506.5. Analytical HPLC, Figure S1.
Synthesis of DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2
5-benzyl-1-tert-butyl-2-(4,10-bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-7-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-yl)pentanedioate [DOTAGA-(COOtBu)3-(NHBoc)-GABz] (7)
First, tert-butyl-(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (6a) was synthesized. 2-Chloroethylamine hydrochloride (500 mg, 4.31 mmol) was dissolved in TEA (0.6 mL, 4.31 mmol) and suspended in dry DCM (11 mL). Di-tert-butyldicarbonate (941 mg, 4.31 mmol) was added in portions within 45 min and then the mixture stirred for 24 h at RT. The solution was washed three times with a H2O-1 M NaCl-solution (1:1) and the organic phase dried over magnesium sulphate and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. (6a) (271 mg, 1.51 mmol, 35%) was obtained as yellowish oil. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ [ppm] =4.97 (s, 1H), 3.63-3.60 (t, J=6.0 Hz, 3H), 3.51-3.46 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 3H), 1.47 (s, 9H). MS (ESI+): m/z=202 [M+Na]+, calculated Mmi for C7H14ClNO2: 179.64 [M].
(6a) (271 mg, 1.51 mmol) was combined with potassium carbonate (147 mg, 1.06 mmol) and DO2A(tBu)-GABz (6) (400 mg, 0.59 mmol) in dry MeCN (12 mL) and the mixture stirred at 90°C. After 24 h, 100 mg of (6a) was added and stirred for another 24 h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue purified by column chromatography with ethyl acetate/n-hexane (1:1, 3% TEA, Rf =0.34). Product (7) (145 mg, 0.18 mmol, 30%) could be achieved as a yellowish oil. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ [ppm] =7.39-7.34 (m, 5H, H-6), 5.13 (d, J =4.3 Hz, 2H), 3.44 (d, J =7.3 Hz, 1H), 3.23 (dd, J =14.3 Hz, 8.9 Hz, 6H), 2.98-2.60 (m, 16H), 2.06 (s, 2H), 2.05-1.98 (m, 2H), 1.89-1.79 (m, 2H), 1.50-1.24 (m, 26H). MS (ESI+): m/z=411 [M+2H]2+, 821 [M+H]+, 843 [M+Na]+, calculated Mmi for C43H73N5O10: 819.5.
4-(4,10-bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-7-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododecan-1-yl)-5-(tert-butoxy)-5-oxopentanoic acid [DOTAGA(COOtBu)3(NHBoc)] (8)
(7) (870 mg, 1.06 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (11 mL) and Pd on activated charcoal (27 mg, 0.25 mmol, 10 wt%) was added to the solution. Stirring at RT was carried out overnight under a hydrogen atmosphere. The suspension was filtered through Celite and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Compound (8) as yellowish oil (798 mg, 1.09 mmol, 100%) was obtained which was used without further purification. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ [ppm] =6.82 (s, 1H), 3.46-2.75 (m, 21H), 2.63-2.30 (m, 4H), 2.05-1.74 (m, 2H), 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.44 (s, 18H), 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.34-1.20 (m, 2H). MS (ESI+): m/z=366 [M+2H]2+, 730 [M+H]+, 753 [M+Na]+, calculated Mmi for C36H67N5O10: 729.4.
Di-tert-butyl-2,2’-(4-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl)-10-(2,2,15,15-tetramethyl-4,9,13-trioxo-3,14-dioxa-5,8-diazahexadecan-12-yl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl)diacetate [DOTAGA(COOtBu)3(NHBoc)(N-Boc-ethylendiamin)] (9)
(8) (171 mg, 0.23 mmol), HATU (136 mg, 0.47 mmol), DIPEA (120 µL, 0.70 mmol) and HOBt (47.6 mg, 0.35 mmol) were dissolved in dry MeCN (2 mL). tert-Butyl-N-(2-amino-ethyl)-carbamate (74 µL, 0.47 mmol) was added within 30 min and the mixture was stirred for 24 h at RT. The residue was removed under reduced pressure and purified by column chromatography with chloroform/methanol (10:1, Rf =0.25). (9) could be received as yellowish oil (88.2 mg, 0.10 mmol, 43%). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ [ppm] =5.35 (s, 2H), 3.40 (q, J=3.4 Hz, 2H), 3.33 (t, J=6.5 Hz, 7H), 3.29 (s, 2H), 2.98-2.23 (m, 18H), 2.19-1.89 (m, 4H), 1.45 (q, J=1.9 Hz, 45H). MS (ESI+): m/z=437 [M+2H]2+, 873 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C43H81N7O11: 871.6.
2,2’-(4-(1-carboxy-4-((2-((2-ethoxy-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)amino)-4-oxobutyl)-10-(2-((2-ethoxy-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl)-diacetic acid [DOTAGA.(SA)2] (11)
(9) (88.2 mg, 0.10 mmol) was dissolved in dry DCM (200 µL) and TFA (800 µL). The solution was stirred at RT for 24 h and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Deprotected intermediate (10) was identified as yellowish oil and used without further processing. MS (ESI+): m/z=504 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C21H41N7O7: 503.3. Deprotected (10) was dissolved in 0.5 M phosphate buffer (pH 7, 2 mL). Afterwards SADE (36,6 µL, 0.25 mmol) was added and the reaction was stirred at pH 7 for 24 h at RT. The solvent was removed by lyophilization and the colorless precursor (11) was used without further purification. MS (ESI+): m/z=752 [M+H]+, calculated Mmi for C33H49N7O13: 751.3.
2,2’-(4-(1-carboxy-4-((2-((2-((4-((4-((2-((S)-2-cyano-4,4-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)carbamoyl)-quinolin-6-yl)oxy)butyl)amino)-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)amino)-4-oxobutyl)-10-(2-((2-((4-((4-((2-((S)-2-cyano-4,4-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)carbamoyl)quinolin-6-yl)oxy)butyl)-amino)-3,4-dioxocyclobut-1-en-1-yl)amino)ethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diyl)diacetic acid [DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2] (12)
(11) was dissolved in 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH 9 (1.5 mL). NH2-FAPi (41.3 mg, 0.10 mmol) was added and the pH was adjusted with 1 M NaOH to pH 9 again. The mixture was shaken for 24 h at RT and after the reaction was completed, the solvent was removed by lyophilization. The residue was purified via HPLC (Phenomenex® Synergi® 10 µm C18(2) 100 Å), flow rate 5 mL/min, H2O (+0.1% TFA)/MeCN (+0.1% TFA) with a linear gradient of 20-25% MeCN in 20 min. The final ligand (12) (18.1 mg, 0.01 mmol, 12%) was obtained as a yellowish powder. MS (ESI+): m/z=762 [M+2H]2+, calculated Mmi for C71H83F4N17O17: 1521.6. Analytical HPLC, Figure S2.
natGa/natLu-complexes
DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 (4.8 mg, 3.1 µmol) was reacted with natGa(NO3)2 (2 eq.) in 0.5 M sodium acetate buffer pH 4.5 (500 µL). After the solution was stirred for 6 h at 95°C, the natGa complexes [natGa]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 were obtained. Complexation was confirmed by ESI-MS and the precursor was purified via HPLC (Phenomenex Synergi® 10 µm C18(2) 100 Å), flow rate 5 mL/min, H2O (+0.1% TFA)/MeCN (+0.1% TFA) with a linear gradient condition of 5-95% MeCN in 10 min. The product was obtained as yellowish powder (4.4 mg, 2.8 µmol, 90%). MS (ESI+): m/z=525.4 [M+3H]3+, 787.4, 787.9, 788.3 [M+2H]2+; calculated Mmi for C70H80F4GaN18O16: 1573.5.
[natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (5.5 mg, 3.6 µmol) and [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.-(SA.FAPi)2 (5.1 mg, 3.3 µmol) could be generated analogously to the natGa-DOTA derivative with natGa(NO3)2 resp. natLuCl3. [natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was ob-tained as yellowish powder (5.1 mg, 3.2 µmol, 89%). MS (ESI+): m/z=530.4 [M+3H]3+, 794.9, 795.4, 795.8 [M+2H]2+; calculated Mmi for C71H81F4GaN17O17: 1588.5 and [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was obtained as yellowish powder (4.7 mg, 2.8 µmol, 85%). MS (ESI+): m/z=565.7 [M+3H]3+, 847.8, 848.3 [M+2H]2+; calculated Mmi for C71H80F4LuN17O17: 1693.5.
Radiocomplexes with gallium-68
Gallium-68 elution was performed using ethanol-based post-processing from a 68Ge/68Ga-generator (ITG Garching, Germany) following the procedure by Eppard et al. [20].
Reaction controls for radiochemical yields (RCY) was executed using radio-TLC (TLC Silica gel 60 F254 Merck) with 0.1 M citrate buffer pH 4. TLC’s were measured in TLC imager CR-35 Bio Test-Imager from Duerr-ndt (Bietigheim-Bissingen, Germany) with the analysis software AIDA Elysia-Raytest (Straubenhardt, Germany).
Stability studies in human serum (HS), phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and saline (0.9% isotonic NaCl-solution): ~5 MBq of the radionuclide tracer solution after >95% radiochemical purity was added to 500 µL of the respective media and stirred at 37°C. Aliquots were taken at the measured time points for gallium-68 were 15, 30, 60, 90, 120 min. HS (human male AB plasma, USA origin) was bought from Sigma Aldrich, PBS was purchased from Sigma Aldrich and 0.9% saline from B. Braun Melsungen AG (Melsungen, Germany). Radiochemical yields was determined with radio-TLC and evaluated by a TLC imager.
Lipophilicity measurement
The shake-flask method was carried out to determine the lipophilicity. After completion of radiolabeling with a RCP >95%, the tracer solution was adjusted to pH 7.4 with 2 M NaOH. ~5 MBq was taken from the solution and adjusted to a total volume of 700 μL with PBS (n=4). 700 μL 1-octanol was added to each PBS solution and stirred for 2 min (1500 rpm). Subsequently, each tube was centrifuged for 1-2 min. 400 μL of the octanol- and PBS phases were pipetted into new tubes and aliquots of each phase (3 µL of the PBS phase and 6 μL of the octanol phase) were measured via radio-TLC. The PBS phases were adjusted up to 700 µL and 700 μL octanol was added to each tube. The procedure was repeated twice more. LogD7.4 values were calculated as the logarithm of the octanol/PBS ratio measured by a TLC imager CR-35 Bio Test-Imager from Duerr-ndt (Bietigheim-Bissingen, Germany) and the software AIDA Elysia-Raytest (Straubenhardt, Germany).
Inhibition assays
Recombinant human FAP, PREP, DPP8 and DPP9 were expressed and purified as described earlier [10]. Human DPP-4 was purified from seminal plasma as published [21]. IC50-measurements of the probes for FAP, PREP and the DPPs were carried out as described before using respectively Z-Gly-Pro-AMC (50 µM), Suc-Gly-Pro-AMC (250 µM) and Ala-Pro-paranitroanilide (pNA) (50 µM for DPP4 and 150 µM for DPP8/9) as the substrates [10,22].
Patient studies
The detailed clinical history of the six patients is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical details of the 6 patients (RAI: Radioiodine, ER: the estrogen receptor, PR: progesterone receptor, HER2/neu: human epidermal growth factor receptor-2, LAR: long-acting)
| S.No | Age/Gender | Histopathology | Prior treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45/F | Papillary thyroid cancer (RAI refractory) | Disease progression on sorafenib, radiotherapy and lenvatinib |
| 2 | 63/F | Papillary thyroid cancer (RAI refractory) | Disease progression on sorafenib, radiotherapy and lenvatinib |
| 3 | 46/F | Papillary thyroid cancer (RAI refractory) | Disease progression on sorafenib and lenvatinib |
| 4 | 56/F | ER-, PR-HER2/neu-left breast cancer | Surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy |
| 5 | 46/M | Pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer | Sandostatin LAR, capecitabine |
| 6 | 58/M | Duodenal neuroendocrine cancer | Sandostatin LAR, [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE+capecitabine |
Clinical image acquisition and analysis
Scans were acquired on a dedicated GE Discovery 710×128 Slice PET/CT Scanner, with a 40-mm detector at a rotation speed of 0.35 sec. The mean injected activities were 74 MBq (range: 48.1 MBq to 88.8 MBq), 122.1 MBq (range; 74 to 185 MBq), 296 MBq (range; 259 to 333 MBq) and 130 MBq for [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi,[18F]FDG radiotracers and [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC respectively. While, in all cancers, a head-to-head comparison was performed between the [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi monomer and [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 dimer, in patients with an additional [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT was also performed to visualize the somatostatin receptor expression. The PET/CT acquisition parameters and post processing were similar to that of [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-FAPi PET/CT.
All scans were acquired within a time interval of one week. For all the three radiotracers, whole-body PET/CT studies were acquired at 1-hour post-injection. The acquisition protocol constituted an initial scout image, followed by a CT scan, and PET, acquired at 2 minutes per bed. A diagnostic whole-body CT scan parameter included 300-350 mAs, 120 kVp, slice thickness 5 mm, pitch 1 was acquired.
[18F]FDG, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 PET/CT scans were loaded simultaneously and co-registered using carina as an anatomical landmark registration technique. Two experienced Nuclear Medicine physicians conducted scan interpretations and disagreement in the reports was reviewed by a third physician. For the quantitative comparison, ROIs were drawn according to the PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors (PERCIST 1.0). The quantitative assessment of standardized uptake values (SUV) corrected for lean body mass was done using a 3D auto-contour ROI at a 40% threshold of SULpeak technique.
The clinical section of this study was approved by the Institute Ethics committee, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, (IECPG-22/27.02.2020). All patients gave their written informed consent.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2
DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 was synthesized starting with the commercially available DOTA-di(tBu)ester (1) in a 4-step route according to Figure 2. In the first step, (1) was reacted with N-Boc-ethylenediamine using the base DIPEA and the coupling agents HATU and HOBt. The obtained compound DOTA-(COOtBu)2(N-Boc-en)2 (2) was treated with trifluoroacetic acid to remove the Boc- and tert-butyl protective groups. In the next step, amidations were carried out with squaric acid diethyl ester (SADE) to get DOTA.(SA)2 (4). In the last synthesis stage, the formed squaric diester was bound to NH2-FAPi at basic pH to obtain DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 (5).
Figure 2.
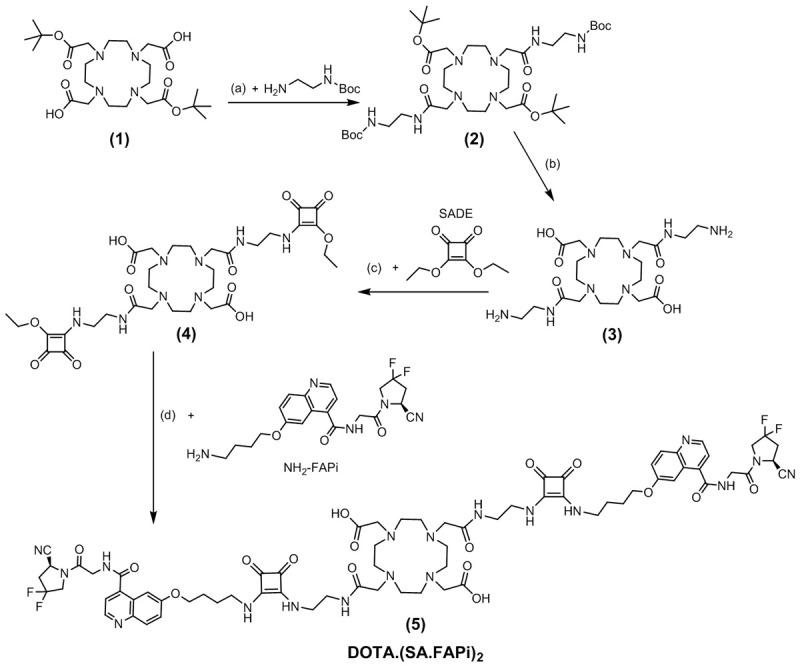
Four-step synthetic route of DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 (5): (a) HATU, HOBt, DIPEA, MeCN, RT, 48 h, 72%; (b) DCM/TFA (1:1), RT, 16 h; (c) 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH=7, RT, 16 h; (d) 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH=9, RT, 16 h, 17%.
Synthesis of DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2
DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 could be obtained in a 7-step synthesis route according to Figure 3. First, 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride was protected with a Boc group by means of triethylamine and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate. The formed tert-butyl-(2-chloroethyl)-carbamate (6a) was introduced to the commercially available DO2A(tBu)-GABz (6) via nucleophilic substitution. This resulted in DOTAGA(COOtBu)3(NHBoc)-GABz (7). Deprotection of the benzyl protective group was achieved by hydrogenolysis using Pd(OH)2 on active charcoal to receive the product DOTAGA(COOtBu)3(NHBoc) (8). Subsequently, commercially available N-Boc-ethylenediamine was bound to the standalone carboxylic acid with the coupling agents HATU, HOBt and the base DIPEA analogously to the DOTA derivative. In the next step, the protecting groups Boc and tert-butyl of DOTAGA(COOtBu)3(NHBoc)(N-Boc-en) (10) were cleaved with TFA in DCM and two identical SADE substituents were coupled to the terminal amines of the DOTAGA derivative at neutral pH. The esters of the obtained DOTAGA.(SA)2 (11) were amidated with two NH2-FAPi molecules at basic conditions. DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (12) could be isolated via HPLC purification.
Figure 3.
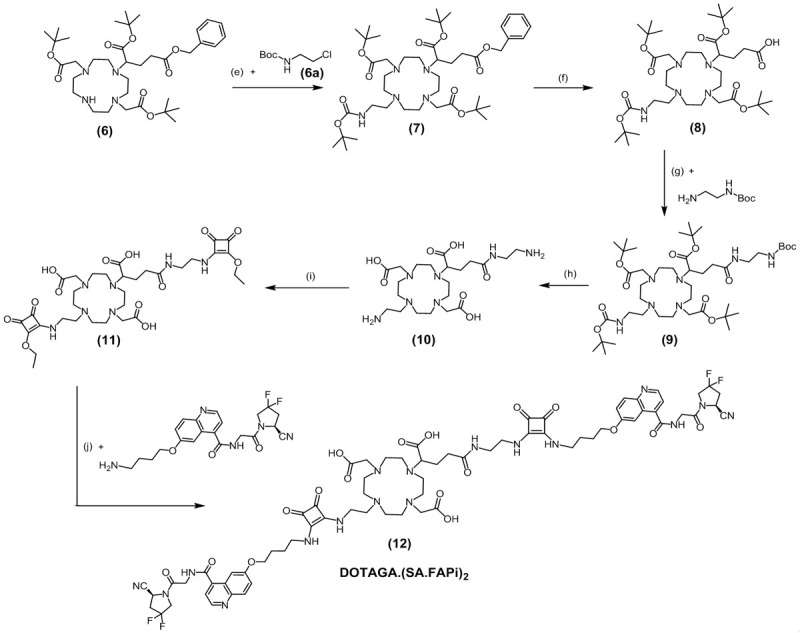
Seven-step synthesis route of DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (12): (e) MeCN, K2CO3, 90°C, 48 h, 30%; (f) Pd/C (10%), MeOH, H2, RT, 16 h, 100%; (g) HATU, HOBt, DIPEA, MeCN, RT, 24 h, 43%; (h) DCM/TFA (20:80)%, RT, 48 h; (i) SADE, 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH=7, RT, 48 h; (j) 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH=9, RT, 24 h, 12%.
Synthesis of non-radioactive complexes
The non-radioactive complexes [natGa]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2, [natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 were synthesized by treating the corresponding precursors with gallium(III) nitrate and lutetium(III) chloride, respectively. The reactions were executed in 0.2 M sodium acetate buffer pH 4.5 at 95°C. After lyophilization of the reaction solution, the residue was purified via HPLC to obtain the final metal-complexed derivatives.
In vitro enzyme inhibition measurements
Confirming the selectivity of the FAPi compounds against the closely related serine proteases of the S9 family (PREP, DPP4, DPP8 and DPP9) is crucial for considering their applicability in in vivo studies. These related proteases are ubiquitously expressed: if DPP or PREP affinity would be present, this could significantly discount on the tumor selectivity of the FAPi compounds. IC50 measurements for FAP, PREP and DPPs (DPP4, DPP8 and DPP9) of both dimeric systems with their natGa/natLu metal complexes were measured. Table 2 shows the IC50 values for the five compounds DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2, [natGa]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2, DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, [natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 compared to the reference FAP inhibitor UAMC1110 and the monomeric probes [natGa]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [natLu]Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi. The IC50 values for FAP of all dimeric tracers were in the same order of magnitude compared to the reference compound UAMC1110 and the monomers natGa/natLu-DOTA.SA.FAPi and are within the subnanomolar to low nanomolar range (0.78-1.54 nM).
Table 2.
IC50 values of the FAPi probes against FAP and the related serine proteases (PREP, DPP4, DPP8, DPP9). Data are described as the mean with standard deviation (n=3 for FAP and n=2 for PREP and the DPPs)
| Compound | IC50 (µM) | IC50 (nM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| DPP4 | DPP8 | DPP9 | PREP | FAP | |
| DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 0.44±0.06 | 1.33±0.11 | 0.96±0.15 | 0.42±0.02 | 0.78±0.05 |
| [natGa]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 0.51±0.09 | 1.44±0.16 | 0.78±0.07 | 0.92±0.07 | 1.05±0.07 |
| DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 0.40±0.07 | 0.42±0.04 | 0.16±0.02 | 0.39±0.02 | 0.92±0.06 |
| [natGa]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 0.70±0.11 | 0.87±0.08 | 0.19±0.01 | 1.60±0.16 | 0.90±0.06 |
| [natLu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 0.63±0.07 | 0.41±0.03 | 0.18±0.02 | 0.56±0.04 | 1.54±0.15 |
| [natGa]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi | >1 | N/A | >1 | 8.7±0.9a | 1.4±0.2a |
| [natLu]Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi | >1 | N/A | >1 | 2.5±0.4a | 0.8±0.2a |
| UAMC1110 | >10 | 10.1±0.6b | 4.7±0.4b | 1.8±0.01 | 0.43±0.02a |
IC50 for FAP and PREP from Moon et al. [10].
The IC50 value of UAMC-1110 for DPP9 (4.7±0.4 μM) is slightly lower compared to what was published before (>12 μM) [2]. This is due to introducing of a new measurement method in combination with new human recombinant DPP9 (instead of bovine DPP9). The IC50 of UAMC1110 for DPP8 was determined as a part of this study.
For all dimeric derivatives, the affinity for PREP was in the µM range (IC50 0.42-1.60 µM) resulting in high FAP/PREP selectivity indices in favor of FAP targeting. Additionally, IC50 values of the dimeric compounds against DPPs were within the low micromolar ranges. Compared to the reference compound UAMC1110, the selectivity towards DPP4, DPP8 and DPP9 is slightly decreased. In summary, selectivity against the DPPs and PREP are high and sufficient for all five dimeric compounds. Furthermore, excellent affinity for the target enzyme FAP was achieved.
Labeling kinetics with gallium-68
DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 was labeled with gallium-68 under various buffer conditions. Ammonium acetate (AmAc), sodium acetate (NaAc) and N-2-hydroxyethyl piperazine-N’-2-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) buffer were used. Figure 4 compares the radiochemical yields (RCY) of the DOTA dimer precursor in the three different buffer systems with identical buffer molarity, pH, volume, reaction temperature, activity and ligand amount (1 M, pH 5.5, 300 µL, 95°C, 100-150 MBq and 20 nmol). The RCY are analyzed by radio-TLC and evaluated with a TLC imager. Initially, radiolabeling was performed in AmAc buffer, analogous to our recently published DOTA.SA.FAPi monomer. However, in contrast to the monomer which led to quantitative yields, DOTA dimer showed an RCY of only 9% after 10 min. Thereupon, labeling was performed in NaAc and HEPES buffer. In both, NaAc and HEPES buffer, complexation with gallium-68 could be obtained with RCY of 87% within 10 min.
Figure 4.
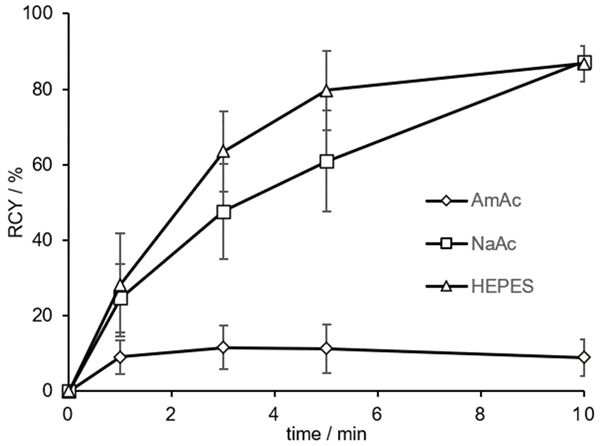
RCY (in %) of 20 nmol [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 in 1 M AmAc, NaAc and HEPES buffers after 10 min at 95°C (n=2 for AmAc and NaAc, n=3 for HEPES; pH 5.5, A(68Ga) =100-150 MBq).
Afterwards, labeling was performed in 1 M HEPES buffer with different precursor amounts of 10-40 nmol (Figure 5). RCY of more than 80% was achieved for precursor quantity of ≥ 20 nmol. At 10 nmol ligand amount only a RCY of 50% could be observed. Complexation with gallium-68 with 20-40 nmol was comparably good in a range of 80-90% RCY. Compared to DOTA.SA.FAPi, no quantitative yields could be attained. Due to the linear arrangement of the bifunctional conjugates, coordination of gallium-68 to the central DOTA core might be sterically difficult.
Figure 5.
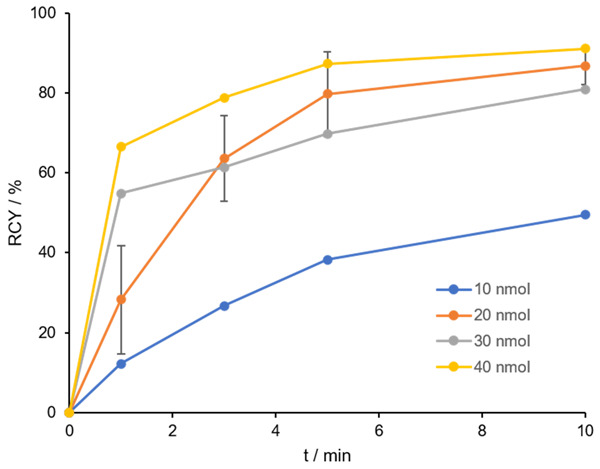
RCY (in %) of 10-40 nmol [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 in 1 M HEPES buffer pH 5.5 after 10 min at 95°C (n=3 for 20 nmol, n=1 for 10, 30 and 40 nmol), A(68Ga) =100-150 MBq.
For synthesis of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, identical conditions as for the [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.(SA.FAPi)2 derivative were used. Figure 6 shows the kinetics of three precursor concentrations (5, 10 and 20 nmol) in 1 M HEPES pH 5.5 at 95°C. In comparison to the DOTA dimer, quantitative yields >99% were obtained after a reaction time of 10 minutes. Even a precursor quantity of 10 nmol led to excellent complexation and at 5 nmol, a RCY of >90% was still obtained. This may confirm the previous statement, since the DOTAGA chelator provides an additional coordination option that might facilitate the faster and better complexation with gallium-68.
Figure 6.
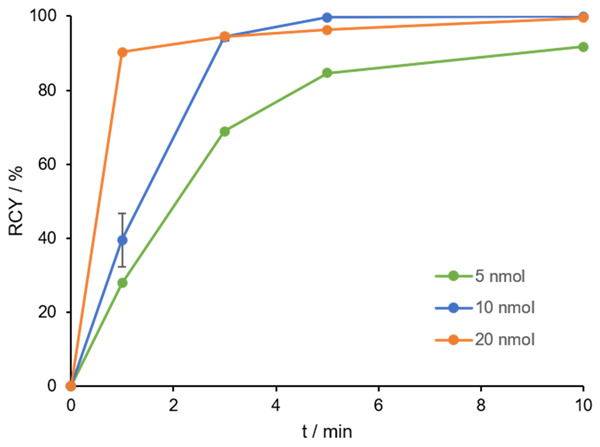
RCY (in %) of 5, 10 and 20 nmol [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 in 1 M HEPES buffer pH 5.5 in 10 min at 95°C (n=3 for 10 nmol, n=1 for 5 and 20 nmol), A(68Ga) =100-150 MBq.
In vitro stability of 68Ga-labeled derivatives
[68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was tested for its stability in different media: HS, PBS and saline at different time points (15-120 min) at 37°C. The RCY of the intact conjugates are analyzed by radio-TLC and evaluated with a TLC imager. In vitro stabilities in HS and in NaCl were >98% and in PBS >91%, respectively, after 120 min (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
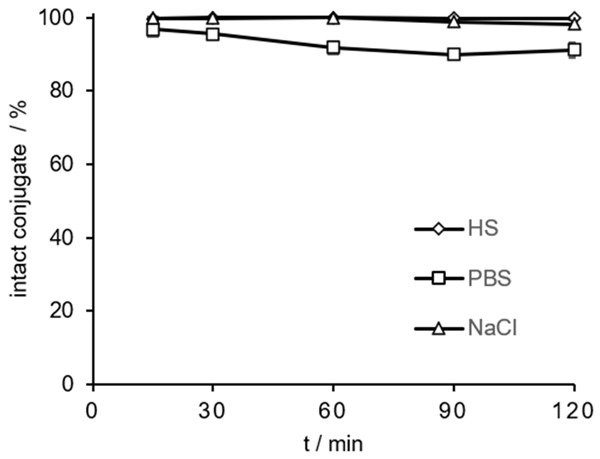
In vitro stability of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (in % intact conjugates) in HS, PBS and saline during a period of 15-120 min at 37°C (n=3 for all media).
Lipophilicity comparison [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi vs. [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2
Lipophilicity (logD7.4 value) was performed via “shake-flask” method for the dimer [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and compared to those of the monomer [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi from [22] (Table 3).
Table 3.
LogD values (pH=7.4) of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (n=3)
| [68Ga]Ga-complex | LogD7.4 value |
|---|---|
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi | -2.68±0.06a |
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 | -2.02±0.06 |
LogD7.4 from Moon et al. [22].
The lipophilicity of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi was already published in our recent work [22] with a logD7.4 of -2.68. [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 displayed a slightly higher lipophilicity with a logD7.4 value of -2.02. Both derivatives have strong hydrophilic characteristics however the dimer showed a more lipophilic character due to the additional linker-targeting vector conjugate.
Clinical studies
Six patients (4 females, 2 males, mean age 52.3±7.6 years; range 45-63 years) who had progressed on all the available cancer treatment options were referred to the Department of Nuclear Medicine at AIIMS, India. None of the patients experienced adverse events from the radiotracers. The detailed clinical history of the six patients is mentioned in Table 1.
Organ distribution of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi vs. [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2
The physiological biodistribution of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi involved the pancreas, liver, heart, spleen, kidneys, gut, bladder, and to a lesser extent, lacrimals, oral mucosa, salivary glands, and thyroid glands. The biodistribution of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was similar to that of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi, yet the intensity of uptake in the corresponding organs varied (Figure 8; Table S1). Visual analysis revealed the pancreas as the organ of the highest uptake on both the radiotracers.
Figure 8.
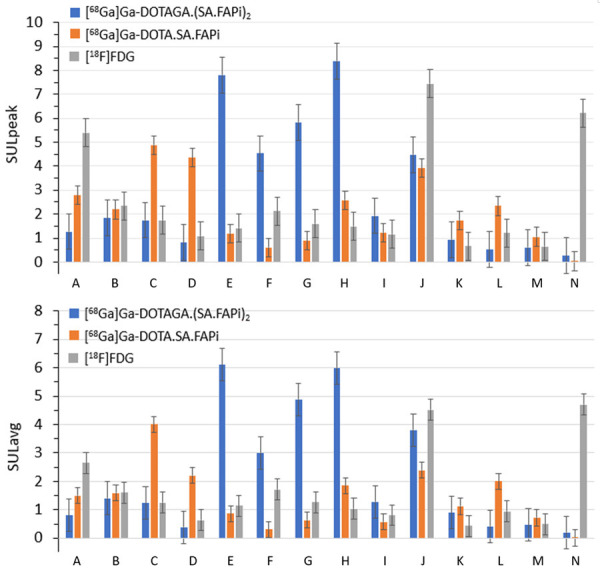
Comparison of SUL (standardized uptake value (SUV) normalized to lean body mass) values among various radiotracers in six patients; above: SULpeak of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (blue), [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi (orange) and [18F]FDG (grey); below: SULavg of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (blue), [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi (orange) and [18F]FDG (grey). A: lacrimal glands; B: oral mucosa; C: salivary glands; D: thyroid; E: heart contents/blood pool; F: liver; G: spleen; H: pancreas; I: duodenum; J: kidneys; K: psoas muscle; L: bone (L4 vertebrae); M: femur; N: brain normal parenchyma.
Normal organ uptake
On quantitative analysis, variable, higher SUL (standardized uptake value (SUV) normalized to lean body mass) peak and higher average uptake values were noted in the blood pool, liver, spleen, pancreas, salivary glands, thyroid and the psoas muscle on [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 compared to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT scans (Figures 8, 9 and 10; Table S1). The main reason for higher uptake in normal tissues is not known yet. However, the change in the structure from a monomer to a dimeric system and thus the introduction of an additional linker-TV unit and the increase of molecular weight have shown an influence to a slightly higher lipophilicity, which could be a reason for the higher retention. The delayed blood pool from [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 in some patients is of concern and may contribute a relatively high bone marrow toxicity, but detailed pharmacokinetic and dosimetry data is warranted to validate the findings. However, while the dosimetry results on [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi are reported and are proven safe for diagnostic use [11], pharmacokinetic data on [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, [177Lu]Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi, and [177Lu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 are currently being investigated. Contrary to the avid uptake of [18F]FDG in the normal brain parenchyma, negligible uptake was quantified on [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT scans (Figures 8 and 10, Table S1).
Figure 9.
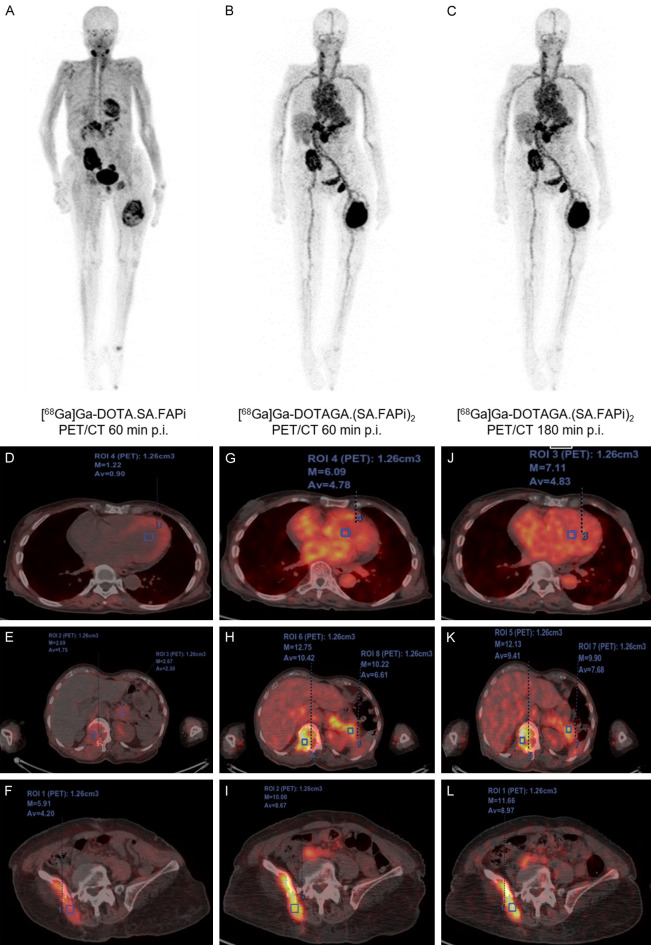
63-year-old female diagnosed with papillary thyroid cancer; (A) PET/CT MIP of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi: normal distribution in the salivary glands, pancreas and myocardium; avid skeletal lesions in the right ilium, left ischial tuberosity, and left femur; (B, C) PET/CT MIP of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2: normal biodistribution in the pancreas, and liver; concordance of tracer avidity in all the lesions compared to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi but demonstrated higher tumor-to-background ratios and avidity in the tumor lesions; higher retention duration of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 in the blood-pool with retention up to 3 h p.i. compared to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi; fused axial PET/CT images demonstrate higher standardized uptake values for [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 in both normal organs (G, H) and lesions (H, I) compared to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT (D-F) which remained stable even up to 3 h p.i. (J-L).
Figure 10.
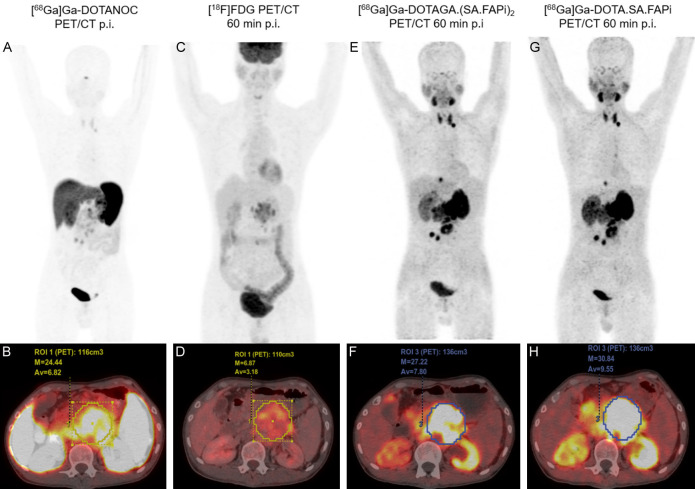
36-year-old male diagnosed with grade III pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, the extent off cancer involved primary tumor in the pancreas and left supra clavicular lymph node. MIP and PET/CT fused axial images 1 h p.i. of (A, B) [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC; (C, D) [18F]FDG; (E, F) [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and (G, H) [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi. Highest primary tumor uptake in pancreas: (H) [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT (SULpeak: 30.84); (F) [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.-(SA.FAPi)2 (SULpeak: 27.22). Left supraclavicular visible on (E) [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and (G) [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi.
Case reports
(I) In a case of the 63-year-old female diagnosed with papillary thyroid cancer (PET/CT scans maximum intensity projection (MIP) of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 in Figure 9; Table S2), the DOTAGA dimer probe showed increased tumor uptake (SULavg: 10.4 in L2 vertebra tumor, 8.7 in right ischium and 8.9 in the left femur) with overall higher tumor-to-background ratios than the DOTA monomer (SULavg: 1.8 in L2 vertebra, 4.2 in right ischium and 1.42 in the left femur) after 1 h p.i. High retention of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 were shown after 3 h p.i. with SULavg: 9.4 in L2 vertebra, 9.0 in right ischium and 8.5 in the left femur, respectively. Yet, higher uptake in the blood-pool with retention duration up to 3 h p.i. was observed.
(II) A 36-year-old male was diagnosed with grade III pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (Figure 10). Due to the neuroendocrine origin and Ki-67 index of >20%, patient underwent [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC (A, B), [18F]FDG (C, D) PET/CT’s, followed by [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (E, F), and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi (G, H), PET/CT scans. The MIP and PET/CT fused axial images of [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC (A, B), [18F]FDG (C, D), [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (E, F) and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi (G, H) revealed highest uptake on [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi PET/CT (SULpeak: 30.84) (H) followed by [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (SULpeak: 27.22) (F) in the primary tumor (pancreas).
All the agents, except [18F]FDG (C, D), demonstrated increased radiotracer uptake in the primary pancreatic tumor. On the other hand, the left supraclavicular lymph node was only remarkably visible on the [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 (E) and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi (G) PET MIP images. Unlike the high blood pool activity noted on the [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 images of the patient described in Figure 9, no or minimal blood pool uptake was observed in this patient (Figure 10E, 10F).
In case II, it seems that the DOTA.SA.FAPi monomer performed better than the DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 dimer. However, the mainstay goal was to design a molecule that can be multifaceted and exploited as a theranostic option for both imaging and treatment. For the DOTA.SA.FAPi monomer labeled with 177Lu though, the uptake in the tumors was instant and the washout from the lesions was rapid. Hence, this was not an ideal agent for therapy. This led to the re-designing of the monomer to dimer with an aim to improve the tumor retention. The dimer DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was further labelled with 68Ga. Unfortunately, as demonstrated in Figure 10, despite the tumor retention, there was also a proportional retention in the normal organs and blood pool. Despite the high blood-pool activity, the DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 was labeled with 177Lu, and interestingly a drastically low blood-pool activity was observed with [177Lu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2. Hence, despite several attempts to improve the biodistribution pattern of [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, we concluded that this tracer has inherent drawbacks in terms of high radiation burden to normal organs and a non-identical distribution pattern among patients. Therefore, we decided that the best approach is to adopt a monomer-guided dimer treatment, involving the use of [68Ga]-DOTA.SA.FAPi for guiding and the dimer [177Lu]-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 for treatment. This current approach has been now adopted routinely at our clinic to treat patients.
Comparison according to the site of malignancy
Though a complete concordance was observed between the tracers in detecting the site of the primary tumor, the intensity of the tracer accumulation in the primary/residual tumor site was highest for [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2. However, there was no significant difference in the median SUL peak (P-0.3488) and average values (P-0.3828) between [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi radiotracers (Table 4). Similarly, the SUL peak and average values did not differ between [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [18F]FDG radiotracers.
Table 4.
Comparison of lesion SUL values between the radiotracers 1 h p.i. for all six patients (Comparison between variable was done by paired sample t-test), For comparison of SULpeak of metastases and lesions, see Table S3
| Radiotracer | SULpeak (mean ± SD, range) | P-value | SULavg (mean ± SD, range) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 | 12±3.9 (9.5-12.5) | 0.3488 | 7.6±2.7 (3.6-9.8) | 0.3828 |
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi | 9.5±3 (5.4-14.6) | 5.7±3 (2.5-8.9) | ||
| [18F]FDG | 7.8±5.4 (4.2-10.9) | 0.1535* | 4.2±2.9 (2.2-8) | 0.0619* |
P-values derived by comparing the SUL peak and average values between [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and [18F]FDG.
Conclusion
Here, we reported two novel PET radiopharmaceuticals based on a homodimer system with DOTA and DOTAGA as chelators. Both were conjugated via squaramide to a FAP inhibitor for targeting the tumor microenvironment. Synthesis of the DOTA dimer derivative was faster and easier to realize, however, complexation with gallium-68 was better and more efficient using the DOTAGA derivative. In vitro affinity studies showed that the formation of bivalent structures with an additional linker-target vector unit has no negative influence regarding the affinity and inhibition potency towards FAP relative to the monomeric derivatives. As a result, IC50 values in the low nanomolar range were obtained, similar to the IC50 values of the monomeric structures reported earlier [10].
In first clinical investigations, [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 demonstrated first of all that relative to the monomer, tumor uptake increased at 1 h p.i. time points and secondly, that even at 3 h p.i. the accumulation in tumor tissue increased compared to the 1 h p.i. time point. In our opinion, this verifies the hypothesis that dimeric FAPi derivatives can function as an approach towards increasing tumor stroma residence times. However, [68Ga]Ga-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 is accompanied by high, delayed, and heterogeneous blood pool uptake across the patients, thereby attributing to a risk of increased radiation dose to the non-target organs. Yet, showing promising pharmaceutical profiles both in vitro and in vivo, DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 and related compounds could be a suitable PET imaging probe for diagnostic approaches targeting FAP in the tumor stroma. In future work, our focus is on the performance of [177Lu]Lu-labeled DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2, which will be investigated in vivo.
Acknowledgements
We thank ITM Isotopen Technologien München AG, Germany for providing us the 68Ga-Generator. This work was funded by the Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek Vlaanderen (FWO, Grant 1S64220N), Y.V.R. is a SB PhD fellow at FWO. This project also received funding from the Agentschap Innoveren en Ondernemen (VLAIO HCB 2019. 2446). All patients gave their written informed consent IECPG-22/27.02.2020, Institute Ethics committee, All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
Abbreviations
- DOTAGA
2-(4,7,10-tris(carboxymethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-yl)pentanedioic acid
- IC50
half maximal inhibitory concentration
- DATA5m
2,2‘-(6-(4carboxybutyl)-6-((carboxymethyl)(methyl)amino)-1,4-diazepane-1,4-diyl)diacetic acid
- PET/CT
positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- DTPA
diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
- HBED
2,2’-{1,2-ethanediylbis[(2-hydroxy-benzyl)imino]}-diacetic acid
- GRPR
gastrin-releasing peptide receptor
- PSMA
prostate specific membrane antigen
- HPLC
high pressure liquid chromatography
- n.c.a.
non carrier added
- TLC
thin layer chromatography
- p.i.
post injection
- SUL
standardized uptake value (SUV) normalized to lean body mass
- RCY
radio chemical yield
- FDG
fluorodeoxyglucose
- MIP
maximum intensity projection
Supporting Information
References
- 1.Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ, Thomas PD, Huang X, Bateman A, Finn RD. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D624–32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jansen K, Heirbaut L, Verkerk R, Cheng JD, Joossens J, Cos P, Maes J, Lambeir AM, De Meester I, Augustyns K, Van der Veken P. Extended structure-activity relationship and pharmacokinetic investigation of (4-quinolinoyl)glycyl-2-cyanopyrrolidine inhibitors of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) J Med Chem. 2014;57:3053–74. doi: 10.1021/jm500031w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Loktev A, Lindner T, Burger EM, Altmann A, Giesel F, Kratochwil C, Debus J, Marme F, Jäger D, Mier W, Haberkorn U. Development of fibroblast activation protein-targeted radiotracers with improved tumor retention. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:1421–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.224469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kratochwil C, Flechsig P, Lindner T, Abderrahim L, Altmann A, Mier W, Adeberg S, Rathke H, Röhrich M, Winter H, Plinkert PK, Marme F, Lang M, Kauczor HU, Jäger D, Debus J, Haberkorn U, Giesel F. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: tracer uptake in 28 different kinds of cancer. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:801–5. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.227967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giesel FL, Kratochwil C, Lindner T, Marschalek MM, Loktev A, Lehnert W, Debus J, Jäger D, Flechsig P, Altmann A, Mier W, Haberkorn W. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: biodistribution and preliminary dosimetry estimate of 2 DOTA-containing FAP-targeting agents in patients with various cancers. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:386–92. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.215913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen H, Pang Y, Wu J, Zhao L, Hao B, Wu J, Wei J, Wu S, Zhao L, Luo Z, Lin X, Xie C, Sun L, Lin Q, Wu H. Comparison of [68Ga] Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F] FDG PET/CT for the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with various types of cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47:1820–32. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04769-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen H, Zhao L, Ruan D, Pang Y, Hao B, Dai Y, Wu X, Guo W, Fan C, Wu J, Huang W, Lin Q, Sun L, Wu H. Usefulness of [68Ga] Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in patients presenting with inconclusive [18F] FDG PET/CT findings. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:73–86. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04940-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meyer C, Dahlbom M, Lindner T, Vauclin S, Mona C, Slavik R, Czernin J, Haberkorn U, Calais J. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution of 68Ga-FAPI-46 PET imaging in cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:1171–1177. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.236786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Syed M, Flechsig P, Liermann J, Windisch P, Staudinger F, Akbaba S, Koerber SA, Freudlsperger C, Plinkert PK, Debus J, Giesel F, Haberkorn U, Adeberg S. Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET for diagnostics and advanced targeted radiotherapy in head and neck cancers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47:2836–45. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04859-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moon ES, Elvas F, Gwendolyn V, De Lombaerde S, Vangestel C, De Bruycker S, Bracke A, Eppard E, Greifenstein L, Klasen B, Kramer V, Staelens S, De Meester I, Van der Veken P, Rösch F. Targeting fibroblast activation protein (FAP): next generation PET radiotracers using squaramide coupled bifunctional DOTA and DATA5m chelators. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2020;5:19. doi: 10.1186/s41181-020-00102-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kreppel B, Gärtner F, Marinova M, Attenberger U, Meisenheimer M, Toma M, Kristiansen G, Feldmann G, Moon ES, Roesch F, Van der Veken P, Essler M. [68Ga] Ga-DATA5m. SA.FAPi PET/CT: specific tracer-uptake in focal nodular hyperplasia and potential role in liver tumor imaging. Nuklearmedizin. 2020;59:387–389. doi: 10.1055/a-1164-5667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ballal S, Yadav MP, Moon ES, Kramer VS, Roesch F, Kumari S, Tripathi M, ArunRaj ST, Sarswat S, Bal C. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, dosimetry of [68Ga] Ga-DOTA. SA. FAPi, and the head-to-head comparison with [18F] F-FDG PET/CT in patients with various cancers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:1915–1931. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05132-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ballal S, Yadav MP, Kramer V, Moon ES, Roesch F, Tripathi M, Mallick S, ArunRaj ST, Bal C. A theranostic approach of [68Ga] Ga-DOTA. SA.FAPi PET/CT-guided [177Lu] Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi radionuclide therapy in an end-stage breast cancer patient: new frontier in targeted radionuclide therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:942–944. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04990-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Burchardt C, Riss PJ, Zoller F, Maschauer S, Prante O, Kuwert T, Roesch F. [68Ga] Ga-DO2A-(OBu-L-tyr)2: synthesis, 68Ga-radiolabeling and in vitro studies of a novel 68Ga-DO2A-tyrosine conjugate as potential tumor tracer for PET. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett. 2009;19:3498–3501. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Riss PJ, Burchardt C, Roesch F. A methodical 68Ga-labelling study of DO2A-(butyl-L-tyrosine)2 with cation-exchanger post-processed 68Ga: practical aspects of radiolabelling. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2011;6:492–8. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chauhan K, Datta A, Adhikari A, Chuttani K, Kumar Singh A, Mishra AK. 68Ga based probe for Alzheimer’s disease: synthesis and preclinical evaluation of homodimeric chalcone in β-amyloid imaging. Org Biomol Chem. 2014;12:7328–37. doi: 10.1039/c4ob00941j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chauhan K, Tiwari AK, Chadha N, Kaul A, Singh AK, Datta A. Chalcone based homodimeric PET agent, 11C-(Chal)2DEA-Me, for beta amyloid imaging: synthesis and bioevaluation. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:1515–25. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b01070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liolios C, Buchmuller B, Bauder-Wüst U, Schäfer M, Leotta K, Haberkorn U, Eder M, Kopka K. Monomeric and dimeric 68Ga-labeled bombesin analogues for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of tumors expressing gastrin-releasing peptide receptors (GRPRs) J Med Chem. 2018;61:2062–74. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zia NA, Cullinane C, Van Zuylekom JK, Waldeck K, McInnes LE, Buncic G, Haskali MB, Roselt PD, Hicks RJ, Donnelly PS. A bivalent inhibitor of prostate specific membrane antigen radiolabeled with copper-64 with high tumor uptake and retention. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58:14991–4. doi: 10.1002/anie.201908964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eppard E, Wuttke M, Nicodemus PL, Rösch F. Ethanol-based post-processing of generator-derived 68Ga: Toward kit-type preparation of 68Ga-radiopharmaceuticals. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:1023–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.133041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.De Meester I, Vanhoof G, Lambeir AM, Scharpé S. Use of immobilized adenosine deaminase (EC 3.5. 4.4) for the rapid purification of native human CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV (EC 3.4.14.5) J Immunol Methods. 1996;189:99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(95)00239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Moon ES, Van Rymenant Y, Battan S, De Loose J, Bracke A, Van der Veken P, De Meester I, Rösch F. In vitro evaluation of the squaramide-conjugated fibroblast activation protein inhibitor-based agents AAZTA5. SA.FAPi and DOTA.SA.FAPi. Molecules. 2021;26:3482. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.