Abstract
Objectives
Liver disease is a leading cause of premature death, partly driven by the increasing incidence of non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Many people with a diagnosis of NAFLD drink moderate amounts of alcohol. There is limited guidance for clinicians looking to advise these patients on the effect this will have on their liver disease progression. This review synthesises the evidence on moderate alcohol consumption and its potential to predict liver disease progression in people with diagnosed NAFLD.
Methods
A systematic review of longitudinal observational cohort studies was conducted. Databases (Medline, Embase, The Cochrane Library and ClinicalTrials.gov) were searched up to September 2020. Studies were included that reported progression of liver disease in adults with NAFLD, looking at moderate levels of alcohol consumption as the exposure of interest. Risk of bias was assessed using the Quality in Prognostic factor Studies tool.
Results
Of 4578 unique citations, 6 met the inclusion criteria. Pooling of data was not possible due to heterogeneity and studies were analysed using narrative synthesis. Evidence suggested that any level of alcohol consumption is associated with worsening of liver outcomes in NAFLD, even for drinking within recommended limits. Well conducted population based studies estimated up to a doubling of incident liver disease outcomes in patients with NAFLD drinking at moderate levels.
Conclusions
This review found that any level of alcohol intake in NAFLD may be harmful to liver health.
Study heterogeneity in definitions of alcohol exposure as well as in outcomes limited quantitative pooling of results. Use of standardised definitions for exposure and outcomes would support future meta-analysis.
Based on this synthesis of the most up to date longitudinal evidence, clinicians seeing patients with NAFLD should currently advise abstinence from alcohol.
PROSPERO registration number
The protocol was registered with PROSPERO (#CRD42020168022).
Keywords: hepatology, general medicine (see internal medicine), primary care
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This is a timely synthesis of the best available evidence on the role of moderate alcohol consumption in non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease.
We used systematic searches to identify literature and prospectively registered our protocol on PROSPERO.
We restricted our inclusion criteria to studies that used longitudinal data to provide evidence of temporal associations.
Due to heterogeneity in definitions of alcohol exposure and outcomes, it was not possible to carry out a meta-analysis.
The existing literature base is limited and only six studies were sufficiently robust to meet our predefined inclusion criteria.
Introduction
Liver disease is an increasing health burden across the world, and it is now a major cause of premature (<65 years) mortality.1 2 As premature mortality rates from many non-communicable diseases have fallen over the last 30 years, the burden of liver disease is increasing.2 3 The most common causes of chronic liver disease in high-income countries are alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) and metabolic-syndrome-related liver disease (or non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease—NAFLD). Chronic liver disease is often diagnosed as a result of abnormal liver blood tests or liver imaging, with a fatty liver (steatosis) progressing in some through inflammation (steatohepatitis) and stiffening (fibrosis) to scarring (cirrhosis) increasing the risk of decompensated liver disease or liver cancer. This process of progressive damage to the liver is common to both aetiologies.
While the labelling of liver disease suggests a dichotomy, the clinical reality is that there is significant overlap between ARLD and NAFLD.4 The incidence of obesity and diabetes is rising, and a substantial proportion of the population is drinking alcohol at above recommended limits.5 It is estimated that up to 17% of the adult population may meet criteria for both NAFLD and ARLD.6 Despite this, there is little guidance available for generalist healthcare professionals, on how to advise people with a diagnosis of NAFLD on safer alcohol consumption.
Recommendations on safe alcohol consumption levels vary worldwide. Increasingly, they take into account the effect that alcohol has on the risk of developing many adverse health outcomes, including cancer. International analysis suggests this should be as low as total abstinence to minimise all health risks.7 Recommended limits for safe alcohol consumption in the UK general population are up to 14 units of alcohol per week in both men and women,8 which equates to 16 g of alcohol per day at 8 g/unit. Moderate alcohol consumption is generally defined in the literature as drinking within, or slightly in excess of, these limits versus complete abstinence.4 There is a significant gap between this recommended ‘moderate’ limit and the levels of alcohol consumption that would prompt an assessment for alcohol-related liver damage. The UK National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends offering a liver cirrhosis test to men drinking over 50 units and women drinking over 35 units a week on an ongoing basis over several months,9 leaving a significant proportion who are drinking at and above 14 units a week, but below the levels to have liver assessment based on their alcohol consumption alone. The international differences in definition of how many grams of alcohol a ‘unit’ contains can create confusion and the reader is directed to table 1 to help in interpreting the study results in the context of UK Government and NICE recommended limits.
Table 1.
International definitions of moderate alcohol consumption, UK recommended limits and levels that would warrant assessment for alcohol-related liver disease, all expressed in grams of alcohol and UK units
| Definitions: | Grams of alcohol | UK units of alcohol | ||
| Daily* | Weekly* | Daily* | Weekly* | |
| Accepted International consensus of moderate alcohol consumption | F: <20 | F: <140 | F: <2.5 | F: <17.5 |
| M: <30 | M: <210 | M: <3.75 | M: <26.25 | |
| UK recommended safe weekly limits | ≤16 | 112 | ≤2 | ≤14 |
| NICE thresholds for assessing for liver cirrhosis | F: >40 | F: >280 | F: >5 | F: >35 |
| M: >57 | M: >400 | M: >7.1 | M: >50 | |
*Daily and weekly figures are given for comparison only. The bold numbering for each definition is the standard format in which this definition is expressed
NICE, National Institute of Health and Care Excellence.
There is still uncertainty, and an absence of guidance, on safe levels of alcohol consumption for people with established NAFLD. Indeed, it is not clear that any level of alcohol consumption is safe to minimise progression of the liver disease in this population. It is known that people with very high levels of alcohol consumption (who would meet criteria for a diagnosis of ARLD), and who also have metabolic risk factors, are at even greater risk of adverse liver outcomes.10 11 But there is also some evidence that for people with metabolic risk factors (but who do not have a NAFLD diagnosis), drinking alcohol at low levels may protect against cardiovascular disease, prevent fatty liver disease and lead to better outcomes than with complete abstinence.12 13 Elucidating the role of alcohol in NAFLD progression is a small part of understanding the interplay of genetic and environmental factors and their effects on the liver; an area of ongoing research and debate.14
The purpose of this systematic review is to synthesise evidence on the role of moderate alcohol consumption on progression to severe liver disease in people with diagnosed NAFLD. This will help guide the advice given to NAFLD populations around safe alcohol consumption in primary care and specialist settings.
Methods
The protocol for this review was registered in advance with PROSPERO (International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews, #CRD42020168022).
Types of studies, inclusion and exclusion criteria
Primary studies were included if they were prospective or retrospective cohort studies. The population of interest was adult patients (>18 years old) with diagnosed NAFLD. The outcome of interest was progression of liver disease in this population. The exposure of interest was no versus moderate alcohol consumption. For our inclusion criteria we defined ‘moderate consumption’ as up to 35 units per week in females, and 50 units per week in males (levels that would be considered the threshold for definite risk of ARLD according to NICE guidelines9). This definition included studies that focused on the effects of alcohol within or just above current weekly recommended limits (the usual definition of moderate alcohol consumption), as well as those who looked beyond these levels of consumption, up to the NICE ARLD levels.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies where the population had diagnosed ARLD; (2) studies where the population was defined according to their alcohol consumption levels rather than their NAFLD status at baseline; (3) studies where patients already had severe liver disease at the time of cohort entry; (4) cross-sectional studies or studies where exposure was only measured at the same time as outcome.
We performed a systematic review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.15
Search strategy and data extraction
Potentially relevant studies were identified through systematic literature searches of relevant databases (Medline, Embase, The Cochrane Library and ClinicalTrials.gov, Conference Proceedings Citation Index—Science, Web of Knowledge, CINAHL(EBSCO)) in January 2020 and updated in September 2020. No language restrictions were applied, and databases searched documents published from 1990 onwards. Reference lists from potentially relevant papers and previous review articles were hand searched. Medical Subject Headings and free-text terms for the NAFLD population, alcohol exposures and liver outcomes of interest were used. Two researchers (HJ and either HO’K or DS) independently screened titles and abstracts. Any disagreement in full-text selection was resolved by consensus. Record screening was also assisted by Rayyan, an online software tool that assesses similarities between selected records and highlights other potentially relevant studies based on the screener’s previous selection.16 Full texts of potentially relevant papers were obtained and read by two independent researchers with reference to the predefined set of criteria to identify final study inclusion. Data were extracted into a standardised form, piloted on three studies before full extraction. Data extraction was based on the updated checklist for critical appraisal and data extraction for systematic reviews of prediction studies checklist for prognostic studies,17 undertaken by one researcher and checked by a second. Two authors (HJ, HO’K) assessed the risk of bias independently. Since the included studies were observational cohort studies of prognostic factors, the Quality in Prognostic factor Studies tool was used.18
Data synthesis
Pooling of data was not possible due to exposure and outcome heterogeneity across studies. A narrative synthesis19 was undertaken, with data synthesised by alcohol exposure level. Due to the small number of studies, even those with high risk of bias are included in the synthesis, although this bias assessment is made clear throughout the narrative.
Patient and public involvement
Patients and the public were not involved in the design or conduct of this review but will be involved in the dissemination of findings through a funded PPI steering group and close collaboration with the British Liver Trust.
Results
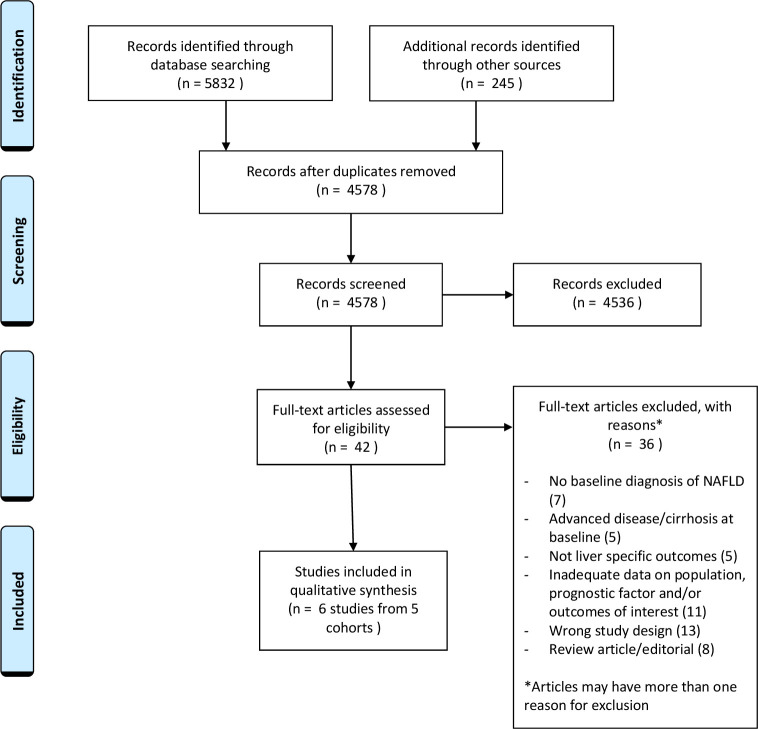
The searches identified 4578 unique citations. Of the titles and abstracts screened, 42 articles were selected for full-text screening. Thirty six were excluded at this stage for reasons summarised in the PRISMA diagram (figure 1). In seven of the excluded studies, the population did not have a baseline diagnosis of NAFLD20–26 and in five studies the population already had advanced liver disease at baseline.27–31 Five of the excluded studied focused on non-liver specific outcomes such as overall mortality,32–36 while 11 were conference abstracts or short papers which held inadequate data on either population, exposure or outcomes.20 21 23 25 29 32 33 37–40 The most common reason for exclusion at full-text stage was study design, mainly cross-sectional studies looking at a single time point to assess exposure and outcome.24 30 31 37–39 41–47 There were also eight studies which on full-text reading were review articles or editorials.48–55 A total of six unique studies representing data from five cohorts were eligible for inclusion in the systematic review, and were assessed for quality (figure 1).56–61
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses diagram of study selection. NAFLD, non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease.
Characteristics of included studies
Further details of included studies are shown in table 2.
Table 2.
Characteristics of included studies
| Author /year | Country | Study design and population | Yrs f/u | Method of NAFLD diag* | Method of measuring alcohol consumption | Definition of moderate consumption studied as RF | Study outcomes of interest and event no | Adjustments of interest considered | Adjusted HRs/OR/ mean differences for liver events with 95% CI and p values | Risk of bias |
| Åberg 201956 | Finland | Retrospective data linkage cohort analysis NAFLD population 6462, mean age 53 years, 60% M |
10.9 | FLI>30 | Questionnaire at cohort entry | <50 g/day in 10 g categories with abstinence as reference | Composite non-fatal and fatal liver disease 58 events |
? unclear other than age, sex | Per increase in 10 g of alcohol per day versus abstinence HR 1.43 (1.12 to 1.82) p=0.004 | High |
| Åberg et al 2020 57 |
Finland (FINRISK Health survey) |
Retrospective data linkage cohort analysis NAFLD population 8345, mean age 53.7 years, 60% M |
11.1 | FLI>60 | Questionnaire at cohort entry (recall for past month) | <50 g/day in 10 g categories with abstinence as reference | Composite non-fatal and fatal liver disease 152 events | Age, sex, smoking, T2DM | g alcohol/day versus abstinence 0–9 hour 1.38 (0.74 to 2.58) 10–19 hour 2.18 (1.04 to 4.53) 20–29 hour 3.62 (1.67 to 7.76) 30–39 hour 3.53 (1.53 to 8.14) 40–49 HR 8.79 (3.95 to 19.56) |
Low |
| Ajmera et al 2018 58 |
USA | Retrospective analysis of longitudinal cohorts within NASH CRN NAFLD population 285, mean age 47 years, 30% M |
3.9 | Liver biopsy | Questionnaire at cohort entry (Skinner lifetime drinking history) | <2 drinks per day and excluded if >6 drinks on 1 occasion ≥monthly | Histological resolution or progressionon follow-up biopsy | Age, sex, race, smoking | Persistent moderate drinkers versus abstinence* resolution of NASH: OR 0.32 (0.11 to 0.92) p=0.04 fibrosis progression: adj mean diff 0.00 (−0.29 to 0.29) p=0.99 |
Mod |
| Chang et al 2019 59 |
South Korea (Kangbuk Samsung Health Study) |
Prospective population cohort NAFLD population 58 927, mean age 37.7, 82% M |
4.9 | US | Questionnaire at each study visit (annual or biennial) | 10–19.9 g/day (F) 10–29.9 g/day (M) (low 1–9.9 g/day) |
Fibrosis progress as estimated by high indirect serum scores** | Age, sex, BMI, smoking, exercise level, education, T2DM, BP | Mod versus abstinence† (repeat observations) Fib4: HR 1.33 (1.13 to 1.57) NFS: HR 1.37 (1.23 to 1.52) low versus abstinence (repeat observations) Fib 4: HR 1.08 (0.91 to 1.27) NFS: HR 1.14 (1.02 to 1.27) |
Low |
| Ekstedt et al 2009 60 |
Sweden | Retrospective cohort NAFLD population 71, mean age 47.3, 72% M |
13.8 | US and liver biopsy | Questionnaire AUDIT-C and interview at follow-up | g/day—no upper limit defined as ‘moderate’ | Fibrosis progress on follow-up biopsy | Age, sex, BMI, T2DM, fibrosis at baseline | Increasing alcohol g/week versus abstinence OR 1.012 (1.000 to 1.025) p=0.055 |
Low |
| Kawamura et al 201661 | Japan | Prospective cohort NAFLD population 9959, mean age 49, 87% M (included 18 patients >70 g alcohol/day defined as ARLD) |
5.4 | US | Questionnaire at baseline and every 6 months | g/day in categories with <20 g/day as reference | HCC on imaging | Age, sex, BMI, T2DM, serum markers | g/day alcohol versus <20 g/day 20–39 hour 0.90 (0.11 to 7.90) p=0.919 ≥40–69 hour 2.48 (1.01 to 6.05) p=0.047 >70 hour 12.61 (5.68 to 28.00) p=0.001 |
Low |
*Note multiple differences in means and OR presented for different histological and biochemical outcomes between abstainers, persistent moderate drinkers, and changes in alcohol consumption between biopsies. Presented data represent histological outcomes of potential clinical prognostic significance within the remit of this review comparing persistent moderate drinking to abstinence.
†Multiple HR presented in paper for different score outcomes for single and repeated outcome measures looking at intermediate/high or high-risk scores in low and moderate drinkers and different subgroups. Presented data represent outcomes best in keeping with remit of this review using widely used indirect serum markers of liver fibrosis.
‡Scores used to estimate fibrosis progression were the Fib4 score, NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and AST to platelet ratio index (APRI) score.
ARLD, alcohol-related liver disease; AUDIT-C, alcohol use disorders identification test - consumption; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; CRN, clinical research network; FINRISK, Finland cardiovascular risk study; FLI, Fatty Liver Index; g, grams; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; M, Male; NAFLD, non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcohol related steatohepatitis; RF, risk factor; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; US, hepatic ultrasound; Yrs, years.
Within the studies meeting inclusion criteria, three58–60 looked at the exposure of alcohol consumption up to, or similar to, the accepted international definition of moderate consumption. This is <20 g/day in women and <30 g/day in men.26 Three of the studies56 57 61 looked at low alcohol consumption but also extended moderate consumption up to levels of alcohol consumption which would be considered more consistent with ARLD.
Moderate alcohol consumption (accepted international definitions) and risk of liver disease progression in NAFLD
Three studies examined the effects of alcohol in NAFLD using definitions in keeping with the accepted international definition of moderate consumption.58–60 Although these studies shared a similar aim, they varied in NAFLD population definition, measurement of alcohol consumption and choice of liver outcomes. Two looked at histological progression outcomes and one used non-invasive indirect blood-based markers of liver fibrosis. Two of the studies were rated as having a low risk of bias59 60 and one was rated as having a moderate risk.58
Ajmera et al58 studied a NAFLD population taken retrospectively from the non-alcohol related steatohepatitis (NASH) clinical research network, including populations from an observational study and the placebo arm of two NASH drug trials, all of whom had biopsy proven NAFLD (285 participants). Alcohol consumption was measured at cohort entry and at varying time points up to, and including, follow-up liver biopsy, which occurred, on average, 3.9 years later. Multiple histological markers of disease progression and resolution were studied, and the authors looked at the association between baseline drinking status and disease, as well as change in drinking status over time and disease progression/resolution. For most of the histological end points studied, there was no significant difference between moderate drinkers and abstainers in outcomes, with the only significant results suggesting that abstainers had less progressive or a higher likelihood of resolution of their disease between biopsies, particularly the persistent abstainers when compared with the persistent moderate drinkers. Results should be interpreted in the knowledge that a large number of related histological outcomes were reported, increasing the likelihood of a statistically significant result by chance. The study also had a relatively short follow-up period between biopsies. The absence of detailed information on which other prognostic factors were taken into account, led to a rating of moderate on risk of bias assessment.
A similar study by Ekstedt et al60 looked at a smaller group (71 participants) of biopsy proven NAFLD, with follow-up histology an average of 13.8 years after initial biopsy. Alcohol consumption was assessed at baseline and follow-up, with heavy episodic drinking assessed in addition to weekly consumption. Primary outcome was significant fibrosis progression, defined as progression by one or more fibrosis stage or the development of end stage liver disease during follow-up. Although higher weekly alcohol consumption showed some tendency to predict fibrosis progression (OR for increase in grams of alcohol per week 1.012 (1.000 to 1.025)) only the presence of heavy episodic drinking (defined as >60 g/day in men and >48 g/day in women more than once a month) reached statistical significance in predicting fibrosis progression.
Of note in both the Ajmera and Ekstedt studies were the very low levels of alcohol consumption in the ‘moderate drinkers’, with the majority (78%) of the moderate drinkers drinking less than monthly in the Ajmera study and the average weekly alcohol consumption in the Ekstedt study being only 39 g/week. Both studies also included a significant number of patients who already had liver inflammation (NASH) at baseline (over 50% in both studies), indicating a higher proportion of patients with a tendency to progressive disease as compared with a general NAFLD population, as would be expected with biopsy-based studies.
In contrast to the relatively selective biopsy studies, Chang et al59 studied a large prospective population cohort (Kangbuk Samsung Health Study) of whom 58 927 had ultrasound evidence of fatty liver but without evidence of other liver diagnoses or advanced disease. Alcohol exposure was weekly units at baseline and follow-up was for a median of 8.3 years with outcome of interest being progression to advanced liver fibrosis using non-invasive blood-based markers of disease. For moderate drinkers (10–30 g/day), the risk of progressing to advanced fibrosis (using intermediate/high Fib4 score as the outcome) was HR 1.33 (1.13 to 1.57), when compared with abstainers. Light drinkers (1–10 g/day) showed a tendency towards more advanced disease when compared with abstainers, but this did not reach statistical significance (HR 1.08 CI 0.91 to 1.27).
Moderate alcohol consumption (below the threshold that would be consistent with ARLD) and risk of liver disease progression in NAFLD
Three studies extended the definition of moderate alcohol consumption beyond the international consensus definition of moderate consumption. Two of the studies were rated as having a low risk of bias,57 61 with one rated as high risk of bias.56
The general population longitudinal data presented by Chang et al59 is supplemented by two recent related studies by Åberg et al,56 57 using data from the same Finnish National Health Surveys (FINRISK, Health 2000) cohort. The definition of moderate alcohol consumption was increased to include anything up to 50 g/day in these studies. Although the exposures and outcome measures were the same in the two related studies, the NAFLD population was defined using different Fatty Liver Index (FLI) cut offs values, generating overlapping but distinct study populations. For this reason, data are presented from both studies.
The first study, only available as a conference abstract,56 used a FLI>30 to retrospectively define their NAFLD population. This low FLI would generally be used as a ‘rule out’ rather than ‘rule in’ cut-off for NAFLD diagnosis62 and the limited data presented suggests that using abstinence as a reference, any increase in alcohol consumption by 10 g/day, increased incident liver events (combined fatal and non-fatal outcomes) by 43% with a presented HR of 1.43 (1.12 to 1.82) for each 10 g rise in daily alcohol consumption. The data presented contained few details of adjustment factors or analysis plan. This study was graded as having a high risk of bias, and these results should be interpreted with caution.
A larger study,57 based on the same cohort, retrospectively identified a NAFLD population based on a FLI of >60 (the accepted and validated cut-off for making a positive diagnosis of NAFLD in the literature63). Alcohol intake at cohort entry was based on estimated consumption over the previous year. Lifetime abstainers were used as the reference group. Fatal and non-fatal liver outcomes were studied in 8345 participants over 92 350 person years of follow-up. The study concluded that incident liver disease is higher at all levels of alcohol consumption, compared with lifetime abstainers with steadily rising HRs as the level of alcohol consumption increases. Although drinking up to 10 g/day was not statistically significantly different to abstaining (HR 1.38 CI 0.74 to 2.58 in the final model), levels of alcohol consumption between 10 g and 19 g, which are roughly equivalent to the 14 units per week recommended limits, prognosticated for over double the number of incident liver events in NAFLD patients (HR 2.18 CI 1.05 to 4.53). At higher levels, which would not necessarily trigger a liver assessment for alcohol related harm in current guidelines, risk of significant liver disease was nearly nine times higher (for consumption of 40–49 g of alcohol a day, HR 8.79 CI 3.95 to 19.56).
A retrospective Japanese cohort study61 also looked at stepwise rises in daily alcohol consumption as a prognostic factor for the more specific outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in people with fatty liver (identified on ultrasound). The Kawamura study with 9959 participants followed for a median of nearly 2000 days, had a reference group of people drinking <20 g of alcohol per day, rather than abstainers. This differed from all the other studies reviewed. Only those drinking at between 40 and 69 g of alcohol a day had a statistically significant increase in rates of HCC (HR 2.48 CI 1.01 to 6.05, p 0.047), with no effect in those drinking at more moderate levels. The population in this retrospective cohort were patients undergoing ultrasound at two tertiary hepatology centres in Japan rather than a general population cohort, and as HCC is known to occur in non-cirrhotic NAFLD64 comparison with outcomes from other studies should be interpreted with caution.
Excluding the only study rated as having a high risk of bias,56 the other good quality longitudinal studies of varying design, all reported either no association or a negative impact of moderate amounts of alcohol on future liver disease outcomes. This was seen across the studies looking at levels of alcohol consumption within the international definition of moderate consumption, and those that extended this definition of moderate consumption.
Discussion
Summary of results
In this systematic review of the latest available longitudinal data, we found evidence to suggest that any amount of alcohol, even at low levels, may be harmful for liver health in people with diagnosed NAFLD. This evidence comes from both general population-based cohorts using coded liver outcomes, as well as tertiary centre NAFLD populations defined using histological end points.
Comparison with existing literature
Until recently the majority of evidence in this area has come from cross-sectional studies where alcohol exposure was assessed at the same time as liver outcomes. These data provide somewhat contradictory results, with several studies indicating that moderate alcohol consumption is associated with lower levels of liver disease progression39 43 65 66 although more recent studies support of our findings, and suggest the opposite.42 45 The design employed in these studies does not allow the assessment of temporal relationships and is open to reverse causality (those with liver damage may be newly abstaining from alcohol for example) in addition to recall and other biases. On the basis of these limitations, cross-sectional studies were excluded from this current review, although they have been widely cited in previous critical reviews in this area, before more recent longitudinal data were available.
In the historical absence of large prospective cohort studies and the impossibility of conducting a controlled trial in the area, comparative work has been undertaken using Mendelian randomisation. This utilises random genetic variations which affects the rate of alcohol metabolism as a proxy measure for alcohol exposure, with randomisation of patients with NAFLD based on an allele known to confer lower lifetime alcohol consumption by necessity due to the unpleasant effects of drinking even low levels of alcohol. Findings from this study were supportive of our review, with the group with higher lifetime alcohol consumption showing markers of more severe disease on biopsy, even though alcohol consumption was at very modest levels.46
In addition to the evidence on the relationship between modest alcohol consumption in NAFLD and liver outcomes, other published studies have focused on overall mortality and cardiovascular outcomes. A study of 4264 participants in an ultrasound diagnosed NAFLD cohort study showed no significant difference in overall mortality in those with alcohol consumption in the low/moderate range versus abstinence after 20 years of follow-up.36 A subsequent study with the same US cohort reported a protective effect of low alcohol consumption on overall survival in NAFLD.67 The evidence for a protective effect of low alcohol consumption on cardiovascular outcomes in the general population is generally accepted.68 The evidence for cardiovascular protection in those with NAFLD is more limited, with some evidence that moderate alcohol may provide some benefit69 but more recent studies finding no protective effects.42 70 The comparative evidence on overall mortality and cardiovascular outcomes highlights the need to assess liver disease risks within these competing contexts.
Strengths and limitations
Although there have been several recent critical reviews of the role of moderate alcohol consumption in NAFLD, the most recent of which reach similar conclusions,4 49 71 these have been wider in their remit with less well-defined inclusion criteria and less systematic methodology. The predetermined inclusion criteria, robust systematic data collection and reporting techniques (in line with PRISMA guidelines) and decision to avoid cross-sectional data are all important in providing the best available evidence to answer the review question of the temporal relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and liver outcomes in NAFLD. The challenges of synthesising observational data, including unmeasured confounding and heterogeneity, were anticipated, but meant that data pooling was not possible.
A particular limitation hindering comparison between studies was the methods of defining moderate alcohol consumption. The consensus for defining a level of alcohol consumption above which a diagnosis of pure NAFLD cannot be made have been supported by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of the Liver Diseases and set at 20 g/day in women and 30 g/day in men,62 72 yet most of the published studies do not use these cut-offs in their data. Until this is standardised across studies, with an additional consensus defining levels above this moderate but not high enough to reach levels associated with a definite diagnosis of ARLD, synthesising the evidence in this area will remain challenging.
Implications for research/practice
This review adds weight to individual studies showing that any level of alcohol intake in NAFLD may be harmful to liver health. Further prospective cohort studies are needed, with detailed definitions/measures of alcohol exposure, and validated clinical liver outcomes, measured at appropriate times. Future research should focus on looking at outcomes in relation to accepted alcohol intake levels used in definitions of NAFLD. It should also take into account that the clinical reality is a dual-aetiology patient who may currently be excluded from both diagnostic categories based on their alcohol intake being too high for NAFLD, and too low for ARLD definitions. This is an ever-expanding patient group seen in many clinical settings.
Based on a synthesis of the evidence presented in this review, clinicians seeing patients with NAFLD in primary or secondary care should currently advise abstinence from alcohol to avoid accelerating liver harm. This is likely to be difficult for patients to accept, and public health messaging will need careful thought if it is to have any impact on liver health.
bmjopen-2021-049767supp001.pdf (50.5KB, pdf)
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Contributors: HJ: conceptualisation, methodology, conduct, analysis, writing of initial draft, guarantor. HO'K: methodology, conduct, figures/infographic, critical review and comments on drafts. DC: supervision of methodology, conduct, critical review and comments on drafts. DS: methodology, conduct, critical review and comments on drafts. BH: conceptualisation, supervision of methodology, conduct, analysis, critical review andcomments on drafts. QMA: conceptualisation, supervision of conduct and analysis, critical review and comments on drafts.
Funding: This work was supported by and NIHR Doctoral Research Fellowship – HJ personal award. Award no: NIHR300716.
Competing interests: HJ reports grants from National Institute for Health research (NIHR), during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Intercept Pharma, personal fees from Norgine, outside the submitted work; QMA reports grants from European Commission, during the conduct of the study; other from Acuitas Medical, grants, personal fees and other from Allergan/Tobira, other from E3Bio, other from Eli Lilly & Company Ltd, other from Galmed, grants, personal fees and other from Genfit SA, personal fees and other from Gilead, other from Grunthal, other from Imperial Innovations, grants and other from Intercept Pharma Europe Ltd, other from Inventiva, other from Janssen, personal fees from Kenes, other from MedImmune, other from NewGene, grants and other from Pfizer Ltd, other from Raptor Pharma, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants and other from Novartis Pharma AG, grants from Abbvie, personal fees from BMS, grants from GSK, other from NGMBio, other from Madrigal, other from Servier, outside the submitted work.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study does not involve human participants.
References
- 1.Williams R, Aspinall R, Bellis M, et al. Addressing liver disease in the UK: a blueprint for attaining excellence in health care and reducing premature mortality from lifestyle issues of excess consumption of alcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis. Lancet 2014;384:1953–97. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61838-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators . The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 20202020;5:245–66. 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Martinez R, Lloyd-Sherlock P, Soliz P, et al. Trends in premature avertable mortality from non-communicable diseases for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a population-based study. Lancet Glob Health 2020;8:e511–23. 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30035-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Boyle M, Masson S, Anstee QM. The bidirectional impacts of alcohol consumption and the metabolic syndrome: cofactors for progressive fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2018;68:251–67. 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Williams R, Alexander G, Armstrong I, et al. Disease burden and costs from excess alcohol consumption, obesity, and viral hepatitis: fourth report of the Lancet standing Commission on liver disease in the UK. Lancet 2018;391:1097–107. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32866-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Baumeister SE, Alte D, Meyer C, et al. [Health Risk drinking and problematic consumption of alcohol in Pomerania: comparative analysis of the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP) compared with the Federal German Health and Examination Survey in 1998]. Gesundheitswesen 2005;67:39–47. 10.1055/s-2004-813829 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.GBD 2016 Alcohol Collaborators . Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet 2018;392:1015–35. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.UK Chief Medical Officers’ Low Risk Drinking Guidelines. Available: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/545937/UK_CMOs__report.pdf
- 9.NICE . Cirrhosis in over 16S: assessment and management. guidance and guidelines. Available: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng50
- 10.Hart CL, Morrison DS, Batty GD, et al. Effect of body mass index and alcohol consumption on liver disease: analysis of data from two prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2010;340:c1240. 10.1136/bmj.c1240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu B, Balkwill A, Reeves G, et al. Body mass index and risk of liver cirrhosis in middle aged UK women: prospective study. BMJ 2010;340:c912. 10.1136/bmj.c912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thun MJ, Peto R, Lopez AD, et al. Alcohol consumption and mortality among middle-aged and elderly U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1705–14. 10.1056/NEJM199712113372401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Pirola CJ. Modest alcohol consumption decreases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of 43 175 individuals. Gut 2014;63:530–2. 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tarantino G, Citro V, Capone D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a challenge from mechanisms to therapy. J Clin Med 2020;9:15. 10.3390/jcm9010015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000097. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, et al. Rayyan-a web and mobile APP for systematic reviews. Syst Rev 2016;5:210. 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moons KGM, de Groot JAH, Bouwmeester W, et al. Critical appraisal and data extraction for systematic reviews of prediction modelling studies: the charms checklist. PLoS Med 2014;11:e1001744. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hayden JA, van der Windt DA, Cartwright JL, et al. Assessing bias in studies of prognostic factors. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:280–6. 10.7326/0003-4819-158-4-201302190-00009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews: a product from the ESRC methods programme. Lancaster: Lancaster university 2006;10:1018–4643. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Akahane T, Fukui K, Yoshiji H. Light-to-moderate alcohol consumption protects against fatty liver and improves insulin resistance. Hepatology;66:1143A–4. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Akahane T, Namisaki T, Kitade M, et al. Moderate alcohol consumption protects against fatty liver in males. Journal of Hepatology;68:S841. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chang Y, Ryu S, Kim Y, et al. Low levels of alcohol consumption, obesity, and development of fatty liver with and without evidence of advanced fibrosis. Hepatology 2020;71:861–73. 10.1002/hep.30867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Colić-Cvrlje V, Naumovski-Mihalić S, Prskalo M, et al. Prognosis for the patients with alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver disease. Coll Antropol 2000;24:249–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cotrim HP, Freitas LA, Alves E, et al. Effects of light-to-moderate alcohol consumption on steatosis and steatohepatitis in severely obese patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;21:969–72. 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328328f3ec [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hara T, Seko Y, Iwai N, et al. Comparison of the effect of light alcohol consumption on Japanese men with and without fatty liver. Biomed Rep 2019;11:191–8. 10.3892/br.2019.1242 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hayashi PH, Harrison SA, Torgerson S, et al. Cognitive lifetime drinking history in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: some cases may be alcohol related. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:76–81. 10.1046/j.1572-0241.2003.04013.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, et al. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010;51:1972–8. 10.1002/hep.23527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kimura T, Tanaka N, Fujimori N, et al. Mild drinking habit is a risk factor for hepatocarcinogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with advanced fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1440–50. 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moylan CA, Dellinger A, Pang H, et al. Modest alcohol consumption attenuates expression of fibrosis-associated genes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Gastroenterology 2011;140:S-914–S-915. 10.1016/S0016-5085(11)63793-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Patel PJ, Smith D, Connor JP, et al. Alcohol consumption in diabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2017:7927685. 10.1155/2017/7927685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Patel PJ, Smith DD, Stuart KA, et al. Can modest alcohol intake be dismissed as a co-factor in diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? J Hepatol 2017;66:S588. 10.1016/S0168-8278(17)31602-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bharmal SJ, Lake J, Boldt M, et al. Long-Term outcomes of patients with non-obese fatty liver disease (NOFLD): a study from the National health and nutrition examination survey. Gastroenterology 2017;152:S683–4. 10.1016/S0016-5085(17)32399-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Clement P, Ellison RC. Alcohol consumption and risk of death in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Revue Medicale Suisse;15:1416. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hajifathalian K, McCullough A. Effect of alcohol consumption on survival in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a national prospective cohort study. Gastroenterology;152:S1054–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xu L, Xie J, Chen S, et al. Light-to-Moderate alcohol consumption is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a nine-year cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 2020;115:876–84. 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Ong J, et al. Effects of alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome on mortality in patients with nonalcoholic and alcohol-related fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:1625–33. 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang A, Chang B, Sun Y. Effect of alcohol consumption on biochemical and histological features of patients with biopsy-proven steatohepatitis. Hepatology;68:1309A. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ivanova R, Alexiev A, Mateva L. Fatty liver disease (fld) and various alcohol intake in patients with obesity. Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases 2012;3:20. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mitchell T, Jeffrey GP, MacQuillan GC, et al. The impact of alcohol consumption on hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology;64:548A. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Ong J, et al. Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD): the impact of alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome on mortality. Hepatology;68:801A–2.29572901 [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hagstrom H, Nasr P, Ekstedt M, et al. Low to moderate lifetime alcohol consumption is associated with less advanced stages of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology;64:18A–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kashiwagi K, Yamaguchi A, Shiba S, et al. Moderate alcohol consumption is not associated with subclinical cardiovascular damage but with hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alcohol 2020;89:1–7. 10.1016/j.alcohol.2020.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kwon HK, Greenson JK, Conjeevaram HS. Effect of lifetime alcohol consumption on the histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 2014;34:129–35. 10.1111/liv.12230 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mitchell T, Jeffrey GP, de Boer B, et al. Type and pattern of alcohol consumption is associated with liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2018;113:1484–93. 10.1038/s41395-018-0133-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mulazzani L, Alvisi M, Tovoli F, et al. Moderate alcohol consumption is associated with risk of fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Digestive and Liver Disease 2020;52:e43–4. 10.1016/j.dld.2019.12.140 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sookoian S, Flichman D, Castaño GO, et al. Mendelian randomisation suggests no beneficial effect of moderate alcohol consumption on the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016;44:1224–34. 10.1111/apt.13828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yamada K, Mizukoshi E, Seike T, et al. Light alcohol consumption has the potential to suppress hepatocellular injury and liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One 2018;13:e0191026. 10.1371/journal.pone.0191026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Åberg F, Färkkilä M. Drinking and obesity: alcoholic liver Disease/Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease interactions. Semin Liver Dis 2020;40:154–62. 10.1055/s-0040-1701443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Åberg F, Färkkilä M, Männistö V. Interaction between alcohol use and metabolic risk factors for liver disease: a critical review of epidemiological studies. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2020;44:384–403. 10.1111/acer.14271 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Åberg F, Puukka P, Salomaa V, et al. Combined effects of alcohol and metabolic disorders in patients with chronic liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:995–7. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.06.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Armstrong MJ, Mellinger JL, Trivedi PJ. Alcohol consumption in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: convenient vs. inconvenient truths. Am J Gastroenterol 2018;113:1437–9. 10.1038/s41395-018-0237-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Glyn-Owen K, Bohning D, Parkes J. The combined effect of alcohol and obesity on risk of liver disease: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Hepatology 2019;70:753A.30854689 [Google Scholar]
- 53.Idalsoaga F, Kulkarni AV, Mousa OY, et al. Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcohol-related liver disease: two intertwined entities. Front Med 2020;7:448. 10.3389/fmed.2020.00448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Petroni ML, Brodosi L, Marchignoli F, et al. Moderate alcohol intake in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: to drink or not to drink? Nutrients 2019;11:3048. 10.3390/nu11123048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Weng G, Dunn W. Effect of alcohol consumption on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;4:70. 10.21037/tgh.2019.09.02 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Åberg F, Puukka P, Sahlman P, et al. LBP-01-In NAFLD, alcohol drinking habits and genetics predict progression to advanced liver disease: follow-up of population surveys. J Hepatol 2019;70:e141. 10.1016/S0618-8278(19)30247-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Åberg F, Puukka P, Salomaa V, et al. Risks of light and moderate alcohol use in fatty liver disease: follow-up of population cohorts. Hepatology 2020;71:835–48. 10.1002/hep.30864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ajmera V, Belt P, Wilson LA, et al. Among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, modest alcohol use is associated with less improvement in histologic steatosis and steatohepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;16:1511–20. 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.01.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chang Y, Cho YK, Kim Y, et al. Nonheavy drinking and worsening of noninvasive fibrosis markers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a cohort study. Hepatology 2019;69:64–75. 10.1002/hep.30170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Holmqvist M, et al. Alcohol consumption is associated with progression of hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2009;44:366–74. 10.1080/00365520802555991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kawamura Y, Arase Y, Ikeda K, et al. Effects of alcohol consumption on hepatocarcinogenesis in Japanese patients with fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:597–605. 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) . EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes Facts 2016;9:65–90. 10.1159/000443344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bedogni G, Bellentani S, Miglioli L, et al. The fatty liver index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol 2006;6:33. 10.1186/1471-230X-6-33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Negro F. Natural history of NASH and HCC. Liver Int 2020;40 Suppl 1:72–6. 10.1111/liv.14362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dunn W, Sanyal AJ, Brunt EM, et al. Modest alcohol consumption is associated with decreased prevalence of steatohepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J Hepatol 2012;57:384–91. 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hagström H, Nasr P, Ekstedt M, et al. Low to moderate lifetime alcohol consumption is associated with less advanced stages of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2017;52:159–65. 10.1080/00365521.2016.1239759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hajifathalian K, Torabi Sagvand B, McCullough AJ. Effect of alcohol consumption on survival in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a national prospective cohort study. Hepatology 2019;70:511–21. 10.1002/hep.30226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Klatsky AL. Alcohol and cardiovascular diseases. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2009;7:499–506. 10.1586/erc.09.22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sinn DH, Gwak G-Y, Cho J, et al. Modest alcohol consumption and carotid plaques or carotid artery stenosis in men with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Atherosclerosis 2014;234:270–5. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.VanWagner LB, Ning H, Allen NB, et al. Alcohol use and cardiovascular disease risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2017;153:1260–72. 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ajmera VH, Terrault NA, Harrison SA. Is moderate alcohol use in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease good or bad? A critical review. Hepatology 2017;65:2090–9. 10.1002/hep.29055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American gastroenterological association, American association for the study of liver diseases, and American College of gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012;142:1592–609. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2021-049767supp001.pdf (50.5KB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.