Abstract
Among others, expression levels of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD‐L1) have been explored as biomarkers of the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. Here, we present the results of a chemical screen that interrogated how medically approved drugs influence PD‐L1 expression. As expected, corticosteroids and inhibitors of Janus kinases were among the top PD‐L1 downregulators. In addition, we identified that PD‐L1 expression is induced by antiestrogenic compounds. Transcriptomic analyses indicate that chronic estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) inhibition triggers a broad immunosuppressive program in ER‐positive breast cancer cells, which is subsequent to their growth arrest and involves the activation of multiple immune checkpoints together with the silencing of the antigen‐presenting machinery. Accordingly, estrogen‐deprived MCF7 cells are resistant to T‐cell‐mediated cell killing, in a manner that is independent of PD‐L1, but which is reverted by estradiol. Our study reveals that while antiestrogen therapies efficiently limit the growth of ER‐positive breast cancer cells, they concomitantly trigger a transcriptional program that favors their immune evasion.
Keywords: breast cancer, estrogen receptor, HLA, immunotherapy, inflammation, PD‐L1
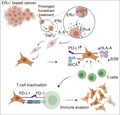
Under prolonged hormone therapy, ER+ breast cancer cells activate an inflammatory transcriptional program, which includes a generalized upregulation of immune checkpoint mediators together with the downregulation of the antigen‐presenting machinery. These findings reveal that, while hormone therapies efficiently arrest the growth of ER+ breast cancer cells, they also promote a phenotype switch that favors their immune evasion.
Abbreviations
- B2M
beta‐2 microglobulin
- BC
breast cancer
- CAPE
caffeic acid phenethyl ester
- CSK
C‐terminal SRC kinase
- E2
17β‐estradiol
- EE
17α‐ethinylestradiol
- EMT
epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- ERα
estrogen receptor alpha
- GSEA
gene set enrichment analysis
- HLA
human leukocyte antigen
- HTM
high‐throughput microscopy
- IFN‐γ
interferon gamma
- IL‐6
interleukin‐6
- JAK
Janus kinase
- MAPK
mitogen‐activated protein kinase
- MMTV‐PyMT
mouse mammary tumor virus–polyoma middle tumor antigen
- NF‐κB
nuclear factor‐kappa B
- PD‐1
programmed cell death protein 1
- PD‐L1
programmed cell death 1 ligand 1
- PD‐L2
programmed cell death 1 ligand 2
- SASP
senescence‐associated secretory phenotype
- SERD
selective estrogen receptor degrader
- SERM
selective estrogen receptor modulator
- SFM
steroid‐free media
- STAT
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TNBC
triple‐negative breast cancer
- TNF‐α
tumor necrosis factor alpha
1. Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequent cancer in women worldwide and the second cause of cancer‐related mortality [1]. In around 75% of BC cases, tumor cells express estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and are dependent on its transcriptional activity for survival and growth [2]. Patients with ERα‐positive tumors (ER+, hereafter) usually receive endocrine therapies such as selective ER modulators (SERM, e.g., tamoxifen), selective ER degraders (SERD, e.g., fulvestrant), or aromatase inhibitors (reviewed in Ref. [3]). Unfortunately, and while hormone therapy is effective in arresting the growth of ER+ cancer cells and reducing tumor burden, a substantial number of patients relapse into a metastatic stage of poor prognosis [4]. Thus, there is intensive effort in testing the efficacy of new therapies, to be used alone or in combination with hormone therapy, to reduce the percentage of recurrences and improve overall survival. In this context, targeting immune checkpoints by blocking programmed cell death 1 (PD‐1) and/or programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD‐L1) is one of the most promising new cancer therapies and has shown to improve progression‐free survival for triple‐negative BC (TNBC) patients [5]. However, initial evidences indicate that ER+ tumors are not very responsive to immunotherapy, which among others might be due to a low mutational burden and low numbers of infiltrating lymphocytes [6].
Estrogens, most frequently 17β‐estradiol (E2), have widespread effects on transcription that are to a large extent mediated by binding to two members of the nuclear receptor family, ERα (ESR1) and ERβ (ESR2). Upon binding to estrogens, these factors homodimerize and bind to target sequences on chromatin where they regulate transcription preferentially at distal enhancers [7, 8]. Besides their well‐known roles in reproductive organs, estrogens have also effects in other tissues including bone, liver, colon, adipose tissue, kidney, skin, and the cardiovascular and central nervous systems [9]. In addition, several lines of evidence indicate a particularly important role of estrogens in suppressing inflammation, which is thought to contribute to the gender‐related differences found in diseases such as multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis [10, 11]. Interestingly, the anti‐inflammatory effects of estrogens might underlie the lower mortality rates of female patients to COVID‐19 [12], which has led to a clinical trial to explore whether estrogen patches can reduce the severity of the infection [13]. Importantly, this effect of estrogens is also relevant in cancers that have been linked to inflammation such as hepatocellular carcinoma, which is three to five times more frequent in men than in women [14].
Despite its relevance for human disease, how estrogens regulate inflammation is yet not fully understood. Most studies in this regard have focused on a crosstalk between ERα and the transcription factor nuclear factor‐kappa B (NF‐κB), a key regulatory element of inflammatory responses associated with the development, progression, and therapy resistance in cancer [15, 16, 17]. An example of this crosstalk relates to ERα preventing the binding of NF‐κB to its target sites in the interleukin‐6 (IL‐6) promoter, thereby preventing the expression of this key proinflammatory cytokine [18]. Surprisingly, and although the link between estrogen signaling and inflammation has been known for decades, the contribution of this phenomenon in the context of the estrogen deprivation therapy for ER+ BC patients remains largely unexplored. We here reveal that while hormone therapy efficiently arrests the growth of epithelial ER+ BC cells, it also triggers a broad inflammatory and immunosuppressive transcriptional program that limits their clearance by the immune system.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Cell culture, transfection, and chemicals
A549, MCF7, T47D, ZR‐75‐1, HCC1937, and MDA‐MB‐231 were a kind gift from T. Helleday laboratory, and cell line identity was confirmed using short‐tandem repeat profiling analysis by ATCC. Except for ZR‐75‐1 and HCC1937, which were cultured in RPMI 1640, all cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin/streptomycin (100 U·mL−1) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator. For experiments requiring hormone depletion, cells were cultured in phenol red‐free DMEM or RPMI 1640 supplemented with 2 mm l‐glutamine and 10% charcoal/dextran stripped fetal bovine serum (Sigma‐Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA; F6765), hereafter termed steroid‐free media (SFM). Where indicated, 10 nm 17α‐ethinylestradiol (Sigma‐Aldrich, E4876) was added to SFM. For fulvestrant treatments, cells were cultured in standard DMEM supplemented with 1 µm fulvestrant (ICI 182, 780, Tocris, Bio‐Techne Ltd., Abingdon, UK, 1047) for the indicated number of days. During all treatments, the respective media were exchanged every 4 days. For siRNA transfections, cells were seeded in six‐well plates and transfected the next day with 30 pmol of ESR1 (Sigma‐Aldrich, SASI_Hs01_00078592), ESR2 (Dharmacon, Horizon Discovery, Cambridge, UK, L‐003402‐00‐0005), or Ctrl (Dharmacon, D‐001810‐10‐20) siRNA using RNAiMAX according to the manufacturer's instructions. Transfection was repeated 3 days later, and cells were harvested for analysis at day 6.
2.2. High‐throughput screening (HTS)
The chemical compound library was provided by the Chemical Biology Consortium Sweden (CBCS) and contained 4126 pharmacologically active compounds from the following libraries: Prestwick, Tocris mini, Selleck tool compounds, Selleck known kinase inhibitors, and ENZO tool compounds, as well as 115 covalent drugs synthesized by Henriksson M. (Karolinska Institutet, Sweden). Plate handling and liquid handling were performed using Echo 550 (Labcyte, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, Indianapolis, IN, USA), Viaflo 384 (Integra Bioscience, Hudson, NH, USA), and MultiFlo FX Multi‐Mode Dispenser (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA). Images were acquired by IN Cell Analyzer 2200 (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with a 10× objective, and quantitative image analyses were run in CellProfiler (https://cellprofiler.org) [19]. Statistical analyses were carried out with Microsoft Excel and graphpad prism software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). For the primary HT screening, A549 cells were trypsinized, resuspended in culture medium containing 100 ng·mL−1 human interferon gamma (IFN‐γ; Sigma‐Aldrich), dispensed into 384‐well plates (BD Falcon, Corning, Glendale, AZ, USA, 353962), and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. The next day, compounds were added to cells achieving a final concentration of 10 μm and a DMSO volume concentration of 0.1%. Cells were incubated for 24 h before staining with PE‐labeled anti‐human CD274 (Clone MIH1; BD Biosciences, Stockholm, Sweden) antibody. Cells were fixed and stained with 2% formaldehyde and 2 mm Hoechst 33342, respectively. For the validation screening, MCF7 cells were hormone‐stripped by preculturing in SFM for 15 days with several medium changes. Cells were subsequently exposed to DMSO or ethinylestradiol (EE) for 3 days, seeded in 384‐well plates, and incubated overnight at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. The next day, the chemical library, comprising 163 compounds, including estrogens and antiestrogens, was added to the cells reaching a final concentration of 0.1, 1.0, and 10 µm. After 72 h of incubation, cells were stained and fixed as described above.
2.3. Immunoblotting
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Sigma‐Aldrich, Stockholm, Sweden), sonicated for 5 min, and centrifuged at 4 °C, at 16 900 g for 15 min. 50 μg whole‐cell extracts were separated by SDS/PAGE and transferred onto Nitrocellulose membrane (Bio‐Rad). After blocking in 5% milk in TBST, immunodetection was done overnight at 4 °C with antibodies against PD‐L1 (CST, 13684), ERα (CST, 8644), C‐terminal SRC kinase (CSK; CST, 4980), Stat1 (CST, 14994), phospho‐Stat1Tyr701 (CST, 9167), p65 (CST, 8242), phospho‐p65Ser536 (CST, 3033), p21(CST, 2947), H3K9me3 (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany, 07‐442), β‐actin (Abcam, Cambridge, UK, ab6276), vinculin (Abcam, ab129002), and GAPDH (Millipore Sigma, Sigma‐Aldrich, ab2302). Appropriate HRP‐coupled secondary antibodies diluted in blocking solution were incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Signals were visualized by chemiluminescence (SuperSignal™ West Dura; Thermo Scientific, 34076) and acquired by an Amersham Imager 600 (GE Healthcare).
2.4. Flow cytometry
Cells were cultured as indicated and harvested using Accutase (BD Biosciences, 561527). After centrifugation, cells were stained with fluorescently labeled PE anti‐human PD‐L1 antibody (Clone MIH1; BD Biosciences), PE anti‐human PD‐L2, PerCP/Cy5.5 anti‐human β2‐microglobulin, and PerCP/Cy5.5 anti‐human human leukocyte antigen (HLA)‐A, HLA‐B, and HLA‐C (all from BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA) diluted in 2% FBS‐PBS blocking solution for 45 min at 4 °C. Samples were washed and immediately measured on a Guava easyCyte flow cytometer (EMD Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). Data were analyzed with Guava InCyte and graphpad prism software (GraphPad Software Inc.).
2.5. Quantitative RT‐PCR
Total RNA was isolated using the PureLink RNA Mini Kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reverse transcription and PCR amplification were performed using TaqMan RNA‐to‐CT 1‐Step Kit and the StepOnePlus™ Real‐Time PCR Instrument (Applied Biosystems, Fisher Scientific, Göteborg, Sweden). The following probes were used in this study: Hs01125301_m1 for CD274, Hs99999901_s1 for 18S, Hs03929097_g1 for GAPDH, Hs01046817_m1 for ESR1, Hs01100353_m1 for ESR2, Hs00174128_m1 for TNFA, Hs00989291_m1 for IFNG, Hs00174131_m1 for IL‐6, and Hs01058806_g1 for HLA‐A.
2.6. Cytokine analysis
MCF7 cells were cultured in different media for indicated number of days, and supernatant culture media were collected every 4 days, centrifuged, and stored at −80 °C until analysis. IL‐6 levels of culture supernatants were determined using the LEGENDplex™ Human Inflammation Panel I (BioLegend, 740809), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, supernatants (50 μL per sample) were incubated with capture beads for 2 h at room temperature on an orbital shaker. Next, detection antibody was added and beads were incubated for 1 h at room temperature. After washing the beads, samples were measured using a BD LSRFortessa™ flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). Cytokine concentration was calculated based on a standard curve using BioLegend's LEGENDplex™ data analysis software.
2.7. Generation of knockout cell lines
For CRISPR/Cas9‐mediated generation of PD‐L1 knockout clones, hybridized oligos (CACCGGCTGCACTAATTGTCTATT) targeting the human CD274 locus were ligated into the pSpCas9(BB)‐2A‐GFP plasmid (a gift from F. Zhang, Addgene #48138, Teddington, UK) according to standard procedures and transfected into MCF7 cells [20]. GFP‐positive cells were FACS‐sorted, and individual PD‐L1 knockout clones were confirmed by western blotting (WB). For the generation of CSK‐deficient MCF7 cells, the pSpCas9(BB)‐2A‐GFP plasmid was cotransfected with crRNA (target sequence: TACCTTGGTGACGGCCACAA, CM‐003110‐02; Horizon Discovery) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Two days after transfection, GFP‐positive cells were FACS‐sorted into a 96‐well plate and single clones were analyzed for CSK deficiency by WB.
2.8. RNA sequencing and data analyses
Next‐generation RNA sequencing was performed to determine changes in gene expression between DMEM (normal)‐, SFM (Treatment 1)‐, fulvestrant (Treatment 2)‐, or SFM+EE (Treatment 3)‐cultured MCF7 cells. Cells were cultured during 20 days in DMEM, SFM, or fulvestrant, and 20 days in SFM with the addition of EE in the last 4 days. The cells were subsequently harvested and frozen at −80 °C, and the samples were processed by Eurofins (Ebersberg, Germany) Genomics Sweden AB, where the RNA was isolated and assessed for QC, and finally, cDNA library preparation was performed. Illumina single‐read sequencing with a read length of 1× 50 bp and 30 million reads per sample was performed.
For gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), genes in each condition were ranked based on the log2 (fold change) value between DMEM (normal) and SFM (Treatment 1) or fulvestrant (Treatment 2). Each treatment was done in triplicate. Genes enriched in each treatment were positive, and genes enriched in normal conditions (DMEM) were negative. The ranked gene lists were loaded into GSEA software and tested against the gene sets of the Hallmark collection (MSigDB).
RNA sequencing and subsequent analyses comparing two different CSK knockout clones with MCF7 WT cells were performed by the Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis core facility of Karolinska Institutet.
RNA sequencing data associated with this work are accessible at the GEO repository, under accession numbers GSE134938 and GSE181909.
2.9. T‐cell‐mediated tumor cell killing assay
MCF7 cells were transfected with mCherry‐Nucleus‐7, a gift from Michael Davidson (Addgene plasmid #55110), and a clone was selected. This MCF7 clone was then subjected to SFM, SFM with 10 nm EE, and fulvestrant treatments, as described above. T cells were isolated 5 days prior to addition of MCF7 cells and were activated with Dynabeads® Human T‐Activator CD3/CD28 (Thermo Fisher, 11131D) and 2.5 ng·mL−1 of recombinant human IL‐2 (Thermo Fisher, PHC0027). T cells were cocultured with the mCherry‐Nucleus‐7 MCF7 cells in the presence of CellEvent™ Caspase‐3/7 Green Detection Reagent (Thermo Fisher, C10423) in 96‐well plates. Images were captured every 2 hours on a MetaXpress Microscope (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). Total MCF7 nuclear count and caspase intensity was analyzed using cellprofiler software.
2.10. METABRIC data set analysis
mRNA expression levels of the indicated genes from the BC data set [21, 22] were retrieved from cBioPortal. Only patients with tumor mRNA data were taken into consideration (n = 1904). The samples were then classified as ERα+ or ERα−, and ERα+ samples were further subdivided in hormone therapy‐treated or not (− or + HT) using the annotation included in the dataset. The expression levels present in cBioPortal are automatically transformed into Z‐scores for comparison purposes. Two‐tailed Student's t‐test was used to assess the statistically significant differences in mRNA expression levels of the specified genes between ERα+ or ERα− and −HT or +HT patients.
2.11. Mouse study
Polyoma middle tumor antigen (PyMT) [FVB/N‐Tg(MMTV‐PyVT)634Mul/J] transgenic animals harboring breast tumors were treated with 4‐hydroxytamoxifen (Sigma‐Aldrich; 1.2 mg·kg−1·daily−1) in 10% ethanol in sunflower oil by oral gavage. Animals were killed in CO2 chamber when tumors reached the humane end point, and the tumors were fixed in 10% formalin solution and embedded in paraffin. For purification of total RNA from formalin‐fixed tumor sections, RNeasy FFPE Kit (Qiagen) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. Reverse transcription was done using SuperScript™ IV VILOTM Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and the real‐time PCR was performed using Fast SYBRTM Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) in a 7500 Fast Real‐Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The following primers were used for Cd274 (FW: 5′ TGCGGACTACAAGCGAATCA and REV: 5′ GCTGGATCCACGGAAATTC) and β‐actin detection (FW: 5′ GGCTCCTAGCACCATGAAGA and REV: 5′ CCACCGATCCACACAGAGTA).
2.12. Human study and tissue
Selection of human ER+ BC tissue samples has been described previously [23]. Briefly, women with a histological diagnosis of hormone receptor positive BC, for whom tissue from a distant metastasis and full medical records were available, were eligible. Patients with synchronous metastases were excluded. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hospital 12 de Octubre (‘Comité Ético de Investigación Clínica—Hospital 12 de Octubre’, Madrid, Spain; Study code: 11/137) and conducted according to the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki. This review board waived the need for consent since all the samples belonged to patients diagnosed of cancer before 2007. According to the Royal Act in Biomedical Research in force in Spain since 2007 (Royal Act 14/2007, July 3), the retrospective collection of archival samples belonging to patients diagnosed before 2007 does not require individual signed informed consent.
2.13. Immunohistochemistry
For histological analyses, tissues were fixed in 10% buffered formalin (Sigma‐Aldrich) and embedded in paraffin. Immunohistochemical staining with anti‐PD‐L1 antibody (rabbit monoclonal antibody (E1L3N); Cell Signaling #13684) was performed on 2.5‐μm tissue sections. Immunohistochemistry was performed using an automated protocol developed for the Autostainer Link automated slide staining system (DAKO, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). All steps were performed on this staining platform using validated reagents, including deparaffinization, antigen retrieval (cell conditioning), and antibody incubation and detection. Corresponding stainings were acquired and digitalized using the AxioScan.Z1 system (Zeiss). Digitalized images were automatically analyzed with the axiovision version 4.6.2 software (Zeiss). The percentage of PD‐L1 positivity was considered as ratio of PD‐L1‐positive cells to total number of cells.
2.14. SA‐β galactosidase assay
Senescence was induced in MCF7 cells by treatment with 5 μm Nutlin‐3 (Selleckchem, M300F‐500) for indicated number of days. Senescent cells were stained for β‐galactosidase activity at pH 6 (CST, 9860).
2.15. Statistics
Statistical parameters and tests are reported in the figures and corresponding figure legends. Statistical analysis was done using graphpad prism version 8.0 (GraphPad Software Inc.). One‐way‐ANOVA was performed for all the datasets that required comparison among multiple data points within a given experimental condition.
3. Results
3.1. Modulation of PD‐L1 expression by medically approved drugs
PD‐L1 levels in tumor biopsies are one of the biomarkers that have been shown to predict the response to cancer immunotherapy using anti‐PD‐L1 inhibitors [24]. In this context, we seek to determine how all medically approved drugs influence the surface expression of PD‐L1. To do so, we conducted a High‐Throughput screen using a library of 4216 compounds including 1200 FDA‐approved drugs and other chemicals at various stages of clinical development (Fig. 1A; see Materials and methods for details). The screening was conducted in the human lung cancer cell line A549, which was previously shown to express PD‐L1 upon IFN‐γ stimulation [25]. Since we were primarily focused on identifying downregulators of PD‐L1 expression, which could limit the efficacy of anti‐PD‐1/PD‐L1 therapies, the screening was conducted on A549 cells that were previously treated with 100 ng·mL−1 of IFN‐γ for 24 h and then subsequently with the compounds from the library for another 24 h. At this point, cells were stained with anti‐PD‐L1 antibodies, fixed, and processed for high‐throughput microscopy (HTM). As expected, wells treated with only IFN‐γ (positive control) showed a significant increase in PD‐L1 expression when compared to DMSO‐treated wells.
Fig. 1.
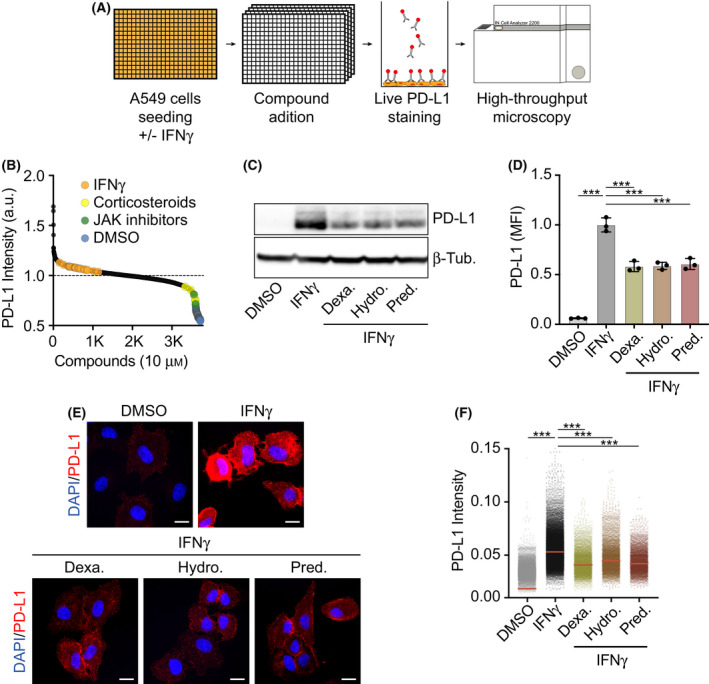
Evaluating the effect of medically approved drugs on IFN‐γ‐induced PD‐L1 expression. (A) Overview of the phenotypic screen workflow. Briefly, A549 cells were seeded in 100 ng·mL−1 IFN‐γ 24 h before addition of 4216 compounds at 10 μm. After 24 h of compound exposure, cells were stained with an anti‐PD‐L1 antibody conjugated to phycoerythrin and fixed with formaldehyde. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst, and the immunofluorescences were analyzed by HTM. (B) Hit distribution of the screen described in (A) illustrating the enrichment of JAK inhibitors and corticosteroids among the compounds reducing PD‐L1 signal in HTM. PD‐L1 levels in wells with only IFN‐γ and negative controls (DMSO) are also shown to illustrate the window of the assay. (C) Western blot illustrating the levels of PD‐L1 in A549 cells grown in the presence of DMSO as control or 100 ng·mL−1 IFN‐γ 24 h before addition of hydrocortisone (10 μm), prednisolone (10 μm), or dexamethasone (10 μm), for 24 h. β‐Tubulin levels are shown for loading control. (D) Quantification of flow cytometry‐mediated assessment of surface PD‐L1 levels in A549 cells after 24 h of control or compound exposure (treated as in (C)). Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) values are relative to those observed in the control. One‐way ANOVA (n = 3) was used for statistical analysis ***P < 0.001, error bars indicate ± SD. (E) Representative immunofluorescence images of PD‐L1 (red) in A549 cells cultured in the presence or absence of IFN‐γ and the indicated compounds (treated as in (C)), nuclei are shown in blue. Scale bar (white), 5 μm. (F) HTM‐based quantification of PD‐L1 levels in A549 cells treated as in (C). One‐way ANOVA test (n = 3) was used to calculate statistical significance of the differences between groups, ***P < 0.001. All datapoints represent single‐cell measurements, with the horizontal red line indicating the median.
After analyzing the results from the screen, corticosteroids were the most enriched compound class among those lowering PD‐L1 expression (Fig. 1B and Table S1). Subsequent validation experiments using WB, flow cytometry, and high‐content microscopy confirmed that three independent corticosteroids (dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, and prednisolone) significantly reduced surface levels of PD‐L1 in IFN‐γ‐treated A549 cells (Fig. 1C–F). Besides corticosteroids, inhibitors of the Janus kinases (JAK1/2) were also found among the top downregulators, which is in agreement with their known role in the IFN‐γ‐dependent induction of PD‐L1 [26]. In addition to validating the usefulness of our approach, our findings help to understand why JAK1/2 mutations [27] or a baseline corticosteroid treatment [28, 29] confer resistance to anti‐PD‐L1 therapy.
3.2. ERα signaling suppresses PD‐L1 expression in ER+ BC cells
In contrast to molecules lowering PD‐L1 expression, there were very few chemicals capable of substantially inducing PD‐L1 beyond the levels observed upon IFN‐γ treatment, which failed to be confirmed in subsequent validation experiments (many of the hits were related to autofluorescence of the compounds). We were nevertheless intrigued by the presence of the SERD fulvestrant among the top compounds from this list (Table S1). Of note, even if the chemical screening was done in A549 cells, these cells express ERα and fulvestrant reduces the growth of A549 xenografts [30]. In any case, and to further investigate the potential effect of antiestrogen therapies on increasing PD‐L1 expression we switched to MCF7, which is a widely used ER+ BC cell line.
First, and in order to evaluate the effect of hormone deprivation on PD‐L1 expression, we grew MCF7 cells in SFM for two weeks. This led to a clear upregulation of PD‐L1, which was present on the cell membrane (Fig. 2A). Using this experimental setup, we conducted a focused chemical screen, where we tested the effects of 25 ER agonists and 11 ER antagonists in a dose–response (Fig. 2B, Table S2). Despite variability on the effects observed with individual compounds, there was a clear overall trend in that ER agonists reduced and antagonists increased PD‐L1 expression in SFM‐grown MCF7 cells (Fig. 2B,C). Flow cytometry data confirmed that either growing MCF7 cells on SFM or treating them with fulvestrant for two weeks led to a clear upregulation of surface PD‐L1 levels (Fig. 2D–G). Similar results were observed by WB (Fig. 2H). It is noteworthy that while a treatment with the synthetic estrogen ethinylestradiol (EE) downregulated PD‐L1 in SFM‐grown cells, it failed to do so in those treated with fulvestrant, which is explained by the fact that these cells lack ERα expression (Fig. 2H). Likewise, even if SFM or fulvestrant induced PD‐L1 expression in several ERα+ cell lines, this effect was not seen in ERα− ones (Fig. S1). Quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR) analyses revealed that the upregulation of PD‐L1 (CD274) levels in SFM‐ or fulvestrant‐treated MCF7 cells occurred at the level of transcription (Fig. 2I,J). Finally, RNA interference‐mediated downregulation of ERα (ESR1) but not ERβ (ESR2) also led to the upregulation of transcription and surface PD‐L1 levels in MCF7 cells (Fig. S2). Collectively, these experiments reveal that estrogens suppress PD‐L1 expression in ER+ BC cells through the stimulation of ERα signaling.
Fig. 2.
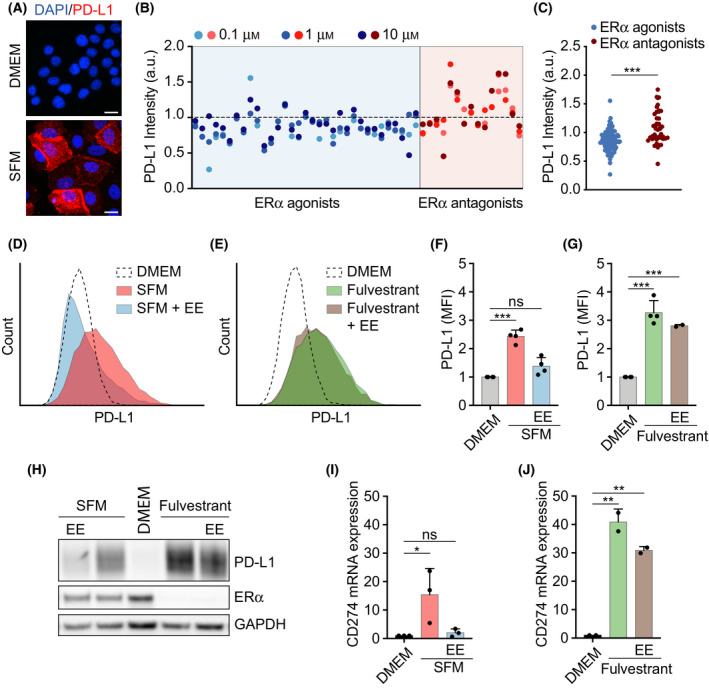
Estrogen‐dependent suppression of PD‐L1 expression in ER+ BC cells. (A) Immunofluorescence of PD‐L1 (red) in MCF7 cells cultured in normal or steroid‐free medium (SFM) for 15 days. DAPI (blue) was used to stain DNA. Representative images are shown. Scale bar (white), 5 μm. (B) Scatterplot of PD‐L1 intensity levels in SFM‐grown MCF7 cells treated with ERα agonists or antagonists, screened at three concentrations, 0.1, 1.0, and 10 µm. (C) Grouped comparison of PD‐L1 levels in response to ERα agonists and ERα antagonists from the experiment shown in (B) using a two‐tailed Student t‐test. (D, E) Flow cytometry‐mediated assessment of surface PD‐L1 levels in MCF7 cells grown in DMEM, SFM (D), or DMEM containing 1 μm fulvestrant (Fulv) (E) for 14 days. Where indicated, EE (10 nm) was added for the final 3 days. (F,G) Quantification of 4 independent flow cytometric experiments as shown in (D, E). Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) values are relative to those observed in the control. Data represent the mean ± SD, ***P < 0.001 calculated by one‐way ANOVA. (H) Western blot illustrating the levels of PD‐L1 and ERα of MCF7 cells cultured as in (D, E). GAPDH levels are shown for loading control. (I, J) qRT‐PCR analysis of PD‐L1 (CD274) expression in MCF7 cells cultured in DMEM and SFM (n = 3 in I) or 1 μm fulvestrant (n = 2 in J) for 18 days. Where indicated, media were supplemented with EE (10 nm) for the last 3 days. 18S RNA served as an internal control. Data represent the mean ± SD, statistical significance was determined by one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
3.3. ERα inversely correlates with PD‐L1 expression in breast cancer
Recent analyses of The Cancer Genome Atlas project have indicated higher levels of PD‐L1 in triple‐negative BC (TNBC) when compared to non‐TNBC subtypes [31]. Based on our findings, we explored whether this correlation could be linked to the expression of ERα. Indeed, gene expression analysis of 1904 BCs (ERα+: 1459; ERα−:445) from the METABRIC cohort of the European Genome‐Phenome Archive (EGA) dataset [21] revealed significantly higher levels of PD‐L1 mRNA expression (CD274) in the ERα− cohort (Fig. S3A). Similar results could be observed at the protein level when comparing PD‐L1 expression between 5 ERα+ cell lines (MCF7, T47D, CAMA‐1, ZR‐75‐1 and BT‐474) and 3 ERα− ones (MDA‐MB‐231, HCC1937 and BT‐549; Fig. S3B).
Next, to determine whether PD‐L1 expression was also induced in vivo in response to an antiestrogen treatment, we used a transgenic mouse model of ER+ BC based on the expression of the Polyoma Virus middle T Antigen downstream of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat (MMTV‐PyMT) [32]. In agreement with our in vitro findings, treatment of MMTV‐PyMT transgenic mice harboring BC with the SERM tamoxifen led to a significant increase in PD‐L1 expression in the tumors (Fig. S3C,D). Finally, we evaluated PD‐L1 expression in tissue from a small cohort of human patients of ER+ BC (clinical and demographic characteristics detailed in Table S3) for which we obtained paired biopsies from the primary tumor and the metastases that emerged during or after adjuvant hormonal therapy. While PD‐L1 expression was virtually absent in the primary tumors, areas of PD‐L1‐expressing cells could be detected in half of the metastatic samples (Fig. S3E,F).
3.4. Estrogen deprivation activates a broad immune‐suppressive transcriptional program in MCF7 cells
To determine the mechanism by which estrogen deprivation induces PD‐L1, we first analyzed how it impacts on the activity of JAK‐signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins (JAK‐STAT) and NF‐κB signaling pathways, both of which are key regulators of PD‐L1 expression [27, 33, 34, 35]. In fact, a time course of MCF7 cells grown in SFM revealed that both pathways were activated, as evidenced by the phosphorylation of STAT1 at Tyr 701 (p‐STAT1Tyr701) and RelA (p65) at Ser 536 (p‐p65Ser536), concomitantly to the upregulation of PD‐L1 (Fig. 3A). Moreover, treatment with a JAK2 inhibitor (CEP‐33779) or the NF‐κB inhibitor [caffeic acid phenethyl ester 9 (CAPE)] reduced the upregulation of PD‐L1 induced by SFM in MCF7 cells (Fig. 3B). Addition of EE after 16 days in SFM for 4 days reverted STAT1 but not p65 phosphorylation, arguing that activation of the JAK/STAT pathway rather than NF‐κB is the primary mediator of upregulating PD‐L1 in response to estrogen deprivation (Fig. 3A).
Fig. 3.
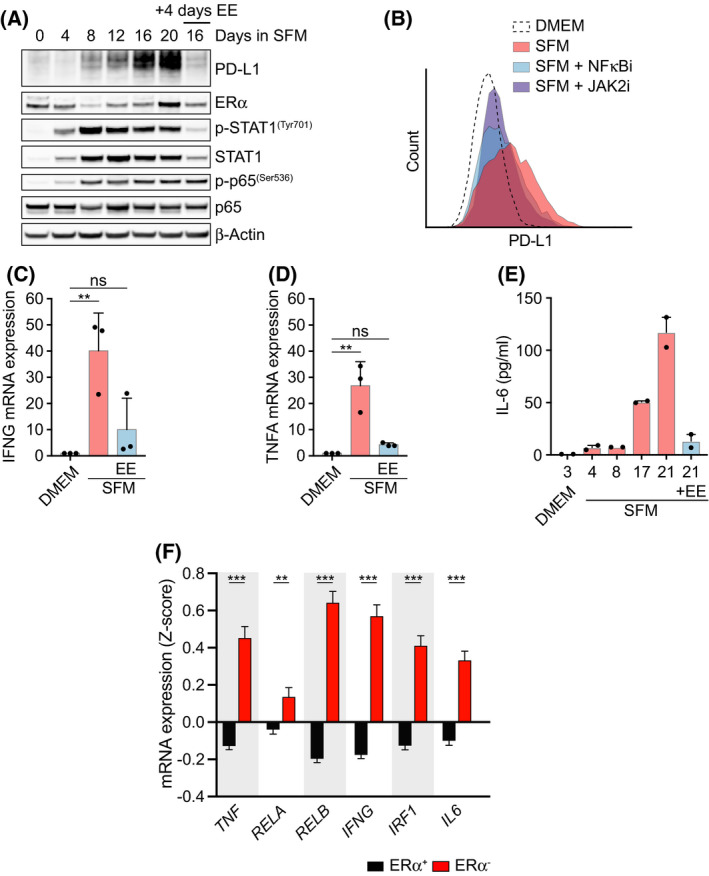
Estrogen signaling suppresses an inflammatory phenotype in MCF7 cells. (A) Whole‐cell lysates from MCF7 cells cultured in SFM for the specified days were analyzed by WB using the indicated antibodies. Where indicated, 10 nm EE was added at 16 days for the final 4 days. Total p65 and β‐Actin served as loading controls. (B) Flow cytometry‐mediated evaluation of PD‐L1 membrane levels in MCF7 cells grown in DMEM or SFM for 21 days, alone or in combination with the NF‐kB inhibitor CAPE (10 μm) or JAK2 inhibitor CEP‐33779 (10 μm) for the last 3 days. Representative data from 3 experiments are shown. (C, D) qRT‐PCR analysis (n = 3) of IFN‐γ (IFNG) (C) or TNF‐α (TNFA) (D) mRNA levels in MCF7 cells cultured as in (A). 18S rRNA was used as an internal control. (E) Levels of IL‐6 in the supernatant of MCF7 cells cultured in DMEM or SFM for the specified days as measured in duplicates by LEGENDplex‐FACS (see Materials and methods). Where indicated, EE (10 nm) was added at day 17 for the last 4 days. (F) TNF, RELA, RELB, IFNG, IRF1, and IL6 mRNA expression levels in ERα+ (n = 1459) and ERα− (n = 445) patient samples. Normalized Z‐scores were extracted from the METABRIC dataset [22]. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and two‐tailed Student's t‐test was used to calculate the statistical significance. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
As to how JAK/STAT and NF‐κB signaling are activated upon estrogen deprivation, we found increased mRNA levels of IFN‐γ and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF‐α) in SFM‐grown MCF7 cells, which are the primary cytokines involved in the activation of each pathway, respectively (Fig. 3C,D). Interestingly, and besides IFN‐γ, estrogen deprivation also induced the secretion of IL‐6, which is a central inflammatory cytokine that stimulates JAK/STAT signaling and that is known to decrease the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy (Fig. 3E) [36]. Consistent with these in vitro findings, analysis of the METABRIC dataset containing transcriptomic analyses of 1904 BC patients revealed significantly higher levels of TNF, RELA, RELB, IFNG, IRF1, and IL6 mRNA expression in ERα− tumors when compared to ERα+ ones (Fig. 3F).
To obtain a general view of the transcriptional changes induced by estrogen deprivation in ER+ BC cells, we conducted RNA sequencing (RNAseq) in MCF7 cells grown in SFM or with fulvestrant for 3 weeks. We should note that while previous works have analyzed the effect of estrogen signaling on the transcriptome, these studies were focused on short‐term treatments aiming to the discovery of direct targets of ERα, days before we observe the induction of PD‐L1 expression or the activation of JAK/STAT and NF‐kB pathways [37, 38]. Analysis of GSEA hallmarks showed a good correlation between the transcriptional changes induced by both conditions (Fig. 4A). One of the common hallmarks was the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is consistent with the change in morphology that is observed with these treatments. Moreover, and in support to the previous data, ‘TNF‐α signaling via NF‐κB’, ‘IFN‐γ response’, or ‘inflammatory response’ was among the most significantly induced hallmarks (Fig. 4B and Fig. S4).
Fig. 4.
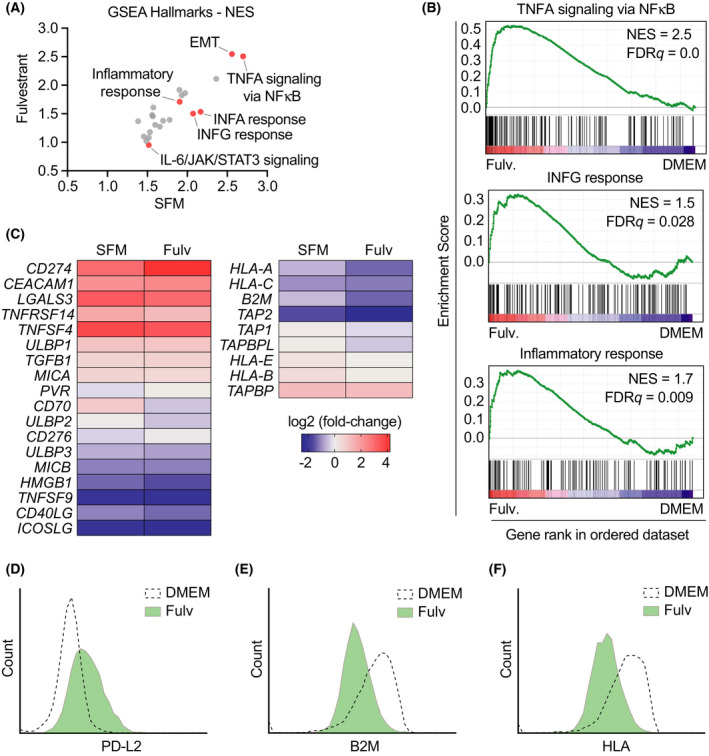
Estrogen deprivation drives expression of immune checkpoints together with silencing of the antigen‐presenting machinery. (A) GSEA hallmark gene sets ranked by normalized enrichment score (NES) comparing the transcriptional programs triggered by 3‐week treatments with fulvestrant (1 μm) or SFM in MCF7 cells, both normalized to DMEM (n = 3 biological replicates). Selected hallmarks are indicated in red. (B) Preranked GSEA on the genes from the hallmarks ‘TNFA signaling via NF‐κB’, ‘IFNG response’, and ‘inflammatory response’ obtained from RNAseq analysis comparing the transcriptome of MCF7 cells grown in DMEM or fulvestrant (1 μm) for 3 weeks. The heatmap representation illustrates the overall upregulation of these pathways in estrogen‐deprived MCF7 cells. (C) Representation of the expression of selected mRNAs related to immune checkpoints (left) and antigen‐presenting machinery (right), comparing the levels in SFM‐ or fulvestrant‐treated cells vs DMEM (as in (A)). (D–F) Flow cytometry‐mediated assessment of PD‐L2 (D), B2M (E), and HLA (F) levels in MCF7 cells grown in DMEM or fulvestrant (1 μm) for 14 days. Note that the antibody that was used for HLA detects 3 isoforms (HLA‐A, HLA‐B, and HLA‐C). Representative results out of three experiments are shown.
Interestingly, a specific analysis of immune‐related genes revealed that prolonged estrogen deprivation triggered the expression of multiple immune checkpoints besides PD‐L1 such as CEACAM1, MICA, or LGALS2, which was concomitant to a generalized suppression of the antigen‐presenting machinery, including reduced expression of HLA‐A, HLA‐C, B2M, and TAP2 (Fig. 4C). Flow cytometry confirmed the upregulation of additional immune checkpoints such as PD‐L2 and reduced levels of beta‐2‐microglobulin (B2M) and HLA‐A in MCF7 cells treated with fulvestrant (Fig. 4D–F). Equivalent results were obtained in another ER+ BC cell line, T47D, both by FACS and by qRT‐PCR (Fig. S5A–G). Furthermore, analysis of transcriptomic data from the METABRIC cohort revealed a generalized increase in expression of multiple immune checkpoints in ER+ BC patients undergoing hormone therapy (Fig. S5H) [22, 23]. Collectively, these analyses reveal that persistent inhibition of estrogen signaling triggers a broad immunosuppressive transcriptional program in MCF7 cells.
3.5. Estrogen deprivation‐induced growth arrest is necessary but not sufficient for the activation of the inflammatory program in ER+ BC cells
Given our observation that estrogen‐deprived MCF7 cells express IL‐6, which is an important component of the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype (SASP) [39], we wondered whether the activation of an inflammatory transcriptional program was part of a SASP response in these cells, which are indeed growth‐arrested. Consistent with this view, MCF7 cells grown in SFM showed several features of senescence such as increased levels of p21Cip1 and histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) or an increased activity of the senescence‐associated beta galactosidase (SA‐βgal; Fig. S6A,B). However, MCF7 cells induced to undergo senescence upon treatment with the p53 activator Nutlin‐3 failed to upregulate PD‐L1, indicating that simply arresting the growth of ER+ BC cells is not sufficient to trigger the same transcriptional response as that induced by estrogen deprivation (Fig. S6C).
Nevertheless, and to further address whether the fulvestrant‐induced growth arrest contributes to the activation of inflammatory signaling, we deleted the CSK kinase in MCF7 cells using CRISPR, as this mutation has been shown to confer estrogen signaling‐independent growth on ER+ BC cells [40, 41]. As reported, CSK knockout (CSKko) MCF7 cells continued to proliferate even in the presence of fulvestrant (Fig. 5A,B). We then conducted RNAseq on WT and CSKko MCF7 cells grown with or without fulvestrant for 3 weeks. Principal component analyses revealed that while the transcriptome of WT and CSKko MCF7 cells was similar in control conditions, the changes induced by fulvestrant were significantly attenuated in two independent clones of CSK‐deficient cells (Fig. 5C). A similar conclusion could be drawn from a heatmap illustrating the clustering of genes that were significantly regulated in this experiment (Fig. 5D). GSEAs identified biological pathways related to cell growth such as ‘E2F targets’, ‘G2M checkpoint’, or ‘MYC targets’ as those that were more significantly different between fulvestrant‐treated WT and CSKko MCF7 (Fig. 5E and Table S4). In contrast, the ‘epithelial–mesenchymal transition’ pathway, which, consistent with our previous analysis, was induced by fulvestrant in WT cells, was less so in CSKko MCF7 cells. Most importantly, the fulvestrant‐dependent induction of pathways such as ‘TNFA signaling via NF‐KB’, ‘inflammatory response’, ‘IL‐6 JAK/STAT3 signaling’, and ‘IFN‐γ response’ was reduced in CSKko cells. Together, these results indicate that the growth arrest triggered by estrogen deprivation is a necessary step for the subsequent activation of the immunosuppressive transcriptional program in ER+ BC cells. However, just arresting the growth of MCF7 cells is not sufficient to trigger this phenotypic change and the concomitant inhibition of estrogen signaling is necessary.
Fig. 5.
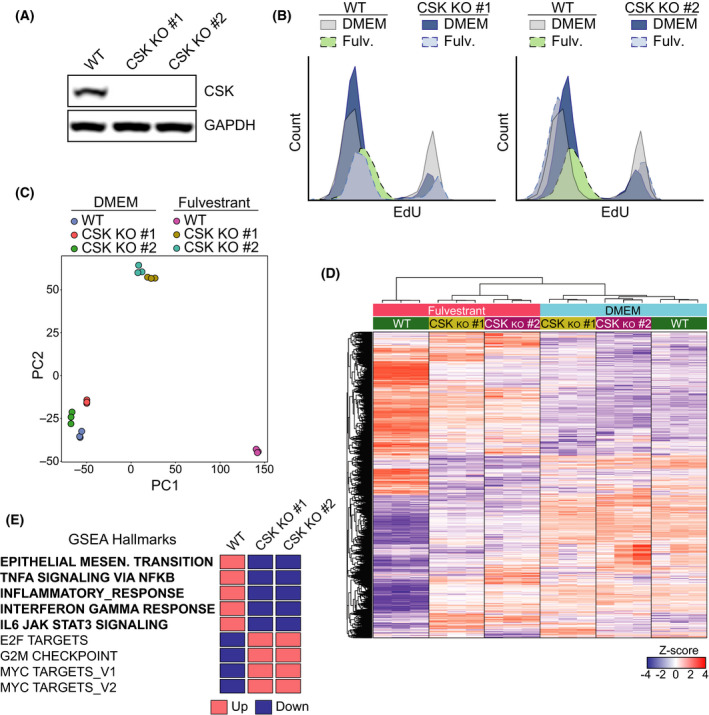
CSK‐dependent growth arrest mediates activation of the inflammatory phenotype in MCF7 cells. (A) Western blot illustrating the loss of CSK expression in 2 independent clones of CSK‐deficient MCF7 generated by CRISPR/Cas9. GAPDH is added as a loading control. (B) Flow cytometric data illustrating the growth arrest that is observed in WT MCF7 cells grown in fulvestrant for 20 days. Two clones of CSK‐deficient cells continue to incorporate EdU in the same conditions. (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of an RNAseq experiment where the transcriptome of two independent MCF7 CSKko clones grown in DMEM with or without fulvestrant (1 μm) for 20 days was compared. The PCA plot was based on normalized gene counts after filtering for low‐expressed genes. (D) Heatmap and clustering of genes from the experiment defined in (C). The genes shown in the heatmap are genes that were found significantly regulated in any of the comparisons. Each gene (row) is standardized (z‐score) to mean = 0 and sd = 1 and then clustered by hierarchical clustering. Note that the fulvestrant‐induced changes in WT MCF7 cells are significantly milder in CSK‐deficient cells. (E) Impact of CSK deficiency on fulvestrant‐dependent expression of genes related to specific GSEA pathways from the experiment defined in (C). The full GSEA is provided in Table S4.
3.6. Estrogen deprivation limits T‐cell‐mediated cell killing of MCF7 cells independently of PD‐L1
Finally, we evaluated how estrogen deprivation in BC cells affected their sensitivity to being killed by immune cells, through a T‐cell‐mediated cell killing assay in MCF7 cells [42]. To do so, MCF7 cells stably expressing mCherry fused to a nuclear localization sequence were cocultured in the presence of activated primary T cells and followed by live cell imaging for 3 days. Remarkably, MCF7 cells that were previously grown in SFM or with fulvestrant were significantly resistant to their killing by T cells (Fig. 6A). In addition, EE was able to alleviate the effects of the SFM treatment and potentiated the elimination of MCF7 cells by T cells. Equivalent results were obtained by measuring apoptosis through the use of a fluorescent caspase‐3/7 target (Fig. 6B). Consistent with the transcriptomic data indicating that estrogen deprivation triggered multiple mechanisms of immunosuppression (including the upregulation of several immune checkpoints and downregulation of the antigen‐presenting machinery), PD‐L1 deficiency did not protect MCF7 cells from T‐cell killing, nor it modified the protection provided by fulvestrant (Fig. 6C,D). In summary, the experiments presented above revealed that, in addition to suppressing their growth, prolonged estrogen deprivation of ER+ BC cells promoted a phenotype switch that rendered them resistant to being killed by T cells through multiple independent immunosuppressive mechanisms (Fig. 6E).
Fig. 6.
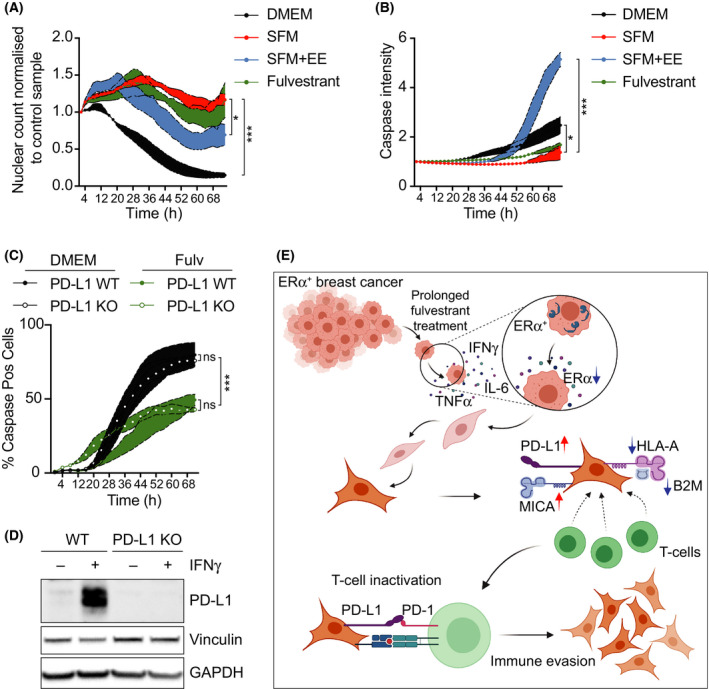
Estrogen signaling inhibition limits T‐cell‐mediated killing of MCF7 cells. (A) Live cell imaging of nuclei count from MCF7 cells after addition of activated primary T lymphocytes isolated from human peripheral blood. Nuclei counts were normalized to the value at time = 0 h for each condition, and then, each timepoint was subsequently normalized to the value of the control to which no T cells were added. (B) Time‐lapse microscopy of the intensity of a fluorescently labeled caspase‐3/7 substrate in MCF7 cells exposed to activated primary T cells. (C) Time‐lapse microscopy of the intensity of a fluorescently labeled caspase‐3/7 substrate in wild‐type (WT) or PD‐L1‐deficient (PD‐L1 KO) MCF7 cells exposed to activated primary T cells. (A–C) For these experiments, indicated cells were grown in normal media, SFM or fulvestrant (1 μm) for 2 weeks, prior to the addition of the activated T cells. Where indicated, EE (10 nm) was added for the last 3 days. One‐way ANOVA for (A, B) and two‐way ANOVA for (C) analyses were used to calculate the statistical significance of the differences between groups. All datapoints indicate mean values (n = 3) ± SEM (colored boundary). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. (D) Western blot illustrating the levels of PD‐L1 in WT and PD‐L1‐deficient MCF7 cells used in (C). Cells were treated with IFN‐γ to stimulate PD‐L1 expression. Vinculin and GAPDH levels are shown as loading controls. (E) Graphical summary of our work depicting that under prolonged hormone therapy, ER+ BC cells activate an inflammatory transcriptional program, which includes a generalized upregulation of immune checkpoint mediators together with the downregulation of the antigen‐presenting machinery. Hence, while hormone therapies efficiently arrest the growth of ER+ BC cells, they also promote a phenotype switch that favors their immune evasion.
4. Discussion
Our work started with the aim to identify how medically approved medicines influence the expression of PD‐L1, as PD‐L1 levels were previously shown to be potential biomarkers of efficacy of cancer immunotherapies using antibodies against PD‐1 or PD‐L1 [24]. We decided to conduct our screen in the presence of IFN‐γ, as this is the situation which we believe most represents the context in which PD‐L1 is actually expressed within tumors [43]. As expected, we were not able to find drugs that substantially increase PD‐L1 expression beyond what is induced by IFN‐γ, and our screen was mainly useful to identify drugs that can counteract this induction. Consistent with current knowledge, corticosteroids and JAK inhibitors were found to suppress PD‐L1 expression, which helps to understand their links to resistance to immunotherapy [27, 28, 29]. Besides these two classes of compounds, our manuscript provides a useful resource where investigators can evaluate how a given medicine affects PD‐L1 expression and could thus potentially affect the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies. As an example of this approach, and given its relevance for ER+ BC, we here explored in depth how the inhibition of estrogen signaling could be inducing PD‐L1 expression in cancer cells.
Estrogen was one of the first hormones to be described, and for decades, it was thought to only act in the female reproductive system [9]. Later studies revealed that estrogen receptors were widely expressed in many organs and that estrogens played pleotropic physiological roles beyond reproduction. Among these, several studies have indicated that estrogen levels influence the severity of diseases linked to inflammation, including cancer [11, 14, 44]. However, somewhat surprisingly, the link between estrogen signaling and inflammation has not been sufficiently addressed in the context of ER+ BC, which is the prototype tumor that is driven by estrogen signaling. Here, we show that estrogen deprivation triggers a broad immunosuppressive transcriptional program in ER+ BC cells, which includes the secretion of cytokines that activate NF‐κB signaling such as TNF‐α, but also additional cytokines such as IFN‐γ and IL‐6 that trigger the activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. As to how ER suppresses this inflammatory program, our work reveals that this is secondary to the persistent growth arrest that follows chronic inhibition of estrogen signaling in a manner that resembles the SASP secretory program that is observed in senescent cells. In this regard, to what extent senolytic compounds could help to eliminate the residual growth‐arrested BC cells that resist to the initial hormone therapy emerges as an interesting possibility to explore. Interestingly, a recent manuscript has revealed that acquired resistance to mitogen‐activated protein kinase inhibitors in melanoma also involves an EMT and the activation of an immunosuppressive transcriptional program that limits the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy, suggesting that this might be a recurrent phenomenon in cancer cells chronically treated with strategies that limit their growth [45].
Among the specific factors that are induced by chronic estrogen signaling deprivation, we found PD‐L1, which is consistent with a previous study that identified ERα as a direct transcriptional repressor of PD‐L1 [46]. Our study indicates that, while a direct regulation of the PD‐L1 promoter by ERα might exist, the main source of PD‐L1 expression upon estrogen deprivation is linked to the activation of JAK/STAT and NF‐κB signaling that occurs only after a prolonged treatment, more reminiscent of the clinical situation. Moreover, our study further demonstrates that the immunosuppressive phenotype of estrogen‐deprived ER+ BC cells is not just restricted to an upregulation of PD‐L1, but it includes the expression of multiple immune checkpoints together with a concomitant silencing of the antigen‐presenting machinery. Of note, and in addition to the activation of the inflammatory signals, sustained estrogen deprivation also triggers an EMT in MCF7 cells, which suggests that while the cancer cells might be growth‐arrested, their invasive properties might be unwantedly enhanced by endocrine therapy. BC has classically been considered as poorly responsive to immunotherapy due to initial failures in vaccination or cytokine treatments in the 1980s and 90s [47, 48], and since ER+ BC has a low mutational burden and is therefore immunologically ‘cold’. Our work here reveals yet another reason that could help to understand the limited efficacy of immunotherapies in BC, as while hormone therapy effectively arrests the growth of ER+ BC cells, it also triggers a broad immunosuppressive transcriptional program that limits their clearance by the immune system.
5. Conclusion
Hormone therapy is the current treatment for ER+ BC, the most frequent type of cancer in women worldwide. Unfortunately, immunotherapy has shown limited efficacy for the treatment of BC, even less so for ER+ tumors. We here report that chronic inhibition of ERα signaling triggers an immunosuppressive transcriptional program in ER+ BC cells, which includes the activation of multiple immune checkpoints such as PD‐L1 and PD‐L2, together with a reduced expression of the antigen‐presenting machinery. These findings indicate that, while hormone therapy succeeds in limiting the growth of ER+ tumors, treatment‐resistant cells acquire an immunosuppressive phenotype that hampers their elimination by the immune system.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
DH and PM‐R contributed to most experiments and data analyses and to the preparation of the figures. CH contributed to the T‐cell killing experiments. SM and MQ‐F helped with experiments using MMTV‐PyMT animals and with human patient material. BP contributed to the experiments validating the effects of glucocorticoids and to the generation of PD‐L1‐deficient MCF7 cells. MH helped with the chemical screen. LL provided general technical support to many of the experiments. OF‐C and JC‐P supervised the study and wrote the MS.
Peer review
The peer review history for this article is available at https://publons.com/publon/10.1002/1878‐0261.13083.
Supporting information
Fig. S1. Estrogen‐deprival induces PD‐L1 expression in ER+ BC cells.
Fig. S2. ERα, and not ERβ, suppresses PD‐L1 expression in MCF7 cells.
Fig. S3. Inverse correlation between ERα and PD‐L1 in BC.
Fig. S4. Estrogen deprivation triggers an inflammatory transcriptional program in MCF7 cells.
Fig. S5. Estrogen‐deprival induces an inflammatory response in ERα+ T47D BC cells.
Fig. S6. Induction of senescence is not sufficient to trigger PD‐L1 expression in MCF7 cells.
Table S1. Results of the primary chemical screen in IFNγ‐stimulated A549 cells.
Table S2. Results of the ERα agonist/antagonist screen in MCF‐7 cells.
Table S3. Clinical and demographic characteristics of the ER+ BC patients used in Fig. S3.
Table S4. GSEA analysis comparing the transcriptomes of WT and CSK‐deficient MCF7 cells grown in fulvestrant or DMEM for 20 days.
Acknowledgments
We would want to thank Andres J Lopez‐Contreras for insightful comments on the manuscript, Hana Imrichova for help with GSEAs, and the core facility at NEO, BEA, Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis, which is supported by the board of research at the Karolinska Institute and the research committee at the Karolinska Hospital. Research was funded by grants from the Cancerfonden Foundation (CAN 2018/381) and the Swedish Research Council (VR) (538‐2014‐31) to OF and from the ISCIII (AES‐PI16/00354; cofunded by the European Regional Development Fund) and from the Call for Coordinated Research Groups from Madrid Region, Madrid Regional Government‐ERDF Funds (B2017/BMD3733) to MQ‐F. This research was supported by Consejería de Sanidad, Comunidad de Madrid.
Daniela Hühn and Pablo Martí‐Rodrigo considered as cofirst authors
Contributor Information
Jordi Carreras‐Puigvert, Email: jordi.carreras.puigvert@farmbio.uu.se.
Oscar Fernandez‐Capetillo, Email: oscar.fernandez-capetillo@ki.se.
Data accessibility
RNA sequencing data associated with this work are openly available from the GEO repository at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, under accession numbers GSE134938 and GSE181909.
References
- 1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA & Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68, 394–424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Prall OW, Rogan EM & Sutherland RL (1998) Estrogen regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65, 169–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Siersbaek R, Kumar S & Carroll JS (2018) Signaling pathways and steroid receptors modulating estrogen receptor alpha function in breast cancer. Genes Dev 32, 1141–1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Osborne CK & Schiff R (2011) Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 62, 233–247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, Dieras V, Hegg R, Im SA, Shaw Wright G et al. (2018) Atezolizumab and Nab‐paclitaxel in advanced triple‐negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 379, 2108–2121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Esteva FJ, Hubbard‐Lucey VM, Tang J & Pusztai L (2019) Immunotherapy and targeted therapy combinations in metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 20, e175–e186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Dethlefsen C, Hojfeldt G & Hojman P (2013) The role of intratumoral and systemic IL‐6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 657–664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hah N, Murakami S, Nagari A, Danko CG & Kraus WL (2013) Enhancer transcripts mark active estrogen receptor binding sites. Genome Res 23, 1210–1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Eyster KM (2016) The estrogen receptors: an overview from different perspectives. Methods Mol Biol 1366, 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Confavreux C, Hutchinson M, Hours MM, Cortinovis‐Tourniaire P & Moreau T (1998) Rate of pregnancy‐related relapse in multiple sclerosis. Pregnancy in multiple sclerosis group. N Engl J Med 339, 285–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Nelson JL & Ostensen M (1997) Pregnancy and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 23, 195–212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Jin JM, Bai P, He W, Wu F, Liu XF, Han DM, Liu S & Yang JK (2020) Gender differences in patients with COVID‐19: focus on severity and mortality. Front Public Health 8, 152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. NCT04359329 (2020) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04359329?term=estrogen&cond=Covid19&draw=2&rank=3.
- 14. Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim K, Elsharkawy AM & Karin M (2007) Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88‐dependent IL‐6 production. Science 317, 121–124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Ben‐Neriah Y & Karin M (2011) Inflammation meets cancer, with NF‐kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat Immunol 12, 715–723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Pratt MA, Bishop TE, White D, Yasvinski G, Menard M, Niu MY & Clarke R (2003) Estrogen withdrawal‐induced NF‐kappaB activity and bcl‐3 expression in breast cancer cells: roles in growth and hormone independence. Mol Cell Biol 23, 6887–6900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Sas L, Lardon F, Vermeulen PB, Hauspy J, Van Dam P, Pauwels P, Dirix LY & Van Laere SJ (2012) The interaction between ER and NFkappaB in resistance to endocrine therapy. Breast Cancer Res 14, 212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Galien R & Garcia T (1997) Estrogen receptor impairs interleukin‐6 expression by preventing protein binding on the NF‐kappaB site. Nucleic Acids Res 25, 2424–2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Jones TR, Kang IH, Wheeler DB, Lindquist RA, Papallo A, Sabatini DM, Golland P & Carpenter AE (2008) Cell profiler analyst: data exploration and analysis software for complex image‐based screens. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ran FA, Hsu PD, Wright J, Agarwala V, Scott DA & Zhang F (2013) Genome engineering using the CRISPR‐Cas9 system. Nat Protoc 8, 2281–2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G, Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y et al. (2012) The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 486, 346–352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Pereira B, Chin SF, Rueda OM, Vollan HK, Provenzano E, Bardwell HA, Pugh M, Jones L, Russell R, Sammut SJ et al. (2016) The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refines their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat Commun 7, 11479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Manso L, Mouron S, Tress M, Gomez‐Lopez G, Morente M, Ciruelos E, Rubio‐Camarillo M, Rodriguez‐Peralto JL, Pujana MA, Pisano DG et al. (2016) Analysis of paired primary‐metastatic hormone‐receptor positive breast tumors (HRPBC) uncovers potential novel drivers of hormonal resistance. PLoS One 11, e0155840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Patel SP & Kurzrock R (2015) PD‐L1 expression as a predictive biomarker in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther 14, 847–856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Stanciu LA, Bellettato CM, Laza‐Stanca V, Coyle AJ, Papi A & Johnston SL (2006) Expression of programmed death‐1 ligand (PD‐L) 1, PD‐L2, B7–H3, and inducible costimulator ligand on human respiratory tract epithelial cells and regulation by respiratory syncytial virus and type 1 and 2 cytokines. J Infect Dis 193, 404–412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Hao Y, Chapuy B, Monti S, Sun HH, Rodig SJ & Shipp MA (2014) Selective JAK2 inhibition specifically decreases Hodgkin lymphoma and mediastinal large B‐cell lymphoma growth in vitro and in vivo . Clin Cancer Res 20, 2674–2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Shin DS, Zaretsky JM, Escuin‐Ordinas H, Garcia‐Diaz A, Hu‐Lieskovan S, Kalbasi A, Grasso CS, Hugo W, Sandoval S, Torrejon DY et al. (2017) Primary resistance to PD‐1 blockade mediated by JAK1/2 mutations. Cancer Discov 7, 188–201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Arbour KC, Mezquita L, Long N, Rizvi H, Auclin E, Ni A, Martinez‐Bernal G, Ferrara R, Lai WV, Hendriks LEL et al. (2018) Impact of baseline steroids on efficacy of programmed cell death‐1 and programmed death‐ligand 1 blockade in patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36, 2872–2878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Gourd E (2018) Baseline corticosteroids reduce activity of PD‐L1 blockade. Lancet Oncol 19, e515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Marquez‐Garban DC, Chen HW, Fishbein MC, Goodglick L & Pietras RJ (2007) Estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human non‐small cell lung cancer. Steroids 72, 135–143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Mittendorf EA, Philips AV, Meric‐Bernstam F, Qiao N, Wu Y, Harrington S, Su X, Wang Y, Gonzalez‐Angulo AM, Akcakanat A et al. (2014) PD‐L1 expression in triple‐negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 2, 361–370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Guy CT, Cardiff RD & Muller WJ (1992) Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: a transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol Cell Biol 12, 954–961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Manguso RT, Pope HW, Zimmer MD, Brown FD, Yates KB, Miller BC, Collins NB, Bi K, LaFleur MW, Juneja VR et al. (2017) In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target. Nature 547, 413–418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Pan D, Kobayashi A, Jiang P, Ferrari de Andrade L, Tay RE, Luoma AM, Tsoucas D, Qiu X, Lim K, Rao P et al. (2018) A major chromatin regulator determines resistance of tumor cells to T cell‐mediated killing. Science 359, 770–775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Peng J, Hamanishi J, Matsumura N, Abiko K, Murat K, Baba T, Yamaguchi K, Horikawa N, Hosoe Y, Murphy SK et al. (2015) Chemotherapy induces programmed cell death‐ligand 1 overexpression via the nuclear factor‐kappaB to foster an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 75, 5034–5045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Johnson DE, O'Keefe RA & Grandis JR (2018) Targeting the IL‐6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15, 234–248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Dutertre M, Gratadou L, Dardenne E, Germann S, Samaan S, Lidereau R, Driouch K, de la Grange P & Auboeuf D (2010) Estrogen regulation and physiopathologic significance of alternative promoters in breast cancer. Cancer Res 70, 3760–3770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Malik S, Jiang S, Garee JP, Verdin E, Lee AV, O'Malley BW, Zhang M, Belaguli NS & Oesterreich S (2010) Histone deacetylase 7 and FoxA1 in estrogen‐mediated repression of RPRM. Mol Cell Biol 30, 399–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Faget DV, Ren Q & Stewart SA (2019) Unmasking senescence: context‐dependent effects of SASP in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 19, 439–453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Xiao T, Li W, Wang X, Xu H, Yang J, Wu Q, Huang Y, Geradts J, Jiang P, Fei T et al. (2018) Estrogen‐regulated feedback loop limits the efficacy of estrogen receptor‐targeted breast cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 7869–7878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Yeh WL, Shioda K, Coser KR, Rivizzigno D, McSweeney KR & Shioda T (2013) Fulvestrant‐induced cell death and proteasomal degradation of estrogen receptor alpha protein in MCF‐7 cells require the CSK c‐Src tyrosine kinase. PLoS One 8, e60889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Li CW, Lim SO, Xia W, Lee HH, Chan LC, Kuo CW, Khoo KH, Chang SS, Cha JH, Kim T et al. (2016) Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand‐1 suppresses T‐cell activity. Nat Commun 7, 12632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL & Hung MC (2019) Mechanisms controlling PD‐L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell 76, 359–370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Khalili H, Higuchi LM, Ananthakrishnan AN, Richter JM, Feskanich D, Fuchs CS & Chan AT (2013) Oral contraceptives, reproductive factors and risk of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 62, 1153–1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Haas L, Elewaut A, Gerard CL, Umkehrer C, Leiendecker L, Pedersen M, Krecioch I, Hoffmann D, Novatchkova M, Kutte M et al. (2021) Acquired resistance to anti‐MAPK targeted therapy confers an immune‐evasive tumor microenvironment and cross‐resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Nat Cancer 2, 693–708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Liu L, Shen Y, Zhu X, Lv R, Li S, Zhang Z, Shi YG & Tan L (2018) ERalpha is a negative regulator of PD‐L1 gene transcription in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505, 157–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Buzdar AU, Blumenschein GR, Smith TL, Powell KC, Hortobagyi GN, Yap HY, Schell FC, Barnes BC, Ames FC, Martin RG et al. (1984) Adjuvant chemotherapy with fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide, with or without Bacillus Calmette‐Guerin and with or without irradiation in operable breast cancer. A prospective randomized trial. Cancer 53, 384–389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Miles D, Roche H, Martin M, Perren TJ, Cameron DA, Glaspy J, Dodwell D, Parker J, Mayordomo J, Tres A et al. (2011) Phase III multicenter clinical trial of the sialyl‐TN (STn)‐keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) vaccine for metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 16, 1092–1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fig. S1. Estrogen‐deprival induces PD‐L1 expression in ER+ BC cells.
Fig. S2. ERα, and not ERβ, suppresses PD‐L1 expression in MCF7 cells.
Fig. S3. Inverse correlation between ERα and PD‐L1 in BC.
Fig. S4. Estrogen deprivation triggers an inflammatory transcriptional program in MCF7 cells.
Fig. S5. Estrogen‐deprival induces an inflammatory response in ERα+ T47D BC cells.
Fig. S6. Induction of senescence is not sufficient to trigger PD‐L1 expression in MCF7 cells.
Table S1. Results of the primary chemical screen in IFNγ‐stimulated A549 cells.
Table S2. Results of the ERα agonist/antagonist screen in MCF‐7 cells.
Table S3. Clinical and demographic characteristics of the ER+ BC patients used in Fig. S3.
Table S4. GSEA analysis comparing the transcriptomes of WT and CSK‐deficient MCF7 cells grown in fulvestrant or DMEM for 20 days.
Data Availability Statement
RNA sequencing data associated with this work are openly available from the GEO repository at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, under accession numbers GSE134938 and GSE181909.


