Figure 3.
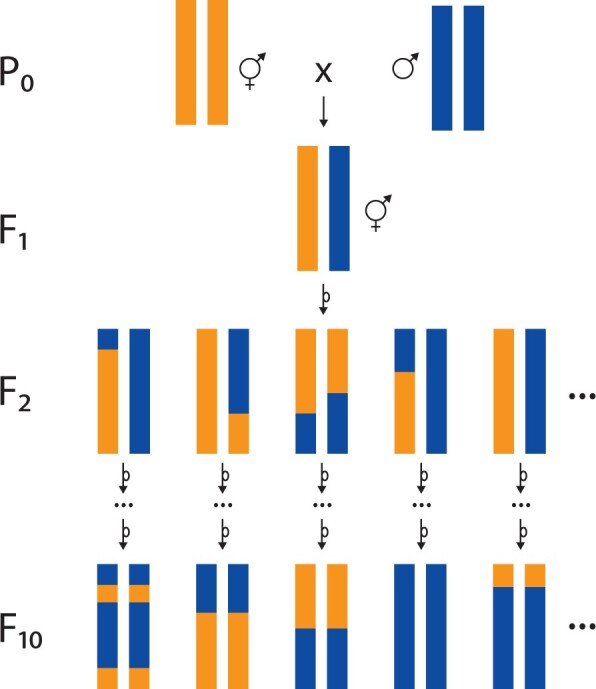
RIL construction. Conventional RILs are generated by crossing two inbred lines (P0), each here represented by a single pair of homologous chromosomes. The cross yields F1s that are heterozygous at every locus that differs between the strains. Self-fertilization of F1 hermaphrodites yields genetically heterogeneous F2s. Because of complete crossover interference in C. elegans, each F2 carries on average one recombinant chromosome with a single crossover. Each F2 is independently inbred by selfing until the F10 generation, at which point the genome is expected to be completely homozygous, with an average of one crossover per chromosome. This collection of homozygous strains is a panel of RILs. Note that this panel will all inherit the mitochondrial genome of the P0 hermaphrodite. To balance the panel with respect to mitochondrial genotype, an equal number of RILs should be constructed from the reciprocal cross.
