Abstract
Cecropins are small helical secreted peptides with antimicrobial activity that are widely distributed among insects. Genes encoding Cecropins are strongly induced upon infection, pointing to their role in host defense. In Drosophila, four cecropin genes clustered in the genome (CecA1, CecA2, CecB, and CecC) are expressed upon infection downstream of the Toll and Imd pathways. In this study, we generated a short deletion ΔCecA-C removing the whole cecropin locus. Using the ΔCecA-C deficiency alone or in combination with other antimicrobial peptide (AMP) mutations, we addressed the function of Cecropins in the systemic immune response. ΔCecA-C flies were viable and resisted challenge with various microbes as wild-type. However, removing ΔCecA-C in flies already lacking 10 other AMP genes revealed a role for Cecropins in defense against Gram-negative bacteria and fungi. Measurements of pathogen loads confirm that Cecropins contribute to the control of certain Gram-negative bacteria, notably Enterobacter cloacae and Providencia heimbachae. Collectively, our work provides the first genetic demonstration of a role for Cecropins in insect host defense and confirms their in vivo activity primarily against Gram-negative bacteria and fungi. Generation of a fly line (ΔAMP14) that lacks 14 immune inducible AMPs provides a powerful tool to address the function of these immune effectors in host–pathogen interactions and beyond.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster, innate immunity, antimicrobial peptides, resistance, CRISPR/Cas9, immune effectors, humoral immunity, Cecropin
Introduction
In the late 1970s when immunologists were characterizing the antibody immune response of mammals, pioneering studies revealed that insects could resist infection by fearsome human pathogens despite lacking an adaptive immune system. Eventually a landmark discovery by Hans Boman et al. showed that insects produced antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) following infection (Steiner et al. 1981), invigorating interest in innate immunity (Ganz et al. 1985; Lemaitre 2004). These AMPs differed from other previously identified immune effectors in their small size, cationic charge, and amphipathic structure, allowing a direct disruption of the negatively charged membrane of microbes. In contrast to another class of well-known immune effectors, the lysozymes, AMPs lack enzymatic activity and require concentrations into the micromolar range to achieve their microbicidal effects (Imler and Bulet 2005; Seo et al. 2012; Hanson and Lemaitre 2020). Research has now shown that AMPs are common across the tree of life, with similar molecules contributing to host defense in both plants and animals (Broekaert et al. 1995). While they contribute to local defense in barrier epithelia of vertebrates, insect AMPs are most famous for being secreted upon systemic infection from the fat body into the hemolymph, where they reach potent concentrations (Bulet et al. 1999). The characterization of a plethora of AMPs with diverse modes of action has enriched our understanding of these immune effectors. However, the functional study of AMPs was limited until recently due to technical challenges in mutating the small AMP genes using traditional genetic approaches. This challenge has now been overcome with the advent of CRISPR/Cas9 technology.
Cecropins were the first inducible AMPs to be isolated, found in the hemolymph of infected pupae of the moth Hyalophora cecropia (Lepidoptera) (Hultmark et al. 1980; Steiner et al. 1981). The helix-form of Cecropins is thought to promote their interaction with negatively charged bacterial membranes, contributing to pore formation and membrane destabilization, and resulting in the lysis of bacteria (Steiner et al. 1988). In vitro studies have shown that Cecropins have high efficacy against a large panel of Gram-negative bacteria at concentrations below the levels induced in insects upon infection (25–50µM) (Samakovlis et al. 1990), as well as against some filamentous fungi (Steiner et al. 1981; DeLucca et al. 1997; Ekengren and Hultmark 1999; Ouyang et al. 2015). Heterologous expression of Cecropin in transgenic rice has also been shown to confer resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae (Coca et al. 2004), and studies have reported an activity of Cecropins against tumor cells, bacterial biofilms, and viruses (Chiou et al. 2002; Suttmann et al. 2008; Deslouches and Di 2017; Kalsy et al. 2020).
AMP regulation and function has been extensively studied in the model insect Drosophila melanogaster. The Drosophila genome encodes four cecropin genes (CecA1 and A2, CecB and CecC) and two pseudogenes (Cec-Ψ1 and Cec-Ψ2) that are clustered at position 99E2 at the tip of the right arm of the third chromosome (Kylsten et al. 1990; Samakovlis et al. 1990; Sackton et al. 2007). The cecropin locus is adjacent to another gene named Andropin, which encodes a related antibacterial peptide expressed in the ejaculatory duct (Samakovlis et al. 1991). CecA1 and CecA2 are identical at the protein level, differing only by a few silent mutations at the nucleotide level, suggesting that they emerged from a recent duplication. The four Drosophila cecropin genes are strongly induced in the fat body and hemocytes upon systemic infection. Cecropin genes are regulated by the Imd pathway, but also receive a considerable input from the Toll pathway upon systemic infection (De Gregorio et al. 2002). Functional studies analyzing the role of Cecropins in vivo are scarce. Overexpression of CecA in an otherwise Imd, Toll immune-deficient background failed to detect a clear protective effect of CecA against a battery of pathogens (Tzou et al. 2002). Other studies using overexpression approaches have pointed to a role of CecA in the regulation of the gut microbiota (Ryu et al. 2008). Transgenic mosquitoes overexpressing both Cecropin and Defensin under the control of the vitellogenin promoter displayed an increased resistance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, indicating that these AMPs could act cooperatively against this pathogenic bacterium (Kokoza et al. 2010).
We have previously generated fly mutants deleting 10 Drosophila AMP genes including: Defensin, two Diptericins (DptA and B), Drosocin, four Attacins (AttA, B, C, and D), Metchnikowin, and Drosomycin (Hanson et al. 2019a). This study revealed that AMPs play an important role in defense against Gram-negative bacteria and also somewhat in defense against fungi. In contrast, another family of host defense peptides with no overt antimicrobial activity in vitro, the bomanins, plays a major role in the elimination of Gram-positive bacteria and fungi (Clemmons et al. 2015; Lindsay et al. 2018). Importantly, Hanson et al. (2019a) revealed evidence for synergy and additivity, but also remarkable specificity in the action of AMPs against certain pathogens. However, this study did not address the function of the four Cecropins due to a failure to generate a proper cecropin locus deletion. In the present study, we have generated fly lines carrying a small deletion that removes the four immune cecropin genes, and by using flies carrying this deletion alone or in combination with other AMP mutations, we address the role of Cecropins in the systemic immune response for the first time (Supplementary Table 1).
Materials and methods
Fly stocks and genetics
The w1118 DrosDel isogenic (iso w1118) wild-type was used as the genetic background for mutant isogenization, as described by Ferreira et al. (2014). The ΔCecA-C mutation was generated using CRISPR with two gRNAs and a homology directed repair vector by cloning 5′ and 3′ region-homologous arms into the pHD-DsRed vector, and consequently ΔCecA-C flies express DsRed in their eyes, ocelli, and abdomen. The ΔCecA-C mutation was generated by Cas9 mediated injection into the iso MtkR1; DrsR1 background. Following this, two rounds of backcrossing were performed to replace the first and second chromosome with the iso DrosDel first and second chromosome, and to recombine the ΔCecA-C mutation away from other mutations. The resulting stock is here called iso ΔCecA-C. Afterwards, the ΔCecA-C mutation was recombined independently with DrsR1 and AttDSK1 on chromosome 3, and introgressed alongside the other AMP mutations on chromosome 2 to generate ΔAMP14 flies lacking the 14 classical AMP genes from the Defensin, Drosocin, Attacin, Diptericin, Metchnikowin, Drosomycin, and Cecropin gene families. The iso ΔAMP10, iso BomΔ55C and iso RelishE20 flies are the same as used in Hanson et al. (2019a); however, we removed the aberrant cecropin locus (CecSK6) detected in the ΔAMP10 line to avoid any potential effects this locus could have on Cecropin-mediated resistance to infection [see Hanson et al. (2019b) correction notice].
Microbial culture conditions
Bacteria were grown overnight on a shaking plate at 200 RPM in their respective growth media and at their optimal temperature conditions. They were then pelleted by centrifugation (4000 RPM) at 4°C. The bacterial pellets were diluted to the desired optical density at 600 nm (OD600).
Pectobacterium carotovorum carotovorum 15 (Ecc15) and Micrococcus luteus were grown in LB media at 29°C. Escherichia coli strain 1106, Providencia burhodogranariea, Providencia rettgeri, and Providencia heimbachae were grown in LB media at 37°C. Enterococcus faecalis, Listeria monocytogenes, and Enterobacter cloacae were cultured in BHI media at 37°C. Streptococcus pneumoniae was grown as described by Krejčová et al. (2019). Candida albicans strain ATCC 2001 was cultured in YPG media at 37°C. Aspergillus fumigatus was grown at 37°C on Malt Agar; spores were collected in sterile PBS, pelleted by centrifugation and resuspended at the desired OD. Beauveria bassiana strain R444 and Metharizium rileyi strain PHP1705 commercial spores were produced by Andermatt Biocontrol, product: BB-PROTEC and Nomu-PROTEC, respectively.
Infection experiments and survival
Systemic infections with P. carotovorum carotovorum 15 (Ecc15) (Basset et al. 2000), M. luteus, E. coli strain 1106, P. burhodogranariea, P. rettgeri, P. heimbachae (Galac and Lazzaro 2011), E. faecalis, L. monocytogenes, E. cloacae, and C. albicans were performed as follows: 3- to 5-day-old adult females were pricked in the thorax with a 100 µm thick needle dipped into a concentrated pellet of bacteria at a desired OD600. Infected flies were then maintained at 25°C or 29°C for survivals. Systemic infection with S. pneumoniae (Krejčová et al. 2019) or M. rileyi was performed by injecting 50 nl of a concentrated pellet of bacteria or suspension of fungal spores using a nanoinjector and glass capillary needles.
Natural infections with B. bassiana were performed by shaking anesthetized flies in a vial with 200 mg of spores. Flies were flipped into fresh vials 1 day after fungal inoculation. Three independent experiments for survivals to infection were performed with 20 flies per vial(s) on standard fly medium without yeast. Survival was scored daily.
Bacterial load of flies
Flies were infected (systemic infection) with bacteria at the desired OD600. At the indicated time postinfection, flies were anesthetized using CO2, surface sterilized by washing briefly in 70% EtOH, and blotted. Pools of five flies were transferred in 200 µl of sterile PBS and macerated using a pestle. The homogenates were centrifuged at 8000 RPM for 3 min. The supernatants were serially diluted and 7 µl droplets were inoculated on LB agar overnight at 29°C. Colony-forming units (CFUs) were manually counted the following day.
Gene expression levels by qRT-PCR
Flies that either were unchallenged or were infected systemically by pricking in the thorax with a needle dipped in a pellet of Ecc15 or M. luteus (OD600 = 200) were frozen at −20°C 6 h or 12 h postinfection, respectively. Three independent experiments (independent day, flies, and bacterial pellet) were performed for each infection with two or three technical repeats according to the number of flies available. Gene expression measurements were then performed by RT-qPCR as previously described (Hanson et al. 2019a). Briefly, five whole flies were homogenized and their RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent and resuspended in RNase-free water. Reverse transcription was carried out using PrimeScript RT (TAKARA) with random hexamers and oligo dTs. Quantitative PCRs were performed on a LightCycler 480 (Roche) using PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix.
Cecropin A injection
Commercially available Cecropin from H. cecropia (Sigma-Aldrich) was diluted in PBS (1.37 M NaCl, 0.027 M KCl, 0.08 M sodium phosphate dibasic, 0.02 M potassium phosphate monobasic, adjusted at pH 7.4 and filtered 0.2 µm) to a concentration of 50 µM. Fifty nanoliters of Cecropin were injected into the thorax using a nanoinjector and glass capillary. Flies were left to recover for 2 h and then pricked with the desired pathogen.
MALDI-TOF
Raw hemolymph samples were collected from either unchallenged flies, or flies pricked with a 1:1 cocktail of E. coli and M. luteus (OD = 200) in 0.1% TFA, as described previously (Hanson et al. 2019a). Samples were then added to an acetonitrile universal matrix. Representative spectra are shown. Immune-induced peaks were identified based on previous studies (Uttenweiler-Joseph et al. 1998; Levy et al. 2004) to confirm the absence of AMP-associated peaks, and presence of immune-induced peptides not affected by the included AMP mutations. Spectra were visualized using mMass and figures were additionally prepared using Inkscape v0.92.
Statistical analysis
Survival analyses were performed using a Cox proportional hazards (CoxPH) multiple comparison model, with Benjamini−Hochberg corrections for P-values, in R 3.6.3. Survival curves included three independent experiments with at least one cohort of 20 flies per treatment. Statistics were represented using a compact letter display (CLD) graphical technique: groups were assigned the same letter if they were not significantly different (P > 0.05). Quantitative PCR data included three independent experiments with at least two technical repeats and were compared by one-way ANOVA with Holm−Šídák multiple test correction in Prism R7. Bacterial load values were transformed as log10(value + 1) to allow graphical representation of the absence (0) of CFUs. Bacterial load data were compared by one-way ANOVA with Holm−Šídák multiple test correction in Prism 7. Statistics were represented using a CLD graphical technique.
Results
Generation and characterization of cecropin mutants
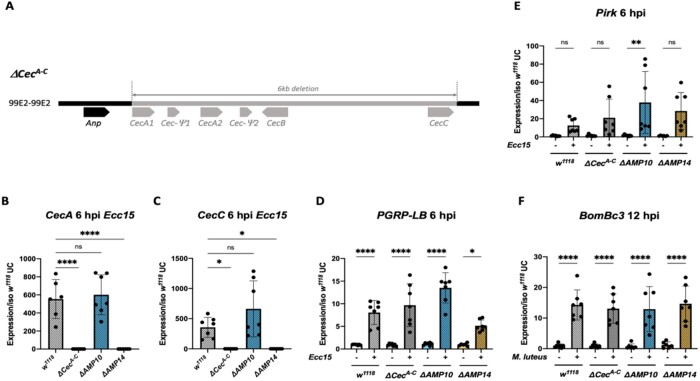
We generated a fly line lacking the four cecropin genes, CecA1, CecA2, CecB, and CecC, which are clustered at 99E and are inducible during the systemic response. For this, we used the CRISPR/Cas9 editing method to generate a 6 kb deletion (referred as ΔCecA-C) that removes the four inducible cecropins but leaves the related Andropin gene intact (Figure 1A). The ΔCecA-C mutation was generated by Cas9 mediated injection in the w, DrosDel (referred to as w1118) background. The background of the ΔCecA-C mutation was then cleaned by two successive crosses to the w1118 iso background to remove potential off-target alterations. To confirm the absence of cecropin genes in ΔCecA-C flies, we performed qRT-PCR for the four cecropin genes as well as the pseudogene Cec-Ψ2. Expression of CecA (cumulative expression of CecA1 and CecA2), CecB, CecC, and Cec-Ψ2 was readily observed in the wild type, but not detected in ΔCecA-C flies; the expression of the nearby Andropin gene was not affected (Figure 1, B and C; Supplementary Figure S1, A−C).
Figure 1.
Description and validation of ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 mutants. (A) Schema of the cecropin locus chromosomal deletion removing CecA1 and A2, CecB and CecC, plus 2 pseudo genes, Cec-Ψ1 and Cec-Ψ2 clustered at position 99E2 (chromosome III). qRT-PCR of CecA (B) and CecC (C) expression in w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies 6 h post Ecc15 infection. The Imd (D, E) and Toll (F) pathways are functional in ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies after challenge as revealed by expression of target genes upon septic injury with Ecc15 or M. luteus. PGRP-LB and Pirk were used as readouts for the Imd pathway and Bomanin (BomBc3) for the Toll pathway. Expression was normalized with w1118 UC set as a value of 1.
We previously generated a fly line in the w1118 iso background here referred to as “ΔAMP10,” harboring six mutations that remove 10 AMP genes: Defensin, Metchnikowin, the four Attacins (A/B/C/D), Drosomycin, two Diptericins (A/B), and Drosocin (Hanson et al., 2019a, 2019b). We recombined the iso ΔCecA-C mutation with the iso ΔAMP10 mutations to generate an iso fly line lacking all 14 “classical” AMPs (referred to as “ΔAMP14”). MALDI-TOF and RT-qPCR analysis confirms the absence of these 14 AMPs in ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies (Figure 1, B and C; Supplementary Figure S2). The ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies were viable and showed no morphological defects. We also confirmed that the two central NF-κB signaling pathways, Toll and Imd, were functional, as measured by measuring expression of genes characteristic of each of these pathways (Figure 1, D–F). Furthermore, MALDI-TOF proteomic analysis of hemolymph from infected flies 24 h postinfection (hpi) reveals a wild-type-like induction of peaks associated with other NF-κB effectors (e.g., Bomanins, Daishos, and Baramicin A) (Supplementary Figure S2). Collectively, our study indicates that we have generated a fly line lacking all the Drosophila “classical” AMPs, and that deleting these AMPs does not impact the production of other NF-κB effectors.
Cecropins contribute to survival against certain Gram-negative bacterial infections
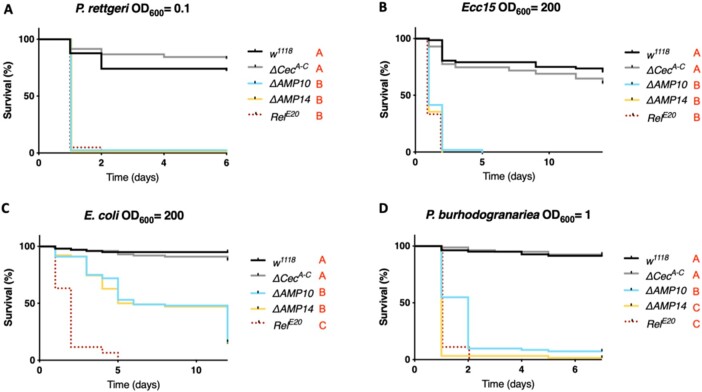
We used wild-type, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies to explore the role that Cecropins play in defense against pathogens during systemic infection. By performing survival analyses with wild-type and ΔCecA-C flies, we assessed if the absence of the four Cecropins is sufficient to cause an immune deficiency. Likewise, any difference in survival rates between ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies would suggest a contribution of Cecropins that is only apparent in the absence of other AMPs. We first focused our attention on Gram-negative bacterial infections, as Cecropins were initially identified for their activity against this class of bacteria. We challenged wild-type, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies with six different Gram-negative bacterial species, using inoculation doses (given as OD600) selected such that Imd deficient, iso RelE20 mutant control flies were killed. Our survival experiments did not reveal an overt contribution of Cecropins to resistance against the Gram-negative bacteria P. rettgeri, P. carotovorum carotovorum (Ecc15), E. coli, or P. burhodogranariea (Figure 2, A–D). In all cases, ΔCecA-C flies survived as well as wild-type flies, while ΔAMP10 flies were as susceptible as ΔAMP14. One exception was found for P. burhodogranariea infection: death of ΔAMP10 flies was delayed by 1 day compared with ΔAMP14 flies, suggesting a contribution of Cecropins in combatting this bacterium early in infection.
Figure 2.
Cecropins do not determine resistance to a broad spectrum of Gram-negative bacteria. w1118 were used as wild-type flies and RelE20 as susceptible flies lacking the Imd pathway for all survival experiments to Gram-negative bacterial infection. Female w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, ΔAMP14, and RelE20 flies were pricked in the thorax with an inoculum of (A) P. rettgeri, (B) Ecc15, (C) E. coli, or (D) P. burhodogranariea. Cecropins were not critically involved in combating infection with any bacteria presented here as ΔCecA-C survived as well as w1118 flies, while ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 mutant flies died as fast as RelE20 mutants. Bacterial concentrations are indicated in the figure.
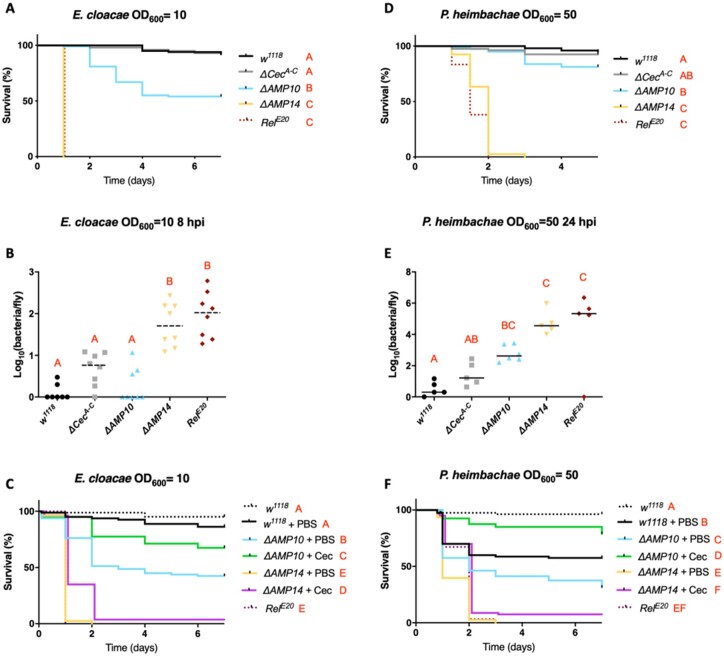
Interestingly, we did identify a prominent role for cecropins against two Gram-negative bacterial strains: E. cloacae and P. heimbachae. Although ΔCecA-C flies survived E. cloacae infection like wild-type flies and many ΔAMP10 flies survived this infection, ΔAMP14 flies, instead behaved like RelE20 mutants lacking Imd signaling entirely (Figure 3A). This result suggests that the presence of the four cecropin genes confers a protective effect against this bacterium in flies that lack 10 other AMP genes. A significant difference in CFUs between ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies at 8 hpi confirmed a role of Cecropins in limiting the growth of E. cloacae (Figure 3B). We also observed a consistently higher bacterial load in ΔCecA-C flies compared with wild-type controls, though this was not significant (P = 0.063). Moreover, ΔAMP14 and RelE20 fly CFUs were similar, consistent with survival data showing complete mortality of these genotypes within 24 h. These results indicate that the knock-out of the “classical” AMPs in the ΔAMP14 line fully explains the susceptibility of Imd pathway mutants to E. cloacae infection. Next, we attempted to rescue the susceptibility of ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies using commercially available Cecropin. We injected 50 nl of 50 µM H. cecropia Cecropin (Sigma-Aldrich) or PBS (control) 2 h before challenging flies with E. cloacae. Interestingly, when we injected Cecropin 2 h prior to E. cloacae infection, ΔAMP10 flies survived significantly better than ΔAMP10 flies previously injected with only PBS (Figure 3C). This result suggests that priming the fly defense by increasing circulating levels of Cecropin is sufficient to combat E. cloacae infection, even in flies lacking a broad range of other AMPs. However, we did not succeed in rescuing the susceptibility of ΔAMP14 flies using the same approach. This suggests the rescue effect we observed using ΔAMP10 flies relies on the total Cecropin levels, which includes both endogenously produced Cecropin and the supplemental Cecropin we injected. Collectively, our in vivo analysis is consistent with previous in vitro studies that showed commercial Cecropin from H. cecropia has activity against E. cloacae (Hultmark et al. 1980).
Figure 3.
Cecropins are essential in the absence of other AMPs to resist E. cloacae and P. heimbachae infection. (A) Survival experiments upon infection with E. cloacae reveal that AMP deficient flies having Cecropins (ΔAMP10) are significantly more resistant than those without Cecropins (ΔAMP14). (B) Bacterial loads (CFU counts) of w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, ΔAMP14, and RelE20 flies 8 h postinfection reveal a significant role for Cecropins in clearing and controlling E. cloacae. (C) Commercial Cecropin injection (50 nl at 50 µM) 2 h prior to E. cloacae infection increases the resistance of ΔAMP10 mutant flies. However, CecA injection did not rescue the susceptibility of ΔAMP14 flies to E. cloacae. Survival analysis (D), bacterial load measurements 24 h postinfection (E), and Cecropin supplementation experiments (F) in w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, ΔAMP14, and RelE20 flies upon infection with P. heimbachae (as described in A–C).
Similarly, we observed a contribution of Cecropins against the Gram-negative bacterium P. heimbachae in flies lacking other AMPs (Figure 3D–F). While ΔAMP10 flies were able to survive this infection at levels close to wild-type flies at OD600 = 50, ΔAMP14 flies again behaved like RelE20 mutants and suffered complete mortality (Figure 3D); the ΔCecA-C mutation alone did not increase susceptibility. Bacterial load measurement performed on flies collected 24 hpi revealed a contribution of Cecropins both in the presence and absence of other AMPs (Figure 3E). We again injected commercial H. cecropia Cecropin in an attempt to rescue the susceptibility of ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies to P. heimbachae (Figure 3F). Using this bacterial infection model, previous injection of PBS increased the susceptibility of wild-type flies to P. heimbachae. Strikingly, however, injection of Cecropin prior to infection rescued survival of ΔAMP10 flies to a level close to previously uninjured wild-type flies.
We have recently shown that the antibacterial peptide Drosocin (Dro) is specially required to resist infection with E. cloacae. This raises the possibility that Cecropin and Drosocin synergistically contribute to the host defense against this bacterium. To investigate this question, we generated a double mutant line for the Drosocin and cecropin genes (DroSK4; ΔCecA-C). Ultimately this double mutant line died with similar kinetics to Drosocin single mutants against E. cloacae (Supplementary Figure S3). We also found no susceptibility of Drosocin or Cecropin single or double mutants to P. heimbachae (data not shown). Thus, we found no prominent synergy between Drosocin and the Cecropins. This suggests that Cecropins are redundant alongside other AMPs in defense against these bacteria, and do not have a highly specific interaction like Drosocin and E. cloacae.
In summary, our results reveal that Cecropins contribute to Drosophila host defense against a subset of Gram-negative bacteria, and that this contribution is more readily apparent when other AMPs are also lacking.
Cecropins are not involved in the resistance to Gram-positive bacteria
Previous work with the ΔAMP10 flies did not reveal a role of Drosophila AMPs against Gram-positive bacteria, indicating instead that other immune effectors—notably the bomanins—play a predominant role against this class of microbes (Hanson et al. 2019a; Lin et al. 2020). Therefore, we were curious if the added loss of Cecropins would reveal a cryptic contribution of Drosophila AMPs to defense against Gram-positive bacteria. For this, we challenged wild-type, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies with three Gram-positive bacteria: E. faecalis, S. pneumoniae, and L. monocytogenes (Figure 4, A–C). Enterococcus faecalis and S. pneumoniae contain Lysine-type peptidoglycan that is known to predominantly activate the Toll pathway while L. monocytogenes has DAP-type peptidoglycan, and is known to activate both the Toll and Imd pathways (Leulier et al. 2003). In these experiments, we included iso BomΔ55C control flies, which lack 10 Bomanin genes and are known to be susceptible to Gram-positive bacterial and fungal infections (Clemmons et al. 2015). Our survival experiments did not reveal a major role of Cecropins individually or alongside other AMPs in combating these Gram-positive bacterial species, but confirmed the importance of bomanins (Figure 4, A–C).
Figure 4.
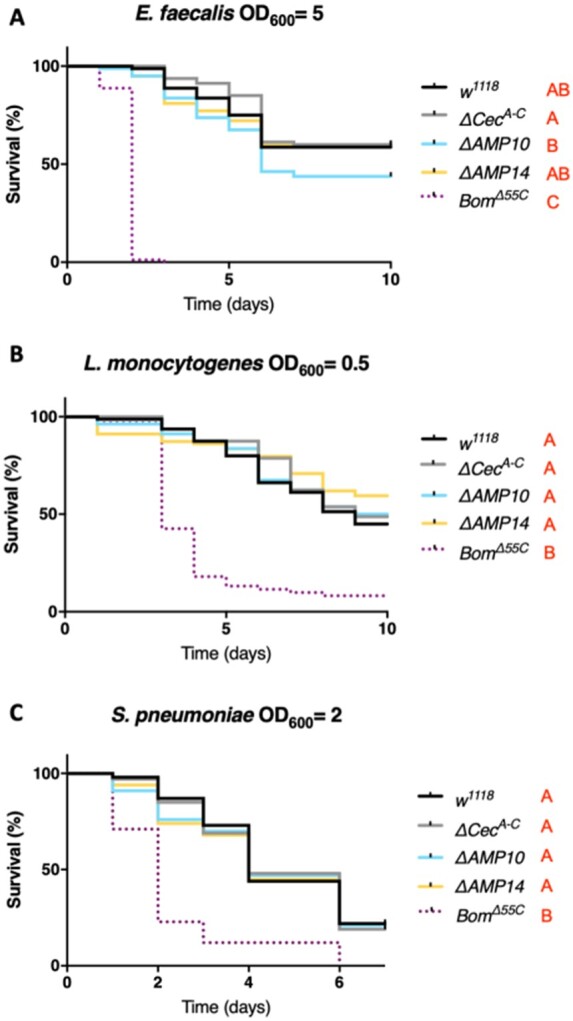
Cecropins are not involved in resistance to Gram-positive bacteria. w1118 were used as wild-type flies and BomΔ55C as susceptible flies lacking 10 Bomanin genes for all survival experiments to Gram-positive bacterial infection. w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, ΔAMP14, and BomΔ55C flies were pricked in the thorax with an inoculum of (A) E. faecalis, (B) L. monocytogenes, or (C) S. pneumoniae. Cecropins were not involved in combating infection of these three bacterial species: ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies survived as well as w1118 flies. Bacterial concentrations are indicated in the figure.
Cecropins can contribute to antifungal defense
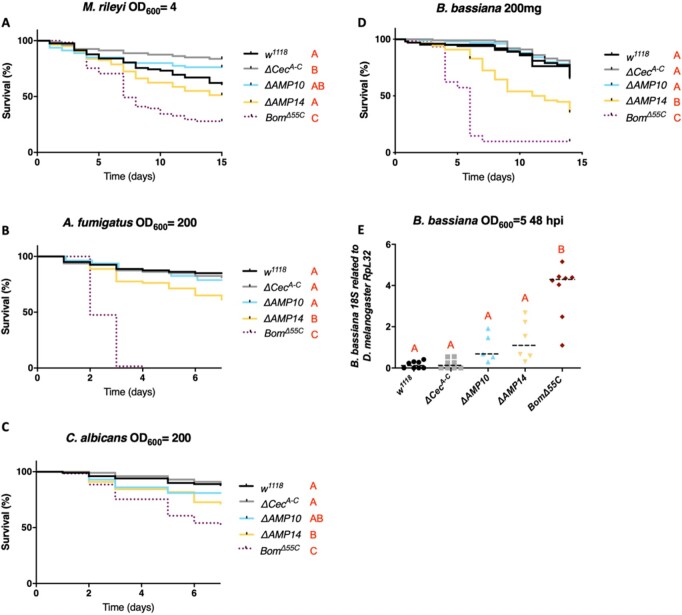
While Cecropins were initially identified as antibacterial peptides, further in vitro studies have also suggested an antifungal activity (Ekengren and Hultmark 1999; Andrä et al. 2001). We therefore investigated the contribution of Cecropins to resistance upon septic injury with four fungal species: the entomopathogenic fungi M. rileyi and B. bassiana, the opportunistic mold A. fumigatus, and the yeast C. albicans. Survival analysis did not reveal a major susceptibility of any AMP mutants against M. rileyi (Figure 5A). However, ΔAMP14 flies were more susceptible to A. fumigatus and C. albicans septic infection, and suffered greater mortality to B. bassiana natural infection, compared to ΔAMP10 and wild-type flies (Figure 5, B–D). This indicates a role for Cecropins in resistance to these three fungi, revealed best in the absence of other AMPs. In order to confirm the importance of Cecropins in limiting fungal proliferation, we introduced B. bassiana spores directly into the hemolymph by septic injury for more controlled fungal infection kinetics, and measured fungal load at 48 h hpi by qPCR. Monitoring pathogen load revealed that in ΔAMP14 flies, B. bassiana loads were higher than levels found in wild type (P = 0.07) and ΔAMP10 flies (Figure 5E), albeit not significantly. Taken together, these results show a contribution of Cecropins to defense against fungal pathogens such as B. bassiana, A. fumigatus and C. albicans.
Figure 5.
Cecropins contribute to antifungal defense against A. fumigatus, C. albicans, and B. bassiana. w1118 were used as wild-type flies and BomΔ55C as susceptible flies lacking 10 Bomanin genes for all survival experiments to fungal infections. Cecropins were not involved in combating infection of (A) M. rileyi as w1118, ΔCecA-C, ΔAMP10, and ΔAMP14 flies survived as well as w1118 flies. Survival upon (B) A. fumigatus or (C) C. albicans septic infection, and (D) natural infection with B. bassiana reveals a significant increase in resistance of ΔAMP10 flies compared to ΔAMP14 flies, suggesting an important role for Cecropins in fighting these fungi. (E) Beauveria bassiana load (measured by B. bassiana 18S expression related to D. melanogaster RpL32) is higher (P = 0.07) in ΔAMP14 flies compared with w1118, ΔCecA-C, and ΔAMP10 flies 48 h postseptic infection. Fungal concentrations are indicated in the figure.
Discussion
In this study, we generated flies lacking the four-immune inducible cecropin genes to address their function alone or in combination with other AMP gene mutations. ΔCecA-C and ΔAMP14 flies were viable, fertile and did not show any morphological defect. Moreover, they display normal activation of the Imd and Toll pathways, suggesting that the classical Drosophila AMPs do not contribute to immune signaling, in contrast to mammalian AMPs (Mookherjee et al. 2020).
Our survival analyses reveal a role of Cecropins in the defense against certain Gram-negative bacterial species (specifically against Gammaproteobacteria). However, we could not identify a bacterial species or context for which flies mutant for cecropin genes alone succumb faster than wild-type. Studies of other AMPs have revealed that certain AMPs exhibit a high degree of specificity in determining host–pathogen interactions, as illustrated by the requirement of Diptericin in defense against P. rettgeri, Drosocin in defense against E. cloacae, and the recently described Daisho and Baramicin A genes in defense against Fusarium oxysporum and B. bassiana fungi, respectively (Unckless et al. 2016; Hanson et al. 2019a, 2021; Cohen et al. 2020). Further studies may reveal bacteria for which the presence of Cecropins is essential for survival.
The most striking phenotype in the present study was that loss of Cecropins has a marked effect on E. cloacae and P. heimbachae infection in flies also lacking other AMP genes. As such, we reveal an important but cryptic contribution of Cecropins in defense against these bacteria. Generation of flies lacking refined subsets of AMPs might narrow down the specific groups of peptides key to defense against E. cloacae and P. heimbachae. The enhanced growth of E. cloacae in AMP mutants that also lack Cecropins is a particularly striking demonstration of their importance. In this infection model, the presence of Cecropins dictates whether AMP mutant flies initially suppress bacterial growth, or phenocopy RelE20 flies deficient for Imd signaling. Cecropins are induced with faster kinetics than most other AMPs, with a peak expression as early as 3 hpi (Lemaitre et al. 1997; De Gregorio et al. 2002; Schlamp et al. 2021). As cecropins encode simple helical peptides that do not require extensive post-translational modification, it is tempting to speculate that they become functional more rapidly, and play an important role in combatting bacteria specifically at this early phase of infection, likely in cooperation with melanization and phagocytosis, two more immediate host defenses (Haine et al. 2008; Dudzic et al. 2019).
Our study also reveals that endogenous Cecropins can play a role in defense against certain fungi, but not against Gram-positive bacteria tested so far (i.e., Firmicutes). Thus, our in vivo study corroborates the antifungal and antibacterial activities of Cecropins previously observed with in vitro studies (Samakovlis et al. 1990; DeLucca et al. 1997; Ekengren and Hultmark 1999). While IMD is crucial for the expression of the four Cecropins, the Cecropin response to infection also relies on Toll signaling (De Gregorio et al. 2002; Hedengren-Olcott et al. 2004). As such, the contribution of Cecropins to defense against fungi could help explain the regulation of the cecropin locus by both the Toll and Imd pathways.
The observations that AMP genes are induced to great extent, reach high peptide concentrations in the hemolymph, and display in vitro microbicidal activity are all consistent with a role as immune effectors. Use of both ΔAMP10 and ΔAMP14 flies has confirmed the important contribution of AMPs to host defense against certain Gram-negative bacteria and fungi, but not against the Gram-positive bacteria tested so far. It is possible that incorporating more diverse bacteria and fungi could reveal additional roles of AMPs, as the pathogens traditionally used in Drosophila immune studies are restricted to only a few major clades. Drosophila AMPs also regulate the gut microbiota downstream of the Imd pathway, a function consistent with their bactericidal activity (Marra et al. 2021). However, recent studies have suggested that AMP-like genes may play more subtle roles in other processes like memory formation (Barajas-Azpeleta et al. 2018), an erect wing response upon infection (Hanson et al. 2021), tumor control (Parvy et al. 2019; Araki et al. 2019), or regulation of JNK signaling in the salivary gland (Krautz et al. 2020). While we confirm a primary importance for Cecropins and other AMPs in the systemic immune response, exploring the functions of AMPs in noncanonical roles is an exciting future direction of research.
Our study and others contribute to the rapid progress made toward understanding the roles of Drosophila immune effectors. Research on the effector response has stagnated for over a decade, but recent functional characterizations by loss of function of key effectors (Cecropins, Defensin, Attacins, Diptericins, Drosocin, Drosomycin, Metchnikowin, Bomanins, Daishos, and Baramicin) has greatly advanced our understanding of the roles of these effectors (Lindsay et al. 2018; Hanson et al. 2019a; Cohen et al. 2020; Huang et al. 2020). Most importantly, these studies amend the assumptions of the previous “cocktail” model for AMP-pathogen interactions (Yan and Hancock 2001; Lazzaro 2008; Zdybicka-Barabas et al. 2012; Rahnamaeian et al. 2016), revealing some AMPs to be general effectors against most pathogens, while others act as “silver bullets” specifically required for defense against certain pathogens. The susceptibility of Toll and Imd pathway mutants to specific pathogens can now be directly linked to the susceptibility of mutants for immune effectors regulated by these pathways (Hanson and Lemaitre 2020). As new genetic techniques allow greater characterization of the roles of known immune effectors, many of them remain to be characterized, notably a number of short peptide genes highlighted by transcriptomic studies (Gregorio et al. 2001; Troha et al. 2018; Tattikota et al. 2020; Cattenoz et al. 2020; Schlamp et al. 2021). However, we are likely still exploring inside the box when assuming a uniquely immune role for these peptides.
Our study also highlights the power of multiple mutation analysis, as the role of Cecropins would not have been uncovered in vivo by mutating individual genes. While we have begun exploring the combinatory potential of AMPs in defense against infection, future studies will benefit from probing the interaction of immune effectors like AMPs with other mechanisms of host defense such as phagocytosis or melanization. With the advent of CRISPR/Cas9 technology and many recently described mutants, the interactions of AMPs in defense are just the tip of the iceberg in developing a global framework to understand the Drosophila immune response.
Data availability
Data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript and its supplementary files.
Supplementary material is available at GENETICS online.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the EPFL Proteomics Core Facility for help with the MALDI-TOF analysis. Brian Lazzaro generously provided Providencia species (Galac and Lazzaro 2011) and Adam Bajgar (Krejčová et al. 2019) provided Streptococcus pneumoniae species used in this study. We thank Hannah Westlake for editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation Sinergia, Grant number CRSII5_186397.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Literature cited
- Andrä J, Berninghausen O, Leippe M. 2001. Cecropins, antibacterial peptides from insects and mammals, are potently fungicidal against Candida albicans. Med Microbiol Immunol. 189:169–173. doi:10.1007/s430-001-8025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki M, Kurihara M, Kinoshita S, Awane R, Sato T, et al. 2019. Anti-tumour effects of antimicrobial peptides, components of the innate immune system, against haematopoietic tumours in Drosophila mxc mutants. Dis Model Mech. 12. doi:10.1242/dmm.037721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas-Azpeleta R, Wu J, Gill J, Welte R, Seidel C, et al. 2018. Antimicrobial peptides modulate long-term memory. PLoS Genet. 14:e1007440. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset A, Khush RS, Braun A, Gardan L, Boccard F, et al. 2000. The phytopathogenic bacteria Erwinia carotovora infects Drosophila and activates an immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:3376–3381. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekaert WF, Terras’ G, Cammue A, Osborn RW. 1995. Plant defensins: nove1 antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system. Plant Physiol. 108:6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulet P, Hetru C, Dimarcq J-L, Hoffmann D. 1999. Antimicrobial peptides in insects; structure and function. Dev Comp Immunol. 23:329–344. doi:10.1016/S0145-305X(99)00015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattenoz PB, Sakr R, Pavlidaki A, Delaporte C, Riba A, et al. 2020. Temporal specificity and heterogeneity of Drosophila immune cells. EMBO J. 39:e104486. doi:10.15252/embj.2020104486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou PP, Lin C-M, Perez L, Chen TT. 2002. Effect of Cecropin B and a synthetic analogue on propagation of fish viruses in vitro. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 4:294–302. doi:10.1007/s10126-002–0021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons AW, Lindsay SA, Wasserman SA. 2015. An effector peptide family required for Drosophila toll-mediated immunity. PLoS Pathog. 11:e1004876. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coca M, Bortolotti C, Rufat M, Peñas G, Eritja R, et al. 2004. Transgenic rice plants expressing the antifungal AFP protein from Aspergillus giganteus Show enhanced resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Mol Biol. 54:245–259. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000028791.34706.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen LB, Lindsay SA, Xu Y, Lin SJH, Wasserman SA. 2020. The Daisho peptides mediate Drosophila defense against a subset of filamentous fungi. Front Immunol. 11:9. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gregorio E, Spellman PT, Tzou P, Rubin GM, Lemaitre B. 2002. The Toll and Imd pathways are the major regulators of the immune response in Drosophila. EMBO J. 21:2568–2579. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.11.2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucca AJ, Bland JM, Jacks TJ, Grimm C, Cleveland TE, et al. 1997. Fungicidal activity of cecropin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 41:481–483. doi:10.1128/AAC.41.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslouches B, Di YP. 2017. Antimicrobial peptides with selective antitumor mechanisms: prospect for anticancer applications. Oncotarget. 8:46635–46651. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudzic JP, Hanson MA, Iatsenko I, Kondo S, Lemaitre B. 2019. More than black or white: melanization and Toll share regulatory serine proteases in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 27:1050–1061.e3. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekengren S, Hultmark D. 1999. Drosophila cecropin as an antifungal agent. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 29:965–972. doi:10.1016/S0965-1748(99)00071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira ÁG, Naylor H, Esteves SS, Pais IS, Martins NE, et al. 2014. The Toll-dorsal pathway is required for resistance to viral oral infection in Drosophila. PLOS Pathog. 10:e1004507. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galac MR, Lazzaro BP. 2011. Comparative pathology of bacteria in the genus Providencia to a natural host, Drosophila melanogaster. Microbes Infect. 13:673–683. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2011.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T, Selsted ME, Szklarek D, Harwig SS, Daher K, et al. 1985. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 76:1427–1435. doi:10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio ED, Spellman PT, Rubin GM, Lemaitre B. 2001. Genome-wide analysis of the Drosophila immune response by using oligonucleotide microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:12590–12595. doi:10.1073/pnas.221458698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haine ER, Moret Y, Siva-Jothy MT, Rolff J. 2008. Antimicrobial defense and persistent infection in insects. Science. 322:1257–1259. doi:10.1126/science.1165265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson MA, Dostálová A, Ceroni C, Poidevin M, Kondo S, et al. 2019a. Synergy and remarkable specificity of antimicrobial peptides in vivo using a systematic knockout approach. eLife. 8:e44341. doi:10.7554/eLife.44341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson MA, Dostálová A, Ceroni C, Poidevin M, Kondo S, et al. 2019b. Correction: synergy and remarkable specificity of antimicrobial peptides in vivo using a systematic knockout approach. eLife. 8:e48778. doi:10.7554/eLife.48778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson MA, Lemaitre B. 2020. New insights on Drosophila antimicrobial peptide function in host defense and beyond. Curr Opin Immunol. 62:22–30. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2019.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson MA, Cohen LB, Marra A, Iatsenko I, Wasserman SA, et al. 2021. The Drosophila Baramicin polypeptide gene protects against fungal infection. PLoS Pathog. 17:e1009846. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedengren-Olcott M, Olcott MC, Mooney DT, Ekengren S, Geller BL, et al. 2004. Differential activation of the NF-κB-like factors relish and Dif in Drosophila melanogaster by fungi and Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 279:21121–21127. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313856200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J, Lou Y, Liu J, Bulet P, Jiao R, et al. 2020. The BaramicinA gene is required at several steps of the host defense against Enterococcus faecalis and Metarhizium robertsii in a septic wound infection model in Drosophila melanogaster. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.11.23.394809.
- Hultmark D, Steiner H, Rasmuson T, Boman HG. 1980. Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 106:7–16. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J-L, Bulet P. 2005. Antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila: structures, activities and gene regulation. Mech Epithelial Defense. 86:1–21. doi:10.1159/000086648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsy M, Tonk M, Hardt M, Dobrindt U, Zdybicka-Barabas A, et al. 2020. The insect antimicrobial peptide cecropin A disrupts uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 6:6–8. doi:10.1038/s41522-020-0116-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokoza V, Ahmed A, Woon Shin S, Okafor N, Zou Z, et al. 2010. Blocking of plasmodium transmission by cooperative action of Cecropin A and Defensin A in transgenic Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:8111–8116. doi:10.1073/pnas.1003056107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounatidis I, Chtarbanova S, Cao Y, Hayne M, Jayanth D, Ganetzky B, et al. 2017. NF-jB Immunity in the brain determines fly lifespan in healthy aging and age-related neurodegeneration. Cell Reports. 19:836–848. 28445733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krautz R, Khalili D, Theopold U. 2020. Tissue-autonomous immune response regulates stress signaling during hypertrophy. Elife. 9:e64919. doi:10.7554/eLife.64919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejčová G, Danielová A, Nedbalová P, Kazek M, Strych L, et al. 2019. Drosophila macrophages switch to aerobic glycolysis to mount effective antibacterial defense. eLife. 8:e50414. doi:10.7554/eLife.50414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylsten P, Samakovlis C, Hultmark D. 1990. The cecropin locus in Drosophila; a compact gene cluster involved in the response to infection. EMBO J. 9:217–224. doi:10.1002/j.1460–2075.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro BP. 2008. Natural selection on the Drosophila antimicrobial immune system. Curr Opin Microbiol. 11:284–289. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2008.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre B, Reichhart J-M, Hoffmann JA. 1997. Drosophila host defense: differential induction of antimicrobial peptide genes after infection by various classes of microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:14614–14619. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre B. 2004. The road to Toll. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:521–527. doi:10.1038/nri1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leulier F, Parquet C, Pili-Floury S, Ryu J-H, Caroff M, et al. 2003. The Drosophila immune system detects bacteria through specific peptidoglycan recognition. Nat Immunol. 4:478–484. doi:10.1038/ni922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy F, Bulet P, Ehret-Sabatier L. 2004. Proteomic analysis of the systemic immune response of Drosophila. Mol Cell Proteomics. 3:156–166. doi:10.1074/mcp.M300114-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin SJH, Cohen LB, Wasserman SA. 2020. Effector specificity and function in Drosophila innate immunity: getting AMPed and dropping Boms. PLoS Pathog. 16:e1008480. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay SA, Lin SJH, Wasserman SA. 2018. Short-form Bomanins mediate humoral immunity in Drosophila. J Innate Immun. 10:306–314. doi:10.1159/000489831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A, Hanson MA, Kondo S, Erkosar B, Lemaitre B. 2021. Drosophila antimicrobial peptides and lysozymes regulate gut microbiota composition and abundance. mBio. 12:e0082421. doi:10.1128/mBio.00824-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mookherjee N, Anderson MA, Haagsman HP, Davidson DJ. 2020. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: functions and clinical potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:311–332. doi:10.1038/s41573-019-0058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang L, Xu X, Freed S, Gao Y, Yu J, et al. 2015. Cecropins from Plutella xylostella and their interaction with Metarhizium anisopliae. PLoS One. 10:e0142451. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvy J-P, Yu Y, Dostalova A, Kondo S, Kurjan A, et al. 2019. The antimicrobial peptide defensin cooperates with tumour necrosis factor to drive tumour cell death in Drosophila. eLife. 8:e45061. doi:10.7554/eLife.45061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahnamaeian M, Cytryńska M, Zdybicka-Barabas A, Vilcinskas A. 2016. The functional interaction between abaecin and pore-forming peptides indicates a general mechanism of antibacterial potentiation. Peptides. 78:17–23. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2016.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu J-H, Kim S-H, Lee H-Y, Bai JY, Nam Y-D, et al. 2008. Innate immune homeostasis by the homeobox gene caudal and commensal-gut mutualism in Drosophila. Science. 319:777–782. doi:10.1126/science.1149357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackton TB, Lazzaro BP, Schlenke TA, Evans JD, Hultmark D, et al. 2007. Dynamic evolution of the innate immune system in Drosophila. Nat Genet. 39:1461–1468. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C, Kimbrell DA, Kylsten P, Engström A, Hultmark D. 1990. The immune response in Drosophila: pattern of cecropin expression and biological activity. EMBO J. 9:2969–2976. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C, Kylsten P, Kimbrell DA, Engström A, Hultmark D. 1991. The andropin gene and its product, a male-specific antibacterial peptide in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 10:163–169. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlamp F, Delbare SYN, Early AM, Wells MT, Basu S, et al. 2021. Dense time-course gene expression profiling of the Drosophila melanogaster innate immune response. BMC Genomics. 22:304. doi:10.1186/s12864-021-07593-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo M-D, Won H-S, Kim J-H, Mishig-Ochir T, Lee B-J. 2012. Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: a review. Molecules. 17:12276–12286. doi:10.3390/molecules171012276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H, Hultmark D, Engström A, Bennich H, Boman HG. 1981. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 292:246–248. doi:10.1038/292246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H, Andreu D, Merrifield RB. 1988. Binding and action of cecropin and cecropin analogues: antibacterial peptides from insects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 939:260–266. doi:10.1016/0005–2736(88)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttmann H, Retz M, Paulsen F, Harder J, Zwergel U, et al. 2008. Antimicrobial peptides of the Cecropin-family show potent antitumor activity against bladder cancer cells. BMC Urol. 8:5. doi:10.1186/1471–2490-8-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattikota SG, Cho B, Liu Y, Hu Y, Barrera V, et al. 2020. A single-cell survey of Drosophila blood. Elife. 9:e54818. doi:10.7554/eLife.54818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troha K, Im JH, Revah J, Lazzaro BP, Buchon N. 2018. Comparative transcriptomics reveals CrebA as a novel regulator of infection tolerance in D. melanogaster. PLoS Pathog. 14:e1006847. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzou P, Reichhart J-M, Lemaitre B. 2002. Constitutive expression of a single antimicrobial peptide can restore wild-type resistance to infection in immunodeficient Drosophila mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:2152–2157. doi:10.1073/pnas.042411999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unckless RL, Howick VM, Lazzaro BP. 2016. Convergent balancing selection on an antimicrobial peptide in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 26:257–262. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenweiler-Joseph S, Moniatte M, Lagueux M, Dorsselaer AV, Hoffmann JA, et al. 1998. Differential display of peptides induced during the immune response of Drosophila: a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:11342–11347. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.19.11342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H, Hancock REW. 2001. Synergistic interactions between mammalian antimicrobial defense peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45:1558–1560. doi:10.1128/AAC.45.5.1558-1560.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdybicka-Barabas A, Mak P, Klys A, Skrzypiec K, Mendyk E, et al. 2012. Synergistic action of Galleria mellonella anionic peptide 2 and lysozyme against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:2623–2635. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y,, Zhao J,, Fang W,, Zhang J,, Luo Z.. et al. 2009. Mitogen-activated protein kinase hog1 in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana regulates environmental stress responses and virulence to insects. Applied and environmental microbiology. 75:3787–3795. 10.1128/AEM.01913-08. 19363067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript and its supplementary files.
Supplementary material is available at GENETICS online.