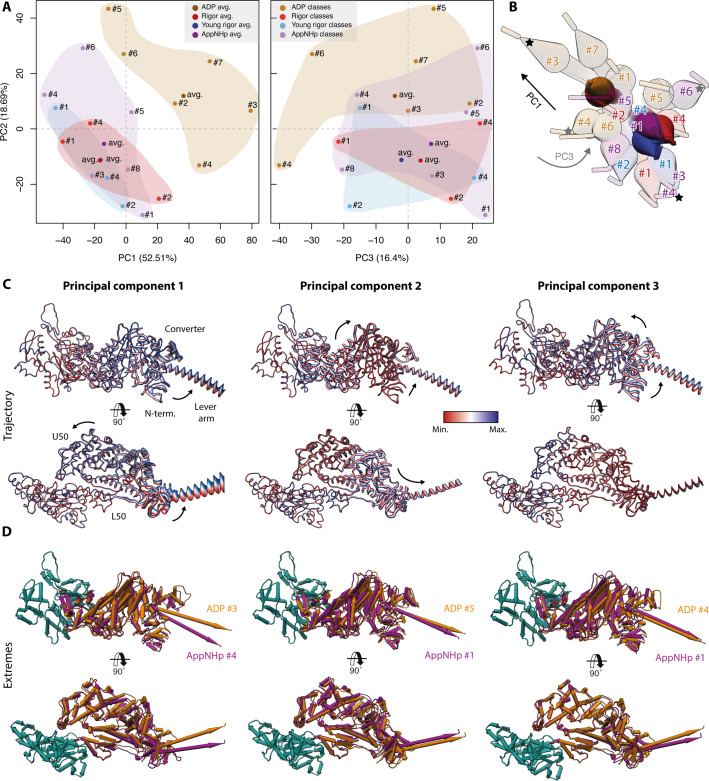
Figure 10. Principal component analysis of all myosin-V models.
Principal component analysis of all atomic models of the actomyosin-V complex, including average and 3D class average models of the strong-ADP, rigor, and post-rigor transition (PRT) state (central actomyosin subunit only). (A) Mapping of atomic models into the first and second as well as the second and third principal components. Data points are colored by the state of the actomyosin-V complex (aged rigor: red; aged strong-ADP: orange; aged AppNHp-bound PRT: purple; and young rigor: blue). Atomic models of average structures are shown as opaque, and models of 3D classes as transparent. The conformational space covered within each state is indicated by a correspondingly colored 2D polygon. (B) Superposition of all lever arm positions reflecting the relative mapping of individual conformational spaces. Changes along the first and third principal components are highlighted by black and gray arrows, respectively (extremes marked with asterisks). (C) Color-coded trajectories along the first, second, and third principal components (red minimum, blue maximum). Arrows indicate the mapped conformational changes. (D) Same views as in (C) but showing the extreme structures along each principal component; see Figure 9 for color code. For an animation of trajectories and morphs of the extreme structures, see Figure 10—video 1; and see Figure 1—figure supplement 6 for an overview of the domain architecture of myosin.