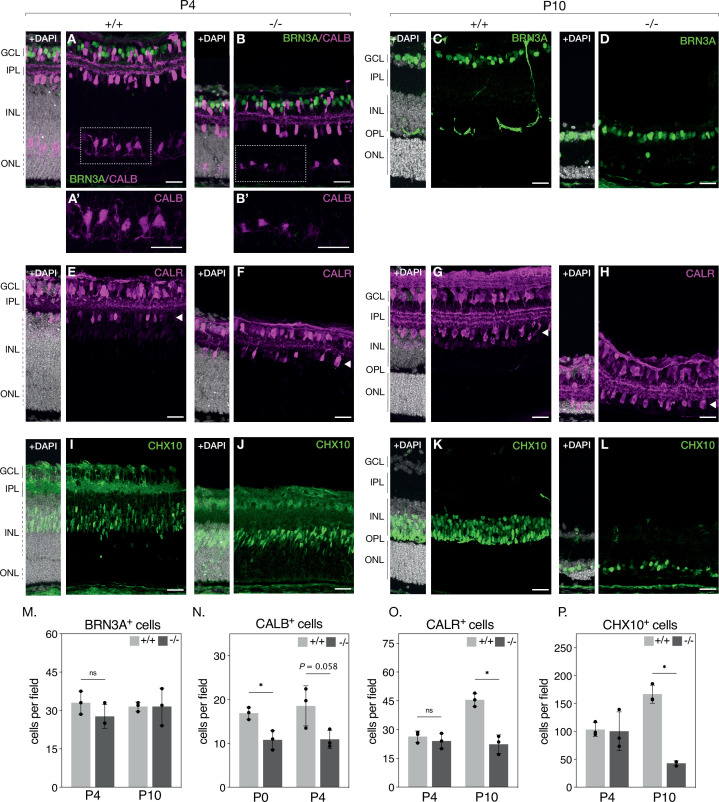
Figure 2. NMNAT1 loss affects retinal bipolar, horizontal and amacrine cells.
Representative retinal sections from knockout (-/-) and floxed littermate control (+/+) mice at the indicated ages labeled with antibodies against BRN3A (A-D, green), Calbindin (CALB) (A–B, magenta) Calretinin (CALR) (E–H), and CHX10 (I–L). Quantification of BRN3A (M), CALB, (N), CALR (O), and CHX10-positive cells (P) are shown. In (O), only CALR-positive cells on the outer side of the IPL (layer indicated by white arrowheads) were counted. Data is represented as mean ± SD. n = 3 biological replicates for all panels; significance determined using Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 30 μm.