Abstract
Objective: To understand the reason for low implementation of clinical and home-based rehabilitation robots and their potential.
Design: Online questionnaire (November 2020 and February 2021).
Subjects: A total of 100 professionals in stroke rehabilitation area were involved (Physiotherapists n = 62, Occupation therapists n = 35).
Interventions: Not applicable.
Main Measures: Descriptive statistics and thematic content analysis were used to analyze the responses: 1. Participants' details, 2. Professionals' views and experience of using clinical rehabilitation robots, 3. Professionals' expectation and concerns of using home-based rehabilitation robots.
Results: Of 100 responses, 37 had experience of rehabilitation robots. Professionals reported that patients enjoyed using them and they increased accessibility, autonomy, and convenience especially when used at home. The main emergent themes were: “aims and objectives for rehabilitation robotics,” “requirements” (functional, software, and safety), “cost,” “patient factors” (contraindications, cautions, and concerns), and “staff issues” (concerns and benefits). The main benefits of rehabilitation robots were that they provided greater choice for therapy, increased the amount/intensity of treatment, and greater motivation to practice. Professionals perceived logistical issues (ease of use, transport, and storage), cost and limited adaptability to patients' needs to be significant barriers to tier use, whilst acknowledging they can reduce staff workload to a certain extent.
Conclusion: The main reported benefit of rehabilitation robots were they increased the amount of therapy and practice after stroke. Ease of use and adaptability are the key requirements. High cost and staffing resources were the main barriers.
Keywords: rehabilitation, robotics, home-based, clinical, stroke
Introduction
Approximately two-thirds of stroke survivors are left with some degree of residual disability, particularly in limitations of the activities of daily living and mobility (1, 2). Physical and occupational therapy is a key to the recovery of function (3). Effective rehabilitation requires high repetition task-oriented training, which while effective, can be labor intensive and time consuming for treating therapists (4–6). One way to address this problem is using rehabilitation robotic devices. Since the first clinical rehabilitation robot MIT-MANUS was adopted for upper limb rehabilitation, the rehabilitation robots started the era of rapid development (7). Additionally, multiple literature review papers have proved the effectiveness of robotic-assisted therapy (4, 8–10). Mehrholz's systematic review identified that the two main types of rehabilitation robot are end-effector and exoskeleton robot, the end effector provides one attachment point for the user, and the exoskeleton can align all the joints of the limb (11). There is good evidence that using rehabilitation robots in addition to usual therapy can improve recovery of motor impairments and functions in both clinical and home environments (7, 12–20). Despite this, the take up of rehabilitation robots during stroke rehabilitation is low due to the high cost, the various settings of clinical practices, accessibility for patients, and other barriers (21–23). The aim of this paper was to better understand the reasons for low levels of implementation and to inform future robot design to ensure they are feasible, safe, and acceptable for stroke survivors and professionals.
Methods
Study Design
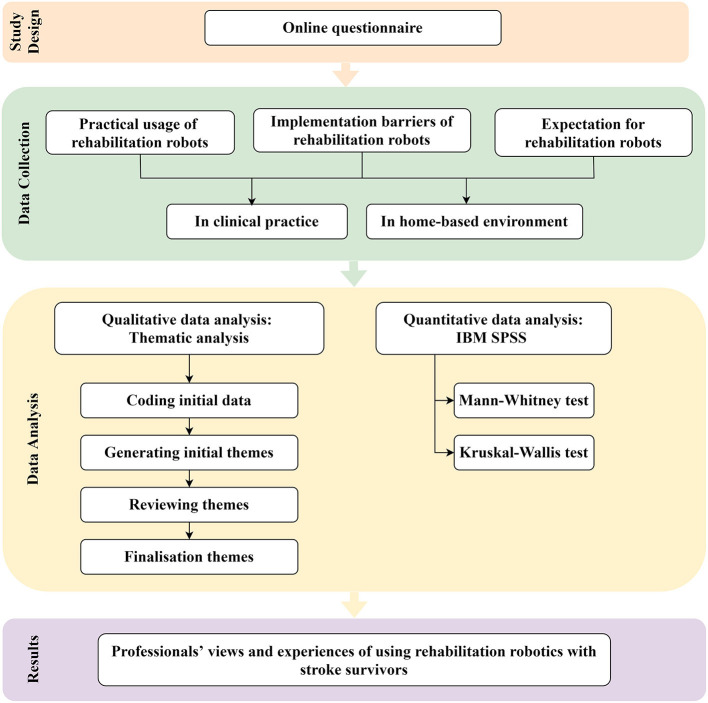
In this mixed method study, an online questionnaire was devised by the authors and optimized with the support of the wider research team (see section Acknowledgment). It included three sections using a mixture of open and closed questions, the latter answered with Likert scales (Figure 1; Supplementary Material 1). The first covered the respondents' demographics, clinical experience and experience of using rehabilitation robots. The second concerned professionals' experience and views of using clinical rehabilitation robots, and the third was specifically about home-based rehabilitation robots. The questionnaire was distributed by email to the authors' clinical and relevant research networks and via social media between Novembers 2020 and February 2021 to health care professionals with current or previous experience of stroke rehabilitation (with or without use of rehabilitation robotics) in any clinical setting. A response indicated consent.
Figure 1.
Illustration of study strategy.
All responses were anonymous and did not contain any sensitive data thus, according to the requirement for ethical approval of the authors' institution(s), it was not required.
All quantitative data were analyzed using IBM SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) v25.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics, RRID:SCR_019096). Descriptive statistics were used to aggregate the collected data. Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis tests compared groups. We categorized groups based on following characteristics: (1) participants' occupation (OT, occupational therapists; PT, physiotherapists); (2) career stage (<1 year, 1–5 years, 6–10 years, and >10 years); and (3) rehabilitation robot type (end-effector and exoskeleton).
For the qualitative data, an inductive thematic content analysis was undertaken using the questions in the questionnaire as a framework (16). Firstly, the respondents' statements were downloaded unedited into Excel (Microsoft Excel, RRID:SCR_016137). Then two of the authors (LT.L and ST) independently developed a coding matrix to categorize the respondents' composite statements. Our coding was shared and revised until a consensus was reached. The resulting coding framework was member checked with two respondents in the questionnaire (who had made themselves known to us—Dr. Verity Longley and Dr. Nick Preston), both experienced stroke professionals. Examples of the coding are shown in the Supplementary Material 2.
Results
One hundred professionals responded to the survey (Table 1; Supplementary Material 3). Two-thirds were physiotherapists; one-third were occupational therapists, plus one doctor and two rehabilitation assistants. Most (71%) were from the UK, had more than 10 years of work experience (58%) and worked in the local public health system (National Health Service) (79%). Inpatient rehabilitation was the most common (78%) work environment.
Table 1.
Respondent characteristics.
| Characteristic | Number (%) of participants |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| United Kingdom | 71 (71%) |
| Australia | 6 (6%) |
| Europe | 9 (9%) |
| Canada | 2 (2%) |
| United States | 2 (2%) |
| Brazil | 1 (1%) |
| India | 1 (1%) |
| New Zealand | 1 (1%) |
| Not answered | 7 (7%) |
| Profession | |
| Occupation therapists | 35 (35%) |
| Physiotherapists | 62 (62%) |
| Doctor | 1 (1%) |
| Other (therapists assistant) | 2 (2%) |
| Work organization* | |
| Local public health system/NHS | 79 (79%) |
| Private practice | 16 (16%) |
| Other (university or charity institution) | 7 (7%) |
| Work setting* | |
| Acute care (inpatient) | 63 (63%) |
| Inpatient rehabilitation unit | 78 (78%) |
| Long-term care | 16 (16%) |
| Outpatient clinical or rehabilitation facility | 53 (53%) |
| Community-based care | 62 (62%) |
| Other | 4 (4%) |
| Career stage | |
| <1 year experience | 6 (6%) |
| 1–5 years' experience | 20 (20%) |
| 6–10 years' experience | 16 (16%) |
| >10 years' experience | 58 (58%) |
| Highest level qualification | |
| BSc/Diploma | 40 (40%) |
| MSc/MA | 30 (30%) |
| Extended scope/Advance care practitioner | 6 (6%) |
| Ph.D. | 15 (15%) |
| Other formal post-graduate qualified | 8 (8%) |
Participants indicated all the areas in which they had experience, so totals exceed 100%.
Only 37% had experience of using rehabilitation robots, mainly in hospital and out-patient clinic environments with patients in the sub-acute stages of stroke recovery (1–3 months post stroke) (Table 2). Powered exoskeleton robots were the most commonly used type of device (Table 2). The most common dose of robotic therapy was a treatment session lasting 30–45 min, 3–5 times per week for 4–8 weeks. The most common aim of treatment for robot therapy was to increase function (89%) but increasing strength and range of movement were also frequent (84 and 76%, respectively). Respondents had used robots more frequently for upper limb rehabilitation (95%) than lower limb (25%), which tended to focus on training sagittal shoulder and elbow movements (76 and 70%, respectively) and grasp grip (51%). Approximately equal proportions of patients for whom the respondents would use a rehabilitation robot had mild, moderate or severe weakness but fewer had very severe weakness. There were no significant differences in the use of rehabilitation robotics between occupational and physiotherapists, between staff at different career stages, nor the type of robot they had used (p <0.05).
Table 2.
How rehabilitation robots were used in clinical practice.
| Robotic-assisted therapy | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Type of robot used | |
| Exoskeleton robot with/without power supply | 16 (43.2%)/10 (27.0%) |
| End-effector robot with/without power supply | 13 (35.1%)/9 (24.3%) |
| Other | 3 (8.1%) |
| Dose of robot therapy | |
| Duration of treatment session | |
| <30 min/≥30–45 min/≥45–60 min | 5 (14.3%)/22 (62.9%)/8 (22.9%) |
| Frequency | |
| <4 weeks/≥4–8 weeks/≥8–12 weeks≥12 weeks | 6 (16.7%)/19 (52.8%)/5 (13.9%)/4 (11.1%)/2 (5.6%) |
| Duration of treatment | |
| <3 times/week/≥3–5 times/week/≥5 times/week/No fixed frequency | 8 (22.9%)/17 (48.6%)/9 (25.7%)/1 (2.9%) |
| Treatment aims for robot therapy | |
| Increase strength | 31 (83.8%) |
| Increase range of movement | 28 (75.7%) |
| Increase function | 33 (89.2%) |
| Reduce muscle tone | 10 (27.0%) |
| Reduce/Prevent contractures | 14 (37.8%) |
| Reduce/Prevent pain | 8 (21.6%) |
| Other | 2 (5.4%) |
| Movements the robot trained | |
| Upper limb | |
| Shoulder flexion or extension/abduction or adduction/internal or external rotation/horizontal abduction or adduction/multiplane movements | 28 (75.7%)/18 (48.6%)/16 (43.2%)/13 (35.1%)/20 (54.1%) |
| Elbow flexion or extension/supination or pronation/multiplane movements | 26 (43.2%)/15 (40.5%)/14 (37.8%) |
| Wrist flexion or extension/ulnar or radial deviation | 18 (48.6%)/8 (21.6%) |
| Fingers flexion/or extension/abduction or adduction | 16 (43.2%)/6 (16.2%) |
| Grasp: grasp/key or pencil/pinch/multiple | 19 (51.4%)/2 (5.4%)/3 (8.1%)/4 (10.8%) |
| Lower limb | |
| Hip joint flexion or extension/abduction or adduction/internal or external rotation/multiplane movement | 6 (16.2%)/3 (8.1%)/2 (5.4%)/3 (8.1%) |
| Knee flexion/extension | 7 (18.9%) |
| Ankle dorsiflexion/plantar flexion | 5 (13.5%)/3 (8.1%) |
| Other | 1 (2.7%) |
| Type of patients that have used robots—weakness | 37 (100%) |
| Upper limb—mild/moderate/severe/very severe | 23 (62.2%)/32 (86.5%)/26 (70.3%)/8 (21.6%) |
| Lower limb—mild/moderate/severe/very severe | 6 (16.2%)/9 (24.3%)/8 (21.6%)/5 (13.5%) |
| Time after stroke that robots have been used | 37 (100%) |
| Acute <1 month | 16 (43.2%) |
| Early sub-acute 1–3 months | 29 (78.4%) |
| Late sub-acute 3–6 months | 22 (59.5%) |
| Chronic >6 months | 19 (51.4%) |
Respondents with and without experience of using rehabilitation robot had similar views regarding the type of patient for whom they were suitable; patients with moderate or severe lower or upper limb weakness were considered the most suitable (Supplementary Material 4).
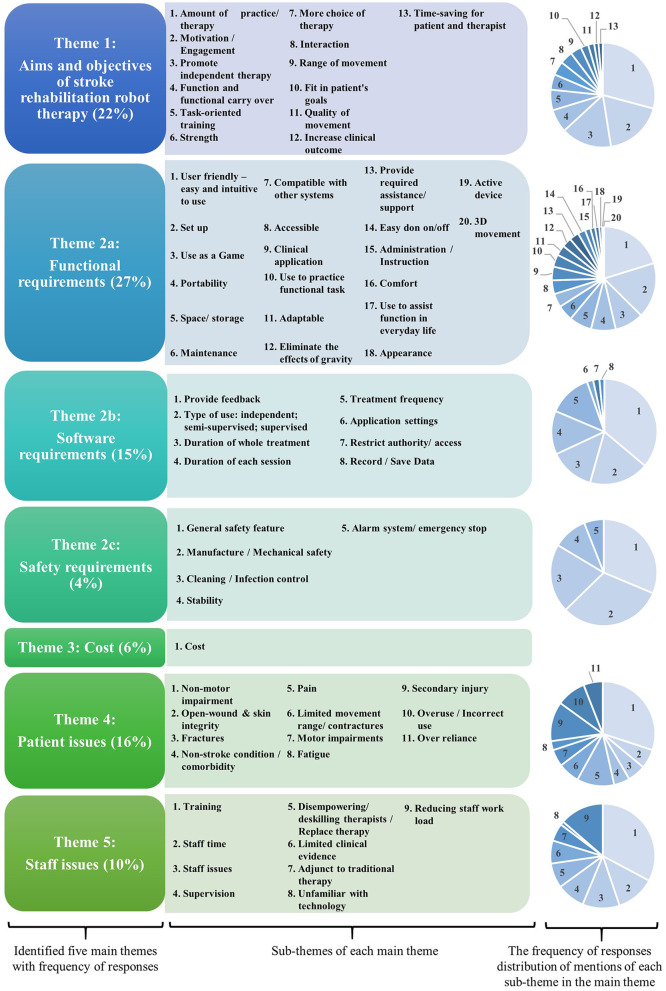
Five main themes emerged from the framework analysis: “aims and objectives for rehabilitation robotics,” “requirements” (functional, software, and safety), “cost,” “patient factors” (contraindications, cautions, and concerns), and “staff issues” (concerns and benefits). These are detailed in Figure 2; Tables 3, 4.
Figure 2.
Identified themes from questionnaire data regarding rehabilitation robots in clinical and home-based settings.
Table 3.
The final coding framework.
| Main theme | Sub-theme | Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Aims and objectives for stroke rehabilitation robots | A rehabilitation robot needs to: | Increase clinical outcomes |
| Increase the amount/intensity of practice of movements and functional activities, thereby increasing the amount of therapy provided | ||
| Provide more choice for therapy | ||
| Increase range of movement and strength | ||
| Promote patients' motivation, engagement, and interaction | ||
| Promote movement, quality of movement, task-oriented training, and functional carry-over | ||
| Promote independent practice/patient autonomy | ||
| Save time for patient (no travel) and therapist (semi-supervised practice) | ||
| To assist function in everyday life | ||
| To fit in with the patients' goals | ||
| Requirements | Functional requirements. A rehabilitation robot needs to: | Provide active and/or active assisted support to eliminate the forces of gravity in 3 Dimensions |
| Be useable as a game or for functional practice | ||
| Be highly adjustable to meet the needs of a wide range of patients' needs | ||
| Be attractive | ||
| Be comfortable | ||
| User-friendly. Everything needs to be easy and intuitive to use, with as little assistance as possible: • Following instructions • Set up and programming • Donning and doffing • Adjusting/progressing program • Transport and store |
||
| Compatible with other devices and systems e.g., clinical notes. | ||
| Minimal maintenance in terms of time and expertise | ||
| Software requirements. The device needs to: | Provide feedback on performance and progress to patient and/or therapist | |
| Record and save data: • Application settings • Usage (duration and frequency of sessions; number of repetitions) • Performance • Easy to download data to clinical notes |
||
| Safety | Alarm system and emergency stop features needed | |
| Needs to fit with cleaning/infection control policies | ||
| Stability | ||
| Restrict access to settings, recorded data etc. so it cannot be hacked or inadvertently altered. | ||
| Cost | Cost | Minimizing cost is important. Rehabilitation robots are often assumed to be too expensive for the NHS. |
| Patient factors | Contraindications | Non-motor impairments e.g., behavioral problems, visual, cognitive, communication, or perceptual impairments such that the patient cannot understand or follow what needs to be done |
| Non-stroke condition/comorbidity that prevents the patient being able to use the device | ||
| Fractures | ||
| Open-wound and skin integrity | ||
| Patients who needs assistance which is not available (for home use) | ||
| Cautions | Fatigue exacerbated by using the device | |
| Pain | ||
| Seizures/Epilepsy if could be triggered by the screen | ||
| Consider | Patient's willingness to use the device | |
| Patient and therapists' familiarity with the technology | ||
| Risk of overuse/incorrect use/secondary injury | ||
| Risk of patient becoming over-reliant on the technology (rely on robotic-assisted therapy to the detriment of other aspects of rehabilitation) | ||
| Staff issues | Concerns | Robotics are an adjunct to, not replacement for traditional therapy |
| Robotics could disempower and deskill therapists | ||
| The clinical evidence to support robotics is limited | ||
| Resources—there needs to be sufficient staff and time to use the robots in addition to all other aspects of therapy | ||
| How much supervision is needed? Can/should patients use robots independently or semi-supervised? | ||
| Will adequate training be provided about how to operate the devices and support clinical reasoning | ||
| Benefits | Reduces staff workload when patients can use robotics unsupervised or semi-supervised |
Table 4.
Frequency of responses to each sub-theme in different groups of respondents.
| Theme | Sub-theme | Number of mentions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Setting | Experience | Category | |||||||||
| Clinical | Home-based | Have used | Have not used | Advantages | Disadvantages | Requirement | Cautions | Factor | Usage | |||
| Aims and objectives of stroke rehabilitation robot therapy | Amount of practice/therapy | 110 | 82 | 28 | 49 | 61 | 97 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| Motivation/Engagement | 69 | 51 | 18 | 29 | 40 | 25 | 10 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 0 | |
| Promote independent therapy | 59 | 28 | 31 | 23 | 36 | 52 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Function and functional carry over | 27 | 22 | 5 | 15 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 0 | |
| Task-oriented training | 24 | 22 | 2 | 6 | 18 | 16 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Strength | 18 | 17 | 1 | 3 | 15 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| More choice of therapy | 16 | 15 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 2 | 13 | 4 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Range of movement | 13 | 12 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Fit in patient's goals | 9 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Quality of movement | 7 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Increase clinical outcome | 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Time-saving for patient and therapist | 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Requirements: Functional | User friendly—easy and intuitive to use: | 95 | 46 | 49 | 26 | 58 | 8 | 21 | 55 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| Set up | 81 | 43 | 38 | 36 | 45 | 1 | 20 | 52 | 3 | 5 | 0 | |
| Use as a game | 42 | 35 | 6 | 9 | 32 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Portability | 36 | 23 | 13 | 5 | 31 | 0 | 12 | 19 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Space/Storage | 33 | 23 | 10 | 11 | 22 | 0 | 14 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Maintenance | 23 | 11 | 13 | 10 | 13 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 0 | |
| Compatible with other systems | 20 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Accessible | 20 | 11 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Clinical application | 20 | 13 | 7 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 0 | |
| Use to practice functional task | 18 | 18 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Adaptable | 15 | 15 | 0 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 4 | |
| Eliminate the effects of gravity | 14 | 14 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Provide required assistance/support | 14 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Easy don on/off | 11 | 0 | 11 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Administration/Instruction | 8 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Comfort | 7 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Use to assist function in everyday life | 6 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | |
| Appearance | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Active device | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3D movement | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Requirements: Software | Provide feedback | 95 | 36 | 59 | 35 | 60 | 18 | 1 | 68 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Type of use: independent; semi-supervised; supervised | 48 | 48 | 0 | 22 | 26 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 2 | |
| Duration of whole treatment | 36 | 36 | 0 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | |
| Duration of each session | 35 | 35 | 0 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 35 | |
| Treatment frequency | 35 | 35 | 0 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 35 | |
| Application settings | 5 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| Restrict authority/access | 5 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Record/Save data | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Requirements: Safety | General safety feature | 21 | 4 | 17 | 3 | 18 | 0 | 4 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Manufacture/Mechanical safety | 21 | 4 | 17 | 6 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cleaning/Infection control | 14 | 11 | 3 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Stability | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Alarm system/emergency stop | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cost | Cost | 103 | 76 | 27 | 20 | 83 | 1 | 55 | 26 | 19 | 2 | 0 |
| Patient issues: Contradictions | Non-motor impairment | 86 | 114 | 2 | 27 | 59 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 78 | 0 | 2 |
| Open-wound and skin integrity | 17 | 17 | 0 | 3 | 14 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fractures | 16 | 16 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| Non-stroke condition/comorbidity | 14 | 12 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 0 | |
| Patient issues: Caution | Pain | 33 | 29 | 4 | 14 | 19 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Limited movement range/contractures | 19 | 19 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | |
| Motor impairments | 15 | 13 | 2 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fatigue | 8 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | |
| Patient issues: Consider | Secondary injury | 35 | 3 | 32 | 10 | 25 | 0 | 9 | 4 | 22 | 0 | 0 |
| Overuse/Incorrect use | 26 | 0 | 26 | 9 | 17 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| Over reliance | 17 | 13 | 4 | 4 | 13 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| Staff issues: Cautions | Training | 60 | 24 | 36 | 16 | 44 | 0 | 20 | 30 | 9 | 1 | 0 |
| Staff time | 22 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | |
| Staff issues | 21 | 17 | 4 | 13 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | |
| Supervision | 16 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | |
| Disempowering/Deskilling therapists/replace therapy | 14 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| Limited clinical evidence | 13 | 10 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Adjunct to traditional therapy | 10 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |
| Unfamiliar with technology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Staff issues: benefits | Reducing staff work load | 25 | 24 | 1 | 7 | 18 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Each theme is described, and the representative quotation for each theme is shown in Table 5.
Table 5.
Representative quotation from professionals.
| Theme | Quotation |
|---|---|
| Theme 1: aims and objectives of stroke rehabilitation robots | “Patients can be set up outside of therapy hours to practice independently—increases dosage” Participant 58. “I wonder if gains would translate to function without the robot assistance. I have reservations about using gaming or games. In speaking to stroke patients, rehabilitation is taken very seriously, and trivializing it is often not appreciated. I have found in practice that patients really need to clearly see the link between therapy and the impact on daily life.” Participant 45. “Promotes independence, can be done without therapist time” Participant 58. “Needs close monitoring” and “requires a qualified person with the patient” Participants 17 and 29. |
| Theme 2a: requirements—functional requirement | “Needs to be mobile, small as possible footprint, engaging and fun.”—participant 16. |
| Theme 2b: requirements—software requirements | “Patients enjoy “beating their own score”—don't think that the games need to be particularly challenging/complex” Participant 1. “Games need to be graded depending on how severe the weakness is.” Participant 13. “Games need to be age appropriate—also culturally appropriate. I think virtual reality would be good in addition to games e.g., environments you could navigate around and view things of interest”—Participant 66. “Need feedback/outcome measures which measure progress not just getting ‘better’ at the game. A larger range of games for people with significant cognitive limitations …. Games [are] often too hard to engage patients with cognitive difficulties” Participant 21. “[Need] clear reporting of results for inclusion in notes”—Participant 22. |
| Theme 2c: requirements—safety requirements | “Inability to accidentally change parameters set by therapist,”—Participant 22. |
| Theme 3: cost | “Please make cheap rehab robots available for everyone who needs one”—Participant 5. “Was effective but too expensive for the amount of effect it had.”—Participant 33. “Too expensive and NHS trusts are not funding them.”—Participant 64. |
| Theme 4: patient factors |
“[Robot therapy] promoted progress with other deficits such as hemianopia/neglect/attentional deficits too as it elicited scanning and seceding and dividing alternating attention.”—Participant 12. “I would think extreme caution would need to be applied with patients with pain.”—Participant 47. |
| Theme 5: staff issues | “In practice, this would mean staffing the robot….which is not the case in reality. Therefore, most of the time, the treatment session is either/or [robot therapy or traditional therapy] rather than robot assisted training as an adjunct to 1:1 therapy time”—Participant 11. “Risk of disempowering the therapist, risk of not letting the patient develop their own motor strategies”—Participant 73. “The risk is that a therapist is not required. It empowers the patient to take charge of their rehab and have input on a daily basis. Therapists will become de-skilled and rely on robots to do their job”—Participant 78. “Needs to have evidence to back up its effectiveness”—Participant 98. “Evidence base isn't exactly overwhelmingly positive”—Participant 68. |
Theme 1: Aims and Objectives of Stroke Rehabilitation Robots
Participants reported that the main objective for using robots in stroke rehabilitation was to increase the amount of therapy patients received. This was expressed in a variety of ways; the terms “therapy,” “practice,” and “movement,” were used interchangeably as was “intensity” and “amount.” This was important, as the amount of therapy is related to the degree of recovery. Additionally, using a rehabilitation robot was thought to improve patients' motivation and engagement with therapy as it was considered an enjoyable activity. An additional objective for some participants was that using the robot enabled the patient to practice movement independently or autonomously of the therapy. However, some respondents had concerns about patients using the robots without professional supervision.
In addition, improving function and functional carry over were also important considerations, although some noted that the transfer from practicing movements with the robot to functional activity in everyday life could not be assumed. Others focused on the potential impact on impairments such as strength and range of movement. A final objective was that robotic therapy was useful to broaden the range of therapy options available to patients, which was also reported as one of the biggest advantages of using rehabilitation robots.
Theme 2: Requirements
Respondents identified many features which were needed to ensure that a stroke rehabilitation robot was feasible and acceptable for use in clinical practice. These were categorized into functional, software, and safety requirements.
Functional Requirements
The participants most frequently noted that a rehabilitation robot needed to be user-friendly. It needed to be easy and intuitive to set up, administer, don and doff (put on and take off), maintain, transport, and store. The device needed to be useable as a game or to practice functional tasks/movements and be operable as either an active or an active-assisted device to eliminate the effects of gravity during three-dimensional movements. To achieve this, a robot needed to be highly adjustable to meet a wide range of patients' needs—in terms of size, level of assistance needed, cognitive demands of the games, and individual preferences. Furthermore, the appearance needed to be appealing so that it did not put patients off using it and it had to be comfortable to use.
Not only was ease of use important, but it also needed to be quick to set up, program, and “put away” as the time taken for these activities impacted on staff resources and ultimately the cost. Compatibility with other systems such as virtual reality systems or other gaming devices was also important.
Software Requirements
The software supporting the robot's function was considered as important as the physical device. Again this needed to be easy and intuitive to use and suitable for a wide range of needs in terms of patients' aims of treatment; level of ability, and preferences.
Participants with experience using rehabilitation robots reported that there was room for improvement with the games available. For example a greater choice and range of difficulty but also suitable for adults.
The software needed to provide feedback on usage and performance to patients and therapists to facilitate motivation and progress treatment. It was also important that the application settings, dose of use (duration, frequency, number of repetitions), and amount of assistance provided by the device were recorded and easily transferred to clinical notes. The need for data security to protect patient confidentiality was noted.
Safety Requirements
Safety is a paramount and non-negotiable issue for any clinical device, which was frequently raised by respondents. Their concerns and requirements went beyond the obvious need to ensure the robot did not make the patient move beyond their range of movement and was comfortable. The risk of pressure points on fragile skin or finger traps were raised, as was the need for the device to be easy to clean and to comply with infection control policies. Given the patients' movement limitations, an alarm system, emergency stop, auto shutdown, and simple/quick release mechanisms were needed to avoid incorrect or over use and to prevent secondary injury, especially for home or unsupervised use. Stability and reliability were also important issues, as was the restricting access to the settings of the robot.
Theme 3: Cost
The high cost of rehabilitation robots and difficulty persuading hospitals to commit funds to pay for them were major barriers to their implementation into practice in both clinical and home-based settings. The cost of current rehabilitation robotics varies from $75,000 to $350,000 without any hidden cost such as taxes, installation or training, maintenance, and shipment (24). According to the “World Health Organization Choosing Interventions that are Cost-Effective” project, if a health intervention costs <3 times of the national annual gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, it will be considered as cost-effective (25). In case of UK, a robotic-assisted therapy is considered cost-effective or low-cost if the total cost is < $120,852 (update by the World Bank in December 2020) (26).
Theme 4: Patient Factors
Participants raised many concerns and issues regarding the type of patients for whom robot therapy would not be suitable. This included people with non-motor stroke related impairments such as behavioral, cognitive, perceptual, communication, or visual difficulties which could make them unable to use or understand how to use the robot. However, one participant noted that using rehabilitation robots could be beneficial for some of these impairments, as well as motor problems, for example encouraging visual scanning and practicing memory and problem solving tasks. Further problems which could limit the patients' ability to engage with robot therapy or safety were pain, fatigue, skin integrity, spasticity, or limited range of movement, particularly fixed joint contractures and should be carefully considered before use. Co-morbidities such as fractures, other musculoskeletal problems, or epilepsy also needed to be borne in mind when considering whether robot therapy was suitable for a patient.
As well as patients' clinical condition, therapists also needed to consider the patients' and their families' willingness to try rehabilitation robots, particularly for home use. The “flip side” to this was concerns that patients could become “over-reliant” on the robots and disengage or refuse other aspects of therapy which may limit progress toward independent practice and activity in everyday life or could be a risk for overuse or secondary injuries.
Theme 5: Staff Issues
Participants highlighted the potential impact of rehabilitation robots on staff as well as patients. A common concern was that using rehabilitation robots to deliver greater amounts of therapy could replace, disempower, or deskill therapists. Respondents were careful to point out that robotic therapy should be an adjunct, but not a substitute to “traditional” care.
Other respondents raised concerns about the resources needed to deliver robotic therapy. As therapists' working days were already full, if they were to incorporate robotic therapy into practice, either more staff were needed or they needed to stop providing some other aspect of care.
While some participants were confident to delegate the supervision of robot rehabilitation to therapy assistants (unqualified staff), family members or, for patients to use the robots unsupervised, others felt that direct supervision from qualified staff was necessary. Furthermore, several pointed out that qualified staff's time was needed to prescribe and set up the robot, problem solve, and oversee progression whether the patient was supervised or not.
Time and staffing were not the only important resourcing issue. Staff also needed adequate training and on-going support to develop clinical skills to use the robots effectively in every-day practice. As many staff regularly change work areas (referred to as “rotation”), this input needed to be on-going to accommodate staff changes. All of which increased the cost of robotic therapy.
Finally, given the professional duty to provide evidence-based care, some respondents raised the limited evidence to support its use as a barrier to implementation.
Discussion
This research identified the benefits, requirements, concerns, and barriers to implementation of rehabilitation robots by analyzing professionals' experience and views of their use in both clinical and home-based environments. The majority (71%) of the survey responses were from UK and as such are representative of this country, it cannot be assumed that these results are necessarily representative of other geographical regions. Participants were generally positive about rehabilitation robots. Their biggest advantages was that they facilitated high repetition task-oriented training, which was consistent with the principle of efficient rehabilitation (27–30). This was achieved not only by providing physical support to enable the patient to move the weak limb but also by increasing patients' motivation and engagement to practice tasks and/or play games, which are also important factors in effective rehabilitation (13). From a professional perspective, the most commonly reported benefit for staff was the potential to reduce their work load, while providing greater amounts of therapy, as the patient could practice moving using the robot unsupervised or with “light touch” supervision, especially when the robots were home-based. However, reduced workload, and therefore cost could not be assumed, as the purchase cost of rehabilitation robots were considered prohibitive by many. Further resources included staffing and training also needed to be taken into account.
Powered upper limb robots (whether exo-skeleton or end-effector) were the most commonly used rehabilitation robot in clinical practice. This may not only be because active robots can provide a wide range of support and functions, but also because upper limb robots are relatively small, which is more convenient, than lower limb robots.
Home-based rehabilitation robots were identified as having great potential to facilitate accessibility, autonomy, and increase choice for therapy. Home-based systems can be convenient for patients as they eliminate the need to travel for access and enable autonomous usage. Professionals would be more confident in prescribing home-based robot therapy with well-developed interaction systems, such as remote monitoring and supervision.
Our findings have provided a wealth of detail regarding professionals' requirements for stroke rehabilitation robots to be fit for purpose and to be adopted into practice. In addition to reducing the costs, rehabilitation robots need to be “user friendly,” safe, and suitable for a wide range of needs. All aspects of use needed to be quick, easy, intuitive, and adaptable. Safety is, of course, a non-negotiable issue especially if the robot is to be used unsupervised. Participants recognized that although there were few absolute contraindications, robots needed to be considered cautiously for people with non-motor stroke related impairments and co-morbidities which could limit their ability to understand or to use a robot safely. Furthermore, patients' preferences also need to be taken into account—not everyone wants to play games, or use technology. However, accommodating this range of needs is likely to increase costs. Alternatively if costs are minimized, then the range of users is likely to be limited. In reality, commercialization of rehabilitation robots needs to balance these competing demands with a priority to ease of use as the mismatch between the demands of operating devices and other aspects of clinical practice has rendered many promising health technologies unfit for purpose (31–33). Future robot development work needs to consider these issues. Rather than focussing on progressing the sophistication and complexity of the technology, focussing on simpler technology and operation at lower cost may be key to successful implementation.
Study Limitations
The main limitations of this study include the convenience of the recruitment strategies, which may be biased toward professionals with positive views or experiences of using rehabilitation robots. Although we received responses from all over the world, most were from the UK. The findings may differ if census or probability style recruitment techniques were used or if participants from other countries were involved. However, we suggest that need for low cost, user-friendly, adaptable devices is probably universal. We have also, to date, only involved professionals. Stroke survivors and their carers/families may have other views, cautions or requirements. For the further research, the involvement of these important stakeholders should be considered.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
LL, ST, and AW conceptualized the paper. LL and ST analyzed the collected data. All authors contributed to the evaluation study itself, the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants and people who helped us to send out the questionnaire. We thank our wider research team, especially Dr. Nick Preston, Dr. Ulrike Hammerbeck, and Dr. Verity Longley who helped us improve the questionnaire organization and development framework.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmedt.2021.780090/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Katan M, Luft A. editors. Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol. (2018) 38:208–211. 10.1055/s-0038-1649503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rothwell PM, Coull AJ, Giles MF, Howard SC, Silver LE, Bull LM, et al. Change in stroke incidence, mortality, case-fatality, severity, and risk factors in Oxfordshire, UK from 1981 to 2004 (Oxford Vascular Study). Lancet. (2004) 363:1925–33. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16405-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Díaz I, Gil JJ, Sánchez E. Lower-limb robotic rehabilitation: literature review and challenges. Journal of Robotics. (2011) 2011:759764. 10.1155/2011/75976430035072 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Veerbeek JM, Langbroek-Amersfoort AC, Van Wegen EE, Meskers CG, Kwakkel G. Effects of robot-assisted therapy for the upper limb after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. (2017) 31:107–21. 10.1177/1545968316666957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lohse KR, Hilderman CG, Cheung KL, Tatla S, Van der Loos HM. Virtual reality therapy for adults post-stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis exploring virtual environments and commercial games in therapy. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e93318. 10.1371/journal.pone.0093318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Veerbeek JM, van Wegen E, van Peppen R, van der Wees PJ, Hendriks E, Rietberg M, et al. What is the evidence for physical therapy poststroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e87987. 10.1371/journal.pone.0087987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Laut J, Porfiri M, Raghavan P. The present and future of robotic technology in rehabilitation. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. (2016) 4:312–9. 10.1007/s40141-016-0139-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Norouzi-Gheidari N, Archambault PS. Fung J. Effects of robot-assisted therapy on stroke rehabilitation in upper limbs: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. J Rehabil Res Dev. (2012) 49:479–96. 10.1682/JRRD.2010.10.0210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mehrholz J, Pohl M, Platz T, Kugler J, Elsner B. Electromechanical and robot-assisted arm training for improving activities of daily living, arm function, and arm muscle strength after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 9:CD006876-CD. 10.1002/14651858.CD006876.pub5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bertani R, Melegari C, De Cola MC, Bramanti A, Bramanti P, Calabro RS. Effects of robot-assisted upper limb rehabilitation in stroke patients: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. (2017) 38:1561–9. 10.1007/s10072-017-2995-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mehrholz J, Pohl M. Electromechanical-assisted gait training after stroke: a systematic review comparing end-effector and exoskeleton devices. J Rehabil Med. (2012) 44:193–9. 10.2340/16501977-0943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Van der Loos HFM, Reinkensmeyer DJ, Guglielmelli E. Rehabilitation and health care robotics. In: Siciliano B, Khatib O. editors. Springer Handbook of Robotics. Cham: Springer International Publishing; (2016). p. 1685–728. 10.1007/978-3-319-32552-1_64 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Metzger J-C, Lambercy O, Califfi A, Dinacci D, Petrillo C, Rossi P, et al. Assessment-driven selection and adaptation of exercise difficulty in robot-assisted therapy: a pilot study with a hand rehabilitation robot. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2014) 11:154. 10.1186/1743-0003-11-154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pellegrino G, Tomasevic L, Tombini M, Assenza G, Bravi M, Sterzi S, et al. Inter-hemispheric coupling changes associate with motor improvements after robotic stroke rehabilitation. Restor Neurol Neurosci. (2012) 30:497–510. 10.3233/RNN-2012-120227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hesse S, Werner C, Pohl M, Rueckriem S, Mehrholz J, Lingnau ML. Computerized arm training improves the motor control of the severely affected arm after stroke. Stroke. (2005) 36:1960–6. 10.1161/01.STR.0000177865.37334.ce [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sivan M, Gallagher J, Makower S, Keeling D, Bhakta B, O'Connor RJ, et al. Home-based Computer Assisted Arm Rehabilitation (hCAAR) robotic device for upper limb exercise after stroke: results of a feasibility study in home setting. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2014) 11:163. 10.1186/1743-0003-11-163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ates S, Mora-Moreno I, Wessels M, Stienen AHA. Combined active wrist and hand orthosis for home use: lessons learned. In: Yu HY, Braun D, Campolo D. editors. Proceedings of the IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). Pisa: (2015). p. 398–403. 10.1109/ICORR.2015.7281232 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ates S, Haarman CJW, Stienen AHA, SCRIPT . passive orthosis: design of interactive hand and wrist exoskeleton for rehabilitation at home after stroke. Auton Robots. (2017) 41:711–23. 10.1007/s10514-016-9589-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ates S, Lobo-Prat J, Lammertse P, van der Kooij H, Stienen AH. editors. SCRIPT passive orthosis: design and technical evaluation of the wrist and hand orthosis for rehabilitation training at home. In: 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). Seattle, WA: IEEE; (2013). 10.1109/ICORR.2013.6650401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mehrholz J, Thomas S, Kugler J, Pohl M, Elsner B. Electromechanical-assisted training for walking after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 10:CD006185. 10.1002/14651858.CD006185.pub5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fong J, Crocher V, Klaic M, Davies K, Rowse A, Sutton E, et al. Promoting clinical best practice in a user-centred design study of an upper limb rehabilitation robot. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. (2020) 2020:1–8. 10.1080/17483107.2020.1785567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Standen P, Threapleton K, Connell L, Richardson A, Brown DJ, Battersby S, et al. Patients' use of a home-based virtual reality system to provide rehabilitation of the upper limb following stroke. Phys Ther. (2015) 95:350–9. 10.2522/ptj.20130564 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shirota C, Balasubramanian S, Melendez-Calderon A. Technology-aided assessments of sensorimotor function: current use, barriers and future directions in the view of different stakeholders. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2019) 16:53. 10.1186/s12984-019-0519-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Duret C, Grosmaire A-G, Krebs HI. Robot-assisted therapy in upper extremity hemiparesis: overview of an evidence-based approach. Front Neurol. (2019) 10:412. 10.3389/fneur.2019.00412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Demofonti A, Carpino G, Zollo L, Johnson MJ. Affordable robotics for upper limb stroke rehabilitation in developing countries: a systematic review. IEEE Trans Med Robot Bion. (2021) 3:11–20. 10.1109/TMRB.2021.3054462 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bank TW. GDP Per Capita (Current US$) - United Kingdom (2020). Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD?locations=GB (accessed October 12, 2021)
- 27.Stinear CM, Lang CE, Zeiler S, Byblow WD. Advances and challenges in stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. (2020) 19:348–60. 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30415-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Langhorne P, Bernhardt J, Kwakkel G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet. (2011) 377:1693–702. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60325-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Popescu D, Manta F, Rusu L, Avramescu TE, Zavaleanu M. Upper limb rehabilitation robotic system requirements analysis. In: Ferraresi C, Quaglia G. editors. Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics. RAAD 2017. Mechanisms and Machine Science, Vol 49. Cham: Springer; (2018). p. 919–27. 10.1007/978-3-319-61276-8_98 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kyto M, Maye L, McGookin D, Assoc Comp M. Using both hands: tangibles for stroke rehabilitation in the home. In: CHI'19: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Glasgow: (2019) 1–14. 10.1145/3290605.3300612 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Organization WH . Medical Devices: Managing the Mismatch: An Outcome of the Priority Medical Devices Project. World Health Organization; (2010). [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bessler J, Prange-Lasonder GB, Schaake L, Saenz JF, Bidard C, Fassi I, et al. Safety assessment of rehabilitation robots: a review identifying safety skills and current knowledge gaps. Front Robot AI. (2021) 8:602878. 10.3389/frobt.2021.602878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Musselman KE, Shah M, Zariffa J. Rehabilitation technologies and interventions for individuals with spinal cord injury: translational potential of current trends. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2018) 15:40. 10.1186/s12984-018-0386-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.