Abstract
Carexmalipoensis, a new species from southeast Yunnan, China, is here described and illustrated. It is morphologically similar to C.trichophylla in sect. Euprepes, but differs from it by its longer inflorescences and peduncles, pendulous spikes, hispidulous female glumes, densely hispidulous utricles, and longer nutlets.
Keywords: Carex sect. Euprepes, Carextrichophylla , morphology, taxonomy
Introduction
As one of the largest angiosperm genera, CarexLinnaeus (1753) (Cyperaceae) comprises an extremely high diversity of about 2000 species (Roalson et al. 2021; WCSP 2021). The genus has a Cosmopolitan distribution. It was placed within the tribe Cariceae and divided into four subgenera by Kükenthal (1909): subg. Psyllophora (Degland 1828) Petermann (1849), subg. Vigneastra (Tuckerman 1843) Kükenthal (1899), subg. Vignea (P. Beauv. ex Lestiboudois 1819) Petermann (1849) and subg. Carex. This classification of Kükenthal had been widely adopted by subsequent researchers for a long time. Recent molecular phylogenetic studies revealed that Cariceae is a natural group, and the previously recognized genera of this tribe, i.e., Cymophyllus Mack. ex Britton & A.Br., Kobresia Willdenow, Schoenoxiphium Nees von Esenbeck, and Uncinia Persoon, should be merged into Carex (Yen and Olmstead 2000; Global Carex Group 2015; Starr et al. 2015; Léveillé-Bourret et al. 2018; Martín‐Bravo et al. 2019; Villaverde et al. 2020; Larridon et al. 2021; Roalson et al. 2021). A framework of the combined giant genus was urgently needed to increase our understanding of Carex. In order to solve this problem, Villaverde et al. (2020) conducted a robust phylogeny of Carex based on molecular data (308 nuclear exon matrices, 543 nuclear intron matrices and 66 plastid exon matrices) and six clades were recognized. Accordingly, Villaverde et al. (2020) proposed an updated infrageneric classification of Carex and classified it into six subgenera: subg. Siderosticta M.J. Waterway, subg. Carex, subg. Euthyceras., subg. Psyllophorae, subg. Uncinia (Pers.) Peterm. and subg. Vignea. However, the classification within the subgenera still remained unresolved, so a more systematic and friendly infrageneric classification system was required. A framework infrageneric classification of Carex was proposed recently which divided Carex into 62 formally named Linnean sections and 49 informal groups based on the current phylogenetic knowledge of Carex (Roalson et al. 2021).
A total of 527 Carex were recorded in Flora of China (Dai et al. 2010), the Catalogue of Life China (Chen and Zhang 2018) recorded 593 species, which represents the most complete and update list of the genus in China. The number of species of Carex continues growing in China as more new species have been reported in recent years (Lu and Jin 2018; Zhang et al. 2018; Jin et al. 2020; Lu et al. 2020; Yang and Liu 2020).
During our field investigations between 2016 and 2018, we collected specimens of an unknown species of Carex in Malipo County, southeast Yunnan Province, China. After careful morphological studies, examination of herbarium specimens and relevant literature, we concluded that it can be assigned to Carexsect.Euprepes based on a combination of some morphological characters: cauline leaves well-developed; leaf blades and involucral bracts elliptic to linear-elliptic, with prominent transverse veins; complex branched inflorescence; spikes androgynous; and presence of utriculiform cladoprophylls (Jiménez-Mejíias et al. 2016) at the base of spikes. Molecular phylogenetic studies indicated that C.sect.Euprepes belongs to the core Carex clade (Starr et al. 2015; Villaverde et al. 2020), and the most recent infrageneric classification framework placed it with the Indica Clade together with species traditionally placed in sections Euprepes and Mapaniifoliae (Roalson et al. 2021). Consisting of seven species, sect. Euprepes are restricted to South and Southeast Asia (Nelmes 1955). Only one species of the section, C.zizaniifoliaRaymond (1959), was previously reported from China, distributed in southeast Yunnan Province (Dai et al. 2010; Chen and Zhang 2018). However, after our research on this section, we conclude that our new collections are different from all known species and represent a species new to science. We describe and illustrate it here below.
Materials and methods
The new species was compared morphologically with specimens of other taxa of Carexsect.Euprepes from the following public herbaria A, BM, E, GH, HNU, IBSC, K, KUN, HUH, MO, MT, NY, P, PE, and US [acronyms follow Theirs (continuously updated)] as well as our new collections across China (especially with material collected from southeast Yunnan and neighboring area; herbarium specimens kept in KUN). Meanwhile, protologues and other related taxonomic literature were collated and reviewed. The characters’ data come from specimens measurements and the prologue (C.atrivaginata Nelmes and C.tricophyllaNelmes (1955), C.euprepes Nelmes and C.laosensisNelmes (1939), C.tavoyensisNelmes (1948), C.zizaniifolia Raymond and C.poilaneiRaymond (1959)). The terminology used by Kükenthal (1909) for the morphological description of Carex species was adopted here. The distribution of the new species was compiled from the herbarium specimen records and our own collections, and shown on the distribution map.
Results
A detailed morphological comparison of the potential new species and the seven species of C.sect.Euprepres is summarized in Table 1. Morphologically, the new species is most similar to C.tricophylla but can be distinguished by the characteristics of culms (70–105 cm long, 2–4 mm thick, sides ribbed in the new species vs. culms 45–65 cm long, 1–1.5 mm thick, sides concave in C.tricophylla); leaf sheaths (1.5–7 cm long vs. 1.2–2 cm long); inflorescences (20–45 cm long, peduncles up to 9 cm long vs. 3–15 cm long, more or less exserted), spikes (15–33 mm long, pendulous vs. 7–10 mm long, erect), female glumes (hispidulous vs. glabrous), utricles (densely hispidulous vs. glabrous below, adpressed-hispid above), and nutlets (4–4.5 mm long vs. 2.25–2.5 mm long). The new taxon can be distinguished from all the other seven species in this section by their culms (length, cross-sectional shape, sides and indumentum); leaves (shape, transverse veins), sheath (length, indumentum and the appendage of mouth); inflorescence bigger (20–45 × 3–5 cm in the new taxa vs. 3–25 × 1–5 cm in the other species) or with different shape (oblong in the new taxon vs. oblong, narrowly oblong or triangular-ovate in other species); peduncles longer (up to 9 cm long in the new taxon vs. scarcely or slightly exserted in other species; only C.atrivaginata has relative long peduncles not exceeding 5 cm); and the female glumes, utricles and nutlets (differences in shape, size and indumentum).
Table 1.
Morphological comparisons between Carexmalipoensis and species in C.sect.Euprepes.
| Characters | C.malipoensis | C.atrivaginata | C.euprepes | C.laosensis | C.poilanei | C.tavoyensis | C.tricophylla | C.zizaniifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culm | ||||||||
| Length | 70–105 cm | 65 cm | 70 cm | unknown | 70–105 cm | unknown | 45–65 cm | 60–70 cm |
| Thick | 2–4 mm | 3 mm | 3 mm | 2 mm | 2–3 mm | 2–2.5 mm | 1–1.5 mm | 2 mm |
| Transverse angle | obtuse | acute | obtuse | obtuse | acute | acute, obtuse to subacute | obtuse | obtuse |
| Sides | ribbed | concave | concave | concave | concave | ribbed, slightly twisted | concave | concave |
| Indumentum | hispidulous | glabrous | glabrous | glabrous | glabrous | glabrous | hispidulous upward | glabrous |
| Leaf | ||||||||
| Number | 3–5 | 7 | 4–6 | 1–4 | 6–8 | unknown | 6 or more | 8 |
| Shape | elliptic | narrowly linear-lanceolate | elliptic | narrowly linear-lanceolate | narrowly linear-lanceolate | Linear-elliptic | elliptic, apex attenuated | narrowly elliptic or lanceolate |
| Length | 12–28 cm | 13–16 cm | 17–24 cm | 20–30 cm | 18–30 cm | 25–28 cm | 12–18 cm | 15–25 cm |
| Width | 2–3 cm | 1–1.3 cm | 3–4.5 cm | 8–15 mm | 1–2 cm | 2.3–3 cm | 1.2–2 cm | 2–2.5 cm |
| Indumentum | glabrous, sparsely hispidulous on undersurface midrib | glabrous, apex hispidulous | scabrid along veins undersurface | glabrous | glabrous | scabrid along veins undersurface | scabrid along veins undersurface | scabrid along veins |
| Leaf sheath | ||||||||
| Length | 1.5–7 cm | 1.5–5 cm | 1–2 cm | 1.5–2 cm | 2–5 cm | unknown | 1.5–2 cm | 1.4–2 cm |
| Indumentum | hispidulous | glabrous | glabrous below, hispidulous above | hispidulous | glabrous | glabrous | hispidulous | glabrous |
| Appendage of sheath mouth | not developed | not developed | prominent | small | small | small | prominent | small |
| Inflorescence | ||||||||
| Shape | oblong | oblong | narrowly oblong | narrowly oblong | triangular-ovate | narrowly oblong | narrowly oblong | narrowly oblong |
| Length | 20–45 cm | 8–10 cm | 10–22 cm | 3.5–13.5 cm | 12–20 cm | 15–25 cm | 3–15 cm long | 5–6 cm |
| Width | 3–5 cm | 2–5 cm | 3–4 cm | 1–2.5 cm | 3–6 cm | 1–2 cm | 1–2 cm | 1–1.5 cm |
| Peduncles | exserted | exserted | scarcely or slightly exserted | scarcely exserted | exserted | scarcely exserted | exserted | scarcely exserted |
| Spikes | ||||||||
| Length | 15–30 (45) mm | 10–25 mm | 8–10 mm | 5 mm | 8–18 mm | 5–9 mm | 7–10 mm | 5–6 mm |
| Male part vs female part | much longer | much longer | equal | longer | much longer | slightly longer | longer | slightly longer |
| Utricles | ||||||||
| Shape | ovate-elliptic | ovate-elliptic | elliptic | broadly ellipsoid or ellipsoid-obovoid | ovate or rhomboid-ovate | ellipsoid or obovoid-ellipsoid | obovoid or ellipsoid-obovoid | ovate-elliptic |
| Length | 6–7.5 mm | 6–7.5 mm | 4–4.5 mm | 4–4.5 mm | 4–5 mm | 4–5 mm | 6–6.5 mm | ca. 3 mm |
| Indumentum | densely hispidulous | densely hispidulous | glabrous, margins hispidulous | glabrous | unknown | glabrous below, adpressed-hispid above | glabrous below, adpressed-hispid above | densely hispidulous |
| nutlets | ca. 4 mm | ca. 4 mm | 2.25–2.5 mm | 2.25–2.8 mm | unknown | ca. 2.3 mm | 2.25–2.5 mm | immature |
The characters marked “unknown” for the missing description of the protologue or the original materials incomplete.
Taxonomy
. Carex malipoensis
Yuan Y. Li & H. Peng sp. nov.
AD0440CA-F598-5CBC-BEA8-277C16DBDDEF
urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77235050-1
Figure 1.
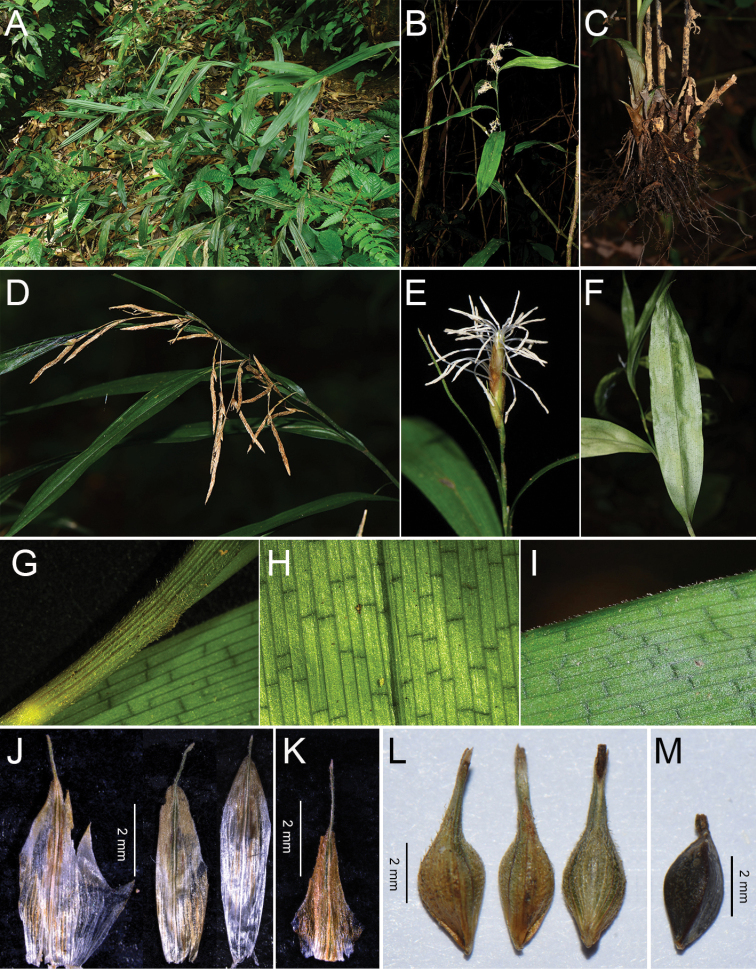
Morphology of CarexmalipoensisA habitat B plant C rhizome D inflorescence E spike F leaf blade G sheath H the transverse veins I leaf margin J male glumes K female glume L utricles M achene. Scale bars: 2 mm. Photographed by X.X. Zhu (A, D, ELiuED6425, LiuED5912 KUN), Y.P. Chen (B, C, F, IY.P. Chen & L.Q. Jiang MLP01 KUN), and Y. Y. Li (G, H, J–KY.P. Chen & L.Q. Jiang MLP01 KUN; L, MLiuED6425 KUN).
Figure 2.
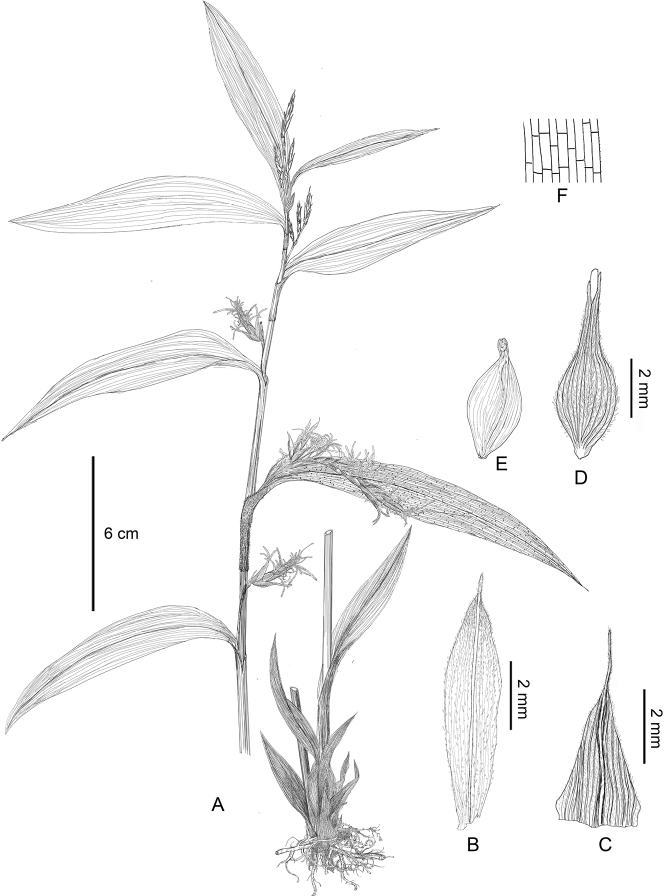
Line drawing of CarexmalipoensisA habit B male glume C female glume D utricles E achene F part of blade, show the transverse veins. Scale bars: 6 cm (A); 2 mm (B–E). Drawn by Yuan Luo from the type specimen.
Type.
China. Yunnan Province, Malipo County, Mengdong Village, Xiangchunping, 22°54'36.77"N, 104°38'54.09"E, alt. 1850 m, 5 December 2016, E.D. Liu et al. LiuED6425 (holotype: KUN! Barcode 1433368; isotype: KUN! Barcode 1347669).
Diagnosis.
The new species is most similar to C.trichophyllaNelmes (1955), but differs in inflorescences 20–45 cm long (vs. shorter than 15 cm in C.trichophylla), peduncles up to 9 cm long (vs. more or less exserted in C.trichophylla), spikes pendulous (vs. erect in C.trichophylla), female glumes hispidulous (vs. glabrous in C.trichophylla), utricles densely hispidulous (vs. glabrous below, adpressed-hispid above in C.trichophylla), and nutlets 4–4.5 mm long (vs. 2.25–2.5 mm long in C.trichophylla).
Description.
Rhizomes elongate. Culms tufted, 70–105 cm long, 2–4 mm in diam, obtusely trigonous, hispidulous, basal sheaths dark brown. Leaves 3–5, basal and cauline, loosely arranged; leaf blade elliptic, 12–28 × 2–3 cm, transverse veins prominent, margin hispidulous-villous, base round to cuneate, apex acute, greyish green when dried; sheaths 1.5–7 cm long, hispidulous, mouth hairy, not developed into prominent appendage. Involucral bracts leaf-like, longer than inflorescence, sheathing; panicles 20–45 × 3–5 cm, with 12–16 branches, single or binate; peduncles up to 9 cm long, reduced toward apex, tenuous, glabrous or slightly pubescent; inflorescence axes sharply trigonous, hairy on edges; bractlets glumiform, ca. 5 mm long, apex awned, awns 4–5 mm long; cladoprophylls utriculiform, 3–4 mm long; spikes bisexual, androgynous, 15–30 (–45) mm long; male part of spike much longer than female part; male part densely many flowered, ca. 2.5 mm wide; female part fewer flowered, 3–4.5 mm wide; male glumes oblong-lanceolate, 6–9 × 1.5–2 (–3.2) mm, awned; female glumes oblong-lanceolate, 3.8–4.2 mm long, pale brown, green at middle, apex acute, midrib extending into a scabrid awn. Utricles ovate-elliptic, 6–7.5 mm long, green to brown, veined, densely hispidulous, apex attenuating into a long beak, ca. 3 mm long, orifice oblique. Nutlets ca. 4 × 1.8–2 mm, dark brown, obovate-elliptic, trigonous. Stigmas 3.
Phenology.
Flowering from November to December, and fruiting in May.
Distribution.
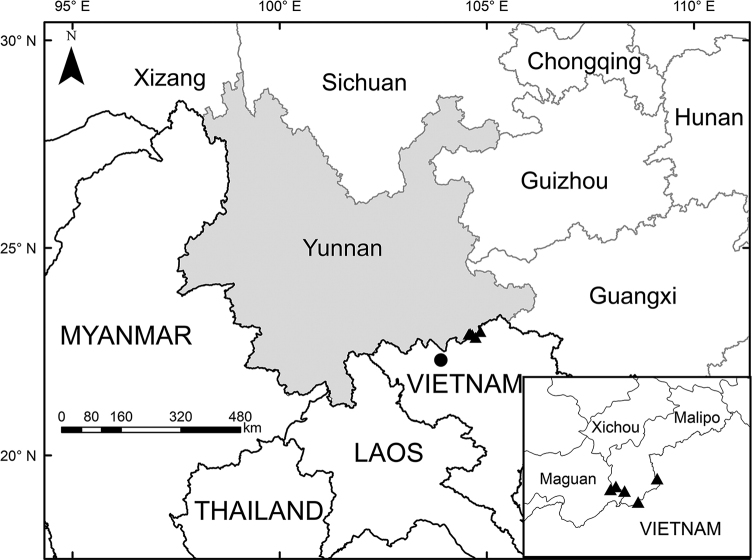
The new species is currently known from Malipo County in southeast Yunnan at the Sino-Vietnamese border (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Distribution map of Carexmalipoensis (▲) and C.trichophylla (•).
Habitat.
The new species usually grows in evergreen broad-leaved forests at altitudes of 1100–1850 m.
Etymology.
The specific epithet refers to Malipo County of Yunnan Province, China, from where the type specimens were collected.
Common name (assigned here).
Ma Li Po Tai Cao (麻栗坡薹草; Chinese name).
Additional specimens examined (paratypes).
China. Yunnan: Maguan County, Ching-kou Loa-chün-shan, 7 December 1947, K.M. Feng 13677 (KUN0368409; KUN1263725); Malipo County, Mengdong Village, 4 December 2016, E.D. Liu et al. LiuED 6336 (KUN1433717), LiuED6403 (KUN1433131); Malipo County, Laojunshan, Bailingyan, 13 May 2017, E.D. Liu et al. LiuED5912 (KUN1340680); Malipo County, Tianbao Town, Bajiaoping Village,1 December 2018, Y.P. Chen & L.Q. Jiang MLP01 (KUN).
Specimens examined of other species.
Carexatrivaginata: Vietnam. Chapa: Pételot, 3179 (P00277787, P00277788); E. Poilane, 27084 (MT00072452, MT00072458); C.euprepes: LAOS. Tawieng, Chiengkwang: 2 April, 1932, Kerr, 20927 (BM001172101, K000291207, K000291208, K000291210, NY04059693, P00282617); C.laosensis: Laos. Pak Munung, Wieng chan: 22 April, 1932, Kerr, 21202 (K000291209, K000291210, P00284722); C.poilanei: LAOS. Phong Saly: 6 September, 1941, E. Poilane, 25984 (MT00117677); E. Poilane, 32994 (MT00072475); C.tavoyensis: Myanmar. Padachaung, Tavoy. 3 April, 1921, P.T. Russell, 1935 (K000999214); C.trichophylla: Vietnam. Chapa (Fig. 3): 1 July, 1930, Pételot, 5325 (GH00027549, P00302178, P00302179, P00302180, US00087306); C.zizaniifolia: China. Yunnan, Pingbian: 1934, H. T. Tsai 62809 (A00027543, IBSC0653006, KUN0368701, PE00030290).
Conservation status.
The new species is currently known from Maguan and Malipo Counties in Yunnan, China. Only six collections have been recorded since 1947. It may be classified as Endangered (EN) or Vulnerable (VU) according to the IUCN Red List criteria(IUCN 2012). However, collections of Carex are often deficient, and a solid suggestion is needed based on a comprehensive investigation about the new species. Therefore, we suggest to characterize the conservation status of C.malipoensis as Data Deficient (DD) at present.
Discussion
In comparison with other species of C.sect.Euprepes, C.malipoensis is morphologically most similar to C.trichophylla. Both species have obtusely trigonous culms and elliptic and subpetioleate leaf blades, inflorescences big and loose, and utricles longer than 6 mm, all characters that differ from all the remaining species of C.sect.Euprepes. Despite their shared similarities, C.malipoensis can be distinguished from C.trichophylla in the length of inflorescences and peduncles, and indumentum of sheath and utricles. Specifically, C.malipoensis has much longer culms and spikes, and larger leaves, panicles, and achenes compared with that of C.trichophylla. Moreover, the female glumes and utricles are hispidulous in C.malipoensis, but glabrous in C.trichophylla.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Chun-Lei Xiang and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions that greatly improved this paper. We are grateful to the staff of herbaria IBSC, KUN and PE for their kind assistance with research facilities. We also thank Dr. Xin-Xin Zhu for providing the photographs of the new species. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31872649).
Citation
Li Y-Y, Chen Y-P, Jiang L-Q, Liu E-D, Luo Y, Peng H (2021) Carex malipoensis (Cyperaceae), a new species from southeast Yunnan, China. PhytoKeys 188: 19–29. https://doi.org/10.3897/phytokeys.18875401
References
- Chen WL, Zhang SR. (2018) Seed Plants. Catalogue of Life China. Science Press, Beijing, 49–91.
- Dai LK, Liang SY, Zhang SR, Tang YC, Koyama T, Tucker GC. (2010) Carex Linnaeus. In: Wu ZY, Raven PH, DY H. (Eds) Flora of China.Science Press & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing & St. Louis, 293–294.
- Degland JV. (1828) Carex. In: Loiseleur-Deslongchamps JLA. (Ed.) Flora Gallica 2.2nd edition. J. B. Baillière, Paris, 281–313.
- Global Carex Group (2015) Making Carex monophyletic (Cyperaceae, tribe Cariceae): A new broader circumscription. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 179(1): 1–42. 10.1111/boj.12298 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- IUCN (2012) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 3.1. 2 ed. Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK, 32 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Mejíias P, Luceno M, Wilson KL, Waterway MJ, Roalson EH. (2016) Clarification of the Use of the Terms Perigynium and Utricle in Carex L. (Cyperaceae). Systematic Botany 41(3): 519–528. 10.1600/036364416X692488 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jin XF, Liu YD, Lu YF, Sun WY, Wang H. (2020) Notes on Carex (Cyperaceae) from China (VI): The identity of Carexretrofracta Kuk. (sect. Confertiflorae). Phytotaxa 429(2): 135–147. 10.11646/phytotaxa.429.2.4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kükenthal G. (1899) Die Carex vegetation des außertropischen Südamerika (ausgenommen Paraguay und Südbrasilien). BotanischeJahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeographie 27: 485–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kükenthal G. (1909) Cyperaceae-Caricoideae. In: Engler HGA (Ed.) Das Pflanzenreich. Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig, 824 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Larridon I, Zuntini AR, Léveillé-Bourret É, Barrett RL, Starr JR, Muasya AM, Villaverde T, Bauters K, Brewer GE, Bruhl JJ, Costa SM, Elliott TL, Epitawalage N, Escudero M, Fairlie I, Goetghebeur P, Hipp AL, Jiménez-Mejías P, Sabino Kikuchi IAB, Luceño M, Márquez-Corro JI, Martín-Bravo S, Maurin O, Pokorny L, Roalson EH, Semmouri I, Simpson DA, Spalink D, Thomas WW, Wilson KL, Xanthos M, Forest F, Baker WJ. (2021) A new classification of Cyperaceae (Poales) supported by phylogenomic data. Journal of Systematics and Evolution 59(4): 852–895. 10.1111/jse.12757 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lestiboudois TG. (1819) Essai sur la famille des Cypéracées. Didot Jeune, Paris, 46 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Léveillé-Bourret É, Starr JR, Ford BA. (2018) Why are there so many sedges? Sumatroscirpeae, a missing piece in the evolutionary puzzle of the giant genus Carex (Cyperaceae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 119: 93–104. 10.1016/j.ympev.2017.10.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnaeus C. (1753) Species Plantarum 2. Impensis Laurentii Salvii, Stockholm, 561–1200.
- Lu YF, Jin XF. (2018) Notes on Carex (Cyperaceae) from China (V): New species, combination and subspecies from Zhejiang. Phytotaxa 372(3): 203–211. 10.11646/phytotaxa.372.3.3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lu ZC, Su YL, Lu YF, Jin XF. (2020) Carexpingleensis (Carexsect.Mitratae), a new species of Cyperaceae from Guangxi, China. Taiwania 65: 391–395. 10.6165/tai.2020.65.391 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Martín‐Bravo S, Jiménez‐Mejías P, Villaverde T, Escudero M, Hahn M, Spalink D, Roalson EH, Hipp AL. (2019) A tale of worldwide success: Behind the scenes of Carex (Cyperaceae) biogeography and diversification. Journal of Systematics and Evolution 57: 695–718. 10.1111/jse.12549 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nelmes E. (1939) Notes on Carex: VIII. Bulletin of Miscellaneous Information (Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew) 6: 305–306 10.2307/4111742 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nelmes E. (1948) A New Species of Carex from Burma. Kew Bulletin 3(1): 67–68. 10.2307/4118923 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nelmes E. (1955) The Genus Carex in Indo-China, including Thailand and Lower Burma. Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle Nouvelle Série Série B, Botanique. Editions Du Musém, Paris, 103–108.
- Petermann WL. (1849) Deutschlands Flora. Wigand, Leipzig, 668 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M. (1959) Carices Indochinenses necnon Siamenses. Memoires de Jardin Botanique de Montreal 53: 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Roalson EH, Jiménez-Mejíias P, Hipp AL, Benítez‐Benítez C, Bruederle LP, Chung K-S, Escudero M, Ford BA, Ford K, Gebauer S, Gehrke B, Hahn M, Hayat MQ, Hoffmann MH, Jin X, Kim S, Larridon I, Léveillé‐Bourret É, Lu Y, Luceño M, Maguilla E, Márquez-Corro JI, Martín-Bravo S, Masaki T, Míguez M, Naczi RFC, Reznicek AA, Spalink D, Starr JR. (2021) A framework infrageneric classification of Carex (Cyperaceae) and its organizing principles. Journal of Systematics and Evolution 59(4): 726–762. 10.1111/jse.12722 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Starr JR, Janzen FH, Ford BA. (2015) Three new, early diverging Carex (Cariceae, Cyperaceae) lineages from East and Southeast Asia with important evolutionary and biogeographic implications. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 88: 105–120. 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.04.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiers B. (continuously updated) Index Herbariorum: A global directory of public herbaria and associated staff. http://sweetgum.nybg.org/ih [accessed 12 August.2021]
- Tuckerman E. (1843) Enumeratio methodica Caricum quarundam I. Riggs, Schenectadiae, 27 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde T, Jiménez-Mejíias P, Luceño M, Waterway MJ, Kim S, Lee B, Rincón-Barrado M, Hahn M, Maguilla E, Roalson EH, Hipp AL. (2020) A new classification of Carex (Cyperaceae) subgenera supported by a HybSeq backbone phylogenetic tree. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 194(2): 141–163. 10.1093/botlinnean/boaa042 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- WCSP (2021) World checklist of selected plant families. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet. http://wcsp.science.kew.org/ [accessed 12 August 2021]
- Yang HB, Liu GD. (2020) Carexledongensis (Cyperaceae), a new sedge from Hainan Isl. Of South China. Phytotaxa 461(2): 72–78. 10.11646/phytotaxa.461.2.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yen AC, Olmstead RG. (2000) Molecular systematics of Cyperaceae tribe Cariceae based on two chloroplast DNA regions: ndhF and trnL intron-intergenic spacer. Systematic Botany 25(3): 479–494. 10.2307/2666691 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang SR, Zhang J, Liu ZY, Qu S, Han RG. (2018) Carexnodosa (Cyperaceae), a new species of C.sect.Occlusae from southwest China. Nordic Journal of Botany 36(8): e01900. 10.1111/njb.01900 [DOI]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.