Figure 4.
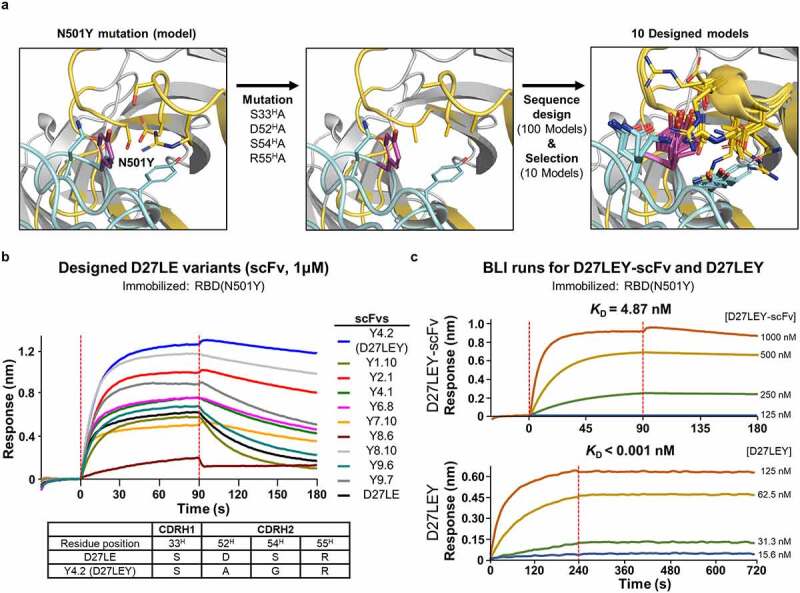
Computational affinity maturation against N501Y mutant RBD. (a) Computational steps. We modeled the Y501 mutation on the crystal structure and replaced four CDR residues (i.e., S33H, D52H, S54H, and R55H) near Y501 with alanine. After subsequent sequence design confined to these four residues, 10 of the resulting 100 models were selected. (b) Screening. These 10 designs in their Fv form evaluated for their binding to the N501Y mutant RBD using BLI. The scFv:RBD(N501Y) concentrations (in nM) were 1000:10. Tabulated below are the amino acid substitutions in the highest-affinity scFv (Y4.2) in comparison with D27LE. (c) The monovalent binding affinity of Y4.2 was measured at the indicated concentrations. Y4.2 was converted to the IgG form (D27LEY), and its bivalent binding affinity was quantified in triplicate at D27LEY concentrations ranging from 15.6–125 nM. The KD value of this interaction is less than 1 pM, which is lower than the instrument sensitivity.
